House of Zähringen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The House of Zähringen (german: Zähringer) was a dynasty of Swabian nobility. The family's name derived from
 The earliest-known ancestor of the family was one Berthold, Count in the
The earliest-known ancestor of the family was one Berthold, Count in the
 Berthold I (ancestor of both the House of Zähringen and the House of Baden) held the comital titles of
Berthold I (ancestor of both the House of Zähringen and the House of Baden) held the comital titles of
 Among the cities founded or expanded by the Zähringer dukes (german: Zähringerstädte) are:
*in Swabia, west of the Black Forest (Baden): Freiburg im Breisgau (1120),
Among the cities founded or expanded by the Zähringer dukes (german: Zähringerstädte) are:
*in Swabia, west of the Black Forest (Baden): Freiburg im Breisgau (1120),

 Adalbert I (d. 1195) was a son of Duke Conrad I of Zähringen. Upon the death of his brother Berthold IV in 1186, he inherited the family estates around
Adalbert I (d. 1195) was a son of Duke Conrad I of Zähringen. Upon the death of his brother Berthold IV in 1186, he inherited the family estates around
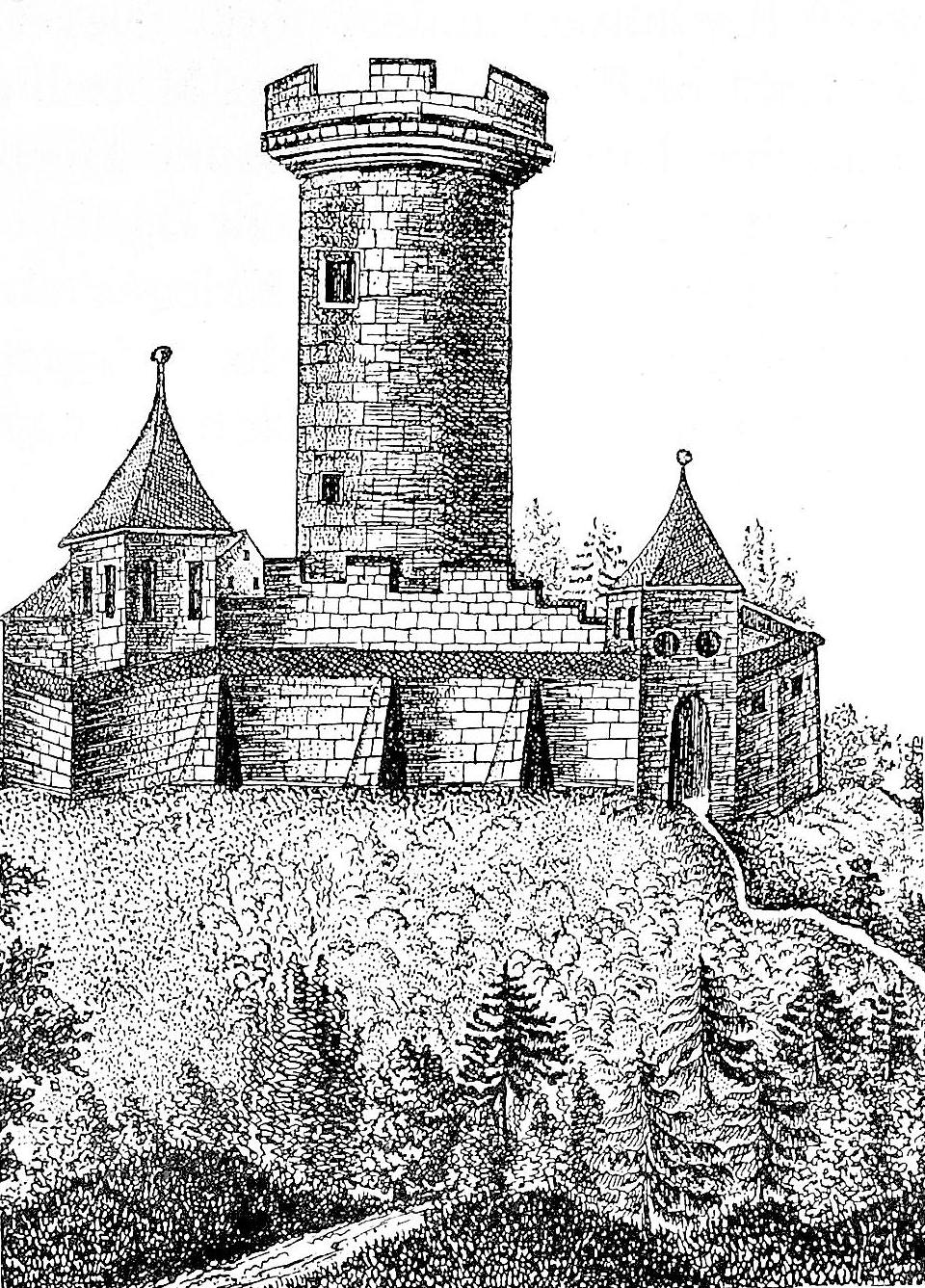
Zähringen Castle
– original castle of the Zähringer {{DEFAULTSORT:Zahringen, House Of German noble families 962 establishments
Zähringen Castle
Zähringen may refer to:
* Zähringen, a suburb of Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany
* Zähringen castle
* House of Zähringen
The House of Zähringen (german: Zähringer) was a dynasty of Swabian nobility. The family's name derived from Zähring ...
near Freiburg im Breisgau. The Zähringer in the 12th century used the title of Duke of Zähringen, in compensation for having conceded the title of Duke of Swabia to the Staufer
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynasty ...
in 1098. The Zähringer were granted the special title of Rector of Burgundy in 1127, and they continued to use both titles until the extinction of the ducal line in 1218.
The territories and fiefs held by the Zähringer were known as the 'Duchy of Zähringen' (), but it was not seen as a duchy
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a Middle Ages, medieval country, territory, fiefdom, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or Queen regnant, queen in Western European tradition.
There once exis ...
in equal standing with the old stem duchies. The Zähringer attempted to expand their territories in Swabia and Burgundy into a fully recognized duchy, but their expansion was halted in the 1130s due to their feud with the Welfs
The House of Welf (also Guelf or Guelph) is a European dynasty that has included many German and British monarchs from the 11th to 20th century and Emperor Ivan VI of Russia in the 18th century. The originally Franconian family from the Meus ...
. Pursuing their territorial ambitions, the Zähringer founded numerous cities and monasteries on either side of the Black Forest
The Black Forest (german: Schwarzwald ) is a large forested mountain range in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is t ...
, as well as in the western Swiss Plateau
The Swiss Plateau or Central Plateau (german: Schweizer Mittelland; french: plateau suisse; it, altopiano svizzero) is one of the three major landscapes in Switzerland, lying between the Jura Mountains and the Swiss Alps. It covers about 30% of ...
. After the extinction of the ducal line in 1218, parts of the family's territories reverted to the crown (attained imperial immediacy
Imperial immediacy (german: Reichsfreiheit or ') was a privileged constitutional and political status rooted in German feudal law under which the Imperial estates of the Holy Roman Empire such as Imperial cities, prince-bishoprics and secular pri ...
), while other parts were divided between the houses of Kyburg, Urach and Fürstenberg Fürstenberg (also Fuerstenberg and Furstenberg) may refer to:
Historical states
* Fürstenberg-Baar, county (1441–1559)
* Fürstenberg-Blumberg, county (1559–1614)
* Fürstenberg-Donaueschingen, county (1617–1698)
* Fürstenberg-Fürsten ...
.
History
 The earliest-known ancestor of the family was one Berthold, Count in the
The earliest-known ancestor of the family was one Berthold, Count in the Breisgau
The Breisgau () is an area in southwest Germany between the Rhine River and the foothills of the Black Forest. Part of the state of Baden-Württemberg, it centers on the city of Freiburg im Breisgau. The district of Breisgau-Hochschwarzwald, ...
(d. 982), who was first mentioned in 962. In view of his name, he may have been related to the Alemannic Ahalolfing dynasty The Alaholfings (occasionally Ahalolfings) were a noble family of Alemannia in the Early Middle Ages. They were related to the previous rulers of Alemannia, to the Bavarian Agilolfings and to the Geroldings. Their original power base was around ...
.
Count Berthold's great-grandson, the later Berthold II, Duke of Carinthia
Berthold II, Duke of Carinthia (c. 1000 – 6 November 1078), also known as Berthold I of Zähringen, was a progenitor of the Swabian House of Zähringen. From 1061 until 1077, he was the Duke of Carinthia and Margrave of Verona.
Life
He was poss ...
(posthumously known as Berthold I of Zähringen, c. 1000–1078), held several lordships (''Herrschaft
The German term ''Herrschaft'' (plural: ''Herrschaften'') covers a broad semantic field and only the context will tell whether it means, "rule", "power", "dominion", "authority", "territory" or "lordship". In its most abstract sense, it refers ...
en'') in the Breisgau, in Thurgau
Thurgau (; french: Thurgovie; it, Turgovia), anglicized as Thurgovia, more formally the Canton of Thurgau, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of five districts and its capital is Frauenfeld.
Thurgau is par ...
, Ortenau
The Ortenau, originally called Mortenau, is a historic region in the present-day German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the right bank of the river Rhine, stretching from the Upper Rhine Plain to the foothill zone of the Black Fore ...
and Baar. By his mother, he was related to the rising Hohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynast ...
family. Emperor Henry III had promised his vassal Berthold the Duchy of Swabia, but this was not fulfilled, as upon Henry's death, his widow Agnes of Poitou appointed Count Rudolf of Rheinfelden
Rudolf of Rheinfelden ( – 15 October 1080) was Duke of Swabia from 1057 to 1079. Initially a follower of his brother-in-law, the Salian emperor Henry IV, his election as German anti-king in 1077 marked the outbreak of the Great Saxon Revolt an ...
to the position of Duke of Swabia in 1057. In compensation, Berthold was made Duke of Carinthia
The Duchy of Carinthia (german: Herzogtum Kärnten; sl, Vojvodina Koroška) was a duchy located in southern Austria and parts of northern Slovenia. It was separated from the Duchy of Bavaria in 976, and was the first newly created Imperial State ...
and Margrave of Verona in 1061. However, this dignity was only a titular one, and Berthold subsequently lost it when, in the course of the Investiture Controversy
The Investiture Controversy, also called Investiture Contest (German: ''Investiturstreit''; ), was a conflict between the Church and the state in medieval Europe over the ability to choose and install bishops (investiture) and abbots of monast ...
, he joined the rising of his former rival Rudolf of Rheinfelden against German king Henry IV in 1073.
Berthold's son Berthold II (c. 1050–1111), who like his father fought against Henry IV, inherited a lot of the lands of Rudolf's son Count Berthold of Rheinfelden in 1090 (though not his comital title, which stayed with the family von Wetter-Rheinfelden). Berthold II is so named both as Duke of Swabia (following Berthold of Rheinfelden, the first duke of Swabia of this name) and as head of the House of Zähringen (following his father, who is counted as Berthold I of Zähringen in spite of not historically having used the name Zähringen). Berthold II did use the name Zähringen, although he moved his main residence from Zähringen Castle
Zähringen may refer to:
* Zähringen, a suburb of Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany
* Zähringen castle
* House of Zähringen
The House of Zähringen (german: Zähringer) was a dynasty of Swabian nobility. The family's name derived from Zähring ...
to the newly built Freiburg Castle
Freiburg Castle is a vanished castle. When it existed it was usually called the ''Burghaldenschloss'' (''motte-and-bailey castle'').
Location
It stood on the Schlossberg (castle hill) above the city of Freiburg in Baden-Württemberg. The locat ...
in 1091.
In 1092, Berthold II was elected Duke of Swabia against Frederick I of Hohenstaufen. In 1098, he reconciled with Frederick, renounced all claims to Swabia and instead concentrated on his possessions in the Breisgau region, assuming the title of Duke of Zähringen. He was succeeded in turn by his sons, Berthold III (d. 1122) and Conrad (d. 1152).
In 1127, upon the assassination of his nephew Count William III, Conrad claimed the inheritance of the County of Burgundy
The Free County of Burgundy or Franche-Comté (french: Franche Comté de Bourgogne; german: Freigrafschaft Burgund) was a medieval county (from 982 to 1678) of the Holy Roman Empire, predecessor to the modern region of Franche-Comté. The name ' ...
against Count Renaud III of Mâcon. Renaud prevailed, although he had to cede large parts of the eastern Transjuranian lands to Conrad, who thereupon was appointed by Emperor Lothair III
Lothair III, sometimes numbered Lothair II and also known as Lothair of Supplinburg (1075 – 4 December 1137), was Holy Roman Emperor from 1133 until his death. He was appointed Duke of Saxony in 1106 and elected King of Germany in 1125 before ...
as a 'rector' of the Imperial Kingdom of Burgundy-Arles
The Kingdom of Burgundy, known from the 12th century as the Kingdom of Arles, also referred to in various context as Arelat, the Kingdom of Arles and Vienne, or Kingdom of Burgundy-Provence, was a realm established in 933 by the merger of the king ...
. This office was confirmed in 1152 and held by the Zähringer dukes until 1218. As a result, they are sometimes referred to as 'Dukes of Burgundy', although the existing Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; la, Ducatus Burgundiae; french: Duché de Bourgogne, ) emerged in the 9th century as one of the successors of the ancient Kingdom of the Burgundians, which after its conquest in 532 had formed a constituent part of the ...
was not an Imperial fief but a French one. Duke Berthold IV (d. 1186), who followed his father Conrad and founded the Swiss city of Fryburg (today's Fribourg-Freiburg) in 1157, spent much of his time in Italy in the train of Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt o ...
.
His son and successor, Berthold V, showed his prowess by reducing the Burgundian nobles to order. This latter duke was the founder of the city of Bern
german: Berner(in)french: Bernois(e) it, bernese
, neighboring_municipalities = Bremgarten bei Bern, Frauenkappelen, Ittigen, Kirchlindach, Köniz, Mühleberg, Muri bei Bern, Neuenegg, Ostermundigen, Wohlen bei Bern, Zollikofen
, website ...
in 1191, and when he died in February 1218, the ducal line of the Zähringer became extinct. Among other titles, the Zähringen family acted as ''Reichsvogt
''Reichsvogt'' (; ''Imperial Advocate'') was the term for the office of a ''Vogt'' that was nominated by the king of the Holy Roman Empire as his representative. Especially in what is now Switzerland, the ''Reichsvogt'' was a very influential pos ...
'' of the Zürichgau area.
After the extinction of the ducal line in 1218, much of its extensive territory in the Breisgau and modern-day Switzerland returned to the crown, except for the allodial titles, which were divided between the counts of Urach (who subsequently called themselves the counts of Freiburg) and the counts of Kyburg
The Kyburg family (; ; also Kiburg) was a noble family of ''grafen'' (counts) in the Duchy of Swabia, a cadet line of the counts of Dillingen, who in the late 12th and early 13th centuries ruled the County of Kyburg, corresponding to much of wha ...
, both descended from the sisters of Berthold V. Less than fifty years later, the Kyburgs died out, and large portions of their domains were inherited by the House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
. Bern achieved the status of a free imperial city
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
, whereas other cities (such as Fribourg-Freiburg) only obtained the same status later in history.
Possessions and territories
 Berthold I (ancestor of both the House of Zähringen and the House of Baden) held the comital titles of
Berthold I (ancestor of both the House of Zähringen and the House of Baden) held the comital titles of Breisgau
The Breisgau () is an area in southwest Germany between the Rhine River and the foothills of the Black Forest. Part of the state of Baden-Württemberg, it centers on the city of Freiburg im Breisgau. The district of Breisgau-Hochschwarzwald, ...
and Thurgau
Thurgau (; french: Thurgovie; it, Turgovia), anglicized as Thurgovia, more formally the Canton of Thurgau, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of five districts and its capital is Frauenfeld.
Thurgau is par ...
, as well as being reeve in Stein am Rhein
Stein am Rhein (abbreviated as Stein a. R.) is a historic town and a municipality in the canton of Schaffhausen in Switzerland.
The town's medieval centre retains the ancient street plan. The site of the city wall, and the city gates are preserve ...
(owned by the bishop of Bamberg This is a list of bishops and archbishops of the Prince-Bishopric of Bamberg and Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Bamberg in Germany.
__TOC__ Bishops, 1007–1245
* Eberhard I 1007-1040
* Suidger von Morsleben 1040-1046 (Later Pope Clement II)
* Hartw ...
). The county of Thurgau was lost around 1077.
In 1098, Berthold II, founder of the House of Zähringen proper, received Zähringen Castle
Zähringen may refer to:
* Zähringen, a suburb of Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany
* Zähringen castle
* House of Zähringen
The House of Zähringen (german: Zähringer) was a dynasty of Swabian nobility. The family's name derived from Zähring ...
and the jurisdiction
Jurisdiction (from Latin 'law' + 'declaration') is the legal term for the legal authority granted to a legal entity to enact justice. In federations like the United States, areas of jurisdiction apply to local, state, and federal levels.
Jur ...
over Zürich
Zürich () is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zürich. It is located in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zürich. As of January 2020, the municipality has 43 ...
(alongside the Counts of Lenzburg
The Counts of Lenzburg (also Counts of Baden by the early 12th century) were a comital family in the Duchy of Swabia in the 11th and 12th centuries, controlling substantial portions of the '' pagi'' of Aargau and Zürichgau.
After the extinction ...
until 1173). Ownership of the county of Rheinfelden and of Burgdorf also dates to c. 1198.
The 'rectorate' of the county of Burgundy
The Free County of Burgundy or Franche-Comté (french: Franche Comté de Bourgogne; german: Freigrafschaft Burgund) was a medieval county (from 982 to 1678) of the Holy Roman Empire, predecessor to the modern region of Franche-Comté. The name ' ...
was granted in 1127 (inheritance of Otto-William, Count of Burgundy
Otto-William (french: Otte-Guillaume; german: Otto Wilhelm; 955/62 – 21 September 1026 AD) was count of Mâcon, Nevers, and Burgundy.
Life
Otto was born in 958 during the joint reign of his grandfather, King Berengar II of Italy, and his fat ...
). Ownership of Burgundy was contested, and Zähringer ''de facto'' rule was limited to the parts of Upper Burgundy
The Kingdom of Upper Burgundy was a Frankish dominion established in 888 by the Welf king Rudolph I of Burgundy on the territory of former Middle Francia. It grew out of the Carolingian margraviate of Transjurane Burgundy (''Transjurania'', ...
east of the Jura and north of Lake Geneva
, image = Lake Geneva by Sentinel-2.jpg
, caption = Satellite image
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = Switzerland, France
, coords =
, lake_type = Glacial la ...
. The territories south of Lake Geneva were conceded to Savoy and Provence
Provence (, , , , ; oc, Provença or ''Prouvènço'' , ) is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which extends from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the Italian border to the east; it is bor ...
in 1156. In compensation, Berthold IV received the investiture right for the bishops of Geneva, Sion and Lausanne, ''de facto'' realised only in the case of Lausanne.
The extinction of the counts of Lenzburg in 1173 strengthened the Zähringer position south of the Rhine, but their territorial expansion was halted following their support of the Welfs
The House of Welf (also Guelf or Guelph) is a European dynasty that has included many German and British monarchs from the 11th to 20th century and Emperor Ivan VI of Russia in the 18th century. The originally Franconian family from the Meus ...
in the unsuccessful feud against Conrad III of Germany during 1138–1152. This frustrated their ambitions to carve out a contiguous territorial duchy wedged between Swabia and Burgundy, in spite of late attempts on the part of Berthold V to increase his territorial sway (who as late as 1210 aimed at receiving the jurisdiction over St. Gallen
, neighboring_municipalities = Eggersriet, Gaiserwald, Gossau, Herisau (AR), Mörschwil, Speicher (AR), Stein (AR), Teufen (AR), Untereggen, Wittenbach
, twintowns = Liberec (Czech Republic)
, website = ...
).
Instead of territorial expansion, the dukes of Zähringen from the 1150s focussed on attaining more immediate feudal control over the territories they already had. This included their policy of expanding settlements into fortified towns or cities and the construction of new castles, mostly in their territories north of the Rhine. Their encroachment on the rights of the comital nobility south of the Rhine seems to have been resisted, mostly passively, but in the case of the lords of Glâne and Thun
, neighboring_municipalities= Amsoldingen, Heiligenschwendi, Heimberg, Hilterfingen, Homberg, Schwendibach, Spiez, Steffisburg, Thierachern, Uetendorf, Zwieselberg
, twintown =
, website = www.thun.ch
Thun (french: Thou ...
in an open revolt in 1191.
The fragmentation of the Zähringer possessions after 1218 was an important factor in the communal movements of the late medieval period in the region, including the imperial immediacy
Imperial immediacy (german: Reichsfreiheit or ') was a privileged constitutional and political status rooted in German feudal law under which the Imperial estates of the Holy Roman Empire such as Imperial cities, prince-bishoprics and secular pri ...
of Bern and Zürich, and the growth of the Old Swiss Confederacy
The Old Swiss Confederacy began as a late medieval alliance between the communities of the valleys in the Central Alps, at the time part of the Holy Roman Empire, to facilitate the management of common interests such as free trade and to ensure ...
in the early 14th century.
Cities
Offenburg
Offenburg ("open borough" - coat of arms showing open gates; Low Alemmanic: ''Offäburg'') is a city located in the state of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. With nearly 60,000 inhabitants (2019), it is the largest city and the administrative capital ...
(before 1148), Neuenburg am Rhein
Neuenburg am Rhein ( High Alemannic: ''Neiburg am Rhi'') is a town in the district Breisgau-Hochschwarzwald in Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany.
Geography
Geographical location
Neuenburg is elevated on the right bank of the Altrhein on a ...
(1175);
*in Swabia, east of the Black Forest (Württemberg): Sankt Peter (1093), Villingen (1119), Bräunlingen
Bräunlingen is a town in the district of Schwarzwald-Baar, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated on the river Breg, 4 km southwest of Donaueschingen.
Sons and daughters of the city
* Johann Baptist Weber (1756-1826), master bu ...
(c. 1200), Weilheim an der Teck
Weilheim an der Teck is a town in the district of Esslingen in Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. It is situated 7 km southeast of Kirchheim unter Teck, and 13 km southwest of Göppingen. Locals often refer to it as just "Weilhe ...
( Limburg castle c. 1060);
*in Burgundy (western Swiss plateau):
**on the Rhine: Rheinfelden (c. 1150);
**Aare basin: Fribourg
, neighboring_municipalities= Düdingen, Givisiez, Granges-Paccot, Marly, Pierrafortscha, Sankt Ursen, Tafers, Villars-sur-Glâne
, twintowns = Rueil-Malmaison (France)
, website = www.ville-fribourg.ch
, Location of , Location of ()
() ...
(Freiburg im Üechtland, 1157) Bern
german: Berner(in)french: Bernois(e) it, bernese
, neighboring_municipalities = Bremgarten bei Bern, Frauenkappelen, Ittigen, Kirchlindach, Köniz, Mühleberg, Muri bei Bern, Neuenegg, Ostermundigen, Wohlen bei Bern, Zollikofen
, website ...
(1191), Burgdorf (castle before 1175), Murten
Murten (German) or Morat (French, ; frp, Morât ) is a bilingual municipality and a city in the See district of the canton of Fribourg in Switzerland.
It is located on the southern shores of Lake Morat (also known as Lake Murten). Morat is si ...
(c. 1180), Thun
, neighboring_municipalities= Amsoldingen, Heiligenschwendi, Heimberg, Hilterfingen, Homberg, Schwendibach, Spiez, Steffisburg, Thierachern, Uetendorf, Zwieselberg
, twintown =
, website = www.thun.ch
Thun (french: Thou ...
(c. 1190).
Other towns owned by or under the jurisdiction (Reichsvogt
''Reichsvogt'' (; ''Imperial Advocate'') was the term for the office of a ''Vogt'' that was nominated by the king of the Holy Roman Empire as his representative. Especially in what is now Switzerland, the ''Reichsvogt'' was a very influential pos ...
ei) of the Zähringer include: Solothurn
Solothurn ( , ; french: Soleure ; it, Soletta ; rm, ) is a town, a municipality, and the capital of the canton of Solothurn in Switzerland. It is located in the north-west of Switzerland on the banks of the Aare and on the foot of the Weissens ...
(acquired 1127), Zürich
Zürich () is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zürich. It is located in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zürich. As of January 2020, the municipality has 43 ...
(acquired 1173), Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; gsw, Schafuuse; french: Schaffhouse; it, Sciaffusa; rm, Schaffusa; en, Shaffhouse) is a town with historic roots, a municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of the same name; it has an estimate ...
(acquired 1198) and Stein am Rhein
Stein am Rhein (abbreviated as Stein a. R.) is a historic town and a municipality in the canton of Schaffhausen in Switzerland.
The town's medieval centre retains the ancient street plan. The site of the city wall, and the city gates are preserve ...
.
The city of Morges
Morges (; la, Morgiis, plural, probably ablative, else dative; frp, Môrges) is a municipality in the Swiss canton of Vaud and the seat of the district of Morges. It is located on Lake Geneva.
History
Morges is first mentioned in 1288 as ' ...
on Lake Geneva is not a Zähringer foundation (having been founded in 1286 by Louis I of Vaud Louis I (1249/50 – 1302) was the Baron of Vaud. At the time of his birth he was a younger son of the House of Savoy, but through a series of deaths and his own effective military service, he succeeded in creating a semi-independent principality in ...
) but shared the characteristic layout of the Zähringer cities.
Genealogy

House of Zähringen
Berthold II, Duke of Carinthia
Berthold II, Duke of Carinthia (c. 1000 – 6 November 1078), also known as Berthold I of Zähringen, was a progenitor of the Swabian House of Zähringen. From 1061 until 1077, he was the Duke of Carinthia and Margrave of Verona.
Life
He was poss ...
, Margrave of Verona
Verona ( , ; vec, Verona or ) is a city on the Adige River in Veneto, Northern Italy, Italy, with 258,031 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region. It is the largest city Comune, municipality in the region and the ...
(c. 1000–1078, r. 1061–1077), is also known as "Berthold I of Zähringen". Therefore, the succession of dukes of Zähringen begins with his son as Berthold II:
Dukes of Zähringen:
* Berthold II (c. 1050–1111), Duke of Swabia from 1092 to 1098 (against Frederick I of Hohenstaufen), then Duke of Zähringen from about 1100. The numeral II carried by Berthold refers to both the House of Zähringen (succeeding his father Berthold I) and the Duchy of Swabia (succeeding Berthold I, Duke of Swabia
Berthold I (c. 1060 – 18 May 1090), better known as Berthold of Rheinfelden, was the Duke of Swabia from 1079 until his death. He was the eldest son of Rudolf of Rheinfelden, duke of Swabia, and German anti-king (r.1077–1079) in opposition to ...
of the House of Rheinfelden).
* Berthold III (c. 1085–1122), son, Duke of Zähringen from 1111
* Conrad I (c. 1090–1152), brother, Duke of Zähringen from 1122, rector of Burgundy from 1127
* Berthold IV (c. 1125–1186), son, Duke of Zähringen from 1152, rector of Burgundy
* Berthold V (1160–1218), son, Duke of Zähringen from 1186, rector of Burgundy
Other notable Zähringer:
* Gebhard of Zähringen (d. 1110), son of Berthold I, became Bishop of Constance
The Prince-Bishopric of Constance, (german: Hochstift Konstanz, Fürstbistum Konstanz, Bistum Konstanz) was a small ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire from the mid-12th century until its secularisation in 1802–1803. In his dua ...
*Clementia of Zähringen
Clementia of Zähringen (died 1175), was a daughter of Conrad I, Duke of Zähringen and his wife Clementia of Namur. By her first marriage, Clementia was Duchess of Bavaria and Saxony. By her second marriage she was Countess of Savoy.
Duchess of ...
(d. 1175), daughter of Conrad I, married Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (german: Heinrich der Löwe; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195) was a member of the Welf dynasty who ruled as the duke of Saxony and Bavaria from 1142 and 1156, respectively, until 1180.
Henry was one of the most powerful German p ...
, Duke of Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
in 1147
*Rudolf of Zähringen
Rudolf of Zähringen (also ''Rudolph'', ''Ralph'' or ''Raoul'') (c. 1135 – 5 August 1191) was the archbishop of Mainz from 1160 to 1161 and prince-bishop of Liège. He was the son of Conrad I of Zähringen and Clemence of Luxembourg-Namur.
...
(d. 1191), son of Conrad I, became Archbishop of Mainz and Bishop of Liège
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ...
House of Baden
The Veronese margravial title was used by Herman I of Baden, the eldest son of Berthold I of Zähringen. Herman's son, Herman II, was the first to use the title ofMargrave of Baden
The Margraviate of Baden (german: Markgrafschaft Baden) was a historical territory of the Holy Roman Empire. Spread along the east side of the Upper Rhine River in southwestern Germany, it was named a margraviate in 1112 and existed until 1535, ...
in 1112.
Now more commonly known as the House of Baden
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
, Herman's descendants ruled successively as margrave
Margrave was originally the medieval title for the military commander assigned to maintain the defence of one of the border provinces of the Holy Roman Empire or of a kingdom. That position became hereditary in certain feudal families in the Em ...
s until the Final Recess
The ' (formally the ', or "Principal Conclusion of the Extraordinary Imperial Delegation"), sometimes referred to in English as the Final Recess or the Imperial Recess of 1803, was a resolution passed by the ' (Imperial Diet) of the Holy Roman Em ...
of 1803, as electors of the Electorate of Baden
The Electorate of Baden was a State of the Holy Roman Empire from 1803 to 1806. In 1803, Napoleon bestowed the office of Prince-elector to Charles Frederick, but in 1806, Francis II dissolved the Empire. Baden then achieved sovereignty, and C ...
until 1806, then as Grand Dukes of Baden until the end of the German monarchy in 1918.
The current holder of the title of "Margrave of Baden, Duke of Zähringen" is Maximilian, Margrave of Baden
Maximilian, Margrave of Baden (Maximilian Andreas Friedrich Gustav Ernst August Bernhard; 3 July 1933 – 29 December 2022), also known as Max von Baden, was a German businessman and the head of House of Baden. Through his mother, Princess Theo ...
(b. 1933), a grandson of the last chancellor
Chancellor ( la, cancellarius) is a title of various official positions in the governments of many nations. The original chancellors were the of Roman courts of justice—ushers, who sat at the or lattice work screens of a basilica or law cou ...
of the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
( Prince Max von Baden) and nephew of Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh
Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh (born Prince Philip of Greece and Denmark, later Philip Mountbatten; 10 June 1921 – 9 April 2021) was the husband of Queen Elizabeth II. As such, he served as the consort of the British monarch from E ...
, who seems to have revived the Zähringen title after it apparently had not been in official usage since the death of Berthold V in 1218. Another branch was that of the Dukes of Teck
Duke of Teck is a title which was created twice in Germanic lands. It was first borne from 1187 to 1439 by the head of a cadet line of the German ducal House of Zähringen, known as the "first House of Teck". The ''caput'' of his territory was Te ...
, descendants of Duke Conrad's son Adalbert, whose line became extinct in 1439.
Dukes of Teck
 Adalbert I (d. 1195) was a son of Duke Conrad I of Zähringen. Upon the death of his brother Berthold IV in 1186, he inherited the family estates around
Adalbert I (d. 1195) was a son of Duke Conrad I of Zähringen. Upon the death of his brother Berthold IV in 1186, he inherited the family estates around Teck Castle
Teck Castle (german: Burg Teck) was a ducal castle in the kingdom of Württemberg, immediately to the north of the Swabian Jura and south of the town of Kirchheim unter Teck (now in the district of Esslingen). The castle took its name from the T ...
and, from 1187, adopted the title of Duke of Teck. His descendant Conrad II of Teck
Conrad II of Teck (1235 – 2 May 1292) was Duke of Teck.
Conrad was a descendant of the House of Zähringen, Zähringen family and a close follower of the Hohenstaufen dynasty. He served the Hohenstaufen claimant Conradin until the latter was ex ...
(1235–1292) allegedly was designated King of the Romans shortly before his assassination. The line became extinct in 1439 with the death of Louis of Teck Louis of Teck (Italian: ''Ludovico di Teck''; 1375 - July 1439) was a duke German prelate, who was Patriarch of Aquileia from 1412 until his death.
Biography
Louis of Teck was the last male descendant of the Dukes of Teck in Swabia, born around 13 ...
, Patriarch of Aquileia
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate (bishop), primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholicism, Independent Catholic Chur ...
.
In 1871, a ducal title with the same name was granted by King Charles I of Württemberg to Prince Francis of Teck
Prince Francis of Teck, (Francis Joseph Leopold Frederick; 9 January 1870 – 22 October 1910) was the younger brother of the British queen Mary of Teck, wife of King George V.
Family
Francis Joseph Leopold Frederick, known as "Frank", was bo ...
(1837–1900), a morganatic
Morganatic marriage, sometimes called a left-handed marriage, is a marriage between people of unequal social rank, which in the context of royalty or other inherited title prevents the principal's position or privileges being passed to the spous ...
son of Duke Alexander of Württemberg. Francis' daughter Mary of Teck
Mary of Teck (Victoria Mary Augusta Louise Olga Pauline Claudine Agnes; 26 May 186724 March 1953) was Queen of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Empress of India, from 6 May 1910 until 20 January 1936 as the wife of King-Empe ...
(1867–1953), as the wife of King George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until Death and state funeral of George V, his death in 1936.
Born duri ...
, became Queen of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Empress of India.
Francis’s surviving children ceased using their German titles during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and (aside from Queen Mary) took the name “Cambridge” with his eldest son Adolphus
Adolf (also spelt Adolph or Adolphe, Adolfo and when Latinised Adolphus) is a given name used in German-speaking countries, Scandinavia, the Netherlands and Flanders, France, Italy, Spain, Portugal, Latin America and to a lesser extent in vari ...
being made Marquess of Cambridge
Marquess of Cambridge was a title that was created twice, once in the Peerage of England and once in the Peerage of the United Kingdom.
The first creation was for Prince George Augustus in 1706, when he was created Duke of Cambridge, Marquess of ...
and his youngest son Alexander
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
being made Earl of Athlone. This branch of the family died out in the male line in 1981 and in its entirety in 1994 with the death of Francis’s granddaughter, Lady Mary Abel Smith.
See also
*Zähringerbrunnen
The Zähringerbrunnen ( Zähringen Fountain) is a fountain on Kramgasse in the Old City of Bern, Switzerland. It is a Swiss Cultural Property of National Significance and is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site of the Old City of Bern.
Hi ...
Notes
References
* *External links
*Zähringen Castle
– original castle of the Zähringer {{DEFAULTSORT:Zahringen, House Of German noble families 962 establishments