History of African Americans in Philadelphia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 This article documents the history of
This article documents the history of
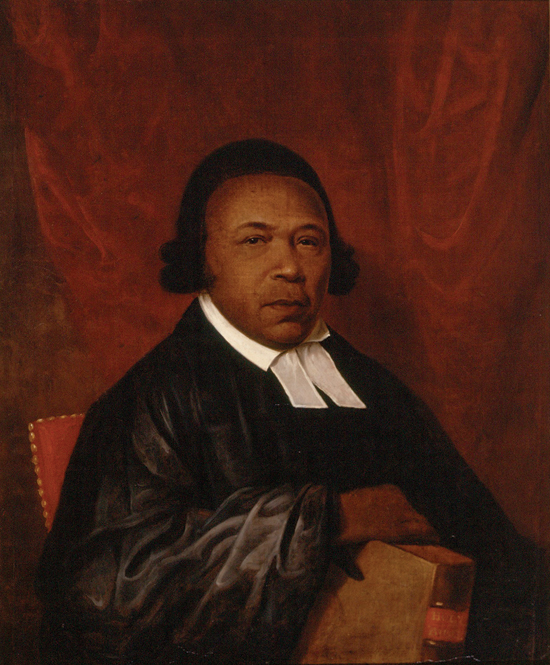 Black people served on both the Loyalist and Patriot sides during the
Black people served on both the Loyalist and Patriot sides during the 
 During the
During the
. "African American Migration"
Encyclopedia of Greater Philadelphia, 2013. Retrieved March 5, 2021. In 1896 Philadelphia poet, suffragist, and abolitionist
 World War I brought an influx of black migrants from the rural South, who moved to Philadelphia lured by wartime jobs there during The great migration. As a result, the black population of Philadelphia doubled again from 63,000 in 1900 to 134,000 in 1920.Most of the new residents came from rural backgrounds and were working poor.
Efforts to build new structures to house the workers were insufficient, so African Americans in search of housing moved into existing houses in white neighborhoods, where they encountered hostility and racism. In July 1918, after two black families on Pine Street were attacked by white neighbors who burned household furnishings, G. Grant Williams, editor of the
World War I brought an influx of black migrants from the rural South, who moved to Philadelphia lured by wartime jobs there during The great migration. As a result, the black population of Philadelphia doubled again from 63,000 in 1900 to 134,000 in 1920.Most of the new residents came from rural backgrounds and were working poor.
Efforts to build new structures to house the workers were insufficient, so African Americans in search of housing moved into existing houses in white neighborhoods, where they encountered hostility and racism. In July 1918, after two black families on Pine Street were attacked by white neighbors who burned household furnishings, G. Grant Williams, editor of the  In 1925, the artist and printmaker
In 1925, the artist and printmaker
 The fight against discrimination and segregation in education and employment continued through the 1950s and 60s, with legal battles and protests occurring throughout those years. Cecil B. Moore, president of the local NAACP, was a leading activist during that time, and Reverend
The fight against discrimination and segregation in education and employment continued through the 1950s and 60s, with legal battles and protests occurring throughout those years. Cecil B. Moore, president of the local NAACP, was a leading activist during that time, and Reverend 
 The
The
Aces Museum
honors WWII veterans and their families. Th
Colored Girls Museum
founded by Vashti DuBois, is dedicated to the history of Black women and girls. Th
National Marian Anderson Museum
celebrates the life of the notable opera singer
 The African Episcopal Church of St. Thomas, established in 1792, was the first house of worship created by and for black people in the United States. While the
The African Episcopal Church of St. Thomas, established in 1792, was the first house of worship created by and for black people in the United States. While the
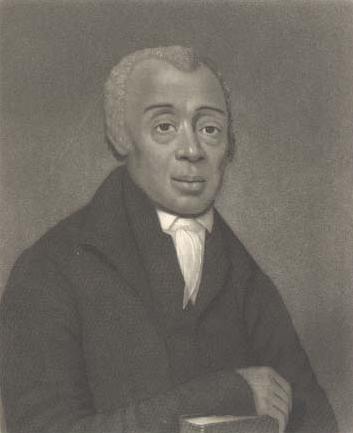



''A Gentleman of Color: The Life of James Forten''
New York: Oxford University Press, 2002, p. 16. *
 This article documents the history of
This article documents the history of African-Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ensl ...
or Black Philadelphians in Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
.
Recent 2010 estimates by the U.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
put the total number of people living in Philadelphia who identify as Black or African-American at 644,287, or 42.2% of the city's total population. People of African descent are currently the largest ethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
in Philadelphia. Originally arriving in the 17th century as enslaved Africans
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
, the population of African Americans in Philadelphia grew in the 18th and 19th centuries to include numerous free black residents who were active in the abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
movement and as conductors in the Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroad was a network of clandestine routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early- to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and Canada. T ...
. In the 20th and 21st centuries, Black Philadelphians actively campaigned against discrimination and continued to contribute to Philadelphia's cultural, economic and political life as workers, activists, artists, musicians and politicians.
History
1639 to 1800
Enslaved Africans arrived in the area that becamePhiladelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
as early as 1639, brought by European settlers. In the 1750s and 60s, when the slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
increased due to a shortage of European workers, 100 to 500 Africans came to Philadelphia each year. In 1765, there were about fifteen hundred black Philadelphians; of these, one hundred were free. By the time the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
broke out in 1775, slaves were one-twelfth of the roughly 16,000 people who lived in Philadelphia./
 Black people served on both the Loyalist and Patriot sides during the
Black people served on both the Loyalist and Patriot sides during the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
. Two on the American side were Cyrus Bustill
Cyrus Bustill (February 2, 1732 1806) was an African-American brewer and baker, abolitionist and community leader.
A notable business owner in the African-American community in Philadelphia, he also became a founding member of the Free Africa ...
, who worked as a ship's baker during the Revolution and later became a prominent Philadelphia businessman and activist, and James Forten
James Forten (September 2, 1766March 4, 1842) was an African-American abolitionist and wealthy businessman in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Born free in the city, he became a sailmaker after the American Revolutionary War. Following an apprenticesh ...
, who served on a privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
at the age of 14 and became a wealthy sailmaker and abolitionist. Some slaves were freed by their owners and others managed to escape or buy their own freedom. As a result, the free Black community in Philadelphia had grown to over 1,000 by the end of the Revolution in 1783, while enslaved residents numbered 400. The Pennsylvania Abolition Society
The Society for the Relief of Free Negroes Unlawfully Held in Bondage was the first American abolition society. It was founded April 14, 1775, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and held four meetings. Seventeen of the 24 men who attended initia ...
was founded by white Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's abil ...
in 1775 and eventually became a biracial organization.
In 1780 a policy of gradual emancipation was instituted in Pennsylvania.
The Quakers immediately established a Burying Place For All Free Negroes or People of Color in Byberry Township. This African Burial Ground remains an obscure anomaly, forgotten today much the same as the day it was placed on the Philadelphia Register of Historic Places. Most of the Black population in Philadelphia were free by 1811, although some remained enslaved until the 1840s. The free community was joined by runaways from the South and refugees from the Haitian Revolution
The Haitian Revolution (french: révolution haïtienne ; ht, revolisyon ayisyen) was a successful insurrection by slave revolt, self-liberated slaves against French colonial rule in Saint-Domingue, now the sovereign state of Haiti. The revolt ...
.
Richard Allen and Absolom Jones founded the Free African Society The Free African Society, founded in 1787, was a benevolent organization that held religious services and provided mutual aid for "free Africans and their descendants" in Philadelphia. The Society was founded by Richard Allen and Absalom Jones. It ...
in 1787, a mutual aid society, and Allen, with his wife Sarah Allen
Sarah Allen is a Canadian actress. She studied acting at the National Theatre School of Canada and graduated in 2002.
''Being Human''
Allen is perhaps best known for playing vampire Rebecca Flynt on SyFy's '' Being Human''. For the role ...
, established the Bethel African Methodist Church in 1794. During the 1793 Philadelphia Yellow Fever Epidemic, Black residents were mistakenly believed to be immune to the disease, so they worked as carriers of the dead and tended to the sick and dying inside their homes. Kidnapping of free Black residents to be sold back into slavery was a risk that continued into the 19th century, especially for children.

1800 to Civil War
The growing free Black community was instrumental in making Philadelphia a hotbed ofabolitionism
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The Britis ...
by the 1830s. Wealthy Black entrepreneur James Forten
James Forten (September 2, 1766March 4, 1842) was an African-American abolitionist and wealthy businessman in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Born free in the city, he became a sailmaker after the American Revolutionary War. Following an apprenticesh ...
gave white abolitionist William Lloyd Garrison
William Lloyd Garrison (December , 1805 – May 24, 1879) was a prominent American Christian, abolitionist, journalist, suffragist, and social reformer. He is best known for his widely read antislavery newspaper '' The Liberator'', which he found ...
funding so he could start the anti-slavery newspaper '' The Liberator'' and contributed articles to it. Black activists were founders and members of the national biracial group the American Anti-Slavery Society
The American Anti-Slavery Society (AASS; 1833–1870) was an abolitionist society founded by William Lloyd Garrison and Arthur Tappan. Frederick Douglass, an escaped slave, had become a prominent abolitionist and was a key leader of this society ...
, created in Philadelphia in 1833, and the Pennsylvania Anti-Slavery Society
The Pennsylvania Anti-Slavery Society was established in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in 1838. Founders included James Mott, Lucretia Mott, Robert Purvis, and John C. Bowers.
In August 1850, William Still while working as a clerk for the Society, ...
, created in 1838. In December 1833, after women were excluded from the American Anti-Slavery Society, a group of black and white women, which included Cyril Bustil's daughter Grace Douglass Grace Bustill Douglass (1782 – March 9, 1842) was an African-American abolitionist and women's rights advocate. Her family was one of the first prominent free black families in the United States. Her family's history is one of the best documented ...
, and James Forten's daughters, Sarah, Harriet and Margaretta launched the Philadelphia Female Anti-Slavery Society
The Philadelphia Female Anti-Slavery Society (PFASS) was founded in December 1833 and dissolved in March 1870 following the ratification of the 14th and 15th Amendments to the U.S. Constitution. It was founded by eighteen women, including Mary ...
(PFASS).
While some African Americans in Philadelphia worked in professional jobs that catered to the Black community like teachers, doctors, ministers, barbers, caterers, and entrepreneurs, most Black Philadelphians at that time worked at physically demanding and low-paying jobs. They competed with working class whites, especially new Irish immigrants, for jobs, which led to racial conflict. In 1834, a race riot broke started at a local tavern that was popular with both black and white Philadelphians. A white mob attacked Black homes, businesses, and churches. In 1838, another white mob attacked Pennsylvania Hall, where black and white abolitionists were meeting, and burned it down. Also in 1838, Pennsylvania's newly ratified constitution officially disfranchised African Americans. In 1842, white mobs again attacked blacks during the Lombard Street Riots.
Despite the risks and racism they encountered, African-Americans continued to come to Philadelphia, since it was the closest major city to the Southern States, where slavery was still legal. In the years leading up to the Civil War, Philadelphia had the largest black population outside the slave states. There were 15,000 black Philadelphians in 1830, 20,000 by 1850, and 22,000 by 1860. Most lived in South Philadelphia near what is today Center City, but there were smaller populations in Northern Liberties, Kensington, and Spring Garden. They came because of Philadelphia's reputation as a thriving political, cultural, and economic center for African Americans.
The city was also a major stop on the Underground Railroad, especially for slaves escaping through Maryland and Delaware. Robert Purvis
Robert Purvis (August 4, 1810 – April 15, 1898) was an American abolitionist in the United States. He was born in Charleston, South Carolina, and was likely educated at Amherst Academy, a secondary school in Amherst, Massachusetts. He ...
, president of the biracial Pennsylvania Anti-Slavery Society
The Pennsylvania Anti-Slavery Society was established in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in 1838. Founders included James Mott, Lucretia Mott, Robert Purvis, and John C. Bowers.
In August 1850, William Still while working as a clerk for the Society, ...
from 1845–50, was also chairman of the General Vigilance Committee
A vigilance committee was a group formed of private citizens to administer law and order or exercise power through violence in places where they considered governmental structures or actions inadequate. A form of vigilantism and often a more stru ...
from 1852–1857, which gave direct aid to fugitive slaves. With his wife Harriet Forten Purvis, he worked as a conductor of the Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroad was a network of clandestine routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early- to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and Canada. T ...
. Purvis estimated that from 1831–61, they helped one slave per day achieve freedom, assisting more than 9,000 slaves to escape to the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
. They used their own house, then located outside the city, in Byberry Township, as a place where fugitives could hide. Purvis built Byberry Hall across the street from his home, on the edge of the Quaker-owned Byberry Friends Meeting campus, to host anti-slavery speakers. It still stands today.
Civil War to 1900
 During the
During the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, eleven African American Philadelphia regiments fought for the North, after the passage of the
1862 Second Militia Act allowing blacks to be enlist in the Army.
After the Civil War, African Americans in Philadelphia, including Octavius V. Catto (1839–71), organized to end segregation of the city’s schools and streetcars and regain the right to vote. Their efforts paid off; in 1867, streetcar segregation was ended throughout the state, and legal segregation of schools ended in 1881 (although de facto segregation continued into the 20th century.) The Fifteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution gave Pennsylvania Black Americans the right to vote in 1870. But Catto himself was shot and killed while trying to cast his ballot in 1871.
In 1879, painter Henry Ossawa Tanner
Henry Ossawa Tanner (June 21, 1859 – May 25, 1937) was an American artist and the first African-American painter to gain international acclaim. Tanner moved to Paris, France, in 1891 to study at the Académie Julian and gained acclaim in Fren ...
enrolled as the first African American student at the Pennsylvania Academy of Fine Arts
Pennsylvania (; (Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, Maryl ...
. After travels abroad, he would return to Philadelphia in 1893 to paint his most famous work, The Banjo Lesson. Also in 1893, Philadelphia high school student Meta Vaux Warrick Fuller
Meta Vaux Warrick Fuller ( ; born Meta Vaux Warrick; June 9, 1877 – March 18, 1968) was an African-American artist who celebrated Afrocentric themes. At the fore of the Harlem Renaissance, Warrick was known for being a poet, painter, theater ...
created an art project that was included in The World's Columbian Exposition in Chicago and led to her future success as a multi-disciplinary artist.
The Black population rose to nearly 32,000 in 1880. In 1884, there were approximately 300 black-owned businesses, including the Philadelphia Tribune (started in 1884) and Douglas Hospital (opened in 1895). By 1900, the Black population at 63,000 people, had nearly doubled.Wolfinger, Jame. "African American Migration"
Encyclopedia of Greater Philadelphia, 2013. Retrieved March 5, 2021. In 1896 Philadelphia poet, suffragist, and abolitionist
Frances Harper
Frances Ellen Watkins Harper (September 24, 1825 – February 22, 1911) was an American abolitionist, suffragist, poet, temperance activist, teacher, public speaker, and writer. Beginning in 1845, she was one of the first African-American women to ...
helped found the National Association of Colored Women
The National Association of Colored Women's Clubs (NACWC) is an American organization that was formed in July 1896 at the First Annual Convention of the National Federation of Afro-American Women in Washington, D.C., United States, by a merger of ...
and served as its vice president. By then, she had already had a long career as a published writer, including works like her poem '' Bury Me In a Free Land'', ''Sketches of Southern Life'', and the novel Iola Leroy
''Iola Leroy'', ''or Shadows Uplifted'', an 1892 novel by Frances E. W. Harper, is one of the first novels published by an African-American woman. While following what has been termed the "sentimental" conventions of late nineteenth-century writ ...
.
Published in 1899 by the University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (also known as Penn or UPenn) is a private research university in Philadelphia. It is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and is ranked among the highest-regarded universitie ...
and conducted by W. E. B. Du Bois, '' The Philadelphia Negro: A Social Study'' was the first sociological race study of the African American community in the United States''.'' The aim of the social study was to identify "The Negro Problems of Philadelphia," the problems facing black communities not only in Philadelphia, but all over the country as well. The study focused on Philadelphia's Seventh Ward (currently Center City Philadelphia) and the socioeconomic conditions of black churches, businesses and homes within the neighborhood. Using statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of ...
Du Bois created from his survey data, Du Bois compared the occupation, income, education, family size, health, drug use, criminal activity, and suffrage of black and white residents living in the Seventh Ward and to Philadelphia's other wards. Du Bois used statistical evidence to highlight the socioeconomic inequalities the black community faced and make the black community's suffrage known to whites. In turn, he disproved stereotypes surrounding the black community which were cited as the sources of "The Negro Problem."
1900 to 1950s
 World War I brought an influx of black migrants from the rural South, who moved to Philadelphia lured by wartime jobs there during The great migration. As a result, the black population of Philadelphia doubled again from 63,000 in 1900 to 134,000 in 1920.Most of the new residents came from rural backgrounds and were working poor.
Efforts to build new structures to house the workers were insufficient, so African Americans in search of housing moved into existing houses in white neighborhoods, where they encountered hostility and racism. In July 1918, after two black families on Pine Street were attacked by white neighbors who burned household furnishings, G. Grant Williams, editor of the
World War I brought an influx of black migrants from the rural South, who moved to Philadelphia lured by wartime jobs there during The great migration. As a result, the black population of Philadelphia doubled again from 63,000 in 1900 to 134,000 in 1920.Most of the new residents came from rural backgrounds and were working poor.
Efforts to build new structures to house the workers were insufficient, so African Americans in search of housing moved into existing houses in white neighborhoods, where they encountered hostility and racism. In July 1918, after two black families on Pine Street were attacked by white neighbors who burned household furnishings, G. Grant Williams, editor of the Philadelphia Tribune
''The Philadelphia Tribune'' is the oldest continuously published African-American newspaper in the United States.
The paper began in 1884 when Christopher J. Perry published its first copy. Throughout its history, ''The Philadelphia Tribune' ...
, wrote of the “Pine Street war Zone”: “We stand for peace,” he said, and advised Black residents to “stand your ground like men,” adding “You are not down in Dixie now and you need not fear the ragged rum crazed hellion crew... They may burn your property, but you burn their hides with any weapon that comes handy while they engage in this illegal pastime.”
Three weeks later, racial violence erupted again which lasted for several days. During the riot, black homes were destroyed by white mobs, three people were killed, one man was nearly lynched, and a white police officer beat up a black man while he was in the hospital. As a result, African Americans in Philadelphia formed the Colored Protective Association, led by Reverend RR Wright Jr., to “have a permanent organization of protection” to fight discrimination in schools, housing, employment and elsewhere, and to investigate cases of police brutality and police collusion with the white rioters. Their efforts eventually led to the removal of the entire police force by the Director of Public Safety.
 In 1925, the artist and printmaker
In 1925, the artist and printmaker Dox Thrash
Dox Thrash (1893–1965) was an African-American artist who was famed as a skilled Drafter, draftsman, master printmaker, and painter and as the co-inventor of the Carborundum printmaking process.Donnelly, Michell"The Art of Dox Thrash" The Encycl ...
moved to Philadelphia, where he would spend most of his career. Black Opals, an African American literary magazine associated with the Harlem Renaissance
The Harlem Renaissance was an intellectual and cultural revival of African American music, dance, art, fashion, literature, theater, politics and scholarship centered in Harlem, Manhattan, New York City, spanning the 1920s and 1930s. At the t ...
was published in Philadelphia between spring 1927 and July 1928,. Co-edited by Arthur Huff Fauset
Arthur Huff Fauset (January 20, 1899 – September 2, 1983) was an American civil rights activist, anthropologist, folklorist, and educator. Born in Flemington, New Jersey, he grew up in Philadelphia, where he attended Central High School.
...
and Nellie Rathbone Bright, the magazine's contributors included Mae Virginia Cowdery, Jessie Redmon Fauset, Marita Bonner, and Gwendolyn B. Bennett
Gwendolyn B. Bennett (July 8, 1902 – May 30, 1981) was an American artist, writer, and journalist who contributed to '' Opportunity: A Journal of Negro Life'', which chronicled cultural advancements during the Harlem Renaissance. Though often ...
. Allan Randall Freelon was the magazine's artistic director. Also in the 1920s, John T Gibson became the wealthiest Black entrepreneur in Philadelphia because of his ownership of the popular Standard Standard may refer to:
Symbols
* Colours, standards and guidons, kinds of military signs
* Standard (emblem), a type of a large symbol or emblem used for identification
Norms, conventions or requirements
* Standard (metrology), an object th ...
and Dunbar
Dunbar () is a town on the North Sea coast in East Lothian in the south-east of Scotland, approximately east of Edinburgh and from the English border north of Berwick-upon-Tweed.
Dunbar is a former royal burgh, and gave its name to an ecc ...
theaters and his management of diverse musical and vaudeville
Vaudeville (; ) is a theatrical genre of variety entertainment born in France at the end of the 19th century. A vaudeville was originally a comedy without psychological or moral intentions, based on a comical situation: a dramatic composition ...
acts.
The Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
hit Black Philadelphians hard. By 1933, 50% of all Black residents were unemployed. And yet by 1935, African Americans owned 9,855 homes and 787 stores; they were also working in more professional occupations, like physicians ( 200); clergymen ( 250); schoolteachers (553) and policemen ( 219). Their neighborhoods were also becoming more concentrated and more segregated from white neighborhoods.
In 1938, Crystal Bird Fauset became the first female African American elected as state legislator.
Though World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
brought wartime jobs to African Americans, they still faced substandard housing and were not allowed to work on Philadelphia public transit as motormen or conductors until the Federal Government stepped in to pressure the Philadelphia Transportation Company
The Philadelphia Transportation Company (PTC) was the main public transit operator in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, from 1940 to 1968. A private company, PTC was the successor to the Philadelphia Rapid Transit Company (PRT), in operation since 19 ...
to open up these jobs to them in 1944. From August 1–6, white transit workers responded by staging a massive sickout strike. After pressure from the NAACP
The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) is a civil rights organization in the United States, formed in 1909 as an interracial endeavor to advance justice for African Americans by a group including W. E.&nb ...
, the Federal Government sent in 5,000 troops to break the strike and keep public transportation running.
Philadelphia was a center for the mid twentieth century Golden Age of Gospel music
Gospel music is a traditional genre of Christian music, and a cornerstone of Christian media. The creation, performance, significance, and even the definition of gospel music varies according to culture and social context. Gospel music is com ...
, attracting performers like the nationally renowned male quartets the Dixie Hummingbirds
Dixie, also known as Dixieland or Dixie's Land, is a nickname for all or part of the Southern United States. While there is no official definition of this region (and the included areas shift over the years), or the extent of the area it cover ...
and the Sensational Nightingales
The Sensational Nightingales are a traditional black gospel quartet that reached its peak of popularity in the 1950s, when it featured Julius Cheeks as its lead singer. The Nightingales, with several changes of membership, continue to tour and r ...
, as well as Marion Willliams before she started her solo career.
1950s to Present
 The fight against discrimination and segregation in education and employment continued through the 1950s and 60s, with legal battles and protests occurring throughout those years. Cecil B. Moore, president of the local NAACP, was a leading activist during that time, and Reverend
The fight against discrimination and segregation in education and employment continued through the 1950s and 60s, with legal battles and protests occurring throughout those years. Cecil B. Moore, president of the local NAACP, was a leading activist during that time, and Reverend Leon Sullivan
Leon Howard Sullivan (October 16, 1922 – April 24, 2001) was a Baptist minister, a civil rights leader and social activist focusing on the creation of job training opportunities for African Americans, a longtime General Motors Board Member, an ...
was instrumental in building Black community and economic power. Marie Hicks successfully organized demonstrations and brought a lawsuit against Girard College
Girard College is an independent college preparatory five-day boarding school located on a 43-acre campus in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The school was founded and permanently endowed from the shipping and banking fortune of Stephen Girard upon h ...
to desegregate
Desegregation is the process of ending the separation of two groups, usually referring to races. Desegregation is typically measured by the index of dissimilarity, allowing researchers to determine whether desegregation efforts are having impact o ...
that institution. In 1964, a clash between police officers and residents sparked a three day riot.
The Sixties saw a rise in the Black Power movement in Philadelphia. Freedom Library on Ridge Avenue in North Philadelphia, started in 1964 by John Churchville, was where Churchville and other activists gathered to form the Black Power Unity Movement in 1965. Another important center of Black Power was The Church of the Advocate
The George W. South Memorial Church of the Advocate, also known as the George W. South Memorial Protestant Episcopal Church, is a historic church at 18th and Diamond Street in North Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA.
History
The church was built ...
in North Central Philadelphia, whose congregation had become increasingly African American. Father Paul Washington
Paul Washington (May 26, 1921 – October 7, 2002) was an Episcopal priest and community activist in Philadelphia. Biography
Washington was born in Charleston, South Carolina, the United States on May 26, 1921. He attended the Avery Institute a ...
organized the first Black Power rally in 1966; soon there were rallies all over the city, and the third national conference in Philadelphia attracted 2,000 people. The newspaper ''Voice of Umuja'' came out of the conference.
Reggie Schell
Richard Reginald Schell (July 6, 1941 – May 9, 2012), better known as Captain Reggie Schell, was a political activist who was a member of the Philadelphia chapter of the Black Panther Party
The Black Panther Party (BPP), originally the Bl ...
became the leader of the Philadelphia chapter of the Black Panther Party
The Black Panther Party (BPP), originally the Black Panther Party for Self-Defense, was a Marxist-Leninist and black power political organization founded by college students Bobby Seale and Huey P. Newton in October 1966 in Oakland, Califo ...
in 1969. Under his leadership, the party held rallies and created food distribution and education programs throughout the city. Black Power spilled onto college and high school campuses, where students demonstrated for more Black faculty and Black studies classes. In 1970, Philadelphia police raids of three offices of Black Power activists at gunpoint, in which they publicly strip searched activists, made international news for their brutality and united the black community in outrage. Later that year, the Panther sponsored Revolutionary People's Constitutional Convention was held at Temple College and attracted 14,000 people.

Philadelphia soul
Philadelphia soul, sometimes called Philly soul, the Philadelphia sound, Phillysound, or The Sound of Philadelphia TSOP, is a genre of late 1960s–1970s soul music characterized by funk influences and lush instrumental arrangements, often feat ...
was a genre of music that arose in the late 1960s and 70s. Influenced by funk, it was characterized by lush instrumental arrangements with sweeping strings and piercing horns. Fred Wesley described it as “putting the bow tie on funk”. It moved funk more towards the disco sound that would become popular in the late 1970s and influenced later Philadelphia-born music makers like singer Jill Scott.
Predominently Black group MOVE
Move may refer to:
People
*Daniil Move (born 1985), a Russian auto racing driver
Brands and enterprises
* Move (company), an online real estate company
* Move (electronics store), a defunct Australian electronics retailer
* Daihatsu Move
Gov ...
was founded in 1972 by John Africa. The organization lived in a communal setting in West Philadelphia
West Philadelphia, nicknamed West Philly, is a section of the city of Philadelphia. Alhough there are no officially defined boundaries, it is generally considered to reach from the western shore of the Schuylkill River, to City Avenue to the nort ...
, following philosophies of anarcho-primitivism
Anarcho-primitivism is an anarchist critique of civilization (anti-civ) that advocates a return to non-civilized ways of life through deindustrialization, abolition of the division of labor or specialization, and abandonment of large-scale organ ...
. In 1978, a standoff between MOVE and the Philadelphia police resulted in the death of one police officer and injuries to sixteen officers and firefighters. Nine members were convicted of killing the officer and received life sentence
Life imprisonment is any sentence of imprisonment for a crime under which convicted people are to remain in prison for the rest of their natural lives or indefinitely until pardoned, paroled, or otherwise commuted to a fixed term. Crimes for ...
s. In 1985, another conflict resulted in a police helicopter dropping a bomb onto the roof of the MOVE compound, a townhouse
A townhouse, townhome, town house, or town home, is a type of terraced housing. A modern townhouse is often one with a small footprint on multiple floors. In a different British usage, the term originally referred to any type of city residence ...
that was located at 6221 Osage Avenue. The ensuing fire killed six MOVE members, and five of their children, and destroyed sixty-five houses in the neighborhood. The police bombing was strongly condemned. The MOVE survivors later filed a civil suit
-
A lawsuit is a proceeding by a party or parties against another in the Civil law (common law), civil court of law. The archaic term "suit in law" is found in only a small number of laws still in effect today. The term "lawsuit" is used in re ...
against the City of Philadelphia and the PPD and were awarded $1.5 million in a 1996 settlement. Other residents displaced by the destruction of the bombing filed a civil suit against the city and in 2005 were awarded $12.83 million in damages in a jury trial.
In 1982, Mumia Abu-Jamal
Mumia Abu-Jamal (born Wesley Cook; April 24, 1954) is an American political activist and journalist who was convicted of murder and sentenced to death in 1982 for the 1981 murder of Philadelphia police officer Daniel Faulkner. While on death r ...
, a Philadelphia activist and journalist, was convicted and sentenced to death for the 1981 murder in Philadelphia of police officer Daniel Faulkner. He became widely known while on death row for his writings and commentary on the U.S. criminal justice system. After numerous appeals, his death penalty sentence was overturned by a Federal court, with the prosecution agreeing in 2011 to a sentence of life imprisonment without parole.
Many Philadelphia activists of the mid to late 20th century went on to achieve political power. In 1975, Cecile B. Moore won a seat on the City Council. C. Delores Tucker (1927-2005) became the first black Pennsylvanian appointed to the office of the secretary of state. David P. Richardson (1948-1995) was elected to the Pennsylvania House of Representatives in 1972. In 1984, W. Wilson Goode (b. 1938) became Philadelphia’s first black mayor. Goode’s administration was followed by black mayors John Street (b. 1943) and Michael Nutter
Michael Anthony Nutter (born June 29, 1957) is an American politician who served as the 98th Mayor of Philadelphia. Elected on November 6, 2007, he was reelected to a second term on November 8, 2011. He is a previous member of the Philadelphia ...
(b. 1957).
Despite the persistence of problems like unemployment and high public school dropout rates, the black community in Philadelphia in the early 21st century continued to attract new residents and contribute its talents and energy to the city. In 2010, its total population stood at 657,343 people or 43.4 percent of Philadelphia's entire population.
Institutions
 The
The African American Museum in Philadelphia
The African American Museum in Philadelphia (AAMP) is notable as the first museum funded and built by a municipality to help preserve, interpret and exhibit the heritage of African Americans. Opened during the 1976 Bicentennial celebrations, th ...
is located in Center City.
ThAces Museum
honors WWII veterans and their families. Th
Colored Girls Museum
founded by Vashti DuBois, is dedicated to the history of Black women and girls. Th
National Marian Anderson Museum
celebrates the life of the notable opera singer
Marian Anderson
Marian Anderson (February 27, 1897April 8, 1993) was an American contralto. She performed a wide range of music, from opera to Spiritual (music), spirituals. Anderson performed with renowned orchestras in major concert and recital venues throu ...
.
The Paul Robeson
Paul Leroy Robeson ( ; April 9, 1898 – January 23, 1976) was an American bass-baritone concert artist, stage and film actor, professional football player, and activist who became famous both for his cultural accomplishments and for his p ...
House hosts tours of Robeson's former residence.
Geography
20th century
Circa 1961Society Hill
Society Hill is a historic neighborhood in Center City Philadelphia, with a population of 6,215 . Settled in the early 1680s, Society Hill is one of the oldest residential neighborhoods in Philadelphia.The Center City District dates the Free Soc ...
was a majority black and low income neighborhood, but by 1976 it became gentrified and mostly white with the remaining black population residing in about three or four high-rise apartment buildings with high rents. ''Black Enterprise
''Black Enterprise'' is a black-owned multimedia company. Since the 1970s, its flagship product ''Black Enterprise'' magazine has covered African-American businesses with a readership of 3.7 million. The company was founded in 1970 by Earl G ...
'' wrote that a possible reason why wealthier blacks opted not to move to Society Hill was "Unpleasant memories of the old neighborhood". By then many blacks were moving to Wynnefield
__NOTOC__
Wynnefield is a diverse middle-class
neighborhood in West Philadelphia. Its borders are 53rd Street at Jefferson to the south, Philadelphia's Fairmount Park to the east, City Avenue (commonly referred to as "City Line") to the north a ...
, with many originating from Cobbs Creek
Cobbs Creek is an U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 1, 2011 tributary of Darby Creek in Delaware County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It forms an approximat ...
and Overbrook; the new residents of Wynnefield had recently become middle class."Blacks in Philadelphia." p. 44. Also Circa 1976 many African-Americans resided in Powelton Village. The majority originated from other states and held professional positions, including artists, graduate students, musicians, teachers, and writers.
21st century
From 1990 to 2010, Black residents moved in significant numbers away from the core areas of North and West Philadelphia to Southwest Philadelphia, Overbrook, the Lower Northeast, and elsewhere. The number of Black residents in zip code 19120—which includes the neighborhoods of Olney and Feltonville and abuts Montgomery County -rose from 9,786 in 1990 to 33,209 in 2010, an increase of 239 percent.Religion
 The African Episcopal Church of St. Thomas, established in 1792, was the first house of worship created by and for black people in the United States. While the
The African Episcopal Church of St. Thomas, established in 1792, was the first house of worship created by and for black people in the United States. While the St. George's United Methodist Church
St. George's United Methodist Church, located at the corner of 4th and New Streets, in the Old City neighborhood of Philadelphia, is the oldest Methodist church in continuous use in the United States,
had initially allowed black worshipers in the main area, its black worshipers left after the church moved them to the gallery area by 1787."Blacks in Philadelphia." p. 36.
Education
The first school for Black males was established by the Pennsylvania Abolition Society in 1794. In 1813, the Society constructed the school building Clarkson Hall on Cherry Street, and in 1854, created Lombard Street Infant School as an aid to working parents. In 1976 66% of all students of theSchool District of Philadelphia
The School District of Philadelphia (SDP) is the school district that includes all school district-operated public schools in Philadelphia. Established in 1818, it is the 8th largest school district in the nation, by enrollment, serving over 200 ...
were black; this number was proportionally high since whites of all economic backgrounds had a tendency to use private schools. Wealthier blacks chose not to use private schools because their neighborhoods were assigned to higher quality public schools.
Notable residents
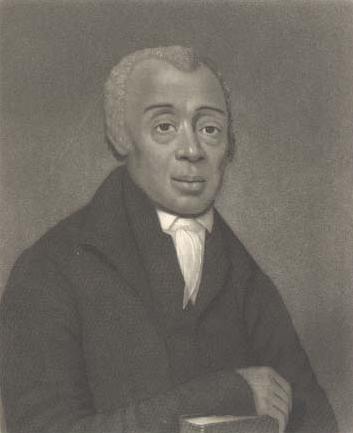



18th–19th centuries
* Richard Allen, religious leader, author, journalist *Sarah Allen
Sarah Allen is a Canadian actress. She studied acting at the National Theatre School of Canada and graduated in 2002.
''Being Human''
Allen is perhaps best known for playing vampire Rebecca Flynt on SyFy's '' Being Human''. For the role ...
, abolitionist, underground railroad conductor, missionary
* Cyrus Bustill
Cyrus Bustill (February 2, 1732 1806) was an African-American brewer and baker, abolitionist and community leader.
A notable business owner in the African-American community in Philadelphia, he also became a founding member of the Free Africa ...
, 18th century entrepreneur, abolitionist and community leader
* Jabez Pitt Campbell
Jabez Pitt Campbell (February 5, 1815 – August 9, 1891)Campbell, Jabez Pitt. Ancestry.com. was an American minister, activist, philanthropist and the eighth bishop of the African Methodist Episcopal Church (AME), the first independent African- ...
, abolitionist, and the 8th Bishop of the Methodist Episcopal Church
The Methodist Episcopal Church (MEC) was the oldest and largest Methodist denomination in the United States from its founding in 1784 until 1939. It was also the first religious denomination in the US to organize itself on a national basis. In ...
* Amy Matilda Cassey, activist, and abolitionist
* Joseph Cassey, businessman, abolitionist, and activist
* Octavius Catto
Octavius Valentine Catto (February 22, 1839 – October 10, 1871) was an educator, intellectual, and civil rights activist in Philadelphia. He became principal of male students at the Institute for Colored Youth, where he had also been educated. ...
, educator and Civil Rights activist
* Rebecca Cole, doctor and social reformer
* Rebecca Cox Jackson
Rebecca Cox Jackson (1795–1871) was a free Black woman, best known for her religious feminism and activism and for her autobiography, ''Gifts of Power: The Writings of Rebecca Cox Jackson, Black Visionary, Shaker Eldress'', which was published ...
, founder of a Shaker community in Philadelphia
* Nathaniel W. Depee
Nathaniel W. Depee (1812 – June 19, 1868) was an American activist, abolitionist, and merchant tailor. He was active in the Underground Railroad, and in Black politics in Philadelphia in the 1830s through 1860s.
Biography
Nathaniel W. Depee w ...
, activist, and abolitionist
* Frederick Douglass
Frederick Douglass (born Frederick Augustus Washington Bailey, February 1817 or 1818 – February 20, 1895) was an American social reformer, abolitionist, orator, writer, and statesman. After escaping from slavery in Maryland, he became ...
, social reformer, writer, and abolitionist
* Charlotte Vandine Forten, abolitionist
* James Forten
James Forten (September 2, 1766March 4, 1842) was an African-American abolitionist and wealthy businessman in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Born free in the city, he became a sailmaker after the American Revolutionary War. Following an apprenticesh ...
, early 19th century businessman and abolitionistWinch, Julie,''A Gentleman of Color: The Life of James Forten''
New York: Oxford University Press, 2002, p. 16. *
Margaretta Forten
Margaretta Forten (September 11, 1806 – January 13, 1875) was an African-American suffragist and abolitionist.Alexander, Leslie''Encyclopedia of African American History, Volume 1''ABC-CLIO (2010), p. 1045.Alexander, Leslie
''Encyclopedia of African American History, Volume 1''
ABC-CLIO (2010), p. 1045. *
''Encyclopedia of African American History, Volume 1''
ABC-CLIO (2010), p. 1045. *
Grace Douglass Grace Bustill Douglass (1782 – March 9, 1842) was an African-American abolitionist and women's rights advocate. Her family was one of the first prominent free black families in the United States. Her family's history is one of the best documented ...
, abolitionist
* Sarah Mapps Douglass
Sarah Mapps Douglass (September 9, 1806 – September 8, 1882) was an American educator, Abolitionism in the United States, abolitionist, writer, and public lecturer. Her painted images on her written letters may be the first or earliest survivi ...
, 19th century educator
* Richard Theodore Greener
Richard Theodore Greener (1844–1922) was a pioneering African-American scholar, excelling in elocution, philosophy, law and classics in the Reconstruction era. He broke ground as Harvard College's first Black graduate in 1870. Within three y ...
, professor, lawyer, scholar
* Charlotte Forten Grimké
Charlotte Louise Bridges Forten Grimké (August 17, 1837 – July 23, 1914) was an African American anti-slavery activist, poet, and educator. She grew up in a prominent abolitionist family in Philadelphia. She taught school for years, including d ...
, 19th century civil rights activist, woman's rights activist
* Frances Ellen Watkins Harper
Frances Ellen Watkins Harper (September 24, 1825 – February 22, 1911) was an American Abolitionism in the United States, abolitionist, suffragist, poet, Temperance movement, temperance activist, teacher, public speaker, and writer. Beginning in 1 ...
, abolitionist, suffragette, poet, author
* Jarena Lee
Jarena Lee (February 11, 1783 – February 3, 1864) was the first woman preacher in the African Methodist Episcopal Church (AME). Born into a free Black family, in New Jersey, Lee asked the founder of the AME church, Richard Allen, to be a preac ...
, preacher
* Absalom Jones
Absalom Jones (November 7, 1746February 13, 1818) was an African-American abolitionist and clergyman who became prominent in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Disappointed at the racial discrimination he experienced in a local Methodist church, he found ...
, minister, abolitionist, and founder of Free African Society
* John McKee, philanthropist, property owner
* Zedekiah Johnson Purnell, activist, and businessman
* Harriet Forten Purvis, abolitionist
* Robert Purvis
Robert Purvis (August 4, 1810 – April 15, 1898) was an American abolitionist in the United States. He was born in Charleston, South Carolina, and was likely educated at Amherst Academy, a secondary school in Amherst, Massachusetts. He ...
, abolitionist, lived most of his life in Philadelphia
* Sarah Louisa Forten Purvis, abolitionist, suffragist
* William B. Purvis, inventor and businessman
* Stephen Smith, businessman, philanthropist, preacher, real estate developer, and abolitionist
* William Whipper
William Whipper (February 22, 1804 – March 9, 1876) was a businessman and Abolitionism in the United States, abolitionist in the United States. Whipper, an African American, advocated nonviolence and co-founded the American Moral Reform Socie ...
, businessman and abolitionist
* Peter Williams Jr., pastor and abolitionist
20th–21st centuries
*Julian Abele
Julian Francis Abele (April 30, 1881April 23, 1950) was a prominent Black American architect, and chief designer in the offices of Horace Trumbauer. He contributed to the design of more than 400 buildings, including the Widener Memorial Library at ...
, architect
* Meta Vaux Warrick Fuller
Meta Vaux Warrick Fuller ( ; born Meta Vaux Warrick; June 9, 1877 – March 18, 1968) was an African-American artist who celebrated Afrocentric themes. At the fore of the Harlem Renaissance, Warrick was known for being a poet, painter, theater ...
, artist
* Henry Ossawa Tanner
Henry Ossawa Tanner (June 21, 1859 – May 25, 1937) was an American artist and the first African-American painter to gain international acclaim. Tanner moved to Paris, France, in 1891 to study at the Académie Julian and gained acclaim in Fren ...
, painter
* Bessie Smith
Bessie Smith (April 15, 1894 – September 26, 1937) was an American blues singer widely renowned during the Jazz Age. Nicknamed the " Empress of the Blues", she was the most popular female blues singer of the 1930s. Inducted into the Rock and ...
, blues singer and actress
* Alain LeRoy Locke
Alain LeRoy Locke (September 13, 1885 – June 9, 1954) was an American writer, philosopher, educator, and patron of the arts. Distinguished in 1907 as the first African-American Rhodes Scholar, Locke became known as the philosophical architect ...
, Harlem Renaissance philosopher, journalist, author, scholar
* Raymond Pace Alexander
Raymond Pace Alexander (October 13, 1897 – November 24, 1974) was an American civil rights leader, lawyer, politician, and the first African American judge appointed to the Pennsylvania Court of Common Pleas. Born and raised in Philadelphia, ...
, Lawyer and civil rights activist
* Rex Stewart
Rex William Stewart Jr. (February 22, 1907 – September 7, 1967) was an American jazz cornetist who was a member of the Duke Ellington orchestra.
Career
As a boy he studied piano and violin; most of his career was spent on cornet. Stewart drop ...
, cornetist/trumpeter, journalist, disk jockey, publisher
* Billie Holiday
Billie Holiday (born Eleanora Fagan; April 7, 1915 – July 17, 1959) was an American jazz and swing music singer. Nicknamed "Lady Day" by her friend and music partner, Lester Young, Holiday had an innovative influence on jazz music and pop si ...
, singer
* Ethel Waters
Ethel Waters (October 31, 1896 – September 1, 1977) was an American singer and actress. Waters frequently performed jazz, swing, and pop music on the Broadway stage and in concerts. She began her career in the 1920s singing blues. Her not ...
, Singer, comedienne and actress
* Marian Anderson
Marian Anderson (February 27, 1897April 8, 1993) was an American contralto. She performed a wide range of music, from opera to Spiritual (music), spirituals. Anderson performed with renowned orchestras in major concert and recital venues throu ...
, contralto opera singer
* Crystal Bird Fausett, first African-American female state legislator (elected 1938)
* Kobe Bryant
Kobe Bean Bryant ( ; August 23, 1978 – January 26, 2020) was an American professional basketball player. A shooting guard, he spent his entire 20-year career with the Los Angeles Lakers in the National Basketball Association (NBA). Widely r ...
, basketball player
* Michael Nutter
Michael Anthony Nutter (born June 29, 1957) is an American politician who served as the 98th Mayor of Philadelphia. Elected on November 6, 2007, he was reelected to a second term on November 8, 2011. He is a previous member of the Philadelphia ...
, Mayor of Philadelphia
The mayor of Philadelphia is the chief executive of the government of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania,
as stipulated by the Charter of the City of Philadelphia. The current mayor of Philadelphia is Jim Kenney.
History
The first mayor of Philadelphia, ...
* John F. Street, Mayor of Philadelphia
* Luckey Roberts
Charles Luckyth Roberts (August 7, 1887 – February 5, 1968), better known as Luckey Roberts, was an American composer and stride pianist who worked in the jazz, ragtime, and blues styles.
Biography
Luckey Roberts was born in Philadelphia, ...
, pianist and composer
* Teddy Pendergrass
Theodore DeReese Pendergrass (March 26, 1950 – January 13, 2010) was an American soul and R&B singer-songwriter. He was born in Kingstree, South Carolina. Pendergrass spent most of his life in the Philadelphia area, and initially rose to musi ...
, Singer, songwriter and drummer
* Ed Bradley
Edward Rudolph Bradley Jr. (June 22, 1941 – November 9, 2006) was an American broadcast journalist and news anchor. He was best known for his reporting on ''60 Minutes'' and CBS News.
Bradley began his journalism career as a radio news repo ...
, News correspondent
* Wilt Chamberlain
Wilton Norman Chamberlain (; August 21, 1936 – October 12, 1999) was an American professional basketball player who played as a Center (basketball), center. Standing at tall, he played in the National Basketball Association (NBA) for 14 yea ...
, basketball player
* Will Smith
Willard Carroll Smith II (born September 25, 1968), also known by his stage name The Fresh Prince, is an American actor and rapper. He began his Will Smith filmography, acting career starring as Will Smith (The Fresh Prince of Bel-Air), a ...
, rapper, actor
* Guion S. Bluford, astronaut, scientist, pilot
* Kevin Hart
Kevin Darnell Hart (born July 6, 1979) is an American comedian and actor. Originally known as a stand-up comedian, he has since starred in Hollywood films and on TV. He has also released several well-received comedy albums.
After winning se ...
, actor, comedian
* Patti LaBelle
Patricia Louise Holte (born May 24, 1944), known professionally as Patti LaBelle, is an American R&B singer, actress and businesswoman.
LaBelle is referred to as the " Godmother of Soul".
She began her career in the early 1960s as lead singe ...
, singer, actor
* Judith Jamison
Judith Ann Jamison (pronounced JAM-ih-son) (born May 10, 1943) is an American dancer and choreographer. She is the artistic director emerita of Alvin Ailey American Dance Theater.
Early training
Judith Jamison was born in 1943 to Tessie Brown Ja ...
, ballet dancer, choreographer
* Jill Scott, singer
* Sherman Hemsley
Sherman Alexander Hemsley (February 1, 1938 – July 24, 2012) was an American actor. He was known for his roles as George Jefferson on the CBS television series ''All in the Family'' (1973–1975; 1978) and ''The Jeffersons'' (1975–1985), Dea ...
, actor
* Solomon Burke
Solomon Vincent McDonald Burke (born James Solomon McDonald, March 21, 1936 or 1940 – October 10, 2010) was an American singer who shaped the sound of rhythm and blues as one of the founding fathers of soul music in the 1960s. He has been ...
, singer
* W. Wilson Goode, Mayor of Philadelphia
The mayor of Philadelphia is the chief executive of the government of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania,
as stipulated by the Charter of the City of Philadelphia. The current mayor of Philadelphia is Jim Kenney.
History
The first mayor of Philadelphia, ...
* Mumia Abu-Jamal
Mumia Abu-Jamal (born Wesley Cook; April 24, 1954) is an American political activist and journalist who was convicted of murder and sentenced to death in 1982 for the 1981 murder of Philadelphia police officer Daniel Faulkner. While on death r ...
(born Wesley Cook)
* Bill Cosby
William Henry Cosby Jr. ( ; born July 12, 1937) is an American stand-up comedian, actor, and media personality. He made significant contributions to American and African-American culture, and is well known in the United States for his eccentric ...
, Comedian and actor
* Raymond Pace Alexander
Raymond Pace Alexander (October 13, 1897 – November 24, 1974) was an American civil rights leader, lawyer, politician, and the first African American judge appointed to the Pennsylvania Court of Common Pleas. Born and raised in Philadelphia, ...
, lawyer, judge and politician
* Lil Uzi Vert
Symere Bysil Woods ( ; born July 31, 1995), known professionally as Lil Uzi Vert, is an American rapper, singer, and songwriter. They are characterized by their face tattoo, facial tattoos, facial piercings, eccentric hairstyles and androgynous ...
, rapper
* Eve
Eve (; ; ar, حَوَّاء, Ḥawwāʾ; el, Εὕα, Heúa; la, Eva, Heva; Syriac: romanized: ) is a figure in the Book of Genesis in the Hebrew Bible. According to the origin story, "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the ...
, rapper, singer, actress, and television presenter
* Meek Mill
Robert Rihmeek Williams (born May 6, 1987), known professionally as Meek Mill, is an American rapper. Born and raised in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, he embarked on his music career as a battle rapper, and later formed a short-lived rap group, ...
, rapper
* Beanie Sigel
Dwight Equan Grant (born March 6, 1974), better known by his stage name Beanie Sigel, is an American rapper from South Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He first became known for his association with Jay-Z and Roc-A-Fella Records, releasing his debut ...
, rapper
See also
*Arch Street Friends Meeting House
__NOTOC__
The Arch Street Friends Meeting House, at 320 Arch Street at the corner of 4th Street in the Old City neighborhood of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, is a Meeting House of the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers). Built to reflect Friend ...
*Vigilant Association of Philadelphia
The Vigilant Association of Philadelphia was an abolitionism in the United States, abolitionist organization founded in August 1837 in Philadelphia to "create a fund to aid colored persons in distress". The initial impetus came from Robert Purv ...
* Demographics of Philadelphia
*Puerto Ricans in Philadelphia
Philadelphia has the second largest Puerto Rican community outside of Puerto Rico after New York City. As of the 2010 U.S. Census, an estimated 121,643 Puerto Ricans were living in Philadelphia, up from 91,527 in 2000. Recent 2017 estimates by th ...
*History of the Jews in Philadelphia
Jews in Philadelphia can trace their history back to Colonial America. Jews have lived in Philadelphia since the arrival of William Penn in 1682.
Colonial History
Jewish traders have operated in southeastern Pennsylvania since at least the 1650s ...
*History of Irish Americans in Philadelphia
People of Irish descent form the largest ethnic group in the city of Philadelphia and its surrounding counties. The Irish have lived in Philadelphia since the pre-American Revolution period. Irishmen had participated in pro-Revolutionary activit ...
*History of Italian Americans in Philadelphia
Philadelphia has a significant Italian American population. In 2010, the Philadelphia metropolitan region had the second-largest Italian-American population in the United States with more than 142,000 residents with Italian ancestry, and about 3,1 ...
*African Americans in New York City
African Americans constitute one of the longer-running ethnic presences in New York City, home to the largest urban African American population, and the world's largest Black population of any city outside Africa, by a significant margin.
Pop ...
References
* "Blacks in Philadelphia." (November 1976). ''Black Enterprise
''Black Enterprise'' is a black-owned multimedia company. Since the 1970s, its flagship product ''Black Enterprise'' magazine has covered African-American businesses with a readership of 3.7 million. The company was founded in 1970 by Earl G ...
''. Start p. 36.
Notes
{{Portal bar, Philadelphia Ethnic groups in Philadelphia African-American cultural history History of Philadelphia