History of dental treatments on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of dental treatments dates back to thousands of years. The scope of this article is limited to the pre-1981
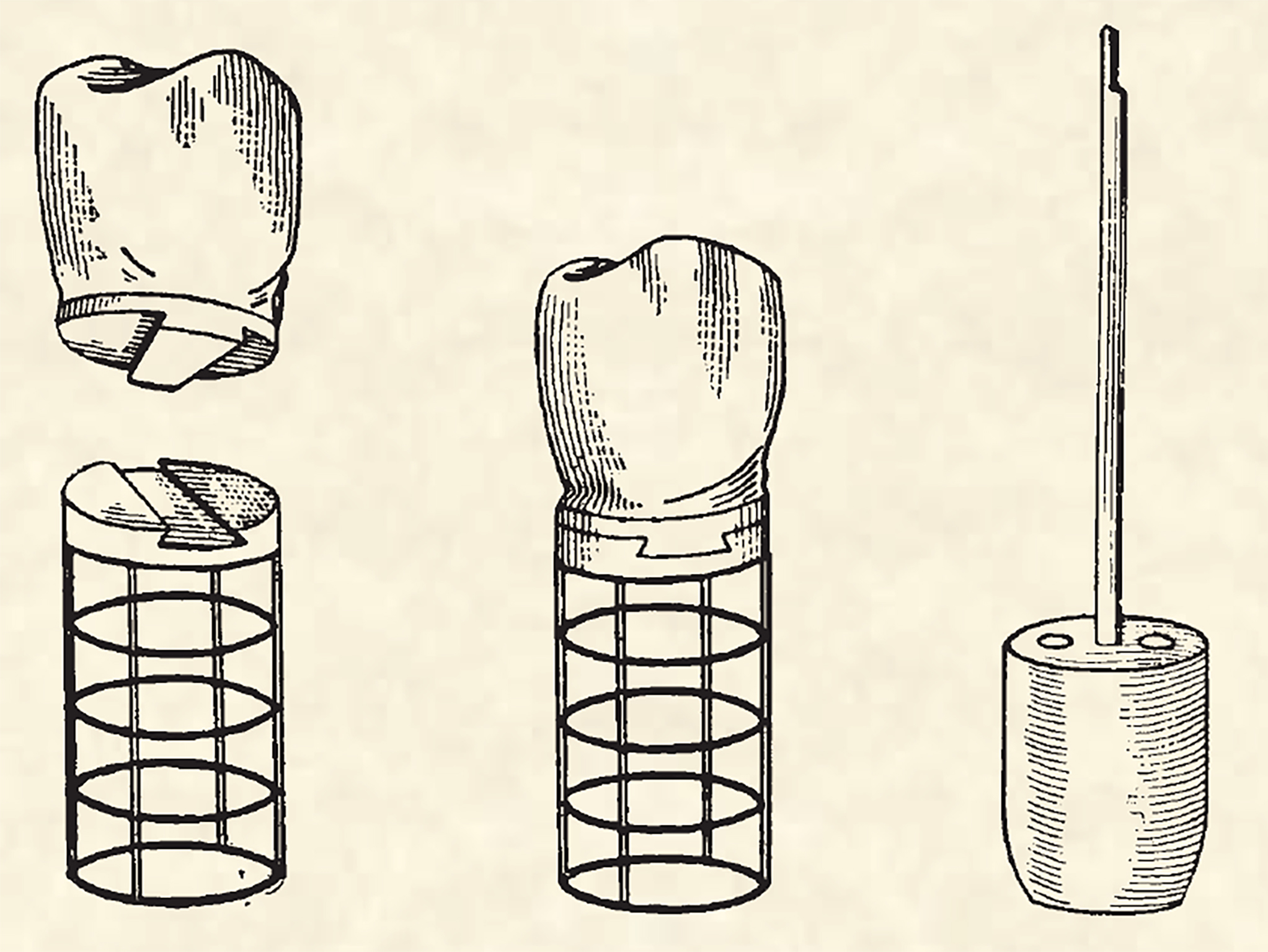
 There is
There is

 As early as the 7th century BC,
As early as the 7th century BC,
"The Private Life of George Washington's Slaves"
Frontline, PBS Washington's dental problems left him in constant pain, for which he took
history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
.
The earliest known example of dental caries
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complicatio ...
manipulation is found in a Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
man, dated between 14,160 and 13,820 BP. The earliest known use of a filling
Filling may refer to:
* a food mixture used for stuffing
* Icing (food), Frosting used between layers of a cake
* Dental restoration
* Symplectic filling, a kind of cobordism in mathematics
* Part of the leather crusting process
See also
* Fi ...
after removal of decayed or infected pulp
Pulp may refer to:
* Pulp (fruit), the inner flesh of fruit
Engineering
* Dissolving pulp, highly purified cellulose used in fibre and film manufacture
* Pulp (paper), the fibrous material used to make paper
* Molded pulp, a packaging material
* ...
is found in a Paleolithic who lived near modern-day Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; it, Toscana ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of about 3.8 million inhabitants. The regional capital is Florence (''Firenze'').
Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, art ...
, Italy, from 13,000 to 12,740 BP. Although inconclusive, researchers have suggested that rudimentary dental procedures have been performed as far back as 130,000 years ago by Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While th ...
s. Regarding implants, one of the milestone
A milestone is a numbered marker placed on a route such as a road, railway line, canal or boundary. They can indicate the distance to towns, cities, and other places or landmarks; or they can give their position on the route relative to so ...
progress is osseointegration
Osseointegration (from Latin ''osseus'' " bony" and ''integrare'' "to make whole") is the direct structural and functional connection between living bone and the surface of a load-bearing artificial implant ("load-bearing" as defined by Albrekt ...
which was termed in 1981 by Tomas Albrektsson.
Dental implants

 There is
There is archeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscape ...
evidence that humans have attempted to replace missing teeth with root form implants for thousands of years. Remains from ancient China (dating 4000 years ago) have carved bamboo pegs, tapped into the bone, to replace lost teeth, and 2000-year-old remains from ancient Egypt have similarly shaped pegs made of precious metals. Some Egyptian mummies were found to have transplanted human teeth, and in other instances, teeth made of ivory. Wilson Popenoe
Frederick Wilson Popenoe (March 9, 1892 – June 20, 1975) was an American Department of Agriculture employee and plant explorer. From 1916 to 1924, Popenoe explored Latin America to look for new strains of avocados. He reported his adventur ...
and his wife in 1931, at a site in Honduras dating back to 600 AD, found the lower mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movabl ...
of a young Mayan
Mayan most commonly refers to:
* Maya peoples, various indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica and northern Central America
* Maya civilization, pre-Columbian culture of Mesoamerica and northern Central America
* Mayan languages, language family spoken ...
woman, with three missing incisors replaced by pieces of sea shells
A seashell or sea shell, also known simply as a shell, is a hard, protective outer layer usually created by an animal or organism that lives in the sea. The shell is part of the body of the animal. Empty seashells are often found washe ...
, shaped to resemble teeth. Bone growth around two of the implants, and the formation of calculus, indicates that they were functional as well as esthetic. The fragment is currently part of the Osteological Collection of the Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology
The Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology is a museum affiliated with Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1866, the Peabody Museum is one of the oldest and largest museums focusing on anthropological material, with ...
at Harvard University.
In modern times, a tooth replica implant was reported as early as 1969, but the polymethacrylate tooth analogue was encapsulated by soft tissue rather than osseointegrated.
The early part of the 20th century saw a number of implants made of a variety of materials. One of the earliest successful implants was the Greenfield implant system of 1913 (also known as the Greenfield crib or basket). Greenfield's implant, an iridioplatinum implant attached to a gold crown, showed evidence of osseointegration and lasted for a number of years. The first use of titanium as an implantable material was by Bothe, Beaton and Davenport in 1940, who observed how close the bone grew to titanium screws, and the difficulty they had in extracting them. Bothe et al. were the first researchers to describe what would later be called osseointegration (a name that would be marketed later on by Per-Ingvar Brånemark
Per-Ingvar Brånemark (May 3, 1929 – December 20, 2014) was a Swedish physician and research professor, acknowledged as the "father of modern dental implantology". The ''Brånemark Osseointegration Center'' (BOC), named after its founder, was fo ...
). In 1951, Gottlieb Leventhal implanted titanium rods in rabbits. Leventhal's positive results led him to believe that titanium represented the ideal metal for surgery.
In the 1950s research was being conducted at Cambridge University
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts.
Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge.
, established =
, other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Schola ...
in England on blood flow in living organisms. These workers devised a method of constructing a chamber of titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
which was then embedded into the soft tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligam ...
of the ears of rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit speci ...
s. In 1952 the Swedish orthopaedic surgeon
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternatively spelt orthopaedics), is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal ...
, Per-Ingvar Brånemark
Per-Ingvar Brånemark (May 3, 1929 – December 20, 2014) was a Swedish physician and research professor, acknowledged as the "father of modern dental implantology". The ''Brånemark Osseointegration Center'' (BOC), named after its founder, was fo ...
, was interested in studying bone healing and regeneration. During his research time at Lund University
, motto = Ad utrumque
, mottoeng = Prepared for both
, established =
, type = Public research university
, budget = SEK 9 billion Leonard Linkow
Leonard I. Linkow (February 25, 1926 – January 26, 2017) was an American dentist and pioneer in the field of oral implantology. In 1969, he was nominated for a Nobel Prize in medicine, making him the only dentist to be nominated for the prize. ...
, in the 1950s, was one of the first to insert titanium and other metal implants into the bones of the jaw. Artificial teeth were then attached to these pieces of metal. In 1965 Brånemark placed his first titanium dental implant into a human volunteer. He began working in the mouth as it was more accessible for continued observations and there was a high rate of missing teeth in the general population offered more subjects for widespread study. He termed the clinically observed adherence of bone with titanium as "osseointegration". Since then implants have evolved into three basic types:
# Root form implants; the most common type of implant indicated for all uses. Within the root form type of implant, there are roughly 18 variants, all made of titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
but with different shapes and surface textures. There is limited evidence showing that implants with relatively smooth surfaces are less prone to peri-implantitis than implants with rougher surfaces and no evidence showing that any particular type of dental implant has superior long-term success.
# Zygoma Implant; a long implant that can anchor to the cheek bone
In the human skull, the zygomatic bone (from grc, ζῠγόν, zugón, yoke), also called cheekbone or malar bone, is a paired irregular bone which articulates with the maxilla, the temporal bone, the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone. It is si ...
by passing through the maxillary sinus
The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus (or antrum of Highmore) is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, and drains into the middle meatus of the nose through the osteomeatal complex.Human Anatomy, Jacobs, Elsevier, 2008, page 209-210
Structure
It is ...
to retain a complete upper denture when bone is absent. While zygomatic implants offer a novel approach to severe bone loss in the upper jaw
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ...
, it has not been shown to offer any advantage over bone grafting
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone in order to repair bone fractures that are extremely complex, pose a significant health risk to the patient, or fail to heal properly. Some small or acute fractures can be cured wit ...
functionally although it may offer a less invasive option, depending on the size of the reconstruction required.
# Small diameter implants are implants of low diameter with one piece construction (implant and abutment) that are sometimes used for denture retention or orthodontic anchorage.
Ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
implants made from alumina were introduced between 1960s and 1970s but were eventually withdrawn from the market in the early 1990s because they presented some biomechanical problems (like low fracture toughness) and were replaced by zirconia
Zirconium dioxide (), sometimes known as zirconia (not to be confused with zircon), is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium. Its most naturally occurring form, with a monoclinic crystalline structure, is the mineral baddeleyite. A dopant stabi ...
implants.
Robot-assisted dental surgery, including for dental implant
A dental implant (also known as an endosseous implant or fixture) is a prosthesis that interfaces with the bone of the jaw or skull to support a dental prosthesis such as a crown, bridge, denture, or facial prosthesis or to act as an orthodonti ...
s, has also been developed in the 2000s.
Dentures

 As early as the 7th century BC,
As early as the 7th century BC, Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, rou ...
in northern Italy made partial dentures out of human or other animal teeth fastened together with gold bands. The Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
had likely borrowed this technique by the 5th century BC.
Wooden full dentures were invented in Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
around the early 16th century. Softened bees wax
Beeswax (''cera alba'') is a natural wax produced by honey bees of the genus ''Apis''. The wax is formed into scales by eight wax-producing glands in the abdominal segments of worker bees, which discard it in or at the hive. The hive workers ...
was inserted into the patient's mouth to create an impression, which was then filled with harder bees wax. Wooden dentures were then meticulously carved based on that model. The earliest of these dentures were entirely wooden, but later versions used natural human teeth or sculpted pagodite
Pagodite or agalmatolite is a variety of pyrophyllite used by Chinese artisans for carvings in pagodas and similar objects. Usually soft and sometimes soapy, it can be a greyish green or greyish yellow colour.
, ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals is ...
, or animal horn
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
for the teeth. These dentures were built with a broad base, exploiting the principles of adhesion
Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another ( cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles/surfaces to cling to one another).
The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can be ...
to stay in place. This was an advanced technique for the era; it would not be replicated in the West
West is a cardinal direction or compass point.
West or The West may also refer to:
Geography and locations
Global context
* The Western world
* Western culture and Western civilization in general
* The Western Bloc, countries allied with NATO ...
until the late 18th century. Wooden dentures continued to be used in Japan until the Opening of Japan
was the final years of the Edo period when the Tokugawa shogunate ended. Between 1853 and 1867, Japan ended its isolationist foreign policy known as and changed from a feudal Tokugawa shogunate to the modern empire of the Meiji government. ...
to the West in the 19th century.
In 1728, Pierre Fauchard
Pierre Fauchard (January 2, 1679 – March 21, 1761) was a French physician, credited as being the "father of modern dentistry". He is widely known for writing the first complete scientific description of dentistry, ''Le Chirurgien Dentiste'' (''" ...
described the construction of dentures using a metal frame and teeth sculpted from animal bone. The first porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises mainl ...
dentures were made around 1770 by Alexis Duchâteau. In 1791, the first British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
patent was granted to Nicholas Dubois De Chemant, previous assistant to Duchateau, for 'De Chemant's Specification':
He began selling his wares in 1792, with most of his porcelain paste supplied by Wedgwood
Wedgwood is an English fine china, porcelain and luxury accessories manufacturer that was founded on 1 May 1759 by the potter and entrepreneur Josiah Wedgwood and was first incorporated in 1895 as Josiah Wedgwood and Sons Ltd. It was rapid ...
.
17th century London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
's Peter de la Roche is believed to be one of the first 'operators for the teeth', men who advertised themselves as specialists in dental work. They were often professional goldsmith
A goldsmith is a Metalworking, metalworker who specializes in working with gold and other precious metals. Nowadays they mainly specialize in jewelry-making but historically, goldsmiths have also made cutlery, silverware, platter (dishware), pl ...
s, ivory turners or students of barber-surgeons
The barber surgeon, one of the most common European medical practitioners of the Middle Ages, was generally charged with caring for soldiers during and after battle. In this era, surgery was seldom conducted by physicians, but instead by barbers ...
.
In 1820, Samuel Stockton, a goldsmith by trade, began manufacturing high-quality porcelain dentures mounted on 18-carat gold plates. Later dentures from the 1850s on were made of Vulcanite
Vulcanite is a rare copper telluride mineral. The mineral has a metallic luster, and has a green or bronze-yellow tint. It has a hardness between 1 and 2 on the Mohs scale (between talc and gypsum). Its crystal structure is orthorhombic.
Vulcanit ...
, a form of hardened rubber into which porcelain teeth were set. In the 20th century, acrylic resin
186 px, Polyhydroxyethylmethacrylate is a typical acrylate resin.
An acrylic resin is a thermoplastic or thermosetting plastic substance typically derived from acrylic acid, methacrylic acid and acrylate monomers such as butyl acrylate and or me ...
and other plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptab ...
s were used. In Britain, sequential Adult Dental Health Surveys revealed that in 1968 79% of those aged 65–74 had no natural teeth; by 1998, this proportion had fallen to 36%.
George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of th ...
(1732–1799) had problems with his teeth throughout his life, and historians have tracked his experiences in great detail. He lost his first adult tooth when he was twenty-two and had only one left by the time he became president. John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, attorney, diplomat, writer, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Befor ...
says he lost them because he used them to crack Brazil nut
The Brazil nut (''Bertholletia excelsa'') is a South American tree in the family Lecythidaceae, and it is also the name of the tree's commercially harvested edible seeds. It is one of the largest and longest-lived trees in the Amazon rainforest. ...
s but modern historians suggest the mercury oxide Mercury oxide can refer to:
* Mercury(I) oxide (mercurous oxide), Hg2O
* Mercury(II) oxide
Mercury(II) oxide, also called mercuric oxide or simply mercury oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula Hg O. It has a red or orange color. Mer ...
, which he was given to treat illnesses such as smallpox and malaria, probably contributed to the loss. He had several sets of false teeth made, four of them by a dentist named John Greenwood. None of the sets, contrary to popular belief, were made from wood or contained any wood. The set made when he became president were carved from hippopotamus and elephant ivory, held together with gold springs. Prior to these, he had a set made with real human teeth, likely ones he purchased from "several unnamed Negroes, presumably Mount Vernon slaves" in 1784.Mary V. Thompson"The Private Life of George Washington's Slaves"
Frontline, PBS Washington's dental problems left him in constant pain, for which he took
laudanum
Laudanum is a tincture of opium containing approximately 10% powdered opium by weight (the equivalent of 1% morphine). Laudanum is prepared by dissolving extracts from the opium poppy (''Papaver somniferum Linnaeus'') in alcohol (ethanol).
Red ...
. This distress may be apparent in many of the portraits painted while he was still in office, including the one still used on the $1 bill.
Notes
References
{{Dentistry Implants (medicine) History of medicine Surgery Oral surgery Dentistry Restorative dentistry Prosthodontology History of dentistry