Illinois Woman Suffrage Association on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Illinois ( ) is a state in the
 American Indians of successive cultures lived along the waterways of the Illinois area for thousands of years before the arrival of Europeans. The Koster Site has been excavated and demonstrates 7,000 years of continuous habitation. Cahokia, the largest regional chiefdom and Urban Center of the
American Indians of successive cultures lived along the waterways of the Illinois area for thousands of years before the arrival of Europeans. The Koster Site has been excavated and demonstrates 7,000 years of continuous habitation. Cahokia, the largest regional chiefdom and Urban Center of the
 French explorers Jacques Marquette and Louis Jolliet explored the
French explorers Jacques Marquette and Louis Jolliet explored the
 The Illinois-Wabash Company was an early claimant to much of Illinois. The Illinois Territory was created on February 3, 1809, with its capital at Kaskaskia, an early French settlement.
During the discussions leading up to Illinois's admission to the Union, the proposed northern boundary of the state was moved twice. The original provisions of the
The Illinois-Wabash Company was an early claimant to much of Illinois. The Illinois Territory was created on February 3, 1809, with its capital at Kaskaskia, an early French settlement.
During the discussions leading up to Illinois's admission to the Union, the proposed northern boundary of the state was moved twice. The original provisions of the
 In 1818, Illinois became the 21st U.S. state. The capital remained at Kaskaskia, headquartered in a small building rented by the state. In 1819, Vandalia became the capital, and over the next 18 years, three separate buildings were built to serve successively as the capitol building. In 1837, the state legislators representing Sangamon County, under the leadership of state representative Abraham Lincoln, succeeded in having the capital moved to
In 1818, Illinois became the 21st U.S. state. The capital remained at Kaskaskia, headquartered in a small building rented by the state. In 1819, Vandalia became the capital, and over the next 18 years, three separate buildings were built to serve successively as the capitol building. In 1837, the state legislators representing Sangamon County, under the leadership of state representative Abraham Lincoln, succeeded in having the capital moved to
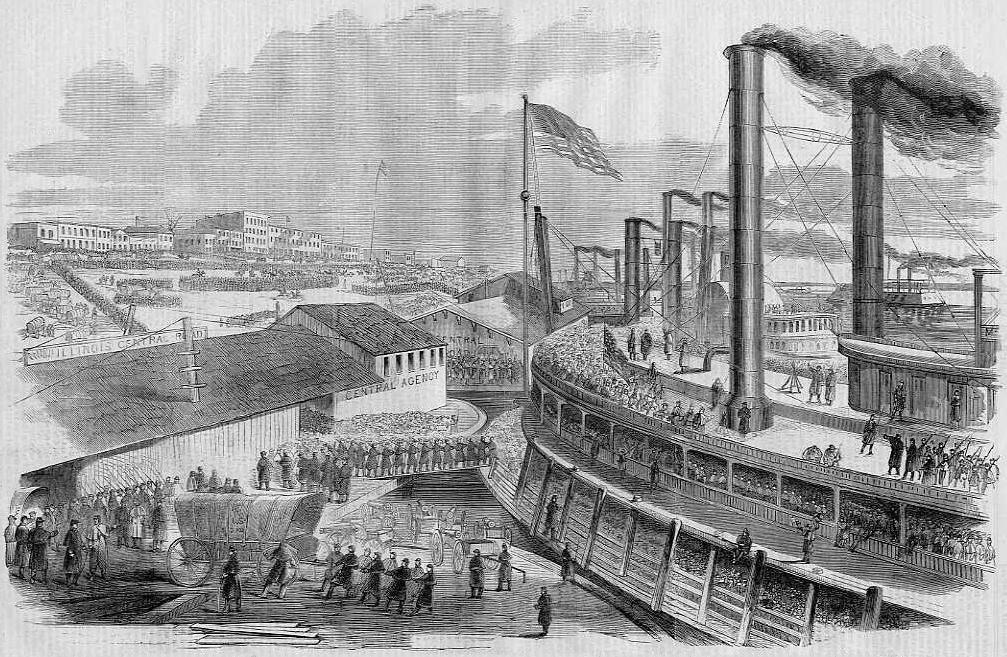 During the American Civil War, Illinois ranked fourth in men who served (more than 250,000) in the Union Army, a figure surpassed by only New York, Pennsylvania, and Ohio. Beginning with President
During the American Civil War, Illinois ranked fourth in men who served (more than 250,000) in the Union Army, a figure surpassed by only New York, Pennsylvania, and Ohio. Beginning with President
 Though Illinois lies entirely in the Interior Plains, it does have some minor variation in its elevation. In extreme northwestern Illinois, the Driftless Area, a region of unglaciated and therefore higher and more rugged topography, occupies a small part of the state. Southern Illinois includes the hilly areas around the Shawnee National Forest.
Charles Mound, located in the Driftless region, has the state's highest natural elevation above sea level at . Other highlands include the Shawnee Hills in the south, and there is varying topography along its rivers; the
Though Illinois lies entirely in the Interior Plains, it does have some minor variation in its elevation. In extreme northwestern Illinois, the Driftless Area, a region of unglaciated and therefore higher and more rugged topography, occupies a small part of the state. Southern Illinois includes the hilly areas around the Shawnee National Forest.
Charles Mound, located in the Driftless region, has the state's highest natural elevation above sea level at . Other highlands include the Shawnee Hills in the south, and there is varying topography along its rivers; the
 Illinois has three major geographical divisions. Northern Illinois is dominated by
Illinois has three major geographical divisions. Northern Illinois is dominated by
 Illinois has a climate that varies widely throughout the year. Because of its nearly 400-mile distance between its northernmost and southernmost extremes, as well as its mid-continental situation, most of Illinois has a humid continental climate ( Köppen climate classification ''Dfa''), with hot, humid summers and cold winters. The southern part of the state, from about Carbondale southward, has a
Illinois has a climate that varies widely throughout the year. Because of its nearly 400-mile distance between its northernmost and southernmost extremes, as well as its mid-continental situation, most of Illinois has a humid continental climate ( Köppen climate classification ''Dfa''), with hot, humid summers and cold winters. The southern part of the state, from about Carbondale southward, has a
. Retrieved April 22, 2006. The all-time high temperature was , recorded on July 14, 1954, at East St. Louis, and the all-time low temperature was , recorded on January 31, 2019, during the January 2019 North American cold wave at a weather station near
", NOAA National Climatic Data Center. Retrieved October 24, 2006. While tornadoes are no more powerful in Illinois than other states, some of Tornado Alley's deadliest tornadoes on record have occurred in the state. The

 The United States Census Bureau found that the population of Illinois was 12,812,508 in the
The United States Census Bureau found that the population of Illinois was 12,812,508 in the
 Illinois played an important role in the early Latter Day Saint movement, with Nauvoo becoming a gathering place for Mormons in the early 1840s. Nauvoo was the location of the
Illinois played an important role in the early Latter Day Saint movement, with Nauvoo becoming a gathering place for Mormons in the early 1840s. Nauvoo was the location of the
Midwestern
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area
The Chicago metropolitan area, also colloquially referred to as Chicagoland, is a metropolitan area in the Midwestern United States. Encompassing 10,286 sq mi (28,120 km2), the metropolitan area includes the city of Chicago, its suburbs and hi ...
, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis
Greater St. Louis is a bi-state metropolitan area that completely surrounds and includes the independent city of St. Louis, the principal city. It includes parts of both Missouri and Illinois. The city core is on the Mississippi Riverfront on t ...
. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockford, as well Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
, its capital. Of the fifty U.S. states, Illinois has the fifth-largest gross domestic product (GDP), the sixth-largest population, and the 25th-largest land area.
Illinois has a highly diverse economy
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
, with the global city of Chicago in the northeast, major industrial and agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating Plant, plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of Sedentism, sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of Domestication, domesticated species created food ...
hubs in the north and center, and natural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. O ...
s such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south. Owing to its central location and favorable geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago has access to the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
through the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
and Saint Lawrence Seaway
The St. Lawrence Seaway (french: la Voie Maritime du Saint-Laurent) is a system of locks, canals, and channels in Canada and the United States that permits oceangoing vessels to travel from the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes of North Americ ...
and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport
Chicago O'Hare International Airport , sometimes referred to as, Chicago O'Hare, or simply O'Hare, is the main international airport serving Chicago, Illinois, located on the city's Northwest Side, approximately northwest of the Chicago Loop, ...
has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Illinois has long been considered a microcosm
Microcosm or macrocosm, also spelled mikrokosmos or makrokosmos, may refer to:
Philosophy
* Microcosm–macrocosm analogy, the view according to which there is a structural similarity between the human being and the cosmos
Music
* Macrocosm (alb ...
of the United States and a bellwether in American culture, exemplified by the phrase ''Will it play in Peoria?
''Will it play in Peoria?'' is an American English figure of speech that is traditionally used to ask whether a given product, person, promotional theme, or event will appeal to mainstream United States audiences or across a broad range of demo ...
''.
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, as part of the sprawling colony of New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spai ...
. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to ...
via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolutionary War. Established in 1 ...
, and in 1818 it achieved statehood
A state is a centralized political organization that imposes and enforces rules over a population within a territory. There is no undisputed definition of a state. One widely used definition comes from the German sociologist Max Weber: a "sta ...
. The Erie Canal
The Erie Canal is a historic canal in upstate New York that runs east-west between the Hudson River and Lake Erie. Completed in 1825, the canal was the first navigable waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes, vastly reducing t ...
brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in southwestern Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that o ...
. The invention of the self-scouring steel plow
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or ...
by Illinoisan John Deere
Deere & Company, doing business as John Deere (), is an American corporation that manufactures agricultural machinery, heavy equipment, forestry machinery, diesel engines, drivetrains (axles, transmissions, gearboxes) used in heavy equipment, ...
turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, and ...
farmers from Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
. In the mid-19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal
The Illinois and Michigan Canal connected the Great Lakes to the Mississippi River and the Gulf of Mexico. In Illinois, it ran from the Chicago River in Bridgeport, Chicago to the Illinois River at LaSalle-Peru. The canal crossed the Chicago Po ...
and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.
By 1900, the growth of industrial jobs in the northern cities, and coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
mining in the central and southern areas, attracted immigrants from Eastern and Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern regions of Europe, region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countrie ...
. Illinois became one of America's most industrialized states and remains a major manufacturing center. The Great Migration from the South established a large community of African Americans, particularly in Chicago, who founded the city's famous jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a major ...
and blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form which originated in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues incorporated spirituals, work songs, field hollers, shouts, chants, and rhymed simple narrative ballads from the Afr ...
cultures. Chicago became a leading cultural, economic, and population center and is today one of the world's major commercial centers; its metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
, informally referred to as Chicagoland
The Chicago metropolitan area, also colloquially referred to as Chicagoland, is a metropolitan area in the Midwestern United States. Encompassing 10,286 sq mi (28,120 km2), the metropolitan area includes the city of Chicago, its suburbs and hint ...
holds about 65% of the state's 12.8 million residents.
Three U.S. presidents
The president of the United States is the head of state and head of government of the United States, indirectly elected to a four-year term
Term may refer to:
* Terminology, or term, a noun or compound word used in a specific context, in pa ...
have been elected while living in Illinois: Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
, Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union Ar ...
, and Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
; additionally, Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
was born and raised in the state. Today, Illinois honors Lincoln with its official state slogan ''Land of Lincoln'', which has been displayed on its license plates
A vehicle registration plate, also known as a number plate (British English), license plate (American English), or licence plate ( Canadian English), is a metal or plastic plate attached to a motor vehicle or trailer for official identificat ...
since 1954. The state is the site of the Abraham Lincoln Presidential Library and Museum
The Abraham Lincoln Presidential Library and Museum documents the life of the 16th U.S. president, Abraham Lincoln, and the course of the American Civil War. Combining traditional scholarship with 21st-century showmanship techniques, the museum ...
in Springfield and the future home of the Barack Obama Presidential Center
The Barack Obama Presidential Center is a planned architectural project in Chicago to commemorate the presidency of Barack Obama, the 44th president of the United States. The center will include a museum and library and is headed by the nonprofi ...
in Chicago.
Etymology
"Illinois" is the modern spelling for the earlyFrench
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
missionaries
A missionary is a member of a religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thomas Hale 'On Being a Mi ...
and explorers' name for the Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
Native Americans, a name that was spelled in many different ways in the early records.
American scholars previously thought the name ''Illinois'' meant 'man' or 'men' in the Miami-Illinois language, with the original transformed via French into Illinois. This etymology is not supported by the Illinois language, as the word for "man" is , and plural of "man" is . The name has also been said to mean 'tribe of superior men', which is a false etymology
A false etymology (fake etymology, popular etymology, etymythology, pseudo-etymology, or par(a)etymology) is a popular but false belief about the origin or derivation of a specific word. It is sometimes called a folk etymology, but this is also a ...
. The name ''Illinois'' derives from the Miami-Illinois verb 'he speaks the regular way'. This was taken into the Ojibwe language
Ojibwe , also known as Ojibwa , Ojibway, Otchipwe,R. R. Bishop Baraga, 1878''A Theoretical and Practical Grammar of the Otchipwe Language''/ref> Ojibwemowin, or Anishinaabemowin, is an indigenous language of North America of the Algonquian lan ...
, perhaps in the Ottawa dialect
The Ottawa, also known as the Odawa dialect of the Ojibwe language is spoken by the Ottawa people in southern Ontario in Canada, and northern Michigan in the United States. Descendants of migrant Ottawa speakers live in Kansas and Oklahoma. Th ...
, and modified into (pluralized as ). The French borrowed these forms, spelling the ending as , a transliteration
Transliteration is a type of conversion of a text from one writing system, script to another that involves swapping Letter (alphabet), letters (thus ''wikt:trans-#Prefix, trans-'' + ''wikt:littera#Latin, liter-'') in predictable ways, such as ...
of that sound in the French of that time. The current spelling form, ''Illinois'', began to appear in the early 1670s, when French colonists had settled in the western area. The Illinois's name for themselves, as attested in all three of the French missionary-period dictionaries of Illinois, was , of unknown meaning and unrelated to the other terms.
History
Pre-European
 American Indians of successive cultures lived along the waterways of the Illinois area for thousands of years before the arrival of Europeans. The Koster Site has been excavated and demonstrates 7,000 years of continuous habitation. Cahokia, the largest regional chiefdom and Urban Center of the
American Indians of successive cultures lived along the waterways of the Illinois area for thousands of years before the arrival of Europeans. The Koster Site has been excavated and demonstrates 7,000 years of continuous habitation. Cahokia, the largest regional chiefdom and Urban Center of the Pre-Columbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, th ...
Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a Native Americans in the United States, Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern United States, Midwestern, Eastern United States, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from appr ...
, was located near present-day Collinsville, Illinois. They built an urban complex of more than 100 platform and burial mounds, a plaza larger than 35 football fields, and a woodhenge of sacred cedar, all in a planned design expressing the culture's cosmology. Monks Mound
Monks Mound is the largest Pre-Columbian earthwork in the Americas and the largest pyramid north of Mesoamerica. The beginning of its construction dates from 900–955 CE. Located at the Cahokia Mounds UNESCO World Heritage Site near Collinsvil ...
, the center of the site, is the largest Pre-Columbian structure north of the Valley of Mexico
The Valley of Mexico ( es, Valle de México) is a highlands plateau in central Mexico roughly coterminous with present-day Mexico City and the eastern half of the State of Mexico. Surrounded by mountains and volcanoes, the Valley of Mexico wa ...
. It is high, long, wide, and covers . It contains about of earth. It was topped by a structure thought to have measured about in length and in width, covered an area , and been as much as high, making its peak above the level of the plaza. The finely crafted ornaments and tools recovered by archaeologists at Cahokia include elaborate ceramics, finely sculptured stonework, carefully embossed and engraved copper and mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into extremely thin elastic plates. This characteristic is described as perfect basal cleavage. Mica is ...
sheets, and one funeral blanket for an important chief fashioned from 20,000 shell beads. These artifacts indicate that Cahokia was truly an urban center, with clustered housing, markets, and specialists in toolmaking, hide dressing, potting, jewelry making, shell engraving, weaving and salt making.
The civilization vanished in the 15th century for unknown reasons, but historians and archeologists have speculated that the people depleted the area of resources. Many indigenous tribes engaged in constant warfare. According to Suzanne Austin Alchon, "At one site in the central Illinois River
The Illinois River ( mia, Inoka Siipiiwi) is a principal tributary of the Mississippi River and is approximately long. Located in the U.S. state of Illinois, it has a drainage basin of . The Illinois River begins at the confluence of the D ...
valley, one third of all adults died as a result of violent injuries." The next major power in the region was the Illinois Confederation or Illini, a political alliance. As the Illini declined during the Beaver Wars
The Beaver Wars ( moh, Tsianì kayonkwere), also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars (french: Guerres franco-iroquoises) were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout t ...
era, members of the Algonquian-speaking Potawatomi
The Potawatomi , also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie (among many variations), are a Native American people of the western Great Lakes region, upper Mississippi River and Great Plains. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, a m ...
, Miami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a East Coast of the United States, coastal metropolis and the County seat, county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade C ...
, Sauk, and other tribes including the Fox ( Meskwaki), Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to the ...
, Kickapoo
Kickapoo may refer to:
People
* Kickapoo people, a Native American nation
** Kickapoo language, spoken by that people
** Kickapoo Tribe of Kansas, a federally recognized tribe of Kickapoo people
** Kickapoo Tribe of Oklahoma, a federally recog ...
, Mascouten
The Mascouten (also ''Mascoutin'', ''Mathkoutench'', ''Muscoden,'' or ''Musketoon'') were a tribe of Algonquian-speaking Native Americans located in the Midwest. They are believed to have dwelt on both sides of the Mississippi River, adjacent to ...
, Piankeshaw, Shawnee, Wea, and Winnebago (Ho-Chunk
The Ho-Chunk, also known as Hoocągra or Winnebago (referred to as ''Hotúŋe'' in the neighboring indigenous Iowa-Otoe language), are a Siouan-speaking Native American people whose historic territory includes parts of Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iow ...
) came into the area from the east and north around the Great Lakes.
European exploration and settlement prior to 1800
 French explorers Jacques Marquette and Louis Jolliet explored the
French explorers Jacques Marquette and Louis Jolliet explored the Illinois River
The Illinois River ( mia, Inoka Siipiiwi) is a principal tributary of the Mississippi River and is approximately long. Located in the U.S. state of Illinois, it has a drainage basin of . The Illinois River begins at the confluence of the D ...
in 1673. Marquette soon after founded a mission at the Grand Village of the Illinois in Illinois Country. In 1680, French explorers under René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle
René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle (; November 22, 1643 – March 19, 1687), was a 17th-century French explorer and fur trader in North America. He explored the Great Lakes region of the United States and Canada, the Mississippi River, ...
and Henri de Tonti constructed a fort at the site of present-day Peoria, and in 1682, a fort atop Starved Rock in today's Starved Rock State Park. French Empire Canadiens came south to settle particularly along the Mississippi River, and Illinois was part of first New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spai ...
, and then of La Louisiane until 1763, when it passed to the British with their defeat of France in the Seven Years' War. The small French settlements continued, although many French migrated west to Ste. Genevieve and St. Louis, Missouri, to evade British rule.
A few British soldiers were posted in Illinois, but few British or American settlers moved there, as the Crown made it part of the territory reserved for Indians west of the Appalachians, and then part of the British Province of Quebec. In 1778, George Rogers Clark
George Rogers Clark (November 19, 1752 – February 13, 1818) was an American surveyor, soldier, and militia officer from Virginia who became the highest-ranking American patriot military officer on the northwestern frontier during the Ame ...
claimed Illinois County
Illinois County, Virginia, was a political and geographic region, part of the British Province of Quebec, claimed during the American Revolutionary War on July 4, 1778 by George Rogers Clark of the Virginia Militia, as a result of the Illinois C ...
for Virginia. In a compromise, Virginia (and other states that made various claims) ceded the area to the new United States in the 1780s and it became part of the Northwest Territory
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolutionary War. Established in 1 ...
, administered by the federal government and later organized as states.
19th century
Prior to statehood
 The Illinois-Wabash Company was an early claimant to much of Illinois. The Illinois Territory was created on February 3, 1809, with its capital at Kaskaskia, an early French settlement.
During the discussions leading up to Illinois's admission to the Union, the proposed northern boundary of the state was moved twice. The original provisions of the
The Illinois-Wabash Company was an early claimant to much of Illinois. The Illinois Territory was created on February 3, 1809, with its capital at Kaskaskia, an early French settlement.
During the discussions leading up to Illinois's admission to the Union, the proposed northern boundary of the state was moved twice. The original provisions of the Northwest Ordinance
The Northwest Ordinance (formally An Ordinance for the Government of the Territory of the United States, North-West of the River Ohio and also known as the Ordinance of 1787), enacted July 13, 1787, was an organic act of the Congress of the Co ...
had specified a boundary that would have been tangent to the southern tip of Lake Michigan. Such a boundary would have left Illinois with no shoreline on Lake Michigan at all. However, as Indiana had successfully been granted a northern extension of its boundary to provide it with a usable lakefront, the original bill for Illinois statehood, submitted to Congress on January 23, 1818, stipulated a northern border at the same latitude as Indiana's, which is defined as 10 miles north of the southernmost extremity of Lake Michigan. However, the Illinois delegate, Nathaniel Pope, wanted more, and lobbied to have the boundary moved further north. The final bill passed by Congress included an amendment to shift the border to 42° 30' north, which is approximately north of the Indiana northern border. This shift added to the state, including the lead mining region near Galena
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver.
Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It cryst ...
. More importantly, it added nearly 50 miles of Lake Michigan shoreline and the Chicago River. Pope and others envisioned a canal that would connect the Chicago and Illinois rivers and thus connect the Great Lakes to the Mississippi.
The State of Illinois prior to the Civil War
 In 1818, Illinois became the 21st U.S. state. The capital remained at Kaskaskia, headquartered in a small building rented by the state. In 1819, Vandalia became the capital, and over the next 18 years, three separate buildings were built to serve successively as the capitol building. In 1837, the state legislators representing Sangamon County, under the leadership of state representative Abraham Lincoln, succeeded in having the capital moved to
In 1818, Illinois became the 21st U.S. state. The capital remained at Kaskaskia, headquartered in a small building rented by the state. In 1819, Vandalia became the capital, and over the next 18 years, three separate buildings were built to serve successively as the capitol building. In 1837, the state legislators representing Sangamon County, under the leadership of state representative Abraham Lincoln, succeeded in having the capital moved to Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
, where a fifth capitol building was constructed. A sixth capitol building was erected in 1867, which continues to serve as the Illinois capitol today.
Though it was ostensibly a " free state", there was nonetheless slavery in Illinois. The ethnic French had owned black slaves since the 1720s, and American settlers had already brought slaves into the area from Kentucky. Slavery was nominally banned by the Northwest Ordinance, but that was not enforced for those already holding slaves. When Illinois became a state in 1818, the Ordinance no longer applied, and about 900 slaves were held in the state. As the southern part of the state, later known as "Egypt" or "Little Egypt", was largely settled by migrants from the South, the section was hostile to free blacks. Settlers were allowed to bring slaves with them for labor, but, in 1822, state residents voted against making slavery legal. Still, most residents opposed allowing free blacks as permanent residents. Some settlers brought in slaves seasonally or as house servants. The Illinois Constitution of 1848 was written with a provision for exclusionary laws to be passed. In 1853, John A. Logan helped pass a law to prohibit all African Americans, including freedmen, from settling in the state.
The winter of 1830–1831 is called the "Winter of the Deep Snow"; a sudden, deep snowfall blanketed the state, making travel impossible for the rest of the winter, and many travelers perished. Several severe winters followed, including the "Winter of the Sudden Freeze". On December 20, 1836, a fast-moving cold front passed through, freezing puddles in minutes and killing many travelers who could not reach shelter. The adverse weather resulted in crop failures in the northern part of the state. The southern part of the state shipped food north, and this may have contributed to its name, " Little Egypt", after the Biblical story of Joseph in Egypt
Joseph (; he, יוֹסֵף, , He shall add; Standard: ''Yōsef'', Tiberian: ''Yōsēp̄''; alternatively: יְהוֹסֵף, lit. 'Yahweh shall add'; Standard: ''Yəhōsef'', Tiberian: ''Yŏhōsēp̄''; ar, يوسف, Yūsuf; grc, Ἰωσ� ...
supplying grain to his brothers.
In 1832, the Black Hawk War was fought in Illinois and present-day Wisconsin between the United States and the Sauk, Fox (Meskwaki), and Kickapoo
Kickapoo may refer to:
People
* Kickapoo people, a Native American nation
** Kickapoo language, spoken by that people
** Kickapoo Tribe of Kansas, a federally recognized tribe of Kickapoo people
** Kickapoo Tribe of Oklahoma, a federally recog ...
Indian tribes. It represents the end of Indian resistance to white settlement in the Chicago region. The Indians had been forced to leave their homes and move to Iowa in 1831; when they attempted to return, they were attacked and eventually defeated by U.S. militia. The survivors were forced back to Iowa.
By 1839, the Latter Day Saints had founded a utopian city called Nauvoo, formerly called Commerce. Located in Hancock County along the Mississippi River, Nauvoo flourished and, by 1844, briefly surpassed Chicago for the position of the state's largest city. But in that same year, the Latter Day Saint movement founder, Joseph Smith, was killed in the Carthage Jail, about 30 miles away from Nauvoo. Following a succession crisis A succession crisis is a crisis that arises when an order of succession fails, for example when a king dies without an indisputable heir. It may result in a war of succession.
Examples include (see List of wars of succession):
*Multiple periods dur ...
, Brigham Young led most Latter Day Saints out of Illinois in a mass exodus
Human migration is the movement of people from one place to another with intentions of settling, permanently or temporarily, at a new location (geographic region). The movement often occurs over long distances and from one country to another (ex ...
to present-day Utah; after close to six years of rapid development, Nauvoo quickly declined afterward.
After it was established in 1833, Chicago gained prominence as a Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
port, and then as an Illinois and Michigan Canal
The Illinois and Michigan Canal connected the Great Lakes to the Mississippi River and the Gulf of Mexico. In Illinois, it ran from the Chicago River in Bridgeport, Chicago to the Illinois River at LaSalle-Peru. The canal crossed the Chicago Po ...
port after 1848, and as a rail hub soon afterward. By 1857, Chicago was Illinois's largest city. With the tremendous growth of mines and factories in the state in the 19th century, Illinois was the ground for the formation of labor unions in the United States
Labor unions in the United States are organizations that represent workers in many industries recognized under US labor law since the 1935 enactment of the National Labor Relations Act. Their activity today centers on collective bargaining over w ...
.
In 1847, after lobbying by Dorothea L. Dix, Illinois became one of the first states to establish a system of state-supported treatment of mental illness and disabilities, replacing local almshouse
An almshouse (also known as a bede-house, poorhouse, or hospital) was charitable housing provided to people in a particular community, especially during the medieval era. They were often targeted at the poor of a locality, at those from certain ...
s. Dix came into this effort after having met J. O. King, a Jacksonville, Illinois
Jacksonville is a city in Morgan County, Illinois, Morgan County, Illinois, United States. The population was 19,446 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Morgan County. It is home to Illinois College, Illinois School for the Deaf, and the ...
businessman, who invited her to Illinois, where he had been working to build an asylum for the insane. With the lobbying expertise of Dix, plans for the Jacksonville State Hospital (now known as the Jacksonville Developmental Center) were signed into law on March 1, 1847.
Civil War and after
 During the American Civil War, Illinois ranked fourth in men who served (more than 250,000) in the Union Army, a figure surpassed by only New York, Pennsylvania, and Ohio. Beginning with President
During the American Civil War, Illinois ranked fourth in men who served (more than 250,000) in the Union Army, a figure surpassed by only New York, Pennsylvania, and Ohio. Beginning with President Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
's first call for troops and continuing throughout the war, Illinois mustered 150 infantry regiments, which were numbered from the 7th to the 156th regiments. Seventeen cavalry regiments were also gathered, as well as two light artillery regiments. The town of Cairo, at the southern tip of the state at the confluence of the Mississippi and Ohio Rivers, served as a strategically important supply base and training center for the Union army. For several months, both General Grant and Admiral Foote had headquarters in Cairo.
During the Civil War, and more so afterwards, Chicago's population skyrocketed, which increased its prominence. The Pullman Strike and Haymarket Riot, in particular, greatly influenced the development of the American labor movement
The labour movement or labor movement consists of two main wings: the trade union movement (British English) or labor union movement (American English) on the one hand, and the political labour movement on the other.
* The trade union movement ...
. From Sunday, October 8, 1871, until Tuesday, October 10, 1871, the Great Chicago Fire burned in downtown Chicago, destroying .
20th century
At the turn of the 20th century, Illinois had a population of nearly 5 million. Many people from other parts of the country were attracted to the state by employment caused by the expanding industrial base. Whites were 98% of the state's population. Bolstered by continued immigration from southern and eastern Europe, and by the African-American Great Migration from the South, Illinois grew and emerged as one of the most important states in the union. By the end of the century, the population had reached 12.4 million. The Century of Progress World's fair was held at Chicago in 1933. Oil strikes in Marion County and Crawford County led to a boom in 1937, and by 1939, Illinois ranked fourth in U.S. oil production. Illinois manufactured 6.1 percent of total United States military armaments produced during World War II, ranking seventh among the 48 states. Chicago became an ocean port with the opening of theSaint Lawrence Seaway
The St. Lawrence Seaway (french: la Voie Maritime du Saint-Laurent) is a system of locks, canals, and channels in Canada and the United States that permits oceangoing vessels to travel from the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes of North Americ ...
in 1959. The seaway and the Illinois Waterway connected Chicago to both the Mississippi River and the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
. In 1960, Ray Kroc opened the first McDonald's franchise in Des Plaines (which still exists as a museum, with a working McDonald's across the street).
Illinois had a prominent role in the emergence of the nuclear age. In 1942, as part of the Manhattan Project, the University of Chicago conducted the first sustained nuclear chain reaction
In nuclear physics, a nuclear chain reaction occurs when one single nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more subsequent nuclear reactions, thus leading to the possibility of a self-propagating series of these reactions. The specific nu ...
. In 1957, Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory is a science and engineering research United States Department of Energy National Labs, national laboratory operated by University of Chicago, UChicago Argonne LLC for the United States Department of Energy. The facil ...
, near Chicago, activated the first experimental nuclear power generating system in the United States. By 1960, the first privately financed nuclear plant in the United States, Dresden 1, was dedicated near Morris. In 1967, Fermilab, a national nuclear research facility near Batavia, opened a particle accelerator, which was the world's largest for over 40 years. With eleven plants currently operating, Illinois leads all states in the amount of electricity generated from nuclear power.
In 1961, Illinois became the first state in the nation to adopt the recommendation of the American Law Institute
The American Law Institute (ALI) is a research and advocacy group of judges, lawyers, and legal scholars established in 1923 to promote the clarification and simplification of United States common law and its adaptation to changing social needs. ...
and pass a comprehensive criminal code revision that repealed the law against sodomy. The code also abrogated common law crimes and established an age of consent
The age of consent is the age at which a person is considered to be legally competent to consent to sexual acts. Consequently, an adult who engages in sexual activity with a person younger than the age of consent is unable to legally claim ...
of 18. The state's fourth constitution was adopted in 1970, replacing the 1870 document.
The first Farm Aid concert was held in Champaign to benefit American farmers, in 1985. The worst upper Mississippi River flood of the century, the Great Flood of 1993, inundated many towns and thousands of acres of farmland.
21st century
On August 28, 2017, Illinois GovernorBruce Rauner
Bruce Vincent Rauner (; born February 18, 1956) is an American businessman, philanthropist, and politician who served as the 42nd governor of Illinois from 2015 to 2019. Prior to his election, he was the chairman of R8 Capital Partners and chai ...
signed a bill into law that prohibited state and local police from arresting anyone solely due to their immigration status or due to federal detainers. Some fellow Republicans criticized Rauner for his action, claiming the bill made Illinois a sanctuary state.
Geology
During the early part of the Paleozoic Era, the area that would one day become Illinois was submerged beneath a shallow sea and located near the Equator. Diverse marine life lived at this time, including trilobites, brachiopods, and crinoids. Changing environmental conditions led to the formation of large coal swamps in theCarboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carbonifero ...
.
Illinois was above sea level for at least part of the Mesozoic, but by its end was again submerged by the Western Interior Seaway. This receded by the Eocene Epoch.
During the Pleistocene Epoch, vast ice sheets covered much of Illinois, with only the Driftless Area remaining exposed. These glaciers carved the basin of Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that o ...
and left behind traces of ancient glacial lakes and moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice shee ...
s.
Geography
Illinois is located in the Midwest region of the United States and is one of the eight states in the Great Lakes region of North America (which also includes Ontario, Canada).Boundaries
Illinois's eastern border with Indiana consists of a north–south line at 87° 31′ 30″ west longitude inLake Michigan
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that o ...
at the north, to the Wabash River in the south above Post Vincennes. The Wabash River continues as the eastern/southeastern border with Indiana until the Wabash enters the Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
. This marks the beginning of Illinois's southern border with Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to ...
, which runs along the northern shoreline of the Ohio River. Most of the western border with Missouri and Iowa is the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
; Kaskaskia is an exclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
of Illinois, lying west of the Mississippi and reachable only from Missouri. The state's northern border with Wisconsin is fixed at 42° 30′ north latitude. The northeastern border of Illinois lies in Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that o ...
, within which Illinois shares a water boundary with the state of Michigan, as well as Wisconsin and Indiana.
Topography
 Though Illinois lies entirely in the Interior Plains, it does have some minor variation in its elevation. In extreme northwestern Illinois, the Driftless Area, a region of unglaciated and therefore higher and more rugged topography, occupies a small part of the state. Southern Illinois includes the hilly areas around the Shawnee National Forest.
Charles Mound, located in the Driftless region, has the state's highest natural elevation above sea level at . Other highlands include the Shawnee Hills in the south, and there is varying topography along its rivers; the
Though Illinois lies entirely in the Interior Plains, it does have some minor variation in its elevation. In extreme northwestern Illinois, the Driftless Area, a region of unglaciated and therefore higher and more rugged topography, occupies a small part of the state. Southern Illinois includes the hilly areas around the Shawnee National Forest.
Charles Mound, located in the Driftless region, has the state's highest natural elevation above sea level at . Other highlands include the Shawnee Hills in the south, and there is varying topography along its rivers; the Illinois River
The Illinois River ( mia, Inoka Siipiiwi) is a principal tributary of the Mississippi River and is approximately long. Located in the U.S. state of Illinois, it has a drainage basin of . The Illinois River begins at the confluence of the D ...
bisects the state northeast to southwest. The floodplain on the Mississippi River from Alton to the Kaskaskia River is known as the American Bottom.
Divisions
 Illinois has three major geographical divisions. Northern Illinois is dominated by
Illinois has three major geographical divisions. Northern Illinois is dominated by Chicago metropolitan area
The Chicago metropolitan area, also colloquially referred to as Chicagoland, is a metropolitan area in the Midwestern United States. Encompassing 10,286 sq mi (28,120 km2), the metropolitan area includes the city of Chicago, its suburbs and hi ...
, or Chicagoland, which is the city of Chicago and its suburbs, and the adjoining exurban area into which the metropolis is expanding. As defined by the federal government, the Chicago metro area includes several counties in Illinois, Indiana, and Wisconsin, and has a population of over 9.8 million. Chicago itself is a cosmopolitan city, densely populated, industrialized, the transportation hub of the nation, and settled by a wide variety of ethnic groups. The city of Rockford, Illinois's third-largest city and center of the state's fourth largest metropolitan area, sits along Interstates 39 and 90 some northwest of Chicago. The Quad Cities region, located along the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
in northern Illinois, had a population of 381,342 in 2011.
The midsection of Illinois is the second major division, called Central Illinois. Historically prairie, it is now mainly agricultural and known as the Heart of Illinois. It is characterized by small towns and medium–small cities. The western section (west of the Illinois River) was originally part of the Military Tract of 1812 and forms the conspicuous western bulge of the state. Agriculture, particularly corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
and soybeans, as well as educational institutions and manufacturing centers, figure prominently in Central Illinois. Cities include Peoria; Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
, the state capital; Quincy; Decatur; Bloomington-Normal; and Champaign-Urbana __NOTOC__
Urbana can refer to:
Places Italy
*Urbana, Italy
United States
*Urbana, Illinois
**Urbana (conference), a Christian conference formerly held in Urbana, Illinois
*Urbana, Indiana
* Urbana, Iowa
*Urbana, Kansas
* Urbana, Maryland
*Urbana, ...
.
The third division is Southern Illinois, comprising the area south of U.S. Route 50
U.S. Route 50 or U.S. Highway 50 (US 50) is a major east–west route of the U.S. Highway system, stretching from Interstate 80 (I-80) in West Sacramento, California, to Maryland Route 528 (MD 528) in Ocean City, Maryland, on the Atlanti ...
, including Little Egypt, near the juncture of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
and Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
. Southern Illinois is the site of the ancient city of Cahokia, as well as the site of the first state capital at Kaskaskia, which today is separated from the rest of the state by the Mississippi River. This region has a somewhat warmer winter climate, different variety of crops (including some cotton farming in the past), more rugged topography (due to the area remaining unglaciated during the Illinoian Stage, unlike most of the rest of the state), as well as small-scale oil deposits and coal mining. The Illinois suburbs of St. Louis, such as East St. Louis, are located in this region, and collectively, they are known as the Metro-East. The other somewhat significant concentration of population in Southern Illinois is the Carbondale-Marion-Herrin, Illinois Combined Statistical Area centered on Carbondale and Marion, a two-county area that is home to 123,272 residents. A portion of southeastern Illinois is part of the extended Evansville, Indiana, Metro Area, locally referred to as the Tri-State with Indiana and Kentucky. Seven Illinois counties are in the area.
In addition to these three, largely latitudinally defined divisions, all of the region outside the Chicago metropolitan area is often called " downstate" Illinois. This term is flexible, but is generally meant to mean everything outside the influence of the Chicago area. Thus, some cities in ''Northern'' Illinois, such as DeKalb, which is west of Chicago, and Rockford—which is actually north of Chicago—are sometimes incorrectly considered to be 'downstate'.
Climate
humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
(Koppen ''Cfa''), with more moderate winters. Average yearly precipitation for Illinois varies from just over at the southern tip to around in the northern portion of the state. Normal annual snowfall exceeds in the Chicago area, while the southern portion of the state normally receives less than .Illinois State Climatologist Office. Retrieved April 22, 2006. The all-time high temperature was , recorded on July 14, 1954, at East St. Louis, and the all-time low temperature was , recorded on January 31, 2019, during the January 2019 North American cold wave at a weather station near
Mount Carroll
Mount Carroll is a city in Carroll County, Illinois, United States. It is the Carroll County seat. The population was 1479 at the 2020 census.
Due to its elevation and northwesterly location, Mount Carroll is subject to unusually cold winter wea ...
, and confirmed on March 5, 2019. This followed the previous record of recorded on January 5, 1999, near Congerville. Prior to the Mount Carroll record, a temperature of was recorded on January 15, 2009, at Rochelle, but at a weather station not subjected to the same quality control as official records.
Illinois averages approximately 51 days of thunderstorm activity a year, which ranks somewhat above average in the number of thunderstorm days for the United States. Illinois is vulnerable to tornadoes, with an average of 35 occurring annually, which puts much of the state at around five tornadoes per annually.Annual average number of tornadoes, 1953–2004", NOAA National Climatic Data Center. Retrieved October 24, 2006. While tornadoes are no more powerful in Illinois than other states, some of Tornado Alley's deadliest tornadoes on record have occurred in the state. The
Tri-State Tornado
On March 18, 1925, one of the deadliest tornado outbreaks in recorded history generated at least twelve significant tornadoes and spanned a large portion of the midwestern and southern United States. In all, at least 751 people were ki ...
of 1925 killed 695 people in three states; 613 of the victims died in Illinois.
Demographics

2020 United States census
The United States census of 2020 was the twenty-fourth decennial United States census. Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2020. Other than a pilot study during the 2000 census, this was the first U.S. census to of ...
, moving from the fifth-largest state to the sixth-largest state (losing out to Pennsylvania). Illinois' population slightly declined in 2020 from the 2010 United States census
The United States census of 2010 was the twenty-third United States national census. National Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2010. The census was taken via mail-in citizen self-reporting, with enumerators servin ...
by just over 18,000 residents and the overall population was quite higher than recent census estimates.
Illinois is the most populous state in the Midwest region. Chicago, the third-most populous city in the United States, is the center of the Chicago metropolitan area
The Chicago metropolitan area, also colloquially referred to as Chicagoland, is a metropolitan area in the Midwestern United States. Encompassing 10,286 sq mi (28,120 km2), the metropolitan area includes the city of Chicago, its suburbs and hi ...
or Chicagoland, as this area is nicknamed. Although the Chicago metropolitan area comprises only 9% of the land area of the state, it contains 65% of the state's residents. The losses of population anticipated from the 2020 census results do not arise from the Chicago metro area; rather the declines are from the Downstate counties.
2019 American Community Survey
According to 2019 U.S. Census Bureau estimates, Illinois's population was 71.4% White (60.7% Non-Hispanic White), 5.6% Asian, 0.2% Some Other Race, 13.9% Black or African American, 0.1% Native Americans and Alaskan Native, 0.1% Pacific Islander and 2.0% from two or more races. The White population continues to remain the largest racial category in Illinois as Hispanics primarily identify as White (61.1%) with others identifying as Some Other Race (32.0%), Multiracial (4.3%), Black (1.4%), American Indian and Alaskan Native (0.2%), Asian (0.1%), and Hawaiian and Pacific Islander (0.1%). By ethnicity, 17.5% of the total population is Hispanic-Latino (of any race) and 82.5% is Non-Hispanic (of any race). If treated as a separate category, Hispanics are the largest minority group in Illinois. The state's most populous ethnic group, non-Hispanic white, has declined from 83.5% in 1970 to 60.90% in 2018. , 49.4% of Illinois's population younger than age 1 were minorities (Note: Children born to white Hispanics or to a sole full or partial minority parent are counted as minorities). At the 2007 estimates from the U.S. Census Bureau, there were 1,768,518 foreign-born inhabitants of the state or 13.8% of the population, with 48.4% from Latin America, 24.6% from Asia, 22.8% from Europe, 2.9% from Africa, 1.2% from Canada, and 0.2% from Oceania. Of the foreign-born population, 43.7% were naturalized U.S. citizens, and 56.3% were not U.S. citizens. In 2007, 6.9% of Illinois's population was reported as being under age 5, 24.9% under age 18 and 12.1% were age 65 and over. Females made up approximately 50.7% of the population. According to the 2007 estimates, 21.1% of the population had German ancestry, 13.3% had Irish ancestry, 8% had British ancestry, 7.9% had Polish ancestry, 6.4% had Italian ancestry, 4.6% listed themselves asAmerican
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
, 2.4% had Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
ancestry, 2.2% had French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
ancestry, other than Basque, 1.6% had Dutch ancestry, and 1.4% had Norwegian ancestry. Illinois also has large numbers of African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
and Latinos (mostly Mexicans
Mexicans ( es, mexicanos) are the citizens of the United Mexican States.
The most spoken language by Mexicans is Spanish language, Spanish, but some may also speak languages from 68 different Languages of Mexico, Indigenous linguistic groups ...
and Puerto Ricans
Puerto Ricans ( es, Puertorriqueños; or boricuas) are the people of Puerto Rico, the inhabitants, and citizens of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico and their descendants.
Overview
The culture held in common by most Puerto Ricans is referred t ...
).
Chicago, along the shores of Lake Michigan, is the nation's third largest city. In 2000, 23.3% of Illinois's population lived in the city of Chicago, 43.3% in Cook County, and 65.6% in the counties of the Chicago metropolitan area
The Chicago metropolitan area, also colloquially referred to as Chicagoland, is a metropolitan area in the Midwestern United States. Encompassing 10,286 sq mi (28,120 km2), the metropolitan area includes the city of Chicago, its suburbs and hi ...
: Will, DuPage, Kane, Lake, and McHenry counties, as well as Cook County. The remaining population lives in the smaller cities and rural areas that dot the state's plains. As of 2000, the state's center of population
In demographics, the center of population (or population center) of a region is a geographical point that describes a centerpoint of the region's population. There are several ways of defining such a "center point", leading to different geogr ...
was at , located in Grundy County, northeast of the village of Mazon Mazon may refer to:
Places in the United States
* Mazon, Illinois, a village
* Mazon Creek fossils
* Mazon River
* Mazon station, Mazon, Illinois
* Mazon Township, Grundy County, Illinois
Organizations
* MAZON: A Jewish Response to Hunger, a no ...
.
Birth data
''Births do not add up, because Hispanics are counted both by ethnicity and by race.'' *Since 2016, data for births of White Hispanic origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.Urban areas
Chicago is the largest city in the state and the third-most populous city in the United States, with its 2020 population of 2,746,388. The U.S. Census Bureau currently lists seven other cities with populations of over 100,000 within Illinois. Based upon the U.S. Census Bureau's official 2010 population: Aurora, a Chicago satellite town that eclipsed Rockford for the title of second-most populous city in Illinois; its 2010 population was 197,899. Rockford, at 152,871, is the third-largest city in the state, and is the largest city in the state not located within the Chicago suburbs. Joliet, located in metropolitan Chicago, is the fourth-largest city in the state, with a population of 147,433. Naperville, a suburb of Chicago, is fifth with 141,853. Naperville and Aurora share a boundary along Illinois Route 59.Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
, the state's capital, comes in as sixth-most populous with 117,352 residents. Peoria, which decades ago was the second-most populous city in the state, is seventh with 115,007. The eighth-largest and final city in the 100,000 club is Elgin
Elgin may refer to:
Places
Canada
* Elgin County, Ontario
* Elgin Settlement, a 19th-century community for freed slaves located in present-day North Buxton and South Buxton, Chatham-Kent, Ontario
* Elgin, a village in Rideau Lakes, Ontario ...
, a northwest suburb of Chicago, with a 2010 population of 108,188.
The most populated city in the state south of Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
is Belleville, with 44,478 people at the 2010 census. It is located in the Illinois portion of Greater St. Louis
Greater St. Louis is a bi-state metropolitan area that completely surrounds and includes the independent city of St. Louis, the principal city. It includes parts of both Missouri and Illinois. The city core is on the Mississippi Riverfront on t ...
(often called the Metro-East area), which has a rapidly growing population of over 700,000.
Other major urban areas include the Champaign-Urbana Metropolitan Area, which has a combined population of almost 230,000 people, the Illinois portion of the Quad Cities area with about 215,000 people, and the Bloomington-Normal area with a combined population of over 165,000.
Languages
The official language of Illinois is English, although between 1923 and 1969, state law gave official status to "the American language". Nearly 80% of people in Illinois speak English natively, and most of the rest speak it fluently as a second language. A number of dialects ofAmerican English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken lan ...
are spoken, ranging from Inland Northern American English and African-American English around Chicago, to Midland American English in Central Illinois, to Southern American English in the far south.
Over 20% of Illinoians speak a language other than English at home, of which Spanish is by far the most widespread, at more than 12% of the total population. A sizeable number of Polish speakers is present in the Chicago Metropolitan Area. Illinois Country French has mostly gone extinct in Illinois, although it is still celebrated in the French Colonial Historic District.
Religion
Christianity
Roman Catholics constitute the single largest religious denomination in Illinois; they are heavily concentrated in and around Chicago and account for nearly 30% of the state's population. However, taken together as a group, the various Protestant denominations comprise a greater percentage of the state's population than do Catholics. In 2010, Catholics in Illinois numbered 3,648,907. The largest Protestant denominations were the United Methodist Church with 314,461 members and theSouthern Baptist Convention
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC) is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist denomination, and the largest Protestant and second-largest Christian denomination in the United States. The wor ...
with 283,519. Illinois has one of the largest concentrations of Missouri Synod Lutherans in the United States.
 Illinois played an important role in the early Latter Day Saint movement, with Nauvoo becoming a gathering place for Mormons in the early 1840s. Nauvoo was the location of the
Illinois played an important role in the early Latter Day Saint movement, with Nauvoo becoming a gathering place for Mormons in the early 1840s. Nauvoo was the location of the succession crisis A succession crisis is a crisis that arises when an order of succession fails, for example when a king dies without an indisputable heir. It may result in a war of succession.
Examples include (see List of wars of succession):
*Multiple per