Iceland Köppen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's
 The Sagas of Icelanders say that a Norwegian named Naddodd (or Naddador) was the first
The Sagas of Icelanders say that a Norwegian named Naddodd (or Naddador) was the first
"Is Iceland Really Green and Greenland Really Icy?"
''
 According to both Landnámabók and Íslendingabók, monks known as the Papar lived in Iceland before Scandinavian settlers arrived, possibly members of a Hiberno-Scottish mission. Recent
According to both Landnámabók and Íslendingabók, monks known as the Papar lived in Iceland before Scandinavian settlers arrived, possibly members of a Hiberno-Scottish mission. Recent
 The Icelandic Commonwealth lasted until the 13th century when the political system devised by the original settlers proved unable to cope with the increasing power of Icelandic chieftains. The internal struggles and civil strife of the Age of the Sturlungs led to the signing of the
The Icelandic Commonwealth lasted until the 13th century when the political system devised by the original settlers proved unable to cope with the increasing power of Icelandic chieftains. The internal struggles and civil strife of the Age of the Sturlungs led to the signing of the
 The Danish–Icelandic Act of Union, an agreement with Denmark signed on 1 December 1918 and valid for 25 years, recognised Iceland as a fully sovereign and independent state in a personal union with Denmark. The Government of Iceland established an embassy in Copenhagen and requested that Denmark carry out on its behalf certain defence and foreign affairs matters, subject to consultation with the Althing. Danish embassies around the world displayed two coats of arms and two flags: those of the Kingdom of Denmark and those of the Kingdom of Iceland. Iceland's legal position became comparable to those of countries belonging to the Commonwealth of Nations, such as Canada, whose sovereign is King Charles III.
During World War II, Iceland joined Denmark in asserting neutrality. After the German occupation of Denmark on 9 April 1940, the Althing replaced the King with a regent and declared that the Icelandic government would take control of its own defence and foreign affairs. A month later, British armed forces conducted Operation Fork, the invasion and occupation of the country, violating Icelandic
The Danish–Icelandic Act of Union, an agreement with Denmark signed on 1 December 1918 and valid for 25 years, recognised Iceland as a fully sovereign and independent state in a personal union with Denmark. The Government of Iceland established an embassy in Copenhagen and requested that Denmark carry out on its behalf certain defence and foreign affairs matters, subject to consultation with the Althing. Danish embassies around the world displayed two coats of arms and two flags: those of the Kingdom of Denmark and those of the Kingdom of Iceland. Iceland's legal position became comparable to those of countries belonging to the Commonwealth of Nations, such as Canada, whose sovereign is King Charles III.
During World War II, Iceland joined Denmark in asserting neutrality. After the German occupation of Denmark on 9 April 1940, the Althing replaced the King with a regent and declared that the Icelandic government would take control of its own defence and foreign affairs. A month later, British armed forces conducted Operation Fork, the invasion and occupation of the country, violating Icelandic
 On 31 December 1943, the Danish–Icelandic Act of Union expired after 25 years. Beginning on 20 May 1944, Icelanders voted in a four-day plebiscite on whether to terminate the personal union with Denmark, abolish the monarchy, and establish a republic. The vote was 97% to end the union, and 95% in favour of the new republican constitution. Iceland formally became a republic on 17 June 1944, with Sveinn Björnsson as its first president.
In 1946, the US Defence Force Allied left Iceland. The nation formally became a member of NATO on 30 March 1949, amid domestic controversy and riots. On 5 May 1951, a defence agreement was signed with the United States. American troops returned to Iceland as the
On 31 December 1943, the Danish–Icelandic Act of Union expired after 25 years. Beginning on 20 May 1944, Icelanders voted in a four-day plebiscite on whether to terminate the personal union with Denmark, abolish the monarchy, and establish a republic. The vote was 97% to end the union, and 95% in favour of the new republican constitution. Iceland formally became a republic on 17 June 1944, with Sveinn Björnsson as its first president.
In 1946, the US Defence Force Allied left Iceland. The nation formally became a member of NATO on 30 March 1949, amid domestic controversy and riots. On 5 May 1951, a defence agreement was signed with the United States. American troops returned to Iceland as the
 Iceland is at the juncture of the North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans. The main island is entirely south of the
Iceland is at the juncture of the North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans. The main island is entirely south of the  Iceland is the world's 18th-largest island, and Europe's second-largest island after Great Britain. (The island of Ireland is third.) The main island covers , but the entire country is in size, of which 62.7% is tundra. Iceland contains about 30 minor islands, including the lightly populated Grímsey and the Vestmannaeyjar archipelago. Lakes and glaciers cover 14.3% of its surface; only 23% is vegetated. The largest lakes are Þórisvatn reservoir: and
Iceland is the world's 18th-largest island, and Europe's second-largest island after Great Britain. (The island of Ireland is third.) The main island covers , but the entire country is in size, of which 62.7% is tundra. Iceland contains about 30 minor islands, including the lightly populated Grímsey and the Vestmannaeyjar archipelago. Lakes and glaciers cover 14.3% of its surface; only 23% is vegetated. The largest lakes are Þórisvatn reservoir: and

 A geologically young land, Iceland is the surface expression of the Iceland Plateau, a large igneous province forming as a result of volcanism from the
A geologically young land, Iceland is the surface expression of the Iceland Plateau, a large igneous province forming as a result of volcanism from the  Another large eruption occurred on 21 May 2011. This time it was the Grímsvötn volcano, located under the thick ice of Europe's largest glacier, Vatnajökull. Grímsvötn is one of Iceland's most active volcanoes, and this eruption was much more powerful than the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull activity, with ash and lava hurled into the atmosphere, creating a large cloud.
A great deal of volcanic activity was occurring in the Reykjanes Peninsula in 2020 and into 2021, after nearly 800 years of inactivity. After the eruption of the Fagradalsfjall volcano on 19 March 2021,
Another large eruption occurred on 21 May 2011. This time it was the Grímsvötn volcano, located under the thick ice of Europe's largest glacier, Vatnajökull. Grímsvötn is one of Iceland's most active volcanoes, and this eruption was much more powerful than the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull activity, with ash and lava hurled into the atmosphere, creating a large cloud.
A great deal of volcanic activity was occurring in the Reykjanes Peninsula in 2020 and into 2021, after nearly 800 years of inactivity. After the eruption of the Fagradalsfjall volcano on 19 March 2021,
 The climate of Iceland's coast is
The climate of Iceland's coast is
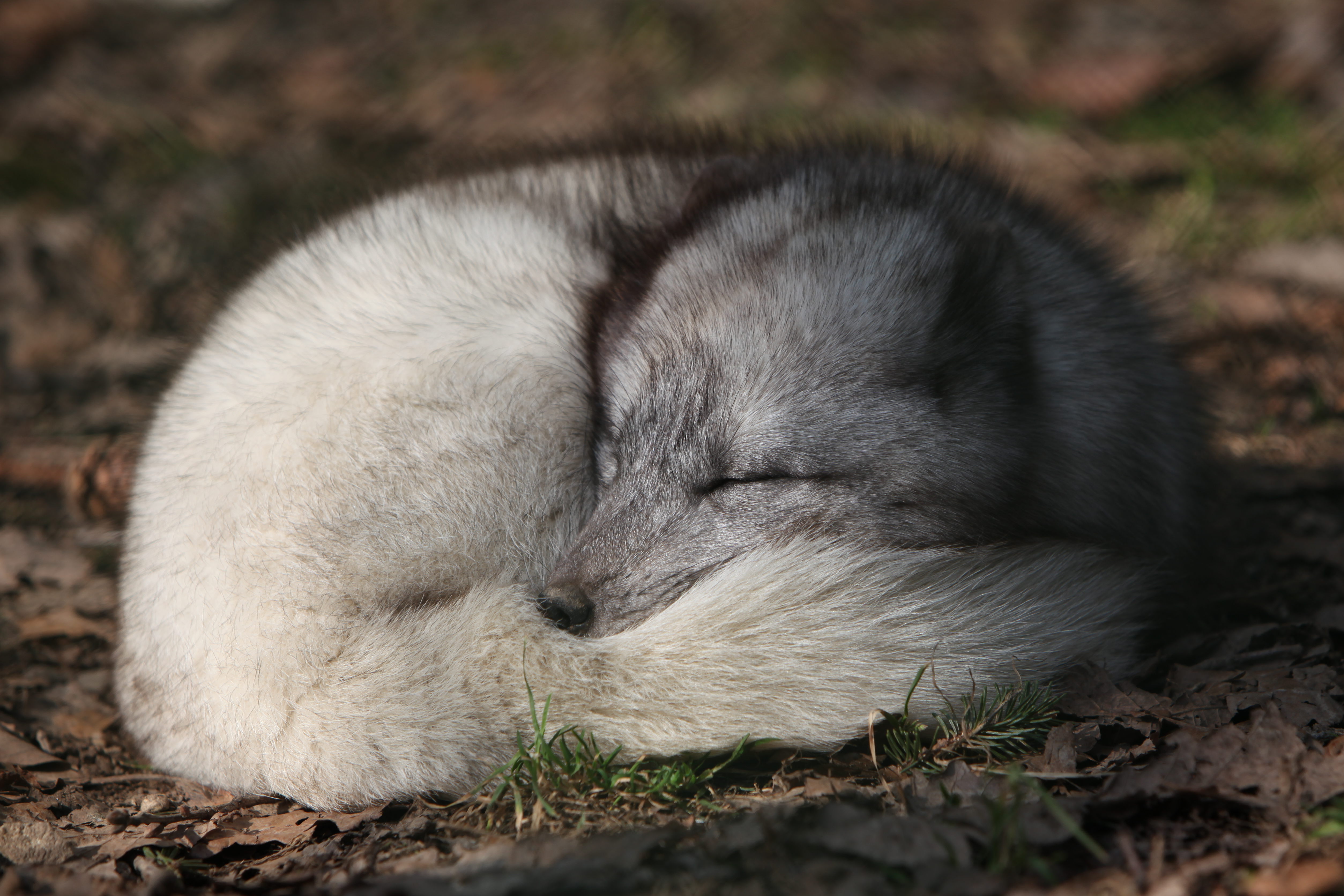 The only native land mammal when humans arrived was the Arctic fox, which came to the island at the end of the ice age, walking over the frozen sea. On rare occasions, bats have been carried to the island with the winds, but they are not able to breed there. No native or free-living reptiles or amphibians are on the island.
The animals of Iceland include the
The only native land mammal when humans arrived was the Arctic fox, which came to the island at the end of the ice age, walking over the frozen sea. On rare occasions, bats have been carried to the island with the winds, but they are not able to breed there. No native or free-living reptiles or amphibians are on the island.
The animals of Iceland include the
 Iceland has a left–right multi-party system. Following the
Iceland has a left–right multi-party system. Following the
Oecdbetterlifeindex.org. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
 Iceland is a representative democracy and a
Iceland is a representative democracy and a
Iceland adm location map.svg, Regions of Iceland
Electoral districts of Iceland.svg, Constituencies of Iceland
Lower level municipalities of Iceland.svg, Municipalities of Iceland
 Iceland, which is a member of the UN, NATO, EFTA,
Iceland, which is a member of the UN, NATO, EFTA, 
 In 2007, Iceland was the seventh-most productive country in the world per capita (US$54,858), and the fifth-most productive by GDP at
In 2007, Iceland was the seventh-most productive country in the world per capita (US$54,858), and the fifth-most productive by GDP at
 Iceland was hit especially hard by the Great Recession that began in December 2007 because of the failure of its banking system and a subsequent economic crisis. Before the crash of the country's three largest banks, Glitnir, Landsbanki and Kaupthing, their combined debt exceeded approximately six times the nation's gross domestic product of €14 billion ($19 billion). In October 2008, the Icelandic parliament passed emergency legislation to minimise the impact of the financial crisis. The Financial Supervisory Authority of Iceland used permission granted by the emergency legislation to take over the domestic operations of the three largest banks. Icelandic officials, including central bank governor Davíð Oddsson, stated that the state did not intend to take over any of the banks' foreign debts or assets. Instead, new banks were established to take on the domestic operations of the banks, and the old banks were to be run into bankruptcy.
On 28 October 2008, the Icelandic government raised interest rates to 18% (, it was 3.5%), a move forced in part by the terms of acquiring a loan from International Monetary Fund (IMF). After the rate hike, trading on the Icelandic króna finally resumed on the open market, with a valuation at around 250 ISK per euro, less than one-third the value of the 1:70 exchange rate during most of 2008, and a significant drop from the 1:150 exchange ratio of the week before. On 20 November 2008, the
Iceland was hit especially hard by the Great Recession that began in December 2007 because of the failure of its banking system and a subsequent economic crisis. Before the crash of the country's three largest banks, Glitnir, Landsbanki and Kaupthing, their combined debt exceeded approximately six times the nation's gross domestic product of €14 billion ($19 billion). In October 2008, the Icelandic parliament passed emergency legislation to minimise the impact of the financial crisis. The Financial Supervisory Authority of Iceland used permission granted by the emergency legislation to take over the domestic operations of the three largest banks. Icelandic officials, including central bank governor Davíð Oddsson, stated that the state did not intend to take over any of the banks' foreign debts or assets. Instead, new banks were established to take on the domestic operations of the banks, and the old banks were to be run into bankruptcy.
On 28 October 2008, the Icelandic government raised interest rates to 18% (, it was 3.5%), a move forced in part by the terms of acquiring a loan from International Monetary Fund (IMF). After the rate hike, trading on the Icelandic króna finally resumed on the open market, with a valuation at around 250 ISK per euro, less than one-third the value of the 1:70 exchange rate during most of 2008, and a significant drop from the 1:150 exchange ratio of the week before. On 20 November 2008, the
 Iceland has a high level of car ownership per capita, with a car for every 1.5 inhabitants; it is the main form of transport. Iceland has of administered roads, of which are paved and are not. A great number of roads remain unpaved, mostly little-used rural roads. The road speed limits are and in towns, on gravel country roads and on hard-surfaced roads.
Iceland has a high level of car ownership per capita, with a car for every 1.5 inhabitants; it is the main form of transport. Iceland has of administered roads, of which are paved and are not. A great number of roads remain unpaved, mostly little-used rural roads. The road speed limits are and in towns, on gravel country roads and on hard-surfaced roads.
 Renewable sources— geothermal and hydropower—provide effectively all of Iceland's electricity and around 85% of the nation's total primary energy consumption, with most of the remainder consisting of imported oil products used in transportation and in the fishing fleet. A 2000 report from the University of Iceland suggested that Iceland could potentially convert from oil to hydrogen power by 2040. Iceland's largest geothermal power plants are Hellisheiði and
Renewable sources— geothermal and hydropower—provide effectively all of Iceland's electricity and around 85% of the nation's total primary energy consumption, with most of the remainder consisting of imported oil products used in transportation and in the fishing fleet. A 2000 report from the University of Iceland suggested that Iceland could potentially convert from oil to hydrogen power by 2040. Iceland's largest geothermal power plants are Hellisheiði and
 The Ministry of Education, Science and Culture is responsible for the policies and methods that schools must use, and they issue the National Curriculum Guidelines. However, playschools, primary schools, and lower secondary schools are funded and administered by the municipalities. The government does allow citizens to home educate their children, however, under a very strict set of demands. Students must adhere closely to the government-mandated curriculum, and the parent teaching must acquire a government approved teaching certificate.
Nursery school, or , is non-compulsory education for children younger than six years and is the first step in the education system. The current legislation concerning playschools was passed in 1994. They are also responsible for ensuring that the curriculum is suitable to make the transition into compulsory education as easy as possible.
Compulsory education, or , comprises primary and lower secondary education, which often is conducted at the same institution. Education is mandatory by law for children aged from 6 to 16 years. The school year lasts nine months, beginning between 21 August and 1 September, and ending between 31 May and 10 June. The minimum number of school days was once 170, but after a new teachers' wage contract, it increased to 180. Lessons take place five days a week. All public schools have mandatory education in Christianity, although an exemption may be considered by the Minister of Education.
Upper secondary education, or , follows lower secondary education. These schools are also known as gymnasia in English. Though not compulsory, everyone who has had a compulsory education has the right to upper secondary education. This stage of education is governed by the Upper Secondary School Act of 1996. All schools in Iceland are mixed-sex schools. The largest seat of higher education is the University of Iceland, which has its main campus in central Reykjavík. Other schools offering university-level instruction include Reykjavík University, University of Akureyri, Agricultural University of Iceland and Bifröst University.
An OECD assessment found that 64% of Icelanders aged 25–64 have earned the equivalent of a high-school degree, which is lower than the OECD average of 73%. Among 25- to 34-year-olds, only 69% have earned the equivalent of a high-school degree, significantly lower than the OECD average of 80%. Nevertheless, Iceland's education system is considered excellent: the Programme for International Student Assessment ranks it as the 16th best performing, above the OECD average. Students were particularly proficient in reading and mathematics.
According to a 2013
The Ministry of Education, Science and Culture is responsible for the policies and methods that schools must use, and they issue the National Curriculum Guidelines. However, playschools, primary schools, and lower secondary schools are funded and administered by the municipalities. The government does allow citizens to home educate their children, however, under a very strict set of demands. Students must adhere closely to the government-mandated curriculum, and the parent teaching must acquire a government approved teaching certificate.
Nursery school, or , is non-compulsory education for children younger than six years and is the first step in the education system. The current legislation concerning playschools was passed in 1994. They are also responsible for ensuring that the curriculum is suitable to make the transition into compulsory education as easy as possible.
Compulsory education, or , comprises primary and lower secondary education, which often is conducted at the same institution. Education is mandatory by law for children aged from 6 to 16 years. The school year lasts nine months, beginning between 21 August and 1 September, and ending between 31 May and 10 June. The minimum number of school days was once 170, but after a new teachers' wage contract, it increased to 180. Lessons take place five days a week. All public schools have mandatory education in Christianity, although an exemption may be considered by the Minister of Education.
Upper secondary education, or , follows lower secondary education. These schools are also known as gymnasia in English. Though not compulsory, everyone who has had a compulsory education has the right to upper secondary education. This stage of education is governed by the Upper Secondary School Act of 1996. All schools in Iceland are mixed-sex schools. The largest seat of higher education is the University of Iceland, which has its main campus in central Reykjavík. Other schools offering university-level instruction include Reykjavík University, University of Akureyri, Agricultural University of Iceland and Bifröst University.
An OECD assessment found that 64% of Icelanders aged 25–64 have earned the equivalent of a high-school degree, which is lower than the OECD average of 73%. Among 25- to 34-year-olds, only 69% have earned the equivalent of a high-school degree, significantly lower than the OECD average of 80%. Nevertheless, Iceland's education system is considered excellent: the Programme for International Student Assessment ranks it as the 16th best performing, above the OECD average. Students were particularly proficient in reading and mathematics.
According to a 2013
 The original population of Iceland was of Nordic and
The original population of Iceland was of Nordic and
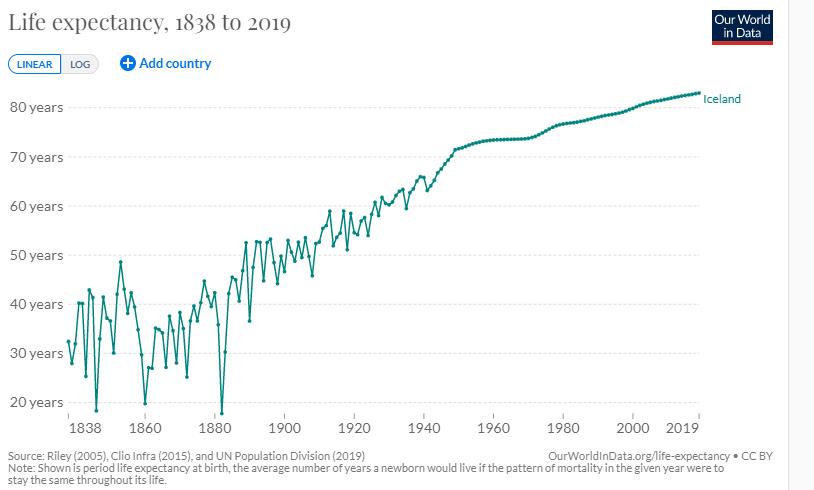 Iceland has a universal health care system that is administered by its Ministry of Welfare () and paid for mostly by taxes (85%) and to a lesser extent by service fees (15%). Unlike most countries, there are no private hospitals, and private insurance is practically nonexistent.
A considerable portion of the government budget is assigned to health care, and Iceland ranks 11th in health care expenditures as a percentage of GDP and 14th in spending per capita. Overall, the country's health care system is one of the best performing in the world, ranked 15th by the World Health Organization. According to an OECD report, Iceland devotes far more resources to healthcare than most industrialised nations. , Iceland had 3.7 doctors per 1,000 people (compared with an average of 3.1 in OECD countries) and 15.3 nurses per 1,000 people (compared with an OECD average of 8.4).
Icelanders are among the world's healthiest people, with 81% reporting they are in good health, according to an OECD survey. Although it is a growing problem, obesity is not as prevalent as in other developed countries. Iceland has many campaigns for health and wellbeing, including the famous television show '' Lazytown'', starring and created by former gymnastics champion
Iceland has a universal health care system that is administered by its Ministry of Welfare () and paid for mostly by taxes (85%) and to a lesser extent by service fees (15%). Unlike most countries, there are no private hospitals, and private insurance is practically nonexistent.
A considerable portion of the government budget is assigned to health care, and Iceland ranks 11th in health care expenditures as a percentage of GDP and 14th in spending per capita. Overall, the country's health care system is one of the best performing in the world, ranked 15th by the World Health Organization. According to an OECD report, Iceland devotes far more resources to healthcare than most industrialised nations. , Iceland had 3.7 doctors per 1,000 people (compared with an average of 3.1 in OECD countries) and 15.3 nurses per 1,000 people (compared with an OECD average of 8.4).
Icelanders are among the world's healthiest people, with 81% reporting they are in good health, according to an OECD survey. Although it is a growing problem, obesity is not as prevalent as in other developed countries. Iceland has many campaigns for health and wellbeing, including the famous television show '' Lazytown'', starring and created by former gymnastics champion
 Icelanders have freedom of religion guaranteed under the Constitution, although the Church of Iceland, a Lutheran body, is the
Icelanders have freedom of religion guaranteed under the Constitution, although the Church of Iceland, a Lutheran body, is the
 Iceland's best-known classical works of literature are the Icelanders' sagas, prose epics set in Iceland's age of settlement. The most famous of these include '' Njáls saga'', about an epic blood feud, and ''
Iceland's best-known classical works of literature are the Icelanders' sagas, prose epics set in Iceland's age of settlement. The most famous of these include '' Njáls saga'', about an epic blood feud, and ''
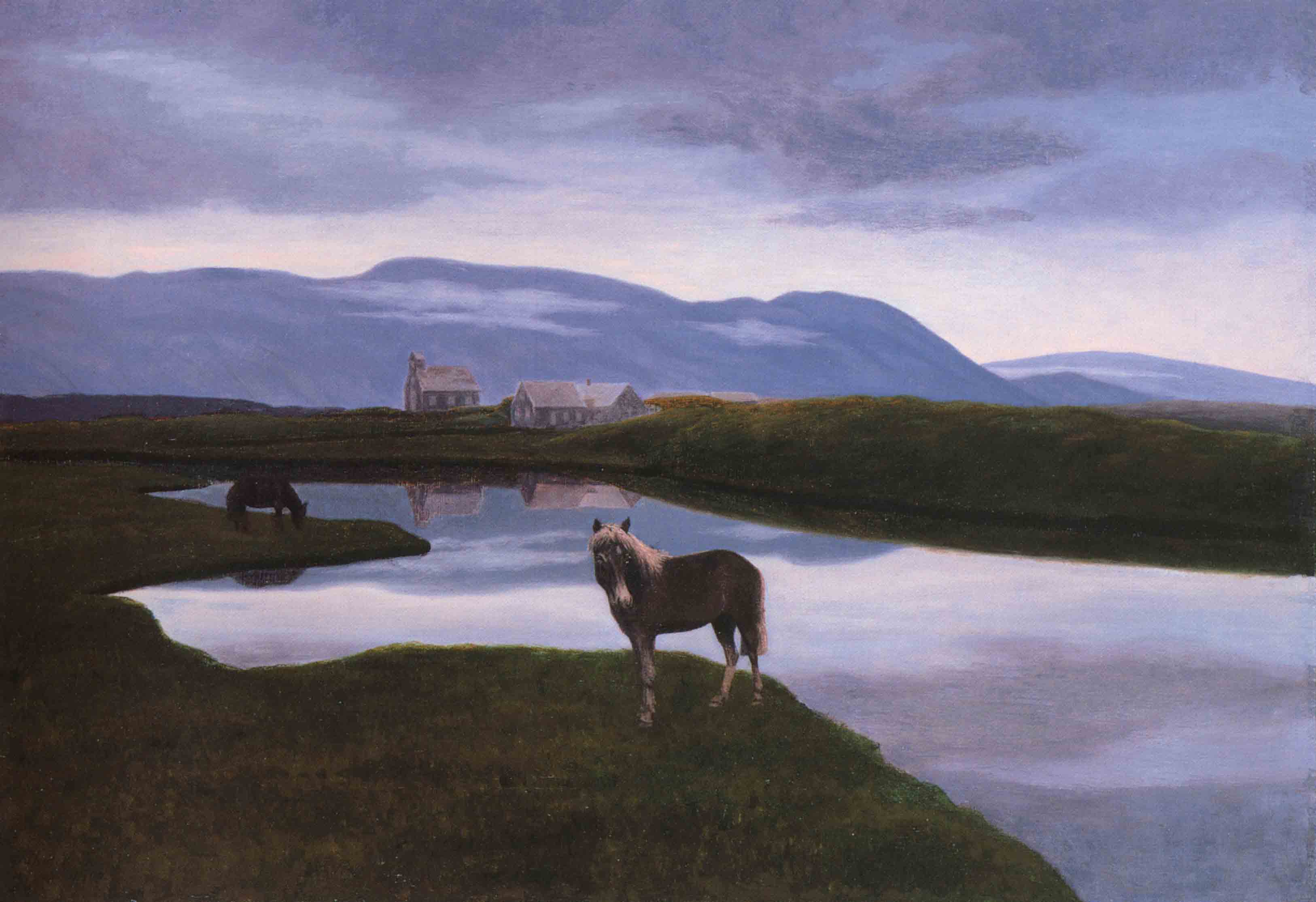 Contemporary Icelandic painting is typically traced to the work of Þórarinn Þorláksson, who, following formal training in art in the 1890s in Copenhagen, returned to Iceland to paint and exhibit works from 1900 to his death in 1924, almost exclusively portraying the Icelandic landscape. Several other Icelandic men and women artists studied at Royal Danish Academy of Fine Arts at that time, including Ásgrímur Jónsson, who together with Þórarinn created a distinctive portrayal of Iceland's landscape in a romantic naturalistic style. Other landscape artists quickly followed in the footsteps of Þórarinn and Ásgrímur. These included
Contemporary Icelandic painting is typically traced to the work of Þórarinn Þorláksson, who, following formal training in art in the 1890s in Copenhagen, returned to Iceland to paint and exhibit works from 1900 to his death in 1924, almost exclusively portraying the Icelandic landscape. Several other Icelandic men and women artists studied at Royal Danish Academy of Fine Arts at that time, including Ásgrímur Jónsson, who together with Þórarinn created a distinctive portrayal of Iceland's landscape in a romantic naturalistic style. Other landscape artists quickly followed in the footsteps of Þórarinn and Ásgrímur. These included
 Much Icelandic music is related to Nordic music, and includes folk and
Much Icelandic music is related to Nordic music, and includes folk and
 Iceland's largest television stations are the state-run Sjónvarpið and the privately owned
Iceland's largest television stations are the state-run Sjónvarpið and the privately owned
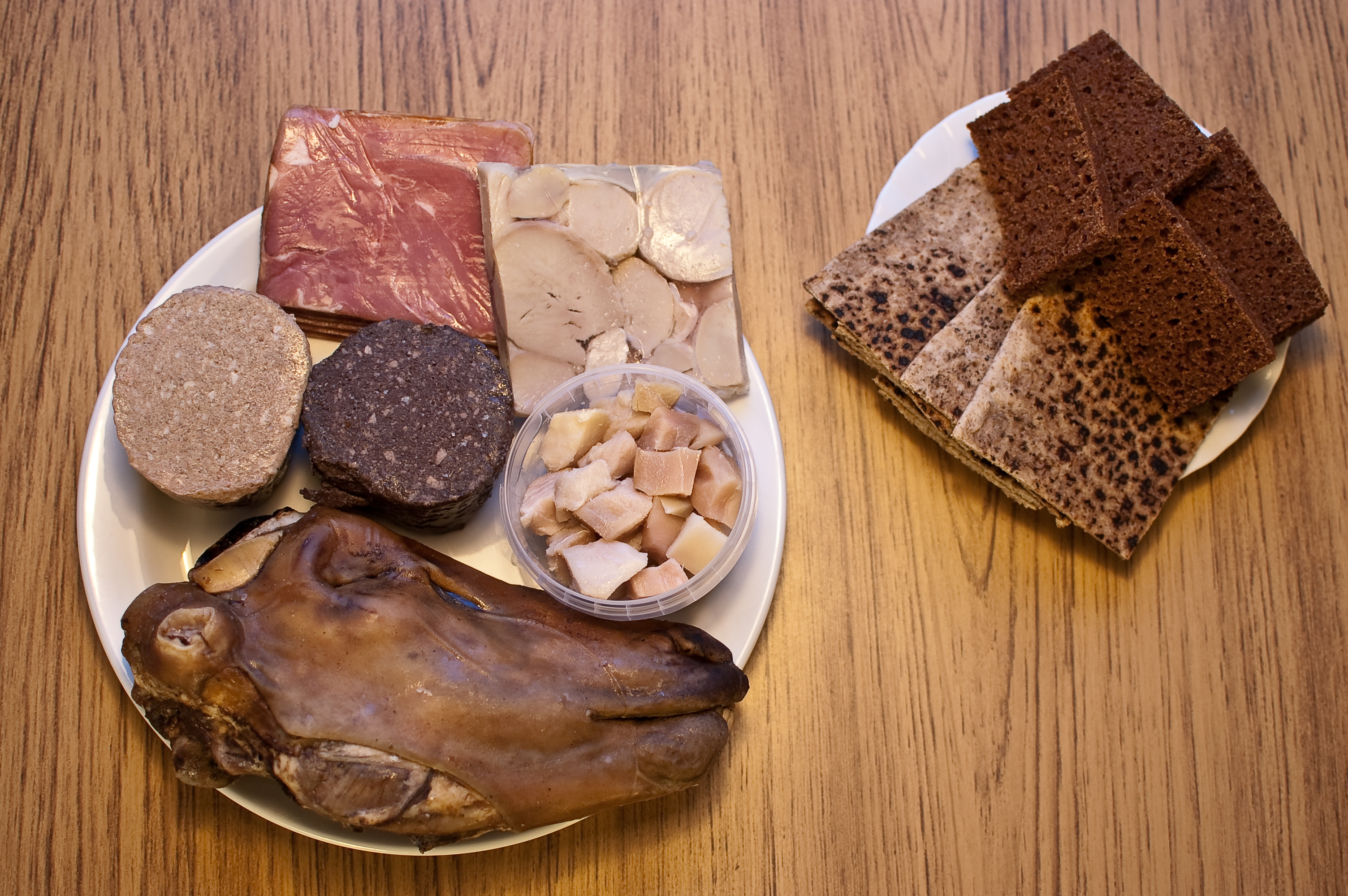 Much of Iceland's cuisine is based on fish, lamb, and
Much of Iceland's cuisine is based on fish, lamb, and
 Sport is an important part of Icelandic culture, as the population is generally quite active. The main traditional sport in Iceland is '' Glíma'', a form of wrestling thought to have originated in medieval times.
Sport is an important part of Icelandic culture, as the population is generally quite active. The main traditional sport in Iceland is '' Glíma'', a form of wrestling thought to have originated in medieval times.
 Popular sports include
Popular sports include
Gateway to Iceland
Government Offices of Iceland
Icelandic Government Information Center & Icelandic Embassies
Visit Iceland
nbsp;– the official Icelandic Tourist Board
Iceland
'' The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Iceland
entry at '' Encyclopædia Britannica'' *
Iceland
from BBC News * *
Incredible Iceland: Fire and Ice
nbsp;– slideshow by ''Life'' magazine
''A Photographer's View of Iceland''
Documentary produced by Prairie Public Television
Arason Steingrimur Writings on Iceland
at Dartmouth College Library {{Authority control Countries in Europe Former Danish colonies Former Norwegian colonies Island countries Islands of Iceland Northwestern European countries Members of the Nordic Council Member states of the European Free Trade Association Member states of NATO Member states of the Council of Europe Member states of the United Nations Republics States and territories established in 1944 Christian states Mid-Atlantic Ridge OECD members
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its surrounding areas) is home to over 65% of the population. Iceland is the biggest part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge that rises above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
, and its central volcanic plateau is erupting almost constantly. The interior consists of a plateau characterised by sand and lava fields, mountains, and glaciers, and many glacial rivers flow to the sea through the lowlands. Iceland is warmed by the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida a ...
and has a temperate climate, despite a high latitude just outside the Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the most northerly of the five major circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth. Its southern equivalent is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circle marks the southernmost latitude at w ...
. Its high latitude and marine influence keep summers chilly, and most of its islands have a polar climate
The polar climate regions are characterized by a lack of warm summers but with varying winters. Every month in a polar climate has an average temperature of less than . Regions with polar climate cover more than 20% of the Earth's area. Most of ...
.
According to the ancient manuscript , the settlement of Iceland
The settlement of Iceland ( is, landnámsöld ) is generally believed to have begun in the second half of the ninth century, when Norse settlers migrated across the North Atlantic. The reasons for the migration are uncertain: later in the Middle ...
began in 874 AD when the Norwegian chieftain Ingólfr Arnarson became the first permanent settler on the island. In the following centuries, Norwegians, and to a lesser extent other Scandinavians, immigrated to Iceland, bringing with them thralls (i.e., slaves or serfs) of Gaelic
Gaelic is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". As a noun it refers to the group of languages spoken by the Gaels, or to any one of the languages individually. Gaelic languages are spoken in Ireland, Scotland, the Isle of Man, and Ca ...
origin.
The island was governed as an independent commonwealth under the native parliament, the Althing, one of the world's oldest functioning legislative assemblies. Following a period of civil strife, Iceland acceded to Norwegian rule in the 13th century. The establishment of the Kalmar Union
The Kalmar Union (Danish language, Danish, Norwegian language, Norwegian, and sv, Kalmarunionen; fi, Kalmarin unioni; la, Unio Calmariensis) was a personal union in Scandinavia, agreed at Kalmar in Sweden, that from 1397 to 1523 joined under ...
in 1397 united the kingdoms of Norway, Denmark, and Sweden. Iceland thus followed Norway's integration into that union, coming under Danish rule after Sweden seceded from the union in 1523. The Danish kingdom forcefully introduced Lutheranism to Iceland in 1550.
In the wake of the French Revolution and the Napoleonic Wars, Iceland's struggle for independence took form and culminated in the Danish–Icelandic Act of Union in 1918, with the establishment of the Kingdom of Iceland, sharing through a personal union the incumbent monarch of Denmark. During the occupation of Denmark in World War II, Iceland voted overwhelmingly to become a republic in 1944, thus ending the remaining formal ties with Denmark. Although the Althing was suspended from 1799 to 1845, the island republic has been credited with sustaining the world's oldest and longest-running parliament.
Until the 20th century, Iceland relied largely on subsistence fishing and agriculture. Industrialization of the fisheries and Marshall Plan aid following World War II brought prosperity, and Iceland became one of the wealthiest and most developed nations in the world. It became a part of the European Economic Area in 1994; this further diversified the economy into sectors such as finance, biotechnology, and manufacturing.
Iceland has a market economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand, where all suppliers and consumers ...
with relatively low taxes, compared to other OECD countries, as well as the highest trade union membership in the world. It maintains a Nordic social welfare system that provides universal health care and tertiary education for its citizens. Iceland ranks high in democracy and equality indexes, ranking third in the world by median wealth per adult. In 2021, it was ranked as the third-most developed country in the world by the United Nations' Human Development Index, and it ranks first on the Global Peace Index. Iceland runs almost completely on renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
.
Icelandic culture is founded upon the nation's Scandinavian heritage. Most Icelanders are descendants of Norse
Norse is a demonym for Norsemen, a medieval North Germanic ethnolinguistic group ancestral to modern Scandinavians, defined as speakers of Old Norse from about the 9th to the 13th centuries.
Norse may also refer to:
Culture and religion
* Nor ...
and Gaelic settlers. Icelandic, a North Germanic language, is descended from Old West Norse and is closely related to Faroese. The country's cultural heritage includes traditional Icelandic cuisine
''Randabrauð'', the cuisine of Iceland, has a long history. Important parts of Icelandic cuisine are lamb, dairy, and fish, the latter due to the fact that Iceland has traditionally been inhabited only near its coastline. Popular foods in Icel ...
, Icelandic literature, and medieval sagas. Iceland has the smallest population of any NATO member
NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) is an international military alliance that consists of 30 member states from Europe and North America. It was established at the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty on 4 April 1949. Article 5 of th ...
and is the only one with no standing army, with a lightly armed coast guard.
Etymology
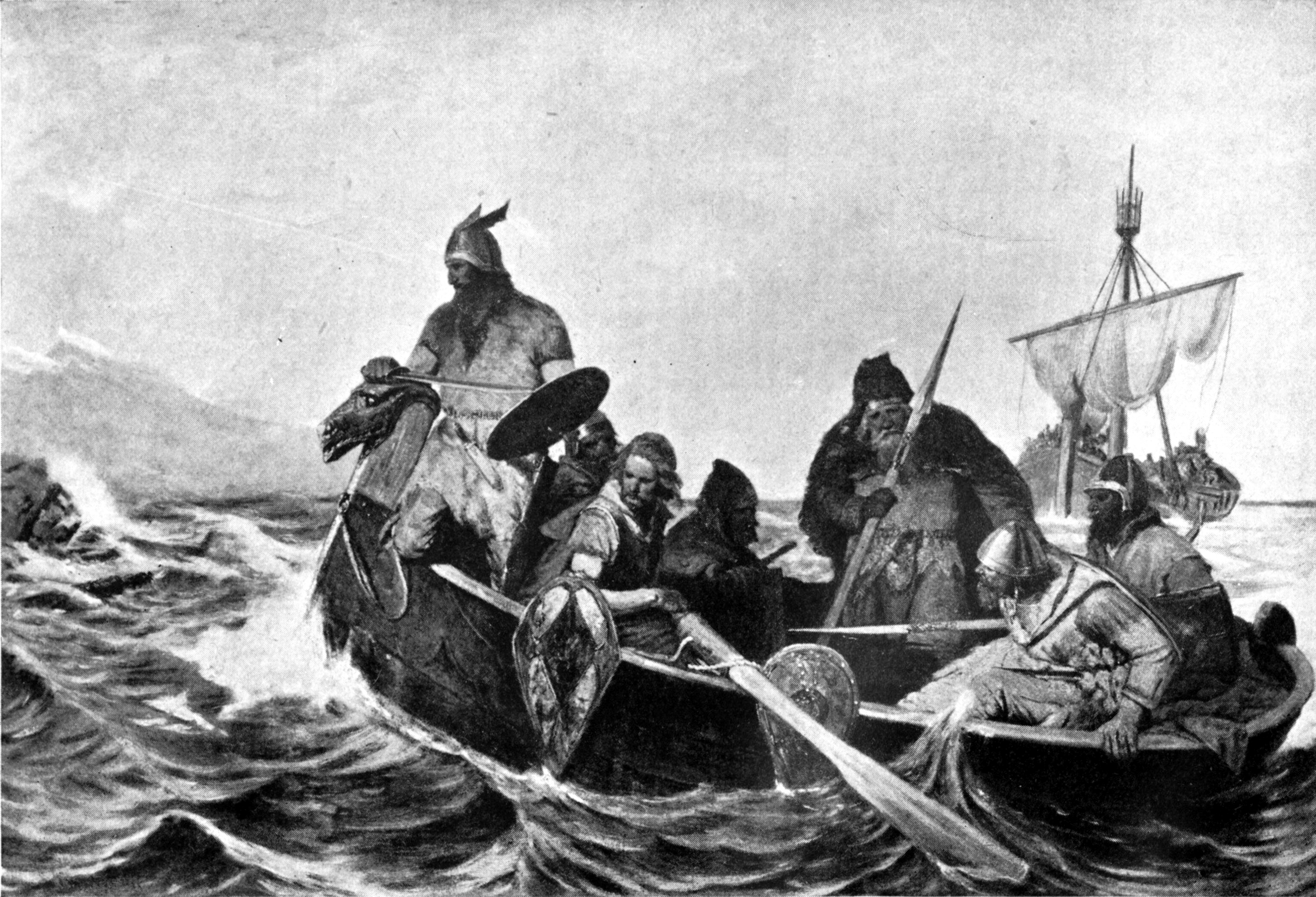
 The Sagas of Icelanders say that a Norwegian named Naddodd (or Naddador) was the first
The Sagas of Icelanders say that a Norwegian named Naddodd (or Naddador) was the first Norseman
The Norsemen (or Norse people) were a North Germanic ethnolinguistic group of the Early Middle Ages, during which they spoke the Old Norse language. The language belongs to the North Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages and is the pre ...
to reach Iceland, and in the ninth century, he named it Snæland or "snow land" because it was snowing. Following Naddodd, the Swede Garðar Svavarsson arrived, and so the island was then called Garðarshólmur which means "Garðar's Isle".
Then came a Viking named Flóki Vilgerðarson; his daughter drowned en route, then his livestock starved to death. The sagas say that the rather despondent Flóki climbed a mountain and saw a fjord () full of icebergs, which led him to give the island its new and present name.Evans, Andrew"Is Iceland Really Green and Greenland Really Icy?"
''
National Geographic
''National Geographic'' (formerly the ''National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as NAT GEO) is a popular American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. Known for its photojournalism, it is one of the most widely ...
'' (30 June 2016). The notion that Iceland's Viking settlers chose that name to discourage the settlement of their verdant isle is a myth.
History
874–1262: Settlement and Commonwealth
 According to both Landnámabók and Íslendingabók, monks known as the Papar lived in Iceland before Scandinavian settlers arrived, possibly members of a Hiberno-Scottish mission. Recent
According to both Landnámabók and Íslendingabók, monks known as the Papar lived in Iceland before Scandinavian settlers arrived, possibly members of a Hiberno-Scottish mission. Recent archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
excavations have revealed the ruins of a cabin in Hafnir on the Reykjanes peninsula. Carbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
indicates that it was abandoned sometime between 770 and 880. In 2016, archaeologists uncovered a longhouse in Stöðvarfjörður that has been dated to as early as 800.
Swedish Viking explorer Garðar Svavarsson was the first to circumnavigate Iceland in 870 and establish that it was an island. He stayed during the winter and built a house in Húsavík. Garðar departed the following summer, but one of his men, Náttfari, decided to stay behind with two slaves. Náttfari settled in what is now known as Náttfaravík, and he and his slaves became the first permanent residents of Iceland to be documented.
The Norwegian-Norse chieftain Ingólfr Arnarson built his homestead in present-day Reykjavík in 874. Ingólfr was followed by many other emigrant settlers, largely Scandinavians and their thralls, many of whom were Irish or Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
. By 930, most arable land on the island had been claimed; the Althing, a legislative and judicial assembly was initiated to regulate the Icelandic Commonwealth. The lack of arable land also served as an impetus to the settlement of Greenland starting in 986. The period of these early settlements coincided with the Medieval Warm Period
The Medieval Warm Period (MWP), also known as the Medieval Climate Optimum or the Medieval Climatic Anomaly, was a time of warm climate in the North Atlantic region that lasted from to . Proxy (climate), Climate proxy records show peak warmth oc ...
, when temperatures were similar to those of the early 20th century. At this time about 25% of Iceland was covered with forest, compared to 1% in the present day. Christianity was adopted by consensus around 999–1000, although Norse paganism persisted among segments of the population for some years afterward.
The Middle Ages
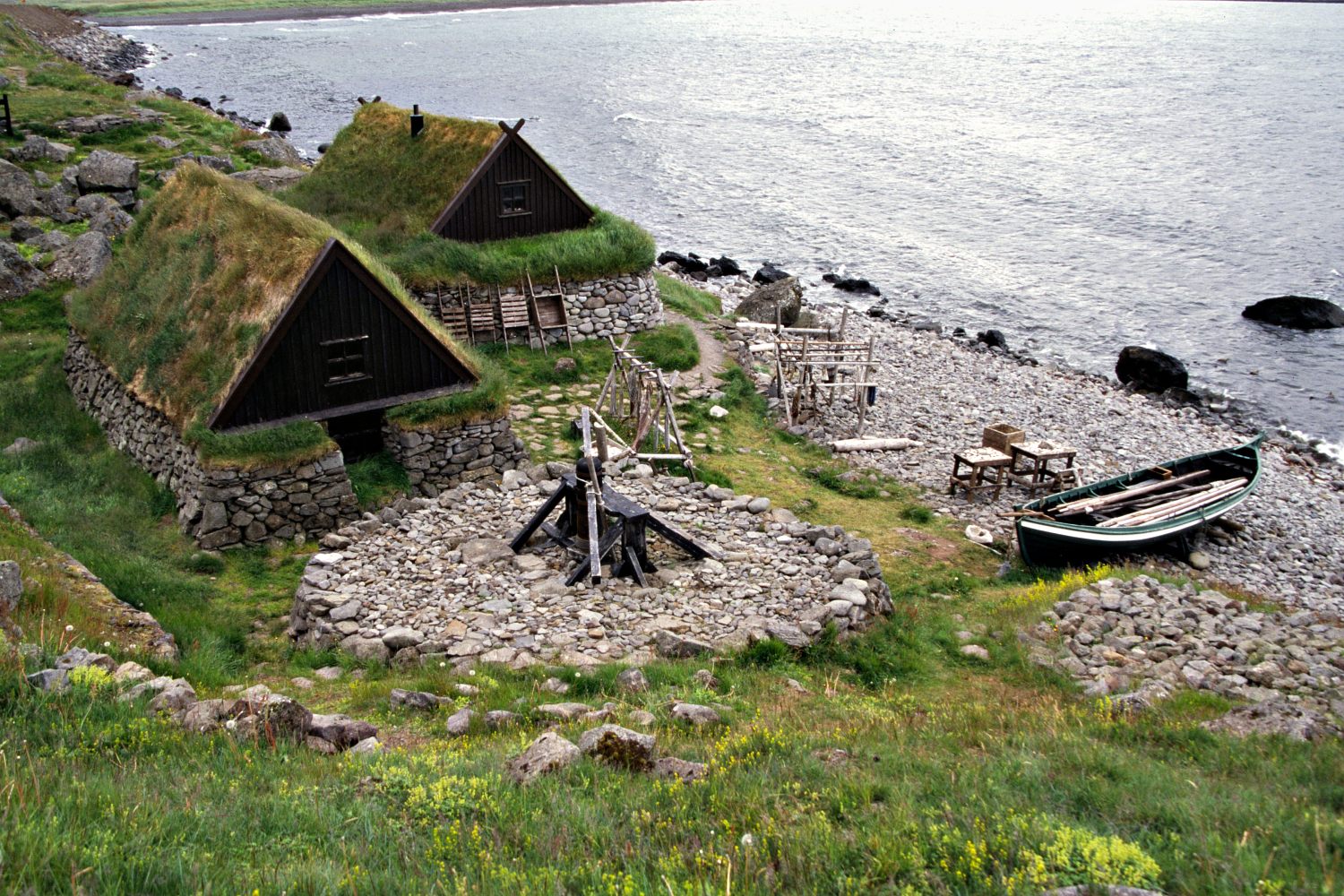
 The Icelandic Commonwealth lasted until the 13th century when the political system devised by the original settlers proved unable to cope with the increasing power of Icelandic chieftains. The internal struggles and civil strife of the Age of the Sturlungs led to the signing of the
The Icelandic Commonwealth lasted until the 13th century when the political system devised by the original settlers proved unable to cope with the increasing power of Icelandic chieftains. The internal struggles and civil strife of the Age of the Sturlungs led to the signing of the Old Covenant
The Mosaic covenant (named after Moses), also known as the Sinaitic covenant (after the biblical Mount Sinai), refers to a covenant between God and the Israelites, including their proselytes, not limited to the ten commandments, nor the event wh ...
in 1262, which ended the Commonwealth and brought Iceland under the Norwegian crown. Possession of Iceland passed from the Kingdom of Norway (872–1397) to the Kalmar Union
The Kalmar Union (Danish language, Danish, Norwegian language, Norwegian, and sv, Kalmarunionen; fi, Kalmarin unioni; la, Unio Calmariensis) was a personal union in Scandinavia, agreed at Kalmar in Sweden, that from 1397 to 1523 joined under ...
in 1415, when the kingdoms of Norway, Denmark, and Sweden were united. After the break-up of the union in 1523, it remained a Norwegian dependency, as a part of Denmark–Norway
Denmark–Norway (Danish and Norwegian: ) was an early modern multi-national and multi-lingual real unionFeldbæk 1998:11 consisting of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Kingdom of Norway (including the then Norwegian overseas possessions: the Faroe I ...
.
Infertile soil, volcanic eruptions, deforestation, and an unforgiving climate made for harsh life in a society where subsistence depended almost entirely on agriculture. The Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
swept Iceland twice, first in 1402–1404 and again in 1494–1495. The former outbreak killed 50% to 60% of the population, and the latter 30% to 50%.
Reformation and the Early Modern period
Around the middle of the 16th century, as part of the Protestant Reformation, KingChristian III of Denmark
Christian III (12 August 1503 – 1 January 1559) reigned as King of Denmark from 1534 and King of Norway from 1537 until his death in 1559. During his reign, Christian formed close ties between the church and the crown. He established ...
began to impose Lutheranism on all his subjects. Jón Arason, the last Catholic bishop of Hólar, was beheaded in 1550 along with two of his sons. The country subsequently became officially Lutheran, and Lutheranism has since remained the dominant religion.
In the 17th and 18th centuries, Denmark imposed harsh trade restrictions on Iceland. Natural disasters, including volcanic eruptions and disease, contributed to a decreasing population. In the summer of 1627, Barbary Pirates
The Barbary pirates, or Barbary corsairs or Ottoman corsairs, were Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from North Africa, based primarily in the ports of Salé, Rabat, Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli. This area was known i ...
committed the events known locally as the Turkish Abductions, in which hundreds of residents were taken into slavery in North Africa and dozens killed; this was the only invasion in Icelandic history to have casualties. The 1707-08 Iceland smallpox epidemic
Iceland experienced one of its deadliest outbreaks of smallpox beginning in 1707. The epidemic ultimately killed around 12,000 Icelanders, close to one-quarter of the island's population at the time.
Iceland in 1707
Iceland in 1707 was a territ ...
is estimated to have killed a quarter to a third of the population. In 1783 the Laki volcano erupted, with devastating effects. In the years following the eruption, known as the Mist Hardships ( is, Móðuharðindin), over half of all livestock in the country died. Around a quarter of the population starved to death in the ensuing famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
.
1814–1918: Independence movement
In 1814, following the Napoleonic Wars, Denmark-Norway was broken up into two separate kingdoms via the Treaty of Kiel but Iceland remained a Danish dependency. Throughout the 19th century, the country's climate continued to grow colder, resulting in mass emigration to the New World, particularly to the region of Gimli, Manitoba in Canada, which was sometimes referred to asNew Iceland
New Iceland ( is, Nýja Ísland ) is the name of a region on Lake Winnipeg in the Canadian province of Manitoba which was named for settlers from Iceland. It was settled in 1875.
Background
In 1875, over 200 Icelanders immigrated to Manitoba es ...
. About 15,000 people emigrated, out of a total population of 70,000.
A national consciousness arose in the first half of the 19th century, inspired by romantic
Romantic may refer to:
Genres and eras
* The Romantic era, an artistic, literary, musical and intellectual movement of the 18th and 19th centuries
** Romantic music, of that era
** Romantic poetry, of that era
** Romanticism in science, of that e ...
and nationalist ideas from mainland Europe. An Icelandic independence movement took shape in the 1850s under the leadership of Jón Sigurðsson, based on the burgeoning Icelandic nationalism inspired by the '' Fjölnismenn'' and other Danish-educated Icelandic intellectuals. In 1874, Denmark granted Iceland a constitution and limited home rule. This was expanded in 1904, and Hannes Hafstein served as the first Minister for Iceland in the Danish cabinet.
1918–1944: Independence and the Kingdom of Iceland
 The Danish–Icelandic Act of Union, an agreement with Denmark signed on 1 December 1918 and valid for 25 years, recognised Iceland as a fully sovereign and independent state in a personal union with Denmark. The Government of Iceland established an embassy in Copenhagen and requested that Denmark carry out on its behalf certain defence and foreign affairs matters, subject to consultation with the Althing. Danish embassies around the world displayed two coats of arms and two flags: those of the Kingdom of Denmark and those of the Kingdom of Iceland. Iceland's legal position became comparable to those of countries belonging to the Commonwealth of Nations, such as Canada, whose sovereign is King Charles III.
During World War II, Iceland joined Denmark in asserting neutrality. After the German occupation of Denmark on 9 April 1940, the Althing replaced the King with a regent and declared that the Icelandic government would take control of its own defence and foreign affairs. A month later, British armed forces conducted Operation Fork, the invasion and occupation of the country, violating Icelandic
The Danish–Icelandic Act of Union, an agreement with Denmark signed on 1 December 1918 and valid for 25 years, recognised Iceland as a fully sovereign and independent state in a personal union with Denmark. The Government of Iceland established an embassy in Copenhagen and requested that Denmark carry out on its behalf certain defence and foreign affairs matters, subject to consultation with the Althing. Danish embassies around the world displayed two coats of arms and two flags: those of the Kingdom of Denmark and those of the Kingdom of Iceland. Iceland's legal position became comparable to those of countries belonging to the Commonwealth of Nations, such as Canada, whose sovereign is King Charles III.
During World War II, Iceland joined Denmark in asserting neutrality. After the German occupation of Denmark on 9 April 1940, the Althing replaced the King with a regent and declared that the Icelandic government would take control of its own defence and foreign affairs. A month later, British armed forces conducted Operation Fork, the invasion and occupation of the country, violating Icelandic neutrality
Neutral or neutrality may refer to:
Mathematics and natural science Biology
* Neutral organisms, in ecology, those that obey the unified neutral theory of biodiversity
Chemistry and physics
* Neutralization (chemistry), a chemical reaction ...
. In 1941, the Government of Iceland, friendly to Britain, invited the then-neutral United States to take over its defence so that Britain could use its troops elsewhere.
1944–present: Republic of Iceland
 On 31 December 1943, the Danish–Icelandic Act of Union expired after 25 years. Beginning on 20 May 1944, Icelanders voted in a four-day plebiscite on whether to terminate the personal union with Denmark, abolish the monarchy, and establish a republic. The vote was 97% to end the union, and 95% in favour of the new republican constitution. Iceland formally became a republic on 17 June 1944, with Sveinn Björnsson as its first president.
In 1946, the US Defence Force Allied left Iceland. The nation formally became a member of NATO on 30 March 1949, amid domestic controversy and riots. On 5 May 1951, a defence agreement was signed with the United States. American troops returned to Iceland as the
On 31 December 1943, the Danish–Icelandic Act of Union expired after 25 years. Beginning on 20 May 1944, Icelanders voted in a four-day plebiscite on whether to terminate the personal union with Denmark, abolish the monarchy, and establish a republic. The vote was 97% to end the union, and 95% in favour of the new republican constitution. Iceland formally became a republic on 17 June 1944, with Sveinn Björnsson as its first president.
In 1946, the US Defence Force Allied left Iceland. The nation formally became a member of NATO on 30 March 1949, amid domestic controversy and riots. On 5 May 1951, a defence agreement was signed with the United States. American troops returned to Iceland as the Iceland Defence Force
The Iceland Defense Force ( is, Varnarlið Íslands; IDF) was a military command of the United States Armed Forces from 1951 to 2006. The IDF, created at the request of NATO, came into existence when the United States signed an agreement to prov ...
and remained throughout the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
. The US withdrew the last of its forces on 30 September 2006.
Iceland prospered during the Second World War. The immediate post-war period was followed by substantial economic growth
Economic growth can be defined as the increase or improvement in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services produced by an economy in a financial year. Statisticians conventionally measure such growth as the percent rate of ...
, driven by the industrialisation of the fishing industry and the US Marshall Plan programme, through which Icelanders received the most aid per capita of any European country (at US$209, with the war-ravaged Netherlands a distant second at US$109).
Vigdís Finnbogadóttir assumed Iceland's presidency on 1 August 1980, making her the first elected female head of state in the world.
The 1970s were marked by the Cod Wars—several disputes with the United Kingdom over Iceland's extension of its fishing limits to offshore. Iceland hosted a summit in Reykjavík in 1986 between United States President Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
and Soviet Premier Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet politician who served as the 8th and final leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
, during which they took significant steps towards nuclear disarmament. A few years later, Iceland became the first country to recognise the independence of Estonia, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, and Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
as they broke away from the USSR. Throughout the 1990s, the country expanded its international role and developed a foreign policy orientated towards humanitarian and peacekeeping causes. To that end, Iceland provided aid and expertise to various NATO-led interventions in Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
, Kosovo, and Iraq.
Iceland joined the European Economic Area in 1994, after which the economy was greatly diversified and liberalised. International economic relations increased further after 2001 when Iceland's newly deregulated banks began to raise great amounts of external debt, contributing to a 32% increase in Iceland's gross national income between 2002 and 2007.
Economic boom and crisis
In 2003–2007, following the privatisation of the banking sector under the government of Davíð Oddsson, Iceland moved towards having an economy based on international investment banking and financial services. It was quickly becoming one of the most prosperous countries in the world, but was hit hard by a major financial crisis. The crisis resulted in the greatest migration from Iceland since 1887, with a net emigration of 5,000 people in 2009.Since 2012
Iceland's economy stabilised under the government of Jóhanna Sigurðardóttir and grew by 1.6% in 2012. The centre-rightIndependence Party
Independence Party may refer to:
Active parties Outside United States
* Independence Party (Egypt)
* Estonian Independence Party
* Independence Party (Finland)
* Independence Party (Iceland)
* Independence Party (Mauritius)
* Independence Part ...
was returned to power in coalition with the Progressive Party in the 2013 election. In the following years, Iceland saw a surge in tourism as the country became a popular holiday destination. In 2016, Prime Minister Sigmundur Davíð Gunnlaugsson resigned after being implicated in the Panama Papers
The Panama Papers ( es, Papeles de Panamá) are 11.5 million leaked documents (or 2.6 terabytes of data) that were published beginning on April 3, 2016. The papers detail financial and attorney–client information for more than 214,488 ...
scandal. Early elections in 2016 resulted in a right-wing coalition government of the Independence Party
Independence Party may refer to:
Active parties Outside United States
* Independence Party (Egypt)
* Estonian Independence Party
* Independence Party (Finland)
* Independence Party (Iceland)
* Independence Party (Mauritius)
* Independence Part ...
, the Reform Party and Bright Future. This government fell when Bright Future quit the coalition due to a scandal involving then-Prime Minister Bjarni Benediktsson's father's letter of support for a convicted child sex offender. Snap elections in October 2017 brought to power a new coalition consisting of the Independence Party, the Progressive Party, and the Left-Green Movement, headed by Katrín Jakobsdóttir.
After the 2021 parliamentary election, the new government was, just like the previous government, a tri-party coalition of the Independence Party, the Progressive Party, and the Left-Green Movement, headed by Prime Minister Katrín Jakobsdóttir.
Geography
Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the most northerly of the five major circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth. Its southern equivalent is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circle marks the southernmost latitude at w ...
, which passes through the small Icelandic island of Grímsey off the main island's northern coast. The country lies between latitudes 63 and 68°N, and longitudes 25 and 13°W.
Iceland is closer to continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous continent of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by ...
than to mainland North America, although it is closest to Greenland (), an island of North America. Iceland is generally included in Europe for geographical, historical, political, cultural, linguistic and practical reasons. Geologically, the island includes parts of both continental plates. The closest bodies of land in Europe are the Faroe Islands (); Jan Mayen Island (); Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the no ...
and the Outer Hebrides
The Outer Hebrides () or Western Isles ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Siar or or ("islands of the strangers"); sco, Waster Isles), sometimes known as the Long Isle/Long Island ( gd, An t-Eilean Fada, links=no), is an island chain off the west coast ...
, both about ; and the Scottish mainland and Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north ...
, both about . The nearest part of Continental Europe is mainland Norway, about away, while mainland North America is away, at the northern tip of Labrador.
 Iceland is the world's 18th-largest island, and Europe's second-largest island after Great Britain. (The island of Ireland is third.) The main island covers , but the entire country is in size, of which 62.7% is tundra. Iceland contains about 30 minor islands, including the lightly populated Grímsey and the Vestmannaeyjar archipelago. Lakes and glaciers cover 14.3% of its surface; only 23% is vegetated. The largest lakes are Þórisvatn reservoir: and
Iceland is the world's 18th-largest island, and Europe's second-largest island after Great Britain. (The island of Ireland is third.) The main island covers , but the entire country is in size, of which 62.7% is tundra. Iceland contains about 30 minor islands, including the lightly populated Grímsey and the Vestmannaeyjar archipelago. Lakes and glaciers cover 14.3% of its surface; only 23% is vegetated. The largest lakes are Þórisvatn reservoir: and Þingvallavatn
Þingvallavatn (), anglicised as Thingvallavatn,The spelling ''Pingvallavatn'' is wrong as the letter “p” should never be used to represent the letter “þ” (thorn). is a rift valley lake in southwestern Iceland. With a surface of 84 km² ...
: ; other important lakes include Lagarfljót and Mývatn. Jökulsárlón is the deepest lake, at .
Geologically, Iceland is part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a ridge along which the oceanic crust spreads and forms a new oceanic crust. This part of the mid-ocean ridge is located above a mantle plume, causing Iceland to be subaerial In natural science, subaerial (literally "under the air"), has been used since 1833,Subaerial
in the Merriam ...
(above the surface of the sea). The ridge marks the boundary between the Eurasian and North American Plates, and Iceland was created by rifting and in the Merriam ...
accretion
Accretion may refer to:
Science
* Accretion (astrophysics), the formation of planets and other bodies by collection of material through gravity
* Accretion (meteorology), the process by which water vapor in clouds forms water droplets around nucl ...
through volcanism along the ridge.
Many fjords punctuate Iceland's 4,970-km-long (3,088-mi) coastline, which is also where most settlements are situated. The island's interior, the Highlands of Iceland, is a cold and uninhabitable combination of sand, mountains, and lava fields. The major towns are the capital city of Reykjavík, along with its outlying towns of Kópavogur, Hafnarfjörður, and Garðabær, nearby Reykjanesbær where the international airport is located, and the town of Akureyri in northern Iceland. The island of Grímsey on the Arctic Circle contains the northernmost habitation of Iceland, whereas Kolbeinsey contains the northernmost point of Iceland. Iceland has three national parks: Vatnajökull National Park, Snæfellsjökull National Park
Snæfellsjökull (, ''snow-fell glacier'') is a 700,000-year-old glacier-capped stratovolcano in western Iceland. It is situated on the westernmost part of the Snæfellsnes peninsula in Iceland. Sometimes it may be seen from the city of Reykjav� ...
, and Þingvellir National Park. The country is considered a "strong performer" in environmental protection, having been ranked 13th in Yale University's Environmental Performance Index of 2012.
Geology

 A geologically young land, Iceland is the surface expression of the Iceland Plateau, a large igneous province forming as a result of volcanism from the
A geologically young land, Iceland is the surface expression of the Iceland Plateau, a large igneous province forming as a result of volcanism from the Iceland hotspot
The Iceland hotspot is a hotspot which is partly responsible for the high volcanic activity which has formed the Iceland Plateau and the island of Iceland.
Iceland is one of the most active volcanic regions in the world, with eruptions occur ...
and along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, the latter of which runs right through it. This means that the island is highly geologically active with many volcanoes including Hekla, Eldgjá, Herðubreið, and Eldfell. The volcanic eruption of Laki in 1783–1784 caused a famine that killed nearly a quarter of the island's population. In addition, the eruption caused dust clouds and haze to appear over most of Europe and parts of Asia and Africa for several months afterwards, and affected climates in other areas.
Iceland has many geyser
A geyser (, ) is a spring characterized by an intermittent discharge of water ejected turbulently and accompanied by steam. As a fairly rare phenomenon, the formation of geysers is due to particular hydrogeological conditions that exist only in ...
s, including Geysir, from which the English word is derived, and the famous Strokkur
Strokkur ( Icelandic , "churn") is a fountain-type geyser located in a geothermal area beside the Hvítá River in Iceland in the southwest part of the country, east of Reykjavík. It typically erupts every 6–10 minutes. Its usual height is , ...
, which erupts every 8–10 minutes. After a phase of inactivity, Geysir started erupting again after a series of earthquakes in 2000. Geysir has since grown quieter and does not erupt often.
With the widespread availability of geothermal power
Geothermal power is electrical power generated from geothermal energy. Technologies in use include dry steam power stations, flash steam power stations and binary cycle power stations. Geothermal electricity generation is currently used in 2 ...
and the harnessing of many rivers and waterfalls for hydroelectricity, most residents have access to inexpensive hot water, heating, and electricity. The island is composed primarily of basalt, a low- silica lava associated with effusive volcanism as has occurred also in Hawaii. Iceland, however, has a variety of volcanic types (composite and fissure), many producing more evolved lavas such as rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral ...
and andesite. Iceland has hundreds of volcanoes with about 30 active volcanic systems.
Surtsey, one of the youngest islands in the world, is part of Iceland. Named after Surtr, it rose above the ocean in a series of volcanic eruptions between 8 November 1963 and 5 June 1968. Only scientists researching the growth of new life are allowed to visit the island.
On 21 March 2010, a volcano in Eyjafjallajökull in the south of Iceland erupted for the first time since 1821, forcing 600 people to flee their homes. Additional eruptions on 14 April forced hundreds of people to abandon their homes. The resultant cloud of volcanic ash brought major disruption to air travel across Europe.
 Another large eruption occurred on 21 May 2011. This time it was the Grímsvötn volcano, located under the thick ice of Europe's largest glacier, Vatnajökull. Grímsvötn is one of Iceland's most active volcanoes, and this eruption was much more powerful than the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull activity, with ash and lava hurled into the atmosphere, creating a large cloud.
A great deal of volcanic activity was occurring in the Reykjanes Peninsula in 2020 and into 2021, after nearly 800 years of inactivity. After the eruption of the Fagradalsfjall volcano on 19 March 2021,
Another large eruption occurred on 21 May 2011. This time it was the Grímsvötn volcano, located under the thick ice of Europe's largest glacier, Vatnajökull. Grímsvötn is one of Iceland's most active volcanoes, and this eruption was much more powerful than the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull activity, with ash and lava hurled into the atmosphere, creating a large cloud.
A great deal of volcanic activity was occurring in the Reykjanes Peninsula in 2020 and into 2021, after nearly 800 years of inactivity. After the eruption of the Fagradalsfjall volcano on 19 March 2021, National Geographic
''National Geographic'' (formerly the ''National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as NAT GEO) is a popular American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. Known for its photojournalism, it is one of the most widely ...
's experts predicted that this "may mark the start of decades of volcanic activity." The eruption was small, leading to a prediction that this volcano was unlikely to threaten "any population centers".
The highest elevation for Iceland is listed as 2,110 m (6,923 ft) at Hvannadalshnúkur (64°00′N 16°39′W).
Climate
subarctic
The subarctic zone is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the true Arctic, north of humid continental regions and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Scandinavia, Siberia, and the Cairngorms. Generally, ...
. The warm North Atlantic Current ensures generally higher annual temperatures than in most places of similar latitude in the world. Regions in the world with similar climates include the Aleutian Islands, the Alaska Peninsula
The Alaska Peninsula (also called Aleut Peninsula or Aleutian Peninsula, ale, Alasxix̂; Sugpiaq: ''Aluuwiq'', ''Al'uwiq'') is a peninsula extending about to the southwest from the mainland of Alaska and ending in the Aleutian Islands. The ...
, and Tierra del Fuego, although these regions are closer to the equator. Despite its proximity to the Arctic, the island's coasts remain ice-free through the winter. Ice incursions are rare, with the last having occurred on the north coast in 1969.
The climate varies between different parts of the island. Generally speaking, the south coast is warmer, wetter, and windier than the north. The Central Highlands are the coldest part of the country. Low-lying inland areas in the north are the aridest. Snowfall in winter is more common in the north than in the south.
The highest air temperature recorded was on 22 June 1939 at Teigarhorn on the southeastern coast. The lowest was on 22 January 1918 at Grímsstaðir and Möðrudalur in the northeastern hinterland. The temperature records for Reykjavík are on 30 July 2008, and on 21 January 1918.
Plants
Phytogeographically, Iceland belongs to the Arctic province of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. Plantlife consists mainly of grassland, which is regularly grazed by livestock. The most common tree native to Iceland is the northern birch ('' Betula pubescens''), which formerly formed forests over much of Iceland, along with aspens ('' Populus tremula''), rowans (''Sorbus aucuparia
''Sorbus aucuparia'', commonly called rowan (UK: /ˈrəʊən/, US: /ˈroʊən/) and mountain-ash, is a species of deciduous tree or shrub in the rose family. It is a highly variable species, and botanists have used different Circumscription (taxo ...
''), common junipers ('' Juniperus communis''), and other smaller trees, mainly willows.
When the island was first settled, it was extensively forested, with around 30% of the land covered in trees. In the late 12th century, Ari the Wise described it in the Íslendingabók as "forested from mountain to sea shore". Permanent human settlement greatly disturbed the isolated ecosystem of thin, volcanic soils and limited species diversity. The forests were heavily exploited over the centuries for firewood and timber. Deforestation, climatic deterioration during the Little Ice Age
The Little Ice Age (LIA) was a period of regional cooling, particularly pronounced in the North Atlantic region. It was not a true ice age of global extent. The term was introduced into scientific literature by François E. Matthes in 1939. Ma ...
, and overgrazing by sheep imported by settlers caused a loss of critical topsoil due to erosion. Today, many farms have been abandoned. Three-quarters of Iceland's is affected by soil erosion; is affected to a degree serious enough to make the land useless. Only a few small birches stands now exist in isolated reserves. The planting of new forests has increased the number of trees, but the result does not compare to the original forests. Some of the planted forests include introduced species. The tallest tree in Iceland is a sitka spruce
''Picea sitchensis'', the Sitka spruce, is a large, coniferous, evergreen tree growing to almost tall, with a trunk diameter at breast height that can exceed 5 m (16 ft). It is by far the largest species of spruce and the fifth-larg ...
planted in 1949 in Kirkjubæjarklaustur; it was measured at in 2013.
Algae such as '' Chondrus crispus'', '' Phyllphora truncata'' and ''Phyllophora crispa'' and others have been recorded from Iceland.
Animals
Icelandic sheep
The Icelandic is the Icelandic breed of domestic sheep. It belongs to the Northern European Short-tailed group of sheep, and is larger than most breeds in that group. It is thought that it was introduced to Iceland by Vikings in the late nint ...
, cattle, chickens
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domesticated junglefowl species, with attributes of wild species such as the grey and the Ceylon junglefowl that are originally from Southeastern Asia. Rooster or cock is a term for an adult m ...
, goats, the sturdy Icelandic horse, and the Icelandic Sheepdog, all descendants of animals imported by Europeans. Wild mammals include the Arctic fox, mink
Mink are dark-colored, semiaquatic, carnivorous mammals of the genera ''Neogale'' and '' Mustela'' and part of the family Mustelidae, which also includes weasels, otters, and ferrets. There are two extant species referred to as "mink": the A ...
, mice, rats, rabbits, and reindeer. Polar bears occasionally visit the island, travelling from Greenland on icebergs, but no Icelandic populations exist. In June 2008, two polar bears arrived in the same month. Marine mammals include the grey seal (''Halichoerus grypus'') and harbour seal (''Phoca vitulina'').
Many species of fish live in the ocean waters surrounding Iceland, and the fishing industry is a major part of Iceland's economy, accounting for roughly half of the country's total exports. Birds, especially seabirds, are an important part of Iceland's animal life. Atlantic puffin
The Atlantic puffin ('), also known as the common puffin, is a species of seabird in the auk family. It is the only puffin native to the Atlantic Ocean; two related species, the tufted puffin and the horned puffin is found in the northeastern ...
s, skuas, and black-legged kittiwake
The black-legged kittiwake (''Rissa tridactyla'') is a seabird species in the gull family Laridae.
This species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his landmark 1758 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' as ''Larus tridactylus''. The English ...
s nest on its sea cliffs.
Commercial whaling is practised intermittently along with scientific whale hunts. Whale watching has become an important part of Iceland's economy since 1997.
Around 1,300 species of insects are known in Iceland. This is low compared with other countries (over one million species have been described worldwide). Iceland is essentially free of mosquitoes.
Politics
2017
File:2017 Events Collage V2.png, From top left, clockwise: The War Against ISIS at the Battle of Mosul (2016-2017); aftermath of the Manchester Arena bombing; The Solar eclipse of August 21, 2017 ("Great American Eclipse"); North Korea tests a ser ...
and 2021 parliamentary elections, the biggest parties are the centre-right Independence Party
Independence Party may refer to:
Active parties Outside United States
* Independence Party (Egypt)
* Estonian Independence Party
* Independence Party (Finland)
* Independence Party (Iceland)
* Independence Party (Mauritius)
* Independence Part ...
(''Sjálfstæðisflokkurinn''), the Progressive Party (''Framsóknarflokkurinn'') and the Left-Green Movement (''Vinstrihreyfingin – grænt framboð''). These three parties form the ruling coalition in the cabinet led by leftist Katrín Jakobsdóttir.
Other political parties with seats in the Althing (Parliament) are the Social Democratic Alliance (''Samfylkingin''), the People's Party (''Flokkur fólksins''), Iceland's Pirates
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
(''Píratar''), the Reform Party (''Viðreisn'') and the Centre Party (''Miðflokkurinn'').
Iceland was the first country in the world to have a political party formed and led entirely by women. Known as the Women's List or Women's Alliance (''Kvennalistinn''), it was founded in 1983 to advance the political, economic, and social needs of women. After participating in its first parliamentary elections, the Women's List helped increase the proportion of female parliamentarians by 15%. It disbanded in 1999, formally merging the next year with the Social Democratic Alliance, although about half of its members joined the Left-Green Movement instead. It did leave a lasting influence on Iceland's politics: every major party has a 40% quota for women, and in 2009 nearly a third of members of parliament were female, compared to the global average of 16%. Following the 2016
File:2016 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Bombed-out buildings in Ankara following the 2016 Turkish coup d'état attempt; the impeachment trial of Brazilian President Dilma Rousseff; Damaged houses during the 2016 Nagorno-Karabakh ...
and 2021 elections, 48% of members of parliament are female.
In 2016, Iceland was ranked second in the strength of its democratic institutions and 13th in government transparency. The country has a high level of civic participation, with 81.4% voter turnout during the most recent elections, compared to an OECD average of 72%. However, only 50% of Icelanders say they trust their political institutions, slightly less than the OECD average of 56% (and most probably a consequence of the political scandals in the wake of the Icelandic financial crisis).Iceland – OECD Better Life IndexOecdbetterlifeindex.org. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
Government
 Iceland is a representative democracy and a
Iceland is a representative democracy and a parliamentary republic
A parliamentary republic is a republic that operates under a parliamentary system of government where the executive branch (the government) derives its legitimacy from and is accountable to the legislature (the parliament). There are a number ...
. The modern parliament, ''Alþingi'' (English: Althing), was founded in 1845 as an advisory body to the Danish monarch. It was widely seen as a re-establishment of the assembly founded in 930 in the Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
period and temporarily suspended from 1799 to 1845. Consequently, "it is arguably the world's oldest parliamentary democracy." It has 63 members, elected for a maximum period of four years.
The head of government is the prime minister who, together with the cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
, is responsible for executive government.
The president of Iceland, in contrast, is a largely ceremonial head of state and serves as a diplomat, but may veto laws voted by the parliament and put them to a national referendum. They are elected by popular vote for a term of four years with no term limit. The current president is Guðni Th. Jóhannesson. On 1 August 2016, he became the new president of Iceland, and he was re-elected with an overwhelming majority of the vote in the 2020 presidential election.
The elections for the president, the Althing, and local municipal councils are all held separately every four years.
The cabinet in the country's government is typically appointed by the president after a general election to the Althing. However, the appointment is usually negotiated by the leaders of the political parties, who decide amongst themselves which parties can form the cabinet and how to distribute its seats, as long as it has majority support in the Althing. If the party leaders are unable to come to an agreement within a reasonable period of time, the president will personally appoint the cabinet. This has not happened since the republic was founded in 1944, although in 1942 the regent, Sveinn Björnsson, appointed a non-parliamentary government. Sveinn held the practical position of a president at the time, and later became the country's first official president in 1944.
The governments of Iceland have always been coalition governments, with two or more parties involved, as no single political party has ever received a majority of seats in the Althing throughout the republican period. There is no legal consensus on the extent of the political power possessed by the office of the president; several provisions of the constitution appear to give the president some important powers, but other provisions and traditions suggest differently. In 1980, Icelanders elected Vigdís Finnbogadóttir as president, the world's first directly elected female head of state. She retired from office in 1996. In 2009, Iceland became the first country with an openly gay head of government when Jóhanna Sigurðardóttir became prime minister.
Administrative divisions
Iceland is divided into regions, constituencies, and municipalities. The eight regions are primarily used for statistical purposes. District court jurisdictions also use an older version of this division. Until 2003, the constituencies for the parliamentary elections were the same as the regions, but by an amendment to the constitution, they were changed to the current six constituencies: * '' Reykjavík North'' and '' Reykjavík South'' (city regions); * '' Southwest'' (four non-contiguous suburban areas around Reykjavík); * ''Northwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sep ...
'' and ''Northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
'' (northern half of Iceland, split); and
* ''South
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
'' (southern half of Iceland, excluding Reykjavík and suburbs).
The redistricting change was made to balance the weight of different districts of the country since previously a vote cast in the sparsely populated areas around the country would count much more than a vote cast in the Reykjavík city area. The imbalance between districts has been reduced by the new system but still exists.
Sixty-nine municipalities in Iceland govern local matters like schools, transport, and zoning. These are the actual second-level subdivisions of Iceland, as the constituencies have no relevance except in elections and for statistical purposes. Reykjavík is by far the most populous municipality, about four times more populous than Kópavogur, the second one.
Foreign relations
 Iceland, which is a member of the UN, NATO, EFTA,
Iceland, which is a member of the UN, NATO, EFTA, Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
, and OECD, maintains diplomatic and commercial relations with practically all nations, but its ties with the Nordic countries, Germany, the United States, Canada, and the other NATO nations are particularly close. Historically, due to cultural, economic, and linguistic similarities, Iceland is a Nordic country, and it participates in intergovernmental cooperation through the Nordic Council
The Nordic Council is the official body for formal inter-parliamentary Nordic cooperation among the Nordic countries. Formed in 1952, it has 87 representatives from Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden as well as from the autonomou ...
.
Iceland is a member of the European Economic Area (EEA), which allows the country access to the single market of the European Union (EU). It was not a member of the EU, but in July 2009, the Icelandic parliament, the Althing, voted in favour of the application for EU membership and officially applied on 17 July 2009. However, in 2013, opinion polls showed that many Icelanders were now against joining the EU; following the 2013 Icelandic parliamentary election
Parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 27 April 2013. Fifteen parties contested the elections, compared to just seven in the previous elections. The result was a victory for the two centre-right opposition parties, the Independence Party ...
the two parties that formed the island's new government—the centrist Progressive Party and the right-wing Independence Party—announced they would hold a referendum on EU membership. In 2015, Minister for Foreign Affairs Gunnar Bragi Sveinsson informed the EU that Iceland would no longer pursue membership, but the application was not formally withdrawn and there have been subsequent calls for a referendum on the issue.

Military
Iceland has nostanding army
A standing army is a permanent, often professional, army. It is composed of full-time soldiers who may be either career soldiers or conscripts. It differs from army reserves, who are enrolled for the long term, but activated only during wars or n ...
but has the Icelandic Coast Guard which also maintains the Iceland Air Defence System
The Iceland Air Defence System ( is, Íslenska Loftvarnarkerfið) is a part of the Icelandic Coast Guard. It was founded in 1987 under the Radar Agency of the Icelandic Ministry for Foreign Affairs after an agreement between Iceland and the Uni ...
, and an Iceland Crisis Response Unit to support peacekeeping missions and perform paramilitary functions.
The Iceland Defense Force (IDF) was a military command of the United States Armed Forces from 1951 to 2006. The IDF, created at the request of NATO, came into existence when the United States signed an agreement to provide for the defence of Iceland. The IDF also consisted of civilian Icelanders and military members of other NATO nations. The IDF was downsized after the end of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
and the U.S. Air Force maintained four to six interceptor aircraft at the Naval Air Station Keflavik until they were withdrawn on 30 September 2006. Since May 2008, NATO nations have periodically deployed fighters to patrol Icelandic airspace under the Icelandic Air Policing mission. Iceland supported the 2003 invasion of Iraq
The 2003 invasion of Iraq was a United States-led invasion of the Republic of Iraq and the first stage of the Iraq War. The invasion phase began on 19 March 2003 (air) and 20 March 2003 (ground) and lasted just over one month, including 26 ...
despite much domestic controversy, deploying a Coast Guard EOD team to Iraq, which was replaced later by members of the Iceland Crisis Response Unit. Iceland has also participated in the conflict in Afghanistan and the 1999 NATO bombing of Yugoslavia
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) carried out an aerial bombing campaign against the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia during the Kosovo War. The air strikes lasted from 24 March 1999 to 10 June 1999. The bombings continued until an a ...
. Despite the ongoing financial crisis the first new patrol ship in decades was launched on 29 April 2009.
Iceland was the neutral host of the historic 1986 Reagan–Gorbachev summit in Reykjavík, which set the stage for the end of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
. Iceland's principal historical international disputes involved disagreements over exclusive economic zones. Conflict with the United Kingdom led to a series of so-called Cod Wars, which included confrontations between the Icelandic Coast Guard and the Royal Navy over British fishermen: in 1952–1956 due to the extension of Iceland's fishing zone from , in 1958–1961 following a further extension to , in 1972–1973 with another extension to , and in 1975–1976 after another extension to .
According to the 2011 Global Peace Index, Iceland is the most peaceful country in the world, due to its lack of armed forces, low crime rate and high level of socio-political stability. Iceland is listed in '' Guinness World Records'' as the "country ranked most at peace" and the "lowest military spending per capita".
Environmental policy
Iceland's official governmental goal is to cutgreenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs and Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse ...
emissions by 40% by the year 2030 and reach carbon neutrality by the year 2040.
The Icelandic Forest Service and other forestry groups promote large-scale reforestation in the country. Before the first human settlement, 25–40% of the country was covered by forest. The Vikings cut them for fuel, building, and making iron. Due to the reforestation efforts, the forest cover of Iceland increased six-fold since the 1990s. This helps to offset carbon emissions, prevent sand storms and increase the productivity of farms.
Economy
purchasing power parity
Purchasing power parity (PPP) is the measurement of prices in different countries that uses the prices of specific goods to compare the absolute purchasing power of the countries' currency, currencies. PPP is effectively the ratio of the price of ...
($40,112). About 85 percent of the total primary energy supply in Iceland is derived from domestically produced renewable energy sources. Use of abundant hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
and geothermal power
Geothermal power is electrical power generated from geothermal energy. Technologies in use include dry steam power stations, flash steam power stations and binary cycle power stations. Geothermal electricity generation is currently used in 2 ...
has made Iceland the world's largest electricity producer per capita. As a result of its commitment to renewable energy, the 2016 Global Green Economy Index ranked Iceland among the top 10 greenest economies in the world. Historically, Iceland's economy depended heavily on fishing, which still provides 40% of export earnings and employs 7% of the workforce. The economy is vulnerable to declining fish stocks and falls in world prices for its main material exports: fish and fish products, aluminium, and ferrosilicon. Whaling in Iceland has been historically significant. Iceland still relies heavily on fishing, but its importance is diminishing from an export share of 90% in the 1960s to 40% in 2006.
Until the 20th century, Iceland was a fairly poor country. It is now one of the most developed countries in the world. Strong economic growth led Iceland to be ranked third
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* Second#Sexagesimal divisions of calendar time and day, 1⁄60 of a ''second'', or 1⁄3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (d ...
in the United Nations' Human Development Index report for 2021/2022. According to the Economist Intelligence Index of 2011, Iceland had the second-highest quality of life in the world. Based on the Gini coefficient, Iceland also has one of the lowest rates of income inequality in the world, and when adjusted for inequality, its HDI ranking is sixth. Iceland's unemployment rate has declined consistently since the crisis, with 4.8% of the labour force being unemployed , compared to 6% in 2011 and 8.1% in 2010.
Many political parties remain opposed to EU membership, primarily due to Icelanders' concern about losing control over their natural resources (particularly fisheries). The national currency of Iceland is the Icelandic króna (ISK). Iceland is the only country in the world to have a population under two million yet still have a floating exchange rate and an independent monetary policy.
A poll released on 5 March 2010 by Capacent Gallup
Gallup may refer to:
*Gallup, Inc., a firm founded by George Gallup, well known for its opinion poll
*Gallup (surname), a surname
*Gallup, New Mexico, a city in New Mexico, United States
**Gallup station, an Amtrak train in downtown Gallup, New Me ...
showed that 31% of respondents were in favour of adopting the euro and 69% opposed. Another Capacent Gallup poll conducted in February 2012 found that 67.4% of Icelanders would reject EU membership in a referendum.
Iceland's economy has been diversifying into manufacturing and service industries in the last decade, including software production, biotechnology, and finance; industry accounts for around a quarter of economic activity, while services comprise close to 70%. The tourism sector is expanding, especially in ecotourism and whale-watching. On average, Iceland receives around 1.1 million visitors annually, which is more than three times the native population. 1.7 million people visited Iceland in 2016, 3 times more than the number that came in 2010. Iceland's agriculture industry, accounting for 5.4% of GDP, consists mainly of potatoes, green vegetables (in greenhouse
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of Transparent ceramics, transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic condit ...
s), mutton, and dairy products. The financial centre is Borgartún in Reykjavík, which hosts a large number of companies and three investment banks. Iceland's stock market
A stock market, equity market, or share market is the aggregation of buyers and sellers of stocks (also called shares), which represent ownership claims on businesses; these may include ''securities'' listed on a public stock exchange, as ...
, the Iceland Stock Exchange (ISE), was established in 1985.
Iceland is ranked 27th in the 2012 Index of Economic Freedom
The ''Index of Economic Freedom'' is an annual index and ranking created in 1995 by The Heritage Foundation and ''The Wall Street Journal'' to measure the degree of economic freedom in the world's nations. The creators of the index claim to tak ...
, lower than in prior years but still among the freest in the world. , it ranks 29th in the World Economic Forum's Global Competitive Index, one place lower than in 2015. According to the Global Innovation Index, Iceland is the 20th most innovative country in the world in 2022. Unlike most Western European countries, Iceland has a flat tax
A flat tax (short for flat-rate tax) is a tax with a single rate on the taxable amount, after accounting for any deductions or exemptions from the tax base. It is not necessarily a fully proportional tax. Implementations are often progressiv ...
system: the main personal income tax rate is a flat 22.75% and combined with municipal taxes, the total tax rate equals no more than 35.7%, not including the many available deductions. The corporate tax
A corporate tax, also called corporation tax or company tax, is a direct tax imposed on the income or capital of corporations or analogous legal entities. Many countries impose such taxes at the national level, and a similar tax may be imposed at ...
rate is a flat 18%, one of the lowest in the world. There is also a value added tax
A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the end ...
, whereas a net wealth tax was eliminated in 2006. Employment regulations are relatively flexible and the labour market is one of the freest in the world. Property rights are strong and Iceland is one of the few countries where they are applied to fishery management. Like other welfare states, taxpayers pay various subsidies to each other, but with spending being less than in most European countries.
Despite low tax rates, agricultural assistance is the highest among OECD countries and a potential impediment to structural change. Also, health care and education spending have relatively poor returns by OECD measures, though improvements have been made in both areas. The OECD ''Economic Survey of Iceland 2008'' highlighted Iceland's challenges in currency and macroeconomic policy. There was a currency crisis that started in the spring of 2008, and on 6 October trading in Iceland's banks was suspended as the government battled to save the economy. An assessment by the OECD 2011 determined that Iceland has made progress in many areas, particularly in creating a sustainable fiscal policy and restoring the health of the financial sector; however, challenges remain in making the fishing industry more efficient and sustainable, as well as in improving monetary policy to address inflation. Iceland's public debt has decreased since the economic crisis, and is the 31st-highest in the world by proportion of national GDP.
Economic contraction
Nordic countries
The Nordic countries (also known as the Nordics or ''Norden''; literal translation, lit. 'the North') are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe and the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic. It includes the sovereign states of Denmar ...
agreed to lend Iceland $2.5 billion.
On 26 January 2009, the coalition government collapsed due to public dissent over the handling of the financial crisis. A new left-wing government was formed a week later and immediately set about removing Central Bank governor Davíð Oddsson and his aides from the bank through changes in the law. Davíð was removed on 26 February 2009 in the wake of protests outside the Central Bank.
Thousands of Icelanders left the country after the collapse, many of those moving to Norway. In 2005, 293 people moved from Iceland to Norway; in 2009, the figure was 1,625. In April 2010, the Icelandic Parliament's Special Investigation Commission published the findings of its investigation, revealing the extent of control fraud in this crisis. By June 2012, Landsbanki managed to repay about half of the Icesave debt.
According to Bloomberg in 2014, Iceland was on the trajectory of 2% unemployment as a result of crisis-management decisions made back in 2008, including allowing the banks to fail.
Transport
 Iceland has a high level of car ownership per capita, with a car for every 1.5 inhabitants; it is the main form of transport. Iceland has of administered roads, of which are paved and are not. A great number of roads remain unpaved, mostly little-used rural roads. The road speed limits are and in towns, on gravel country roads and on hard-surfaced roads.
Iceland has a high level of car ownership per capita, with a car for every 1.5 inhabitants; it is the main form of transport. Iceland has of administered roads, of which are paved and are not. A great number of roads remain unpaved, mostly little-used rural roads. The road speed limits are and in towns, on gravel country roads and on hard-surfaced roads.
Route 1
The following highways are numbered 1.
For roads numbered A1, see list of A1 roads.
For roads numbered B1, see list of B1 roads.
For roads numbered M1, see List of M1 roads.
For roads numbered N1, see list of N1 roads.
For roads numbered ...
, or the Ring Road ( is, Þjóðvegur 1 or ), was completed in 1974, and is the main road that runs around Iceland and connects all the inhabited parts of the island, with the interior of the island being uninhabited. This paved road is long with one lane in each direction, except near larger towns and cities and in the Hvalfjörður Tunnel
The Hvalfjörður Tunnel ( is, Hvalfjarðargöng ) is a road tunnel under the Hvalfjörður fjord in Iceland and a part of Route 1. It is long and reaches a depth of below sea level. Opened on 11 July 1998, it shortens the distance from Reykjav ...
where it has more lanes. Many bridges on it, especially in the north and east, are single lanes and made of timber or steel.
Keflavík International Airport (KEF) is the largest airport and the main aviation hub for international passenger transport. It serves several international and domestic airline companies. KEF is in the vicinity of the larger metropolitan capital areas, to the WSW of Reykjavík centre, and public bus services are available.
Iceland has no passenger railways.
Reykjavík Airport (RKV) is the second-largest airport, located just 1.5 km from the capital centre. RKV serves general aviation traffic and has daily or regular domestic flights to 12 local townships within Iceland. RKV also serves international flights to Greenland and the Faroe Islands, business and private aeroplanes along with aviation training.
Akureyri Airport (AEY) and Egilsstaðir Airport (EGS) are two other domestic airports with limited international service capacity. There are a total of 103 registered airports and airfields in Iceland; most of them are unpaved and located in rural areas. The second-longest runway is at Geitamelur, a four-runway glider field around east of Reykjavík.
Several ferry services provide regular access to various outpost communities or shorten travel distances.
Energy
 Renewable sources— geothermal and hydropower—provide effectively all of Iceland's electricity and around 85% of the nation's total primary energy consumption, with most of the remainder consisting of imported oil products used in transportation and in the fishing fleet. A 2000 report from the University of Iceland suggested that Iceland could potentially convert from oil to hydrogen power by 2040. Iceland's largest geothermal power plants are Hellisheiði and
Renewable sources— geothermal and hydropower—provide effectively all of Iceland's electricity and around 85% of the nation's total primary energy consumption, with most of the remainder consisting of imported oil products used in transportation and in the fishing fleet. A 2000 report from the University of Iceland suggested that Iceland could potentially convert from oil to hydrogen power by 2040. Iceland's largest geothermal power plants are Hellisheiði and Nesjavellir
The Nesjavellir Geothermal Power Station ( is, Nesjavallavirkjun, ) is the second-largest geothermal power station in Iceland. The facility is located above sea level in the southwestern part of the country, near Þingvellir National Park and th ...
, while Kárahnjúkar Hydropower Plant
Kárahnjúkar Hydropower Plant ( is, Kárahnjúkavirkjun ), officially called Fljótsdalur Power Station ( is, Fljótsdalsstöð ) is a hydroelectric power plant in Fljótsdalshérað municipality in eastern Iceland, designed to produce annually ...
is the country's largest hydroelectric power station. When the Kárahnjúkavirkjun started operating, Iceland became the world's largest electricity producer per capita. Iceland is one of the few countries that have filling stations dispensing hydrogen fuel for cars powered by fuel cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most batteries in requ ...
s.
Despite this, Icelanders emitted 16.9 tonnes of CO2 per capita in 2016, the highest among EFTA and EU members, mainly resulting from transport and aluminium smelting. Nevertheless, in 2010, Iceland was reported by ''Guinness World Records'' as "the Greenest Country", reaching the highest score by the Environmental Sustainability Index, which measures a country's water use, biodiversity and adoption of clean energies, with a score of 93.5/100.
On 22 January 2009, Iceland announced its first round of offshore
Offshore may refer to:
Science and technology
* Offshore (hydrocarbons)
* Offshore construction, construction out at sea
* Offshore drilling, discovery and development of oil and gas resources which lie underwater through drilling a well
* Off ...
licences for companies wanting to conduct hydrocarbon exploration and production in a region northeast of Iceland, known as the Dreki area. Three exploration licences were awarded but all were subsequently relinquished.
Education and science
 The Ministry of Education, Science and Culture is responsible for the policies and methods that schools must use, and they issue the National Curriculum Guidelines. However, playschools, primary schools, and lower secondary schools are funded and administered by the municipalities. The government does allow citizens to home educate their children, however, under a very strict set of demands. Students must adhere closely to the government-mandated curriculum, and the parent teaching must acquire a government approved teaching certificate.
Nursery school, or , is non-compulsory education for children younger than six years and is the first step in the education system. The current legislation concerning playschools was passed in 1994. They are also responsible for ensuring that the curriculum is suitable to make the transition into compulsory education as easy as possible.
Compulsory education, or , comprises primary and lower secondary education, which often is conducted at the same institution. Education is mandatory by law for children aged from 6 to 16 years. The school year lasts nine months, beginning between 21 August and 1 September, and ending between 31 May and 10 June. The minimum number of school days was once 170, but after a new teachers' wage contract, it increased to 180. Lessons take place five days a week. All public schools have mandatory education in Christianity, although an exemption may be considered by the Minister of Education.
Upper secondary education, or , follows lower secondary education. These schools are also known as gymnasia in English. Though not compulsory, everyone who has had a compulsory education has the right to upper secondary education. This stage of education is governed by the Upper Secondary School Act of 1996. All schools in Iceland are mixed-sex schools. The largest seat of higher education is the University of Iceland, which has its main campus in central Reykjavík. Other schools offering university-level instruction include Reykjavík University, University of Akureyri, Agricultural University of Iceland and Bifröst University.
An OECD assessment found that 64% of Icelanders aged 25–64 have earned the equivalent of a high-school degree, which is lower than the OECD average of 73%. Among 25- to 34-year-olds, only 69% have earned the equivalent of a high-school degree, significantly lower than the OECD average of 80%. Nevertheless, Iceland's education system is considered excellent: the Programme for International Student Assessment ranks it as the 16th best performing, above the OECD average. Students were particularly proficient in reading and mathematics.
According to a 2013
The Ministry of Education, Science and Culture is responsible for the policies and methods that schools must use, and they issue the National Curriculum Guidelines. However, playschools, primary schools, and lower secondary schools are funded and administered by the municipalities. The government does allow citizens to home educate their children, however, under a very strict set of demands. Students must adhere closely to the government-mandated curriculum, and the parent teaching must acquire a government approved teaching certificate.
Nursery school, or , is non-compulsory education for children younger than six years and is the first step in the education system. The current legislation concerning playschools was passed in 1994. They are also responsible for ensuring that the curriculum is suitable to make the transition into compulsory education as easy as possible.
Compulsory education, or , comprises primary and lower secondary education, which often is conducted at the same institution. Education is mandatory by law for children aged from 6 to 16 years. The school year lasts nine months, beginning between 21 August and 1 September, and ending between 31 May and 10 June. The minimum number of school days was once 170, but after a new teachers' wage contract, it increased to 180. Lessons take place five days a week. All public schools have mandatory education in Christianity, although an exemption may be considered by the Minister of Education.
Upper secondary education, or , follows lower secondary education. These schools are also known as gymnasia in English. Though not compulsory, everyone who has had a compulsory education has the right to upper secondary education. This stage of education is governed by the Upper Secondary School Act of 1996. All schools in Iceland are mixed-sex schools. The largest seat of higher education is the University of Iceland, which has its main campus in central Reykjavík. Other schools offering university-level instruction include Reykjavík University, University of Akureyri, Agricultural University of Iceland and Bifröst University.
An OECD assessment found that 64% of Icelanders aged 25–64 have earned the equivalent of a high-school degree, which is lower than the OECD average of 73%. Among 25- to 34-year-olds, only 69% have earned the equivalent of a high-school degree, significantly lower than the OECD average of 80%. Nevertheless, Iceland's education system is considered excellent: the Programme for International Student Assessment ranks it as the 16th best performing, above the OECD average. Students were particularly proficient in reading and mathematics.
According to a 2013 Eurostat
Eurostat ('European Statistical Office'; DG ESTAT) is a Directorate-General of the European Commission located in the Kirchberg, Luxembourg, Kirchberg quarter of Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. Eurostat's main responsibilities are to provide statis ...
report by the European Commission, Iceland spends around 3.11% of its GDP on scientific research and development (R&D), over 1 percentage point higher than the EU average of 2.03%, and has set a target of 4% to reach by 2020. Iceland was ranked 17th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021, up from 20th in 2019. A 2010 UNESCO report found that out of 72 countries that spend the most on R&D (US$100 million or more), Iceland ranked ninth by proportion of GDP, tied with Taiwan, Switzerland, and Germany and ahead of France, the United Kingdom and Canada.
Demographics
Gaelic
Gaelic is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". As a noun it refers to the group of languages spoken by the Gaels, or to any one of the languages individually. Gaelic languages are spoken in Ireland, Scotland, the Isle of Man, and Ca ...
origin. This is evident from literary evidence dating from the settlement period as well as from later scientific studies such as blood type
A blood type (also known as a blood group) is a classification of blood, based on the presence and absence of antibodies and inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrate ...
and genetic analyses. One such genetic study indicated that the majority of the male settlers were of Nordic origin while the majority of the women were of Gaelic origin, meaning many settlers of Iceland were Norsemen who brought Gaelic slaves with them.
Iceland has extensive genealogical records dating back to the late 17th century and fragmentary records extending back to the Age of Settlement. The biopharmaceutical company deCODE genetics has funded the creation of a genealogy database that is intended to cover all of Iceland's known inhabitants. It views the database, called '' Íslendingabók'', as a valuable tool for conducting research on genetic diseases, given the relative isolation of Iceland's population.
The population of the island is believed to have varied from 40,000 to 60,000 in the period ranging from initial settlement until the mid-19th century. During that time, cold winters, ash fall from volcanic eruptions, and bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium (''Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as well a ...
s adversely affected the population several times. There were 37 famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
years in Iceland between 1500 and 1804. The first census was carried out in 1703 and revealed that the population was then 50,358. After the destructive volcanic eruptions of the Laki volcano during 1783–1784, the population reached a low of about 40,000. Improving living conditions have triggered a rapid increase in population since the mid-19th century—from about 60,000 in 1850 to 320,000 in 2008. Iceland has a relatively young population for a developed country, with one out of five people being 14 years old or younger. With a fertility rate of 2.1, Iceland is one of only a few European countries with a birth rate sufficient for long-term population growth (see table below).
In December 2007, 33,678 people (13.5% of the total population) living in Iceland had been born abroad, including children of Icelandic parents living abroad. Around 19,000 people (6% of the population) held foreign citizenship. Polish people make up the largest minority group by a considerable margin and still form the bulk of the foreign workforce. About 8,000 Poles now live in Iceland, 1,500 of them in Fjarðabyggð where they make up 75% of the workforce who are constructing the Fjarðarál aluminium plant. Large-scale construction projects in the east of Iceland (see Kárahnjúkar Hydropower Plant
Kárahnjúkar Hydropower Plant ( is, Kárahnjúkavirkjun ), officially called Fljótsdalur Power Station ( is, Fljótsdalsstöð ) is a hydroelectric power plant in Fljótsdalshérað municipality in eastern Iceland, designed to produce annually ...
) have also brought in many people whose stay is expected to be temporary. Many Polish immigrants were also considering leaving in 2008 as a result of the Icelandic financial crisis.
The southwest corner of Iceland is by far the most densely populated region. It is also the location of the capital Reykjavík, the northernmost national capital in the world. More than 70 percent of Iceland's population lives in the southwest corner (Greater Reykjavík
The Capital Region ( is, Höfuðborgarsvæðið ) is a region in southwestern Iceland that comprises the national capital Reykjavík and six municipalities around it.Sigurður Guðmundsson. „Hvernig eru hugtökin dreifbýli og landsbyggð skil ...
and the nearby Southern Peninsula
Southern Peninsula ( is, Suðurnes ) is an administrative unit and part of Reykjanesskagi (pronounced ), or Reykjanes Peninsula, a region in southwest Iceland. It was named after Reykjanes, the southwestern tip of Reykjanesskagi.
The region ...
), which covers less than two percent of Iceland's land area. The largest town outside Greater Reykjavík is Reykjanesbær, which is located on the Southern Peninsula, less than from the capital. The largest town outside the southwest corner is Akureyri in northern Iceland.
Some 500 Icelanders under the leadership of Erik the Red
Erik Thorvaldsson (), known as Erik the Red, was a Norse explorer, described in medieval and Icelandic saga sources as having founded the first settlement in Greenland. He most likely earned the epithet "the Red" due to the color of his hair a ...
settled Greenland in the late tenth century. The total population reached a high point of perhaps 5,000, and developed independent institutions before disappearing by 1500. People from Greenland attempted to set up a settlement at Vinland in North America, but abandoned it in the face of hostility from the indigenous residents.
Emigration of Icelanders to the United States and Canada began in the 1870s. , Canada had over 88,000 people of Icelandic descent, while there are more than 40,000 Americans of Icelandic descent, according to the 2000 US census.
Urbanisation
Iceland's 10 most populous urban areas:Language
Iceland's official written and spoken language is Icelandic, a North Germanic language descended from Old Norse. In grammar and vocabulary, it has changed less from Old Norse than the other Nordic languages; Icelandic has preserved more verb and noun inflection, and has to a considerable extent developed new vocabulary based on native roots rather than borrowings from other languages. The puristic tendency in the development of Icelandic vocabulary is to a large degree a result of conscious language planning, in addition to centuries of isolation. Icelandic is the only living language to retain the use of the runic letter Þ in Latin script. The closest living relative of the Icelandic language is Faroese. Icelandic Sign Language was officially recognised as a minority language in 2011. In education, its use for Iceland's deaf community is regulated by the ''National Curriculum Guide''. English and Danish are compulsory subjects in the school curriculum. English is widely understood and spoken, while basic to moderate knowledge of Danish is common mainly among the older generations. Polish is mostly spoken by the local Polish community (the largest minority of Iceland), and Danish is mostly spoken in a way largely comprehensible to Swedes and Norwegians—it is often referred to as (i. e. ''Scandinavian'') in Iceland. Rather than usingfamily name
In some cultures, a surname, family name, or last name is the portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family, tribe or community.
Practices vary by culture. The family name may be placed at either the start of a person's full name ...
s, as is the usual custom in most Western nations, Icelanders carry patronymic or matronymic surnames, patronyms being far more commonly practised. Patronymic last names are based on the first name of the father, while matronymic names are based on the first name of the mother. These follow the person's given name, e.g. ("Elísabet, Jón's daughter" (Jón being the father)) or ("Ólafur, Katrín's son" (Katrín being the mother)). Consequently, Icelanders refer to one another by their given name, and the Icelandic telephone directory is listed alphabetically by the first name rather than by surname. All new names must be approved by the Icelandic Naming Committee.
Health
 Iceland has a universal health care system that is administered by its Ministry of Welfare () and paid for mostly by taxes (85%) and to a lesser extent by service fees (15%). Unlike most countries, there are no private hospitals, and private insurance is practically nonexistent.
A considerable portion of the government budget is assigned to health care, and Iceland ranks 11th in health care expenditures as a percentage of GDP and 14th in spending per capita. Overall, the country's health care system is one of the best performing in the world, ranked 15th by the World Health Organization. According to an OECD report, Iceland devotes far more resources to healthcare than most industrialised nations. , Iceland had 3.7 doctors per 1,000 people (compared with an average of 3.1 in OECD countries) and 15.3 nurses per 1,000 people (compared with an OECD average of 8.4).
Icelanders are among the world's healthiest people, with 81% reporting they are in good health, according to an OECD survey. Although it is a growing problem, obesity is not as prevalent as in other developed countries. Iceland has many campaigns for health and wellbeing, including the famous television show '' Lazytown'', starring and created by former gymnastics champion
Iceland has a universal health care system that is administered by its Ministry of Welfare () and paid for mostly by taxes (85%) and to a lesser extent by service fees (15%). Unlike most countries, there are no private hospitals, and private insurance is practically nonexistent.
A considerable portion of the government budget is assigned to health care, and Iceland ranks 11th in health care expenditures as a percentage of GDP and 14th in spending per capita. Overall, the country's health care system is one of the best performing in the world, ranked 15th by the World Health Organization. According to an OECD report, Iceland devotes far more resources to healthcare than most industrialised nations. , Iceland had 3.7 doctors per 1,000 people (compared with an average of 3.1 in OECD countries) and 15.3 nurses per 1,000 people (compared with an OECD average of 8.4).
Icelanders are among the world's healthiest people, with 81% reporting they are in good health, according to an OECD survey. Although it is a growing problem, obesity is not as prevalent as in other developed countries. Iceland has many campaigns for health and wellbeing, including the famous television show '' Lazytown'', starring and created by former gymnastics champion Magnus Scheving
Magnus, meaning "Great" in Latin, was used as cognomen of Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus in the first century BC. The best-known use of the name during the Roman Empire is for the fourth-century Western Roman Emperor Magnus Maximus. The name gained wid ...
. Infant mortality
Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the probability of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. The under-five morta ...
is one of the lowest in the world, and the proportion of the population that smokes is lower than the OECD average. Almost all women choose to terminate pregnancies of children with Down syndrome in Iceland. The average life expectancy is 81.8 (compared to an OECD average of 79.5), the fourth-highest in the world.
Iceland has a very low level of pollution, thanks to an overwhelming reliance on cleaner geothermal energy, a low population density, and a high level of environmental consciousness among citizens
Citizenship is a "relationship between an individual and a state to which the individual owes allegiance and in turn is entitled to its protection".
Each state determines the conditions under which it will recognize persons as its citizens, and ...
. According to an OECD assessment, the amount of toxic materials in the atmosphere is far lower than in any other industrialised country measured.
Religion
 Icelanders have freedom of religion guaranteed under the Constitution, although the Church of Iceland, a Lutheran body, is the
Icelanders have freedom of religion guaranteed under the Constitution, although the Church of Iceland, a Lutheran body, is the state church
A state religion (also called religious state or official religion) is a religion or creed officially endorsed by a sovereign state. A state with an official religion (also known as confessional state), while not secular, is not necessarily a t ...
:
Approximately 80 percent of Icelanders legally affiliate with a religious denomination, a process that happens automatically at birth and from which they can choose to opt out. They also pay a church tax (sóknargjald), which the government directs to help support their registered religion, or, in the case of no religion, the University of Iceland.
The Registers Iceland keeps account of the religious affiliation of every Icelandic citizen. In 2017, Icelanders were divided into religious groups as follows:
* 67.22% members of the Church of Iceland;
* 11.56% members of other Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
denomination;
* 11.29% other religions and not specified;
* 6.69% unaffiliated;
* 1.19% members of Germanic Heathen groups (99% of them belonging to Ásatrúarfélagið);
* 0.67% members of the Icelandic Ethical Humanist Association
The Icelandic Ethical Humanist Association () is a humanist lifestance organization in Iceland, that promotes secularism, offers celebrancy services and contributes to the spreading of humanism in Iceland and abroad. It is a member of the European ...
;
* 0.55% members of Zuist groups.
On March 8, 2021, Iceland formally recognised Judaism as a religion for the first time. Iceland's Jews will have the choice to register as such and direct their taxes to their own religion. Among other benefits, the recognition will also allow Jewish marriage, baby-naming and funeral ceremonies to be civilly recognised.
Iceland is a very secular country; as with other Nordic nations, church attendance is relatively low. The above statistics represent administrative membership of religious organisations, which does not necessarily reflect the belief demographics of the population. According to a study published in 2001, 23% of the inhabitants were either atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
or agnostic
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, of the divine or the supernatural is unknown or unknowable. (page 56 in 1967 edition) Another definition provided is the view that "human reason is incapable of providing sufficient ...
. A Gallup poll conducted in 2012 found that 57% of Icelanders considered themselves "religious", 31% considered themselves "non-religious", while 10% defined themselves as "convinced atheists", placing Iceland among the ten countries with the highest proportions of atheists in the world. Registration of Icelanders in the state church, the Church of Iceland, is declining at a rate of more than 1% per year.
Culture
Icelandic culture has its roots in North Germanic traditions. Icelandic literature is popular, in particular the sagas and eddas that were written during theHigh
High may refer to:
Science and technology
* Height
* High (atmospheric), a high-pressure area
* High (computability), a quality of a Turing degree, in computability theory
* High (tectonics), in geology an area where relative tectonic uplift ...
and Late Middle Ages. Centuries of isolation have helped to insulate the country's Nordic culture from external influence; a prominent example is the preservation of the Icelandic language, which remains the closest to Old Norse of all modern Nordic languages.
In contrast to other Nordic countries, Icelanders place relatively great importance on independence and self-sufficiency; in a public opinion analysis conducted by the European Commission, over 85% of Icelanders believe independence is "very important", compared to 47% of Norwegians, 49% of Danes, and an average of 53% for the EU25. Icelanders also have a very strong work ethic, working some of the longest hours of any industrialised nation.
According to a poll conducted by the OECD, 66% of Icelanders were satisfied with their lives, while 70% believed that their lives will be satisfying in the future. Similarly, 83% reported having more positive experiences in an average day than negative ones, compared to an OECD average of 72%, which makes Iceland one of the happiest countries in the OECD. A more recent 2012 survey found that around three-quarters of respondents stated they were satisfied with their lives, compared to a global average of about 53%.
Iceland is liberal about LGBT rights issues. In 1996, the Icelandic parliament passed legislation to create registered partnerships for same-sex couples, conferring nearly all the rights and benefits of marriage. In 2006, parliament voted unanimously to grant same-sex couples the same rights as heterosexual couples in adoption, parenting, and assisted insemination treatment. In 2010, the Icelandic parliament amended the marriage law, making it gender-neutral and defining marriage as between two individuals, making Iceland one of the first countries in the world to legalise same-sex marriages. The law took effect on 27 June 2010. The amendment to the law also means registered partnerships for same-sex couples are now no longer possible, and marriage is their only option—identical to the existing situation for opposite-sex couples.
Icelanders are known for their strong sense of community and lack of social isolation: An OECD survey found that 98% believe they know someone they could rely on in a time of need, higher than in any other industrialised country. Similarly, only 6% reported "rarely" or "never" socialising with others. This high level of social cohesion is attributed to the small size and homogeneity of the population, as well as to a long history of harsh survival in an isolated environment, which reinforced the importance of unity and cooperation.
Egalitarianism is highly valued among the people of Iceland, with income inequality being among the lowest in the world. The constitution explicitly prohibits the enactment of noble privileges, titles, and ranks. Wilcox and Latif, pp. 60–61. Everyone is addressed by their first name. As in other Nordic countries, equality between the sexes is very high; Iceland is consistently ranked among the top three countries in the world for women to live in.
Literature
In 2011, Reykjavík was designated a UNESCO City of Literature. Iceland's best-known classical works of literature are the Icelanders' sagas, prose epics set in Iceland's age of settlement. The most famous of these include '' Njáls saga'', about an epic blood feud, and ''
Iceland's best-known classical works of literature are the Icelanders' sagas, prose epics set in Iceland's age of settlement. The most famous of these include '' Njáls saga'', about an epic blood feud, and ''Grænlendinga saga
''Grœnlendinga saga'' () (spelled ''Grænlendinga saga'' in modern Icelandic and translated into English as the Saga of the Greenlanders) is one of the sagas of Icelanders. Like the ''Saga of Erik the Red'', it is one of the two main sources on t ...
'' and '' Eiríks saga'', describing the discovery and settlement of Greenland and Vinland (modern Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
). '' Egils saga'', '' Laxdæla saga'', '' Grettis saga'', '' Gísla saga'' and '' Gunnlaugs saga ormstungu'' are also notable and popular Icelanders' sagas.
A translation of the Bible was published in the 16th century. Important compositions from the 15th to the 19th century include sacred verse, most famously the Passion Hymns of Hallgrímur Pétursson, and '' rímur'', rhyming epic poems. Originating in the 14th century, ''rímur'' were popular into the 19th century, when the development of new literary forms was provoked by the influential National-Romantic writer Jónas Hallgrímsson. In recent times, Iceland has produced many great writers, the best-known of whom is arguably Halldór Laxness
Halldór Kiljan Laxness (; born Halldór Guðjónsson; 23 April 1902 – 8 February 1998) was an Icelandic writer and winner of the 1955 Nobel Prize in Literature. He wrote novels, poetry, newspaper articles, essays, plays, travelogues and s ...
, who received the Nobel Prize in Literature
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, caption =
, awarded_for = Outstanding contributions in literature
, presenter = Swedish Academy
, holder = Annie Ernaux (2022)
, location = Stockholm, Sweden
, year = 1901
, ...
in 1955 (the only Icelander to win a Nobel Prize thus far). Steinn Steinarr was an influential modernist poet during the early 20th century who remains popular.
Icelanders are avid consumers of literature, with the highest number of bookstores per capita in the world. For its size, Iceland imports and translates more international literature than any other nation. Iceland also has the highest per capita publication of books and magazines, and around 10% of the population will publish a book in their lifetimes.
Most books in Iceland are sold between late September to early November. This period is known as ''Jólabókaflóð'', the Christmas Book Flood. The Flood begins with the Iceland Publisher's Association distributing ''Bókatíðindi'', a catalogue of all new publications, free to each Icelandic home.
Art
The distinctive rendition of the Icelandic landscape by its painters can be linked to nationalism and the movement for home rule and independence, which was very active in the mid-19th century. Contemporary Icelandic painting is typically traced to the work of Þórarinn Þorláksson, who, following formal training in art in the 1890s in Copenhagen, returned to Iceland to paint and exhibit works from 1900 to his death in 1924, almost exclusively portraying the Icelandic landscape. Several other Icelandic men and women artists studied at Royal Danish Academy of Fine Arts at that time, including Ásgrímur Jónsson, who together with Þórarinn created a distinctive portrayal of Iceland's landscape in a romantic naturalistic style. Other landscape artists quickly followed in the footsteps of Þórarinn and Ásgrímur. These included
Contemporary Icelandic painting is typically traced to the work of Þórarinn Þorláksson, who, following formal training in art in the 1890s in Copenhagen, returned to Iceland to paint and exhibit works from 1900 to his death in 1924, almost exclusively portraying the Icelandic landscape. Several other Icelandic men and women artists studied at Royal Danish Academy of Fine Arts at that time, including Ásgrímur Jónsson, who together with Þórarinn created a distinctive portrayal of Iceland's landscape in a romantic naturalistic style. Other landscape artists quickly followed in the footsteps of Þórarinn and Ásgrímur. These included Jóhannes Kjarval
Johannes is a Medieval Latin form of the personal name that usually appears as " John" in English language contexts. It is a variant of the Greek and Classical Latin variants (Ιωάννης, '' Ioannes''), itself derived from the Hebrew name '' Y ...
and Júlíana Sveinsdóttir
Júlíana Sveinsdóttir (31 July 1889 – 17 April 1966) was one of Iceland's first female painters and textile artists. Taught initially by prominent Icelandic artist Þórarinn B. Þorláksson, Júlíana settled in Denmark and returned to I ...
. Kjarval in particular is noted for the distinct techniques in the application of paint that he developed in a concerted effort to render the characteristic volcanic rock that dominates the Icelandic environment. Einar Hákonarson is an expressionistic and figurative painter who by some is considered to have brought the figure back into Icelandic painting. In the 1980s, many Icelandic artists worked with the subject of the new painting in their work.
In recent years the artistic practice has multiplied, and the Icelandic art scene has become a setting for many large-scale projects and exhibitions. The artist-run gallery space Kling og Bang, members of which later ran the studio complex and exhibition venue Klink og Bank, has been a significant part of the trend of self-organised spaces, exhibitions, and projects. The Living Art Museum
The Living Art Museum (Nýló) is a not-for-profit, artist-run museum and exhibition platform for innovative and experimental contemporary art in Reykjavík, Iceland. The Living Art Museum is committed to presenting, collecting and preserving wor ...
, Reykjavík Municipal Art Museum, Reykjavík Art Museum, and the National Gallery of Iceland
The National Gallery of Iceland ( is, Listasafn Íslands ) is an art museum in Reykjavík which contains a collection of Icelandic art. The gallery features artwork of famous Icelandic artists and artwork that helps explain the traditional Icelan ...
are the larger, more established institutions, curating shows and festivals.
Music
 Much Icelandic music is related to Nordic music, and includes folk and
Much Icelandic music is related to Nordic music, and includes folk and pop
Pop or POP may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* Pop music, a musical genre Artists
* POP, a Japanese idol group now known as Gang Parade
* Pop!, a UK pop group
* Pop! featuring Angie Hart, an Australian band
Albums
* ''Pop'' (G ...
traditions. Notable Icelandic music acts include medieval music group Voces Thules Voces Thules is an Icelandic music ensemble formed in 1992. The ensemble consists of five male singers (Eggert Pálsson, Einar Jóhannesson, Eiríkur Hreinn Helgason, Guðlaugur Viktorsson and Sigurður Halldórsson) who have studied in Reykjavík, ...
, alternative and indie rock acts such as The Sugarcubes, Sóley and Of Monsters and Men
Of Monsters and Men is an Icelandic indie folk/rock band formed in Reykjavík in 2010. The members are lead singer and guitarist Nanna Bryndís Hilmarsdóttir, singer and guitarist Ragnar "Raggi" Þórhallsson, lead guitarist Brynjar Leifsson ...
, jazz fusion band Mezzoforte, pop singers such as Hafdís Huld, Emilíana Torrini and Björk
Björk Guðmundsdóttir ( , ; born 21 November 1965), known mononymously as Björk, is an Icelandic singer, songwriter, composer, record producer, and actress. Noted for her distinct three-octave vocal range and eccentric persona, she has de ...
, solo ballad singers like Bubbi Morthens, and post-rock
Post-rock is a form of experimental rock characterized by a focus on exploring textures and timbre over traditional rock song structures, chords, or riffs. Post-rock artists are often instrumental, typically combining rock instrumentation with ...
bands such as Amiina and Sigur Rós
Sigur Rós () is an Icelandic post-rock band from Reykjavík, active since 1994. The band comprises singer and guitarist Jón Þór "Jónsi" Birgisson, bassist Georg Hólm, and keyboardist Kjartan Sveinsson. Known for their ethereal sound, fron ...
. Independent music is strong in Iceland, with bands such as múm and solo artists such as Daði Freyr.
Traditional Icelandic music is strongly religious. Hymns, both religious and secular, are a particularly well-developed form of music, due to the scarcity of musical instruments throughout much of Iceland's history. Hallgrímur Pétursson wrote many Protestant hymns in the 17th century. Icelandic music was modernised in the 19th century when Magnús Stephensen brought pipe organs, which were followed by harmoniums. Other vital traditions of Icelandic music are epic alliterative and rhyming ballads called ''rímur''. ''Rímur'' are epic tales, usually a cappella
''A cappella'' (, also , ; ) music is a performance by a singer or a singing group without instrumental accompaniment, or a piece intended to be performed in this way. The term ''a cappella'' was originally intended to differentiate between Ren ...
, which can be traced back to skald
A skald, or skáld (Old Norse: , later ; , meaning "poet"), is one of the often named poets who composed skaldic poetry, one of the two kinds of Old Norse poetry, the other being Eddic poetry, which is anonymous. Skaldic poems were traditionally ...
ic poetry, using complex metaphors and elaborate rhyme schemes. The best-known rímur poet of the 19th century was Sigurður Breiðfjörð (1798–1846). A modern revitalisation of the tradition began in 1929 with the formation of .
Among Iceland's best-known classical composers are Daníel Bjarnason and Anna S. Þorvaldsdóttir
Anna Sigríður Þorvaldsdóttir (Anna Thorvaldsdottir) (born 11 July 1977) is "one of Iceland's most celebrated composers" and 2012 winner of the Nordic Council Music Prize. Her music is frequently performed in Europe and in the United States, ...
, who in 2012 received the Nordic Council Music Prize
The Nordic Council Music Prize is awarded annually by NOMUS, the Nordic Music Committee. Every two years it is awarded for a work by a living composer. In the intervening years it is awarded to a performing musician or ensemble.
The Nordic ...
and in 2015 was chosen as the New York Philharmonic's Kravis Emerging Composer, an honour that includes a $50,000 cash prize and a commission to write a composition for the orchestra; she is the second recipient.
The national anthem of Iceland is ''Lofsöngur
"" (, lit. "Hymn"), also known as "" (; en, "O, God of Our Land"), is the national anthem of Iceland. Sveinbjörn Sveinbjörnsson composed the music, while the lyrics were authored by Matthías Jochumsson. It was adopted as the national anthem i ...
'', written by Matthías Jochumsson
Matthías Jochumsson (11 November 1835 – 18 November 1920) was an Icelandic Lutheran clergyman, poet, playwright, and translator. He is best known for his lyrical poetry and for writing the national anthem of Iceland, "Lofsöngur", in 1874.
, with music by Sveinbjörn Sveinbjörnsson
Sveinbjörn Sveinbjörnsson (28 June 1847 – 23 February 1927) was an Icelandic composer best known for composing " Lofsöngur", the national anthem of Iceland.
Early life and education
Sveinbjörn was born in Seltjarnarnes. He was studying divi ...
.
Media
 Iceland's largest television stations are the state-run Sjónvarpið and the privately owned
Iceland's largest television stations are the state-run Sjónvarpið and the privately owned Stöð 2
Stöð 2 (literally Station 2) is an Icelandic subscription television channel, owned and operated by Sýn. Founded in 1986, it was the first privately owned television station in Iceland following the lifting of the state monopoly on televisi ...
and SkjárEinn. Smaller stations exist, many of them local. Radio is broadcast throughout the country, including in some parts of the interior. The main radio stations are Rás 1, Rás 2, X-ið 977, Bylgjan and FM957. The daily newspapers are ''Morgunblaðið
''Morgunblaðið'' (, ''The Morning Paper'') is an Icelandic newspaper. ''Morgunblaðið''s website, mbl.is, is the most popular website in Iceland.
History
''Morgunblaðið'' was founded by Vilhjálmur Finsen and Ólafur Björnsson, brother of ...
'' and '' Fréttablaðið''. The most popular websites are the news sites Vísir and Mbl.is.
Iceland is home to '' LazyTown'' (Icelandic: ''Latibær''), a children's educational musical comedy programme created by Magnús Scheving
Magnús Örn Scheving (; born 10 November 1964) is an Icelandic writer, entrepreneur, television producer, actor and athlete. He is the creator, director, and star of the children's television show '' LazyTown'', in which he also portrayed th ...
. It has become a very popular programme for children and adults and is shown in over 100 countries, including the Americas, the UK and Sweden. The ''LazyTown'' studios are located in Garðabær. The 2015 television crime series '' Trapped'' aired in the UK on BBC4 in February and March 2016, to critical acclaim and according to the Guardian "the unlikeliest TV hit of the year".
In 1992, the Icelandic film industry achieved its greatest recognition hitherto, when Friðrik Þór Friðriksson was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film
The Academy Award for Best International Feature Film (known as Best Foreign Language Film prior to 2020) is one of the Academy Awards handed out annually by the U.S.-based Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS). It is given to a ...
for his '' Children of Nature''. It features the story of an old man who is unable to continue running his farm. After being unwelcomed in his daughter's and father-in-law's house in town, he is put in a home for the elderly. There, he meets an old girlfriend of his youth, and they both begin a journey through the wilds of Iceland to die together. This is the only Icelandic movie to have ever been nominated for an Academy Award.
Singer-songwriter Björk
Björk Guðmundsdóttir ( , ; born 21 November 1965), known mononymously as Björk, is an Icelandic singer, songwriter, composer, record producer, and actress. Noted for her distinct three-octave vocal range and eccentric persona, she has de ...
received international acclaim for her starring role in the Danish musical drama '' Dancer in the Dark'', directed by Lars von Trier, in which she plays Selma Ježková, a factory worker who struggles to pay for her son's eye operation. The film premiered at the 2000 Cannes Film Festival
The 53rd Cannes Film Festival started on 14 May and ran until 25 May 2000. French film director, screenwriter, and producer Luc Besson was the Jury President. The Palme d'Or went to the Danish film ''Dancer in the Dark'' by Lars von Trier.
The fe ...
, where she won the Best Actress Award. The movie also led Björk to nominations for Best Original Song at the 73rd Academy Awards, with the song ''I've Seen It All
"I've Seen It All" is a song recorded by Icelandic singer Björk for the ''Dancer in the Dark'' soundtrack, ''Selmasongs'' (2000). It was written by the singer, along with Sjón and Lars von Trier, who also directed the film. It was released as ...
'' and for a Golden Globe Award for Best Actress in a Motion Picture - Drama.
Guðrún S. Gísladóttir, who is Icelandic, played one of the major roles in Russian filmmaker Andrei Tarkovsky
Andrei Arsenyevich Tarkovsky ( rus, Андрей Арсеньевич Тарковский, p=ɐnˈdrʲej ɐrˈsʲenʲjɪvʲɪtɕ tɐrˈkofskʲɪj; 4 April 1932 – 29 December 1986) was a Russian filmmaker. Widely considered one of the greates ...
's film '' The Sacrifice'' (1986). Anita Briem
Anita Briem (born 29 May 1982) is an Icelandic actress. She is known for her role as Queen Jane Seymour on '' The Tudors'' and her role as Hannah Ásgeirsson in '' Journey to the Center of the Earth''.
Personal life
Briem was born on 29 May ...
, known for her performance in Showtime's '' The Tudors'', is also Icelandic. Briem starred in the film '' Journey to the Center of the Earth'' (2008), which shot scenes in Iceland. The James Bond movie '' Die Another Day'' (2002) is set for a large part in Iceland. Christopher Nolan's film '' Interstellar'' (2014) was also filmed in Iceland for some of its scenes, as was Ridley Scott
Sir Ridley Scott (born 30 November 1937) is a British film director and producer. Directing, among others, science fiction films, his work is known for its atmospheric and highly concentrated visual style. Scott has received many accolades thr ...
's '' Prometheus'' (2012).
On 17 June 2010, the parliament passed the Icelandic Modern Media Initiative, proposing greater protection of free speech rights and the identity of journalists and whistle-blowers—the strongest journalist protection law in the world. According to a 2011 report by Freedom House
Freedom House is a non-profit, majority U.S. government funded organization in Washington, D.C., that conducts research and advocacy on democracy, political freedom, and human rights. Freedom House was founded in October 1941, and Wendell Wil ...
, Iceland is one of the highest-ranked countries in press freedom.
CCP Games, developers of the critically acclaimed ''EVE Online'' and ''Dust 514'', are headquartered in Reykjavík. CCP Games hosts the third-most populated MMO in the world, which also has the largest total game area for an online game, according to ''Guinness World Records''.
Iceland has a highly developed internet culture, with around 95% of the population having internet access, the highest proportion in the world. Iceland ranked 12th in the World Economic Forum's 2009–2010 Network Readiness Index
The Networked Readiness Index is an index published annually by the World Economic Forum in collaboration with INSEAD, as part of their annual ''Global Information Technology Report''. It aims to measure the degree of readiness of countries to expl ...
, which measures a country's ability to competitively exploit communications technology. The United Nations International Telecommunication Union ranks the country third in its development of information and communications technology, having moved up four places between 2008 and 2010. In February 2013 the country (ministry of the interior) was researching possible methods to protect children in regards to Internet pornography, claiming that pornography online is a threat to children as it supports child slavery and abuse. Strong voices within the community expressed concerns with this, stating that it is impossible to block access to pornography without compromising freedom of speech.
Cuisine
 Much of Iceland's cuisine is based on fish, lamb, and
Much of Iceland's cuisine is based on fish, lamb, and dairy product
Dairy products or milk products, also known as lacticinia, are food products made from (or containing) milk. The most common dairy animals are cow, water buffalo, nanny goat, and ewe. Dairy products include common grocery store food items in th ...
s, with little to no use of herbs or spices. Due to the island's climate, fruits and vegetables are not generally a component of traditional dishes, although the use of greenhouses has made them more common in contemporary food. Þorramatur is a selection of traditional cuisine consisting of many dishes and is usually consumed around the month of Þorri, which begins on the first Friday after 19 January. Traditional dishes also include skyr (a yogurt-like cheese), hákarl (cured shark), cured ram, singed sheep heads, and black pudding, Flatkaka (flatbread), dried fish and dark rye bread traditionally baked in the ground in geothermal areas. Puffin
Puffins are any of three species of small alcids (auks) in the bird genus ''Fratercula''. These are pelagic seabirds that feed primarily by diving in the water. They breed in large colonies on coastal cliffs or offshore islands, nesting in crev ...
is considered a local delicacy that is often prepared through broiling.
Breakfast usually consists of pancakes, cereal, fruit, and coffee, while lunch may take the form of a smörgåsbord. The main meal of the day for most Icelanders is dinner, which usually involves fish or lamb as the main course. Seafood is central to most Icelandic cooking, particularly cod and haddock but also salmon, herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans, i ...
, and halibut. It is often prepared in a wide variety of ways, either smoked, pickled, boiled, or dried. Lamb is by far the most common meat, and it tends to be either smoke-cured (known as ''hangikjöt
Hangikjöt (; lit. "hung meat") is a traditional festive food in Iceland, served at Christmas.
Etymology and history
This Icelandic smoked lamb, mutton, or horse meat is usually boiled and served either hot or cold in slices, traditionally with ...
'') or salt-preserved (''saltkjöt''). Many older dishes make use of every part of the sheep, such as ''slátur
Slátur (, "slaughter") is an Icelandic food made from the innards of sheep. There are two types of slátur; ''blóðmör'' (Icelandic) or "blood pudding" and ''lifrarpylsa'' ("liver sausage"). The first is similar to Irish and British black pudd ...
'', which consists of offal (internal organs and entrails) minced together with blood and served in sheep stomach. Additionally, boiled or mashed potatoes, pickled cabbage, green beans, and rye bread are prevalent side dishes.
Coffee is a popular beverage in Iceland, with the country being third placed by per capita consumption worldwide in 2016, and is drunk at breakfast, after meals, and with a light snack in mid-afternoon. Coca-Cola is also widely consumed, to the extent that the country is said to have one of the highest per capita consumption rates in the world.
Iceland's signature alcoholic beverage is '' brennivín'' (literally "burnt .e., distilledwine"), which is similar in flavouring to the akvavit variant of Scandinavian brännvin. It is a type of schnapps made from distilled potatoes and flavoured with either caraway seeds or angelica. Its potency has earned it the nickname ''svarti dauði'' ("Black Death"). Modern distilleries on Iceland produce vodka ( Reyka), gin
Gin () is a distilled alcoholic drink that derives its flavour from juniper berries (''Juniperus communis'').
Gin originated as a medicinal liquor made by monks and alchemists across Europe, particularly in southern Italy, Flanders and the Ne ...
(Ísafold), moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hor ...
schnapps (Fjallagrasa), and a birch-flavoured schnapps and liqueur
A liqueur (; ; ) is an alcoholic drink composed of spirits (often rectified spirit) and additional flavorings such as sugar, fruits, herbs, and spices. Often served with or after dessert, they are typically heavily sweetened and un-aged beyond ...
(Foss Distillery's Birkir and Björk). Martin Miller blends Icelandic water with its England-distilled gin on the island. Strong beer was banned until 1989, so ''bjórlíki'', a mixture of legal, low-alcohol pilsner beer and vodka, became popular. Several strong beers are now made by Icelandic breweries.
Sport
 Sport is an important part of Icelandic culture, as the population is generally quite active. The main traditional sport in Iceland is '' Glíma'', a form of wrestling thought to have originated in medieval times.
Sport is an important part of Icelandic culture, as the population is generally quite active. The main traditional sport in Iceland is '' Glíma'', a form of wrestling thought to have originated in medieval times.
 Popular sports include
Popular sports include football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
, track and field, handball
Handball (also known as team handball, European handball or Olympic handball) is a team sport in which two teams of seven players each (six outcourt players and a goalkeeper) pass a ball using their hands with the aim of throwing it into the g ...
and basketball. Handball is often referred to as the national sport. Wilcox and Latif, p. 110 The Icelandic national football team qualified for the 2016
File:2016 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Bombed-out buildings in Ankara following the 2016 Turkish coup d'état attempt; the impeachment trial of Brazilian President Dilma Rousseff; Damaged houses during the 2016 Nagorno-Karabakh ...
UEFA European football championship for the first time. They recorded a draw against later winners Portugal in the group stage, and defeated England 2–1 in the round of 16, with goals from Ragnar Sigurðsson and Kolbeinn Sigþórsson
Kolbeinn Sigþórsson (; born 14 March 1990) is an Icelandic professional footballer who plays as a forward. Currently a free agent, he most recently played for Allsvenskan club IFK Göteborg.
Before being signed by Ajax for a fee of €4.5&n ...
. They then lost to hosts and later finalists France in the quarter-finals. Following up on this, Iceland made its debut at the 2018 FIFA World Cup
The 2018 FIFA World Cup was the 21st FIFA World Cup, the quadrennial world championship for men's national Association football, football teams organized by FIFA. It took place in Russia from 14 June to 15 July 2018, after the country was awa ...
. For both the European and the world championships, Iceland is to date the smallest nation in terms of population to qualify.
Iceland is also the smallest country to ever qualify for Eurobasket
EuroBasket, also commonly referred to as the European Basketball Championship, is the main international basketball competition that is contested quadrennially, by the senior men's national teams that are governed by FIBA Europe, which is the E ...
, having done so in both 2015 and 2017. However, they have not managed to win a single game in the European Basketball final stages.
Iceland has excellent conditions for skiing, fishing, snowboarding
Snowboarding is a recreational and competitive activity that involves descending a snow-covered surface while standing on a snowboard that is almost always attached to a rider's feet. It features in the Winter Olympic Games and Winter Paralympi ...
, ice climbing and rock climbing
Rock climbing is a sport in which participants climb up, across, or down natural rock formations. The goal is to reach the summit of a formation or the endpoint of a usually pre-defined route without falling. Rock climbing is a physically and ...
, although mountain climbing
Mountaineering or alpinism, is a set of outdoor activities that involves ascending tall mountains. Mountaineering-related activities include traditional outdoor climbing, skiing, and traversing via ferratas. Indoor climbing, sport climbing, a ...
and hiking are preferred by the general public. Iceland is also a world-class destination for alpine ski touring and Telemark skiing, with the Troll Peninsula in Northern Iceland being the main centre of activity. Although the country's environment is generally ill-suited for golf, there are nevertheless many golf courses throughout the island, and Iceland has a greater percentage of the population playing golf than Scotland with over 17,000 registered golfers out of a population of approximately 300,000. Iceland hosts an annual international golf tournament known as the Arctic Open played through the night during the summer solstice at Akureyri Golf Club
Akureyri Golf Club is a golf course located in Akureyri, Iceland, at ''Jaðarsvöllur'', it was named "the most northerly 18-hole golf course" according to The Royal and Ancient Golf Club of St Andrews. It features a moorland course, broad ridges, ...
. Wilcox and Latif, p. 111 Iceland has also won the second most World's Strongest Man competitions of any country with nine titles, including four by both Magnús Ver Magnússon
Magnús Ver Magnússon (born 23 April 1963) is an Icelandic former powerlifter and strongman competitor. He is a four-time World's Strongest Man, having won in 1991, 1994, 1995, 1996 and is widely regarded as one of the greatest strongmen ...
and Jón Páll Sigmarsson and most recently Hafþór Júlíus Björnsson in 2018.
Iceland is also one of the leading countries in ocean rowing. Icelandic explorer and endurance athlete Fiann Paulholds the highest number of performance-based '' Guinness World Records'' within a single athletic discipline. As of 2020, he is the first and only person to achieve the Ocean Explorers Grand Slam (performing open-water crossings on each of the five oceans using human-powered vessels) and has claimed overall speed ''Guinness World Records'' for the fastest rowing of all four oceans (Atlantic, Indian, Pacific, and the Arctic) in a human-powered row boat. He had achieved a total of 41, including 33 performance based ''Guinness World Records'' by 2020.
Swimming is popular in Iceland. Geothermally heated outdoor pools are widespread, and swimming courses are a mandatory part of the national curriculum. Horseback riding, which was historically the most prevalent form of transportation on the island, remains a common pursuit for many Icelanders.
The oldest sports association in Iceland is the Reykjavík Shooting Association, founded in 1867. Rifle shooting became very popular in the 19th century with the encouragement of politicians and nationalists who were pushing for Icelandic independence. To this day, it remains a significant pastime.
Iceland has also produced many chess masters and hosted the historic World Chess Championship 1972 in Reykjavík during the height of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
. , there have been nine Icelandic chess grandmasters, a considerable number given the small size of the population. Bridge is also popular, with Iceland participating in several international tournaments. Iceland won the world bridge championship (the Bermuda Bowl) in Yokohama, Japan, in 1991 and took second place (with Sweden) in Hamilton, Bermuda, in 1950.
See also
*Index of Iceland-related articles
This page lists all articles that have been classified as being part of WikiProject Iceland. It is used in order to show 'recent changes'' pertaining to the project.
The list currently contains 4,548 articles (and their talk pages) and was last ...
* Outline of Iceland
* Greenland
* Viking
Notes
References
Bibliography
*Further reading
* Bjarnason, Egill.(2021) ''How Iceland Changed the World: The Big History of a Small Island.'' (Penguin. 2021.) * Byock, Jesse (1990) ''Medieval Iceland Society, Sagas, and Power University of California Press''. . * Heiðarsson, Jakob Oskar (2015) 'Iceland – My Small Island'. * * Jonsson, Ivar (2012) 'Explaining the Crisis of Iceland – A Realist Approach' in ''Journal of Critical Realism'', 11,1.External links
Gateway to Iceland
Government Offices of Iceland
Icelandic Government Information Center & Icelandic Embassies
Visit Iceland
nbsp;– the official Icelandic Tourist Board
Iceland
'' The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Iceland
entry at '' Encyclopædia Britannica'' *
Iceland
from BBC News * *
Incredible Iceland: Fire and Ice
nbsp;– slideshow by ''Life'' magazine
''A Photographer's View of Iceland''
Documentary produced by Prairie Public Television
Arason Steingrimur Writings on Iceland
at Dartmouth College Library {{Authority control Countries in Europe Former Danish colonies Former Norwegian colonies Island countries Islands of Iceland Northwestern European countries Members of the Nordic Council Member states of the European Free Trade Association Member states of NATO Member states of the Council of Europe Member states of the United Nations Republics States and territories established in 1944 Christian states Mid-Atlantic Ridge OECD members