|
Candle Clock
A candle clock is a thin candle with consistently spaced marking that, when burned, indicates the passage of periods of time. While no longer used today, candle clocks provided an effective way to tell time indoors, at night, or on a cloudy day. History It is unknown where and when candle clocks were first used. The earliest reference to their use occurs in a Chinese poem by You Jiangu (AD 520). Here, the graduated candle supplied a means of determining time at night. Similar candles were used in Japan until the early 10th century. You Jiangu's device consisted of six candles made from 72 pennyweights (24 grains each), of wax, each being 12 inches high, of uniform thickness, and divided into 12 sections each of one inch. Each candle burned away completely in four hours, making each marking 20 minutes. The candles were placed for protection inside cases made of a wooden frame with transparent horn panels in the sides. Similar methods of measuring time were used in medieval chur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Jazari
Badīʿ az-Zaman Abu l-ʿIzz ibn Ismāʿīl ibn ar-Razāz al-Jazarī (1136–1206, ar, بديع الزمان أَبُ اَلْعِزِ إبْنُ إسْماعِيلِ إبْنُ الرِّزاز الجزري, ) was a polymath: a scholar, inventor, mechanical engineer, artisan, artist and mathematician from the Artuqid Dynasty of Jazira in Mesopotamia. He is best known for writing '' The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices'' ( ar, كتاب في معرفة الحيل الهندسية, lit=Book in knowledge of engineering tricks, translit=Kitab fi ma'rifat al-hiyal al-handasiya) in 1206, where he described 50 mechanical devices, along with instructions on how to construct them. He is credited with the invention of the elephant clock. He has been described as the "father of robotics" and modern day engineering. Biography Al-Jazari was born in the area of Upper Mesopotamia in 1136. Sources state his exact location is unknown, but they speculate he could have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clocks
A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate time. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month and the year. Devices operating on several physical processes have been used over the millennia. Some predecessors to the modern clock may be considered as "clocks" that are based on movement in nature: A sundial shows the time by displaying the position of a shadow on a flat surface. There is a range of duration timers, a well-known example being the hourglass. Water clocks, along with the sundials, are possibly the oldest time-measuring instruments. A major advance occurred with the invention of the verge escapement, which made possible the first mechanical clocks around 1300 in Europe, which kept time with oscillating timekeepers like balance wheels., pp. 103–104., p. 31. Traditionally, in horology, the term ''clock'' was used for a striki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Inventions
China has been the source of many innovations, scientific discoveries and inventions. This includes the ''Four Great Inventions'': papermaking, the compass, gunpowder, and printing (both woodblock and movable type). The list below contains these and other inventions in ancient and modern China attested by archaeological or historical evidence, excluding prehistoric inventions of Neolithic and early Bronze Age China. The historical region now known as China experienced a history involving mechanics, hydraulics and mathematics applied to horology, metallurgy, astronomy, agriculture, engineering, music theory, craftsmanship, naval architecture and warfare. Use of the plow during the Neolithic period Longshan culture (c. 3000–c. 2000 BC) allowed for high agricultural production yields and rise of Chinese civilization during the Shang Dynasty (c. 1600–c. 1050 BC). Later inventions such as the multiple-tube seed drill and the heavy moldboard iron plow enabled China to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candles
A candle is an ignitable wick embedded in wax, or another flammable solid substance such as tallow, that provides light, and in some cases, a fragrance. A candle can also provide heat or a method of keeping time. A person who makes candles is traditionally known as a chandler. Various devices have been invented to hold candles, from simple tabletop candlesticks, also known as candle holders, to elaborate candelabra and chandeliers. For a candle to burn, a heat source (commonly a naked flame from a match or lighter) is used to light the candle's wick, which melts and vaporizes a small amount of fuel (the wax). Once vaporized, the fuel combines with oxygen in the atmosphere to ignite and form a constant flame. This flame provides sufficient heat to keep the candle burning via a self-sustaining chain of events: the heat of the flame melts the top of the mass of solid fuel; the liquefied fuel then moves upward through the wick via capillary action; the liquefied fuel finally vap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald Routledge Hill
Donald Routledge Hill (6 August 1922 – 30 May 1994)D. A. King, “In Memoriam: Donald Routledge Hill (1922-1994)”, ''Arabic Sciences and Philosophy,'' Volume 5 / Issue 02 / September 1995, pp 297-302 was a British engineer and historian of science and technology best known for his translation of ''The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices'' of the Muslim engineer Ismail al-Jazari.Hill Donald(1993) Life and work Born in London, after secondary school Hill served in the British army, in the Royal Engineers from 1941 to 1946. Two years he served in the Eighth Army in North Africa until he was wounded in action in Italy. Back in England he studied Engineering at the London University, obtaining his engineering degree in 1949. In 1964 he obtained his M.Litt in Islamic History at the University of Durham, and in 1970 his PhD from the University of London. Late 1940s Hill started his career working for the Iraq Petroleum Company in Lebanon, Syria and Qatar. Back in En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History (U
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fastener
A fastener (US English) or fastening (UK English) is a hardware device that mechanically joins or affixes two or more objects together. In general, fasteners are used to create non-permanent joints; that is, joints that can be removed or dismantled without damaging the joining components. Welding is an example of creating permanent joints. Steel fasteners are usually made of stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy steel. Other alternative methods of joining materials include: crimping, welding, soldering, brazing, taping, gluing, cement, or the use of other adhesives. Force may also be used, such as with magnets, vacuum (like suction cups), or even friction (like sticky pads). Some types of woodworking joints make use of separate internal reinforcements, such as dowels or biscuits, which in a sense can be considered fasteners within the scope of the joint system, although on their own they are not general purpose fasteners. Furniture supplied in flat-pack form often uses c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayonet Mount
A bayonet mount (mainly as a method of mechanical attachment, such as fitting a lens to a camera using a matching lens mount) or bayonet connector (for electrical use) is a fastening mechanism consisting of a cylindrical male side with one or more radial pins, and a female receptor with matching L-shaped slot(s) and with spring(s) to keep the two parts locked together. The slots are shaped like a capital letter L with serif (a short upward segment at the end of the horizontal arm); the pin slides into the vertical arm of the L, rotates across the horizontal arm, then is pushed slightly upwards into the short vertical "serif" by the spring; the connector is no longer free to rotate unless pushed down against the spring until the pin is out of the "serif". The bayonet mount is the standard light bulb fitting in the United Kingdom and in many countries that were members of the British Empire including Pakistan, Australia, Hong Kong, Fiji India, Sri Lanka, Ireland, and New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dial (measurement)
A dial is generally a flat surface, circular or rectangular, with numbers or similar markings on it, used for displaying the setting or output of a timepiece, radio, clock, watch, or measuring instrument. There are many instruments used in scientific and industrial applications that use dials with pointers as indicators of a specific physical property. Typical examples include pressure and vacuum gauges, fluid-level gauges (for fuel, engine oil, and so on), voltmeters and ammeters, thermometers and hygrometers, speedometers and tachometers, and indicators (distance amplifying instruments). Traditionally these have been mechanical devices, but with the advent of electronic displays, analog dials are often simulated from digital measurements. The term may also refer to a movable control knob used to change the settings of the controlled instrument, for example, to change the frequency of the radio, or the desired temperature on a thermostat. Styles of dials: * Circular, * Fixed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
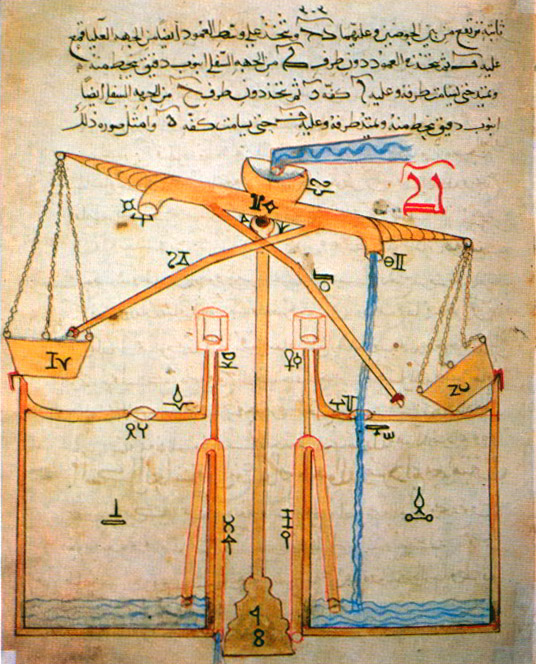
Al-Jazari - A Candle Clock
Badīʿ az-Zaman Abu l-ʿIzz ibn Ismāʿīl ibn ar-Razāz al-Jazarī (1136–1206, ar, بديع الزمان أَبُ اَلْعِزِ إبْنُ إسْماعِيلِ إبْنُ الرِّزاز الجزري, ) was a polymath: a scholar, inventor, mechanical engineer, artisan, artist and mathematician from the Artuqid Dynasty of Jazira in Mesopotamia. He is best known for writing '' The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices'' ( ar, كتاب في معرفة الحيل الهندسية, lit=Book in knowledge of engineering tricks, translit=Kitab fi ma'rifat al-hiyal al-handasiya) in 1206, where he described 50 mechanical devices, along with instructions on how to construct them. He is credited with the invention of the elephant clock. He has been described as the "father of robotics" and modern day engineering. Biography Al-Jazari was born in the area of Upper Mesopotamia in 1136. Sources state his exact location is unknown, but they speculate he could have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
