Iberia (television Station) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a

 The Iberian Peninsula has always been associated with the River Ebro (Ibēros in ancient Greek and Ibērus or Hibērus in Latin). The association was so well known it was hardly necessary to state; for example, Ibēria was the country "this side of the Ibērus" in Strabo. Pliny goes so far as to assert that the Greeks had called "the whole of Spain" Hiberia because of the Hiberus River. The river appears in the Ebro Treaty of 226 BCE between Rome and Carthage, setting the limit of Carthaginian interest at the Ebro. The fullest description of the treaty, stated in Appian, uses Ibērus. With reference to this border,
The Iberian Peninsula has always been associated with the River Ebro (Ibēros in ancient Greek and Ibērus or Hibērus in Latin). The association was so well known it was hardly necessary to state; for example, Ibēria was the country "this side of the Ibērus" in Strabo. Pliny goes so far as to assert that the Greeks had called "the whole of Spain" Hiberia because of the Hiberus River. The river appears in the Ebro Treaty of 226 BCE between Rome and Carthage, setting the limit of Carthaginian interest at the Ebro. The fullest description of the treaty, stated in Appian, uses Ibērus. With reference to this border,
Basque-English dictionary means "valley" or "watered meadow", while ''ibai'' means "river", but there is no proof relating the etymology of the Ebro River with these Basque names.
 In the Chalcolithic ( 3000 BCE), a series of complex cultures developed that would give rise to the peninsula's first civilizations and to extensive exchange networks reaching to the Baltic, Middle East and North Africa. Around 2800 – 2700 BCE, the Beaker culture, which produced the ''Maritime Bell Beaker'', probably originated in the vibrant copper-using communities of the Tagus estuary in Portugal and spread from there to many parts of western Europe.
In the Chalcolithic ( 3000 BCE), a series of complex cultures developed that would give rise to the peninsula's first civilizations and to extensive exchange networks reaching to the Baltic, Middle East and North Africa. Around 2800 – 2700 BCE, the Beaker culture, which produced the ''Maritime Bell Beaker'', probably originated in the vibrant copper-using communities of the Tagus estuary in Portugal and spread from there to many parts of western Europe.

 By the Iron Age, starting in the 7th century BCE, the Iberian Peninsula consisted of complex agrarian and urban civilizations, either Pre-Celtic or Celtic (such as the
By the Iron Age, starting in the 7th century BCE, the Iberian Peninsula consisted of complex agrarian and urban civilizations, either Pre-Celtic or Celtic (such as the
 In 218 BCE, during the
In 218 BCE, during the
 In the early fifth century, Germanic peoples occupied the peninsula, namely the
In the early fifth century, Germanic peoples occupied the peninsula, namely the 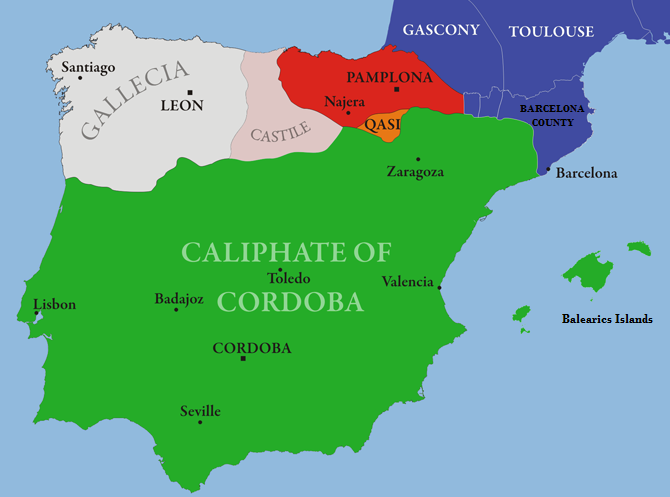 Al-Andalus became a center of culture and learning, especially during the Caliphate of Córdoba. The Caliphate reached the height of its power under the rule of
Al-Andalus became a center of culture and learning, especially during the Caliphate of Córdoba. The Caliphate reached the height of its power under the rule of  The Caliphate of Córdoba was subsumed in a period of upheaval and civil war (the Fitna of al-Andalus) and collapsed in the early 11th century, spawning a series of ephemeral statelets, the '' taifas''. Until the mid 11th century, most of the territorial expansion southwards of the Kingdom of Asturias/León was carried out through a policy of agricultural colonization rather than through military operations; then, profiting from the feebleness of the taifa principalities, Ferdinand I of León seized Lamego and Viseu (1057–1058) and Coimbra (1064) away from the Taifa of Badajoz (at times at war with the Taifa of Seville); Meanwhile, in the same year Coimbra was conquered, in the Northeastern part of the Iberian Peninsula, the Kingdom of Aragon took Barbastro from the Hudid Taifa of Lérida as part of an international expedition sanctioned by Pope Alexander II. Most critically, Alfonso VI of León-Castile conquered Toledo and its wider taifa in 1085, in what it was seen as a critical event at the time, entailing also a huge territorial expansion, advancing from the Sistema Central to La Mancha. In 1086, following the siege of Zaragoza by Alfonso VI of León-Castile, the Almoravids, religious zealots originally from the deserts of the Maghreb, landed in the Iberian Peninsula, and, having inflicted a serious defeat to Alfonso VI at the
The Caliphate of Córdoba was subsumed in a period of upheaval and civil war (the Fitna of al-Andalus) and collapsed in the early 11th century, spawning a series of ephemeral statelets, the '' taifas''. Until the mid 11th century, most of the territorial expansion southwards of the Kingdom of Asturias/León was carried out through a policy of agricultural colonization rather than through military operations; then, profiting from the feebleness of the taifa principalities, Ferdinand I of León seized Lamego and Viseu (1057–1058) and Coimbra (1064) away from the Taifa of Badajoz (at times at war with the Taifa of Seville); Meanwhile, in the same year Coimbra was conquered, in the Northeastern part of the Iberian Peninsula, the Kingdom of Aragon took Barbastro from the Hudid Taifa of Lérida as part of an international expedition sanctioned by Pope Alexander II. Most critically, Alfonso VI of León-Castile conquered Toledo and its wider taifa in 1085, in what it was seen as a critical event at the time, entailing also a huge territorial expansion, advancing from the Sistema Central to La Mancha. In 1086, following the siege of Zaragoza by Alfonso VI of León-Castile, the Almoravids, religious zealots originally from the deserts of the Maghreb, landed in the Iberian Peninsula, and, having inflicted a serious defeat to Alfonso VI at the  The 1348–1350 bubonic plague devastated large parts of the Iberian Peninsula, leading to a sudden economic cessation. Many settlements in northern Castile and Catalonia were left forsaken. The plague marked the start of the hostility and downright violence towards religious minorities (particularly the Jews) as an additional consequence in the Iberian realms.
The 14th century was a period of great upheaval in the Iberian realms. After the death of Peter the Cruel of Castile (reigned 1350–69), the
The 1348–1350 bubonic plague devastated large parts of the Iberian Peninsula, leading to a sudden economic cessation. Many settlements in northern Castile and Catalonia were left forsaken. The plague marked the start of the hostility and downright violence towards religious minorities (particularly the Jews) as an additional consequence in the Iberian realms.
The 14th century was a period of great upheaval in the Iberian realms. After the death of Peter the Cruel of Castile (reigned 1350–69), the  The last Muslim stronghold,
The last Muslim stronghold,
 Challenging the conventions about the advent of modernity, Immanuel Wallerstein pushed back the origins of the capitalist modernity to the Iberian expansion of the 15th century. During the 16th century Spain created a vast empire in the Americas, with a state monopoly in Seville becoming the center of the ensuing transatlantic trade, based on
Challenging the conventions about the advent of modernity, Immanuel Wallerstein pushed back the origins of the capitalist modernity to the Iberian expansion of the 15th century. During the 16th century Spain created a vast empire in the Americas, with a state monopoly in Seville becoming the center of the ensuing transatlantic trade, based on
 The Iberian Peninsula is the westernmost of the three major southern European peninsulas—the Iberian, Italian, and
The Iberian Peninsula is the westernmost of the three major southern European peninsulas—the Iberian, Italian, and
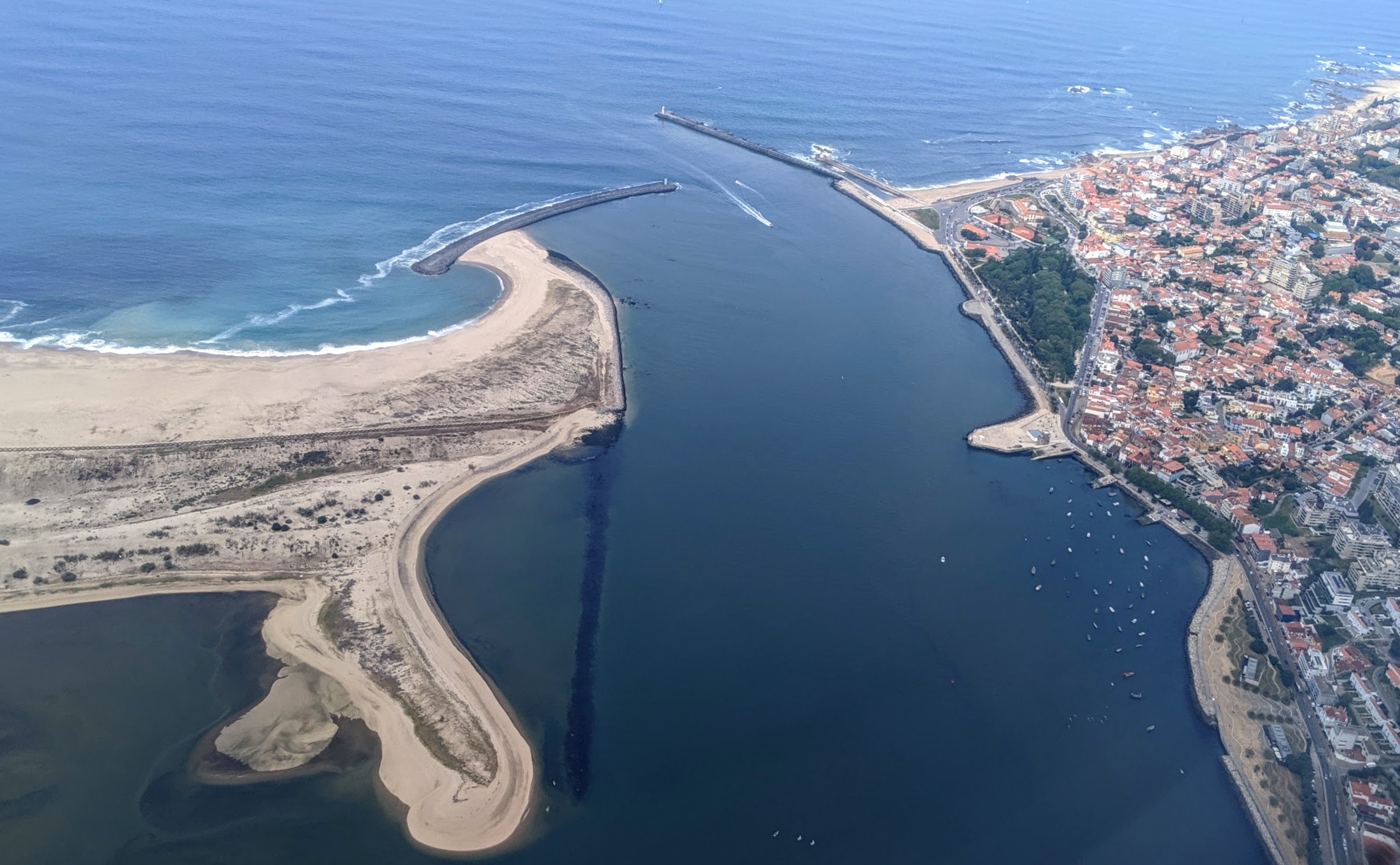 The major rivers flow through the wide valleys between the mountain systems. These are the Ebro, Douro, Tagus, Guadiana and Guadalquivir. All rivers in the Iberian Peninsula are subject to seasonal variations in flow.
The Tagus is the longest river on the peninsula and, like the Douro, flows westwards with its lower course in Portugal. The Guadiana river bends southwards and forms the border between Spain and Portugal in the last stretch of its course.
The major rivers flow through the wide valleys between the mountain systems. These are the Ebro, Douro, Tagus, Guadiana and Guadalquivir. All rivers in the Iberian Peninsula are subject to seasonal variations in flow.
The Tagus is the longest river on the peninsula and, like the Douro, flows westwards with its lower course in Portugal. The Guadiana river bends southwards and forms the border between Spain and Portugal in the last stretch of its course.
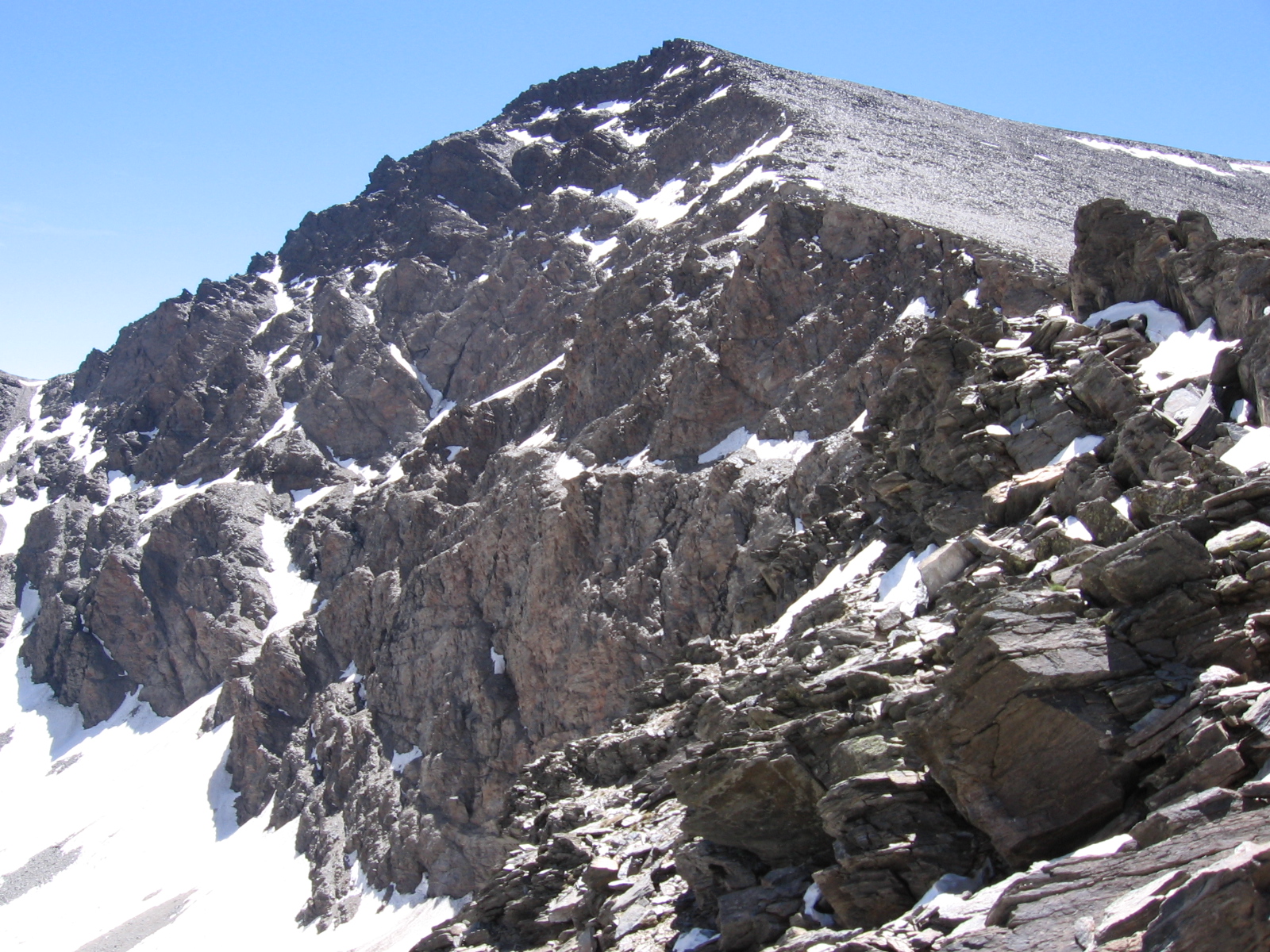 * The Cantabrian Mountains along the northern coast with the massive Picos de Europa.
* The Cantabrian Mountains along the northern coast with the massive Picos de Europa.
 The Iberian Peninsula contains rocks of every geological period from the
The Iberian Peninsula contains rocks of every geological period from the
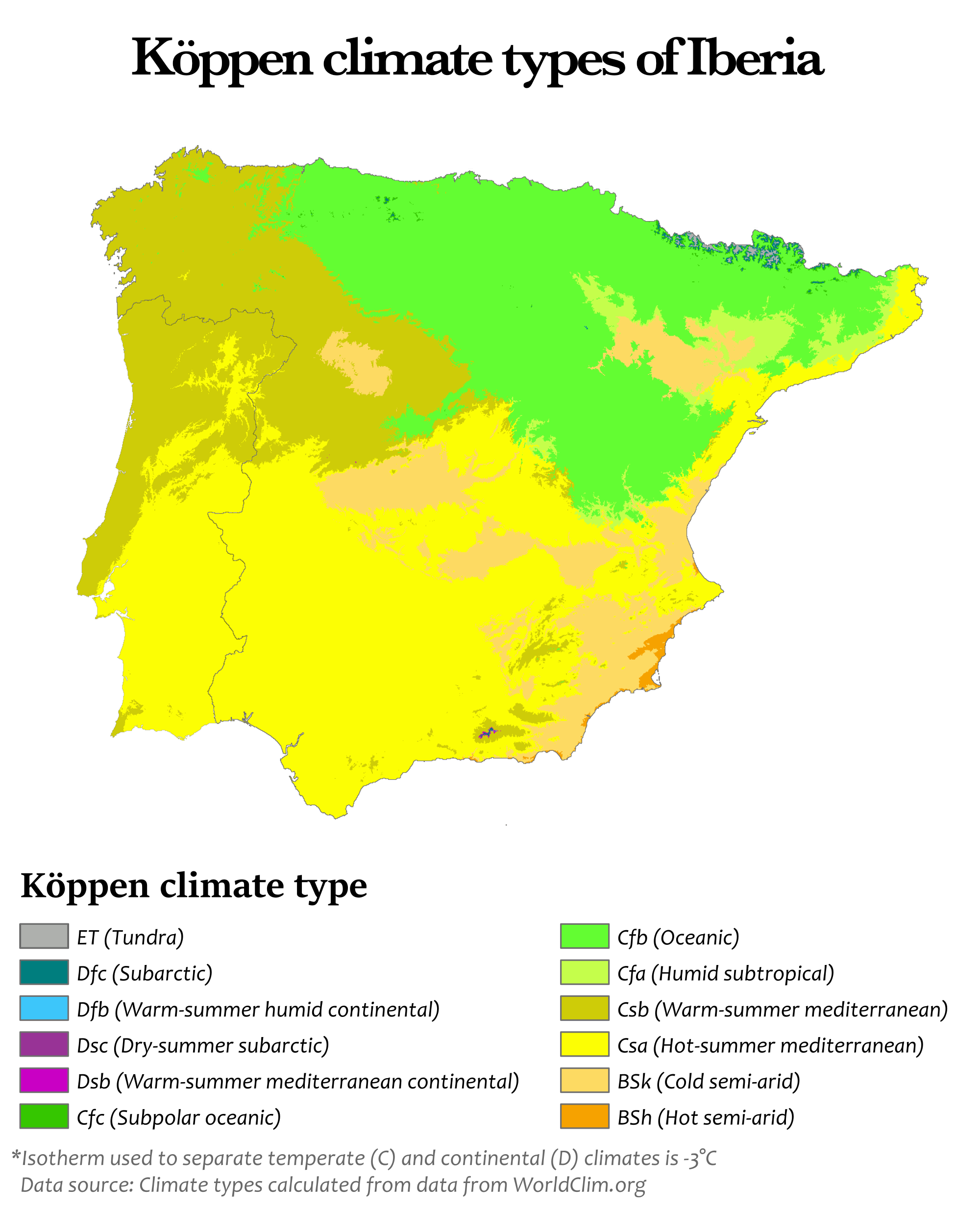 The Iberian Peninsula's location and topography, as well as the effects of large atmospheric circulation patterns induce a NW to SE gradient of yearly precipitation (roughly from 2,000 mm to 300 mm).
The Iberian peninsula has three dominant climate types. One of these is the
The Iberian Peninsula's location and topography, as well as the effects of large atmospheric circulation patterns induce a NW to SE gradient of yearly precipitation (roughly from 2,000 mm to 300 mm).
The Iberian peninsula has three dominant climate types. One of these is the
 The current political configuration of the Iberian Peninsula comprises the bulk of Spain and Portugal, the whole microstate of Andorra, a small part of the
The current political configuration of the Iberian Peninsula comprises the bulk of Spain and Portugal, the whole microstate of Andorra, a small part of the
 The woodlands of the Iberian Peninsula are distinct ecosystems. Although the various regions are each characterized by distinct vegetation, there are some similarities across the peninsula.
While the borders between these regions are not clearly defined, there is a mutual influence that makes it very hard to establish boundaries and some species find their optimal habitat in the intermediate areas.
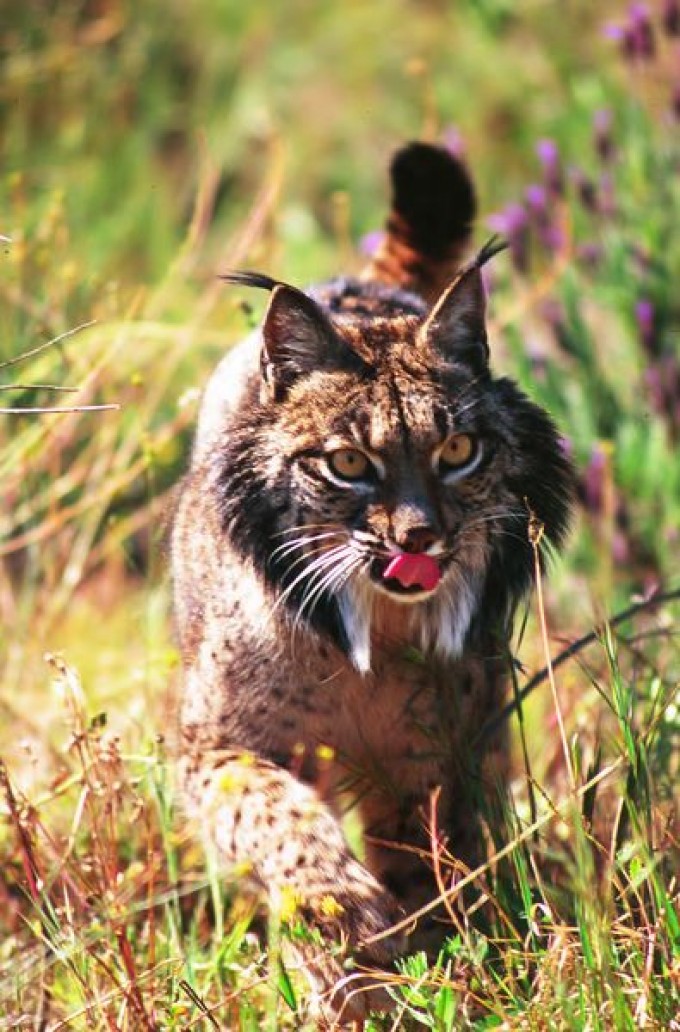
The endangered Iberian lynx (''Lynx pardinus'') is a symbol of the Iberian mediterranean forest and of the fauna of the Iberian Peninsula altogether.
A new '' Podarcis'' lizard species, ''
The woodlands of the Iberian Peninsula are distinct ecosystems. Although the various regions are each characterized by distinct vegetation, there are some similarities across the peninsula.
While the borders between these regions are not clearly defined, there is a mutual influence that makes it very hard to establish boundaries and some species find their optimal habitat in the intermediate areas.
The endangered Iberian lynx (''Lynx pardinus'') is a symbol of the Iberian mediterranean forest and of the fauna of the Iberian Peninsula altogether.
A new '' Podarcis'' lizard species, ''
peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on all ...
in southwestern Europe, defining the westernmost edge of Eurasia. It is principally divided between Spain and Portugal, comprising most of their territory, as well as a small area of Southern France
Southern France, also known as the South of France or colloquially in French language, French as , is a defined geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin,Louis Papy, ''Le midi ...
, Andorra, and Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
. With an area of approximately , and a population of roughly 53 million, it is the second largest European peninsula by area, after the Scandinavian Peninsula
The Scandinavian Peninsula ( sv, Skandinaviska halvön; no, Den skandinaviske halvøy (Bokmål) or nn, Den skandinaviske halvøya; fi, Skandinavian niemimaa) is a peninsula located in Northern Europe, which roughly comprises the mainlands ...
.
Name

Greek name
The word ''Iberia'' is a noun adapted from the Latin word "Hiberia" originating in the Ancient Greek word Ἰβηρία ('), used by Greek geographers under the rule of the Roman Empire to refer to what is known today in English as the Iberian Peninsula. At that time, the name did not describe a single geographical entity or a distinct population; the same name was used for theKingdom of Iberia
In Greco-Roman geography, Iberia (Ancient Greek: ''Iberia''; la, Hiberia) was an exonym for the Georgians, Georgian kingdom of Kartli ( ka, ქართლი), known after its Kartli, core province, which during Classical Antiquity and the E ...
, natively known as Kartli in the Caucasus, the core region of what would later become the Kingdom of Georgia. It was Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
who first reported the delineation of "Iberia" from Gaul (''Keltikē'') by the Pyrenees and included the entire land mass southwest (he says "west") from there. With the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the consolidation of romanic languages, the word "Iberia" continued the Roman word "Hiberia" and the Greek word "Ἰβηρία".
The ancient Greeks reached the Iberian Peninsula, of which they had heard from the Phoenicians, by voyaging westward on the Mediterranean. Hecataeus of Miletus
Hecataeus of Miletus (; el, Ἑκαταῖος ὁ Μιλήσιος; c. 550 BC – c. 476 BC), son of Hegesander, was an early Greek historian and geographer.
Biography
Hailing from a very wealthy family, he lived in Miletus, then under Per ...
was the first known to use the term ''Iberia'', which he wrote about circa 500 BCE. Herodotus of Halicarnassus says of the Phocaeans that "it was they who made the Greeks acquainted with ��Iberia." According to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
,Geography III.4.19. prior historians used ''Iberia'' to mean the country "this side of the Ἶβηρος" (', the Ebro) as far north as the Rhône, but in his day they set the Pyrenees as the limit. Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail.
Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed ...
respects that limit, but identifies Iberia as the Mediterranean side as far south as Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
, with the Atlantic side having no name. Elsewhere he says that Saguntum is "on the seaward foot of the range of hills connecting Iberia and Celtiberia."
Strabo refers to the Carretanians as people "of the Iberian stock" living in the Pyrenees, who are distinct from either Celts or Celtiberians
The Celtiberians were a group of Celts and Celticized peoples inhabiting an area in the central-northeastern Iberian Peninsula during the final centuries BCE. They were explicitly mentioned as being Celts by several classic authors (e.g. Strab ...
.
Roman names
According toCharles Ebel
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*k ...
, the ancient sources in both Latin and Greek use Hispania and Hiberia (Greek: Iberia) as synonyms. The confusion of the words was because of an overlapping in political and geographic perspectives. The Latin word ''Hiberia'', similar to the Greek ''Iberia'', literally translates to "land of the Hiberians". This word was derived from the river ''Hiberus'' (now called Ebro or Ebre). ''Hiber'' (Iberian) was thus used as a term for peoples living near the river Ebro. The first mention in Roman literature was by the annalist poet Ennius in 200 BCE. Virgil wrote ''impacatos (H)iberos'' ("restless Iberi") in his Georgics. The Roman geographers and other prose writers from the time of the late Roman Republic called the entire peninsula '' Hispania''.
In Greek and Roman antiquity, the name ''Hesperia'' was used for both the Italian and Iberian Peninsula; in the latter case ''Hesperia Ultima'' (referring to its position in the far west) appears as form of disambiguation from the former among Roman writers.
Also since Roman antiquity, Jews gave the name '' Sepharad'' to the peninsula.
As they became politically interested in the former Carthaginian territories, the Romans began to use the names ''Hispania Citerior'' and ''Hispania Ulterior'' for 'near' and 'far' Hispania. At the time Hispania was made up of three Roman provinces: Hispania Baetica, Hispania Tarraconensis
Hispania Tarraconensis was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. It encompassed much of the northern, eastern and central territories of modern Spain along with modern northern Portugal. Southern Spain, the region now called Andalusia was the ...
, and Hispania Lusitania
Lusitania (; ) was an ancient Iberian Roman province located where modern Portugal (south of the Douro river) and
a portion of western Spain (the present Extremadura and the province of Salamanca) lie. It was named after the Lusitani or Lusit ...
. Strabo says that the Romans use ''Hispania'' and ''Iberia'' synonymously, distinguishing between the ''near'' northern and the ''far'' southern provinces. (The name "Iberia" was ambiguous, being also the name of the Kingdom of Iberia
In Greco-Roman geography, Iberia (Ancient Greek: ''Iberia''; la, Hiberia) was an exonym for the Georgians, Georgian kingdom of Kartli ( ka, ქართლი), known after its Kartli, core province, which during Classical Antiquity and the E ...
in the Caucasus.)
Whatever languages may generally have been spoken on the peninsula soon gave way to Latin, except for that of the Vascones, which was preserved as a language isolate
Language isolates are languages that cannot be classified into larger language families. Korean and Basque are two of the most common examples. Other language isolates include Ainu in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, and Haida in North America. The num ...
by the barrier of the Pyrenees.
Modern name
The modern phrase "Iberian Peninsula" was coined by the French geographer Jean-Baptiste Bory de Saint-Vincent on his 1823 work ''"Guide du Voyageur en Espagne"''. Prior to that date, geographers had used the terms 'Spanish Peninsula' or 'Pyrenaean Peninsula'.Etymology
Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail.
Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed ...
states that the "native name" is ''Ibēr'', apparently the original word, stripped of its Greek or Latin ''-os'' or ''-us'' termination.
The early range of these natives, which geographers and historians place from the present southern Spain to the present southern France along the Mediterranean coast, is marked by instances of a readable script expressing a yet unknown language, dubbed " Iberian". Whether this was the native name or was given to them by the Greeks for their residence near the Ebro remains unknown. Credence in Polybius imposes certain limitations on etymologizing: if the language remains unknown, the meanings of the words, including Iber, must also remain unknown. In modern Basque, the word ''ibar''Morris Student PlusBasque-English dictionary means "valley" or "watered meadow", while ''ibai'' means "river", but there is no proof relating the etymology of the Ebro River with these Basque names.
Prehistory
Palaeolithic
The Iberian Peninsula has been inhabited by members of the '' Homo'' genus for at least 1.2 million years as remains found in the sites in the Atapuerca Mountains demonstrate. Among these sites is the cave of Gran Dolina, where six hominin skeletons, dated between 780,000 and one million years ago, were found in 1994. Experts have debated whether these skeletons belong to the species ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor' ...
'', '' Homo heidelbergensis'', or a new species called '' Homo antecessor''.
Around 200,000 BP, during the Lower Paleolithic
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears in ...
period, Neanderthals first entered the Iberian Peninsula. Around 70,000 BP, during the Middle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Paleoli ...
period, the last glacial event began and the Neanderthal Mousterian culture was established. Around 37,000 BP, during the Upper Paleolithic, the Neanderthal Châtelperronian cultural period began. Emanating from Southern France
Southern France, also known as the South of France or colloquially in French language, French as , is a defined geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin,Louis Papy, ''Le midi ...
, this culture extended into the north of the peninsula. It continued to exist until around 30,000 BP, when Neanderthal man faced extinction.
About 40,000 years ago, anatomically modern humans entered the Iberian Peninsula from Southern France
Southern France, also known as the South of France or colloquially in French language, French as , is a defined geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin,Louis Papy, ''Le midi ...
. Haplogroup R1b
Haplogroup R1b (R-M343), previously known as Hg1 and Eu18, is a human Y-chromosome haplogroup.
It is the most frequently occurring paternal lineage in Western Europe, as well as some parts of Russia (e.g. the Bashkirs) and pockets of Central A ...
is common in modern Portuguese and Spanish males. On the Iberian Peninsula, modern humans developed a series of different cultures, such as the Aurignacian
The Aurignacian () is an archaeological industry of the Upper Paleolithic
associated with European early modern humans (EEMH) lasting from 43,000 to 26,000 years ago. The Upper Paleolithic developed in Europe some time after the Levant, where t ...
, Gravettian, Solutrean and Magdalenian
The Magdalenian cultures (also Madelenian; French: ''Magdalénien'') are later cultures of the Upper Paleolithic and Mesolithic in western Europe. They date from around 17,000 to 12,000 years ago. It is named after the type site of La Madele ...
cultures, some of them characterized by the complex forms of the art of the Upper Paleolithic.
Neolithic
During the Neolithic expansion, variousmegalithic
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The ...
cultures developed in the Iberian Peninsula. An open seas navigation culture from the east Mediterranean, called the Cardium culture, also extended its influence to the eastern coasts of the peninsula, possibly as early as the 5th millennium BCE. These people may have had some relation to the subsequent development of the Iberian civilization.
As is the case for most of the rest of Southern Europe, the principal ancestral origin of modern Iberians are Early European Farmers who arrived during the Neolithic. The large predominance of Y-Chromosome Haplogroup R1b, common throughout Western Europe, is testimony to a considerable input from various waves of (predominantly male) Western Steppe Herders from the Pontic–Caspian steppe during the Bronze Age. Iberia experienced a significant genetic turnover, with 100% of the paternal ancestry and 40% of the overall ancestry being replaced by peoples with steppe-related ancestry.
Chalcolithic
 In the Chalcolithic ( 3000 BCE), a series of complex cultures developed that would give rise to the peninsula's first civilizations and to extensive exchange networks reaching to the Baltic, Middle East and North Africa. Around 2800 – 2700 BCE, the Beaker culture, which produced the ''Maritime Bell Beaker'', probably originated in the vibrant copper-using communities of the Tagus estuary in Portugal and spread from there to many parts of western Europe.
In the Chalcolithic ( 3000 BCE), a series of complex cultures developed that would give rise to the peninsula's first civilizations and to extensive exchange networks reaching to the Baltic, Middle East and North Africa. Around 2800 – 2700 BCE, the Beaker culture, which produced the ''Maritime Bell Beaker'', probably originated in the vibrant copper-using communities of the Tagus estuary in Portugal and spread from there to many parts of western Europe.
Bronze Age
Bronze Age cultures developed beginning 1800 BCE, when the culture of Los Millares was followed by that of El Argar. During the Early Bronze Age, southeastern Iberia saw the emergence of important settlements, a development that has compelled some archeologists to propose that these settlements indicate the advent of state-level social structures. From this centre, bronze metalworking technology spread to other cultures like the Bronze of Levante,South-Western Iberian Bronze
The South-Western Iberian Bronze is a loosely defined Bronze Age culture of Southern Portugal and nearby areas of SW Spain (Huelva (province), Huelva, Sevilla (province), Seville, Extremadura). It replaced the earlier urban and European Megalithic ...
and Las Cogotas.
In the Late Bronze Age, the urban civilisation of Tartessos developed in Southwestern Iberia, characterized by Phoenician influence and using the Southwest Paleohispanic script for its Tartessian language, not related to the Iberian language
The Iberian language was the language of an indigenous western European people identified by Greek and Roman sources who lived in the eastern and southeastern regions of the Iberian Peninsula in the pre-Migration Era (before about 375 AD). The a ...
.
Early in the first millennium BCE, several waves of Pre-Celts and Celts migrated from Central Europe, thus partially changing the peninsula's ethnic landscape to Indo-European-speaking in its northern and western regions. In Northwestern Iberia (modern Northern Portugal, Asturias and Galicia), a Celtic culture developed, the Castro culture, with a large number of hill forts and some fortified cities.
Proto-history
 By the Iron Age, starting in the 7th century BCE, the Iberian Peninsula consisted of complex agrarian and urban civilizations, either Pre-Celtic or Celtic (such as the
By the Iron Age, starting in the 7th century BCE, the Iberian Peninsula consisted of complex agrarian and urban civilizations, either Pre-Celtic or Celtic (such as the Celtiberians
The Celtiberians were a group of Celts and Celticized peoples inhabiting an area in the central-northeastern Iberian Peninsula during the final centuries BCE. They were explicitly mentioned as being Celts by several classic authors (e.g. Strab ...
, Gallaeci, Astures, Celtici, Lusitanians and others), the cultures of the Iberians in the eastern and southern zones and the cultures of the Aquitanian in the western portion of the Pyrenees.
As early as the 12th century BCE, the Phoenicians, a thalassocratic civilization originally from the Eastern Mediterranean, began to explore the coastline of the peninsula, interacting with the metal-rich communities in the southwest of the peninsula (contemporarily known as the semi-mythical Tartessos). Around 1100 BCE, Phoenician merchants founded the trading colony of Gadir or Gades (modern day Cádiz). Phoenicians established a permanent trading port in the Gadir colony circa 800 BCE in response to the increasing demand of silver from the Assyrian Empire.
The seafaring Phoenicians, Greeks and Carthaginians successively settled along the Mediterranean coast and founded trading colonies there over a period of several centuries. In the 8th century BCE, the first Greek colonies, such as Emporion (modern Empúries), were founded along the Mediterranean coast on the east, leaving the south coast to the Phoenicians.
Together with the presence of Phoenician and Greek epigraphy, a number of paleohispanic scripts developed in the Iberian Peninsula along the 1st millennium BCE. The development of a primordial paleohispanic script antecessor to the rest of paleohispanic scripts (originally supposed to be a non-redundant semi-syllabary
A semi-syllabary is a writing system that behaves partly as an alphabet and partly as a syllabary. The main group of semi-syllabic writing are the Paleohispanic scripts of ancient Spain, a group of semi-syllabaries that transform redundant plosive ...
) derived from the Phoenician alphabet and originated in Southwestern Iberia by the 7th century BCE has been tentatively proposed.
In the sixth century BCE, the Carthaginians arrived in the peninsula while struggling with the Greeks for control of the Western Mediterranean. Their most important colony was Carthago Nova (modern-day Cartagena, Spain
Cartagena () is a Spanish city and a major naval station on the Mediterranean coast, south-eastern Iberia. As of January 2018, it has a population of 218,943 inhabitants, being the region's second-largest municipality and the country's sixth-lar ...
).
History
Roman rule
Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Ital ...
against the Carthaginians, the first Roman troops occupied the Iberian Peninsula; however, it was not until the reign of Augustus that it was annexed after 200 years of war with the Celts and Iberians. The result was the creation of the province of Hispania. It was divided into Hispania Ulterior and Hispania Citerior
Hispania Citerior (English: "Hither Iberia", or "Nearer Iberia") was a Roman province in Hispania during the Roman Republic. It was on the eastern coast of Iberia down to the town of Cartago Nova, today's Cartagena in the autonomous community of ...
during the late Roman Republic, and during the Roman Empire, it was divided into Hispania Tarraconensis
Hispania Tarraconensis was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. It encompassed much of the northern, eastern and central territories of modern Spain along with modern northern Portugal. Southern Spain, the region now called Andalusia was the ...
in the northeast, Hispania Baetica in the south and Lusitania
Lusitania (; ) was an ancient Iberian Roman province located where modern Portugal (south of the Douro river) and
a portion of western Spain (the present Extremadura and the province of Salamanca) lie. It was named after the Lusitani or Lusita ...
in the southwest.
Hispania supplied the Roman Empire with silver, food, olive oil, wine, and metal. The emperors Trajan, Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania B ...
, Marcus Aurelius, and Theodosius I, the philosopher Seneca the Younger, and the poets Martial
Marcus Valerius Martialis (known in English as Martial ; March, between 38 and 41 AD – between 102 and 104 AD) was a Roman poet from Hispania (modern Spain) best known for his twelve books of ''Epigrams'', published in Rome between AD 86 and ...
and Lucan
Marcus Annaeus Lucanus (3 November 39 AD – 30 April 65 AD), better known in English as Lucan (), was a Roman poet, born in Corduba (modern-day Córdoba), in Hispania Baetica. He is regarded as one of the outstanding figures of the Imperial ...
were born from families living on the Iberian Peninsula.
During their 600-year occupation of the Iberian Peninsula, the Romans introduced the Latin language that influenced many of the languages that exist today in the Iberian peninsula.
Pre-modern Iberia
Suebi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own names ...
, the Vandals ( Silingi and Hasdingi) and their allies, the Alans. Only the kingdom of the Suebi (Quadi
The Quadi were a Germanic
*
*
*
people who lived approximately in the area of modern Moravia in the time of the Roman Empire. The only surviving contemporary reports about the Germanic tribe are those of the Romans, whose empire had its bord ...
and Marcomanni) would endure after the arrival of another wave of Germanic invaders, the Visigoths, who occupied all of the Iberian Peninsula and expelled or partially integrated the Vandals and the Alans. The Visigoths eventually occupied the Suebi kingdom and its capital city, Bracara (modern day Braga), in 584–585. They would also occupy the province of the Byzantine Empire (552–624) of Spania in the south of the peninsula. However, Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands ( es, Islas Baleares ; or ca, Illes Balears ) are an archipelago in the Balearic Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago is an autonomous community and a province of Spain; its capital is ...
remained in Byzantine hands until Umayyad conquest in 707.
In 711, a Muslim army conquered the Visigothic Kingdom in Hispania. Under Tariq ibn Ziyad, the Islamic army landed at Gibraltar and, in an eight-year campaign, occupied all except the northern kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula in the Umayyad conquest of Hispania. Al-Andalus ( ar, الإندلس, tr. ''al-ʾAndalūs'', possibly "Land of the Vandals"), is the Arabic name given to Muslim Iberia. The Muslim conquerors were Arabs and Berbers
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg
, caption = The Berber ethnic flag
, population = 36 million
, region1 = Morocco
, pop1 = 14 million to 18 million
, region2 = Algeria
, pop2 ...
; following the conquest, conversion and arabization of the Hispano-Roman population took place, (''muwalladum'' or '' Muladí''). After a long process, spurred on in the 9th and 10th centuries, the majority of the population in Al-Andalus eventually converted to Islam. The Muslims were referred to by the generic name '' Moors''. The Muslim population was divided per ethnicity (Arabs, Berbers, Muladí), and the supremacy of Arabs over the rest of group was a recurrent causal for strife, rivalry and hatred, particularly between Arabs and Berbers. Arab elites could be further divided in the Yemenites (first wave) and the Syrians (second wave). Christians and Jews were allowed to live as part of a stratified society under the ''dhimmah'' system, although Jews became very important in certain fields. Some Christians migrated to the Northern Christian kingdoms, while those who stayed in Al-Andalus progressively arabised and became known as ''musta'arab'' (mozarab
The Mozarabs ( es, mozárabes ; pt, moçárabes ; ca, mossàrabs ; from ar, مستعرب, musta‘rab, lit=Arabized) is a modern historical term for the Iberian Christians, including Christianized Iberian Jews, who lived under Muslim rule in A ...
s). The slave population comprised the ''Ṣaqāliba
Saqaliba ( ar, صقالبة, ṣaqāliba, singular ar, صقلبي, ṣaqlabī) is a term used in medieval Arabic sources to refer to Slavs and other peoples of Central, Southern, and Eastern Europe, or in a broad sense to European slaves. The te ...
'' (literally meaning "slavs", although they were slaves of generic European origin) as well as Sudanese
Sudanese or Sudanic may refer to:
*pertaining to the country of Sudan
**the people of Sudan, see Demographics of Sudan
*pertaining to Sudan (region)
**Sudanic languages
**Sudanic race, subtype of the Africoid racial category
See also
*Sudanese Civ ...
slaves.
The Umayyad rulers faced a major Berber Revolt in the early 740s; the uprising originally broke out in North Africa (Tangier) and later spread across the peninsula. Following the Abbasid takeover from the Umayyads and the shift of the economic centre of the Islamic Caliphate from Damascus to Baghdad, the western province of al-Andalus was marginalised and ultimately became politically autonomous as independent emirate in 756, ruled by one of the last surviving Umayyad royals, Abd al-Rahman I.
 Al-Andalus became a center of culture and learning, especially during the Caliphate of Córdoba. The Caliphate reached the height of its power under the rule of
Al-Andalus became a center of culture and learning, especially during the Caliphate of Córdoba. The Caliphate reached the height of its power under the rule of Abd-ar-Rahman III
ʿAbd al-Rahmān ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd al-Raḥmān ibn al-Ḥakam al-Rabdī ibn Hishām ibn ʿAbd al-Raḥmān al-Dākhil () or ʿAbd al-Rahmān III (890 - 961), was the Umayyad Emir of Córdoba from 912 to 92 ...
and his successor al-Hakam II, becoming then, in the view of Jaime Vicens Vives, "the most powerful state in Europe". Abd-ar-Rahman III also managed to expand the clout of Al-Andalus across the Strait of Gibraltar, waging war, as well as his successor, against the Fatimid Empire
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dyna ...
.
Between the 8th and 12th centuries, Al-Andalus enjoyed a notable urban vitality, both in terms of the growth of the preexisting cities as well as in terms of founding of new ones: Córdoba reached a population of 100,000 by the 10th century, Toledo
Toledo most commonly refers to:
* Toledo, Spain, a city in Spain
* Province of Toledo, Spain
* Toledo, Ohio, a city in the United States
Toledo may also refer to:
Places Belize
* Toledo District
* Toledo Settlement
Bolivia
* Toledo, Orur ...
30,000 by the 11th century and Seville 80,000 by the 12th century.
During the Middle Ages, the North of the peninsula housed many small Christian polities including the Kingdom of Castile, the Kingdom of Aragon
The Kingdom of Aragon ( an, Reino d'Aragón, ca, Regne d'Aragó, la, Regnum Aragoniae, es, Reino de Aragón) was a medieval and early modern kingdom on the Iberian Peninsula, corresponding to the modern-day autonomous community of Aragon, ...
, the Kingdom of Navarre
The Kingdom of Navarre (; , , , ), originally the Kingdom of Pamplona (), was a Basque kingdom that occupied lands on both sides of the western Pyrenees, alongside the Atlantic Ocean between present-day Spain and France.
The medieval state took ...
, the Kingdom of León
The Kingdom of León; es, Reino de León; gl, Reino de León; pt, Reino de Leão; la, Regnum Legionense; mwl, Reino de Lhion was an independent kingdom situated in the northwest region of the Iberian Peninsula. It was founded in 910 when t ...
or the Kingdom of Portugal
The Kingdom of Portugal ( la, Regnum Portugalliae, pt, Reino de Portugal) was a monarchy in the western Iberian Peninsula and the predecessor of the modern Portuguese Republic. Existing to various extents between 1139 and 1910, it was also kno ...
, as well as a number of counties that spawned from the Carolingian Marca Hispanica
The Hispanic March or Spanish March ( es, Marca Hispánica, ca, Marca Hispànica, Aragonese and oc, Marca Hispanica, eu, Hispaniako Marka, french: Marche d'Espagne), was a military buffer zone beyond the former province of Septimania, esta ...
. Christian and Muslim polities fought and allied among themselves in variable alliances. The Christian kingdoms progressively expanded south taking over Muslim territory in what is historiographically known as the " Reconquista" (the latter concept has been however noted as product of the claim to a pre-existing Spanish Catholic nation and it would not necessarily convey adequately "the complexity of centuries of warring and other more peaceable interactions between Muslim and Christian kingdoms in medieval Iberia between 711 and 1492").
 The Caliphate of Córdoba was subsumed in a period of upheaval and civil war (the Fitna of al-Andalus) and collapsed in the early 11th century, spawning a series of ephemeral statelets, the '' taifas''. Until the mid 11th century, most of the territorial expansion southwards of the Kingdom of Asturias/León was carried out through a policy of agricultural colonization rather than through military operations; then, profiting from the feebleness of the taifa principalities, Ferdinand I of León seized Lamego and Viseu (1057–1058) and Coimbra (1064) away from the Taifa of Badajoz (at times at war with the Taifa of Seville); Meanwhile, in the same year Coimbra was conquered, in the Northeastern part of the Iberian Peninsula, the Kingdom of Aragon took Barbastro from the Hudid Taifa of Lérida as part of an international expedition sanctioned by Pope Alexander II. Most critically, Alfonso VI of León-Castile conquered Toledo and its wider taifa in 1085, in what it was seen as a critical event at the time, entailing also a huge territorial expansion, advancing from the Sistema Central to La Mancha. In 1086, following the siege of Zaragoza by Alfonso VI of León-Castile, the Almoravids, religious zealots originally from the deserts of the Maghreb, landed in the Iberian Peninsula, and, having inflicted a serious defeat to Alfonso VI at the
The Caliphate of Córdoba was subsumed in a period of upheaval and civil war (the Fitna of al-Andalus) and collapsed in the early 11th century, spawning a series of ephemeral statelets, the '' taifas''. Until the mid 11th century, most of the territorial expansion southwards of the Kingdom of Asturias/León was carried out through a policy of agricultural colonization rather than through military operations; then, profiting from the feebleness of the taifa principalities, Ferdinand I of León seized Lamego and Viseu (1057–1058) and Coimbra (1064) away from the Taifa of Badajoz (at times at war with the Taifa of Seville); Meanwhile, in the same year Coimbra was conquered, in the Northeastern part of the Iberian Peninsula, the Kingdom of Aragon took Barbastro from the Hudid Taifa of Lérida as part of an international expedition sanctioned by Pope Alexander II. Most critically, Alfonso VI of León-Castile conquered Toledo and its wider taifa in 1085, in what it was seen as a critical event at the time, entailing also a huge territorial expansion, advancing from the Sistema Central to La Mancha. In 1086, following the siege of Zaragoza by Alfonso VI of León-Castile, the Almoravids, religious zealots originally from the deserts of the Maghreb, landed in the Iberian Peninsula, and, having inflicted a serious defeat to Alfonso VI at the battle of Zalaca
The Battle of Sagrajas (23 October 1086), also called Zalaca or Zallaqa ( ar, معركة الزلاقة, translit=Maʿrakat az-Zallāqa), was a battle between the Almoravid army led by their King Yusuf ibn Tashfin and an army led by the Ca ...
, began to seize control of the remaining taifas.
The Almoravids in the Iberian peninsula progressively relaxed strict observance of their faith, and treated both Jews and Mozarabs harshly, facing uprisings across the peninsula, initially in the Western part. The Almohads, another North-African Muslim sect of Masmuda Berber origin who had previously undermined the Almoravid rule south of the Strait of Gibraltar, first entered the peninsula in 1146.
Somewhat straying from the trend taking place in other locations of the Latin West since the 10th century, the period comprising the 11th and 13th centuries was not one of weakening monarchical power in the Christian kingdoms. The relatively novel concept of "frontier" (Sp: ''frontera''), already reported in Aragon by the second half of the 11th century become widespread in the Christian Iberian kingdoms by the beginning of the 13th century, in relation to the more or less conflictual border with Muslim lands.
By the beginning of the 13th century, a power reorientation took place in the Iberian Peninsula (parallel to the Christian expansion in Southern Iberia and the increasing commercial impetus of Christian powers across the Mediterranean) and to a large extent, trade-wise, the Iberian Peninsula reorientated towards the North away from the Muslim World.
During the Middle Ages, the monarchs of Castile and León, from Alfonso V and Alfonso VI
Alphons (Latinized ''Alphonsus'', ''Adelphonsus'', or ''Adefonsus'') is a male given name recorded from the 8th century (Alfonso I of Asturias, r. 739–757) in the Christian successor states of the Visigothic kingdom in the Iberian peninsula. ...
(crowned ''Hispaniae Imperator'') to Alfonso X and Alfonso XI tended to embrace an imperial ideal based on a dual Christian and Jewish ideology.
Merchants from Genoa and Pisa were conducting an intense trading activity in Catalonia already by the 12th century, and later in Portugal. Since the 13th century, the Crown of Aragon expanded overseas; led by Catalans, it attained an overseas empire in the Western Mediterranean, with a presence in Mediterranean islands such as the Balearics, Sicily and Sardinia, and even conquering Naples in the mid-15th century. Genoese merchants invested heavily in the Iberian commercial enterprise with Lisbon becoming, according to Virgínia Rau
Virgínia de Bivar Robertes Rau (4/9 December 1907 – 2 November 1973) was a Portuguese archaeologist and historian. She was an expert on Portuguese and Portuguese colonial history and author of many history books.
She was the daughter of Luís R ...
, the "great centre of Genoese trade" in the early 14th century. The Portuguese would later detach their trade to some extent from Genoese
Genoese may refer to:
* a person from Genoa
* Genoese dialect, a dialect of the Ligurian language
* Republic of Genoa (–1805), a former state in Liguria
See also
* Genovese, a surname
* Genovesi, a surname
*
*
*
*
* Genova (disambiguati ...
influence. The Nasrid Kingdom of Granada
)
, common_languages = Official language:Classical ArabicOther languages: Andalusi Arabic, Mozarabic, Berber, Ladino
, capital = Granada
, religion = Majority religion:Sunni IslamMinority religions:Roman C ...
, neighbouring the Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar ( ar, مضيق جبل طارق, Maḍīq Jabal Ṭāriq; es, Estrecho de Gibraltar, Archaic: Pillars of Hercules), also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Medi ...
and founded upon a vassalage relationship with the Crown of Castile, also insinuated itself into the European mercantile network, with its ports fostering intense trading relations with the Genoese as well, but also with the Catalans, and to a lesser extent, with the Venetians, the Florentines, and the Portuguese.
Between 1275 and 1340, Granada became involved in the "crisis of the Strait", and was caught in a complex geopolitical struggle ("a kaleidoscope of alliances") with multiple powers vying for dominance of the Western Mediterranean, complicated by the unstable relations of Muslim Granada with the Marinid Sultanate. The conflict reached a climax in the 1340 Battle of Río Salado, when, this time in alliance with Granada, the Marinid Sultan (and Caliph pretender) Abu al-Hasan Ali ibn Othman made the last Marinid attempt to set up a power base in the Iberian Peninsula. The lasting consequences of the resounding Muslim defeat to an alliance of Castile and Portugal with naval support from Aragon and Genoa ensured Christian supremacy over the Iberian Peninsula and the preeminence of Christian fleets in the Western Mediterranean.
 The 1348–1350 bubonic plague devastated large parts of the Iberian Peninsula, leading to a sudden economic cessation. Many settlements in northern Castile and Catalonia were left forsaken. The plague marked the start of the hostility and downright violence towards religious minorities (particularly the Jews) as an additional consequence in the Iberian realms.
The 14th century was a period of great upheaval in the Iberian realms. After the death of Peter the Cruel of Castile (reigned 1350–69), the
The 1348–1350 bubonic plague devastated large parts of the Iberian Peninsula, leading to a sudden economic cessation. Many settlements in northern Castile and Catalonia were left forsaken. The plague marked the start of the hostility and downright violence towards religious minorities (particularly the Jews) as an additional consequence in the Iberian realms.
The 14th century was a period of great upheaval in the Iberian realms. After the death of Peter the Cruel of Castile (reigned 1350–69), the House of Trastámara
The House of Trastámara (Spanish, Aragonese and Catalan: Casa de Trastámara) was a royal dynasty which first ruled in the Crown of Castile and then expanded to the Crown of Aragon in the late middle ages to the early modern period.
They were a ...
succeeded to the throne in the person of Peter's half brother, Henry II (reigned 1369–79). In the kingdom of Aragón, following the death without heirs of John I John I may refer to:
People
* John I (bishop of Jerusalem)
* John Chrysostom (349 – c. 407), Patriarch of Constantinople
* John of Antioch (died 441)
* Pope John I, Pope from 523 to 526
* John I (exarch) (died 615), Exarch of Ravenna
* John I o ...
(reigned 1387–96) and Martin I Martin I may refer to:
* Pope Martin I (c. 590/600–655), bishop of Rome 649–655
* Martin I (bishop of Oviedo) (died 1101)
* Martin I (archbishop of Gniezno) (died after 1112)
* Martin I of Aragon (1356–1410)
* Martin I of Sicily (1374/6–14 ...
(reigned 1396–1410), a prince of the House of Trastámara, Ferdinand I Ferdinand I or Fernando I may refer to:
People
* Ferdinand I of León, ''the Great'' (ca. 1000–1065, king from 1037)
* Ferdinand I of Portugal and the Algarve, ''the Handsome'' (1345–1383, king from 1367)
* Ferdinand I of Aragon and Sicily, '' ...
(reigned 1412–16), succeeded to the Aragonese throne. The Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
also spilled over into the Iberian peninsula, with Castile particularly taking a role in the conflict by providing key naval support to France that helped lead to that nation's eventual victory. After the accession of Henry III to the throne of Castile, the populace, exasperated by the preponderance of Jewish influence, perpetrated a massacre of Jews at Toledo. In 1391, mobs went from town to town throughout Castile and Aragon, killing an estimated 50,000 Jews, or even as many as 100,000, according to Jane Gerber
Jane S. Gerber (born 1938) is a professor of Jewish history and director of the Institute for Sephardic Studies at the City University of New York.
Life and education
Gerber, née Jane Satlow was born in 1938 to Israeli mother Elise Kliegman an ...
. Women and children were sold as slaves to Muslims, and many synagogues were converted into churches. According to Hasdai Crescas, about 70 Jewish communities were destroyed.
During the 15th century, Portugal, which had ended its southwards territorial expansion across the Iberian Peninsula in 1249 with the conquest of the Algarve, initiated an overseas expansion in parallel to the rise of the House of Aviz
The House of Aviz (Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''Casa de Avis''), also known as the Joanine Dynasty (''Dinastia Joanina''), was a dynasty of Portuguese people, Portuguese origin which flourished during the Portuguese Renaissance, Renaissance ...
, conquering Ceuta (1415) arriving at Porto Santo
Porto Santo Island () is a Portuguese island northeast of Madeira Island in the North Atlantic Ocean; it is the northernmost and easternmost island of the archipelago of Madeira, located in the Atlantic Ocean west of Europe and Africa.
The muni ...
(1418), Madeira
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
and the Azores, as well as establishing additional outposts along the North-African Atlantic coast. In addition, already in the Early Modern Period, between the completion of the Granada War in 1492 and the death of Ferdinand of Aragon in 1516, the Hispanic Monarchy would make strides in the imperial expansion along the Mediterranean coast of the Maghreb.
During the Late Middle Ages, the Jews acquired considerable power and influence in Castile and Aragon.
Throughout the late Middle Ages, the Crown of Aragon took part in the mediterranean slave trade, with Barcelona (already in the 14th century), Valencia (particularly in the 15th century) and, to a lesser extent, Palma de Mallorca
Palma (; ; also known as ''Palma de Mallorca'', officially between 1983–88, 2006–08, and 2012–16) is the capital and largest city of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of the Balearic Islands in Spain. It is situate ...
(since the 13th century), becoming dynamic centres in this regard, involving chiefly eastern and Muslim peoples. Castile engaged later in this economic activity, rather by adhering to the incipient atlantic slave trade involving sub-saharan people thrusted by Portugal (Lisbon being the largest slave centre in Western Europe) since the mid 15th century, with Seville becoming another key hub for the slave trade. Following the advance in the conquest of the Nasrid kingdom of Granada, the seizure of Málaga
Málaga (, ) is a municipality of Spain, capital of the Province of Málaga, in the autonomous community of Andalusia. With a population of 578,460 in 2020, it is the second-most populous city in Andalusia after Seville and the sixth most pop ...
entailed the addition of another notable slave centre for the Crown of Castile.
By the end of the 15th century (1490) the Iberian kingdoms (including here the Balearic Islands) had an estimated population of 6.525 million (Crown of Castile, 4.3 million; Portugal, 1.0 million; Principality of Catalonia, 0.3 million; Kingdom of Valencia, 0.255 million; Kingdom of Granada, 0.25 million; Kingdom of Aragon, 0.25 million; Kingdom of Navarre, 0.12 million and the Kingdom of Mallorca, 0.05 million).
For three decades in the 15th century, the ''Hermandad de las Marismas'', the trading association formed by the ports of Castile along the Cantabrian coast, resembling in some ways the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German to ...
, fought against the latter, an ally of England, a rival of Castile in political and economic terms. Castile sought to claim the Gulf of Biscay
The Bay of Biscay (), known in Spain as the Gulf of Biscay ( es, Golfo de Vizcaya, eu, Bizkaiko Golkoa), and in France and some border regions as the Gulf of Gascony (french: Golfe de Gascogne, oc, Golf de Gasconha, br, Pleg-mor Gwaskogn), ...
as its own. In 1419, the powerful Castilian navy thoroughly defeated a Hanseatic fleet in La Rochelle.
In the late 15th century, the imperial ambition of the Iberian powers was pushed to new heights by the Catholic Monarchs in Castile and Aragon, and by Manuel I in Portugal.
Granada
Granada (,, DIN 31635, DIN: ; grc, Ἐλιβύργη, Elibýrgē; la, Illiberis or . ) is the capital city of the province of Granada, in the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the fo ...
, was conquered by a combined Castilian and Aragonese force in 1492. As many as 100,000 Moors died or were enslaved in the military campaign, while 200,000 fled to North Africa. Muslims and Jews throughout the period were variously tolerated or shown intolerance in different Christian kingdoms. After the fall of Granada, all Muslims and Jews were ordered to convert to Christianity or face expulsion—as many as 200,000 Jews were expelled from Spain. Historian Henry Kamen estimates that some 25,000 Jews died en route from Spain. The Jews were also expelled from Sicily and Sardinia, which were under Aragonese rule, and an estimated 37,000 to 100,000 Jews left.
In 1497, King Manuel I of Portugal forced all Jews in his kingdom to convert or leave. That same year he expelled all Muslims that were not slaves, and in 1502 the Catholic Monarchs followed suit, imposing the choice of conversion to Christianity
Conversion to Christianity is the religious conversion of a previously non-Christian person to Christianity. Different Christian denominations may perform various different kinds of rituals or ceremonies initiation into their community of believ ...
or exile and loss of property. Many Jews and Muslims fled to North Africa and the Ottoman Empire, while others publicly converted to Christianity and became known respectively as Marrano
Marranos were Spanish and Portuguese Jews living in the Iberian Peninsula who converted or were Forced conversion#Spanish Inquisition, forced to convert to Christianity during the Middle Ages, but continued to Crypto-Judaism, practice Judaism i ...
s and Moriscos (after the old term ''Moors''). However, many of these continued to practice their religion in secret. The Moriscos revolted several times and were ultimately forcibly expelled from Spain in the early 17th century. From 1609 to 1614, over 300,000 Moriscos were sent on ships to North Africa and other locations, and, of this figure, around 50,000 died resisting the expulsion, and 60,000 died on the journey.
The change of relative supremacy from Portugal to the Hispanic Monarchy in the late 15th century has been described as one of the few cases of avoidance of the Thucydides Trap.
Modern Iberia
 Challenging the conventions about the advent of modernity, Immanuel Wallerstein pushed back the origins of the capitalist modernity to the Iberian expansion of the 15th century. During the 16th century Spain created a vast empire in the Americas, with a state monopoly in Seville becoming the center of the ensuing transatlantic trade, based on
Challenging the conventions about the advent of modernity, Immanuel Wallerstein pushed back the origins of the capitalist modernity to the Iberian expansion of the 15th century. During the 16th century Spain created a vast empire in the Americas, with a state monopoly in Seville becoming the center of the ensuing transatlantic trade, based on bullion
Bullion is non-ferrous metal that has been refined to a high standard of elemental purity. The term is ordinarily applied to bulk metal used in the production of coins and especially to precious metals such as gold and silver. It comes from t ...
. Iberian imperialism, starting by the Portuguese establishment of routes to Asia and the posterior transatlantic trade with the New World by Spaniards and Portuguese (along Dutch, English and French), precipitated the economic decline of the Italian Peninsula. The 16th century was one of population growth with increased pressure over resources; in the case of the Iberian Peninsula a part of the population moved to the Americas meanwhile Jews and Moriscos were banished, relocating to other places in the Mediterranean Basin. Most of the Moriscos remained in Spain after the Morisco revolt in Las Alpujarras during the mid-16th century, but roughly 300,000 of them were expelled from the country in 1609–1614, and emigrated ''en masse'' to North Africa.
In 1580, after the political crisis that followed the 1578 death of King Sebastian
Sebastian may refer to:
People
* Sebastian (name), including a list of persons with the name
Arts, entertainment, and media
Films and television
* ''Sebastian'' (1968 film), British spy film
* ''Sebastian'' (1995 film), Swedish drama film
...
, Portugal became a dynastic composite entity of the Hapsburg Monarchy; thus, the whole peninsula was united politically during the period known as the Iberian Union (1580–1640). During the reign of Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from ...
(I of Portugal), the Councils of Portugal, Italy, Flanders and Burgundy were added to the group of counselling institutions of the Hispanic Monarchy, to which the Councils of Castile, Aragon, Indies, Chamber of Castile, Inquisition, Orders, and Crusade already belonged, defining the organization of the Royal court that underpinned the through which the empire operated. During the Iberian union, the "first great wave" of the transatlantic slave trade happened, according to Enriqueta Vila Villar
Enriqueta is a given name. Notable people with the name include:
*Ana Enriqueta Terán (born 1918), Venezuelan poet
*Enriqueta Augustina Rylands (1843–1908), the founder of the John Rylands Library, Manchester
*Enriqueta Basilio (born 1948), Mex ...
, as new markets opened because of the unification gave thrust to the slave trade.
By 1600, the percentage of urban population for Spain was roughly 11.4%, while for Portugal the urban population was estimated as 14.1%, which were both above the 7.6% European average of the time (edged only by the Low Countries and the Italian Peninsula). Some striking differences appeared among the different Iberian realms. Castile, extending across a 60% of the territory of the peninsula and having 80% of the population was a rather urbanised country, yet with a widespread distribution of cities. Meanwhile, the urban population in the Crown of Aragon was highly concentrated in a handful of cities: Zaragoza (Kingdom of Aragon
The Kingdom of Aragon ( an, Reino d'Aragón, ca, Regne d'Aragó, la, Regnum Aragoniae, es, Reino de Aragón) was a medieval and early modern kingdom on the Iberian Peninsula, corresponding to the modern-day autonomous community of Aragon, ...
), Barcelona (Principality of Catalonia
The Principality of Catalonia ( ca, Principat de Catalunya, la, Principatus Cathaloniæ, oc, Principat de Catalonha, es, Principado de Cataluña) was a Middle Ages, medieval and early modern state (polity), state in the northeastern Iberian P ...
), and, to a lesser extent in the Kingdom of Valencia
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
, in Valencia, Alicante
Alicante ( ca-valencia, Alacant) is a city and municipality in the Valencian Community, Spain. It is the capital of the province of Alicante and a historic Mediterranean port. The population of the city was 337,482 , the second-largest in th ...
and Orihuela. The case of Portugal presented an hypertrophied capital, Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Grande Lisboa, Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administr ...
(which greatly increased its population during the 16th century, from 56,000 to 60,000 inhabitants by 1527, to roughly 120,000 by the third quarter of the century) with its demographic dynamism stimulated by the Asian trade, followed at great distance by Porto and Évora (both roughly accounting for 12,500 inhabitants). Throughout most of the 16th century, both Lisbon and Seville were among the Western Europe's largest and most dynamic cities.
The 17th century has been largely considered as a very negative period for the Iberian economies, seen as a time of recession, crisis or even decline, the urban dynamism chiefly moving to Northern Europe. A dismantling of the inner city network in the Castilian plateau took place during this period (with a parallel accumulation of economic activity in the capital, Madrid), with only New Castile resisting recession in the interior. Regarding the Atlantic façade of Castile, aside from the severing of trade with Northern Europe, inter-regional trade with other regions in the Iberian Peninsula also suffered to some extent. In Aragon, suffering from similar problems than Castile, the expelling of the Moriscos in 1609 in the Kingdom of Valencia aggravated the recession. Silk turned from a domestic industry into a raw commodity to be exported. However, the crisis was uneven (affecting longer the centre of the peninsula), as both Portugal and the Mediterranean coastline recovered in the later part of the century by fuelling a sustained growth.
The aftermath of the intermittent 1640–1668 Portuguese Restoration War brought the House of Braganza
The Most Serene House of Braganza ( pt, Sereníssima Casa de Bragança), also known as the Brigantine Dynasty (''Dinastia Brigantina''), is a dynasty of emperors, kings, princes, and dukes of Portuguese origin which reigned in Europe and the Ame ...
as the new ruling dynasty in the Portuguese territories across the world (bar Ceuta), putting an end to the Iberian Union.
Despite both Portugal and Spain starting their path towards modernization with the liberal revolutions of the first half of the 19th century, this process was, concerning structural changes in the geographical distribution of the population, relatively tame compared to what took place after World War II in the Iberian Peninsula, when strong urban development ran in parallel to substantial rural flight
Rural flight (or rural exodus) is the migratory pattern of peoples from rural areas into urban areas. It is urbanization seen from the rural perspective.
In industrializing economies like Britain in the eighteenth century or East Asia in the ...
patterns.
Geography and geology
Balkan
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. It is bordered on the southeast and east by the Mediterranean Sea, and on the north, west, and southwest by the Atlantic Ocean. The Pyrenees mountains are situated along the northeast edge of the peninsula, where it adjoins the rest of Europe. Its southern tip, located in Tarifa is the southernmost point of the European continent and is very close to the northwest coast of Africa, separated from it by the Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar ( ar, مضيق جبل طارق, Maḍīq Jabal Ṭāriq; es, Estrecho de Gibraltar, Archaic: Pillars of Hercules), also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Medi ...
and the Mediterranean Sea.
The Iberian Peninsula encompasses 583,254 km2 and has very contrasting and uneven relief. The mountain ranges of the Iberian Peninsula are mainly distributed from west to east, and in some cases reach altitudes of approximately 3000 mamsl
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
, resulting in the region having the second highest mean altitude (637 mamsl) in Western Europe.
The Iberian Peninsula extends from the southernmost extremity at Punta de Tarifa
Punta de Tarifa or Punta Marroquí (Tarifa Point or Moroccan Point) is the southernmost point of the Iberian Peninsula and Continental Europe. It is located in the province of Cádiz and the autonomous community of Andalusia on the Atlantic end ...
to the northernmost extremity at Punta de Estaca de Bares
Punta da Estaca de Bares is the northernmost point of Spain and the Iberian Peninsula, at a latitude of 43° 47′ 38″ North. It is located in Galicia. Conventionally, it marks the western end of the Cantabrian Sea, or Bay of Biscay, in the ...
over a distance between lines of latitude of about based on a degree length of per degree, and from the westernmost extremity at Cabo da Roca to the easternmost extremity at Cap de Creus
The Cap de Creus (Cabo de Creus in Spanish) is a peninsula and a headland located at the far northeast of Catalonia, some south from the French border. The cape lies in the municipal area of Cadaqués, and the nearest large town is Figueres, ...
over a distance between lines of longitude at 40° N latitude of about based on an estimated degree length of about for that latitude. The irregular, roughly octagonal shape of the peninsula contained within this spherical quadrangle was compared to an ox-hide by the geographer Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
.
About three quarters of that rough octagon is the Meseta Central, a vast plateau ranging from 610 to 760 m in altitude. It is located approximately in the centre, staggered slightly to the east and tilted slightly toward the west (the conventional centre of the Iberian Peninsula has long been considered Getafe just south of Madrid). It is ringed by mountains and contains the sources of most of the rivers, which find their way through gaps in the mountain barriers on all sides.
Coastline
The coastline of the Iberian Peninsula is , on the Mediterranean side and on the Atlantic side. The coast has been inundated over time, with sea levels having risen from a minimum of lower than today at theLast Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eur ...
(LGM) to its current level at 4,000 years BP. The coastal shelf created by sedimentation during that time remains below the surface; however, it was never very extensive on the Atlantic side, as the continental shelf drops rather steeply into the depths. An estimated length of Atlantic shelf is only wide. At the isobath, on the edge, the shelf drops off to .
The submarine topography of the coastal waters of the Iberian Peninsula has been studied extensively in the process of drilling for oil. Ultimately, the shelf drops into the Bay of Biscay
The Bay of Biscay (), known in Spain as the Gulf of Biscay ( es, Golfo de Vizcaya, eu, Bizkaiko Golkoa), and in France and some border regions as the Gulf of Gascony (french: Golfe de Gascogne, oc, Golf de Gasconha, br, Pleg-mor Gwaskogn), ...
on the north (an abyss), the Iberian abyssal plain at on the west, and Tagus abyssal plain to the south. In the north, between the continental shelf and the abyss, is an extension called the Galicia Bank, a plateau that also contains the Porto, Vigo, and Vasco da Gama seamount
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abru ...
s, which form the Galicia interior basin. The southern border of these features is marked by Nazaré Canyon
The Nazaré Canyon is an undersea canyon just off the coast of Nazaré, Portugal, in the eastern North Atlantic Ocean. It is the largest submarine canyon in Europe, reaching depths of about deep and a length of about .
The canyon is being stud ...
, which splits the continental shelf and leads directly into the abyss.
Rivers
 The major rivers flow through the wide valleys between the mountain systems. These are the Ebro, Douro, Tagus, Guadiana and Guadalquivir. All rivers in the Iberian Peninsula are subject to seasonal variations in flow.
The Tagus is the longest river on the peninsula and, like the Douro, flows westwards with its lower course in Portugal. The Guadiana river bends southwards and forms the border between Spain and Portugal in the last stretch of its course.
The major rivers flow through the wide valleys between the mountain systems. These are the Ebro, Douro, Tagus, Guadiana and Guadalquivir. All rivers in the Iberian Peninsula are subject to seasonal variations in flow.
The Tagus is the longest river on the peninsula and, like the Douro, flows westwards with its lower course in Portugal. The Guadiana river bends southwards and forms the border between Spain and Portugal in the last stretch of its course.
Mountains
The terrain of the Iberian Peninsula is largely mountainous. The major mountain systems are: * The Pyrenees and their foothills, the Pre-Pyrenees, crossing the isthmus of the peninsula so completely as to allow no passage except by mountain road, trail, coastal road or tunnel.Aneto
Aneto (''pic d'Aneto'' in French language, French, formerly ''pic de Néthou'') is the highest mountain in the Pyrenees and in Aragon, and Spain's third-highest mountain, reaching a height of . It stands in the Spanish province of Huesca (provi ...
in the Maladeta massif, at 3,404 m, is the highest point
Torre de Cerredo
Torre Cerredo, also called Torrecerredo or Torre de Cerredo ( Asturian: ''La Torre Cerréu''), is the highest peak of the Cantabrian Mountains, northern Spain.
With a prominence of 1,931 m, it is an ultra-prominent peak and the third most promine ...
, at 2,648 m, is the highest point
* The Galicia/Trás-os-Montes Massif in the Northwest is made up of very old heavily eroded rocks. Pena Trevinca, at 2,127 m, is the highest point
* The Sistema Ibérico, a complex system at the heart of the peninsula, in its central/eastern region. It contains a great number of ranges and divides the watershed of the Tagus, Douro and Ebro rivers. Moncayo, at 2,313 m, is the highest point
* The Sistema Central, dividing the Iberian Plateau into a northern and a southern half and stretching into Portugal (where the highest point of Continental Portugal
Continental Portugal ( pt, Portugal continental, ) or mainland Portugal comprises the bulk of the Portuguese Republic, namely that part on the Iberian Peninsula and so in Continental Europe, having approximately 95% of the total population and ...
(1,993 m) is located in the Serra da Estrela). Pico Almanzor in the Sierra de Gredos is the highest point, at 2,592 m
* The Montes de Toledo, which also stretches into Portugal from the La Mancha natural region at the eastern end. Its highest point, at 1,603 m, is La Villuerca in the Sierra de Villuercas
Sierra de Villuercas or Sierra de las Villuercas, also known as Sierra de Guadalupe after nearby Guadalupe town, is a mountain range in the greater Montes de Toledo range, Spain. It is located in province of Cáceres, autonomous community of Extr ...
, Extremadura
* The Sierra Morena, which divides the watershed of the Guadiana and Guadalquivir rivers. At 1,332 m, Bañuela is the highest point
* The Baetic System, which stretches between Cádiz and Gibraltar and northeast towards Alicante Province
Alicante ( ca-valencia, Alacant) is a province of eastern Spain, in the southern part of the Valencian Community. It is the second most populated Valencian province. Likewise, the second and third biggest cities in the Valencian Community (Alica ...
. It is divided into three subsystems:
** Prebaetic System, which begins west of the Sierra Sur de Jaén, reaching the Mediterranean Sea shores in Alicante Province
Alicante ( ca-valencia, Alacant) is a province of eastern Spain, in the southern part of the Valencian Community. It is the second most populated Valencian province. Likewise, the second and third biggest cities in the Valencian Community (Alica ...
. La Sagra
La Sagra is a Castilian comarca delineated by natural formations but not legally recognized. The comarca includes localities belonging to both the province of Madrid and the province of Toledo. La Sagra covers an area of 1322 km2, and is bordered ...
is the highest point at 2,382 m.
** Subbaetic System
The Subbaetic or Sub-Baetic System ( es, Sistema Subbético or ''Cordillera Subbética'') is one of the three systems of mountain ranges of the Baetic System in the southern Iberian Peninsula. Highest point high Peña de la Cruz in Sierra Ara ...
, which is in a central position within the Baetic Systems, stretching from Cape Trafalgar in Cádiz Province
Cádiz (, , ) is a city and port in southwestern Spain. It is the capital of the Province of Cádiz, one of eight that make up the autonomous community of Andalusia.
Cádiz, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Western Europe, w ...
across Andalusia to the Region of Murcia. The highest point, at , is Peña de la Cruz in Sierra Arana
The Sierra Arana or Sierra de Arana, also known as Sierra Harana, is a mountain range in the center of the province of Granada, southern Spain. Its highest peak is the Peña de la Cruz, at .
Description
The Sierra Arana is a mostly karstic range ...
.
** Penibaetic System, located in the far southeastern area stretching between Gibraltar across the Mediterranean coastal Andalusian provinces. It includes the highest point in the peninsula, the 3,478 m high Mulhacén in the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada () is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primarily ...
.
Geology
Ediacaran
The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period 635 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 538.8 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and th ...
to the Recent
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together ...
, and almost every kind of rock is represented. World-class mineral deposits can also be found there. The core of the Iberian Peninsula consists of a Hercynian cratonic block known as the Iberian Massif. On the northeast, this is bounded by the Pyrenean fold belt, and on the southeast it is bounded by the Baetic System. These twofold chains are part of the Alpine belt
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine Nation ...
. To the west, the peninsula is delimited by the continental boundary formed by the magma-poor opening of the Atlantic Ocean. The Hercynian Foldbelt is mostly buried by Mesozoic and Tertiary cover rocks to the east, but nevertheless outcrops through the Sistema Ibérico and the Catalan Mediterranean System
The Catalan Mediterranean System, also known as Mediterranean System, Transversal Ibero-Pyrenaean System, and Catalanid System,Josep Guitart i Duran, Maria del Tura Bolòs et al. ''Història agrària dels Països Catalans (Volum 1) Antiguitat'', 2 ...
.
The Iberian Peninsula features one of the largest Lithium deposits belts in Europe (an otherwise relatively scarce resource in the continent), scattered along the Iberian Massif's and . Also in the Iberian Massif, and similarly to other Hercynian blocks in Europe, the peninsula hosts some uranium deposits, largely located in the Central Iberian Zone unit.
The Iberian Pyrite Belt, located in the SW quadrant of the Peninsula, ranks among the most important volcanogenic massive sulphide districts on Earth, and it has been exploited for millennia.
Climate
 The Iberian Peninsula's location and topography, as well as the effects of large atmospheric circulation patterns induce a NW to SE gradient of yearly precipitation (roughly from 2,000 mm to 300 mm).
The Iberian peninsula has three dominant climate types. One of these is the
The Iberian Peninsula's location and topography, as well as the effects of large atmospheric circulation patterns induce a NW to SE gradient of yearly precipitation (roughly from 2,000 mm to 300 mm).
The Iberian peninsula has three dominant climate types. One of these is the oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
seen in the northeast in which precipitation has barely any difference between winter and summer. However, most of Portugal and Spain have a Mediterranean climate; the Warm-summer Mediterranean climate and the Hot-summer Mediterranean climate, with various differences in precipitation and temperature depending on latitude and position versus the sea, this applies greatly to the Portuguese and Galician Atlantic coasts where, due to upwelling/ downwelling phenomena average temperatures in summer can vary through as much as in only a few kilometers (e.g. Peniche vs Santarém) There are also more localized semi-arid climates in central Spain, with temperatures resembling a more continental Mediterranean climate. In other extreme cases highland alpine climates such as in Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada () is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primarily ...
and areas with extremely low precipitation and desert climates or semi-arid climates such as the Almería area, Murcia area and southern Alicante
Alicante ( ca-valencia, Alacant) is a city and municipality in the Valencian Community, Spain. It is the capital of the province of Alicante and a historic Mediterranean port. The population of the city was 337,482 , the second-largest in th ...
area. In the southwestern interior of the Iberian Peninsula the hottest temperatures in Europe are found, with Córdoba averaging around in July. The Spanish Mediterranean coast usually averages around in summer. In sharp contrast A Coruña at the northern tip of Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
has a summer daytime high average at just below . This cool and wet summer climate is replicated throughout most of the northern coastline. Winters in the Peninsula are for the most part, mild, although frosts are common in higher altitude areas of central Spain. The warmest winter nights are usually found in downwelling favourable areas of the west coast, such as on capes. Precipitation varies greatly between regions on the Peninsula, in December for example the northern west coast averages above whereas the southeast can average below . Insolation
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area (surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument.
Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre (W/m ...
can vary from just 1,600 hours in the Bilbao area, to above 3,000 hours in the Algarve and Gulf of Cádiz.
Major modern countries
 The current political configuration of the Iberian Peninsula comprises the bulk of Spain and Portugal, the whole microstate of Andorra, a small part of the
The current political configuration of the Iberian Peninsula comprises the bulk of Spain and Portugal, the whole microstate of Andorra, a small part of the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
department of Pyrénées-Orientales
Pyrénées-Orientales (; ca, Pirineus Orientals ; oc, Pirenèus Orientals ; ), also known as Northern Catalonia, is a department of the region of Occitania, Southern France, adjacent to the northern Spanish frontier and the Mediterranean Sea. ...
(the French Cerdagne), and the British Overseas Territory
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen dependent territory, territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remna ...
of Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
.
French Cerdagne is on the south side of the Pyrenees mountain range, which runs along the border between Spain and France. For example, the Segre Segre may refer to:
* Segre (surname)
* Sègre (department), a former department of France
* Segre River, a river in Catalonia
* Segré, a commune in Maine-et-Loire, France
* Segré, Burkina Faso
* '' Diari Segre'' or ''Segre'', a Spanish- and Ca ...
river, which runs west and then south to meet the Ebro, has its source on the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
side. The Pyrenees range is often considered the northeastern boundary of Iberian Peninsula, although the French coastline curves away from the rest of Europe north of the range, which is the reason why Perpignan
Perpignan (, , ; ca, Perpinyà ; es, Perpiñán ; it, Perpignano ) is the prefecture of the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France, in the heart of the plain of Roussillon, at the foot of the Pyrenees a few kilometres from the ...
, which is also known as the capital of Northern Catalonia
Northern Catalonia, North Catalonia, ; french: Catalogne (du) Nord ; oc, Catalonha (del) Nòrd; es, Cataluña (del) Norte) French Catalonia or Roussillon refers to the Catalan-speaking and Catalan-culture territory ceded to France by Spain ...
, is often considered as the entrance to the Iberian Peninsula.
Regarding Spain and Portugal, this chiefly excludes the Macaronesian
Macaronesia (Portuguese: ''Macaronésia,'' Spanish: ''Macaronesia'') is a collection of four volcanic archipelagos in the North Atlantic, off the coasts of Africa and Europe. Each archipelago is made up of a number of Atlantic oceanic islands ...
archipelagos ( Azores and Madeira
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
vis-à-vis Portugal and the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
vis-à-vis Spain), the Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands ( es, Islas Baleares ; or ca, Illes Balears ) are an archipelago in the Balearic Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago is an autonomous community and a province of Spain; its capital is ...
(Spain); and the Spanish territories in North Africa (most conspicuously the cities of Ceuta and Melilla
Melilla ( , ; ; rif, Mřič ; ar, مليلية ) is an autonomous city of Spain located in north Africa. It lies on the eastern side of the Cape Three Forks, bordering Morocco and facing the Mediterranean Sea. It has an area of . It was par ...
), as well as unpopulated islets and rocks.
Political divisions of the Iberian Peninsula:
Cities
The Iberian city network is dominated by 3 international metropolises ( Madrid, Barcelona andLisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Grande Lisboa, Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administr ...
) and four regional metropolises ( Valencia, Seville, Porto and Bilbao). The relatively weak integration of the network favours a competitive approach vis-à-vis the inter-relation between the different centres. Among these metropolises, Madrid stands out within the global urban hierarchy in terms of its status as a major service centre and enjoys the greatest degree of connectivity.
Major metropolitan regions
According toEurostat
Eurostat ('European Statistical Office'; DG ESTAT) is a Directorate-General of the European Commission located in the Kirchberg, Luxembourg, Kirchberg quarter of Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. Eurostat's main responsibilities are to provide statis ...
(2019), the metropolitan regions with a population over one million are listed as follows:
Ecology
Forests
 The woodlands of the Iberian Peninsula are distinct ecosystems. Although the various regions are each characterized by distinct vegetation, there are some similarities across the peninsula.
While the borders between these regions are not clearly defined, there is a mutual influence that makes it very hard to establish boundaries and some species find their optimal habitat in the intermediate areas.
The endangered Iberian lynx (''Lynx pardinus'') is a symbol of the Iberian mediterranean forest and of the fauna of the Iberian Peninsula altogether.
A new '' Podarcis'' lizard species, ''
The woodlands of the Iberian Peninsula are distinct ecosystems. Although the various regions are each characterized by distinct vegetation, there are some similarities across the peninsula.
While the borders between these regions are not clearly defined, there is a mutual influence that makes it very hard to establish boundaries and some species find their optimal habitat in the intermediate areas.
The endangered Iberian lynx (''Lynx pardinus'') is a symbol of the Iberian mediterranean forest and of the fauna of the Iberian Peninsula altogether.
A new '' Podarcis'' lizard species, ''Podarcis virescens
''Podarcis virescens'', also known by its common name as Geniez's wall lizard, is a lizard species of the Lacertidae family (biology), family. ''Podarcis virescens'' is commonly found in the Iberian Peninsula, including Spain and Portugal. The li ...
'', was accepted as a species by the Taxonomic Committee of the ''Societas Europaea Herpetologica'' in 2020. This lizard is native to the Iberian Peninsula and found near rivers in the region.
East Atlantic flyway
The Iberian Peninsula is an important stopover on the East Atlantic flyway for birds migrating from northern Europe to Africa. For example, curlew sandpipers rest in the region of the Bay of Cádiz. In addition to the birds migrating through, some seven million wading birds from the north spend the winter in the estuaries and wetlands of the Iberian Peninsula, mainly at locations on the Atlantic coast. InGalicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
are Ría de Arousa (a home of grey plover), Ria de Ortigueira, Ria de Corme and Ria de Laxe. In Portugal, the Aveiro Lagoon hosts ''Recurvirostra avosetta'', the common ringed plover, grey plover and little stint. Ribatejo Province on the Tagus supports ''Recurvirostra arosetta'', grey plover, dunlin, bar-tailed godwit and common redshank. In the Sado Estuary are dunlin, Eurasian curlew, grey plover and common redshank. The Algarve hosts red knot, common greenshank and turnstone. The Guadalquivir Marshes
The Guadalquivir Marshes (in es, Marismas del Guadalquivir or simply ''Las Marismas'') are a natural region of marshy lowlands on the lower Guadalquivir River.
The ''Las Marismas'' zone forms a large part of the province of Huelva, province o ...
region of Andalusia and the Salinas de Cádiz are especially rich in wintering wading birds: Kentish plover, common ringed plover, sanderling, and black-tailed godwit
The black-tailed godwit (''Limosa limosa'') is a large, long-legged, long-billed shorebird first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758. It is a member of the godwit genus, ''Limosa''. There are four subspecies, all with orange head, neck and chest ...
in addition to the others. And finally, the Ebro delta is home to all the species mentioned above.
Languages
With the sole exception of Basque, which is of unknown origin, all modern Iberian languages descend fromVulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve ...
and belong to the Western Romance languages. Throughout history (and pre-history), many different languages have been spoken in the Iberian Peninsula, contributing to the formation and differentiation of the contemporaneous languages of Iberia; however, most of them have become extinct or fallen into disuse. Basque is the only non-Indo-European surviving language in Iberia and Western Europe.
In modern times, Spanish (the official language of Spain, spoken by the entire 45 million population in the country, the native language of about 36 million in Europe), Portuguese (the official language of Portugal, with a population over 10 million), Catalan (over 7 million speakers in Europe, 3.4 million with Catalan as first language), Galician (understood by the 93% of the 2.8 million Galician population) and Basque (cf. around 1 million speakers) are the most widely spoken languages in the Iberian Peninsula. Spanish and Portuguese have expanded beyond Iberia to the rest of world, becoming global languages.
Other minority romance languages with some degree of recognition include the several varieties of Astur-leonese
Asturleonese ( ast, Asturlleonés; es, Asturleonés; pt, Asturo-leonês; mwl, Asturlhionés) is a Romance language spoken primarily in northwestern Spain, namely in the historical regions and Spain's modern-day autonomous communities of Asturi ...
, collectively amounting to about 0.6 million speakers, and the Aragonese (barely spoken by the 8% of the 130,000 people inhabiting the Alto Aragón).
English is the official language of Gibraltar. Llanito is a unique language in the territory, an amalgamation of mostly English and Spanish. In Spain, only 54.3% could speak a foreign language, below that of the EU-28 average. Portugal meanwhile achieved 69%, above the EU average, but still below the EU median. Spain ranks 25th out of 33 European countries in the English Proficiency Index.
Transportation
Both Spain and Portugal have traditionally used a non-standard rail gauge (the 1,668 mm Iberian gauge) since the construction of the first railroads in the 19th century. Spain has progressively introduced the 1,435 mmstandard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), International gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in Ea ...
in its new high-speed rail network (one of the most extensive in the world), inaugurated in 1992 with the Madrid–Seville line, followed to name a few by the Madrid–Barcelona (2008), Madrid–Valencia (2010), an Alicante branch of the latter (2013) and the connection to France of the Barcelona line. Portugal however suspended all the high-speed rail projects in the wake of the 2008 financial crisis
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9.
In mathematics
8 is:
* a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2.
* a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of t ...
, putting an end for the time being to the possibility of a high-speed rail connection between Lisbon, Porto and Madrid.
Handicapped by a mountainous range (the Pyrenees) hindering the connection to the rest of Europe, Spain (and subsidiarily Portugal) only has two meaningful rail connections to France able for freight transport, located at both ends of the mountain range. An international rail line across the Central Pyrenees linking Zaragoza and the French city of Pau through a tunnel existed in the past; however, an accident in the French part destroyed a stretch of the railroad in 1970 and the Canfranc Station has been a cul-de-sac
A dead end, also known as a cul-de-sac (, from French for 'bag-bottom'), no through road or no exit road, is a street with only one inlet or outlet.
The term "dead end" is understood in all varieties of English, but the official terminology ...
since then.
There are four points connecting the Portuguese and Spanish rail networks: Valença do Minho
Valença may refer to:
People
*Marquis of Valença, a Portuguese title of nobility
*Count of Valença, a Portuguese title of nobility
*Alceu Valença (born 1946), a Brazilian composer
*Valença (footballer) (born 1982), full name Manoel Cordeiro ...
– Tui, Vilar Formoso–Fuentes de Oñoro
Fuentes de Oñoro is a village and Municipalities of Spain, municipality in the province of Salamanca (province), Salamanca, western Spain, part of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Castile-Leon. It is located from the ...
, Marvão-Beirã– Valencia de Alcántara and Elvas– Badajoz.
The prospect of the development (as part of a European-wide effort) of the Central, Mediterranean and Atlantic rail corridors is expected to be a way to improve the competitiveness of the ports of Tarragona, Valencia, Sagunto, Bilbao, Santander, Sines and Algeciras vis-à-vis the rest of Europe and the World.
In 1980, Morocco and Spain started a joint study on the feasibility of a fixed link (tunnel or bridge) across the Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar ( ar, مضيق جبل طارق, Maḍīq Jabal Ṭāriq; es, Estrecho de Gibraltar, Archaic: Pillars of Hercules), also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Medi ...
, possibly through a connection of with Cape Malabata
__NOTOC__
Cape Malabata (french: Cap Malabata; es, Punta Malabata; ar, رأس ملباطا, ''Ras Malabata'', or ''Rās al-Manār'', "Lighthouse Cape") is a cape located about east of central Tangier, Morocco, facing the Strait of Gibraltar. Th ...
. Years of studies have, however, made no real progress thus far.
A transit point for many submarine cables, the Fibre-optic Link Around the Globe, Europe India Gateway, and the SEA-ME-WE 3 feature landing stations in the Iberian Peninsula. The West Africa Cable System, Main One
The Main One Cable is a submarine communications cable stretching from Portugal to South Africa with landings along the route in various west African countries. On April 28, 2008, it was announced that Main Street Technologies has awarded a turn ...
, SAT-3/WASC, Africa Coast to Europe also land in Portugal. MAREA, a high capacity communication transatlantic cable, connects the north of the Iberian Peninsula (Bilbao) to North America (Virginia), whereas Grace Hopper is an upcoming cable connecting the Iberian Peninsula (Bilbao) to the UK and the US intended to be operative by 2022 and EllaLink is an upcoming high-capacity communication cable expected to connect the Peninsula (Sines) to South America and the mammoth 2Africa project intends to connect the peninsula to the United Kingdom, Europe and Africa (via Portugal and Barcelona) by 2023–24.
Two gas pipelines: the Pedro Duran Farell pipeline and (more recently) the Medgaz (from, respectively, Morocco and Algeria) link the Maghreb and the Iberian Peninsula, providing Spain with Algerian natural gas. However the contract for the first pipeline expires on 31 October 2021 and—amidst a tense climate of Algerian–Moroccan relations—there are no plans to renew it.
Economy
The official currency across Iberia is the Euro, with the exception of Gibraltar, which uses theGibraltar Pound
The pound ( sign: £; ISO code: GIP) is the currency of Gibraltar. It is pegged to – and exchangeable with – sterling at par value. Coins and banknotes of the Gibraltar pound are issued by the Government of Gibraltar.
History
Until 1872, ...
(at parity with Sterling
Sterling may refer to:
Common meanings
* Sterling silver, a grade of silver
* Sterling (currency), the currency of the United Kingdom
** Pound sterling, the primary unit of that currency
Places United Kingdom
* Stirling, a Scottish city w ...
).
Major industries include mining, tourism, small farms, and fishing. Because the coast is so long, fishing is popular, especially sardines, tuna and anchovies. Most of the mining occurs in the Pyrenees mountains. Commodities mined include: iron, gold, coal, lead, silver, zinc, and salt.
Regarding their role in the global economy, both the microstate of Andorra and the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
have been described as tax havens.
The Galician region of Spain, in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula, became one of the biggest entry points of cocaine in Europe, on a par with the Dutch ports. Hashish
Hashish ( ar, حشيش, ()), also known as hash, "dry herb, hay" is a drug made by compressing and processing parts of the cannabis plant, typically focusing on flowering buds (female flowers) containing the most trichomes. European Monitorin ...
is smuggled from Morocco via the Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar ( ar, مضيق جبل طارق, Maḍīq Jabal Ṭāriq; es, Estrecho de Gibraltar, Archaic: Pillars of Hercules), also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Medi ...
.
See also
* Iberian Federalism * MacaronesiaNotes
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* * * * {{Authority control Peninsulas of Europe Geography of Southwestern Europe Regions of Europe Regions of Eurasia Geography of Portugal Geography of Spain Geography of France Geography of Andorra Geography of Gibraltar Historic Jewish communities Peninsulas of Portugal Peninsulas of Spain Peninsulas of France Southwestern Europe