Importin β on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Importin is a type of
Enno Hartmann
based at the
SRP1p
was purified from ''
Dirk Görlich
These groups found that importin-α requires another protein, importin-β to function, and that together they form a receptor for nuclear localization signals (NLS), thus allowing transport into the
Nup2
and
karyopherin
Karyopherins are proteins involved in transporting molecules between the cytoplasm and the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The inside of the nucleus is called the karyoplasm (or nucleoplasm). Generally, karyopherin-mediated transport occurs through ...
that transports protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
molecules from the cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
's cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
to the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
. It does so by binding to specific recognition sequence
A recognition sequence is a DNA sequence to which a structural motif of a DNA-binding domain exhibits binding specificity. Recognition sequences are palindromes.
The transcription factor Sp1 for example, binds the sequences 5'-(G/T)GGGCGG(G/A)(G/ ...
s, called nuclear localization sequence A nuclear localization signal ''or'' sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines o ...
s (NLS).
Importin has two subunits, importin α and importin β. Members of the importin-β family can bind and transport cargo by themselves, or can form heterodimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has ...
s with importin-α. As part of a heterodimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has ...
, importin-β mediates interactions with the pore complex, while importin-α acts as an adaptor protein to bind the nuclear localization signal A nuclear localization signal ''or'' sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines o ...
(NLS) on the cargo. The NLS-Importin α-Importin β trimer dissociates after binding to Ran
Ran, RaN and ran may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Ran'' (film), a 1985 film directed by Akira Kurosawa
* "Ran" (song), a 2013 Japanese song by Luna Sea
* '' Ran Online'', a 2004 MMORPG (massively multiplayer online role playing game)
* ...
GTP inside the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
, with the two importin proteins being recycled to the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
for further use.
Discovery
Importin can exist as either aheterodimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has ...
of importin-α/β or as a monomer
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Mo ...
of Importin-β. Importin-α was first isolated in 1994 by a group includinEnno Hartmann
based at the
Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine
Max or MAX may refer to:
Animals
* Max (dog) (1983–2013), at one time purported to be the world's oldest living dog
* Max (English Springer Spaniel), the first pet dog to win the PDSA Order of Merit (animal equivalent of OBE)
* Max (gorilla) ...
. The process of nuclear protein import had already been characterised in previous reviews, but the key proteins involved had not been elucidated up until that point. A 60 kDa cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells (intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
ic protein, essential for protein import into the nucleus, and with a 44% sequence identity
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Ali ...
tSRP1p
was purified from ''
Xenopus
''Xenopus'' () (Gk., ξενος, ''xenos''=strange, πους, ''pous''=foot, commonly known as the clawed frog) is a genus of highly aquatic frogs native to sub-Saharan Africa. Twenty species are currently described within it. The two best-known ...
'' eggs. It was cloned, sequenced and expressed in ''E.coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Esche ...
'' and in order to completely reconstitute signal dependent transport, had to be combined with Ran
Ran, RaN and ran may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Ran'' (film), a 1985 film directed by Akira Kurosawa
* "Ran" (song), a 2013 Japanese song by Luna Sea
* '' Ran Online'', a 2004 MMORPG (massively multiplayer online role playing game)
* ...
(TC4). Other key stimulatory factors were also found in the study.
Importin-β, unlike importin-α, has no direct homologues in yeast, but was purified as a 90-95 kDa protein and found to form a heterodimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has ...
with importin-α in a number of different cases. These included a study led by Michael Rexach
and further studies bDirk Görlich
These groups found that importin-α requires another protein, importin-β to function, and that together they form a receptor for nuclear localization signals (NLS), thus allowing transport into the
nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
. Since these initial discoveries in 1994 and 1995, a host of Importin genes, such as IPO4
Importin-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IPO4'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or '' ...
and IPO7
Importin-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IPO7'' gene.
The importin-alpha/beta complex and the GTPase Ran mediate nuclear import of proteins with a classical nuclear localization signal. The protein encoded by this gene is a membe ...
, have been found that facilitate the import of slightly different cargo proteins, due to their differing structure and locality.
Structure
Importin-α
A large proportion of the importin-α adaptor protein is made up of several armadillo repeats (ARM) arranged intandem
Tandem, or in tandem, is an arrangement in which a team of machines, animals or people are lined up one behind another, all facing in the same direction.
The original use of the term in English was in ''tandem harness'', which is used for two ...
. These repeats can stack together to form a curved shaped structure, which facilitates binding to the NLS of specific cargo proteins. The major NLS binding site is found towards the N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the ami ...
, with a minor site being found at the C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is ...
. As well as the ARM
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between the ...
structures, Importin-α also contains a 90 amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
N-terminal
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the ami ...
region, responsible for binding to Importin-β, known as the Importin-β binding (IBB)domain. This is also a site of autoinhibition, and is implicated in the release of cargo once importin-α reaches the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
.
Importin-β
Importin-β is the typical structure of a largersuperfamily
SUPERFAMILY is a database and search platform of structural and functional annotation for all proteins and genomes. It classifies amino acid sequences into known structural domains, especially into SCOP superfamilies. Domains are functional, str ...
of karyopherin
Karyopherins are proteins involved in transporting molecules between the cytoplasm and the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The inside of the nucleus is called the karyoplasm (or nucleoplasm). Generally, karyopherin-mediated transport occurs through ...
s. The basis of their structure is 18-20 tandem repeats of the HEAT
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is al ...
motif. Each one of these repeats contains two antiparallel alpha helices
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid located four residues ear ...
linked by a turn, which stack together to form the overall structure of the protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
.
In order to transport cargo into the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
, importin-β must associate with the nuclear pore complexes. It does this by forming weak, transient bonds with nucleoporin
Nucleoporins are a family of proteins which are the constituent building blocks of the nuclear pore complex (NPC). The nuclear pore complex is a massive structure embedded in the nuclear envelope at sites where the inner and outer nuclear membr ...
s at their various F G (Phe-Gly) motifs. Crystallographic
Crystallography is the experimental science of determining the arrangement of atoms in crystalline solids. Crystallography is a fundamental subject in the fields of materials science and solid-state physics (condensed matter physics). The word ...
analysis has shown that these motifs bind to importin-β at shallow hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, th ...
pockets found on its surface.
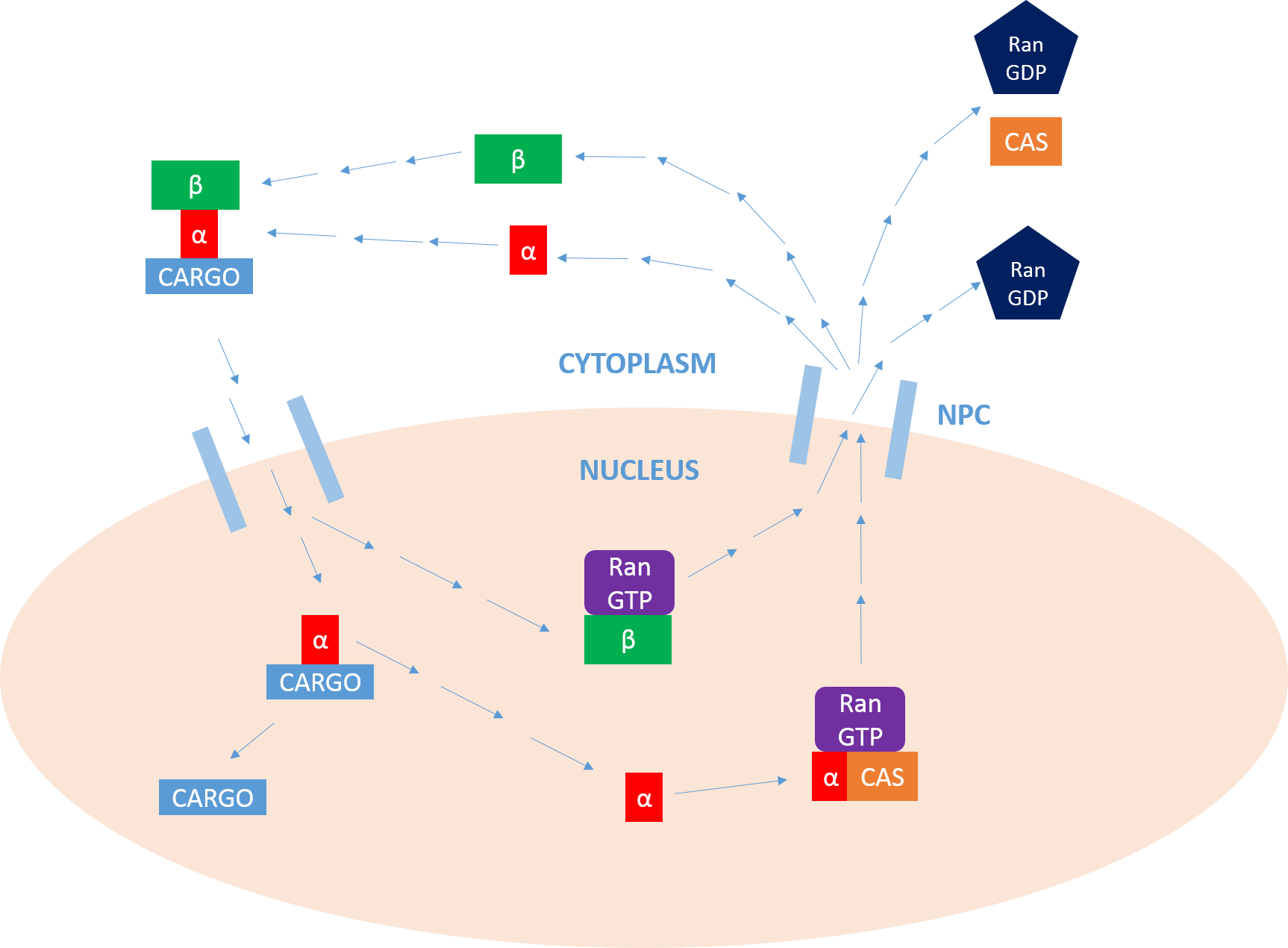
Nuclear protein import cycle
The primary function of importin is to mediate the translocation ofprotein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s with nuclear localization signals A nuclear localization signal ''or'' sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines o ...
into the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
, through nuclear pore complexes (NPC), in a process known as the nuclear protein import cycle.
Cargo binding
The first step of this cycle is the binding of cargo. Importin can perform this function as amonomer
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Mo ...
ic importin-β protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
, but usually requires the presence of importin-α, which acts as an adaptor
An adapter or adaptor is a device that converts attributes of one electrical device or system to those of an otherwise incompatible device or system. Some modify power or signal attributes, while others merely adapt the physical form of one con ...
to cargo proteins (via interactions with the NLS). The NLS is a sequence of basic amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
s that tags the protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
as cargo destined for the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
. A cargo protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
can contain either one or two of these motifs, which will bind to the major and/or minor binding sites on importin-α.

Cargo transport
Once the cargo protein is bound, importin-β interacts with the NPC, and the complex diffuses into thenucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
from the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
. The rate of diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
depends on both the concentration of importin-α present in the cytoplasm and also the binding affinity
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a mol ...
of importin-α to the cargo. Once inside the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
, the complex interacts with the Ras-family GTPase, Ran-GTP. This leads to the dissociation of the complex by altering the conformation of importin-β. Importin-β is left bound to Ran
Ran, RaN and ran may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Ran'' (film), a 1985 film directed by Akira Kurosawa
* "Ran" (song), a 2013 Japanese song by Luna Sea
* '' Ran Online'', a 2004 MMORPG (massively multiplayer online role playing game)
* ...
- GTP, ready to be recycled.
Cargo release
Now that the importin-α/cargo complex is free of importin-β, the cargo protein can be released into thenucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
. The N-terminal
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the ami ...
importin-β-binding (IBB) domain of importin-α contains an auto-regulatory region that mimics the NLS motif. The release of importin-β frees this region and allows it to loop back and compete for binding with the cargo protein at the major NLS-binding site. This competition leads to the release of the protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
. In some cases, specific release factors such aNup2
and
Nup50
Nucleoporin 50 (Nup50) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NUP50'' gene.
The nuclear pore complex is a massive structure that extends across the nuclear envelope, forming a gateway that regulates the flow of macromolecules between the ...
can be employed to help release the cargo as well.
Recycling
Finally, in order to return to thecytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
, importin-α must associate with a Ran-GTP/CAS
Cas may refer to:
* Caș, a type of cheese made in Romania
* ' (1886–) Czech magazine associated with Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk
* '' Čas'' (19 April 1945–February 1948), the official, daily newspaper of the Democratic Party of Slovakia
* ''CA ...
(nuclear export factor) complex which facilitates its exit from the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
. CAS (cellular apoptosis susceptibility protein) is part of the importin-β superfamily of karyopherin
Karyopherins are proteins involved in transporting molecules between the cytoplasm and the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The inside of the nucleus is called the karyoplasm (or nucleoplasm). Generally, karyopherin-mediated transport occurs through ...
s and is defined as a nuclear export factor. Importin-β returns to the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
, still bound to Ran
Ran, RaN and ran may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Ran'' (film), a 1985 film directed by Akira Kurosawa
* "Ran" (song), a 2013 Japanese song by Luna Sea
* '' Ran Online'', a 2004 MMORPG (massively multiplayer online role playing game)
* ...
- GTP. Once in the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
, Ran
Ran, RaN and ran may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Ran'' (film), a 1985 film directed by Akira Kurosawa
* "Ran" (song), a 2013 Japanese song by Luna Sea
* '' Ran Online'', a 2004 MMORPG (massively multiplayer online role playing game)
* ...
- GTP is hydrolysed
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
by Ran
Ran, RaN and ran may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Ran'' (film), a 1985 film directed by Akira Kurosawa
* "Ran" (song), a 2013 Japanese song by Luna Sea
* '' Ran Online'', a 2004 MMORPG (massively multiplayer online role playing game)
* ...
GAP, forming Ran
Ran, RaN and ran may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Ran'' (film), a 1985 film directed by Akira Kurosawa
* "Ran" (song), a 2013 Japanese song by Luna Sea
* '' Ran Online'', a 2004 MMORPG (massively multiplayer online role playing game)
* ...
-GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is often ...
, and releasing the two importins for further activity. It is this hydrolysis of GTP that provides the energy for the cycle as a whole. In the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
, a GEF
Gef ( ), also referred to as the Talking Mongoose or the Dalby Spook, was the name given to an allegedly talking mongoose which was claimed to inhabit a farmhouse owned by the Irving family. The Irvings' farm was located at Cashen's Gap near ...
will charge Ran
Ran, RaN and ran may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Ran'' (film), a 1985 film directed by Akira Kurosawa
* "Ran" (song), a 2013 Japanese song by Luna Sea
* '' Ran Online'', a 2004 MMORPG (massively multiplayer online role playing game)
* ...
with a GTP molecule, which is then hydrolysed by a GAP in the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
, as stated above. It is this activity of Ran
Ran, RaN and ran may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Ran'' (film), a 1985 film directed by Akira Kurosawa
* "Ran" (song), a 2013 Japanese song by Luna Sea
* '' Ran Online'', a 2004 MMORPG (massively multiplayer online role playing game)
* ...
that allows for the unidirectional transport of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s.
Disease
There are several disease states and pathologies that are associated withmutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mi ...
s or changes in expression of importin-α and importin-β.
Importins are vital regulatory protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s during the processes of gametogenesis
Gametogenesis is a biological process by which diploid or haploid precursor cells undergo cell division and differentiation to form mature haploid gametes. Depending on the biological life cycle of the organism, gametogenesis occurs by meiotic d ...
and embryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ...
. As a result, a disruption in the expression patterns of importin-α has been shown to cause fertility defects in ''Drosophila melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the "vinegar fly" or "pomace fly". Starting with Ch ...
''.
There have also been studies that link altered importin-α to some cases of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
. Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a re ...
studies have implicated a truncated form of importin-α in which the NLS binding domain is missing.
In addition, importin-α has been shown to transport the tumour suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or red ...
, BRCA1 (breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein), into the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
. The overexpression of importin-α has also been linked with poor survival rates seen in certain melanoma
Melanoma, also redundantly known as malignant melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that develops from the pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanomas typically occur in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye ( ...
patients.
Importin activity is also associated with some viral pathologies. For instance, in the infection pathway of the Ebola virus
''Zaire ebolavirus'', more commonly known as Ebola virus (; EBOV), is one of six known species within the genus ''Ebolavirus''. Four of the six known ebolaviruses, including EBOV, cause a severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever in humans and ot ...
, a key step is the inhibition of the nuclear import of PY-STAT1. This is achieved by the virus sequestering importin-α in the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
, meaning it can no longer bind its cargo at the NLS.
As a result, importin cannot function and the cargo protein stays in the cytoplasm.
Types of cargo
Many different cargoprotein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s can be transported into the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
by importin. Often, different proteins will require different combinations of α and β in order to translocate. Some examples of different cargo are listed below.
Human importin genes
Although importin-α and importin-β are used to describe importin as a whole, they actually represent largerfamilies
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideall ...
of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s that share a similar structure and function. Various different genes have been identified for both α and β, with some of them listed below. Note that often karyopherin
Karyopherins are proteins involved in transporting molecules between the cytoplasm and the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The inside of the nucleus is called the karyoplasm (or nucleoplasm). Generally, karyopherin-mediated transport occurs through ...
and importin are used interchangeably.
* Importin: IPO4
Importin-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IPO4'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or '' ...
, IPO5
Importin-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IPO5'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the importin beta family. Structurally, the protein adopts the shape of a right hand solenoid and is composed of 24 HEAT repeat ...
, IPO7
Importin-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IPO7'' gene.
The importin-alpha/beta complex and the GTPase Ran mediate nuclear import of proteins with a classical nuclear localization signal. The protein encoded by this gene is a membe ...
, IPO8, IPO9
Importin-9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IPO9'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or '' ...
, IPO11, IPO13
Importin-13 is a protein encoded by the IPO13 gene in humans. Importin-13 is a member of the importin-β family of nuclear transport receptors (NTRs) and was first identified as a transport receptor in 2000. According to PSI-blast based secondary s ...
* Karyopherin-α: KPNA1
Importin subunit alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KPNA1'' gene.
Interactions
Importin subunit alpha-5 has been shown to interact with KPNB1 and UBR5
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by ...
, KPNA2
Importin subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KPNA2'' gene.
The import of proteins into the nucleus is a process that involves at least 2 steps. The first is an energy-independent docking of the protein to the nuclear ...
, KPNA3
Importin subunit alpha-4 also known as karyopherin subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KPNA3'' gene.
The transport of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells is mediated by the nuclear pore ...
, KPNA4
Importin subunit alpha-3, also known as karyopherin subunit alpha-4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KPNA4'' gene.
Function
The nuclear import of karyophilic proteins is directed by short amino acid sequences termed nuclear loca ...
, KPNA5
Importin subunit alpha-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KPNA5'' gene.
The transport of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells is mediated by the nuclear pore complex (NPC) which consists of 60-100 prot ...
, KPNA6
Importin subunit alpha-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KPNA6'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ...
* Karyopherin-β: KPNB1
Importin subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KPNB1'' gene.
Function
Nucleocytoplasmic transport, a signal- and energy-dependent process, takes place through nuclear pore complexes embedded in the nuclear envelope. T ...
See also
*Karyopherin
Karyopherins are proteins involved in transporting molecules between the cytoplasm and the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The inside of the nucleus is called the karyoplasm (or nucleoplasm). Generally, karyopherin-mediated transport occurs through ...
* Nuclear localization sequence A nuclear localization signal ''or'' sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines o ...
* Nuclear pore complex
A nuclear pore is a part of a large complex of proteins, known as a nuclear pore complex that spans the nuclear envelope, which is the double membrane surrounding the eukaryotic cell nucleus. There are approximately 1,000 nuclear pore complexes ...
* Nuclear transport Nuclear transport refers to the mechanisms by which molecules move across the nuclear membrane of a cell. The entry and exit of large molecules from the cell nucleus is tightly controlled by the nuclear pore complexes (NPCs). Although small molecule ...
* Ran (gene)
Ran (RAs-related Nuclear protein) also known as GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAN gene. Ran is a small 25 kDa protein that is involved in transport into and out of the cell nucleus during interphase ...
References
External links
* * {{Membrane transport proteins Protein families Transport proteins