The history of medicine is both a study of medicine throughout history as well as a multidisciplinary field of study that seeks to explore and understand medical practices, both past and present, throughout human societies.
More than just
history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
and
medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pr ...
, this field of study incorporates learnings from across disciplines such as
anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of be ...
,
economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes ...
,
health sciences
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to health sciences:
Health sciences are those sciences which focus on health, or health care, as core parts of their subject matter. Health sciences relate to multiple ac ...
,
sociology
Sociology is a social science that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. It uses various methods of empirical investigation an ...
, and
politics
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that stud ...
to better understand the institutions, practices, people, professions, and social systems that have influenced and shaped medicine throughout the ages.
As a documentation of medicine over time, the history of medicine shows how societies have changed in their approach to illness and disease from ancient times to the present. Early medical traditions include
those of Babylon,
China,
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
and
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. The
Hippocratic Oath was written in
ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of Classical Antiquity, classical antiquity ( AD 600), th ...
in the 5th century BCE, and is a direct inspiration for oaths of office that physicians swear upon entry into the profession today. In the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, surgical practices inherited from the ancient masters were improved and then systematized in
Rogerius's ''The Practice of Surgery''. Universities began systematic training of physicians around 1220 CE in Italy.
Invention of the microscope was a consequence of improved understanding, during the Renaissance. Prior to the 19th century,
humorism
Humorism, the humoral theory, or humoralism, was a system of medicine detailing a supposed makeup and workings of the human body, adopted by Ancient Greek and Roman physicians and philosophers.
Humorism began to fall out of favor in the 1850s ...
(also known as humoralism) was thought to explain the cause of disease but it was gradually replaced by the
germ theory of disease
The germ theory of disease is the currently accepted scientific theory for many diseases. It states that microorganisms known as pathogens or "germs" can lead to disease. These small organisms, too small to be seen without magnification, invade ...
, leading to effective treatments and even cures for many infectious diseases. Military doctors advanced the methods of trauma treatment and surgery. Public health measures were developed especially in the 19th century as the rapid growth of cities required systematic sanitary measures. Advanced research centers opened in the early 20th century, often connected with major hospitals. The mid-20th century was characterized by new biological treatments, such as antibiotics. These advancements, along with developments in chemistry, genetics, and
radiography
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeu ...
led to
modern medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
. Medicine was heavily professionalized in the 20th century, and new careers opened to women as nurses (from the 1870s) and as physicians (especially after 1970).
Prehistoric medicine
Although there is little record to establish when plants were first used for medicinal purposes (
herbalism
Herbal medicine (also herbalism) is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are a basis of traditional medicine. With worldwide research into pharmacology, some herbal medicines have been translated into modern reme ...
), the use of plants as healing agents, as well as clays and soils is ancient. Over time, through emulation of the behavior of fauna, a medicinal knowledge base developed and passed between generations. Even earlier, Neanderthals may have engaged in medical practices.
As tribal culture specialized specific castes,
shaman
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spir ...
s and
apothecaries
''Apothecary'' () is a mostly archaic term for a medical professional who formulates and dispenses '' materia medica'' (medicine) to physicians, surgeons, and patients. The modern chemist (British English) or pharmacist (British and North Ameri ...
fulfilled the role of healer.
The first known
dentistry dates to c. 7000 BCE in
Baluchistan where Neolithic dentists used flint-tipped drills and bowstrings. The first known
trepanning
Trepanning, also known as trepanation, trephination, trephining or making a burr hole (the verb ''trepan'' derives from Old French from Medieval Latin from Greek , literally "borer, auger"), is a surgical intervention in which a hole is drill ...
operation was carried out c. 5000 BCE in
Ensisheim
Ensisheim (; gsw-FR, Anze) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It is also the birthplace of the composer Léon Boëllmann. The Germanic origins of the village's name reflect the area's history.
Amon ...
, France. A possible
amputation was carried out c. 4,900 BCE in Buthiers-Bulancourt, France.
Ancient medicine
Asia
Places
Ancient China

China also developed a large body of traditional medicine. Much of the philosophy of
traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. It has been described as "fraught with pseudoscience", with the majority of its treatments having no logical mechanism of acti ...
derived from empirical observations of disease and illness by
Taoist
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Tao ...
physicians and reflects the classical Chinese belief that individual human experiences express causative principles effective in the environment at all scales. These causative principles, whether material, essential, or mystical, correlate as the expression of the natural order of the universe.
The foundational text of Chinese medicine is the ''
Huangdi neijing
''Huangdi Neijing'' (), literally the ''Inner Canon of the Yellow Emperor'' or ''Esoteric Scripture of the Yellow Emperor'', is an ancient Chinese medical text or group of texts that has been treated as a fundamental doctrinal source for Chines ...
'', (or ''Yellow Emperor's Inner Canon''), written 5th century to 3rd century BCE. Near the end of the 2nd century CE, during the Han dynasty,
Zhang Zhongjing
Zhang Zhongjing (; 150–219), formal name Zhang Ji (), was a Chinese pharmacologist, physician, inventor, and writer of the Eastern Han dynasty and one of the most eminent Chinese physicians during the later years of the Han dynasty. He estab ...
, wrote a ''
Treatise on Cold Damage'', which contains the earliest known reference to the ''
Neijing Suwen
''Huangdi Neijing'' (), literally the ''Inner Canon of the Yellow Emperor'' or ''Esoteric Scripture of the Yellow Emperor'', is an ancient Chinese medical text or group of texts that has been treated as a fundamental doctrinal source for Chines ...
''. The
Jin dynasty practitioner and advocate of
acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientif ...
and
moxibustion
Moxibustion () is a traditional Chinese medicine therapy which consists of burning dried mugwort ('' wikt:moxa'') on particular points on the body. It plays an important role in the traditional medical systems of China, Japan, Korea, Vietna ...
,
Huangfu Mi
Huangfu Mi (215–282), courtesy name Shi'an (), was a Chinese physician, essayist, historian, poet, and writer who lived through the late Eastern Han dynasty, Three Kingdoms period and early Western Jin dynasty. He was born in a poor farming fam ...
(215–282), also quotes the
Yellow Emperor
The Yellow Emperor, also known as the Yellow Thearch or by his Chinese name Huangdi (), is a deity ('' shen'') in Chinese religion, one of the legendary Chinese sovereigns and culture heroes included among the mytho-historical Three Soverei ...
in his ''Jiayi jing'', c. 265. During the
Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdom ...
, the ''Suwen'' was expanded and revised and is now the best extant representation of the foundational roots of traditional Chinese medicine.
Traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. It has been described as "fraught with pseudoscience", with the majority of its treatments having no logical mechanism of acti ...
that is based on the use of herbal medicine, acupuncture, massage and other forms of therapy has been practiced in China for thousands of years.
In the 18th century, during the Qing dynasty, there was a proliferation of popular books as well as more advanced encyclopedias on traditional medicine. Jesuit missionaries introduced Western science and medicine to the royal court, although the Chinese physicians ignored them.
Finally in the 19th century, Western medicine was introduced at the local level by Christian medical missionaries from the
London Missionary Society
The London Missionary Society was an interdenominational evangelical missionary society formed in England in 1795 at the instigation of Welsh Congregationalist minister Edward Williams. It was largely Reformed in outlook, with Congregational m ...
(Britain), the
Methodist Church (Britain) and the
Presbyterian Church (US).
Benjamin Hobson
Benjamin Hobson (1816–1873) (Chinese:合信) was a Protestant medical missionary who served with the London Missionary Society in imperial China during its Qing dynasty. His ''Treatise on Physiology'', reproducing and elaborating on work by Wil ...
(1816–1873) in 1839, set up a highly successful Wai Ai Clinic in Guangzhou, China. The
Hong Kong College of Medicine for Chinese was founded in 1887 by the
London Missionary Society
The London Missionary Society was an interdenominational evangelical missionary society formed in England in 1795 at the instigation of Welsh Congregationalist minister Edward Williams. It was largely Reformed in outlook, with Congregational m ...
, with its first graduate (in 1892) being
Sun Yat-sen, who later led the
Chinese Revolution (1911)
The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China. The revolution was the culmination of a ...
. The
Hong Kong College of Medicine for Chinese was the forerunner of the School of Medicine of the
University of Hong Kong
The University of Hong Kong (HKU) (Chinese: 香港大學) is a public research university in Hong Kong. Founded in 1887 as the Hong Kong College of Medicine for Chinese, it is the oldest tertiary institution in Hong Kong. HKU was also the f ...
, which started in 1911.
Because of the social custom that men and women should not be near to one another, the women of China were reluctant to be treated by male doctors. The missionaries sent women doctors such as Dr.
Mary Hannah Fulton (1854–1927). Supported by the Foreign Missions Board of the Presbyterian Church (US) she in 1902 founded the first medical college for women in China, the Hackett Medical College for Women, in Guangzhou.
Historiography of Chinese medicine
When reading the
Chinese classics
Chinese classic texts or canonical texts () or simply dianji (典籍) refers to the Chinese texts which originated before the imperial unification by the Qin dynasty in 221 BC, particularly the "Four Books and Five Classics" of the Neo-Confuci ...
, it is important for scholars to examine these works from the Chinese perspective. Historians have noted two key aspects of Chinese medical history: understanding conceptual differences when translating the term , and observing the history from the perspective of
cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', and in 1731 taken up in Latin by German philosopher ...
rather than biology.
In Chinese classical texts, the term is the closest historical translation to the English word "body" because it sometimes refers to the physical human body in terms of being weighed or measured, but the term is to be understood as an "ensemble of functions" encompassing both the human psyche and emotions. This concept of the human body is opposed to the European duality of a separate mind and body.
It is critical for scholars to understand the fundamental differences in concepts of the body in order to connect the medical theory of the classics to the "human organism" it is explaining.
Chinese scholars established a correlation between the cosmos and the "human organism." The basic components of cosmology, qi, yin yang and the Five Phase theory, were used to explain health and disease in texts such as ''
Huangdi neijing
''Huangdi Neijing'' (), literally the ''Inner Canon of the Yellow Emperor'' or ''Esoteric Scripture of the Yellow Emperor'', is an ancient Chinese medical text or group of texts that has been treated as a fundamental doctrinal source for Chines ...
''.
Yin and yang
Yin and yang ( and ) is a Chinese philosophical concept that describes opposite but interconnected forces. In Chinese cosmology, the universe creates itself out of a primary chaos of material energy, organized into the cycles of yin and ya ...
are the changing factors in cosmology, with
qi as the vital force or energy of life. The Five Phase theory
Wu Xing Wuxing may refer to:
Places in China Counties and districts
*Huzhou, formerly Wuxing County, Zhejiang, China
*Wuxing District (吴兴区), central district of Huzhou
Subdistricts (五星街道)
*Wuxing Subdistrict, Mudanjiang, in Dong'an District ...
of the Han dynasty contains the elements wood, fire, earth, metal, and water. By understanding medicine from a cosmology perspective, historians better understand Chinese medical and social classifications such as gender, which was defined by a domination or remission of yang in terms of yin.
These two distinctions are imperative when analyzing the history of traditional Chinese medical science.
A majority of Chinese medical history written after the classical canons comes in the form of primary source case studies where academic physicians record the illness of a particular person and the healing techniques used, as well as their effectiveness.
Historians have noted that Chinese scholars wrote these studies instead of "books of prescriptions or advice manuals;" in their historical and environmental understanding, no two illnesses were alike so the healing strategies of the practitioner was unique every time to the specific diagnosis of the patient.
Medical case studies existed throughout Chinese history, but "individually authored and published case history" was a prominent creation of the Ming dynasty.
An example such case studies would be the literati physician, Cheng Congzhou, collection of 93 cases published in 1644.
Ancient India

The
Atharvaveda, a sacred text of
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
dating from the
Early Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
, is one of the first Indian texts dealing with medicine. The Atharvaveda also contains prescriptions of herbs for various ailments. The use of herbs to treat ailments would later form a large part of
Ayurveda
Ayurveda () is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. The theory and practice of Ayurveda is pseudoscientific. Ayurveda is heavily practiced in India and Nepal, where around 80% of the population rep ...
.
Ayurveda, meaning the "complete knowledge for long life" is another medical system of India. Its two most famous texts belong to the schools of
Charaka
Charaka was one of the principal contributors to Ayurveda, a system of medicine and lifestyle developed in Ancient India. He is known as an editor of the medical treatise entitled ''Charaka Samhita'', one of the foundational texts of classical ...
and
Sushruta. The earliest foundations of Ayurveda were built on a synthesis of traditional herbal practices together with a massive addition of theoretical conceptualizations, new
nosologies and new therapies dating from about 600 BCE onwards, and coming out of the communities of thinkers which included the
Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in L ...
and others.
According to the compendium of
Charaka
Charaka was one of the principal contributors to Ayurveda, a system of medicine and lifestyle developed in Ancient India. He is known as an editor of the medical treatise entitled ''Charaka Samhita'', one of the foundational texts of classical ...
, the
Charakasamhitā, health and disease are not predetermined and life may be prolonged by human effort. The compendium of
Suśruta, the
Suśrutasamhitā defines the purpose of medicine to cure the diseases of the sick, protect the healthy, and to prolong life. Both these ancient compendia include details of the examination, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of numerous ailments. The
Suśrutasamhitā is notable for describing procedures on various forms of
surgery, including
rhinoplasty
Rhinoplasty ( grc, ῥίς, rhī́s, nose + grc, πλάσσειν, plássein, to shape), commonly called nose job, medically called nasal reconstruction is a plastic surgery procedure for altering and reconstructing the nose. There are two typ ...
, the repair of torn ear lobes, perineal
lithotomy
Lithotomy from Greek for "lithos" (stone) and "tomos" ( cut), is a surgical method for removal of calculi, stones formed inside certain organs, such as the urinary tract (kidney stones), bladder ( bladder stones), and gallbladder (gallstones), ...
, cataract surgery, and several other excisions and other surgical procedures. Most remarkable was Susruta's surgery specially the rhinoplasty for which he is called father of modern plastic surgery. Susruta also described more than 125 surgical instruments in detail. Also remarkable is Sushruta's penchant for scientific classification:
His medical treatise consists of 184 chapters, 1,120 conditions are listed, including injuries and illnesses relating to aging and mental illness.
The Ayurvedic classics mention eight branches of medicine: kāyācikitsā (
internal medicine), śalyacikitsā (surgery including anatomy), śālākyacikitsā (eye, ear, nose, and throat diseases), kaumārabhṛtya (pediatrics with obstetrics and gynaecology), bhūtavidyā (spirit and psychiatric medicine), agada tantra (
toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating e ...
with treatments of stings and bites), rasāyana (science of rejuvenation), and vājīkaraṇa (
aphrodisiac
An aphrodisiac is a substance that increases sexual desire, sexual attraction, sexual pleasure, or sexual behavior. Substances range from a variety of plants, spices, foods, and synthetic chemicals. Natural aphrodisiacs like cannabis or cocai ...
and fertility). Apart from learning these, the student of Āyurveda was expected to know ten arts that were indispensable in the preparation and application of his medicines: distillation, operative skills, cooking, horticulture, metallurgy, sugar manufacture, pharmacy, analysis and separation of minerals, compounding of metals, and preparation of
alkalis. The teaching of various subjects was done during the instruction of relevant clinical subjects. For example, the teaching of anatomy was a part of the teaching of surgery, embryology was a part of training in pediatrics and obstetrics, and the knowledge of physiology and pathology was interwoven in the teaching of all the clinical disciplines.
The normal length of the student's training appears to have been seven years. But the physician was to continue to learn.
As an alternative form of medicine in India,
Unani medicine
Unani or Yunani medicine (Urdu: ''tibb yūnānī'') is Perso-Arabic traditional medicine as practiced in Muslim culture in South Asia and modern day Central Asia. Unani medicine is pseudoscientific. The Indian Medical Association describes Un ...
found deep roots and royal patronage during medieval times. It progressed during the Indian sultanate and
mughal periods. Unani medicine is very close to Ayurveda. Both are based on the theory of the presence of the elements (in Unani, they are considered to be fire, water, earth, and air) in the human body. According to followers of Unani medicine, these elements are present in different fluids and their balance leads to health and their imbalance leads to illness.
By the 18th century CE, Sanskrit medical wisdom still dominated. Muslim rulers built large hospitals in 1595 in
Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern India ...
, and in
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders ...
in 1719, and numerous commentaries on ancient texts were written.
Africa/Middle East
Places
Ancient Egypt
 Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt developed a large, varied and fruitful medical tradition.
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
described the Egyptians as "the healthiest of all men, next to the Libyans", because of the dry climate and the notable
public health system that they possessed. According to him, "the practice of medicine is so specialized among them that each physician is a healer of one disease and no more." Although Egyptian medicine, to a considerable extent, dealt with the supernatural, it eventually developed a practical use in the fields of anatomy, public health, and clinical diagnostics.
Medical information in the
Edwin Smith Papyrus may date to a time as early as 3000 BCE.
Imhotep in the
3rd dynasty
The Third Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty III) is the first dynasty of the Old Kingdom. Other dynasties of the Old Kingdom include the Fourth, Fifth and Sixth. The capital during the period of the Old Kingdom was at Memphis.
Overview
A ...
is sometimes credited with being the founder of ancient Egyptian medicine and with being the original author of the ''Edwin Smith Papyrus'', detailing cures, ailments and
anatomical observations. The ''Edwin Smith Papyrus'' is regarded as a copy of several earlier works and was written c. 1600 BCE. It is an ancient textbook on surgery almost completely devoid of magical thinking and describes in exquisite detail the ''examination, diagnosis, treatment,'' and ''prognosis'' of numerous ailments.
The
Kahun Gynaecological Papyrus
The Kahun Gynaecological Papyrus (also Petrie Medical Papyrus, Kahun Medical Papyrus, Lahun Medical Papyrus, or UC32057) is the oldest known medical text in Egypt, although not the oldest in the world as in Philadelphia museum a Sumerian medical c ...
treats women's complaints, including problems with conception. Thirty four cases detailing diagnosis and
treatment survive, some of them fragmentarily. Dating to 1800 BCE, it is the oldest surviving medical text of any kind.
Medical institutions, referred to as Houses of Life are known to have been established in ancient Egypt as early as 2200 BCE.
The
Ebers Papyrus is the oldest written text mentioning
enema
An enema, also known as a clyster, is an injection of fluid into the lower bowel by way of the rectum.Cullingworth, ''A Manual of Nursing, Medical and Surgical'':155 The word enema can also refer to the liquid injected, as well as to a device ...
s. Many medications were administered by enemas and one of the many types of medical specialists was an Iri, the Shepherd of the Anus.
The earliest known physician is also credited to
ancient Egypt:
Hesy-Ra
Hesy-Ra (also read Hesy-Re and Hesire) was an ancient Egyptian high official during the early Third Dynasty of Egypt. His most notable title was ''Wer-ibeḥsenjw'', meaning either "Great one of the ivory cutters" or "Great one of the dentists", ...
, "Chief of Dentists and Physicians" for King
Djoser
Djoser (also read as Djeser and Zoser) was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the 3rd Dynasty during the Old Kingdom, and was the founder of that epoch. He is also known by his Hellenized names Tosorthros (from Manetho) and Sesorthos (from Eusebiu ...
in the 27th century BCE. Also, the earliest known woman physician,
Peseshet
Peseshet, who lived under the Fourth Dynasty (albeit a date in the Fifth Dynasty is also possible), is often credited with being the earliest known female physician in history. Some have credited Merit-Ptah with being the first female physician ...
, practiced in
Ancient Egypt at the time of the
4th dynasty
The Fourth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty IV) is characterized as a "golden age" of the Old Kingdom of Egypt. Dynasty IV lasted from to 2494 BC. It was a time of peace and prosperity as well as one during which trade with other ...
. Her title was "Lady Overseer of the Lady Physicians."
Mesopotamia
The ancient Mesopotamians had no distinction between "rational science" and
magic
Magic or Magick most commonly refers to:
* Magic (supernatural), beliefs and actions employed to influence supernatural beings and forces
* Ceremonial magic, encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic
* Magical thinking, the belief that unrela ...
.
When a person became ill, doctors would prescribe both magical formulas to be recited as well as medicinal treatments.
The earliest medical prescriptions appear in
Sumerian during the
Third Dynasty of Ur
The Third Dynasty of Ur, also called the Neo-Sumerian Empire, refers to a 22nd to 21st century BC ( middle chronology) Sumerian ruling dynasty based in the city of Ur and a short-lived territorial-political state which some historians consider t ...
( 2112 BCE – 2004 BCE). The oldest Babylonian texts on medicine date back to the
Old Babylonian
Old Babylonian may refer to:
*the period of the First Babylonian dynasty (20th to 16th centuries BC)
*the historical stage of the Akkadian language
Akkadian (, Akkadian: )John Huehnergard & Christopher Woods, "Akkadian and Eblaite", ''The Camb ...
period in the first half of the
2nd millennium BCE. The most extensive Babylonian medical text, however, is the ''Diagnostic Handbook'' written by the ''ummânū'', or chief scholar,
Esagil-kin-apli Esagil-kin-apli was the ''ummânū'', or chief scholar, of Babylonian king Adad-apla-iddina, 1067–1046 BCE, as he appears on the Uruk ''List of Sages and Scholars'' (165 BCE)W 20030,7 the Seleucid ''List of Sages and Scholars'', obverse line 16, r ...
of
Borsippa,
during the reign of the Babylonian king
Adad-apla-iddina (1069–1046 BCE). Along with the Egyptians, the Babylonians introduced the practice of diagnosis, prognosis, physical examination, and remedies. In addition, the ''Diagnostic Handbook'' introduced the methods of
therapy
A therapy or medical treatment (often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx) is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis.
As a rule, each therapy has indications and contraindications. There are many different ...
and cause. The text contains a list of medical symptoms and often detailed empirical observations along with logical rules used in combining observed symptoms on the body of a patient with its diagnosis and prognosis.
The ''Diagnostic Handbook'' was based on a logical set of axioms and assumptions, including the modern view that through the examination and inspection of the symptoms of a patient, it is possible to determine the patient's disease, its cause and future development, and the chances of the patient's recovery. The symptoms and diseases of a patient were treated through therapeutic means such as bandages, herbs and
creams.
In
East Semitic
The East Semitic languages are one of three divisions of the Semitic languages. The East Semitic group is attested by three distinct languages, Akkadian, Eblaite and possibly Kishite, all of which have been long extinct. They were influenced b ...
cultures, the main medicinal authority was a kind of exorcist-healer known as an ''
āšipu''.
The profession was generally passed down from father to son
and was held in extremely high regard.
Of less frequent recourse was another kind of healer known as an ''asu'', who corresponds more closely to a modern physician
and treated physical symptoms using primarily
folk remedies
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) comprises medical aspects of traditional knowledge that developed over generations within the folk beliefs of various societies, including indigenous peoples, before the ...
composed of various herbs, animal products, and minerals, as well as potions, enemas, and ointments or
poultices
A poultice, also called a cataplasm, is a soft moist mass, often heated and medicated, that is spread on cloth and placed over the skin to treat an aching, inflamed, or painful part of the body. It can be used on wounds, such as cuts.
'Poultice' ...
.
These physicians, who could be either male or female, also dressed wounds, set limbs, and performed simple surgeries.
The ancient Mesopotamians also practiced
prophylaxis
Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, consists of measures taken for the purposes of disease prevention.Hugh R. Leavell and E. Gurney Clark as "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical and mental hea ...
and took measures to prevent the spread of disease.
Mental illnesses were well known in ancient
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
,
where diseases and mental disorders were believed to be caused by specific deities.
Because
hands symbolized control over a person, mental illnesses were known as "hands" of certain deities.
One psychological illness was known as ''Qāt Ištar'', meaning "Hand of
Ishtar
Inanna, also sux, 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒀭𒈾, nin-an-na, label=none is an ancient Mesopotamian goddess of love, war, and fertility. She is also associated with beauty, sex, divine justice, and political power. She was originally worshiped in Su ...
".
Others were known as "Hand of
Shamash", "Hand of the Ghost", and "Hand of the God".
Descriptions of these illnesses, however, are so vague that it is usually impossible to determine which illnesses they correspond to in modern terminology.
Mesopotamian doctors kept detailed record of their patients'
hallucination
A hallucination is a perception in the absence of an external stimulus that has the qualities of a real perception. Hallucinations are vivid, substantial, and are perceived to be located in external objective space. Hallucination is a combinati ...
s and assigned spiritual meanings to them.
A patient who hallucinated that he was seeing a dog was predicted to die;
whereas, if he saw a gazelle, he would recover.
The royal family of
Elam was notorious for its members frequently suffering from insanity.
was recognized as being rooted in psychological problems.
Europe
Ideas
Humors
The theory of humors was derived from ancient medical works, dominated western medicine until the 19th century, and is credited to Greek philosopher and surgeon Galen of Pergamon (129–).
In Greek medicine, there are thought to be four humors, or bodily fluids that are linked to illness: blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile.
Early scientists believed that food is digested into blood, muscle, and bones, while the humors that weren't blood were then formed by indigestible materials that are left over. An excess or shortage of any one of the four humors is theorized to cause an imbalance that results in sickness; the aforementioned statement was hypothesized by sources before Hippocrates.
Hippocrates () deduced that the four seasons of the year and four ages of man that affect the body in relation to the humors.
The four ages of man are childhood, youth, prime age, and old age.
The four humors as associated with the four seasons are black bileautumn, yellow bilesummer, phlegmwinter and bloodspring.
In ''De temperamentis,'' Galen linked what he called temperaments, or personality characteristics, to a person's natural mixture of humors. He also said that the best place to check the balance of temperaments was in the palm of the hand. A person that is considered to be phlegmatic is said to be an introvert, even-tempered, calm, and peaceful.
This person would have an excess of phlegm, which is described as a viscous substance or mucous.
Similarly, a melancholic temperament related to being moody, anxious, depressed, introverted, and pessimistic.
A melancholic temperament is caused by an excess of black bile, which is sedimentary and dark in color.
Being extroverted, talkative, easygoing, carefree, and sociable coincides with a sanguine temperament, which is linked to too much blood.
Finally, a choleric temperament is related to too much yellow bile, which is actually red in color and has the texture of foam; it is associated with being aggressive, excitable, impulsive, and also extroverted.
There are numerous ways to treat a disproportion of the humors. For example, if someone was suspected to have too much blood, then the physician would perform bloodletting as a treatment. Likewise, if a person that had too much phlegm would feel better after expectorating, and someone with too much yellow bile would purge.
Another factor to be considered in the balance of humors is the quality of air in which one resides, such as the climate and elevation. Also, the standard of food and drink, balance of sleeping and waking, exercise and rest, retention and evacuation are important. Moods such as anger, sadness, joy, and love can affect the balance. During that time, the importance of balance was demonstrated by the fact that women lose blood monthly during menstruation, and have a lesser occurrence of gout, arthritis, and epilepsy then men do.
Galen also hypothesized that there are three faculties. The natural faculty affects growth and reproduction and is produced in the liver. Animal or vital faculty controls respiration and emotion, coming from the heart. In the brain, the psychic faculty commands the senses and thought.
The structure of bodily functions is related to the humors as well. Greek physicians understood that food was cooked in the stomach; this is where the nutrients are extracted. The best, most potent and pure nutrients from food are reserved for blood, which is produced in the liver and carried through veins to organs. Blood enhanced with pneuma, which means wind or breath, is carried by the arteries.
The path that blood take is as follows: venous blood passes through the vena cava and is moved into the right ventricle of the heart; then, the pulmonary artery takes it to the lungs.
Later, the pulmonary vein then mixes air from the lungs with blood to form arterial blood, which has different observable characteristics.
After leaving the liver, half of the yellow bile that is produced travels to the blood, while the other half travels to the gallbladder. Similarly, half of the black bile produced gets mixed in with blood, and the other half is used by the spleen.
Places
Ancient Greek medicine
Around 800 BCE
Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
in the ''
Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the '' Odys ...
'' gives descriptions of wound treatment by the two sons of
Asklepios, the admirable physicians
Podaleirius
In Greek mythology, Podalirius or Podaleirius or Podaleirios ( grc, Ποδαλείριος) was a son of Asclepius.
Description
In the account of Dares the Phrygian, Podalirius was illustrated as ". . .sturdy, strong, haughty, and moody."
...
and
Machaon and one acting doctor,
Patroclus. Because Machaon is wounded and Podaleirius is in combat
Eurypylus In Greek mythology, Eurypylus (; grc, Εὐρύπυλος ''Eurypylos'') was the name of several different people:
* Eurypylus, was a Thessalian king, son of Euaemon and Ops. He was a former suitor of Helen thus he led the Thessalians during Tr ...
asks Patroclus to "cut out the arrow-head, and wash the dark blood from my thigh with warm water, and sprinkle soothing herbs with power to heal on my wound". Asklepios, like
Imhotep, came to be associated as a god of healing over time.
Temples dedicated to the healer-god
Asclepius
Asclepius (; grc-gre, Ἀσκληπιός ''Asklēpiós'' ; la, Aesculapius) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Greek religion and mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis, or Arsinoe, or of Apollo alone. Asclepius represe ...
, known as ''
Asclepieia'' ( grc, Ἀσκληπιεῖα, sing. , ''Asclepieion''), functioned as centers of medical advice, prognosis, and healing.
At these shrines, patients would enter a dream-like state of induced sleep known as ''enkoimesis'' () not unlike anesthesia, in which they either received guidance from the deity
in a dream or were cured by surgery.
Asclepeia provided carefully controlled spaces conducive to healing and fulfilled several of the requirements of institutions created for healing.
In the Asclepeion of
Epidaurus, three large marble boards dated to 350 BCE preserve the names, case histories, complaints, and cures of about 70 patients who came to the temple with a problem and shed it there. Some of the surgical cures listed, such as the opening of an abdominal abscess or the removal of traumatic foreign material, are realistic enough to have taken place, but with the patient in a state of enkoimesis induced with the help of soporific substances such as opium.
Alcmaeon of Croton
Alcmaeon of Croton (; el, Ἀλκμαίων ὁ Κροτωνιάτης, ''Alkmaiōn'', ''gen''.: Ἀλκμαίωνος; fl. 5th century BC) was an early Greek medical writer and philosopher-scientist. He has been described as one of the most ...
wrote on medicine between 500 and 450 BCE. He argued that channels linked the sensory organs to the brain, and it is possible that he discovered one type of channel, the optic nerves, by dissection.
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history o ...
of
Kos
Kos or Cos (; el, Κως ) is a Greek island, part of the Dodecanese island chain in the southeastern Aegean Sea. Kos is the third largest island of the Dodecanese by area, after Rhodes and Karpathos; it has a population of 36,986 (2021 census), ...
(), considered the "father of modern medicine." The
Hippocratic Corpus
The Hippocratic Corpus (Latin: ''Corpus Hippocraticum''), or Hippocratic Collection, is a collection of around 60 early Ancient Greek medical works strongly associated with the physician Hippocrates and his teachings. The Hippocratic Corpus cov ...
is a collection of around seventy early medical works from ancient Greece strongly associated with Hippocrates and his students. Most famously, the Hippocratics invented the
Hippocratic Oath for physicians. Contemporary physicians swear an oath of office which includes aspects found in early editions of the Hippocratic Oath.
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history o ...
and his followers were first to describe many diseases and medical conditions. Though
humorism
Humorism, the humoral theory, or humoralism, was a system of medicine detailing a supposed makeup and workings of the human body, adopted by Ancient Greek and Roman physicians and philosophers.
Humorism began to fall out of favor in the 1850s ...
(humoralism) as a medical system predates 5th-century Greek medicine, Hippocrates and his students systematized the thinking that illness can be explained by an imbalance of blood, phlegm, black bile, and yellow bile. Hippocrates is given credit for the first description of
clubbing of the fingers, an important diagnostic sign in chronic suppurative lung disease,
lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
and
cyanotic heart disease
A cyanotic heart defect is any congenital heart defect (CHD) that occurs due to deoxygenated blood bypassing the lungs and entering the systemic circulation, or a mixture of oxygenated and unoxygenated blood entering the systemic circulation. It ...
. For this reason, clubbed fingers are sometimes referred to as "Hippocratic fingers". Hippocrates was also the first physician to describe the
Hippocratic face
The Hippocratic facies ( la, facies Hippocratica, links=no) is the change produced in the face recognisable as a medical sign known as facies and prognostic of death. It may also be seen as due to long illness, excessive defecation, or excessive ...
in ''Prognosis''.
Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's natio ...
famously alludes to this description when writing of
Falstaff
Sir John Falstaff is a fictional character who appears in three plays by William Shakespeare and is eulogised in a fourth. His significance as a fully developed character is primarily formed in the plays '' Henry IV, Part 1'' and '' Part 2'', w ...
's death in Act II, Scene iii. of ''
Henry V Henry V may refer to:
People
* Henry V, Duke of Bavaria (died 1026)
* Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor (1081/86–1125)
* Henry V, Duke of Carinthia (died 1161)
* Henry V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (c. 1173–1227)
* Henry V, Count of Luxembourg (1 ...
''. Hippocrates began to categorize illnesses as
acute
Acute may refer to:
Science and technology
* Acute angle
** Acute triangle
** Acute, a leaf shape in the glossary of leaf morphology
* Acute (medicine), a disease that it is of short duration and of recent onset.
** Acute toxicity, the adverse eff ...
,
chronic,
endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
and
epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics of infectious ...
, and use terms such as, "exacerbation,
relapse
In internal medicine, relapse or recidivism is a recurrence of a past (typically medical) condition. For example, multiple sclerosis and malaria often exhibit peaks of activity and sometimes very long periods of dormancy, followed by relapse or ...
, resolution, crisis,
paroxysm
Paroxysmal attacks or paroxysms (from Greek παροξυσμός) are a sudden recurrence or intensification of symptoms, such as a spasm or seizure. These short, frequent symptoms can be observed in various clinical conditions. They are usually ...
, peak, and
convalescence
Convalescence is the gradual recovery of health and strength after illness or injury. It refers to the later stage of an infectious disease or illness when the patient recovers and returns to previous health, but may continue to be a source of ...
."
The Greek
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one ...
(c. ) was one of the greatest physicians of the ancient world, as his theories dominated all medical studies for nearly 1500 years.
His theories and experimentation laid the foundation for modern medicine surrounding the heart and blood. Galen's influence and innovations in medicine can be attributed to the experiments he conducted, which were unlike any other medical experiments of his time. Galen strongly believed that medical dissection was one of the essential procedures in truly understanding medicine. He began to dissect different animals that were anatomically similar to humans, which allowed him to learn more about the internal organs and extrapolate the surgical studies to the human body.
In addition, he performed many audacious operations—including brain and eye surgeries—that were not tried again for almost two millennia. Through the dissections and surgical procedures, Galen concluded that blood is able to circulate throughout the human body, and the heart is most similar to the human soul.
In ''Ars medica'' ("Arts of Medicine"), he further explains the mental properties in terms of specific mixtures of the bodily organs. While much of his work surrounded the physical anatomy, he also worked heavily in humoral physiology.
Galen's medical work was regarded as authoritative until well into the Middle Ages. He left a physiological model of the human body that became the mainstay of the medieval physician's university anatomy curriculum. Although he attempted to extrapolate the animal dissections towards the model of the human body, some of Galen's theories were incorrect. This caused his model to suffer greatly from stasis and intellectual stagnation. Greek and Roman taboos caused dissection of the human body to usually be banned in ancient times, but in the Middle Ages it changed.
In 1523 Galen's ''On the Natural Faculties'' was published in London. In the 1530s Belgian anatomist and physician
Andreas Vesalius
Andreas Vesalius (Latinized from Andries van Wezel) () was a 16th-century anatomist, physician, and author of one of the most influential books on human anatomy, ''De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (''On the fabric of the human body'' ' ...
launched a project to translate many of Galen's Greek texts into Latin. Vesalius's most famous work, ''
De humani corporis fabrica
''De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (Latin, lit. "On the fabric of the human body in seven books") is a set of books on human anatomy written by Andreas Vesalius (1514–1564) and published in 1543. It was a major advance in the history ...
'' was greatly influenced by Galenic writing and form.
Ancient Roman medicine
The
Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
invented numerous
surgical instruments, including the first instruments unique to women,
as well as the surgical uses of
forceps
Forceps (plural forceps or considered a plural noun without a singular, often a pair of forceps; the Latin plural ''forcipes'' is no longer recorded in most dictionaries) are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Fo ...
,
scalpel
A scalpel, lancet, or bistoury is a small and extremely sharp bladed instrument used for surgery, anatomical dissection, podiatry and various arts and crafts (either called a hobby knife or an X-acto knife.). Scalpels may be single-use dispos ...
s,
cautery
Cauterization (or cauterisation, or cautery) is a medical practice or technique of burning a part of a body to remove or close off a part of it. It destroys some tissue in an attempt to mitigate bleeding and damage, remove an undesired growth, or ...
,
cross-bladed scissors, the
surgical needle, the
sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' b ...
, and
speculas.
[]] Romans also performed
cataract surgery
Cataract surgery, also called lens replacement surgery, is the removal of the natural lens of the eye (also called "crystalline lens") that has developed an opacification, which is referred to as a cataract, and its replacement with an intra ...
.
The Roman army physician
Dioscorides
Pedanius Dioscorides ( grc-gre, Πεδάνιος Διοσκουρίδης, ; 40–90 AD), “the father of pharmacognosy”, was a Greek physician, pharmacologist, botanist, and author of '' De materia medica'' (, On Medical Material) —a 5-vo ...
(–90 CE), was a Greek botanist and pharmacologist. He wrote the encyclopedia ''
De Materia Medica
(Latin name for the Greek work , , both meaning "On Medical Material") is a pharmacopoeia of medicinal plants and the medicines that can be obtained from them. The five-volume work was written between 50 and 70 CE by Pedanius Dioscorides, ...
'' describing over 600 herbal cures, forming an influential pharmacopoeia which was used extensively for the following 1,500 years.
Early Christians in the Roman Empire incorporated medicine into their theology, ritual practices, and metaphors.
People
File:Hippocrates rubens.jpg, Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history o ...
(c. 460 - 370 BCE). Known as the "father of medicine".
File:Galenus.jpg, Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one ...
(129 - 216 CE). Known for their wide insights into anatomy.
Herophilus and Erasistratus
Two great
Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
ns laid the foundations for the scientific study of anatomy and physiology,
Herophilus of Chalcedon and
Erasistratus of Ceos.
Other Alexandrian surgeons gave us ligature (hemostasis),
lithotomy
Lithotomy from Greek for "lithos" (stone) and "tomos" ( cut), is a surgical method for removal of calculi, stones formed inside certain organs, such as the urinary tract (kidney stones), bladder ( bladder stones), and gallbladder (gallstones), ...
,
hernia
A hernia is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. Various types of hernias can occur, most commonly involving the abdomen, and specifically the groin. Groin herni ...
operations,
ophthalmic surgery
Eye surgery, also known as ophthalmic or ocular surgery, is surgery performed on the eye or its adnexa, by an ophthalmologist or sometimes, an optometrist. Eye surgery is synonymous with ophthalmology. The eye is a very fragile organ, and requ ...
,
plastic surgery
Plastic surgery is a surgical specialty involving the restoration, reconstruction or alteration of the human body. It can be divided into two main categories: reconstructive surgery and cosmetic surgery. Reconstructive surgery includes cranio ...
, methods of reduction of dislocations and fractures,
tracheotomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea (windpipe). The r ...
, and
mandrake
A mandrake is the root of a plant, historically derived either from plants of the genus '' Mandragora'' found in the Mediterranean region, or from other species, such as ''Bryonia alba'', the English mandrake, which have similar properties. The ...
as an
anaesthetic
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two ...
. Some of what we know of them comes from
Celsus
Celsus (; grc-x-hellen, Κέλσος, ''Kélsos''; ) was a 2nd-century Greek philosopher and opponent of early Christianity. His literary work, ''The True Word'' (also ''Account'', ''Doctrine'' or ''Discourse''; Greek: grc-x-hellen, Λόγ� ...
and
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one ...
of Pergamum.
, the renowned Alexandrian physician, was one of the pioneers of human anatomy. Though his knowledge of the anatomical structure of the human body was vast, he specialized in the aspects of neural anatomy.
Thus, his experimentation was centered around the anatomical composition of the blood-vascular system and the pulsations that can be analyzed from the system.
Furthermore, the surgical experimentation he administered caused him to become very prominent throughout the field of medicine, as he was one of the first physicians to initiate the exploration and dissection of the human body.
The banned practice of human dissection was lifted during his time within the scholastic community. This brief moment in the history of Greek medicine allowed him to further study the brain, which he believed was the core of the nervous system.
He also distinguished between
vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenat ...
s and
arteries
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pu ...
, noting that the latter
pulse
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the n ...
and the former do not. Thus, while working at the medical school of
Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
, Herophilus placed intelligence in the brain based on his surgical exploration of the body, and he connected the nervous system to motion and sensation. In addition, he and his contemporary,
Erasistratus of Chios, continued to research the role of veins and
nerves. After conducting extensive research, the two Alexandrians mapped out the course of the veins and nerves across the human body. Erasistratus connected the increased complexity of the surface of the human brain compared to other animals to its superior
intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can be des ...
. He sometimes employed
experiment
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into Causality, cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome oc ...
s to further his research, at one time repeatedly weighing a caged bird, and noting its weight loss between feeding times.
In
Erasistratus
Erasistratus (; grc-gre, Ἐρασίστρατος; c. 304 – c. 250 BC) was a Greek anatomist and royal physician under Seleucus I Nicator of Syria. Along with fellow physician Herophilus, he founded a school of anatomy in Alexandria, where th ...
' physiology, air enters the body, is then drawn by the lungs into the heart, where it is transformed into vital spirit, and is then pumped by the arteries throughout the body. Some of this vital spirit reaches the
brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
, where it is transformed into animal spirit, which is then distributed by the nerves.
5th to 15th century medicine

Middle East
Places
Byzantine medicine
Byzantine medicine encompasses the common medical practices of the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
from about 400 CE to 1453 CE. Byzantine medicine was notable for building upon the knowledge base developed by its Greco-Roman predecessors. In preserving medical practices from antiquity, Byzantine medicine influenced
Islamic medicine
In the history of medicine, "Islamic medicine" is the science of medicine developed in the Middle East, and usually written in Arabic, the ''lingua franca'' of Islamic civilization.
Islamic medicine adopted, systematized and developed the medi ...
as well as fostering the Western rebirth of medicine during the Renaissance.
Byzantine physicians often compiled and standardized medical knowledge into textbooks. Their records tended to include both diagnostic explanations and technical drawings. The
Medical Compendium in Seven Books
Paul of Aegina or Paulus Aegineta ( el, Παῦλος Αἰγινήτης; Aegina, ) was a 7th-century Byzantine Greek physician best known for writing the medical encyclopedia '' Medical Compendium in Seven Books.'' He is considered the “Fathe ...
, written by the leading physician
Paul of Aegina
Paul of Aegina or Paulus Aegineta ( el, Παῦλος Αἰγινήτης; Aegina, ) was a 7th-century Byzantine Greek physician best known for writing the medical encyclopedia ''Medical Compendium in Seven Books.'' He is considered the “Father ...
, survived as a particularly thorough source of medical knowledge. This compendium, written in the late seventh century, remained in use as a standard textbook for the following 800 years.
Late antiquity ushered in a revolution in medical science, and historical records often mention civilian hospitals (although battlefield medicine and wartime triage were recorded well before Imperial Rome).
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
stood out as a center of medicine during the Middle Ages, which was aided by its crossroads location, wealth, and accumulated knowledge.
The first ever known example of separating conjoined twins occurred in the Byzantine Empire in the 10th century. The next example of separating conjoined twins will be first recorded many centuries later in Germany in 1689.
The
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
's neighbors, the Persian
Sassanid Empire, also made their noteworthy contributions mainly with the establishment of the
Academy of Gondeshapur, which was "the most important medical center of the ancient world during the 6th and 7th centuries." In addition,
Cyril Elgood, British physician and a historian of medicine in Persia, commented that thanks to medical centers like the Academy of Gondeshapur, "to a very large extent, the credit for the whole hospital system must be given to Persia."
Islamic medicine

The
Islamic civilization rose to primacy in medical science as its
physician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through th ...
s contributed significantly to the field of medicine, including
anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having it ...
,
ophthalmology
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medic ...
,
pharmacology,
pharmacy,
physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
, and
surgery. Islamic civilization's contribution to these fields within medicine was a gradual process that took hundreds of years. During the time of the first great Muslim dynasty, the
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
(661-750 CE), these fields that were in their very early stages of development, and not much progress was made.
One reason for the limited advancement in medicine during the Umayyad Caliphate was the Caliphate's focus on expansion after the death of Prophet
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
(632 CE).
The focus on expansionism redirected resources from other fields, such as medicine. The priority on these factors led a dense amount of the population to believe that God will provide cures for their illnesses and diseases because of the attention on spirituality.
There were also many other areas of interest during that time before there was a rising interest in the field of medicine.
Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan, the fifth caliph of the Umayyad, developed governmental administration, adopted Arabic as the main language, and focused on many other areas. However, this rising interest in Islamic medicine grew significantly when the
Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
(750-1258 CE) overthrew the Umayyad Caliphate in 750 CE. This change in dynasty from the Umayyad Caliphate to the Abbasid Caliphate served as a turning point towards scientific and medical developments. A big contributor to this is because, under Abbasid rule, there was a great part of the Greek legacy that was transmitted into Arabic which by then, was the main language of Islamic nations.
Because of this, many Islamic physicians were heavily influenced by the works of Greek scholars of Alexandria and Egypt and were able to further expand on those texts to produce new medical pieces of knowledge. This period of time is also known as the
Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
where there was a period of development for development and flourishments of technology, commerce, and sciences including medicine. Additionally, during this time the creation of the first Islamic Hospital in 805 CE by the Abbasid caliph
Harun al-Rashid
Abu Ja'far Harun ibn Muhammad al-Mahdi ( ar
, أبو جعفر هارون ابن محمد المهدي) or Harun ibn al-Mahdi (; or 766 – 24 March 809), famously known as Harun al-Rashid ( ar, هَارُون الرَشِيد, translit=Hārūn ...
in Baghdad was recounted as a glorious event of the Golden Age.
This hospital in Baghdad contributed immensely to Baghdad's success and also provided educational opportunities for Islamic physicians. During the Islamic Golden Age, there were many famous Islamic physicians that paved the way for medical advancements and understandings.
Muhammad ibn Zakariya al-Razi (965-1040 CE), sometimes referred to as the father of modern optics, is the author of the monumental
Book of Optics and also was known for his work in differentiating smallpox from measles. However, this would not be possible without the influence from many different areas of the world that influenced the Arabs.
The Arabs were influenced by ancient Indian, Persian, Greek, Roman and Byzantine medical practices, and helped them develop further.
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one ...
&
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history o ...
were pre-eminent authorities. The translation of 129 of Galen's works into
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
by the Nestorian Christian
Hunayn ibn Ishaq
Hunayn ibn Ishaq al-Ibadi (also Hunain or Hunein) ( ar, أبو زيد حنين بن إسحاق العبادي; (809–873) was an influential Nestorian Christian translator, scholar, physician, and scientist. During the apex of the Islamic ...
and his assistants, and in particular Galen's insistence on a rational systematic approach to medicine, set the template for
Islamic medicine
In the history of medicine, "Islamic medicine" is the science of medicine developed in the Middle East, and usually written in Arabic, the ''lingua franca'' of Islamic civilization.
Islamic medicine adopted, systematized and developed the medi ...
, which rapidly spread throughout the
Arab Empire.
(cf.
The abbreviation ''cf.'' (short for the la, confer/conferatur, both meaning "compare") is used in writing to refer the reader to other material to make a comparison with the topic being discussed. Style guides recommend that ''cf.'' be used onl ...
Its most famous physicians included the Persian polymaths
Muhammad ibn Zakarīya al-Rāzi and
Avicenna, who wrote more than 40 works on health, medicine, and well-being. Taking leads from Greece and Rome, Islamic scholars kept both the art and science of medicine alive and moving forward.
Persian polymath
Avicenna has also been called the "father of medicine". He wrote ''
The Canon of Medicine
''The Canon of Medicine'' ( ar, القانون في الطب, italic=yes ''al-Qānūn fī al-Ṭibb''; fa, قانون در طب, italic=yes, ''Qanun-e dâr Tâb'') is an encyclopedia of medicine in five books compiled by Persian physician-phi ...
'' which became a standard medical text at many medieval European
universities
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, ...
, considered one of the most famous books in the history of medicine. ''
The Canon of Medicine
''The Canon of Medicine'' ( ar, القانون في الطب, italic=yes ''al-Qānūn fī al-Ṭibb''; fa, قانون در طب, italic=yes, ''Qanun-e dâr Tâb'') is an encyclopedia of medicine in five books compiled by Persian physician-phi ...
'' presents an overview of the contemporary
medical knowledge of the medieval Islamic world, which had been influenced by earlier traditions including
Greco-Roman medicine (particularly
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one ...
),
,
Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. It has been described as "fraught with pseudoscience", with the majority of its treatments having no logical mechanism of action ...
and
Indian medicine. Persian physician
al-Rāzi was one of the first to question the Greek theory of
humorism
Humorism, the humoral theory, or humoralism, was a system of medicine detailing a supposed makeup and workings of the human body, adopted by Ancient Greek and Roman physicians and philosophers.
Humorism began to fall out of favor in the 1850s ...
, which nevertheless remained influential in both medieval Western and medieval
Islamic medicine
In the history of medicine, "Islamic medicine" is the science of medicine developed in the Middle East, and usually written in Arabic, the ''lingua franca'' of Islamic civilization.
Islamic medicine adopted, systematized and developed the medi ...
. Some volumes of al-Rāzi's work ''Al-Mansuri'', namely "On Surgery" and "A General Book on Therapy", became part of the medical curriculum in European universities. Additionally, he has been described as a doctor's doctor, the father of
pediatrics,
and a pioneer of
ophthalmology
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medic ...
. For example, he was the first to recognize the reaction of the eye's pupil to light.
In addition to contributions to humanity's understanding of human anatomy, Islamicate scientists and scholars, physicians specifically, played an invaluable role in the development of the modern hospital system, creating the foundations on which more contemporary medical professionals would build models of public health systems in Europe and elsewhere.
During the time of the Safavid empire (16th–18th centuries) in Iran and the Mughal empire (16th–19th centuries) in India, Muslim scholars radically transformed the institution of the hospital, creating an environment in which rapidly developing medical knowledge of the time could be passed among students and teachers from a wide range of cultures.
There were two main schools of thought with patient care at the time. These included humoral physiology from the Persians and Ayurvedic practice. After these theories were translated from Sanskrit to Persian and vice-versa, hospitals could have a mix of culture and techniques. This allowed for a sense of collaborative medicine. Hospitals became increasingly common during this period as wealthy patrons commonly founded them. Many features that are still in use today, such as an emphasis on hygiene, a staff fully dedicated to the care of patients, and separation of individual patients from each other were developed in Islamicate hospitals long before they came into practice in Europe. At the time, the patient care aspects of hospitals in Europe had not taken effect. European hospitals were places of religion rather than institutions of science. As was the case with much of the scientific work done by Islamicate scholars, many of these novel developments in medical practice were transmitted to European cultures hundreds of years after they had long been used throughout the Islamicate world. Although Islamicate scientists were responsible for discovering much of the knowledge that allows the hospital system to function safely today, European scholars who built on this work still receive the majority of the credit historically.
Before the development of scientific medical practices in the Islamicate empires, medical care was mainly performed by religious figures such as priests.
Without a profound understanding of how infectious diseases worked and why sickness spread from person to person, these early attempts at caring for the ill and injured often did more harm than good. Contrarily, with the development of new and safer practices by Islamicate scholars and physicians in Arabian hospitals, ideas vital for the effective care of patients were developed, learned, and transmitted widely. Hospitals developed novel "concepts and structures" which are still in use today: separate wards for male and female patients, pharmacies, medical record-keeping, and personal and institutional sanitation and hygiene.
Much of this knowledge was recorded and passed on through Islamicate medical texts, many of which were carried to Europe and translated for the use of European medical workers. The Tasrif, written by surgeon Abu Al-Qasim Al-Zahrawi, was translated into Latin; it became one of the most important medical texts in European universities during the Middle Ages and contained useful information on surgical techniques and spread of bacterial infection.
The hospital was a typical institution included in the majority of Muslim cities, and although they were often physically attached to religious institutions, they were not themselves places of religious practice.
Rather, they served as facilities in which education and scientific innovation could flourish. If they had places of worship, they were secondary to the medical side of the hospital. Islamicate hospitals, along with observatories used for astronomical science, were some of the most important points of exchange for the spread of scientific knowledge. Undoubtedly, the hospital system developed in the Islamicate world played an invaluable role in the creation and evolution of the hospitals we as a society know and depend on today.
Europe
After 400 CE, the study and practice of medicine in the Western Roman Empire went into deep decline. Medical services were provided, especially for the poor, in the thousands of monastic hospitals that sprang up across Europe, but the care was rudimentary and mainly palliative. Most of the writings of Galen and Hippocrates were lost to the West, with the summaries and compendia of St. Isidore of Seville being the primary channel for transmitting Greek medical ideas. The Carolingian renaissance brought increased contact with Byzantium and a greater awareness of ancient medicine, but only with the
twelfth-century renaissance and the new translations coming from Muslim and Jewish sources in Spain, and the fifteenth-century flood of resources after the fall of Constantinople did the West fully recover its acquaintance with classical antiquity.
Greek and Roman taboos had meant that dissection was usually banned in ancient times, but in the Middle Ages it changed: medical teachers and students at Bologna began to open human bodies, and
Mondino de Luzzi
Mondino de Luzzi, or de Liuzzi or de Lucci,The family name is spelled variously: Liucci, Lucci, Luzzi or Luzzo (Latin: de Luciis, de Liuccis, de Leuciis); the ''dei'' may be contracted to ''de'' or ''de''. SeeGiorgi, P.P. (2004) "Mondino de' Li ...
(–1326) produced the first known anatomy textbook based on human dissection.
Wallis identifies a prestige hierarchy with university educated physicians on top, followed by learned surgeons; craft-trained surgeons; barber surgeons; itinerant specialists such as dentist and oculists; empirics; and midwives.
Institutions
The first medical schools were opened in the 9th century, most notably the
Schola Medica Salernitana
The Schola Medica Salernitana ( it, Scuola Medica Salernitana) was a Medieval medical school, the first and most important of its kind. Situated on the Tyrrhenian Sea in the south Italian city of Salerno, it was founded in the 9th century and rose ...
at Salerno in southern Italy. The cosmopolitan influences from Greek, Latin, Arabic, and Hebrew sources gave it an international reputation as the Hippocratic City. Students from wealthy families came for three years of preliminary studies and five of medical studies. The medicine, following the laws of Federico II, that he founded in 1224 the university and improved the Schola Salernitana, in the period between 1200 and 1400, it had in Sicily (so-called Sicilian Middle Ages) a particular development so much to create a true school of Jewish medicine.
As a result of which, after a legal examination, was conferred to a Jewish Sicilian woman,
Virdimura
Virdimura () was a History of the Jews in Sicily, Sicilian Jewish doctor, the first woman officially certified to practice medicine in Sicily.
Biography
Though few biographical details of Virdimura are known, she was a Jewish woman living in Ca ...
, wife of another physician Pasquale of Catania, the historical record of before woman officially trained to exercise of the medical profession.
At the
University of Bologna
The University of Bologna ( it, Alma Mater Studiorum – Università di Bologna, UNIBO) is a public research university in Bologna, Italy. Founded in 1088 by an organised guild of students (''studiorum''), it is the oldest university in continu ...
the training of physicians began in 1219. The Italian city attracted students from across Europe. Taddeo Alderotti built a tradition of medical education that established the characteristic features of Italian learned medicine and was copied by medical schools elsewhere.
Turisanus (d. 1320) was his student.
The
University of Padua
The University of Padua ( it, Università degli Studi di Padova, UNIPD) is an Italian university located in the city of Padua, region of Veneto, northern Italy. The University of Padua was founded in 1222 by a group of students and teachers from ...
was founded about 1220 by walkouts from the
University of Bologna
The University of Bologna ( it, Alma Mater Studiorum – Università di Bologna, UNIBO) is a public research university in Bologna, Italy. Founded in 1088 by an organised guild of students (''studiorum''), it is the oldest university in continu ...
, and began teaching medicine in 1222. It played a leading role in the identification and treatment of diseases and ailments, specializing in autopsies and the inner workings of the body. Starting in 1595, Padua's famous anatomical theatre drew artists and scientists studying the human body during public dissections. The intensive study of Galen led to critiques of Galen modeled on his own writing, as in the first book of Vesalius's ''De humani corporis fabrica.''
Andreas Vesalius
Andreas Vesalius (Latinized from Andries van Wezel) () was a 16th-century anatomist, physician, and author of one of the most influential books on human anatomy, ''De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (''On the fabric of the human body'' ' ...
held the chair of Surgery and Anatomy (''explicator chirurgiae'') and in 1543 published his anatomical discoveries in ''
De Humani Corporis Fabrica
''De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (Latin, lit. "On the fabric of the human body in seven books") is a set of books on human anatomy written by Andreas Vesalius (1514–1564) and published in 1543. It was a major advance in the history ...
''. He portrayed the human body as an interdependent system of organ groupings. The book triggered great public interest in dissections and caused many other European cities to establish anatomical theatres.

By the thirteenth century, the medical school at Montpellier began to eclipse the Salernitan school. In the 12th century, universities were founded in Italy, France, and England, which soon developed schools of medicine. The
University of Montpellier
The University of Montpellier (french: Université de Montpellier) is a public research university located in Montpellier, in south-east of France. Established in 1220, the University of Montpellier is one of the oldest universities in the wor ...
in France and Italy's
University of Padua
The University of Padua ( it, Università degli Studi di Padova, UNIPD) is an Italian university located in the city of Padua, region of Veneto, northern Italy. The University of Padua was founded in 1222 by a group of students and teachers from ...
and
University of Bologna
The University of Bologna ( it, Alma Mater Studiorum – Università di Bologna, UNIBO) is a public research university in Bologna, Italy. Founded in 1088 by an organised guild of students (''studiorum''), it is the oldest university in continu ...
were leading schools. Nearly all the learning was from lectures and readings in Hippocrates, Galen, Avicenna, and Aristotle. In later centuries, the importance of universities founded in the late Middle Ages gradually increased, e.g.
Charles University in
Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and List of cities in the Czech Republic, largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 milli ...
(established in 1348),
Jagiellonian University in
Cracow (1364),
University of Vienna
The University of Vienna (german: Universität Wien) is a public research university located in Vienna, Austria. It was founded by Duke Rudolph IV in 1365 and is the oldest university in the German-speaking world. With its long and rich hist ...
(1365), Heidelberg University (1386) and University of Greifswald (1456).
People
Women
In 1376, in Sicily, it was historically given, in relationship to the laws of Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Federico II that they foresaw an examination with a regal errand of physicists, the first qualification to the exercise of the medicine to a woman,
Virdimura
Virdimura () was a History of the Jews in Sicily, Sicilian Jewish doctor, the first woman officially certified to practice medicine in Sicily.
Biography
Though few biographical details of Virdimura are known, she was a Jewish woman living in Ca ...
a Jewish woman of Catania, whose document is preserved in Palermo to the Italian national archives.
16th century medicine
Places
England
In England, there were but three small hospitals after 1550. Pelling and Webster estimate that in London in the 1580 to 1600 period, out of a population of nearly 200,000 people, there were about 500 medical practitioners. Nurses and midwives are not included. There were about 50 physicians, 100 licensed surgeons, 100 apothecaries, and 250 additional unlicensed practitioners. In the last category about 25% were women. All across England—and indeed all of the world—the vast majority of the people in city, town or countryside depended for medical care on local amateurs with no professional training but with a reputation as wise healers who could diagnose problems and advise sick people what to do—and perhaps set broken bones, pull a tooth, give some traditional herbs or brews or perform a little magic to cure what ailed them.
People
File:Hirschvogel Paracelsus.jpg, Paracelsus (1493-1541). Known as the "father" of toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating e ...
.
File:Michael Servetus.jpg, Michael Servetus (1511-1553). Known as the first European to correctly describe pulmonary circulation.
File:Andreas Vesalius Bruxellensis, Anatomicorum Princeps (BM 1925,1117.92).jpg, Andreas Vesalius
Andreas Vesalius (Latinized from Andries van Wezel) () was a 16th-century anatomist, physician, and author of one of the most influential books on human anatomy, ''De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (''On the fabric of the human body'' ' ...
(1514-1564). Known as the modern founder of Human body, human anatomy.
17th century medicine
Europe
The Renaissance brought an intense focus on scholarship to Christian Europe. A major effort to translate the Arabic and Greek scientific works into Latin emerged. Europeans gradually became experts not only in the ancient writings of the Romans and Greeks, but in the contemporary writings of Islamic scientists. During the later centuries of the Renaissance came an increase in experimental investigation, particularly in the field of dissection and body examination, thus advancing our knowledge of human anatomy.

Ideas
* Animalcules: In 1677 Antonie van Leeuwenhoek identified "animalcules", which we now know as microorganisms, within their paper "letter on the protozoa".
* Blood circulation: In 1628 the English physician William Harvey made a ground-breaking discovery when he correctly described the circulatory system, circulation of the blood in his ''Exercitatio Anatomica de Motu Cordis et Sanguinis in Animalibus''. Before this time the most useful manual in medicine used both by students and expert physicians was Dioscorides' ''
De Materia Medica
(Latin name for the Greek work , , both meaning "On Medical Material") is a pharmacopoeia of medicinal plants and the medicines that can be obtained from them. The five-volume work was written between 50 and 70 CE by Pedanius Dioscorides, ...
'', a pharmacopoeia.
Inventions
* Microscopes: Bacteria and protists were first observed with a microscope by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1676, initiating the scientific field of microbiology.
Institutions
At the
University of Bologna
The University of Bologna ( it, Alma Mater Studiorum – Università di Bologna, UNIBO) is a public research university in Bologna, Italy. Founded in 1088 by an organised guild of students (''studiorum''), it is the oldest university in continu ...
the curriculum was revised and strengthened in 1560–1590. A representative professor was Julius Caesar Aranzi (Arantius) (1530–1589). He became Professor of Anatomy and Surgery at the University of Bologna in 1556, where he established anatomy as a major branch of medicine for the first time. Aranzi combined anatomy with a description of pathological processes, based largely on his own research, Galen, and the work of his contemporary Italians. Aranzi discovered the 'Nodules of Aranzio' in the semilunar valves of the heart and wrote the first description of the superior levator palpebral and the coracobrachialis muscles. His books (in Latin) covered surgical techniques for many conditions, including hydrocephalus, nasal polyp, goitre and tumor, tumours to phimosis, ascites, hemorrhoid, haemorrhoids, anorectal abscess, anal abscess and fistulae.
People
Women
Catholic women played large roles in health and healing in medieval and early modern Europe. A life as a nun was a prestigious role; wealthy families provided dowries for their daughters, and these funded the convents, while the nuns provided free nursing care for the poor.
The Catholic elites provided hospital services because of their theology of salvation that good works were the route to heaven. The Protestant reformers rejected the notion that rich men could gain God's grace through good works—and thereby escape purgatory—by providing cash endowments to charitable institutions. They also rejected the Catholic idea that the poor patients earned grace and salvation through their suffering. Protestants generally closed all the convents and most of the hospitals, sending women home to become housewives, often against their will. On the other hand, local officials recognized the public value of hospitals, and some were continued in Protestant lands, but without monks or nuns and in the control of local governments.
In London, the crown allowed two hospitals to continue their charitable work, under nonreligious control of city officials. The convents were all shut down but Harkness finds that women—some of them former nuns—were part of a new system that delivered essential medical services to people outside their family. They were employed by parishes and hospitals, as well as by private families, and provided nursing care as well as some medical, pharmaceutical, and surgical services.
Meanwhile, in Catholic lands such as France, rich families continued to fund convents and monasteries, and enrolled their daughters as nuns who provided free health services to the poor. Nursing was a religious role for the nurse, and there was little call for science.
18th century medicine
Europe
Events
European Age of Enlightenment
During the Age of Enlightenment, the 18th century, science was held in high esteem and physicians upgraded their social status by becoming more scientific. The health field was crowded with self-trained barber-surgeons, apothecaries, midwives, drug peddlers, and charlatans.
Across Europe medical schools relied primarily on lectures and readings. The final year student would have limited clinical experience by trailing the professor through the wards. Laboratory work was uncommon, and dissections were rarely done because of legal restrictions on cadavers. Most schools were small, and only Edinburgh, Scotland, with 11,000 alumni, produced large numbers of graduates.
Places
Spain and the Spanish Empire
In the Spanish Empire, the viceregal capital of Mexico City was a site of medical training for physicians and the creation of hospitals. Epidemic disease had decimated indigenous populations starting with the early sixteenth-century Spanish conquest of the Aztec empire, when a black auxiliary in the armed forces of conqueror Hernán Cortés, with an active case of smallpox, set off a virgin land epidemic among indigenous peoples, Spanish allies and enemies alike. Aztec emperor Cuitlahuac died of smallpox. Disease was a significant factor in the Spanish conquest elsewhere as well.

Medical education instituted at the Royal and Pontifical University of Mexico chiefly served the needs of urban elites. Male and female ''curanderos'' or lay practitioners, attended to the ills of the popular classes. The Spanish crown began regulating the medical profession just a few years after the conquest, setting up the Royal Tribunal of the Protomedicato, a board for licensing medical personnel in 1527. Licensing became more systematic after 1646 with physicians, druggists, surgeons, and bleeders requiring a license before they could publicly practice. Crown regulation of medical practice became more general in the Spanish empire.
Elites and the popular classes alike called on divine intervention in personal and society-wide health crises, such as the epidemic of 1737. The intervention of the Virgin of Guadalupe was depicted in a scene of dead and dying Indians, with elites on their knees praying for her aid. In the late eighteenth century, the crown began implementing secularizing policies on the Iberian peninsula and its overseas empire to control disease more systematically and scientifically.
Spanish Quest for Medicinal Spices
Botanical medicines also became popular during the 16th, 17th, and 18th Centuries. Spanish pharmaceutical books during this time contain medicinal recipes consisting of spices, herbs, and other botanical products. For example, nutmeg oil was documented for curing stomach ailments and cardamom oil was believed to relieve intestinal ailments.
During the rise of the global trade market, spices and herbs, along with many other goods, that were indigenous to different territories began to appear in different locations across the globe. Herbs and spices were especially popular for their utility in cooking and medicines. As a result of this popularity and increased demand for spices, some areas in Asia, like China and Indonesia, became hubs for spice cultivation and trade.
The Spanish Empire also wanted to benefit from the international spice trade, so they looked towards their American colonies.
The Spanish American colonies became an area where the Spanish searched to discover new spices and indigenous American medicinal recipes. The Florentine Codex, a 16th-century ethnographic research study in Mesoamerica by the Spanish Franciscan friar Bernardino de Sahagún, is a major contribution to the history of Nahuas, Nahua medicine. The Spanish did discover many spices and herbs new to them, some of which were reportedly similar to Asian spices. A Spanish physician by the name of Nicolás Monardes studied many of the American spices coming into Spain. He documented many of the new American spices and their medicinal properties in his survey ''Historia medicinal de las cosas que se traen de nuestras Indias Occidentales''. For example, Monardes describes the "Long Pepper" (Pimienta luenga), found along the coasts of the countries that are now known Panama and Colombia, as a pepper that was more flavorful, healthy, and spicy in comparison to the Eastern black pepper.
The Spanish interest in American spices can first be seen in the commissioning of the ''Libellus de Medicinalibus Indorum Herbis'', which was a Spanish-American codex describing indigenous American spices and herbs and describing the ways that these were used in natural Aztec medicines. The codex was commissioned in the year 1552 by Francisco de Mendoza, the son of Antonio de Mendoza, who was the first Viceroy of New Spain.
Francisco de Mendoza was interested in studying the properties of these herbs and spices, so that he would be able to profit from the trade of these herbs and the medicines that could be produced by them.
Francisco de Mendoza recruited the help of Monardez in studying the traditional medicines of the indigenous people living in what was then the Spanish colonies. Monardez researched these medicines and performed experiments to discover the possibilities of spice cultivation and medicine creation in the Spanish colonies. The Spanish transplanted some herbs from Asia, but only a few foreign crops were successfully grown in the Spanish Colonies. One notable crop brought from Asia and successfully grown in the Spanish colonies was ginger, as it was considered Hispaniola's number 1 crop at the end of the 16th Century.
The Spanish Empire did profit from cultivating herbs and spices, but they also introduced pre-Columbian American medicinal knowledge to Europe. Other Europeans were inspired by the actions of Spain and decided to try to establish a botanical transplant system in colonies that they controlled, however, these subsequent attempts were not successful.
United Kingdom and the British Empire

The London Dispensary opened in 1696, the first clinic in the British Empire to dispense medicines to poor sick people. The innovation was slow to catch on, but new dispensaries were open in the 1770s. In the colonies, small hospitals opened in Philadelphia in 1752, New York in 1771, and Boston (Massachusetts General Hospital) in 1811.
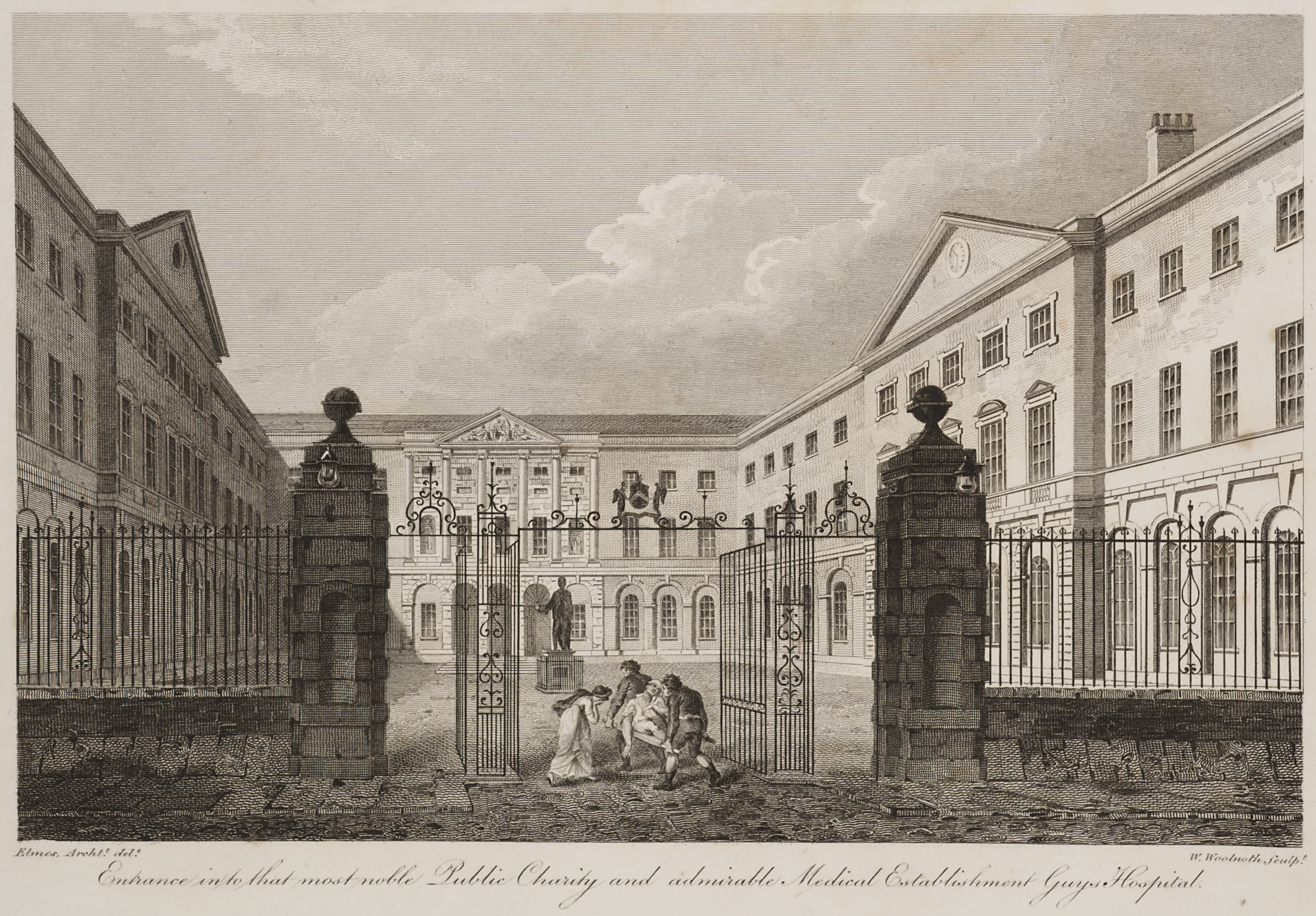

Guy's Hospital, the first great British hospital with a modern foundation opened in 1721 in London, with funding from businessman Thomas Guy. It had been preceded by St Bartholomew's Hospital and St Thomas's Hospital, both medieval foundations. In 1821 a bequest of £200,000 by William Hunt in 1829 funded expansion for an additional hundred beds at Guy's. Samuel Sharp (surgeon), Samuel Sharp (1709–78), a surgeon at Guy's Hospital from 1733 to 1757, was internationally famous; his ''A Treatise on the Operations of Surgery'' (1st ed., 1739), was the first British study focused exclusively on operative technique.
English physician Thomas Percival (1740–1804) wrote a comprehensive system of medical conduct, ''Medical Ethics; or, a Code of Institutes and Precepts, Adapted to the Professional Conduct of Physicians and Surgeons'' (1803) that set the standard for many textbooks.
19th century medicine
Germ theory and bacteriology
In the 1830s in Italy, Agostino Bassi traced the silkworm disease muscardine to microorganisms. Meanwhile, in Germany, Theodor Schwann led research on ethanol, alcoholic fermentation by yeast, proposing that living microorganisms were responsible.
Leading chemists, such as Justus von Liebig, seeking solely physical chemistry, physicochemical explanations, derided this claim and alleged that Schwann was regressing to vitalism.
In 1847 in Vienna, Ignaz Semmelweis (1818–1865), dramatically reduced the death rate of new mothers (due to childbed fever) by requiring physicians to hand washing, clean their hands before attending childbirth, yet his principles were marginalized and attacked by professional peers. At that time most people still believed that infections were caused by foul odors called Miasma theory, miasmas.

French scientist Louis Pasteur confirmed Theodor Schwann, Schwann's fermentation experiments in 1857 and afterwards supported the hypothesis that yeast were microorganisms. Moreover, he suggested that such a process might also explain contagious disease. In 1860, Pasteur's report on bacterial fermentation of butyric acid motivated fellow Frenchman Casimir Davaine to identify a similar species (which he called ) as the pathogen of the deadly disease anthrax. Others dismissed "" as a mere byproduct of the disease. British surgeon Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, Joseph Lister, however, took these findings seriously and subsequently introduced antisepsis to wound treatment in 1865.
German physician Robert Koch, noting fellow German Ferdinand Cohn's report of a spore stage of a certain bacterial species, traced the life cycle of Casimir Davaine, Davaine's , identified spores, inoculated laboratory animals with them, and reproduced anthrax—a breakthrough for experimental pathology and
germ theory of disease
The germ theory of disease is the currently accepted scientific theory for many diseases. It states that microorganisms known as pathogens or "germs" can lead to disease. These small organisms, too small to be seen without magnification, invade ...
. Pasteur's group added ecological investigations confirming spores' role in the natural setting, while Koch published a landmark treatise in 1878 on the bacterial pathology of wounds. In 1881, Koch reported discovery of the "Mycobacterium tuberculosis, tubercle bacillus", cementing germ theory and Koch's acclaim.
Upon the outbreak of a cholera epidemic in Alexandria, Egypt, two medical missions went to investigate and attend the sick, one was sent out by Pasteur and the other led by Koch.
Koch's group returned in 1883, having successfully discovered the Vibrio cholerae, cholera pathogen.
In Germany, however, Koch's bacteriologists had to vie against Max von Pettenkofer, Germany's leading proponent of miasmatic theory.
Pettenkofer conceded bacteria's casual involvement, but maintained that other, environmental factors were required to turn it pathogenic, and opposed water treatment as a misdirected effort amid more important ways to improve public health.
The massive cholera epidemic in Hamburg in 1892 devastated Pettenkoffer's position, and yielded German public health to "Koch's bacteriology".
On losing the 1883 rivalry in Alexandria, Pasteur switched research direction, and introduced his third vaccine—rabies vaccine—the first vaccine for humans since Edward Jenner, Jenner's smallpox vaccine, for smallpox.
From across the globe, donations poured in, funding the founding of Pasteur Institute, the globe's first biomedical institute, which opened in 1888.
Along with Koch's bacteriologists, Pasteur's group—which preferred the term ''microbiology''—led medicine into the new era of "scientific medicine" upon bacteriology and germ theory.
Accepted from Jakob Henle, Koch's steps to confirm a species' pathogenicity became famed as "Koch's postulates". Although his proposed tuberculosis treatment, tuberculin, seemingly failed, it soon was used to test for infection with the Mycobacterium tuberculosis, involved species. In 1905, Koch was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, and remains renowned as the founder of medical microbiology.
Nursing
The breakthrough to professionalization based on knowledge of advanced medicine was led by Florence Nightingale in England. She resolved to provide more advanced training than she saw on the Continent. At Kaiserswerth, where the first German nursing schools were founded in 1836 by Theodor Fliedner, she said, "The nursing was nil and the hygiene horrible.") Britain's male doctors preferred the old system, but Nightingale won out and her Nightingale Training School opened in 1860 and became a model. The Nightingale solution depended on the patronage of upper-class women, and they proved eager to serve. Royalty became involved. In 1902 the wife of the British king took control of the nursing unit of the British army, became its president, and renamed it after herself as the Queen Alexandra's Royal Army Nursing Corps; when she died the next queen became president. Today its Colonel In Chief is Sophie, Countess of Wessex, the daughter-in-law of Queen Elizabeth II. In the United States, upper-middle-class women who already supported hospitals promoted nursing. The new profession proved highly attractive to women of all backgrounds, and schools of nursing opened in the late 19th century. They were soon a function of large hospitals , where they provided a steady stream of low-paid idealistic workers. The International Red Cross began operations in numerous countries in the late 19th century, promoting nursing as an ideal profession for middle-class women.
Statistical methods

A major breakthrough in epidemiology came with the introduction of statistical maps and graphs. They allowed careful analysis of seasonality issues in disease incidents, and the maps allowed public health officials to identify critical loci for the dissemination of disease. John Snow (physician), John Snow in London developed the methods. In 1849, he observed that the symptoms of cholera, which had already claimed around 500 lives within a month, were vomiting and diarrhoea. He concluded that the source of contamination must be through ingestion, rather than inhalation as was previously thought. It was this insight that resulted in the removal of The Pump On Broad Street, after which deaths from cholera plummeted. English nurse Florence Nightingale pioneered analysis of large amounts of statistical data, using graphs and tables, regarding the condition of thousands of patients in the Crimean War to evaluate the efficacy of hospital services. Her methods proved convincing and led to reforms in military and civilian hospitals, usually with the full support of the government.>
By the late 19th and early 20th century English statisticians led by Francis Galton, Karl Pearson and Ronald Fisher developed the mathematical tools such as correlations and hypothesis tests that made possible much more sophisticated analysis of statistical data.
During the U.S. Civil War the Sanitary Commission collected enormous amounts of statistical data, and opened up the problems of storing information for fast access and mechanically searching for data patterns. The pioneer was John Shaw Billings (1838–1913). A senior surgeon in the war, Billings built the Library of the Surgeon General's Office (now the National Library of Medicine), the centerpiece of modern medical information systems. Billings figured out how to mechanically analyze medical and demographic data by turning facts into numbers and punching the numbers onto cardboard cards that could be sorted and counted by machine. The applications were developed by his assistant Herman Hollerith; Hollerith invented the punch card and counter-sorter system that dominated statistical data manipulation until the 1970s. Hollerith's company became IBM, International Business Machines (IBM) in 1911.
Psychiatry

Until the nineteenth century, the care of the insanity, insane was largely a communal and family responsibility rather than a medical one. The vast majority of the mental disorder, mentally ill were treated in domestic contexts with only the most unmanageable or burdensome likely to be institutionally confined. This situation was transformed radically from the late eighteenth century as, amid changing cultural conceptions of madness, a new-found optimism in the curability of insanity within the asylum setting emerged. Increasingly, lunacy was perceived less as a physiology, physiological condition than as a mental and moral one to which the correct response was persuasion, aimed at inculcating internal restraint, rather than external coercion. This new therapeutic sensibility, referred to as moral treatment, was epitomised in French physician Philippe Pinel's quasi-mythological unchaining of the lunatics of the Bicêtre Hospital in Paris and realised in an institutional setting with the foundation in 1796 of the Quaker-run York The Retreat, Retreat in England.

From the early nineteenth century, as lay-led lunacy reform movements gained in influence, ever more state governments in the West extended their authority and responsibility over the mentally ill.
Small-scale asylums, conceived as instruments to reshape both the mind and behaviour of the disturbed,
proliferated across these regions.
[; ] By the 1830s, moral treatment, together with the asylum itself, became increasingly medicalised and asylum doctors began to establish a distinct medical identity with the establishment in the 1840s of associations for their members in France, Germany, the United Kingdom and America, together with the founding of medico-psychological journals.
Medical optimism in the capacity of the asylum to cure insanity soured by the close of the nineteenth century as the growth of the asylum population far outstripped that of the general population. Processes of long-term institutional segregation, allowing for the psychiatric conceptualisation of the Natural history of disease, natural course of mental illness, supported the perspective that the insane were a distinct population, subject to mental pathologies stemming from specific medical causes.
As Social degeneration, degeneration theory grew in influence from the mid-nineteenth century, heredity was seen as the central causal element in chronic mental illness, and, with national asylum systems overcrowded and insanity apparently undergoing an inexorable rise, the focus of psychiatric therapeutics shifted from a concern with treating the individual to maintaining the racial and biological health of national populations.
Emil Kraepelin (1856–1926) introduced new medical categories of mental illness, which eventually came into psychiatry, psychiatric usage despite their basis in behavior rather than Biopsychiatry controversy, pathology or underlying cause. Shell shock among frontline soldiers exposed to heavy artillery bombardment was first diagnosed by British Army doctors in 1915. By 1916, similar symptoms were also noted in soldiers not exposed to explosive shocks, leading to questions as to whether the disorder was physical or psychiatric. In the 1920s surrealism, surrealist opposition to psychiatry was expressed in a number of surrealist publications. In the 1930s several controversial medical practices were introduced including inducing seizures (by electroshock, insulin or other drugs) or cutting parts of the brain apart (leucotomy or lobotomy). Both came into widespread use by psychiatry, but there were grave concerns and much opposition on grounds of basic morality, harmful effects, or misuse.
In the 1950s new psychiatric drugs, notably the antipsychotic chlorpromazine, were designed in laboratories and slowly came into preferred use. Although often accepted as an advance in some ways, there was some opposition, due to serious adverse effects such as tardive dyskinesia. Patients often opposed psychiatry and refused or stopped taking the drugs when not subject to psychiatric control. There was also increasing opposition to the use of psychiatric hospitals, and attempts to move people back into the community on a collaborative World Network of Users and Survivors of Psychiatry, user-led group approach ("therapeutic communities") not controlled by psychiatry. Campaigns against masturbation were done in the Victorian era and elsewhere. Lobotomy was used until the 1970s to treat schizophrenia. This was denounced by the anti-psychiatric movement in the 1960s and later.
Women
It was very difficult for women to become doctors in any field before the 1970s. Elizabeth Blackwell (doctor), Elizabeth Blackwell became the first woman to formally study and practice medicine in the United States. She was a leader in women's medical education. While Blackwell viewed medicine as a means for social and moral reform, her student Mary Putnam Jacobi (1842–1906) focused on curing disease. At a deeper level of disagreement, Blackwell felt that women would succeed in medicine because of their humane female values, but Jacobi believed that women should participate as the equals of men in all medical specialties using identical methods, values and insights. In the Soviet Union although the majority of medical doctors were women, they were paid less than the mostly male factory workers.
Asia
Places
Japan

European ideas of modern medicine were spread widely through the world by medical missionaries, and the dissemination of textbooks. Japanese elites enthusiastically embraced Western medicine after the Meiji Restoration of the 1860s. However they had been prepared by their knowledge of the Dutch and German medicine, for they had some contact with Europe through the Dutch. Highly influential was the 1765 edition of Hendrik van Deventer's pioneer work ''Nieuw Ligt'' ("A New Light") on Japanese obstetrics, especially on Katakura Kakuryo's publication in 1799 of ''Sanka Hatsumo'' ("Enlightenment of Obstetrics"). A cadre of Japanese physicians began to interact with Dutch doctors, who introduced smallpox vaccinations. By 1820 Japanese ranpô medical practitioners not only translated Dutch medical texts, they integrated their readings with clinical diagnoses. These men became leaders of the modernization of medicine in their country. They broke from Japanese traditions of closed medical fraternities and adopted the European approach of an open community of collaboration based on expertise in the latest scientific methods.
Kitasato Shibasaburō (1853–1931) studied bacteriology in Germany under Robert Koch. In 1891 he founded the Institute of Infectious Diseases in Tokyo, which introduced the study of bacteriology to Japan. He and French researcher Alexandre Yersin went to Hong Kong in 1894, where; Kitasato confirmed Yersin's discovery that the bacterium ''Yersinia pestis'' is the agent of the plague. In 1897 he isolated and described the organism that caused dysentery. He became the first dean of medicine at Keio University, and the first president of the Japan Medical Association.
Japanese physicians immediately recognized the values of X-Rays. They were able to purchase the equipment locally from the Shimadzu Company, which developed, manufactured, marketed, and distributed X-Ray machines after 1900. Japan not only adopted German methods of public health in the home islands, but implemented them in its colonies, especially Korea and Taiwan, and after 1931 in Manchuria. A heavy investment in sanitation resulted in a dramatic increase of life expectancy.
Europe
The practice of medicine changed in the face of rapid advances in science, as well as new approaches by physicians. Hospital doctors began much more systematic analysis of patients' symptoms in diagnosis. Among the more powerful new techniques were anaesthesia, and the development of both antiseptic and aseptic operating theatres. Effective cures were developed for certain endemic infectious diseases. However, the decline in many of the most lethal diseases was due more to improvements in public health and nutrition than to advances in medicine.
Medicine was revolutionized in the 19th century and beyond by advances in chemistry, laboratory techniques, and equipment. Old ideas of infectious disease epidemiology were gradually replaced by advances in bacteriology and virology.
The Russian Orthodox Church sponsored seven orders of nursing sisters in the late 19th century.
They ran hospitals, clinics, almshouses, pharmacies, and shelters as well as training schools for nurses. In the Soviet era (1917–1991), with the aristocratic sponsors gone, nursing became a low-prestige occupation based in poorly maintained hospitals.
Places
France
Paris (France) and Vienna were the two leading medical centers on the Continent in the era 1750–1914.
In the 1770s–1850s Paris became a world center of medical research and teaching. The "Paris School" emphasized that teaching and research should be based in large hospitals and promoted the professionalization of the medical profession and the emphasis on sanitation and public health. A major reformer was Jean-Antoine Chaptal (1756–1832), a physician who was Minister of Internal Affairs. He created the Paris Hospital, health councils, and other bodies.
Louis Pasteur (1822–1895) was one of the most important founders of medical microbiology. He is remembered for his remarkable breakthroughs in the causes and preventions of diseases. His discoveries reduced mortality from puerperal fever, and he created the first vaccines for rabies and anthrax. His experiments supported the
germ theory of disease
The germ theory of disease is the currently accepted scientific theory for many diseases. It states that microorganisms known as pathogens or "germs" can lead to disease. These small organisms, too small to be seen without magnification, invade ...
. He was best known to the general public for inventing a method to treat milk and wine in order to prevent it from causing sickness, a process that came to be called pasteurization. He is regarded as one of the three main founders of microbiology, together with Ferdinand Cohn and Robert Koch. He worked chiefly in Paris and in 1887 founded the Pasteur Institute there to perpetuate his commitment to basic research and its practical applications. As soon as his institute was created, Pasteur brought together scientists with various specialties. The first five departments were directed by Emile Duclaux (general microbiology research) and Charles Chamberland (microbe research applied to hygiene), as well as a biologist, Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov (morphological microbe research) and two
physician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through th ...
s, Jacques-Joseph Grancher (rabies) and Emile Roux (technical microbe research). One year after the inauguration of the Institut Pasteur, Roux set up the first course of microbiology ever taught in the world, then entitled ''Cours de Microbie Technique'' (Course of microbe research techniques). It became the model for numerous research centers around the world named "Pasteur Institutes.
Vienna
The First Viennese School of Medicine, 1750–1800, was led by the Dutchman Gerard van Swieten (1700–1772), who aimed to put medicine on new scientific foundations—promoting unprejudiced clinical observation, botanical and chemical research, and introducing simple but powerful remedies. When the Vienna General Hospital opened in 1784, it at once became the world's largest hospital and physicians acquired a facility that gradually developed into the most important research centre. Progress ended with the Napoleonic wars and the government shutdown in 1819 of all liberal journals and schools; this caused a general return to traditionalism and eclecticism in medicine.
Vienna was the capital of a diverse empire and attracted not just Germans but Czechs, Hungarians, Jews, Poles and others to its world-class medical facilities. After 1820 the Second Viennese School of Medicine emerged with the contributions of physicians such as Carl Freiherr von Rokitansky, Josef Škoda, Ferdinand Ritter von Hebra, and Ignaz Philipp Semmelweis. Basic medical science expanded and specialization advanced. Furthermore, the first dermatology, eye, as well as ear, nose, and throat clinics in the world were founded in Vienna. The textbook of ophthalmologist Georg Joseph Beer (1763–1821) ''Lehre von den Augenkrankheiten'' combined practical research and philosophical speculations, and became the standard reference work for decades.
Berlin
After 1871 Berlin, the capital of the new German Empire, became a leading center for medical research. Robert Koch (1843–1910) was a representative leader. He became famous for isolating ''Bacillus anthracis'' (1877), the ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Tuberculosis bacillus'' (1882) and ''Vibrio cholerae'' (1883) and for his development of Koch's postulates. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1905 for his tuberculosis findings. Koch is one of the founders of microbiology, inspiring such major figures as Paul Ehrlich and Gerhard Domagk.
North America
Events
American Civil War

In the American Civil War (1861–65), as was typical of the 19th century, more soldiers died of disease than in battle, and even larger numbers were temporarily incapacitated by wounds, disease and accidents. Conditions were poor in the Confederate States of America, Confederacy, where doctors and medical supplies were in short supply. The war had a dramatic long-term impact on medicine in the U.S., from surgical technique to hospitals to nursing and to research facilities. Weapon development -particularly the appearance of rifles, Springfield Model 1861, mass-produced and much more accurate than muskets led to generals underestimating the risks of long range rifle fire; risks exemplified in the death of John Sedgwick and the disastrous George Pickett#Gettysburg and Pickett's Charge, Pickett's Charge. The rifles could shatter bone forcing amputation and longer ranges meant casualties were sometimes not quickly found. Evacuation of the wounded from Second Battle of Bull Run took a week.
As in earlier wars, untreated casualties sometimes survived unexpectedly due to maggots debridement, debriding the wound -an observation which led to the Maggot therapy#History, surgical use of maggots -still a useful method in the absence of effective antibiotics.
The hygiene of the training and field camps was poor, especially at the beginning of the war when men who had seldom been far from home were brought together for training with thousands of strangers. First came epidemics of the childhood diseases of chicken pox, mumps, whooping cough, and, especially, measles. Operations in the South meant a dangerous and new disease environment, bringing diarrhea, dysentery, typhoid fever, and malaria. There were no antibiotics, so the surgeons prescribed coffee, whiskey, and quinine. Harsh weather, bad water, inadequate shelter in winter quarters, poor policing of camps, and dirty camp hospitals took their toll.
This was a common scenario in wars from time immemorial, and conditions faced by the Confederate army were even worse. The Union responded by building army hospitals in every state. What was different in the Union was the emergence of skilled, well-funded medical organizers who took proactive action, especially in the much enlarged United States Army Medical Department, and the United States Sanitary Commission, a new private agency. Numerous other new agencies also targeted the medical and morale needs of soldiers, including the United States Christian Commission as well as smaller private agencies.
The U.S. Army learned many lessons and in August 1886, it established the Hospital Corps.
Institutions
Johns Hopkins Hospital, founded in 1889, originated several modern medical practices, including Residency (medicine), residency and Grand rounds, rounds.
People
File:Louis Pasteur, foto av Paul Nadar, Crisco edit.jpg, Louis Pasteur (1822-1895) known for their modern founding of bacteriology, contributions to Germ theory of disease, germ theory, and pasteurization.
File:Rebecca-Lee-Crumpler.jpg, Rebecca Lee Crumpler (1831-1895) known as the first African Americans, African-American woman to become a physician.
20th century medicine
Cardiovascular
Blood groups
The ABO blood group system was discovered in 1901 by Karl Landsteiner at the
University of Vienna
The University of Vienna (german: Universität Wien) is a public research university located in Vienna, Austria. It was founded by Duke Rudolph IV in 1365 and is the oldest university in the German-speaking world. With its long and rich hist ...
. Karl Landsteiner, Landsteiner experimented on his staff, mixing their various blood components together, and found that some people's blood agglutinated (clumped together) with other blood, whilst some did not. This then lead him identifying three blood groups, ABC, which would later be renamed to ABO. The less frequently found blood group ABO blood group system, AB was discovered later in 1902 by Alfred Von Decastello and Adriano Sturli.
In 1937 Karl Landsteiner, Landsteiner and Alexander S. Wiener further discovered the Rh factor (misnamed from early thinking that this blood group was similar to that found in Rhesus macaque, rhesus monkies) whose antigens further determine blood reaction between people.
This was demonstrated in a 1939 case study by Phillip Levine and Rufus Stetson where a mother who had recently given birth had reacted to their partner's blood, highlighting the Rh factor.
Blood transfusion
Canadian physician Norman Bethune, M.D. developed a mobile Blood transfusion, blood-transfusion service for frontline operations in the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939), but ironically, he himself died of sepsis.
Pacemaker
In 1958, Arne Larsson (patient), Arne Larsson in Sweden became the first patient to depend on an artificial cardiac pacemaker. He died in 2001 at age 86, having outlived its inventor, the surgeon, and 26 pacemakers.
Cancer
Cancer treatment has been developed with radiotherapy, chemotherapy and surgical oncology.
Diagnosis
Medical radiography, X-ray imaging was the first kind of medical imaging, and later ultrasonic imaging, CT scanning, MR scanning and other imaging methods became available.
Disabilities

Prosthetics have improved with lightweight materials as well as neural prosthetics emerging in the end of the 20th century.
Diseases
Oral rehydration therapy has been extensively used since the 1970s to treat cholera and other diarrhea-inducing infections.
As infectious diseases have become less lethal, and the most common cause of death, causes of death in developed countries are now tumors and cardiovascular diseases, these conditions have received increased attention in medical research.
Disease eradication
Malaria eradication
Starting in World War II, DDT was used as insecticide to combat insect vectors carrying malaria, which was endemic in most tropical regions of the world. The first goal was to protect soldiers, but it was widely adopted as a public health device. In Liberia, for example, the United States had large military operations during the war and the U.S. Public Health Service began the use of DDT for indoor residual spraying (IRS) and as a larvicide, with the goal of controlling malaria in Monrovia, the Liberian capital. In the early 1950s, the project was expanded to nearby villages. In 1953, the World Health Organization (WHO) launched an antimalaria program in parts of Liberia as a pilot project to determine the feasibility of malaria eradication in tropical Africa. However these projects encountered a spate of difficulties that foreshadowed the general retreat from malaria eradication efforts across tropical Africa by the mid-1960s.
Pandemics
1918 influenza pandemic (1918-1920)
The Spanish flu, 1918 influenza pandemic was a global pandemic in the early 20th century that occurred between 1918 to 1920. Sometimes known as Spanish Flu due to popular opinion at the time thinking the flu originated from Spain, this pandemic caused close to 50 million deaths around the world. Spreading at the end of World War I.
Public health
Public health measures became particularly important during the 1918 flu pandemic, which killed at least 50 million people around the world. It became an Spanish flu research, important case study in epidemiology. Bristow shows there was a gendered response of health caregivers to the pandemic in the United States. Male doctors were unable to cure the patients, and they felt like failures. Women nurses also saw their patients die, but they took pride in their success in fulfilling their professional role of caring for, ministering, comforting, and easing the last hours of their patients, and helping the families of the patients cope as well.
Research
Evidence-based medicine is a modern concept, not introduced to literature until the 1990s.
Sexual and reproductive health

The sexual revolution included taboo-breaking research in human sexuality such as the 1948 and 1953 Kinsey reports, invention of hormonal contraception, and the normalization of abortion and homosexuality in many countries. Family planning has promoted a demographic transition in most of the world. With threatening sexually transmitted infections, not least HIV, use of barrier contraception has become imperative. The struggle against HIV has improved antiretroviral treatments.
Smoking
Tobacco smoking as a cause of
lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
was first researched in the 1920s, but was not widely supported by publications until the 1950s.
Surgery
Cardiac surgery was revolutionized in 1948 as open-heart surgery was introduced for the first time since 1925. In 1954 Joseph Murray, J. Hartwell Harrison and others accomplished the first kidney transplantation. organ transplant, Transplantations of other organs, such as heart, liver and pancreas, were also introduced during the later 20th century. The first partial face transplant was performed in 2005, and the first full one in 2010. By the end of the 20th century, microtechnology had been used to create tiny robotic devices to assist microsurgery using micro-video and fiber optics, fiber-optic cameras to view internal tissues during surgery with minimally invasive practices.
Laparoscopic surgery was broadly introduced in the 1990s. Natural orifice surgery has followed.
War
Mexican Revolution (1910-1920)
During the 19th century, large-scale wars were attended with medics and mobile hospital units which developed advanced techniques for healing massive injuries and controlling infections rampant in battlefield conditions. During the Mexican Revolution (1910–1920), General Pancho Villa organized hospital trains for wounded soldiers. Boxcars marked ''Servicio Sanitario'' ("sanitary service") were re-purposed as surgical operating theaters and areas for recuperation, and staffed by up to 40 Mexican and U.S. physicians. Severely wounded soldiers were shuttled back to base hospitals.
World War I (1914-1918)

Thousands of scarred troops provided the need for improved prosthetic limbs and expanded techniques in plastic surgery or reconstructive surgery. Those practices were combined to broaden cosmetic surgery and other forms of elective surgery.
Interwar period (1918-1939)
From 1917 to 1932, the American Red Cross moved into Europe with a battery of long-term child health projects. It built and operated hospitals and clinics, and organized antituberculosis and antityphus campaigns. A high priority involved child health programs such as clinics, better baby shows, playgrounds, fresh air camps, and courses for women on infant hygiene. Hundreds of U.S. doctors, nurses, and welfare professionals administered these programs, which aimed to reform the health of European youth and to reshape European public health and welfare along American lines.
World War II (1939-1945)
The advances in medicine made a dramatic difference for Allied troops, while the Germans and especially the Japanese and Chinese suffered from a severe lack of newer medicines, techniques and facilities. Harrison finds that the chances of recovery for a badly wounded British infantryman were as much as 25 times better than in the First World War. The reason was that:
:"By 1944 most casualties were receiving treatment within hours of wounding, due to the increased mobility of field hospitals and the extensive use of aeroplanes as ambulances. The care of the sick and wounded had also been revolutionized by new medical technologies, such as active immunization against tetanus, sulphonamide drugs, and penicillin."
During the second World War, Alexis Carrel and Henry Drysdale Dakin, Henry Dakin developed the Carrel-Dakin method of treating wounds with an irrigation, Dakin's solution, a germicide which helped prevent gangrene.
The War spurred the usage of Wilhelm Röntgen, Roentgen's X-ray, and the electrocardiograph, for the monitoring (medicine), monitoring of internal bodily functions. This was followed in the inter-war period by the development of the first anti-bacterial agents such as the sulpha antibiotics.
Nazi and Japanese medical research
Unethical human subject research, and killing of patients with disabilities, peaked during the Nazi era, with Nazi human experimentation and Aktion T4 during the Holocaust as the most significant examples. Many of the details of these and related events were the focus of the Doctors' Trial. Subsequently, principles of medical ethics, such as the Nuremberg Code, were introduced to prevent a recurrence of such atrocities. After 1937, the Japanese Army established programs of biological warfare in China. In Unit 731, Japanese doctors and research scientists conducted large numbers of vivisections and experiments on human beings, mostly Chinese victims.
Institutions
World Health Organization

The World Health Organization was founded in 1948 as a United Nations agency to improve global health. In most of the world, life expectancy has improved since then, and was about 67 years , and well above 80 years in some countries. Eradication of infectious diseases is an international effort, and several new vaccines have been developed during the post-war years, against infections such as measles, mumps, several strains of influenza and human papilloma virus. The long-known vaccine against Smallpox finally eradicated the disease in the 1970s, and Rinderpest was wiped out in 2011. Eradication of polio is underway. Tissue culture is important for development of vaccines. Though the early success of antiviral vaccines and antibacterial drugs, antiviral drugs were not introduced until the 1970s. Through the WHO, the international community has developed a response protocol against epidemics, displayed during the SARS epidemic in 2003, the Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 from 2004, the Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa and onwards.
People
File:MaryCorinnaPutnamJacobi.jpg, Mary Putnam Jacobi (1842-1906) known for debunking myths around menstruation and female intelligence.
File:Florence Nightingale CDV by H Lenthall.jpg, Florence Nightingale (1820-1910) known for their social action and reforms to nursing.
File:Elizabeth Blackwell NLM 02.jpg, Elizabeth Blackwell (1821-1910) known as the first women to gain a medical degree in the United States.
File:Doctor.susan.la.flesche.picotte.jpg, Susan La Flesche Picotte (1865-1915) known for their activism and as the first Native Americans in the United States, indigenous woman to gain a medical degree in the United States.
File:Linda Richards (page 8 crop).jpg, Linda Richards (1841-1930) known for their pioneering work in nursing.
File:Karl Landsteiner 1930b-cr2.jpg, Karl Landsteiner (1868-1943) known for discovering the ABO blood group system.
File:Synthetic Production of Penicillin TR1468.jpg, Alexander Fleming (1881-1955) known for the discovery of History of penicillin, penicillin and lysozyme.
File:Gerty Theresa Cori.jpg, Gerty Cori (1896-1957) known for their discovery of the Cori cycle, catalytic conversion of glycogen and first woman awarded a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
File:Virginia-Apgar-July-6-1959.jpg, Virginia Apgar (1909-1974) known for the Apgar score and improving infant mortality.
21st century medicine
Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance
The discovery of penicillin in the 20th century by Alexander Fleming provided a vital line of defence against baterical infections that, without them, often cause patients to suffer prelonged recovery periods and highly increased chances of death. Its discovery and application within medicine allowed previously impossible treatments to take place, including Treatment of cancer, cancer treatments, Organ transplantation, organ transplants, to Cardiac surgery, open heart surgery.
Throughout the 20th century, though, their overprescribed use to humans, as well as to animals that need them due to the conditions of intensive animal farming, has led to the development of List of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, antibiotic resistant bacteria.
Robotics

Pandemics
The early 21st century, facilitated by extensive global connections, international travel, and unprecedented human disruption of ecological systems, has been defined by a number of noval as well as continuing global Pandemic, pandemics from the 20th century.
Past
The SARS 2002 to 2004 2002–2004 SARS outbreak, outbreak affected a number of countries around the world and killed hundreds. This outbreak gave rise to a number of lessons learnt from viral infection control, including more effective isolation room protocols to better hand washing techniques for medical staff. A mutated strain of SARS would go on to develop into COVID-19, causing the future COVID-19 pandemic. A significant Influenza, influenza strain, Influenza A virus subtype H1N1, H1N1, caused a further 2009 swine flu pandemic, pandemic between 2009 to 2010. Known as swine flu, due to its indirect source from pigs, it went on to infect over 700 million people.
Ongoing
The continuing Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS, HIV pandemic, starting in 1981, has infected and led to the deaths of millions of people around the world. Emerging and improved pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) treatments that aim to reduce the spread of the disease have proven effective in limiting the spread of HIV alongside combined use of safe sex methods, Sexual and reproductive health, sexual health education, Needle and syringe programmes, needle exchange programmes, and sexual health screenings. Efforts to find a HIV vaccine development, HIV vaccine are ongoing whilst Health equity, health inequities have left certain population groups, like Trans woman, trans women, as well as resource limited regions, like sub-Saharan Africa, at greater risk of contracting HIV compared with, for example, Developed country, developed countries.
The outbreak of COVID-19, starting in 2019, and subsequent declaration of the COVID-19 pandemic by the World Health Organization, WHO is a major pandemic event within the early 21st century. Causing global disruptions, millions of infections and deaths, the pandemic has caused suffering throughout communities. The pandemic has also seen some of the largest logistical organisations of goods, medical equipment, medical professionals, and military personnel since World War II that highlights its far-reaching impact.
Personalised medicine
The rise of Personalized medicine, personalised medicine in the 21st century has generated the possibility to develop diagnosis and treatments based on the individual characteristics of a person, rather than through generic practices that defined 20th century medicine. Areas like DNA sequencing, Genetic linkage, genetic mapping, gene therapy, imaging protocols, proteomics, Stem-cell therapy, stem cell therapy, and wireless health monitoring devices are all rising innovations that can help medical professionals fine tune treatment to the individual.
Telemedicine
Remote surgery is another recent development, with the transatlantic Lindbergh operation in 2001 as a groundbreaking example.
Institutions
People
File:Maria Goldman-Rakic - 10.1371 journal.pbio.0000038.g001-O.jpg, Patricia Goldman-Rakic (1937-2003) known for research around the prefrontal cortex and working memory.
File:Luc Montagnier-press conference Dec 06th, 2008-1 crop.jpg, Luc Montagnier (1932-2022) known as one of the co-discoverers of HIV.
File:Tu Youyou 5012-1-2015.jpg, 屠呦呦 [Tu Youyou] (1930-present) known for discovering malaria treatments.
File:Joycelyn Elders official photo portrait.jpg, Joycelyn Elders (1933-present) known as the first African Americans, Black American women to serve as the Surgeon General of the United States.
File:Antonia Novello, photo portrait as surgeon general.jpg, Antonia Novello (1944-present) known as the first woman and first Hispanic to serve as the Surgeon General of the United States.
File:Françoise Barré-Sinoussi-press conference Dec 06th, 2008-2.jpg, Françoise Barré-Sinoussi (1947-present) known as one of the co-discoverers of HIV.
File:Mukhisa Kituyi, Houlin Zhao, Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus with Sophia - AI for Good Global Summit 2018 (41223188035) (cropped).jpg, Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus (1965-present) first African Director-General of the World Health Organization.
Themes in medical history
Racism in medicine
Racism has a long history in how medicine has evolved and established itself, both in terms of racism experience upon patients, professionals, and wider systematic violence within medical institutions and systems.
See: medical racism in the United States, race and health, and scientific racism.
Women in medicine
Women have always served as healers and midwives since ancient times. However, the professionalization of medicine forced them increasingly to the sidelines. As hospitals multiplied they relied in Europe on orders of Roman Catholic nun-nurses, and German Protestant and Anglican deaconesses in the early 19th century. They were trained in traditional methods of physical care that involved little knowledge of medicine.
See also
* Health care in the United States
* History of dental treatments
* History of herbalism
* History of hospitals
* History of medicine in Canada
* History of medicine in the United States
* History of nursing
* History of pathology
* History of pharmacy
* History of surgery
* Timeline of nursing history
* Timeline of medicine and medical technology
* History of health care (disambiguation)
Explanatory notes
References
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Donahue, M. Patricia. ''Nursing, The Finest Art: An Illustrated History'' (3r ed. 2010
excerpt and text search*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
* [http://wwwcf.nlm.nih.gov/hmddirectory/index.cfm/ Directory of History of Medicine Collections], Index to the major collections in the United States and Canada, selected by the US National Institute of Health
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Medicine
History of medicine,
History of science by discipline, Medicine
 China also developed a large body of traditional medicine. Much of the philosophy of
China also developed a large body of traditional medicine. Much of the philosophy of  The Atharvaveda, a sacred text of
The Atharvaveda, a sacred text of  Ancient Egypt developed a large, varied and fruitful medical tradition.
Ancient Egypt developed a large, varied and fruitful medical tradition.  Two great
Two great 
 The Islamic civilization rose to primacy in medical science as its
The Islamic civilization rose to primacy in medical science as its  By the thirteenth century, the medical school at Montpellier began to eclipse the Salernitan school. In the 12th century, universities were founded in Italy, France, and England, which soon developed schools of medicine. The
By the thirteenth century, the medical school at Montpellier began to eclipse the Salernitan school. In the 12th century, universities were founded in Italy, France, and England, which soon developed schools of medicine. The 
 In the Spanish Empire, the viceregal capital of Mexico City was a site of medical training for physicians and the creation of hospitals. Epidemic disease had decimated indigenous populations starting with the early sixteenth-century Spanish conquest of the Aztec empire, when a black auxiliary in the armed forces of conqueror Hernán Cortés, with an active case of smallpox, set off a virgin land epidemic among indigenous peoples, Spanish allies and enemies alike. Aztec emperor Cuitlahuac died of smallpox. Disease was a significant factor in the Spanish conquest elsewhere as well.
In the Spanish Empire, the viceregal capital of Mexico City was a site of medical training for physicians and the creation of hospitals. Epidemic disease had decimated indigenous populations starting with the early sixteenth-century Spanish conquest of the Aztec empire, when a black auxiliary in the armed forces of conqueror Hernán Cortés, with an active case of smallpox, set off a virgin land epidemic among indigenous peoples, Spanish allies and enemies alike. Aztec emperor Cuitlahuac died of smallpox. Disease was a significant factor in the Spanish conquest elsewhere as well.
 Medical education instituted at the Royal and Pontifical University of Mexico chiefly served the needs of urban elites. Male and female ''curanderos'' or lay practitioners, attended to the ills of the popular classes. The Spanish crown began regulating the medical profession just a few years after the conquest, setting up the Royal Tribunal of the Protomedicato, a board for licensing medical personnel in 1527. Licensing became more systematic after 1646 with physicians, druggists, surgeons, and bleeders requiring a license before they could publicly practice. Crown regulation of medical practice became more general in the Spanish empire.
Elites and the popular classes alike called on divine intervention in personal and society-wide health crises, such as the epidemic of 1737. The intervention of the Virgin of Guadalupe was depicted in a scene of dead and dying Indians, with elites on their knees praying for her aid. In the late eighteenth century, the crown began implementing secularizing policies on the Iberian peninsula and its overseas empire to control disease more systematically and scientifically.
Spanish Quest for Medicinal Spices
Botanical medicines also became popular during the 16th, 17th, and 18th Centuries. Spanish pharmaceutical books during this time contain medicinal recipes consisting of spices, herbs, and other botanical products. For example, nutmeg oil was documented for curing stomach ailments and cardamom oil was believed to relieve intestinal ailments. During the rise of the global trade market, spices and herbs, along with many other goods, that were indigenous to different territories began to appear in different locations across the globe. Herbs and spices were especially popular for their utility in cooking and medicines. As a result of this popularity and increased demand for spices, some areas in Asia, like China and Indonesia, became hubs for spice cultivation and trade. The Spanish Empire also wanted to benefit from the international spice trade, so they looked towards their American colonies.
The Spanish American colonies became an area where the Spanish searched to discover new spices and indigenous American medicinal recipes. The Florentine Codex, a 16th-century ethnographic research study in Mesoamerica by the Spanish Franciscan friar Bernardino de Sahagún, is a major contribution to the history of Nahuas, Nahua medicine. The Spanish did discover many spices and herbs new to them, some of which were reportedly similar to Asian spices. A Spanish physician by the name of Nicolás Monardes studied many of the American spices coming into Spain. He documented many of the new American spices and their medicinal properties in his survey ''Historia medicinal de las cosas que se traen de nuestras Indias Occidentales''. For example, Monardes describes the "Long Pepper" (Pimienta luenga), found along the coasts of the countries that are now known Panama and Colombia, as a pepper that was more flavorful, healthy, and spicy in comparison to the Eastern black pepper. The Spanish interest in American spices can first be seen in the commissioning of the ''Libellus de Medicinalibus Indorum Herbis'', which was a Spanish-American codex describing indigenous American spices and herbs and describing the ways that these were used in natural Aztec medicines. The codex was commissioned in the year 1552 by Francisco de Mendoza, the son of Antonio de Mendoza, who was the first Viceroy of New Spain. Francisco de Mendoza was interested in studying the properties of these herbs and spices, so that he would be able to profit from the trade of these herbs and the medicines that could be produced by them.
Francisco de Mendoza recruited the help of Monardez in studying the traditional medicines of the indigenous people living in what was then the Spanish colonies. Monardez researched these medicines and performed experiments to discover the possibilities of spice cultivation and medicine creation in the Spanish colonies. The Spanish transplanted some herbs from Asia, but only a few foreign crops were successfully grown in the Spanish Colonies. One notable crop brought from Asia and successfully grown in the Spanish colonies was ginger, as it was considered Hispaniola's number 1 crop at the end of the 16th Century. The Spanish Empire did profit from cultivating herbs and spices, but they also introduced pre-Columbian American medicinal knowledge to Europe. Other Europeans were inspired by the actions of Spain and decided to try to establish a botanical transplant system in colonies that they controlled, however, these subsequent attempts were not successful.
United Kingdom and the British Empire
Medical education instituted at the Royal and Pontifical University of Mexico chiefly served the needs of urban elites. Male and female ''curanderos'' or lay practitioners, attended to the ills of the popular classes. The Spanish crown began regulating the medical profession just a few years after the conquest, setting up the Royal Tribunal of the Protomedicato, a board for licensing medical personnel in 1527. Licensing became more systematic after 1646 with physicians, druggists, surgeons, and bleeders requiring a license before they could publicly practice. Crown regulation of medical practice became more general in the Spanish empire.
Elites and the popular classes alike called on divine intervention in personal and society-wide health crises, such as the epidemic of 1737. The intervention of the Virgin of Guadalupe was depicted in a scene of dead and dying Indians, with elites on their knees praying for her aid. In the late eighteenth century, the crown began implementing secularizing policies on the Iberian peninsula and its overseas empire to control disease more systematically and scientifically.
Spanish Quest for Medicinal Spices
Botanical medicines also became popular during the 16th, 17th, and 18th Centuries. Spanish pharmaceutical books during this time contain medicinal recipes consisting of spices, herbs, and other botanical products. For example, nutmeg oil was documented for curing stomach ailments and cardamom oil was believed to relieve intestinal ailments. During the rise of the global trade market, spices and herbs, along with many other goods, that were indigenous to different territories began to appear in different locations across the globe. Herbs and spices were especially popular for their utility in cooking and medicines. As a result of this popularity and increased demand for spices, some areas in Asia, like China and Indonesia, became hubs for spice cultivation and trade. The Spanish Empire also wanted to benefit from the international spice trade, so they looked towards their American colonies.
The Spanish American colonies became an area where the Spanish searched to discover new spices and indigenous American medicinal recipes. The Florentine Codex, a 16th-century ethnographic research study in Mesoamerica by the Spanish Franciscan friar Bernardino de Sahagún, is a major contribution to the history of Nahuas, Nahua medicine. The Spanish did discover many spices and herbs new to them, some of which were reportedly similar to Asian spices. A Spanish physician by the name of Nicolás Monardes studied many of the American spices coming into Spain. He documented many of the new American spices and their medicinal properties in his survey ''Historia medicinal de las cosas que se traen de nuestras Indias Occidentales''. For example, Monardes describes the "Long Pepper" (Pimienta luenga), found along the coasts of the countries that are now known Panama and Colombia, as a pepper that was more flavorful, healthy, and spicy in comparison to the Eastern black pepper. The Spanish interest in American spices can first be seen in the commissioning of the ''Libellus de Medicinalibus Indorum Herbis'', which was a Spanish-American codex describing indigenous American spices and herbs and describing the ways that these were used in natural Aztec medicines. The codex was commissioned in the year 1552 by Francisco de Mendoza, the son of Antonio de Mendoza, who was the first Viceroy of New Spain. Francisco de Mendoza was interested in studying the properties of these herbs and spices, so that he would be able to profit from the trade of these herbs and the medicines that could be produced by them.
Francisco de Mendoza recruited the help of Monardez in studying the traditional medicines of the indigenous people living in what was then the Spanish colonies. Monardez researched these medicines and performed experiments to discover the possibilities of spice cultivation and medicine creation in the Spanish colonies. The Spanish transplanted some herbs from Asia, but only a few foreign crops were successfully grown in the Spanish Colonies. One notable crop brought from Asia and successfully grown in the Spanish colonies was ginger, as it was considered Hispaniola's number 1 crop at the end of the 16th Century. The Spanish Empire did profit from cultivating herbs and spices, but they also introduced pre-Columbian American medicinal knowledge to Europe. Other Europeans were inspired by the actions of Spain and decided to try to establish a botanical transplant system in colonies that they controlled, however, these subsequent attempts were not successful.
United Kingdom and the British Empire The London Dispensary opened in 1696, the first clinic in the British Empire to dispense medicines to poor sick people. The innovation was slow to catch on, but new dispensaries were open in the 1770s. In the colonies, small hospitals opened in Philadelphia in 1752, New York in 1771, and Boston (Massachusetts General Hospital) in 1811.
The London Dispensary opened in 1696, the first clinic in the British Empire to dispense medicines to poor sick people. The innovation was slow to catch on, but new dispensaries were open in the 1770s. In the colonies, small hospitals opened in Philadelphia in 1752, New York in 1771, and Boston (Massachusetts General Hospital) in 1811.
 Guy's Hospital, the first great British hospital with a modern foundation opened in 1721 in London, with funding from businessman Thomas Guy. It had been preceded by St Bartholomew's Hospital and St Thomas's Hospital, both medieval foundations. In 1821 a bequest of £200,000 by William Hunt in 1829 funded expansion for an additional hundred beds at Guy's. Samuel Sharp (surgeon), Samuel Sharp (1709–78), a surgeon at Guy's Hospital from 1733 to 1757, was internationally famous; his ''A Treatise on the Operations of Surgery'' (1st ed., 1739), was the first British study focused exclusively on operative technique.
English physician Thomas Percival (1740–1804) wrote a comprehensive system of medical conduct, ''Medical Ethics; or, a Code of Institutes and Precepts, Adapted to the Professional Conduct of Physicians and Surgeons'' (1803) that set the standard for many textbooks.
Guy's Hospital, the first great British hospital with a modern foundation opened in 1721 in London, with funding from businessman Thomas Guy. It had been preceded by St Bartholomew's Hospital and St Thomas's Hospital, both medieval foundations. In 1821 a bequest of £200,000 by William Hunt in 1829 funded expansion for an additional hundred beds at Guy's. Samuel Sharp (surgeon), Samuel Sharp (1709–78), a surgeon at Guy's Hospital from 1733 to 1757, was internationally famous; his ''A Treatise on the Operations of Surgery'' (1st ed., 1739), was the first British study focused exclusively on operative technique.
English physician Thomas Percival (1740–1804) wrote a comprehensive system of medical conduct, ''Medical Ethics; or, a Code of Institutes and Precepts, Adapted to the Professional Conduct of Physicians and Surgeons'' (1803) that set the standard for many textbooks.
 French scientist Louis Pasteur confirmed Theodor Schwann, Schwann's fermentation experiments in 1857 and afterwards supported the hypothesis that yeast were microorganisms. Moreover, he suggested that such a process might also explain contagious disease. In 1860, Pasteur's report on bacterial fermentation of butyric acid motivated fellow Frenchman Casimir Davaine to identify a similar species (which he called ) as the pathogen of the deadly disease anthrax. Others dismissed "" as a mere byproduct of the disease. British surgeon Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, Joseph Lister, however, took these findings seriously and subsequently introduced antisepsis to wound treatment in 1865.
German physician Robert Koch, noting fellow German Ferdinand Cohn's report of a spore stage of a certain bacterial species, traced the life cycle of Casimir Davaine, Davaine's , identified spores, inoculated laboratory animals with them, and reproduced anthrax—a breakthrough for experimental pathology and
French scientist Louis Pasteur confirmed Theodor Schwann, Schwann's fermentation experiments in 1857 and afterwards supported the hypothesis that yeast were microorganisms. Moreover, he suggested that such a process might also explain contagious disease. In 1860, Pasteur's report on bacterial fermentation of butyric acid motivated fellow Frenchman Casimir Davaine to identify a similar species (which he called ) as the pathogen of the deadly disease anthrax. Others dismissed "" as a mere byproduct of the disease. British surgeon Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, Joseph Lister, however, took these findings seriously and subsequently introduced antisepsis to wound treatment in 1865.
German physician Robert Koch, noting fellow German Ferdinand Cohn's report of a spore stage of a certain bacterial species, traced the life cycle of Casimir Davaine, Davaine's , identified spores, inoculated laboratory animals with them, and reproduced anthrax—a breakthrough for experimental pathology and  A major breakthrough in epidemiology came with the introduction of statistical maps and graphs. They allowed careful analysis of seasonality issues in disease incidents, and the maps allowed public health officials to identify critical loci for the dissemination of disease. John Snow (physician), John Snow in London developed the methods. In 1849, he observed that the symptoms of cholera, which had already claimed around 500 lives within a month, were vomiting and diarrhoea. He concluded that the source of contamination must be through ingestion, rather than inhalation as was previously thought. It was this insight that resulted in the removal of The Pump On Broad Street, after which deaths from cholera plummeted. English nurse Florence Nightingale pioneered analysis of large amounts of statistical data, using graphs and tables, regarding the condition of thousands of patients in the Crimean War to evaluate the efficacy of hospital services. Her methods proved convincing and led to reforms in military and civilian hospitals, usually with the full support of the government.>
By the late 19th and early 20th century English statisticians led by Francis Galton, Karl Pearson and Ronald Fisher developed the mathematical tools such as correlations and hypothesis tests that made possible much more sophisticated analysis of statistical data.
During the U.S. Civil War the Sanitary Commission collected enormous amounts of statistical data, and opened up the problems of storing information for fast access and mechanically searching for data patterns. The pioneer was John Shaw Billings (1838–1913). A senior surgeon in the war, Billings built the Library of the Surgeon General's Office (now the National Library of Medicine), the centerpiece of modern medical information systems. Billings figured out how to mechanically analyze medical and demographic data by turning facts into numbers and punching the numbers onto cardboard cards that could be sorted and counted by machine. The applications were developed by his assistant Herman Hollerith; Hollerith invented the punch card and counter-sorter system that dominated statistical data manipulation until the 1970s. Hollerith's company became IBM, International Business Machines (IBM) in 1911.
A major breakthrough in epidemiology came with the introduction of statistical maps and graphs. They allowed careful analysis of seasonality issues in disease incidents, and the maps allowed public health officials to identify critical loci for the dissemination of disease. John Snow (physician), John Snow in London developed the methods. In 1849, he observed that the symptoms of cholera, which had already claimed around 500 lives within a month, were vomiting and diarrhoea. He concluded that the source of contamination must be through ingestion, rather than inhalation as was previously thought. It was this insight that resulted in the removal of The Pump On Broad Street, after which deaths from cholera plummeted. English nurse Florence Nightingale pioneered analysis of large amounts of statistical data, using graphs and tables, regarding the condition of thousands of patients in the Crimean War to evaluate the efficacy of hospital services. Her methods proved convincing and led to reforms in military and civilian hospitals, usually with the full support of the government.>
By the late 19th and early 20th century English statisticians led by Francis Galton, Karl Pearson and Ronald Fisher developed the mathematical tools such as correlations and hypothesis tests that made possible much more sophisticated analysis of statistical data.
During the U.S. Civil War the Sanitary Commission collected enormous amounts of statistical data, and opened up the problems of storing information for fast access and mechanically searching for data patterns. The pioneer was John Shaw Billings (1838–1913). A senior surgeon in the war, Billings built the Library of the Surgeon General's Office (now the National Library of Medicine), the centerpiece of modern medical information systems. Billings figured out how to mechanically analyze medical and demographic data by turning facts into numbers and punching the numbers onto cardboard cards that could be sorted and counted by machine. The applications were developed by his assistant Herman Hollerith; Hollerith invented the punch card and counter-sorter system that dominated statistical data manipulation until the 1970s. Hollerith's company became IBM, International Business Machines (IBM) in 1911.
 Until the nineteenth century, the care of the insanity, insane was largely a communal and family responsibility rather than a medical one. The vast majority of the mental disorder, mentally ill were treated in domestic contexts with only the most unmanageable or burdensome likely to be institutionally confined. This situation was transformed radically from the late eighteenth century as, amid changing cultural conceptions of madness, a new-found optimism in the curability of insanity within the asylum setting emerged. Increasingly, lunacy was perceived less as a physiology, physiological condition than as a mental and moral one to which the correct response was persuasion, aimed at inculcating internal restraint, rather than external coercion. This new therapeutic sensibility, referred to as moral treatment, was epitomised in French physician Philippe Pinel's quasi-mythological unchaining of the lunatics of the Bicêtre Hospital in Paris and realised in an institutional setting with the foundation in 1796 of the Quaker-run York The Retreat, Retreat in England.
Until the nineteenth century, the care of the insanity, insane was largely a communal and family responsibility rather than a medical one. The vast majority of the mental disorder, mentally ill were treated in domestic contexts with only the most unmanageable or burdensome likely to be institutionally confined. This situation was transformed radically from the late eighteenth century as, amid changing cultural conceptions of madness, a new-found optimism in the curability of insanity within the asylum setting emerged. Increasingly, lunacy was perceived less as a physiology, physiological condition than as a mental and moral one to which the correct response was persuasion, aimed at inculcating internal restraint, rather than external coercion. This new therapeutic sensibility, referred to as moral treatment, was epitomised in French physician Philippe Pinel's quasi-mythological unchaining of the lunatics of the Bicêtre Hospital in Paris and realised in an institutional setting with the foundation in 1796 of the Quaker-run York The Retreat, Retreat in England.
 From the early nineteenth century, as lay-led lunacy reform movements gained in influence, ever more state governments in the West extended their authority and responsibility over the mentally ill. Small-scale asylums, conceived as instruments to reshape both the mind and behaviour of the disturbed, proliferated across these regions.; By the 1830s, moral treatment, together with the asylum itself, became increasingly medicalised and asylum doctors began to establish a distinct medical identity with the establishment in the 1840s of associations for their members in France, Germany, the United Kingdom and America, together with the founding of medico-psychological journals. Medical optimism in the capacity of the asylum to cure insanity soured by the close of the nineteenth century as the growth of the asylum population far outstripped that of the general population. Processes of long-term institutional segregation, allowing for the psychiatric conceptualisation of the Natural history of disease, natural course of mental illness, supported the perspective that the insane were a distinct population, subject to mental pathologies stemming from specific medical causes. As Social degeneration, degeneration theory grew in influence from the mid-nineteenth century, heredity was seen as the central causal element in chronic mental illness, and, with national asylum systems overcrowded and insanity apparently undergoing an inexorable rise, the focus of psychiatric therapeutics shifted from a concern with treating the individual to maintaining the racial and biological health of national populations.
Emil Kraepelin (1856–1926) introduced new medical categories of mental illness, which eventually came into psychiatry, psychiatric usage despite their basis in behavior rather than Biopsychiatry controversy, pathology or underlying cause. Shell shock among frontline soldiers exposed to heavy artillery bombardment was first diagnosed by British Army doctors in 1915. By 1916, similar symptoms were also noted in soldiers not exposed to explosive shocks, leading to questions as to whether the disorder was physical or psychiatric. In the 1920s surrealism, surrealist opposition to psychiatry was expressed in a number of surrealist publications. In the 1930s several controversial medical practices were introduced including inducing seizures (by electroshock, insulin or other drugs) or cutting parts of the brain apart (leucotomy or lobotomy). Both came into widespread use by psychiatry, but there were grave concerns and much opposition on grounds of basic morality, harmful effects, or misuse.
In the 1950s new psychiatric drugs, notably the antipsychotic chlorpromazine, were designed in laboratories and slowly came into preferred use. Although often accepted as an advance in some ways, there was some opposition, due to serious adverse effects such as tardive dyskinesia. Patients often opposed psychiatry and refused or stopped taking the drugs when not subject to psychiatric control. There was also increasing opposition to the use of psychiatric hospitals, and attempts to move people back into the community on a collaborative World Network of Users and Survivors of Psychiatry, user-led group approach ("therapeutic communities") not controlled by psychiatry. Campaigns against masturbation were done in the Victorian era and elsewhere. Lobotomy was used until the 1970s to treat schizophrenia. This was denounced by the anti-psychiatric movement in the 1960s and later.
From the early nineteenth century, as lay-led lunacy reform movements gained in influence, ever more state governments in the West extended their authority and responsibility over the mentally ill. Small-scale asylums, conceived as instruments to reshape both the mind and behaviour of the disturbed, proliferated across these regions.; By the 1830s, moral treatment, together with the asylum itself, became increasingly medicalised and asylum doctors began to establish a distinct medical identity with the establishment in the 1840s of associations for their members in France, Germany, the United Kingdom and America, together with the founding of medico-psychological journals. Medical optimism in the capacity of the asylum to cure insanity soured by the close of the nineteenth century as the growth of the asylum population far outstripped that of the general population. Processes of long-term institutional segregation, allowing for the psychiatric conceptualisation of the Natural history of disease, natural course of mental illness, supported the perspective that the insane were a distinct population, subject to mental pathologies stemming from specific medical causes. As Social degeneration, degeneration theory grew in influence from the mid-nineteenth century, heredity was seen as the central causal element in chronic mental illness, and, with national asylum systems overcrowded and insanity apparently undergoing an inexorable rise, the focus of psychiatric therapeutics shifted from a concern with treating the individual to maintaining the racial and biological health of national populations.
Emil Kraepelin (1856–1926) introduced new medical categories of mental illness, which eventually came into psychiatry, psychiatric usage despite their basis in behavior rather than Biopsychiatry controversy, pathology or underlying cause. Shell shock among frontline soldiers exposed to heavy artillery bombardment was first diagnosed by British Army doctors in 1915. By 1916, similar symptoms were also noted in soldiers not exposed to explosive shocks, leading to questions as to whether the disorder was physical or psychiatric. In the 1920s surrealism, surrealist opposition to psychiatry was expressed in a number of surrealist publications. In the 1930s several controversial medical practices were introduced including inducing seizures (by electroshock, insulin or other drugs) or cutting parts of the brain apart (leucotomy or lobotomy). Both came into widespread use by psychiatry, but there were grave concerns and much opposition on grounds of basic morality, harmful effects, or misuse.
In the 1950s new psychiatric drugs, notably the antipsychotic chlorpromazine, were designed in laboratories and slowly came into preferred use. Although often accepted as an advance in some ways, there was some opposition, due to serious adverse effects such as tardive dyskinesia. Patients often opposed psychiatry and refused or stopped taking the drugs when not subject to psychiatric control. There was also increasing opposition to the use of psychiatric hospitals, and attempts to move people back into the community on a collaborative World Network of Users and Survivors of Psychiatry, user-led group approach ("therapeutic communities") not controlled by psychiatry. Campaigns against masturbation were done in the Victorian era and elsewhere. Lobotomy was used until the 1970s to treat schizophrenia. This was denounced by the anti-psychiatric movement in the 1960s and later.
 European ideas of modern medicine were spread widely through the world by medical missionaries, and the dissemination of textbooks. Japanese elites enthusiastically embraced Western medicine after the Meiji Restoration of the 1860s. However they had been prepared by their knowledge of the Dutch and German medicine, for they had some contact with Europe through the Dutch. Highly influential was the 1765 edition of Hendrik van Deventer's pioneer work ''Nieuw Ligt'' ("A New Light") on Japanese obstetrics, especially on Katakura Kakuryo's publication in 1799 of ''Sanka Hatsumo'' ("Enlightenment of Obstetrics"). A cadre of Japanese physicians began to interact with Dutch doctors, who introduced smallpox vaccinations. By 1820 Japanese ranpô medical practitioners not only translated Dutch medical texts, they integrated their readings with clinical diagnoses. These men became leaders of the modernization of medicine in their country. They broke from Japanese traditions of closed medical fraternities and adopted the European approach of an open community of collaboration based on expertise in the latest scientific methods.
Kitasato Shibasaburō (1853–1931) studied bacteriology in Germany under Robert Koch. In 1891 he founded the Institute of Infectious Diseases in Tokyo, which introduced the study of bacteriology to Japan. He and French researcher Alexandre Yersin went to Hong Kong in 1894, where; Kitasato confirmed Yersin's discovery that the bacterium ''Yersinia pestis'' is the agent of the plague. In 1897 he isolated and described the organism that caused dysentery. He became the first dean of medicine at Keio University, and the first president of the Japan Medical Association.
Japanese physicians immediately recognized the values of X-Rays. They were able to purchase the equipment locally from the Shimadzu Company, which developed, manufactured, marketed, and distributed X-Ray machines after 1900. Japan not only adopted German methods of public health in the home islands, but implemented them in its colonies, especially Korea and Taiwan, and after 1931 in Manchuria. A heavy investment in sanitation resulted in a dramatic increase of life expectancy.
European ideas of modern medicine were spread widely through the world by medical missionaries, and the dissemination of textbooks. Japanese elites enthusiastically embraced Western medicine after the Meiji Restoration of the 1860s. However they had been prepared by their knowledge of the Dutch and German medicine, for they had some contact with Europe through the Dutch. Highly influential was the 1765 edition of Hendrik van Deventer's pioneer work ''Nieuw Ligt'' ("A New Light") on Japanese obstetrics, especially on Katakura Kakuryo's publication in 1799 of ''Sanka Hatsumo'' ("Enlightenment of Obstetrics"). A cadre of Japanese physicians began to interact with Dutch doctors, who introduced smallpox vaccinations. By 1820 Japanese ranpô medical practitioners not only translated Dutch medical texts, they integrated their readings with clinical diagnoses. These men became leaders of the modernization of medicine in their country. They broke from Japanese traditions of closed medical fraternities and adopted the European approach of an open community of collaboration based on expertise in the latest scientific methods.
Kitasato Shibasaburō (1853–1931) studied bacteriology in Germany under Robert Koch. In 1891 he founded the Institute of Infectious Diseases in Tokyo, which introduced the study of bacteriology to Japan. He and French researcher Alexandre Yersin went to Hong Kong in 1894, where; Kitasato confirmed Yersin's discovery that the bacterium ''Yersinia pestis'' is the agent of the plague. In 1897 he isolated and described the organism that caused dysentery. He became the first dean of medicine at Keio University, and the first president of the Japan Medical Association.
Japanese physicians immediately recognized the values of X-Rays. They were able to purchase the equipment locally from the Shimadzu Company, which developed, manufactured, marketed, and distributed X-Ray machines after 1900. Japan not only adopted German methods of public health in the home islands, but implemented them in its colonies, especially Korea and Taiwan, and after 1931 in Manchuria. A heavy investment in sanitation resulted in a dramatic increase of life expectancy.
 In the American Civil War (1861–65), as was typical of the 19th century, more soldiers died of disease than in battle, and even larger numbers were temporarily incapacitated by wounds, disease and accidents. Conditions were poor in the Confederate States of America, Confederacy, where doctors and medical supplies were in short supply. The war had a dramatic long-term impact on medicine in the U.S., from surgical technique to hospitals to nursing and to research facilities. Weapon development -particularly the appearance of rifles, Springfield Model 1861, mass-produced and much more accurate than muskets led to generals underestimating the risks of long range rifle fire; risks exemplified in the death of John Sedgwick and the disastrous George Pickett#Gettysburg and Pickett's Charge, Pickett's Charge. The rifles could shatter bone forcing amputation and longer ranges meant casualties were sometimes not quickly found. Evacuation of the wounded from Second Battle of Bull Run took a week. As in earlier wars, untreated casualties sometimes survived unexpectedly due to maggots debridement, debriding the wound -an observation which led to the Maggot therapy#History, surgical use of maggots -still a useful method in the absence of effective antibiotics.
The hygiene of the training and field camps was poor, especially at the beginning of the war when men who had seldom been far from home were brought together for training with thousands of strangers. First came epidemics of the childhood diseases of chicken pox, mumps, whooping cough, and, especially, measles. Operations in the South meant a dangerous and new disease environment, bringing diarrhea, dysentery, typhoid fever, and malaria. There were no antibiotics, so the surgeons prescribed coffee, whiskey, and quinine. Harsh weather, bad water, inadequate shelter in winter quarters, poor policing of camps, and dirty camp hospitals took their toll.
This was a common scenario in wars from time immemorial, and conditions faced by the Confederate army were even worse. The Union responded by building army hospitals in every state. What was different in the Union was the emergence of skilled, well-funded medical organizers who took proactive action, especially in the much enlarged United States Army Medical Department, and the United States Sanitary Commission, a new private agency. Numerous other new agencies also targeted the medical and morale needs of soldiers, including the United States Christian Commission as well as smaller private agencies.
The U.S. Army learned many lessons and in August 1886, it established the Hospital Corps.
In the American Civil War (1861–65), as was typical of the 19th century, more soldiers died of disease than in battle, and even larger numbers were temporarily incapacitated by wounds, disease and accidents. Conditions were poor in the Confederate States of America, Confederacy, where doctors and medical supplies were in short supply. The war had a dramatic long-term impact on medicine in the U.S., from surgical technique to hospitals to nursing and to research facilities. Weapon development -particularly the appearance of rifles, Springfield Model 1861, mass-produced and much more accurate than muskets led to generals underestimating the risks of long range rifle fire; risks exemplified in the death of John Sedgwick and the disastrous George Pickett#Gettysburg and Pickett's Charge, Pickett's Charge. The rifles could shatter bone forcing amputation and longer ranges meant casualties were sometimes not quickly found. Evacuation of the wounded from Second Battle of Bull Run took a week. As in earlier wars, untreated casualties sometimes survived unexpectedly due to maggots debridement, debriding the wound -an observation which led to the Maggot therapy#History, surgical use of maggots -still a useful method in the absence of effective antibiotics.
The hygiene of the training and field camps was poor, especially at the beginning of the war when men who had seldom been far from home were brought together for training with thousands of strangers. First came epidemics of the childhood diseases of chicken pox, mumps, whooping cough, and, especially, measles. Operations in the South meant a dangerous and new disease environment, bringing diarrhea, dysentery, typhoid fever, and malaria. There were no antibiotics, so the surgeons prescribed coffee, whiskey, and quinine. Harsh weather, bad water, inadequate shelter in winter quarters, poor policing of camps, and dirty camp hospitals took their toll.
This was a common scenario in wars from time immemorial, and conditions faced by the Confederate army were even worse. The Union responded by building army hospitals in every state. What was different in the Union was the emergence of skilled, well-funded medical organizers who took proactive action, especially in the much enlarged United States Army Medical Department, and the United States Sanitary Commission, a new private agency. Numerous other new agencies also targeted the medical and morale needs of soldiers, including the United States Christian Commission as well as smaller private agencies.
The U.S. Army learned many lessons and in August 1886, it established the Hospital Corps.
 Prosthetics have improved with lightweight materials as well as neural prosthetics emerging in the end of the 20th century.
Prosthetics have improved with lightweight materials as well as neural prosthetics emerging in the end of the 20th century.
 Thousands of scarred troops provided the need for improved prosthetic limbs and expanded techniques in plastic surgery or reconstructive surgery. Those practices were combined to broaden cosmetic surgery and other forms of elective surgery.
Thousands of scarred troops provided the need for improved prosthetic limbs and expanded techniques in plastic surgery or reconstructive surgery. Those practices were combined to broaden cosmetic surgery and other forms of elective surgery.
 The advances in medicine made a dramatic difference for Allied troops, while the Germans and especially the Japanese and Chinese suffered from a severe lack of newer medicines, techniques and facilities. Harrison finds that the chances of recovery for a badly wounded British infantryman were as much as 25 times better than in the First World War. The reason was that:
:"By 1944 most casualties were receiving treatment within hours of wounding, due to the increased mobility of field hospitals and the extensive use of aeroplanes as ambulances. The care of the sick and wounded had also been revolutionized by new medical technologies, such as active immunization against tetanus, sulphonamide drugs, and penicillin."
During the second World War, Alexis Carrel and Henry Drysdale Dakin, Henry Dakin developed the Carrel-Dakin method of treating wounds with an irrigation, Dakin's solution, a germicide which helped prevent gangrene.
The War spurred the usage of Wilhelm Röntgen, Roentgen's X-ray, and the electrocardiograph, for the monitoring (medicine), monitoring of internal bodily functions. This was followed in the inter-war period by the development of the first anti-bacterial agents such as the sulpha antibiotics.
Nazi and Japanese medical research
Unethical human subject research, and killing of patients with disabilities, peaked during the Nazi era, with Nazi human experimentation and Aktion T4 during the Holocaust as the most significant examples. Many of the details of these and related events were the focus of the Doctors' Trial. Subsequently, principles of medical ethics, such as the Nuremberg Code, were introduced to prevent a recurrence of such atrocities. After 1937, the Japanese Army established programs of biological warfare in China. In Unit 731, Japanese doctors and research scientists conducted large numbers of vivisections and experiments on human beings, mostly Chinese victims.
The advances in medicine made a dramatic difference for Allied troops, while the Germans and especially the Japanese and Chinese suffered from a severe lack of newer medicines, techniques and facilities. Harrison finds that the chances of recovery for a badly wounded British infantryman were as much as 25 times better than in the First World War. The reason was that:
:"By 1944 most casualties were receiving treatment within hours of wounding, due to the increased mobility of field hospitals and the extensive use of aeroplanes as ambulances. The care of the sick and wounded had also been revolutionized by new medical technologies, such as active immunization against tetanus, sulphonamide drugs, and penicillin."
During the second World War, Alexis Carrel and Henry Drysdale Dakin, Henry Dakin developed the Carrel-Dakin method of treating wounds with an irrigation, Dakin's solution, a germicide which helped prevent gangrene.
The War spurred the usage of Wilhelm Röntgen, Roentgen's X-ray, and the electrocardiograph, for the monitoring (medicine), monitoring of internal bodily functions. This was followed in the inter-war period by the development of the first anti-bacterial agents such as the sulpha antibiotics.
Nazi and Japanese medical research
Unethical human subject research, and killing of patients with disabilities, peaked during the Nazi era, with Nazi human experimentation and Aktion T4 during the Holocaust as the most significant examples. Many of the details of these and related events were the focus of the Doctors' Trial. Subsequently, principles of medical ethics, such as the Nuremberg Code, were introduced to prevent a recurrence of such atrocities. After 1937, the Japanese Army established programs of biological warfare in China. In Unit 731, Japanese doctors and research scientists conducted large numbers of vivisections and experiments on human beings, mostly Chinese victims.
 The World Health Organization was founded in 1948 as a United Nations agency to improve global health. In most of the world, life expectancy has improved since then, and was about 67 years , and well above 80 years in some countries. Eradication of infectious diseases is an international effort, and several new vaccines have been developed during the post-war years, against infections such as measles, mumps, several strains of influenza and human papilloma virus. The long-known vaccine against Smallpox finally eradicated the disease in the 1970s, and Rinderpest was wiped out in 2011. Eradication of polio is underway. Tissue culture is important for development of vaccines. Though the early success of antiviral vaccines and antibacterial drugs, antiviral drugs were not introduced until the 1970s. Through the WHO, the international community has developed a response protocol against epidemics, displayed during the SARS epidemic in 2003, the Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 from 2004, the Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa and onwards.
The World Health Organization was founded in 1948 as a United Nations agency to improve global health. In most of the world, life expectancy has improved since then, and was about 67 years , and well above 80 years in some countries. Eradication of infectious diseases is an international effort, and several new vaccines have been developed during the post-war years, against infections such as measles, mumps, several strains of influenza and human papilloma virus. The long-known vaccine against Smallpox finally eradicated the disease in the 1970s, and Rinderpest was wiped out in 2011. Eradication of polio is underway. Tissue culture is important for development of vaccines. Though the early success of antiviral vaccines and antibacterial drugs, antiviral drugs were not introduced until the 1970s. Through the WHO, the international community has developed a response protocol against epidemics, displayed during the SARS epidemic in 2003, the Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 from 2004, the Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa and onwards.
