History of timekeeping devices on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The history of timekeeping devices dates back to when ancient civilizations first observed
The history of timekeeping devices dates back to when ancient civilizations first observed
 The first devices used for measuring the position of the Sun were shadow clocks, which later developed into the sundial. Egyptian
The first devices used for measuring the position of the Sun were shadow clocks, which later developed into the sundial. Egyptian
 The
The
 Incense clocks were first used in China around the 6th century, mainly for religious purposes, but also for social gatherings or by scholars. Due to their frequent use of
Incense clocks were first used in China around the 6th century, mainly for religious purposes, but also for social gatherings or by scholars. Due to their frequent use of
 The 12th century Muslim inventor Al-Jazari described four different designs for a candle clock in his book ''The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices'' (). His so-called 'scribe' candle clock was invented to mark the passing of 14 hours of equal length: a precisely engineered mechanism caused a candle of specific dimensions to be slowly pushed upwards, which caused an indicator to move along a scale. Every hour a small ball emerged from the beak of a bird.
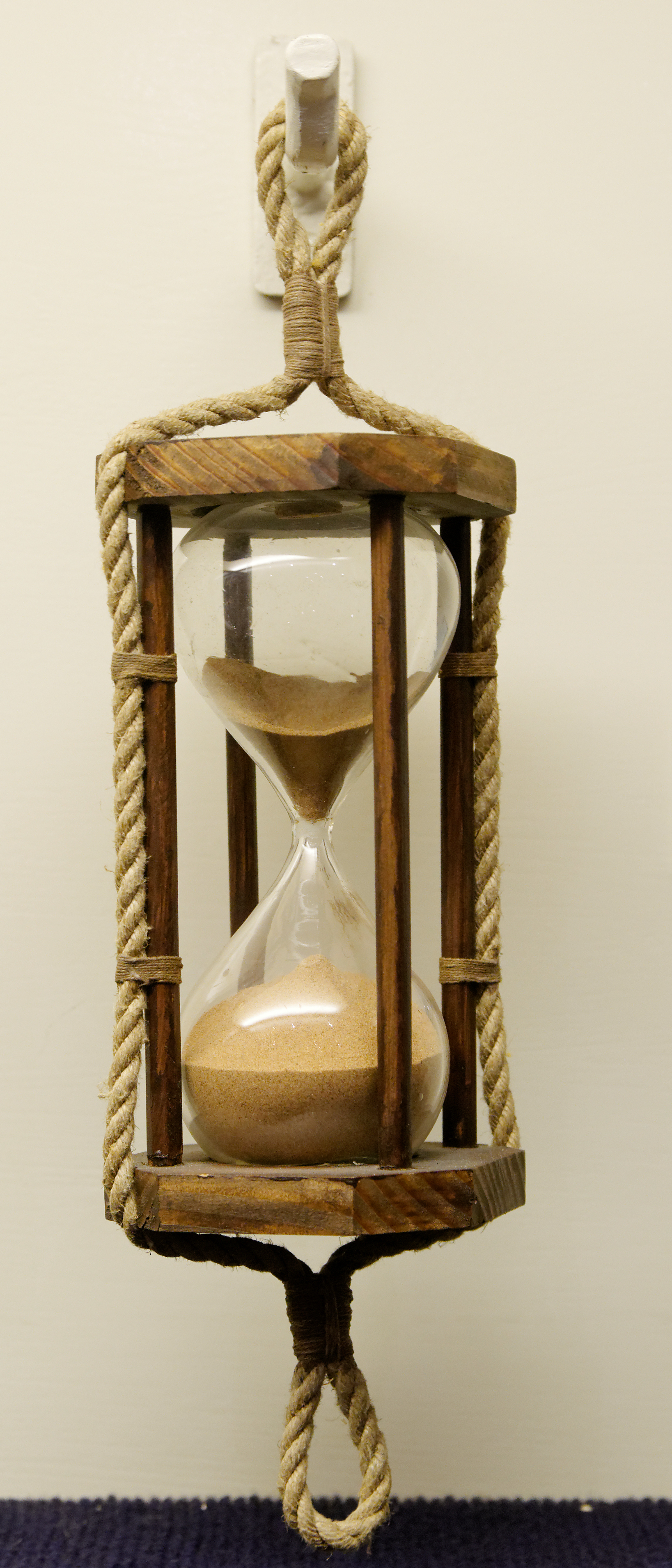
The hourglass was one of the few reliable methods of measuring time at sea, and it has been speculated that it was used on board ships as far back as the 11th century, when it would have complemented the
The 12th century Muslim inventor Al-Jazari described four different designs for a candle clock in his book ''The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices'' (). His so-called 'scribe' candle clock was invented to mark the passing of 14 hours of equal length: a precisely engineered mechanism caused a candle of specific dimensions to be slowly pushed upwards, which caused an indicator to move along a scale. Every hour a small ball emerged from the beak of a bird.
The hourglass was one of the few reliable methods of measuring time at sea, and it has been speculated that it was used on board ships as far back as the 11th century, when it would have complemented the
 The first innovations to improve on the accuracy of the hourglass and the water clock occurred in the 10th century, when attempts were made to slow their rate of flow using
The first innovations to improve on the accuracy of the hourglass and the water clock occurred in the 10th century, when attempts were made to slow their rate of flow using
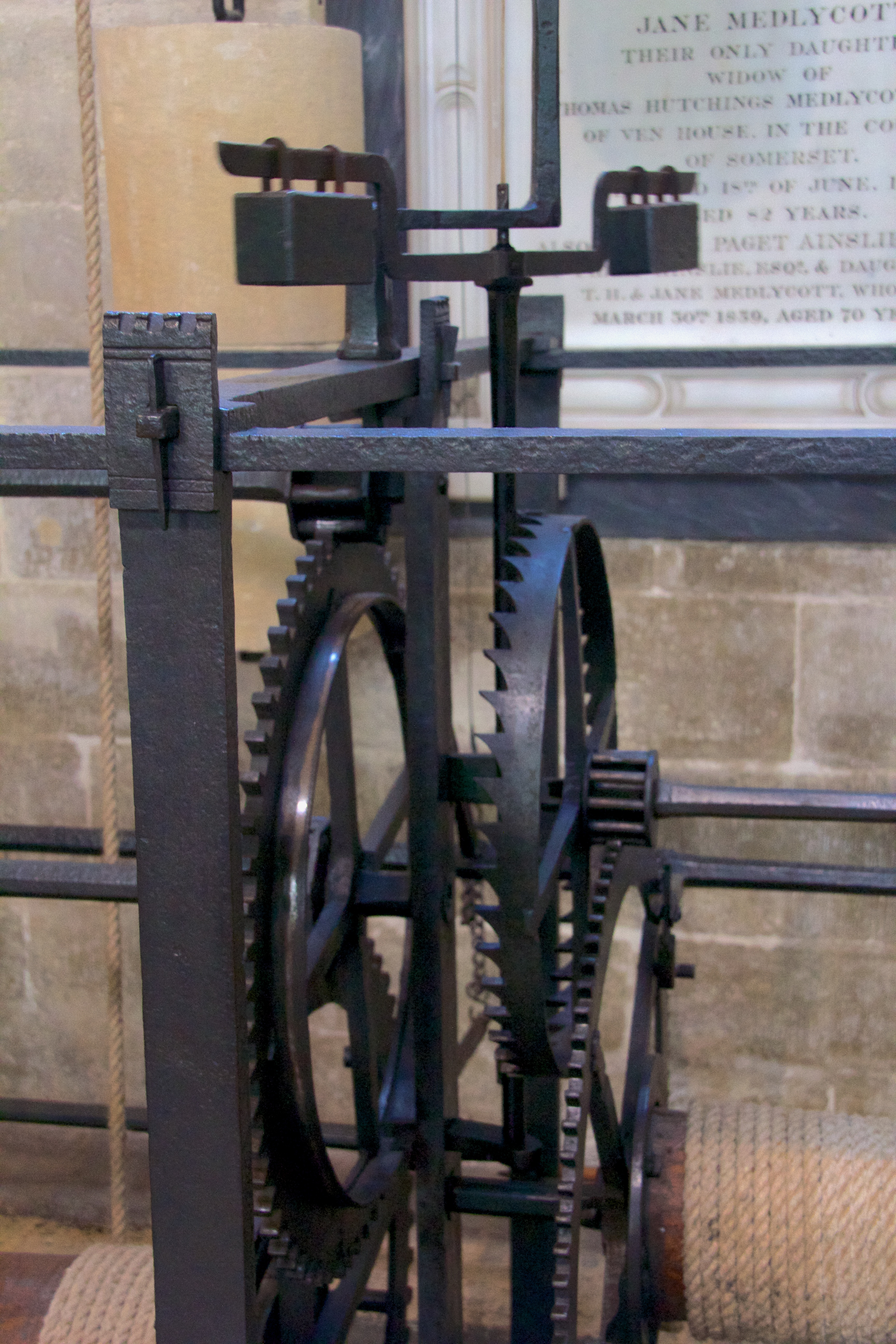 The invention of the verge and foliot escapement in 1275 was one of the most important inventions in both the history of the clock and the history of technology. It was the first type of regulator in
The invention of the verge and foliot escapement in 1275 was one of the most important inventions in both the history of the clock and the history of technology. It was the first type of regulator in
 The invention of the
The invention of the
 Huygens first used a clock to calculate the
Huygens first used a clock to calculate the  Any inherent errors in early pendulum clocks were smaller than other errors caused by factors such as temperature variation. In 1729 the Yorkshire carpenter and self-taught clockmaker
Any inherent errors in early pendulum clocks were smaller than other errors caused by factors such as temperature variation. In 1729 the Yorkshire carpenter and self-taught clockmaker
 In 1715, at the age of 22, Harrison had used his carpentry skills to construct a wooden eight-day clock. His clocks had innovations that included the use of wooden parts to remove the need for additional lubrication (and cleaning), rollers to reduce friction, a new kind of escapement, and the use of two different metals to reduce the problem of expansion caused by temperature variation.
He traveled to London to seek assistance from the Board of Longitude in making a sea clock. He was sent to visit Graham, who assisted Harrison by arranging to finance his work to build a clock. After 30 years, his device, now named "H1" was built and in 1736 it was tested at sea. Harrison then went on to design and make two other sea clocks, "H2" (completed in around 1739) and "H3", both of which were ready by 1755.
Harrison made two watches, "H4" and "H5". Eric Bruton, in his book ''The History of Clocks and Watches'', has described H4 as "probably the most remarkable timekeeper ever made". After the completion of its sea trials during the winter of 17611762 it was found that it was three times more accurate than was needed for Harrison to be awarded the Longitude prize.
In 1715, at the age of 22, Harrison had used his carpentry skills to construct a wooden eight-day clock. His clocks had innovations that included the use of wooden parts to remove the need for additional lubrication (and cleaning), rollers to reduce friction, a new kind of escapement, and the use of two different metals to reduce the problem of expansion caused by temperature variation.
He traveled to London to seek assistance from the Board of Longitude in making a sea clock. He was sent to visit Graham, who assisted Harrison by arranging to finance his work to build a clock. After 30 years, his device, now named "H1" was built and in 1736 it was tested at sea. Harrison then went on to design and make two other sea clocks, "H2" (completed in around 1739) and "H3", both of which were ready by 1755.
Harrison made two watches, "H4" and "H5". Eric Bruton, in his book ''The History of Clocks and Watches'', has described H4 as "probably the most remarkable timekeeper ever made". After the completion of its sea trials during the winter of 17611762 it was found that it was three times more accurate than was needed for Harrison to be awarded the Longitude prize.
Relativity Science Calculator – Philosophic Question: are clocks and time separable?
Ancient Discoveries Islamic Science Part 4
clip from ''History Repeating'' of Islamic time-keeping inventions (YouTube). {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Timekeeping Devices Timekeeping devices Timekeeping History of measurement History of timekeeping
 The history of timekeeping devices dates back to when ancient civilizations first observed
The history of timekeeping devices dates back to when ancient civilizations first observed astronomical bodies
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often us ...
as they moved across the sky. Devices and methods for keeping time have since then improved through a long series of new inventions and ideas. Sundials and water clock
A water clock or clepsydra (; ; ) is a timepiece by which time is measured by the regulated flow of liquid into (inflow type) or out from (outflow type) a vessel, and where the amount is then measured.
Water clocks are one of the oldest time- ...
s originated from ancient Egypt, and were later used by the Babylonians, the Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
and the Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
; medieval Islamic water clocks were unrivalled in their sophistication until the mid-14th century. Incense
Incense is aromatic biotic material that releases fragrant smoke when burnt. The term is used for either the material or the aroma. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, religious worship, aromatherapy, meditation, and ceremony. It may also b ...
clocks, which may have been invented in India, were being used in China by the 6th century. The hourglass, one of the few reliable methods of measuring time at sea, was a European invention and does not seem to have been used in China before the mid-16th century.
In medieval Europe, purely mechanical clocks were developed after the invention of the bell-striking alarm, used to warn a man to toll the monastic
Monasticism (from Ancient Greek , , from , , 'alone'), also referred to as monachism, or monkhood, is a religion, religious way of life in which one renounces world (theology), worldly pursuits to devote oneself fully to spiritual work. Monastic ...
bell. The weight-driven mechanical clock, controlled by the action of a verge and foliot
The verge (or crown wheel) escapement is the earliest known type of mechanical escapement, the mechanism in a mechanical clock that controls its rate by allowing the gear train to advance at regular intervals or 'ticks'. Its origin is unknown. V ...
, was a synthesis of earlier ideas derived from European and Islamic science, and one of the most important inventions in the history of timekeeping. The most famous mechanical clock was designed and built by Henry de Vick in 1360—for the next 300 years, all the improvements in timekeeping were essentially developments based on it. The invention of the mainspring
A mainspring is a spiral torsion spring of metal ribbon—commonly spring steel—used as a power source in mechanical watches, some clocks, and other clockwork mechanisms. ''Winding'' the timepiece, by turning a knob or key, stores energy in ...
in the early 15th century allowed small clocks to be built for the first time.
From the 17th century, the discovery that clocks could be controlled by harmonic oscillators led to the most productive era in the history of timekeeping. Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially res ...
had produced the earliest known drawings of a pendulum
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting, equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward th ...
in 14931494, and in 1582 Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He wa ...
had investigated the regular swing of the pendulum, discovering that frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
was only dependent on length. The pendulum clock
A pendulum clock is a clock that uses a pendulum, a swinging weight, as its timekeeping element. The advantage of a pendulum for timekeeping is that it is a harmonic oscillator: It swings back and forth in a precise time interval dependent on i ...
, designed and built by Dutch polymath Christiaan Huygens in 1656, was so much more accurate than other kinds of mechanical timekeepers that few clocks have survived with their verge and foliot mechanisms intact. Other innovations in timekeeping during this period include inventions for striking clocks, the repeating clock and the deadbeat escapement
In horology, the anchor escapement is a type of escapement used in pendulum clocks. The escapement is a mechanism in a mechanical clock that maintains the swing of the pendulum by giving it a small push each swing, and allows the clock's wheels ...
. Errors in early pendulum clocks were eclipsed by those caused by temperature variation, a problem tackled during the 18th century by the English clockmakers John Harrison
John Harrison ( – 24 March 1776) was a self-educated English carpenter and clockmaker who invented the marine chronometer, a long-sought-after device for solving the problem of calculating longitude while at sea.
Harrison's solution revol ...
and George Graham
George Graham (born 30 November 1944), nicknamed "Stroller", is a Scottish former Association football, football player and manager (association football), manager.
In his successful playing career, he made 455 appearances in England's Football ...
; only the invention of invar
Invar, also known generically as FeNi36 (64FeNi in the US), is a nickel–iron alloy notable for its uniquely low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE or α). The name ''Invar'' comes from the word ''invariable'', referring to its relative lac ...
in 1895 eliminated the need for such innovations.
From the 18th century, a succession of innovations and inventions led to timekeeping devices becoming increasingly accurate. Following the Scilly naval disaster of 1707
The Scilly naval disaster of 1707 was the loss of four warships of a Royal Navy fleet off the Isles of Scilly in severe weather on 22 October 1707. Between 1,400 and 2,000 sailors lost their lives aboard the wrecked vessels, making the incident ...
, after which governments offered a prize
A prize is an award to be given to a person or a group of people (such as sporting teams and organizations) to recognize and reward their actions and achievements.
to anyone who could discover a way to determine longitude, Harrison built a succession of accurate timepieces. The electric clock, invented in 1840, was used to control the most accurate pendulum clocks until the 1940s, when quartz timers became the basis for the precise measurement of time and frequency. The wristwatch, which had been recognised as a valuable military tool during the Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the Sou ...
, became a symbol of masculinity and bravado after World War I. During the 20th century the non-magnetic wristwatch
A watch is a portable timepiece intended to be carried or worn by a person. It is designed to keep a consistent movement despite the motions caused by the person's activities. A wristwatch is designed to be worn around the wrist, attached by ...
, battery-driven watches, the quartz wristwatch, and transistors
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
and plastic parts were all invented. The most accurate timekeeping devices in practical use today are atomic clock
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions betwe ...
s, which can be accurate to within a few billionths of a second per year. They are used to calibrate other clocks and timekeeping instruments.
Continuous timekeeping devices
Ancient civilizations observedastronomical bodies
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often us ...
, often the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
and Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
, to determine time. According to the historian Eric Bruton, Stonehenge is likely to have been the Stone Age equivalent of an astronomical observatory, used to seasonal and annual events such as equinox
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun crosses the Earth's equator, which is to say, appears directly above the equator, rather than north or south of the equator. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise "due east" and se ...
es or solstice
A solstice is an event that occurs when the Sun appears to reach its most northerly or southerly excursion relative to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. Two solstices occur annually, around June 21 and December 21. In many countr ...
s. As megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The ...
ic civilizations left no recorded history, little is known of their timekeeping methods.
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica ...
ns modified their usual vigesimal (base-20) counting system when dealing with calendars to produce a 360-day year. The Aboriginal Australians
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Isl ...
understood the movement of objects in the sky well, and used their knowledge to construct calendars and aid navigation; most Aboriginal cultures had seasons that were well-defined and determined by natural changes throughout the year, including celestial events. Lunar phases
Concerning the lunar month of ~29.53 days as viewed from Earth, the lunar phase or Moon phase is the shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion, which can be expressed quantitatively using areas or angles, or described qualitatively using the t ...
were used to mark shorter periods of time; the Yaraldi of South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
being one of the few people recorded as having a way to measure time during the day, which was divided into seven parts using the position of the Sun.
All timekeepers before the 13th century relied upon methods that used something that moved continuously. No early method of keeping time changed at a steady rate. Devices and methods for keeping time have improved continuously through a long series of new inventions and ideas.
Shadow clocks and sundials
 The first devices used for measuring the position of the Sun were shadow clocks, which later developed into the sundial. Egyptian
The first devices used for measuring the position of the Sun were shadow clocks, which later developed into the sundial. Egyptian obelisks
An obelisk (; from grc, ὀβελίσκος ; diminutive of ''obelos'', " spit, nail, pointed pillar") is a tall, four-sided, narrow tapering monument which ends in a pyramid-like shape or pyramidion at the top. Originally constructed by An ...
, constructed BC, are among the earliest shadow clocks. The oldest of all known sundials dates back to BC (during the 19th Dynasty), and was discovered in the Valley of the Kings
The Valley of the Kings ( ar, وادي الملوك ; Late Coptic: ), also known as the Valley of the Gates of the Kings ( ar, وادي أبوا الملوك ), is a valley in Egypt where, for a period of nearly 500 years from the 16th to 11th ...
in 2013. Obelisks could indicate whether it was morning or afternoon, as well as the summer and winter solstice
The winter solstice, also called the hibernal solstice, occurs when either of Earth's poles reaches its maximum tilt away from the Sun. This happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere (Northern and Southern). For that hemisphere, the winter ...
s. A kind of shadow clock was developed BC that was similar in shape to a bent T-square
A T-square is a technical drawing instrument used by draftsmen primarily as a guide for drawing horizontal lines on a drafting table. The instrument is named after its resemblance to the letter T, with a long shaft called the "blade" and a sh ...
. It measured the passage of time by the shadow cast by its crossbar, and was oriented eastward in the mornings, and turned around at noon, so it could cast its shadow in the opposite direction.
A sundial is referred to in the Bible, in 2 Kings 20:911, when Hezekiah
Hezekiah (; hbo, , Ḥīzqīyyahū), or Ezekias); grc, Ἐζεκίας 'Ezekías; la, Ezechias; also transliterated as or ; meaning "Yahweh, Yah shall strengthen" (born , sole ruler ), was the son of Ahaz and the 13th king of Kingdom of Jud ...
, king of Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous sou ...
during the 8th century BC, is recorded as being healed by the prophet Isaiah
Isaiah ( or ; he, , ''Yəšaʿyāhū'', "God is Salvation"), also known as Isaias, was the 8th-century BC Israelite prophet after whom the Book of Isaiah is named.
Within the text of the Book of Isaiah, Isaiah himself is referred to as "the ...
and asks for a sign that he would recover:
A clay tablet
In the Ancient Near East, clay tablets ( Akkadian ) were used as a writing medium, especially for writing in cuneiform, throughout the Bronze Age and well into the Iron Age.
Cuneiform characters were imprinted on a wet clay tablet with a sty ...
from the late Babylonian period describes the lengths of shadows at different times of the year. The Babylonian writer Berossos () is credited by the Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
with the invention of a hemispherical sundial hollowed out of stone; the path of the shadow was divided into 12 parts to mark the time. Greek sundials evolved to become highly sophisticated—Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
's ''Analemma'', written in the 2nd century AD, used an early form of trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies ...
to derive the position of the sun from data such as the hour of day and the geographical latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
.
The Romans borrowed the idea of the sundial from the Greeks. The military commander Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
recorded that the first sundial in Rome arrived in 264 BC, looted from Catania in Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
; according to him, it gave the incorrect time for a century, until the markings and angle appropriate for Rome's latitude were used.
According to the German historian of astronomy Ernst Zinner
Ernst Zinner (2 February 1886 in Goldberg, Silesia – 30 August 1970) was a German astronomer and noted historian of astronomy. After studies in Munich and Jena he obtained his PhD in 1907 at the University of Jena, followed by stays at ...
, sundials were developed during the 13th century with scales that showed equal hours. The first based on polar time appeared in Germany ; an alternative theory proposes that a Damascus sundial measuring in polar time can be dated to 1372. European treatises on sundial design appeared .
An Egyptian method of determining the time during the night, used from at least 600 BC, was a type of plumb-line called a merkhet. A north–south meridian
Meridian or a meridian line (from Latin ''meridies'' via Old French ''meridiane'', meaning “midday”) may refer to
Science
* Meridian (astronomy), imaginary circle in a plane perpendicular to the planes of the celestial equator and horizon
* ...
was created using two merkhets aligned with Polaris, the north pole star
A pole star or polar star is a star, preferably bright, nearly aligned with the axis of a rotating astronomical body.
Currently, Earth's pole stars are Polaris (Alpha Ursae Minoris), a bright magnitude-2 star aligned approximately with its ...
. The time was determined by observing particular stars as they crossed the meridian.
Water clocks
The oldest description of a clepsydra, orwater clock
A water clock or clepsydra (; ; ) is a timepiece by which time is measured by the regulated flow of liquid into (inflow type) or out from (outflow type) a vessel, and where the amount is then measured.
Water clocks are one of the oldest time- ...
, is from the tomb inscription of an early 18th Dynasty ( BC) Egyptian court official named Amenemhet, who is identified as its inventor. It is assumed that the object described on the inscription is a bowl with markings to indicate the time. The oldest surviving water clock was found in the tomb of pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the ...
Amenhotep III ( 14171379 BC). There are no recognised examples in existence of outflowing water clocks from ancient Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
, but written references have survived.
The introduction of the water clock to China, perhaps from Mesopotamia, occurred as far back as the 2nd millennium BC, during the Shang Dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and ...
, and at the latest by the 1st millennium BC. Around 550 AD, Yin Gui was the first in China to write of the overflow or constant-level tank. Around 610, two Sui Dynasty inventors, Geng Xun and Yuwen Kai, created the first balance clepsydra, with standard positions for the steelyard balance
A steelyard balance, steelyard, or stilyard is a straight-beam balance with arms of unequal length. It incorporates a counterweight which slides along the longer arm to counterbalance the load and indicate its weight. A steelyard is also known as ...
. In 721 the mathematician Yi Xing
Yi Xing (, 683–727), born Zhang Sui (), was a Chinese astronomer, Buddhist monk, inventor, mathematician, mechanical engineer, and philosopher during the Tang dynasty. His astronomical celestial globe featured a liquid-driven escapement, the ...
and government official Liang Lingzan
Liang Lingzan () was a Chinese artist, astronomer, inventor, mechanical engineer and politician of the Kaiyuan era during the Tang Dynasty. He invented a mechanized water clock with the Tantric monk and mathematician Yi Xing (). It was actually a ...
regulated the power of the water driving an astronomical clock
An astronomical clock, horologium, or orloj is a clock with special mechanisms and dials to display astronomical information, such as the relative positions of the Sun, Moon, zodiacal constellations, and sometimes major planets.
Definition ...
, dividing the power into unit impulses so that motion of the planets and stars could be duplicated. In 976, the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
astronomer Zhang Sixun
Zhang Sixun (, fl. 10th century) was a Chinese astronomer and mechanical engineer from Bazhong, Sichuan during the early Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD).Liu, 577. He is credited with creating an armillary sphere for his astronomical clock tower that ...
addressed the problem of the water in clepsydrae freezing in cold weather when he replaced the water with liquid mercury. A water-powered astronomical clock tower was built by the polymath Su Song in 1088, which featured the first known endless power-transmitting chain drive.
 The
The Greek philosophers
Ancient Greek philosophy arose in the 6th century BC, marking the end of the Greek Dark Ages. Greek philosophy continued throughout the Hellenistic period and the period in which Greece and most Greek-inhabited lands were part of the Roman Empire ...
Anaxagoras and Empedocles
Empedocles (; grc-gre, Ἐμπεδοκλῆς; , 444–443 BC) was a Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a native citizen of Akragas, a Greek city in Sicily. Empedocles' philosophy is best known for originating the cosmogonic theory of the ...
both referred to water clocks that were used to enforce time limits or measure the passing of time. The Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
philosopher Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
is supposed to have invented an alarm clock that used lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
balls cascading noisily onto a copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
platter to wake his students.
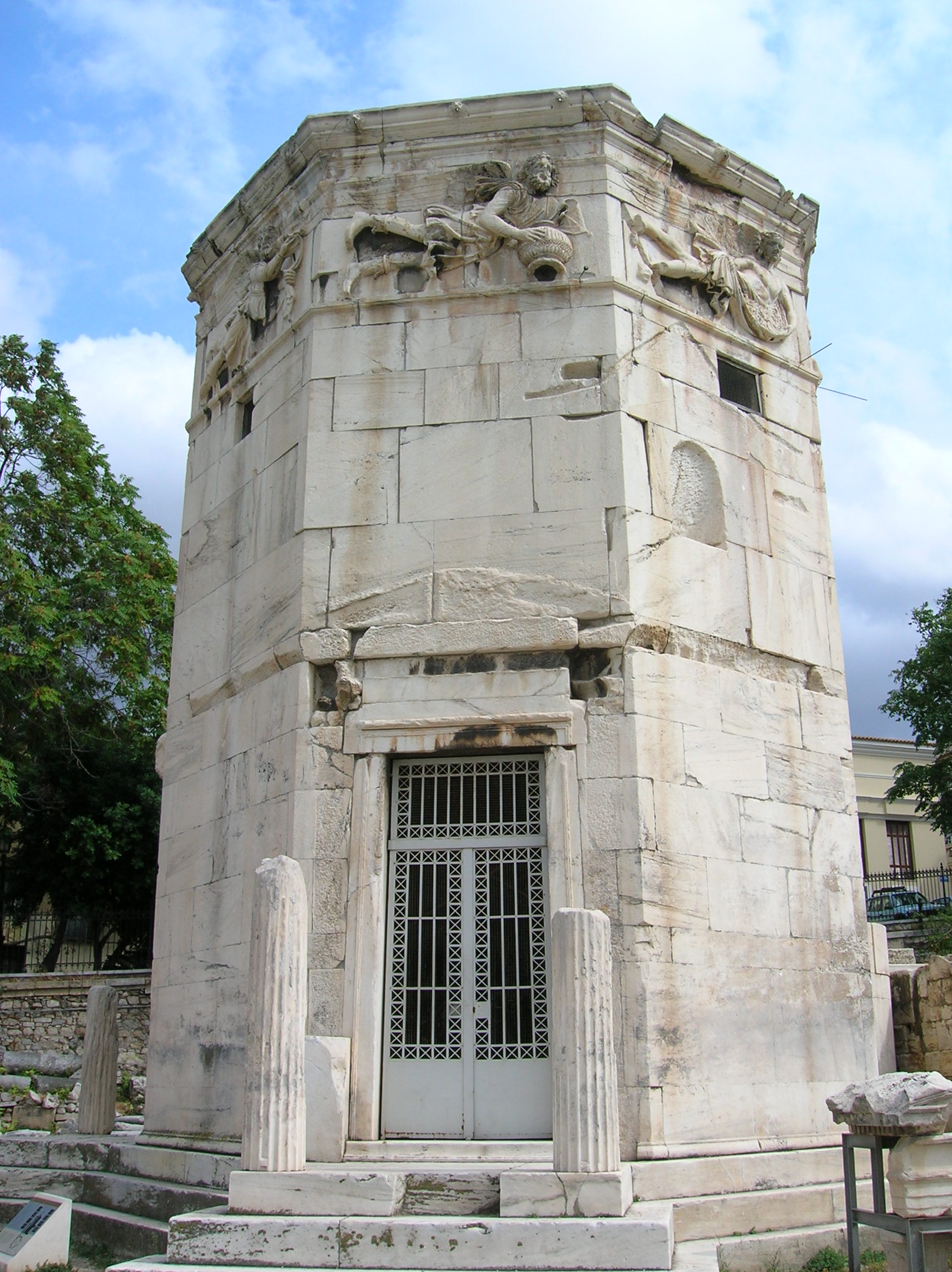
A problem with most clepsydrae was the variation in the flow of water due to the change in fluid pressure, which was addressed from 100 BC when the clock's water container was given a conical shape. They became more sophisticated when innovations such as gongs and moving mechanisms were included. There is evidence that the 1st century BC Tower of the Winds
The Tower of the Winds or the Horologion of Andronikos Kyrrhestes is an octagonal Pentelic marble clocktower in the Roman Agora in Athens that functioned as a ''horologion'' or "timepiece". It is considered the world's first meteorological stat ...
in Athens once had eight sundials, a water clock, and a wind vane. In Greek tradition, clepsydrae were used in court
A court is any person or institution, often as a government institution, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and carry out the administration of justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in acco ...
, a practise later adopted by the Ancient Romans
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 ...
.
The first geared clock, invented in the 11th century by the Arab engineer Ibn Khalaf al-Muradi
Ibn Khalaf al-Murādī, (; 11th century) was an Andalusian engineer.
Al-Murādī was the author of the technological manuscript entitled ''Kitāb al-asrār fī natā'ij al-afkār'' ('', The Book of Secrets in the Results of Thoughts'' or ''The ...
in Islamic Iberia
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label=Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the Mus ...
, was a water clock that employed both segmental and epicyclic gearing
An epicyclic gear train (also known as a planetary gearset) consists of two gears mounted so that the center of one gear revolves around the center of the other. A carrier connects the centers of the two gears and rotates the planet and sun gea ...
. Islamic water clocks, which used complex gear train
A gear train is a mechanical system formed by mounting gears on a frame so the teeth of the gears engage.
Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, providing a smooth transmission ...
s and included arrays of automata
An automaton (; plural: automata or automatons) is a relatively self-operating machine, or control mechanism designed to automatically follow a sequence of operations, or respond to predetermined instructions.Automaton – Definition and More ...
, were unrivalled in their sophistication until the mid-14th century. Liquid-driven mechanisms (using heavy floats and a constant-head system) were developed that enabled water clocks to work at a slower rate.
The 12th-century Jayrun Water Clock at the Umayyad Mosque
The Umayyad Mosque ( ar, الجامع الأموي, al-Jāmiʿ al-Umawī), also known as the Great Mosque of Damascus ( ar, الجامع الدمشق, al-Jāmiʿ al-Damishq), located in the old city of Damascus, the capital of Syria, is one of the ...
in Damascus was constructed by Muhammad al-Sa'ati, and was later described by his son Ridwan ibn al-Sa'ati in his ''On the Construction of Clocks and their Use'' (1203). A sophisticated water-powered astronomical clock was described by Al-Jazari in his treatise on machines, written in 1206. This castle clock
Clock towers are a specific type of structure which house a turret clock and have one or more clock faces on the upper exterior walls. Many clock towers are freestanding structures but they can also adjoin or be located on top of another buildi ...
was about high, and included a display of the zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in celestial latitude) of the ecliptic, the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The pat ...
and the solar and lunar paths, and doors that opened on the hour, to reveal a mannequin
A mannequin (also called a dummy, lay figure, or dress form) is a doll, often articulated, used by artists, tailors, dressmakers, window dressers and others, especially to display or fit clothing and show off different fabrics and textiles. P ...
. In 1235, a water-powered clock that "announced the appointed hours of prayer and the time both by day and by night" stood in the entrance hall of the Mustansiriya Madrasah in Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
.
Chinese incense clocks
 Incense clocks were first used in China around the 6th century, mainly for religious purposes, but also for social gatherings or by scholars. Due to their frequent use of
Incense clocks were first used in China around the 6th century, mainly for religious purposes, but also for social gatherings or by scholars. Due to their frequent use of Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; , , Sanskrit pronunciation: ), also called Nagari (),Kathleen Kuiper (2010), The Culture of India, New York: The Rosen Publishing Group, , page 83 is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental writing system), based on the ...
characters, American sinologist Edward H. Schafer has speculated that incense clocks were invented in India. As incense burns evenly and without a flame, the clocks were safe for indoor use. To mark different hours, differently scented incenses (made from different recipes) were used.
The incense stick
Incense is aromatic biotic material that releases fragrant smoke when burnt. The term is used for either the material or the aroma. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, religious worship, aromatherapy, meditation, and ceremony. It may also be ...
s used could be straight or spiralled; the spiralled ones were intended for long periods of use, and often hung from the roofs of homes and temples. Some clocks were designed to drop weights at even intervals,
Incense seal clocks had a disk etched with one or more grooves, into which incense was placed. The length of the trail of incense, directly related to the size of the seal, was the primary factor in determining how long the clock would last; to burn 12 hours an incense path of around has been estimated. The gradual introduction of metal disks, most likely beginning during the Song dynasty, allowed craftsmen to more easily create seals of different sizes, design and decorate them more aesthetically, and vary the paths of the grooves, to allow for the changing length of the days in the year. As smaller seals became available, incense seal clocks grew in popularity and were often given as gifts.
Astrolabes
Sophisticated timekeeping astrolabes with geared mechanisms were made in Persia. Examples include those built by the polymath Abū Rayhān Bīrūnī in the 11th century and the astronomer Muhammad ibn Abi Bakr al‐Farisi in 1221. Abrass
Brass is an alloy of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), in proportions which can be varied to achieve different mechanical, electrical, and chemical properties. It is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other wit ...
and silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
astrolabe (which also acts as a calendar) made in Isfahan by al‐Farisi is the earliest surviving machine with its gears still intact. Openings on the back of the astrolabe depict the lunar phases and gives the Moon's age; within a zodiacal scale are two concentric rings that show the relative positions of the Sun and the Moon.
Muslim astronomers constructed a variety of highly accurate astronomical clocks for use in their mosques and observatories
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysical, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. His ...
, such as the astrolabic clock by Ibn al-Shatir in the early 14th century.
Candle clocks and hourglasses
One of the earliest references to a candle clock is in a Chinese poem, written in 520 by You Jianfu, who wrote of the graduated candle being a means of determining time at night. Similar candles were used in Japan until the early 10th century. The invention of the candle clock was attributed by theAnglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
to Alfred the Great, king of Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
, who used six candles marked at intervals of , each made from 12 pennyweight
A pennyweight (dwt) is a unit of mass equal to 24 grains, of a troy ounce, of a troy pound, approximately 0.054857 avoirdupois ounce and exactly 1.55517384 grams. It is abbreviated dwt, ''d'' standing for ''denarius'' (an ancien ...
s of wax, and made to be high and of a uniform thickness.
 The 12th century Muslim inventor Al-Jazari described four different designs for a candle clock in his book ''The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices'' (). His so-called 'scribe' candle clock was invented to mark the passing of 14 hours of equal length: a precisely engineered mechanism caused a candle of specific dimensions to be slowly pushed upwards, which caused an indicator to move along a scale. Every hour a small ball emerged from the beak of a bird.
The hourglass was one of the few reliable methods of measuring time at sea, and it has been speculated that it was used on board ships as far back as the 11th century, when it would have complemented the
The 12th century Muslim inventor Al-Jazari described four different designs for a candle clock in his book ''The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices'' (). His so-called 'scribe' candle clock was invented to mark the passing of 14 hours of equal length: a precisely engineered mechanism caused a candle of specific dimensions to be slowly pushed upwards, which caused an indicator to move along a scale. Every hour a small ball emerged from the beak of a bird.
The hourglass was one of the few reliable methods of measuring time at sea, and it has been speculated that it was used on board ships as far back as the 11th century, when it would have complemented the compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself wit ...
as an aid to navigation. The earliest unambiguous evidence of the use an hourglass appears in the painting '' Allegory of Good Government'', by the Italian artist Ambrogio Lorenzetti
Ambrogio Lorenzetti (; – 9 June 1348) or Ambruogio Laurati was an Italian painter of the Sienese school. He was active from approximately 1317 to 1348. He painted '' The Allegory of Good and Bad Government'' in the Sala dei Nove (Salon of Nin ...
, from 1338.
The Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
navigator Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the Eas ...
used 18 hourglasses on each ship during his circumnavigation of the globe in 1522. Though used in China, the hourglass's history there is unknown, but does not seem to have been used before the mid-16th century, as the hourglass implies the use of glassblowing
Glassblowing is a glassforming technique that involves inflating molten glass into a bubble (or parison) with the aid of a blowpipe (or blow tube). A person who blows glass is called a ''glassblower'', ''glassmith'', or ''gaffer''. A '' lampworke ...
, then an entirely European and Western art.
From the 15th century onwards, hourglasses were used in a wide range of applications at sea, in churches, in industry, and in cooking; they were the first dependable, reusable, reasonably accurate, and easily constructed time-measurement devices. The hourglass took on symbolic meanings, such as that of death, temperance
Temperance may refer to:
Moderation
*Temperance movement, movement to reduce the amount of alcohol consumed
*Temperance (virtue), habitual moderation in the indulgence of a natural appetite or passion
Culture
*Temperance (group), Canadian danc ...
, opportunity, and Father Time
Father Time is a personification of time. In recent centuries he is usually depicted as an elderly bearded man, sometimes with wings, dressed in a robe and carrying a scythe and an hourglass or other timekeeping device.
As an image, "Father Ti ...
, usually represented as a bearded, old man.
History of early oscillating devices in timekeepers
The English word ''clock'' first appeared inMiddle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English ...
as , , or . The origin of the word is not known for certain; it may be a borrowing from French or Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, and can perhaps be traced to the post-classical Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
('bell'). 7th century Irish and 9th century Germanic sources recorded ''clock'' as meaning 'bell'.
Judaism, Christianity and Islam all had times set aside for prayer, although Christians alone were expected to attend prayers at specific hours of the day and night—what the historian Jo Ellen Barnett describes as "a rigid adherence to repetitive prayers said many times a day". The bell-striking alarms warned the monk
A monk (, from el, μοναχός, ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a person who practices religious asceticism by monastic living, either alone or with any number of other monks. A monk may be a person who decides to dedica ...
on duty to toll the monastic
Monasticism (from Ancient Greek , , from , , 'alone'), also referred to as monachism, or monkhood, is a religion, religious way of life in which one renounces world (theology), worldly pursuits to devote oneself fully to spiritual work. Monastic ...
bell. His alarm was a timer that used a form of escapement to ring a small bell. This mechanism was the forerunner of the escapement device found in the mechanical clock.
13th century
 The first innovations to improve on the accuracy of the hourglass and the water clock occurred in the 10th century, when attempts were made to slow their rate of flow using
The first innovations to improve on the accuracy of the hourglass and the water clock occurred in the 10th century, when attempts were made to slow their rate of flow using friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:
*Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of ...
or the force of gravity. The earliest depiction of a clock powered by a hanging weight is from the Bible of St Louis
The Bible of St Louis, also called the Rich Bible of Toledo or simply the Toledo Bible, is a ''Bible moralisée'' in three volumes, made between 1226 and 1234 for King Louis IX of France (b. 1214) at the request of his mother Blanche of Castile. I ...
, an illuminated manuscript that shows a clock being slowed by water acting on a wheel. The illustration seems to show that weight-driven clocks were invented in western Europe. A treatise written by Robertus Anglicus in 1271 shows that medieval craftsmen were attempting to design a purely mechanical clock (i.e. only driven by gravity) during this period. Such clocks were a synthesis of earlier ideas derived from European and Islamic science, such as gearing systems, weight drives, and striking mechanisms.
In 1250, the artist Villard de Honnecourt
Villard de Honnecourt (''Wilars dehonecort'', ''Vilars de Honecourt'') was a 13th-century artist from Picardy in northern France. He is known to history only through a surviving portfolio or "sketchbook" containing about 250 drawings and designs ...
illustrated a device that was the step towards the development of the escapement
An escapement is a mechanical linkage in mechanical watches and clocks that gives impulses to the timekeeping element and periodically releases the gear train to move forward, advancing the clock's hands. The impulse action transfers energy ...
. Another forerunner of the escapement was the , which used an early kind of verge mechanism to operate a knocker that continuously struck a bell. The weight-driven clock was probably a Western European invention, as a picture of a clock shows a weight pulling an axle around, its motion slowed by a system of holes that slowly released water. In 1271, the English astronomer Robertus Anglicus wrote of his contemporaries that they were in the process of developing a form of mechanical clock.
14th century
 The invention of the verge and foliot escapement in 1275 was one of the most important inventions in both the history of the clock and the history of technology. It was the first type of regulator in
The invention of the verge and foliot escapement in 1275 was one of the most important inventions in both the history of the clock and the history of technology. It was the first type of regulator in horology
Horology (; related to Latin '; ; , interfix ''-o-'', and suffix ''-logy''), . is the study of the measurement of time. Clocks, watches, clockwork, sundials, hourglasses, clepsydras, timers, time recorders, marine chronometers, and atomic clo ...
. A verge, or vertical shaft, is forced to rotate by a weight-driven crown wheel, but is stopped from rotating freely by a foliot. The foliot, which cannot vibrate freely, swings back and forth, which allows a wheel to rotate one tooth at a time. Although the verge and foliot was an advancement on previous timekeepers, it was impossible to avoid fluctuations in the beat caused by changes in the applied forces—the earliest mechanical clocks were regularly reset using a sundial.
At around the same time as the invention of the escapement, the Florentine poet Dante Alighieri
Dante Alighieri (; – 14 September 1321), probably baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante (, ), was an Italian poet, writer and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', originally called (modern Italian: '' ...
used clock imagery to depict the souls of the blessed in '' Paradiso'', the third part of the ''Divine Comedy
The ''Divine Comedy'' ( it, Divina Commedia ) is an Italian narrative poem by Dante Alighieri, begun 1308 and completed in around 1321, shortly before the author's death. It is widely considered the pre-eminent work in Italian literature ...
'', written in the early part of the 14th century. It may be the first known literary description of a mechanical clock. There are references to house clocks from 1314 onwards; by 1325 the development of the mechanical clock can be assumed to have occurred.
Large mechanical clocks were built that were mounted in towers so as to ring the bell directly. The tower clock of Norwich Cathedral (constructed 1321 1325) is the earliest such large clock known. The clock has not survived. The first clock known to strike regularly on the hour, a clock with a verge and foliot mechanism, is recorded in Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
in 1336. By 1341, clocks driven by weights were familiar enough to be able to be adapted for grain mills
Mills is the plural form of mill, but may also refer to:
As a name
* Mills (surname), a common family name of English or Gaelic origin
* Mills (given name)
*Mills, a fictional British secret agent in a trilogy by writer Manning O'Brine
Places Uni ...
, and by 1344 the clock in London's Old St Paul's Cathedral had been replaced by one with an escapement. The foliot was first illustrated by Dondi in 1364, and mentioned by the court historian Jean Froissart
Jean Froissart (Old and Middle French: ''Jehan'', – ) (also John Froissart) was a French-speaking medieval author and court historian from the Low Countries who wrote several works, including ''Chronicles'' and ''Meliador'', a long Arthurian ...
in 1369.
The most famous example of a timekeeping device during the medieval period was a clock designed and built by the clockmaker Henry de Vick in 1360, which was said to have varied by up to two hours a day. For the next 300 years, all the improvements in timekeeping were essentially developments based on the principles of de Vick's clock. Between 1348 and 1364, Giovanni Dondi dell'Orologio
Giovanni Dondi dell'Orologio (c. 1330 – 1388), also known as Giovanni de' Dondi, was an Italian physician, astronomer and mechanical engineer in Padua, now in Italy. He is remembered today as a pioneer in the art of clock design and construct ...
, the son of Jacopo Dondi, built a complex astrarium
An astrarium, also called a planetarium, is the mechanical representation of the cyclic nature of astronomical objects in one timepiece. It is an astronomical clock.
History Greek and Roman World
The first astraria were mechanical devices. Archi ...
in Florence.
During the 14th century, striking clocks appeared with increasing frequency in public spaces, first in Italy, slightly later in France and England—between 1371 and 1380, public clocks were introduced in over 70 European cites. Salisbury Cathedral clock, dating from about 1386, is one of the oldest working clocks in the world, and may be the oldest; it still has most of its original parts. The Wells Cathedral clock
The Wells Cathedral clock is an astronomical clock in the north transept of Wells Cathedral, England. The clock is one of the group of famous 14th to 16th century astronomical clocks to be found in the West of England. The surviving mechanism, ...
, built in 1392, is unique in that it still has its original medieval face. Above the clock are figures which hit the bells, and a set of jousting knights who revolve around a track every 15 minutes.
Later developments
 The invention of the
The invention of the mainspring
A mainspring is a spiral torsion spring of metal ribbon—commonly spring steel—used as a power source in mechanical watches, some clocks, and other clockwork mechanisms. ''Winding'' the timepiece, by turning a knob or key, stores energy in ...
in the early 15th century—a device first used in locks and for flintlocks
Flintlock is a general term for any firearm that uses a flint-striking ignition mechanism, the first of which appeared in Western Europe in the early 16th century. The term may also apply to a particular form of the mechanism itself, also known ...
in guns— allowed small clocks to be built for the first time. The need for an escapement mechanism that steadily controlled the release of the stored energy, led to the development of two devices, the stackfreed (which although invented in the 15th century can be documented no earlier than 1535) and the fusee, which first originated from medieval weapons such as the crossbow
A crossbow is a ranged weapon using an elastic launching device consisting of a bow-like assembly called a ''prod'', mounted horizontally on a main frame called a ''tiller'', which is hand-held in a similar fashion to the stock of a long fire ...
. There is a fusee in the earliest surviving spring-driven clock, a chamber clock made for Philip the Good in 1430. Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially res ...
, who produced the earliest known drawings of a pendulum in 14931494, illustrated a fusee in 1500, a quarter of a century after the coiled spring first appeared.
Clock towers in Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
in the Middle Ages struck the time. Early clock dials showed hours; a clock with a minutes dial is mentioned in a 1475 manuscript. During the 16th century, timekeepers became more refined and sophisticated, so that by 1577 the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe
Tycho Brahe ( ; born Tyge Ottesen Brahe; generally called Tycho (14 December 154624 October 1601) was a Danish astronomer, known for his comprehensive astronomical observations, generally considered to be the most accurate of his time. He was ...
was able to obtain the first of four clocks that measured in seconds, and in Nuremberg, the clockmaker Peter Henlein
Peter Henlein (also spelled Henle or Hele) (1485 - August 1542), a locksmith and clockmaker of Nuremberg, Germany, is often considered the inventor of the watch., p.31 He was one of the first craftsmen to make small ornamental portable clocks wh ...
was paid for making what is thought to have been the earliest example of a watch
A watch is a portable timepiece intended to be carried or worn by a person. It is designed to keep a consistent movement despite the motions caused by the person's activities. A wristwatch is designed to be worn around the wrist, attached b ...
, made in 1524. By 1500, the use of the foliot in clocks had begun to decline. The oldest surviving spring-driven clock is a device made by in 1525. The first person to suggest travelling with a clock to determine longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lette ...
, in 1530, was the Dutch instrument maker Gemma Frisius
Gemma Frisius (; born Jemme Reinerszoon; December 9, 1508 – May 25, 1555) was a Frisian physician, mathematician, cartographer, philosopher, and instrument maker. He created important globes, improved the mathematical instruments of his d ...
. The clock would be set to the local time of a starting point whose longitude was known, and the longitude of any other place could be determined by comparing its local time with the clock time.
The Ottoman engineer Taqi ad-Din described a weight-driven clock with a verge-and-foliot escapement, a striking train of gears, an alarm, and a representation of the moon's phases in his book ''The Brightest Stars for the Construction of Mechanical Clocks'' (), written around 1556. Jesuit missionaries brought the first European clocks to China as gifts.
The Italian polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He wa ...
is thought to have first realised that the pendulum could be used as an accurate timekeeper after watching the motion of suspended lamps at Pisa Cathedral
Pisa Cathedral ( it, Cattedrale Metropolitana Primaziale di Santa Maria Assunta; Duomo di Pisa) is a medieval Roman Catholic cathedral dedicated to the Assumption of the Virgin Mary, in the Piazza dei Miracoli in Pisa, Italy, the oldest of the t ...
. In 1582, he investigated the regular swing of the pendulum
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting, equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward th ...
, and discovered that this was only dependent on its length. Galileo never constructed a clock based on his discovery, but prior to his death he dictated instructions for building a pendulum clock to his son, Vincenzo
Vincenzo is an Italian male given name, derived from the Latin name Vincentius (the verb ''vincere'' means to win or to conquer). Notable people with the name include:
Art
* Vincenzo Amato (born 1966), Italian actor and sculptor
*Vincenzo Bell ...
.
Era of precision timekeeping
Pendulum clocks
The first accurate timekeepers depended on the phenomenon known as harmonic motion, in which the restoring force acting on an object moved away from its equilibrium position—such as a pendulum or an extended spring—acts to return the object to that position, and causes it tooscillate
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
. Harmonic oscillators can be used as accurate timekeepers as the period of oscillation does not depend on the amplitude of the motion—and so it always takes the same time to complete one oscillation. The period of a harmonic oscillator is completely dependent on the physical characteristics of the oscillating system and not the starting conditions or the amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of am ...
.
The period when clocks were controlled by harmonic oscillators was the most productive era in timekeeping. The first invention of this type was the pendulum clock
A pendulum clock is a clock that uses a pendulum, a swinging weight, as its timekeeping element. The advantage of a pendulum for timekeeping is that it is a harmonic oscillator: It swings back and forth in a precise time interval dependent on i ...
, which was designed and built by Dutch polymath Christiaan Huygens in 1656. Early versions erred by less than one minute per day, and later ones only by 10 seconds, very accurate for their time. Dials that showed minutes and seconds became common after the increase in accuracy made possible by the pendulum clock. Brahe used clocks with minutes and seconds to observe stellar positions. The pendulum clock outperformed all other kinds of mechanical timekeepers to such an extent that these were usually refitted with a pendulum—a task that could be done without difficulty—so that few verge escapement devices have survived in their original form.
The first pendulum clocks used a verge escapement, which required wide swings of about 100° and so had short, light pendulums. The swing was reduced to around 6° after the invention of the anchor mechanism enabled the use of longer, heavier pendulums with slower beats that had less variation, as they more closely resembled simple harmonic motion, required less power, and caused less friction and wear. The first known anchor escapement clock was built by the English clockmaker William Clement in 1671 for King's College, Cambridge, now in the Science Museum, London. The anchor escapement originated with Hooke, although it has been argued that it was invented by Clement, or the English clockmaker Joseph Knibb
Joseph Knibb (1640–1711) was an English clockmaker of the Restoration era. According to author Herbert Cescinsky, a leading authority on English clocks, Knibb, "next to Tompion, must be regarded as the greatest horologist of his time."
Life a ...
.
The Jesuits made major contributions to the development of pendulum clocks in the 17th and 18th centuries, having had an "unusually keen appreciation of the importance of precision". In measuring an accurate one-second pendulum, for example, the Italian astronomer Father Giovanni Battista Riccioli
Giovanni Battista Riccioli, SJ (17 April 1598 – 25 June 1671) was an Italian astronomer and a Catholic priest in the Jesuit order. He is known, among other things, for his experiments with pendulums and with falling bodies, for his discussion ...
persuaded nine fellow Jesuits "to count nearly 87,000 oscillations in a single day". They served a crucial role in spreading and testing the scientific ideas of the period, and collaborated with Huygens and his contemporaries.
 Huygens first used a clock to calculate the
Huygens first used a clock to calculate the equation of time
In mathematics, an equation is a formula that expresses the equality of two expressions, by connecting them with the equals sign . The word ''equation'' and its cognates in other languages may have subtly different meanings; for example, in F ...
(the difference between the apparent solar time and the time given by a clock), publishing his results in 1665. The relationship enabled astronomers to use the stars to measure sidereal time, which provided an accurate method for setting clocks. The equation of time was engraved on sundials so that clocks could be set using the sun. In 1720, Joseph Williamson claimed to have invented a clock that showed solar time, fitted with a cam
Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells. It is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2+, and the bin ...
and differential gearing, so that the clock indicated true solar time.
Other innovations in timekeeping during this period include the invention of the rack and snail striking mechanism for striking clocks by the English mechanician
A mechanician is an engineer or a scientist working in the field of mechanics, or in a related or sub-field: engineering or computational mechanics, applied mechanics, geomechanics, biomechanics, and mechanics of materials. Names other than mecha ...
Edward Barlow, the invention by either Barlow or Daniel Quare, a London clock-maker, in 1676 of the repeating clock that chimes the number of hours or minutes, and the deadbeat escapement
In horology, the anchor escapement is a type of escapement used in pendulum clocks. The escapement is a mechanism in a mechanical clock that maintains the swing of the pendulum by giving it a small push each swing, and allows the clock's wheels ...
, invented around 1675 by the astronomer Richard Towneley
Richard Towneley (10 October 1629 – 22 January 1707) was an English mathematician, natural philosopher and astronomer, resident at Towneley Hall, near Burnley in Lancashire. His uncle was the antiquarian and mathematician Christopher Townele ...
.
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), ma ...
and Blois
Blois ( ; ) is a commune and the capital city of Loir-et-Cher department, in Centre-Val de Loire, France, on the banks of the lower Loire river between Orléans and Tours.
With 45,898 inhabitants by 2019, Blois is the most populated city of the ...
were the early centres of clockmaking in France, and French clockmakers such as Julien Le Roy, clockmaker of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, ...
, were leaders in case design and ornamental clocks. Le Roy belonged to the fifth generation of a family of clockmakers, and was described by his contemporaries as "the most skillful clockmaker in France, possibly in Europe". He invented a special repeating mechanism which improved the precision of clocks and watches, a face that could be opened to view the inside clockwork, and made or supervised over 3,500 watches during his career of almost five decades, which ended with his death in 1759. The competition and scientific rivalry resulting from his discoveries further encouraged researchers to seek new methods of measuring time more accurately.
 Any inherent errors in early pendulum clocks were smaller than other errors caused by factors such as temperature variation. In 1729 the Yorkshire carpenter and self-taught clockmaker
Any inherent errors in early pendulum clocks were smaller than other errors caused by factors such as temperature variation. In 1729 the Yorkshire carpenter and self-taught clockmaker John Harrison
John Harrison ( – 24 March 1776) was a self-educated English carpenter and clockmaker who invented the marine chronometer, a long-sought-after device for solving the problem of calculating longitude while at sea.
Harrison's solution revol ...
invented the gridiron pendulum
The gridiron pendulum was a temperature-compensated clock pendulum invented by British clockmaker John Harrison around 1726 and later modified by John Ellicott. It was used in precision clocks. In ordinary clock pendulums, the pendulum rod expan ...
, which used at least three metals of different lengths and expansion properties, connected so as to maintain the overall length of the pendulum when it is heated or cooled by its surroundings. In 1781 the clockmaker George Graham
George Graham (born 30 November 1944), nicknamed "Stroller", is a Scottish former Association football, football player and manager (association football), manager.
In his successful playing career, he made 455 appearances in England's Football ...
compensated for temperature variation in an iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
pendulum by using a bob made from a glass jar of mercury—a liquid metal at room temperature that expands faster than glass. More accurate versions of this innovation contained the mercury in thinner iron jars to make them more responsive. This type of temperature compensating pendulum was improved still further when the mercury was contained within the rod itself, which allowed the two metals to be thermally coupled more tightly. In 1895, the invention of invar
Invar, also known generically as FeNi36 (64FeNi in the US), is a nickel–iron alloy notable for its uniquely low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE or α). The name ''Invar'' comes from the word ''invariable'', referring to its relative lac ...
, an alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductilit ...
made from iron and nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow ...
that expands very little, largely eliminated the need for earlier inventions designed to compensate for the variation in temperature.
Between 1794 and 1795, in the aftermath of the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
, the French government mandated the use of decimal time
Decimal time is the representation of the time of day using units which are decimally related. This term is often used specifically to refer to the time system used in France for a few years beginning in 1792 during the French Revolution, whi ...
, with a day divided into 10 hours of 100 minutes each. A clock in the Palais des Tuileries
The Tuileries Palace (french: Palais des Tuileries, ) was a royal and imperial palace in Paris which stood on the right bank of the River Seine, directly in front of the Louvre. It was the usual Parisian residence of most French monarchs, ...
kept decimal time as late as 1801.
Marine chronometer
After theScilly naval disaster of 1707
The Scilly naval disaster of 1707 was the loss of four warships of a Royal Navy fleet off the Isles of Scilly in severe weather on 22 October 1707. Between 1,400 and 2,000 sailors lost their lives aboard the wrecked vessels, making the incident ...
where four ships ran aground due to navigational mistakes, the British government offered a prize
A prize is an award to be given to a person or a group of people (such as sporting teams and organizations) to recognize and reward their actions and achievements.
of £20,000, equivalent to millions of pounds today, for anyone who could determine the longitude to within at a latitude just north of the equator. The position of a ship at sea could be determined to within if a navigator could refer to a clock that lost or gained less than about six seconds per day. Proposals were examined by a newly created Board of Longitude
The Commissioners for the Discovery of the Longitude at Sea, or more popularly Board of Longitude, was a British government body formed in 1714 to administer a scheme of prizes intended to encourage innovators to solve the problem of finding lon ...
. Among the many people who attempted to claim the prize was the Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other English counties, functions have ...
clockmaker Jeremy Thacker, who first used the term ''chronometer
A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate time. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month and th ...
'' in a pamphlet published in 1714. Huygens built the first sea clock, designed to remain horizontal aboard a moving ship, but that stopped working if the ship moved suddenly.
 In 1715, at the age of 22, Harrison had used his carpentry skills to construct a wooden eight-day clock. His clocks had innovations that included the use of wooden parts to remove the need for additional lubrication (and cleaning), rollers to reduce friction, a new kind of escapement, and the use of two different metals to reduce the problem of expansion caused by temperature variation.
He traveled to London to seek assistance from the Board of Longitude in making a sea clock. He was sent to visit Graham, who assisted Harrison by arranging to finance his work to build a clock. After 30 years, his device, now named "H1" was built and in 1736 it was tested at sea. Harrison then went on to design and make two other sea clocks, "H2" (completed in around 1739) and "H3", both of which were ready by 1755.
Harrison made two watches, "H4" and "H5". Eric Bruton, in his book ''The History of Clocks and Watches'', has described H4 as "probably the most remarkable timekeeper ever made". After the completion of its sea trials during the winter of 17611762 it was found that it was three times more accurate than was needed for Harrison to be awarded the Longitude prize.
In 1715, at the age of 22, Harrison had used his carpentry skills to construct a wooden eight-day clock. His clocks had innovations that included the use of wooden parts to remove the need for additional lubrication (and cleaning), rollers to reduce friction, a new kind of escapement, and the use of two different metals to reduce the problem of expansion caused by temperature variation.
He traveled to London to seek assistance from the Board of Longitude in making a sea clock. He was sent to visit Graham, who assisted Harrison by arranging to finance his work to build a clock. After 30 years, his device, now named "H1" was built and in 1736 it was tested at sea. Harrison then went on to design and make two other sea clocks, "H2" (completed in around 1739) and "H3", both of which were ready by 1755.
Harrison made two watches, "H4" and "H5". Eric Bruton, in his book ''The History of Clocks and Watches'', has described H4 as "probably the most remarkable timekeeper ever made". After the completion of its sea trials during the winter of 17611762 it was found that it was three times more accurate than was needed for Harrison to be awarded the Longitude prize.
Electric clocks
In 1815, the prolific English inventorFrancis Ronalds
Sir Francis Ronalds FRS (21 February 17888 August 1873) was an English scientist and inventor, and arguably the first electrical engineer. He was knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph over a substantial distance. In 1816 ...
produced the forerunner of the electric clock, the electrostatic
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies electric charges at rest ( static electricity).
Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amb ...
clock. It was powered with dry piles, a high voltage battery with extremely long life but the disadvantage of its electrical properties varying according to the air temperature and humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity dep ...
. He experimented with ways of regulating the electricity and his improved devices proved to be more reliable.
In 1840 the Scottish clock and instrument maker Alexander Bain, first used electricity to sustain the motion of a pendulum clock, and so can be credited with the invention of the electric clock. On January 11, 1841, Bain and the chronometer maker John Barwise took out a patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A ...
describing a clock with an electromagnetic
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions o ...
pendulum. The English scientist Charles Wheatstone
Sir Charles Wheatstone FRS FRSE DCL LLD (6 February 1802 – 19 October 1875), was an English scientist and inventor of many scientific breakthroughs of the Victorian era, including the English concertina, the stereoscope (a device for di ...
, whom Bain met in London to discuss his ideas for an electric clock, produced his own version of the clock in November 1840, but Bain won a legal battle to establish himself as the inventor.
In 1857, the French physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe.
Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate cau ...
Jules Lissajous showed how an electric current can be used to vibrate a tuning fork
A tuning fork is an acoustic resonator in the form of a two-pronged fork with the prongs ( tines) formed from a U-shaped bar of elastic metal (usually steel). It resonates at a specific constant pitch when set vibrating by striking it agains ...
indefinitely, and was probably the first to use the invention as a method for accurately measuring frequency. The piezoelectric
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied mechanical stress. The word '' ...
properties of crystalline quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
were discovered by the French physicist brothers Jacques
Ancient and noble French family names, Jacques, Jacq, or James are believed to originate from the Middle Ages in the historic northwest Brittany region in France, and have since spread around the world over the centuries. To date, there are over ...
and Pierre Curie
Pierre Curie ( , ; 15 May 1859 – 19 April 1906) was a French physicist, a pioneer in crystallography, magnetism, piezoelectricity, and radioactivity. In 1903, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics with his wife, Marie Curie, and Henri Becq ...
in 1880.
The most accurate pendulum clocks were controlled electrically. The Shortt–Synchronome clock, an electrical driven pendulum clock designed in 1921, was the first clock to be a more accurate timekeeper than the Earth itself.
A succession of innovations and discoveries led to the invention of the modern quartz timer. The vacuum tube oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave or a triangle wave. Oscillators convert direct current (DC) from a power supply to an alternating curr ...
was invented in 1912. An electrical oscillator was first used to sustain the motion of a tuning fork by the British physicist William Eccles in 1919; his achievement removed much of the damping associated with mechanical devices and maximised the stability of the vibration's frequency.
The first quartz crystal oscillator
A crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses a piezoelectric crystal as a frequency-selective element. The oscillator frequency is often used to keep track of time, as in quartz wristwatches, to provide a stable clock ...
was built by the American engineer Walter G. Cady in 1921, and in October 1927 the first quartz clock
Quartz clocks and quartz watches are timepieces that use an electronic oscillator regulated by a quartz crystal to keep time. This crystal oscillator creates a signal with very precise frequency, so that quartz clocks and watches are at least a ...
was described by Joseph Horton and Warren Marrison at Bell Telephone Laboratories
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mult ...
. The following decades saw the development of quartz clocks as precision time measurement devices in laboratory settings—the bulky and delicate counting electronics, built with vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
s, limited their practical use elsewhere. In 1932, a quartz clock able to measure small weekly variations in the rotation rate of the Earth was developed. Their inherent physical and chemical stability and accuracy has resulted in the subsequent proliferation, and since the 1940s they have formed the basis for precision measurements of time and frequency worldwide.
Development of the watch
The first wristwatches were made in the 16th century. Elizabeth I of England had made an inventory in 1572 of the watches she acquired, all of which were considered to be part of her jewellery collection. The firstpocketwatch
A pocket watch (or pocketwatch) is a watch that is made to be carried in a pocket, as opposed to a wristwatch, which is strapped to the wrist.
They were the most common type of watch from their development in the 16th century until wristwatc ...
es were inaccurate, as their size precluded them from having sufficiently well-made moving parts. Unornamented watches began to appear in 1625.
Dials that showed minutes and seconds became common after the increase in accuracy made possible by the balance spring
A balance spring, or hairspring, is a spring attached to the balance wheel in mechanical timepieces. It causes the balance wheel to oscillate with a resonant frequency when the timepiece is running, which controls the speed at which the wheels of ...
(or hairspring). Invented separately in 1675 by Huygens and Hooke, it enabled the oscillations of the balance wheel to have a fixed frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
. The invention resulted in a great advance in the accuracy of the mechanical watch
A mechanical watch is a watch that uses a clockwork mechanism to measure the passage of time, as opposed to quartz watches which function using the vibration modes of a piezoelectric quartz tuning fork, or radio watches, which are quartz wat ...
, from around half an hour to within a few minutes per day. Some dispute remains as to whether the balance spring was first invented by Huygens or by Hooke; both scientists claimed to have come up with the idea of the balance spring first. Huygens' design for the balance spring is the type used in virtually all watches up to the present day.
Thomas Tompion
Thomas Tompion, FRS (1639–1713) was an English clockmaker, watchmaker and mechanician who is still regarded to this day as the "Father of English Clockmaking". Tompion's work includes some of the most historic and important clocks and watc ...
was one of the first clockmakers to recognise the potential of the balance spring and use it successfully in his pocket watches; the improved accuracy enabled watches to perform as well as they are generally used today, as a second hand to be added to the face
The face is the front of an animal's head that features the eyes, nose and mouth, and through which animals express many of their emotions. The face is crucial for human identity, and damage such as scarring or developmental deformities may aff ...
, a development that occurred during the 1690s. The concentric minute hand was an earlier invention, but a mechanism was devised by Quare that enabled the hands to be actuated
An actuator is a component of a Mechanical system, machine that is responsible for moving and controlling a mechanism or system, for example by opening a valve. In simple terms, it is a "mover".
An actuator requires a control device (controlled by ...
together. Nicolas Fatio de Duillier
Nicolas Fatio de Duillier (also spelled Faccio or Facio; 16 February 1664 – 10 May 1753) was a mathematician, natural philosopher, astronomer, inventor, and religious campaigner. Born in Basel, Switzerland, Fatio mostly grew up in the then- ...
, a Swiss natural philosopher
Natural philosophy or philosophy of nature (from Latin ''philosophia naturalis'') is the philosophical study of physics, that is, nature and the physical universe. It was dominant before the development of modern science.
From the ancient wo ...
, is credited with the design of the first jewel bearings in watches in 1704.
Other notable 18th-century English horologists include John Arnold and Thomas Earnshaw
Thomas Earnshaw (4 February 1749 in Ashton-under-Lyne – 1 March 1829 in London) was an English watchmaker who, following John Arnold's earlier work, further simplified the process of marine chronometer production, making them available to the ...
, who devoted their careers to constructing high-quality chronometers and so-called 'deck watches', smaller versions of the chronometer that could be kept in a pocket.
Military use of the watch
Watches were worn during the Franco-Prussian War (18701871), and by the time of theBoer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the Sou ...
(18991902), watches had been recognised as a valuable tool. Early models were essentially standard pocket watches fitted to a leather strap, but, by the early 20th century, manufacturers began producing purpose-built wristwatches. In 1904, Alberto Santos-Dumont
Alberto Santos-Dumont ( Palmira, 20 July 1873 — Guarujá, 23 July 1932) was a Brazilian aeronaut, sportsman, inventor, and one of the few people to have contributed significantly to the early development of both lighter-than-air and heavie ...
, an early aviator, asked his friend the French watchmaker Louis Cartier
Cartier International SNC, or simply Cartier (; ), is a French high-end luxury goods conglomerate that designs, manufactures, distributes, and sells jewellery, leather goods, and watches. Founded by Louis-François Cartier (1819–1904) in Paris ...
to design a watch that could be useful during his flights.
During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, wristwatches were used by artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
officers. The so-called trench watch
The trench watch (wristlet) was a type of watch that came into use by the military during World War I, as pocket watches were not practical in combat. It was a transitional design between pocket watches and wristwatches, incorporating features of ...
, or 'wristlets' were practical, as they freed up one hand that would normally be used to operate a pocket watch, and became standard equipment. The demands of trench warfare
Trench warfare is a type of land warfare using occupied lines largely comprising military trenches, in which troops are well-protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from artillery. Trench warfare became ar ...
meant that soldiers needed to protect the glass of their watches, and a guard in the form of a hinged cage was sometimes used. The guard was designed to allow the numerals to be read easily, but it obscured the hands—a problem that was solved after the introduction of shatter-resistant Plexiglass
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) belongs to a group of materials called engineering plastics. It is a transparent thermoplastic. PMMA is also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, as well as by the trade names and brands Crylux, Plexiglas, Acrylite, ...
in the 1930s. Prior to the advent of its military use, the wristwatch was typically only worn by women, but during World War I they became symbols of masculinity and bravado.
Modern watches
Fob watches were starting to be replaced at the turn of the 20th century. The Swiss, who were neutral throughout World War I, produced wristwatches for both sides of the conflict. The introduction of the tank influenced the design of the Cartier Tank watch, and the design of watches during the 1920s was influenced by theArt Deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the Unite ...
style. The automatic watch
An automatic watch, also known as a self-winding watch or simply an automatic, is a mechanical watch where the natural motion of the wearer provides energy to wind the mainspring, making manual winding unnecessary if worn enough. It is distingu ...
, first introduced with limited success in the 18th century, was reintroduced in the 1920s by the English watchmaker John Harwood. After he went bankrupt in 1929, restrictions on automatic watches were lifted and companies such as Rolex
Rolex SA () is a British-founded Swiss watch designer and manufacturer based in Geneva, Switzerland. Founded in 1905 as ''Wilsdorf and Davis'' by Hans Wilsdorf and Alfred Davis in London, the company registered ''Rolex'' as the brand name of ...
were able to produce them. In 1930, Tissot
Tissot SA () is a Swiss watchmaker. The company was founded in Le Locle, Switzerland by Charles-Félicien Tissot and his son, Charles-Émile Tissot, in 1853. After several mergers and name changes, the group which Tissot SA belonged to was renam ...
produced the first ever non-magnetic wristwatch
A watch is a portable timepiece intended to be carried or worn by a person. It is designed to keep a consistent movement despite the motions caused by the person's activities. A wristwatch is designed to be worn around the wrist, attached by ...
.
The first battery-driven watches were developed in the 1950s. High quality watches were produced by firms such as Patek Philippe
Patek Philippe SA is a Swiss luxury watch and clock manufacturer, located in the Canton of Geneva and the Vallée de Joux. Established in 1839, it is named after two of its founders, Antoni Patek and Adrien Philippe. Since 1932, the company ha ...
, an example made in 1933, an example being a Patek Philippe ref. 1518, possibly the most complicated wristwatch ever made in stainless steel, which fetched a world record price in 2016 when it was sold at auction for $11,136,642.
The manual winding Speedmaster Professional or "Moonwatch" was worn during the first United States spacewalk as part of NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
's Gemini 4
Gemini 4 (officially Gemini IV) With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations. was the second crewed spaceflight in NASA's Project Gemini, occurring in June 1965. It was the tenth crewed American spaceflight (in ...
mission and was the first watch worn by an astronaut walking on the Moon during the Apollo 11
Apollo 11 (July 16–24, 1969) was the American spaceflight that first landed humans on the Moon. Commander Neil Armstrong and lunar module pilot Buzz Aldrin landed the Apollo Lunar Module ''Eagle'' on July 20, 1969, at 20:17 UTC, ...
mission. In 1969, Seiko
, commonly known as Seiko ( , ), is a Japanese maker of watches, clocks, electronic devices, semiconductors, jewelry, and optical products. Founded in 1881 by Kintarō Hattori in Tokyo, Seiko introduced one of the first quartz watches and the ...
produced the world's first quartz wristwatch, the Astron Astron may refer to:
* Mitsubishi Astron engine
* ASTRON, the Dutch foundation for astronomy research, operating the Westerbork Synthesis Radio Telescope and LOFAR
* Astron (comics), a fictional character, a member of the Marvel Comics group The ...
.
During the 1960s, the introduction of watches made using transistors
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
and plastic parts enabled companies to reduce their work force. By the 1970s, many of those firms that maintained more complicated metalworking techniques had gone bankrupt.
Atomic clocks

Atomic clocks
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions betwee ...
are the most accurate timekeeping devices in practical use today. Accurate to within a few seconds over many thousands of years, they are used to calibrate other clocks and timekeeping instruments. The U.S. National Bureau of Standards
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical sci ...
(NBS, now National Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical s ...
(NIST)) changed the way it based the time standard of the United States from quartz to atomic clock
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions betwe ...
s in the 1960s.
The idea of using atomic transitions to measure time was first suggested by the British scientist Lord Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, (26 June 182417 December 1907) was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, he did important ...
in 1879, although it was only in the 1930s with the development of magnetic resonance
Magnetic resonance is a process by which a physical excitation (resonance) is set up via magnetism.
This process was used to develop magnetic resonance imaging and Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy technology.
It is also being used to ...
that there was a practical method for measuring time in this way. A prototype ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous wa ...
maser
A maser (, an acronym for microwave amplification by stimulated emission of radiation) is a device that produces coherent electromagnetic waves through amplification by stimulated emission. The first maser was built by Charles H. Townes, Ja ...
device was built in 1948 at NIST. Although less accurate than existing quartz clocks it served to prove the concept of an atomic clock.
The first accurate atomic clock, a caesium standard based on a certain transition of the caesium-133 atom, was built by the English physicist Louis Essen in 1955 at the National Physical Laboratory in London. It was calibrated by the use of the astronomical time scale '' ephemeris time'' (ET).
In 1967 the International System of Units (SI) standardized its unit of time, the second, on the properties of cesium. The SI defined the second as 9,192,631,770 cycles of the radiation which corresponds to the transition between two electron spin
In atomic physics, the electron magnetic moment, or more specifically the electron magnetic dipole moment, is the magnetic moment of an electron resulting from its intrinsic properties of spin and electric charge. The value of the electron magnet ...
energy levels of the ground state of the 133Cs atom. The cesium atomic clock maintained by NIST is accurate to 30 billionths of a second per year. Atomic clocks have employed other elements, such as hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
and rubidium vapor, offering greater stability (in the case of hydrogen clocks) and smaller size, lower power consumption, and thus lower cost (in the case of rubidium clocks).
See also
*Clock synchronization
Clock synchronization is a topic in computer science and engineering that aims to coordinate otherwise independent clocks. Even when initially set accurately, real clocks will differ after some amount of time due to clock drift, caused by clocks ...
* Clockmaker
A clockmaker is an artisan who makes and/or repairs clocks. Since almost all clocks are now factory-made, most modern clockmakers only repair clocks. Modern clockmakers may be employed by jewellers, antique shops, and places devoted strictly to ...
* Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time or UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is within about one second of mean solar time (such as UT1) at 0° longitude (at the IERS Reference Meridian as the currently use ...
(UTC)
* History of timekeeping devices in Egypt
* Quartz crisis
The quartz crisis was the upheaval in the watchmaking industry caused by the advent of quartz watches in the 1970s and early 1980s, that largely replaced mechanical watches around the world.
* Seconds pendulum
A seconds pendulum is a pendulum whose period is precisely two seconds; one second for a swing in one direction and one second for the return swing, a frequency of 0.5 Hz.
Pendulum
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that ...
* Time metrology
Time metrology or time and frequency metrology is the application of metrology for time keeping, including frequency stability.
Its main tasks are the realization of the second as the SI unit of measurement for time and the establishment of ti ...
* Time standard
A time standard is a specification for measuring time: either the rate at which time passes or points in time or both. In modern times, several time specifications have been officially recognized as standards, where formerly they were matters o ...
* Watchmaker
A watchmaker is an artisan who makes and repairs watches. Since a majority of watches are now factory-made, most modern watchmakers only repair watches. However, originally they were master craftsmen who built watches, including all their part ...
Explanatory notes
Citations
General and cited references
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Relativity Science Calculator – Philosophic Question: are clocks and time separable?
Ancient Discoveries Islamic Science Part 4
clip from ''History Repeating'' of Islamic time-keeping inventions (YouTube). {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Timekeeping Devices Timekeeping devices Timekeeping History of measurement History of timekeeping