High Middle Ages on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the
 A key geo-strategic development in the
A key geo-strategic development in the
 By the time of the High Middle Ages, the
By the time of the High Middle Ages, the
 In the High Middle Ages, the
In the High Middle Ages, the
 In the mid-10th century Poland emerged as a duchy after Mieszko I, the ruler of the Western Polans, Polans, conquered the surrounding Lechites, Lechitic tribes in the region. Then in 1025 under the rule of Bolesław I the Brave, Poland became a kingdom.
In the mid-10th century Poland emerged as a duchy after Mieszko I, the ruler of the Western Polans, Polans, conquered the surrounding Lechites, Lechitic tribes in the region. Then in 1025 under the rule of Bolesław I the Brave, Poland became a kingdom.
 The High Middle Ages saw the height and decline of the Slavic state of Kievan Rus' and emergence of Cumania. Later, the Mongol invasions, Mongol invasion in the 13th century had great impact on the east of Europe, as many countries of the region were invaded, pillaged, conquered and/or vassalized.
During the first half of this period (1185) the
The High Middle Ages saw the height and decline of the Slavic state of Kievan Rus' and emergence of Cumania. Later, the Mongol invasions, Mongol invasion in the 13th century had great impact on the east of Europe, as many countries of the region were invaded, pillaged, conquered and/or vassalized.
During the first half of this period (1185) the
 The Catholic Crusades occurred between the 11th and 13th centuries. They were conducted under papal authority, initially with the intent of reestablishing Christian rule in ''The Holy Land'' by taking the area from the Muslim Fatimid Caliphate. The Fatimids had captured Palestine in AD 970, lost it to the
The Catholic Crusades occurred between the 11th and 13th centuries. They were conducted under papal authority, initially with the intent of reestablishing Christian rule in ''The Holy Land'' by taking the area from the Muslim Fatimid Caliphate. The Fatimids had captured Palestine in AD 970, lost it to the
 Catharism was a movement with Gnosticism, Gnostic elements that originated around the middle of the 10th century, branded by the contemporary Roman Catholic Church as heresy, heretical. It existed throughout much of Western Europe, but its origination was in Languedoc and surrounding areas in southern France.
The name ''Cathar'' stems from Greek language, Greek ''katharos'', "pure". One of the first recorded uses is Eckebert, Eckbert von Schönau who wrote on heretics from Cologne in 1181: "Hos nostra Germania catharos appellat." ([In] our Germany [one] calls these [people] "Cathars".)
The Cathars are also called Albigensians. This name originates from the end of the 12th century, and was used by the chronicler Geoffroy du Breuil of Vigeois in 1181. The name refers to the southern town of Albi (the ancient Albiga). The designation is hardly exact, for the centre was at Toulouse and in the neighbouring districts.
The Catharism, Albigensians were strong in southern France, northern Italy, and the southwestern
Catharism was a movement with Gnosticism, Gnostic elements that originated around the middle of the 10th century, branded by the contemporary Roman Catholic Church as heresy, heretical. It existed throughout much of Western Europe, but its origination was in Languedoc and surrounding areas in southern France.
The name ''Cathar'' stems from Greek language, Greek ''katharos'', "pure". One of the first recorded uses is Eckebert, Eckbert von Schönau who wrote on heretics from Cologne in 1181: "Hos nostra Germania catharos appellat." ([In] our Germany [one] calls these [people] "Cathars".)
The Cathars are also called Albigensians. This name originates from the end of the 12th century, and was used by the chronicler Geoffroy du Breuil of Vigeois in 1181. The name refers to the southern town of Albi (the ancient Albiga). The designation is hardly exact, for the centre was at Toulouse and in the neighbouring districts.
The Catharism, Albigensians were strong in southern France, northern Italy, and the southwestern
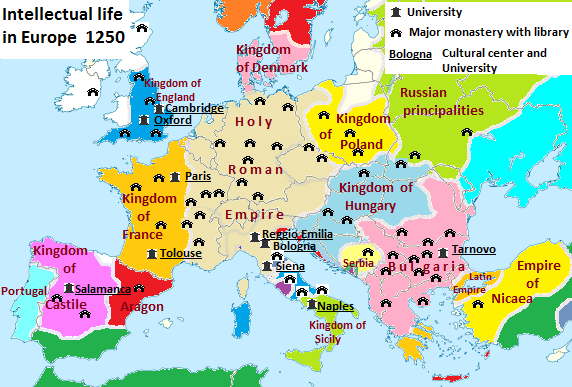 Philosophical and scientific teaching of the
Philosophical and scientific teaching of the  At the beginning of the 13th century there were reasonably accurate Latin translations of the main works of almost all the intellectually crucial ancient authors, allowing a sound transfer of scientific ideas via both the universities and the monasteries. By then, the natural science contained in these texts began to be extended by notable scholastics such as Robert Grosseteste, Roger Bacon, Albertus Magnus and Duns Scotus. Precursors of the modern scientific method can be seen already in Grosseteste's emphasis on mathematics as a way to understand nature, and in the empirical approach admired by Bacon, particularly in his ''Opus Majus''.
At the beginning of the 13th century there were reasonably accurate Latin translations of the main works of almost all the intellectually crucial ancient authors, allowing a sound transfer of scientific ideas via both the universities and the monasteries. By then, the natural science contained in these texts began to be extended by notable scholastics such as Robert Grosseteste, Roger Bacon, Albertus Magnus and Duns Scotus. Precursors of the modern scientific method can be seen already in Grosseteste's emphasis on mathematics as a way to understand nature, and in the empirical approach admired by Bacon, particularly in his ''Opus Majus''.
 * The earliest written record of a windmill is from Yorkshire, England, dated 1185.
* Paper manufacture began in Italy around 1270.
* The spinning wheel was brought to Europe (probably from India) in the 13th century.
* The magnetic compass aided navigation, first reaching Europe some time in the late 12th century.
* Eye glasses were invented in Italy in the late 1280s.
* The astrolabe returned to Europe via Islamic Spain.
* Fibonacci introduces Hindu-Arabic numerals to Europe with his book ''Liber Abaci'' in 1202.
* The West's oldest known depiction of a stern-mounted rudder can be found on church carvings dating to around 1180.
* The earliest written record of a windmill is from Yorkshire, England, dated 1185.
* Paper manufacture began in Italy around 1270.
* The spinning wheel was brought to Europe (probably from India) in the 13th century.
* The magnetic compass aided navigation, first reaching Europe some time in the late 12th century.
* Eye glasses were invented in Italy in the late 1280s.
* The astrolabe returned to Europe via Islamic Spain.
* Fibonacci introduces Hindu-Arabic numerals to Europe with his book ''Liber Abaci'' in 1202.
* The West's oldest known depiction of a stern-mounted rudder can be found on church carvings dating to around 1180.
 Art in the High Middle Ages includes these important movements:
* Anglo-Saxon art was influential on the British Isles until the Norman Invasion of 1066
* Romanesque art continued traditions from the Classical world (not to be confused with Romanesque architecture)
* Gothic art developed a distinct Germanic flavor (not to be confused with Gothic architecture).
* Indo-Islamic architecture begins when Muhammad of Ghor made Delhi a Muslim capital
*
Art in the High Middle Ages includes these important movements:
* Anglo-Saxon art was influential on the British Isles until the Norman Invasion of 1066
* Romanesque art continued traditions from the Classical world (not to be confused with Romanesque architecture)
* Gothic art developed a distinct Germanic flavor (not to be confused with Gothic architecture).
* Indo-Islamic architecture begins when Muhammad of Ghor made Delhi a Muslim capital
*

 Gothic architecture superseded the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque style by combining flying buttresses, gothic (or pointed) arches and ribbed vaults. It was influenced by the spiritual background of the time, being religious in essence: thin horizontal lines and grates made the building strive towards the sky. Architecture was made to appear light and weightless, as opposed to the dark and bulky forms of the previous Romanesque architecture, Romanesque style. Saint Augustine of Hippo taught that light was an expression of God. Architectural techniques were adapted and developed to build churches that reflected this teaching. Colorful glass windows enhanced the spirit of lightness. As color was much rarer at medieval times than today, it can be assumed that these virtuoso works of art had an awe-inspiring impact on the common man from the street. High-rising intricate ribbed, and later fan vaultings demonstrated movement toward heaven. Veneration of God was also expressed by the relatively large size of these buildings. A gothic cathedral therefore not only invited the visitors to elevate themselves spiritually, it was also meant to demonstrate the greatness of God. The floor plan of a gothic cathedral corresponded to the rules of scholasticism: According to Erwin Panofsky's ''Gothic Architecture and Scholasticism'', the plan was divided into sections and uniform subsections. These characteristics are exhibited by the most famous sacral building of the time: Notre Dame de Paris.
Gothic architecture superseded the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque style by combining flying buttresses, gothic (or pointed) arches and ribbed vaults. It was influenced by the spiritual background of the time, being religious in essence: thin horizontal lines and grates made the building strive towards the sky. Architecture was made to appear light and weightless, as opposed to the dark and bulky forms of the previous Romanesque architecture, Romanesque style. Saint Augustine of Hippo taught that light was an expression of God. Architectural techniques were adapted and developed to build churches that reflected this teaching. Colorful glass windows enhanced the spirit of lightness. As color was much rarer at medieval times than today, it can be assumed that these virtuoso works of art had an awe-inspiring impact on the common man from the street. High-rising intricate ribbed, and later fan vaultings demonstrated movement toward heaven. Veneration of God was also expressed by the relatively large size of these buildings. A gothic cathedral therefore not only invited the visitors to elevate themselves spiritually, it was also meant to demonstrate the greatness of God. The floor plan of a gothic cathedral corresponded to the rules of scholasticism: According to Erwin Panofsky's ''Gothic Architecture and Scholasticism'', the plan was divided into sections and uniform subsections. These characteristics are exhibited by the most famous sacral building of the time: Notre Dame de Paris.
 A variety of cultures influenced the literature of the High Middle Ages, one of the strongest among them being Christianity. The connection to Christianity was greatest in Latin literature, which influenced the vernacular languages in the Literature cycle, literary cycle of the Matter of Rome. Other literary cycles, or interrelated groups of stories, included the Matter of France (stories about Charlemagne and his court), the Acritic songs dealing with the chivalry of Byzantine Empire, Byzantium's frontiersmen, and perhaps the best known cycle, the Matter of Britain, which featured tales about King Arthur, his court, and related stories from Brittany, Cornwall,
A variety of cultures influenced the literature of the High Middle Ages, one of the strongest among them being Christianity. The connection to Christianity was greatest in Latin literature, which influenced the vernacular languages in the Literature cycle, literary cycle of the Matter of Rome. Other literary cycles, or interrelated groups of stories, included the Matter of France (stories about Charlemagne and his court), the Acritic songs dealing with the chivalry of Byzantine Empire, Byzantium's frontiersmen, and perhaps the best known cycle, the Matter of Britain, which featured tales about King Arthur, his court, and related stories from Brittany, Cornwall,

 The surviving music of the High Middle Ages is primarily religious in nature, since music notation developed in religious institutions, and the application of notation to secular music was a later development. Early in the period, Gregorian chant was the dominant form of church music; other forms, beginning with organum, and later including Clausula (music), clausulae, conductus, and the motet, developed using the chant as source material.
During the 11th century, Guido of Arezzo was one of the first to develop musical notation, which made it easier for singers to remember Gregorian chants.
It was during the 12th and 13th centuries that Gregorian plainchant gave birth to polyphony, which appeared in the works of French Notre Dame School (Léonin and Pérotin). Later it evolved into the ''ars nova'' (Philippe de Vitry, Guillaume de Machaut) and the musical genres of late Middle Ages. An important composer during the 12th century was the nun Hildegard of Bingen.
The most significant secular movement was that of the troubadours, who arose in Occitania (Southern France) in the late 11th century. The troubadours were often itinerant entertainer, itinerant, came from all classes of society, and wrote songs on a variety of topics, though with a particular focus on courtly love. Their style went on to influence the trouvères of northern France, the minnesingers of Germany, and the composers of secular music of the Trecento in northern Italy.
The surviving music of the High Middle Ages is primarily religious in nature, since music notation developed in religious institutions, and the application of notation to secular music was a later development. Early in the period, Gregorian chant was the dominant form of church music; other forms, beginning with organum, and later including Clausula (music), clausulae, conductus, and the motet, developed using the chant as source material.
During the 11th century, Guido of Arezzo was one of the first to develop musical notation, which made it easier for singers to remember Gregorian chants.
It was during the 12th and 13th centuries that Gregorian plainchant gave birth to polyphony, which appeared in the works of French Notre Dame School (Léonin and Pérotin). Later it evolved into the ''ars nova'' (Philippe de Vitry, Guillaume de Machaut) and the musical genres of late Middle Ages. An important composer during the 12th century was the nun Hildegard of Bingen.
The most significant secular movement was that of the troubadours, who arose in Occitania (Southern France) in the late 11th century. The troubadours were often itinerant entertainer, itinerant, came from all classes of society, and wrote songs on a variety of topics, though with a particular focus on courtly love. Their style went on to influence the trouvères of northern France, the minnesingers of Germany, and the composers of secular music of the Trecento in northern Italy.
online
* Power, Daniel, ed. ''The Central Middle Ages: Europe 950–1320'' (Oxford UP, 2006).
in the ''Columbia Encyclopedia'' at Infoplease
Provençal literature
in the ''Columbia Encyclopedia'' at Infoplease {{Authority control High Middle Ages, Middle Ages, .02 11th century in Europe, . 12th century in Europe, . 13th century in Europe, . 11th-century establishments in Europe, . 13th-century disestablishments in Europe, . pt:Idade Média#Alta Idade Média
period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
of European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD 500), the Middle Ages (AD 500 to AD 1500), and the modern era (since AD 1500).
The first early ...
that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
were preceded by the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
and were followed by the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the Periodization, period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Eur ...
, which ended around AD 1500 (by historiographical
Historiography is the study of the methods of historians in developing history as an academic discipline, and by extension is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiography of a specific topic covers how historians hav ...
convention).
Key historical trends of the High Middle Ages include the rapidly increasing population of Europe, which brought about great social and political change from the preceding era, and the Renaissance of the 12th century, including the first developments of rural exodus
Rural flight (or rural exodus) is the migratory pattern of peoples from rural areas into urban areas. It is urbanization seen from the rural perspective.
In industrializing economies like Britain in the eighteenth century or East Asia in the ...
and urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly t ...
. By 1250, the robust population increase had greatly benefited the European economy, which reached levels that would not be seen again in some areas until the 19th century. That trend faltered during the Late Middle Ages because of a series of calamities, most notably the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
, but also numerous wars as well as economic stagnation.
From around 780, Europe saw the last of the barbarian invasions and became more socially and politically organized. The Carolingian Renaissance
The Carolingian Renaissance was the first of three medieval renaissances, a period of cultural activity in the Carolingian Empire. It occurred from the late 8th century to the 9th century, taking inspiration from the State church of the Roman Emp ...
stimulated scientific and philosophical activity in Northern Europe. The first universities started operating in Bologna
Bologna (, , ; egl, label= Emilian, Bulåggna ; lat, Bononia) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna region in Northern Italy. It is the seventh most populous city in Italy with about 400,000 inhabitants and 150 different nat ...
, Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
, Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, Salamanca
Salamanca () is a city in western Spain and is the capital of the Province of Salamanca in the autonomous community of Castile and León. The city lies on several rolling hills by the Tormes River. Its Old City was declared a UNESCO World Heritag ...
, Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
and Modena
Modena (, , ; egl, label=Emilian language#Dialects, Modenese, Mòdna ; ett, Mutna; la, Mutina) is a city and ''comune'' (municipality) on the south side of the Po Valley, in the Province of Modena in the Emilia-Romagna region of northern I ...
. The Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
s settled in the British Isles, France and elsewhere, and Norse Christian kingdoms started developing in their Scandinavian homelands. The Magyars ceased their expansion in the 10th century, and by the year 1000, a Christian Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
had become a recognized state in Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the area' ...
that was forming alliances with regional powers. With the brief exception of the Mongol invasions
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire ( 1206- 1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastati ...
in the 13th century, major nomadic incursions ceased. The powerful Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
of the Macedonian and Komnenos
Komnenos ( gr, Κομνηνός; Latinized Comnenus; plural Komnenoi or Comneni (Κομνηνοί, )) was a Byzantine Greek noble family who ruled the Byzantine Empire from 1081 to 1185, and later, as the Grand Komnenoi (Μεγαλοκομνην� ...
dynasties gradually gave way to the resurrected Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
and Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon ...
and to a successor crusader state
The Crusader States, also known as Outremer, were four Catholic realms in the Middle East that lasted from 1098 to 1291. These feudal polities were created by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade through conquest and political in ...
(1204 to 1261), who continually fought each other until the end of the Latin Empire. The Byzantine Empire was reestablished in 1261 with the recapture of Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
from the Latins, though it was no longer a major power and would continue to falter through the 14th century, with remnants lasting until the mid 15th century.
In the 11th century, populations north of the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
began a more intensive settlement, targeting "new" lands, some areas of which had reverted to wilderness after the end of the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
. In what historian Charles Higounet
Charles Higounet (13 January 1911 – 8 April 1988, aged 77) was a French historian medievalist, specialising in bastides and the Middle Ages in the southwest of France.
Biography
Charles Higounet was a French medievalist who taught in Bordeau ...
called the "great clearances", Europeans cleared and cultivated some of the vast forests and marshes that lay across much of the continent. At the same time, settlers moved beyond the traditional boundaries of the Frankish Empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks dur ...
to new frontiers beyond the Elbe River
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Repu ...
, which tripled the size of Germany in the process. The Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, which reached the peak of its political power around then, called armies from across Europe to a series of Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
against the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
. The crusaders occupied the Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
and founded the Crusader States
The Crusader States, also known as Outremer, were four Catholic realms in the Middle East that lasted from 1098 to 1291. These feudal polities were created by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade through conquest and political in ...
in the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
. Other wars led to the Northern Crusades
The Northern Crusades or Baltic Crusades were Christianity and colonialism, Christian colonization and Christianization campaigns undertaken by Catholic Church, Catholic Christian Military order (society), military orders and kingdoms, primarily ...
. The Christian kingdoms took much of the Iberian Peninsula from Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
control, and the Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Fran ...
conquered southern Italy, all part of the major population increases and the resettlement patterns of the era.
The High Middle Ages produced many different forms of intellectual, spiritual and artistic works. The age also saw the rise of ethnocentrism
Ethnocentrism in social science and anthropology—as well as in colloquial English discourse—means to apply one's own culture or ethnicity as a frame of reference to judge other cultures, practices, behaviors, beliefs, and people, instead of ...
, which evolved later into modern national identities
National identity is a person's identity or sense of belonging to one or more states or to one or more nations. It is the sense of "a nation as a cohesive whole, as represented by distinctive traditions, culture, and language". National identity ...
in most of Europe, the ascent of the great Italian city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
s and the rise and fall of the Islamic civilization of Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus DIN 31635, translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label=Berber languages, Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, ...
. The rediscovery of the works of Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
, at first indirectly through medieval Jewish and Islamic philosophy
Islamic philosophy is philosophy that emerges from the Islamic tradition. Two terms traditionally used in the Islamic world are sometimes translated as philosophy—falsafa (literally: "philosophy"), which refers to philosophy as well as logic, ...
, led Maimonides
Musa ibn Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (); la, Moses Maimonides and also referred to by the acronym Rambam ( he, רמב״ם), was a Sephardic Jewish philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah ...
, Ibn Sina, Ibn Rushd
Ibn Rushd ( ar, ; full name in ; 14 April 112611 December 1198), often Latinized as Averroes ( ), was an
Andalusian polymath and jurist who wrote about many subjects, including philosophy, theology, medicine, astronomy, physics, psychology, ...
, Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas, OP (; it, Tommaso d'Aquino, lit=Thomas of Aquino; 1225 – 7 March 1274) was an Italian Dominican friar and priest who was an influential philosopher, theologian and jurist in the tradition of scholasticism; he is known wi ...
and other thinkers of the period to expand Scholasticism
Scholasticism was a medieval school of philosophy that employed a critical organic method of philosophical analysis predicated upon the Aristotelian 10 Categories. Christian scholasticism emerged within the monastic schools that translate ...
, a combination of Judeo-Islamic and Catholic ideologies with the ancient philosophy. For much of this period, Constantinople remained Europe's most populous city, and Byzantine art
Byzantine art comprises the body of Christian Greek artistic products of the Eastern Roman Empire, as well as the nations and states that inherited culturally from the empire. Though the empire itself emerged from the decline of Rome and lasted ...
reached a peak in the 12th century. In architecture, many of the most notable Gothic cathedrals
Gothic cathedrals and churches are religious buildings created in Europe between the mid-12th century and the beginning of the 16th century. The cathedrals are notable particularly for their great height and their extensive use of stained glass ...
were built or completed around this period.
The Crisis of the Late Middle Ages
The Crisis of the Late Middle Ages was a series of events in the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries that ended centuries of European stability during the Late Middle Ages. Three major crises led to radical changes in all areas of society: demog ...
began at the start of the 14th century and marked the end of the period.
Historical events and politics

Great Britain and Ireland
In England, theNorman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conque ...
of 1066 resulted in a kingdom ruled by a Francophone
French became an international language in the Middle Ages, when the power of the Kingdom of France made it the second international language, alongside Latin. This status continued to grow into the 18th century, by which time French was the l ...
nobility. The Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Fran ...
invaded Ireland in 1169 and soon established themselves throughout most of the country, although their stronghold was the southeast. Likewise, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
and Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
were subdued into vassal states
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to t ...
at about the same time, though Scotland later asserted its independence and Wales remained largely under the rule of independent native princes until the death of Llywelyn ap Gruffydd in 1282. The Exchequer
In the civil service of the United Kingdom, His Majesty’s Exchequer, or just the Exchequer, is the accounting process of central government and the government's '' current account'' (i.e., money held from taxation and other government revenu ...
was founded in the 12th century under King Henry I, and the first parliaments
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. T ...
were convened. In 1215, after the loss of Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
, King John signed the Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the ...
into law, which limited the power of English monarchs
This list of kings and reigning queens of the Kingdom of England begins with Alfred the Great, who initially ruled Wessex, one of the seven Anglo-Saxon kingdoms which later made up modern England. Alfred styled himself King of the Anglo-Sax ...
.
Iberia
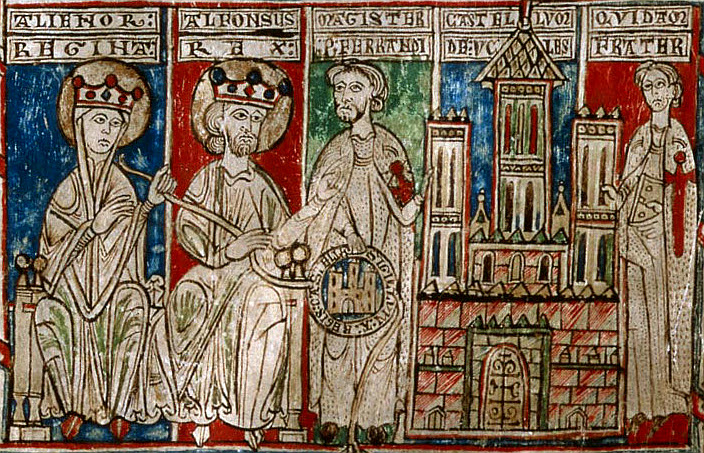
 A key geo-strategic development in the
A key geo-strategic development in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
was the Christian conquest of Toledo in 1085. Dominated by war, the societal structures and relations in the northern Christian kingdoms were subordinated to the demands of omnipresent military conflict. The territorial expansion of the northern Christian kingdoms to the south brought the creation of border societies, where military demands on knights and foot soldiers and the promotion of settlement
Settlement may refer to:
*Human settlement, a community where people live
*Settlement (structural), the distortion or disruption of parts of a building
* Closing (real estate), the final step in executing a real estate transaction
*Settlement (fin ...
were privileged to possible seigneurial income; military orders also played an important role in the borderlands in the southern meseta. Agricultural models in areas with Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
were generally based on biennial crop rotation
Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the same area across a sequence of growing seasons. It reduces reliance on one set of nutrients, pest and weed pressure, and the probability of developing resistant ...
. Despite population growth, agricultural output remained relatively rigid throughout the period; between the 10th and 13th centuries, migration southwards to exposed areas was incentivized by the possibility of enjoying privileges and acquiring properties. Conversely, the intensive agriculture
Intensive agriculture, also known as intensive farming (as opposed to extensive farming), conventional, or industrial agriculture, is a type of agriculture, both of crop plants and of animals, with higher levels of input and output per unit of ag ...
-prevalent model in Muslim-ruled lands did not require territorial expansion. While Muslim lands enjoyed from a certain demographic and financial edge, Almoravid
The Almoravid dynasty ( ar, المرابطون, translit=Al-Murābiṭūn, lit=those from the ribats) was an imperial Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire in the 11th century that ...
s and Almohad
The Almohad Caliphate (; ar, خِلَافَةُ ٱلْمُوَحِّدِينَ or or from ar, ٱلْمُوَحِّدُونَ, translit=al-Muwaḥḥidūn, lit=those who profess the Tawhid, unity of God) was a North African Berbers, Berber M ...
s from northern Africa featured volatile state structures. Barring (unsuccessful) attempts to take Toledo, Almoravids and Almohads did not stand out for carrying out an expansionist policy.
Italy
In Italy, with the Norman conquest, the first great and powerful state was formed, theKingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
with hereditary monarchy. Subsequently joined to the Holy Roman Empire, it had its moment of maximum splendor with the emperor Frederick II.
In the rest of Italy, independent city states grew affluent on Eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to communi ...
maritime trade. These were in particular the thalassocracies
A thalassocracy or thalattocracy sometimes also maritime empire, is a state with primarily maritime realms, an empire at sea, or a seaborne empire. Traditional thalassocracies seldom dominate interiors, even in their home territories. Examples ...
of Pisa
Pisa ( , or ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, central Italy, straddling the Arno just before it empties into the Ligurian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa. Although Pisa is known worldwide for its leaning tower, the cit ...
, Amalfi
Amalfi (, , ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Salerno, in the region of Campania, Italy, on the Gulf of Salerno. It lies at the mouth of a deep ravine, at the foot of Monte Cerreto (1,315 metres, 4,314 feet), surrounded by dramatic c ...
, Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the List of cities in Italy, sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian ce ...
and Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
, which played a key role in European trade from then on, making these cities become major financial centers.
Scandinavia
From the mid-tenth to the mid-11th centuries, the Scandinavian kingdoms were unified and Christianized, resulting in an end ofViking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
raids, and greater involvement in European politics. King Cnut
Cnut (; ang, Cnut cyning; non, Knútr inn ríki ; or , no, Knut den mektige, sv, Knut den Store. died 12 November 1035), also known as Cnut the Great and Canute, was King of England from 1016, King of Denmark from 1018, and King of Norwa ...
of Denmark ruled over both England and Norway. After Cnut's death in 1035, England and Norway were lost, and with the defeat of Valdemar II
Valdemar (28 June 1170 – 28 March 1241), later remembered as Valdemar the Victorious (), was the King of Denmark (being Valdemar II) from 1202 until his death in 1241.
Background
He was the second son of King Valdemar I of Denmark and Soph ...
in 1227, Danish predominance in the region came to an end. Meanwhile, Norway extended its Atlantic possessions, ranging from Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is t ...
to the Isle of Man
)
, anthem = "O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europe ...
, while Sweden, under Birger Jarl
Birger Jarl, also known as ''Birger Magnusson'' (21 October 1266), was a Swedish statesman, ''jarl'', and a member of the House of Bjelbo, who played a pivotal role in the consolidation of Sweden. Birger also led the Second Swedish Crusade, w ...
, built up a power-base in the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
. However, the Norwegian influence started to decline already in the same period, marked by the Treaty of Perth
The Treaty of Perth, signed 2 July 1266, ended military conflict between Magnus VI of Norway and Alexander III of Scotland over possession of the Hebrides and the Isle of Man. The text of the treaty.
The Hebrides and the Isle of Man had become ...
of 1266. Also, civil wars raged in Norway between 1130 and 1240.
France and Germany
 By the time of the High Middle Ages, the
By the time of the High Middle Ages, the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lom ...
had been divided and replaced by separate successor kingdoms called France and Germany, although not with their modern boundaries. Germany was under the banner of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
, which reached its high-water mark of unity and political power.
Georgia
During the successful reign of KingDavid IV of Georgia
David IV, also known as David the Builder ( ka, დავით აღმაშენებელი, ') (1073–1125), of the Bagrationi dynasty, was the 5th king of United Georgia from 1089 until his death in 1125.
Popularly considered to be ...
(1089–1125), Kingdom of Georgia
The Kingdom of Georgia ( ka, საქართველოს სამეფო, tr), also known as the Georgian Empire, was a medieval Eurasian monarchy that was founded in circa 1008 AD. It reached its Golden Age of political and economic ...
grew in strength and expelled the Seljuk Empire
The Great Seljuk Empire, or the Seljuk Empire was a high medieval, culturally Turco-Persian tradition, Turko-Persian, Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim empire, founded and ruled by the Qiniq (tribe), Qïnïq branch of Oghuz Turks. It spanned a total are ...
from its lands. David's decisive victory in the Battle of Didgori
The Battle of Didgori was fought between the armies of the Kingdom of Georgia and the Seljuk Empire at the narrow place of Didgori, 40 km west of Tbilisi, on August 12, 1121. The large Muslim army, under the command of Ilghazi, was unable to ...
(1121) against the Seljuk Turks, as a result of which Georgia recaptured its lost capital Tbilisi
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), is the Capital city, capital and the List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), largest city of Georgia (country), Georgia, lying on the ...
, marked the beginning of the Georgian Golden Age. David's granddaughter Tamar of Georgia, Queen Tamar continued the upward rise, successfully neutralizing internal opposition and embarking on an energetic foreign policy aided by further decline of the hostile Seljuk Empire, Seljuk Turks. Relying on a powerful military élite, Tamar was able to build on the successes of her predecessors to consolidate an empire which dominated vast lands spanning from present-day southern Russian Federation, Russia on the Black Sea to the Caspian Sea. Georgia remained a leading regional power until its collapse under the Mongol Empire, Mongol attacks within two decades after Tamar's death.
Hungary
 In the High Middle Ages, the
In the High Middle Ages, the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
(founded in 1000), became one of the most powerful medieval states in central Europe and Western Europe. King Saint Stephen I of Hungary introduced Christianity to the region; he was remembered by the contemporary chroniclers as a very religious monarch, with wide knowledge in Latin grammar, strict with his own people but kind to the foreigners. He eradicated the remnants of the tribal organisation in the Kingdom and forced the people to sedentarize and adopt the Christianity, Christian religion, ethics, way of life and founded the Hungarian medieval state, organising it politically in counties using the Germanic system as a model.
The following monarchs usually kept a close relationship with Rome like Saint Ladislaus I of Hungary, and a tolerant attitude with the paganism, pagans that escaped to the Kingdom searching for sanctuary (for example Cumans in the 13th century), which eventually created certain discomfort for some Popes. With entering in Personal union with the Kingdom of Croatia (medieval)#Controversies, Kingdom of Croatia and the establishment of other vassal states, Hungary became a small empire that extended its control over the Balkans and the Carpathian region. The Hungarians, Hungarian royal house was the one that gave the most saints to the Catholic Church during medieval times.
Lithuania
During the High Middle Ages Lithuania emerged as a Duchy of Lithuania in the early 13th century, then briefly becoming the Kingdom of Lithuania from 1251 to 1263. After the assassination of its first Christian king Mindaugas Lithuania was known as Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Unconquered during the Lithuanian Crusade, Lithuania itself rapidly expanded to the East due to conquests and became one of the largest states in Europe.Poland
Southeastern Europe
 The High Middle Ages saw the height and decline of the Slavic state of Kievan Rus' and emergence of Cumania. Later, the Mongol invasions, Mongol invasion in the 13th century had great impact on the east of Europe, as many countries of the region were invaded, pillaged, conquered and/or vassalized.
During the first half of this period (1185) the
The High Middle Ages saw the height and decline of the Slavic state of Kievan Rus' and emergence of Cumania. Later, the Mongol invasions, Mongol invasion in the 13th century had great impact on the east of Europe, as many countries of the region were invaded, pillaged, conquered and/or vassalized.
During the first half of this period (1185) the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
dominated the Balkans, and under the Byzantine Empire under the Komnenos dynasty, Komnenian emperors there was a revival of prosperity and urbanization; however, their domination of Southeastern Europe came to an end with a successful Uprising of Asen and Peter, Vlach-Bulgarian rebellion in 1185, and henceforth the region was divided between the Byzantines in Greece, some parts of Macedonia (region), Macedonia, and Thrace, the Bulgarians in Moesia and most of Thrace and Macedonia, and the Serbian Grand Principality, Serbs to the northwest. Eastern and Western churches had formally split in the 11th century, and despite occasional periods of co-operation during the 12th century, in 1204 the Fourth Crusade treacherously captured Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
. This severely damaged the Byzantines, and their power was ultimately weakened by the Seljuq Empire, Seljuks and the rising Ottoman Empire in the 14–15th century. The power of the Latin Empire, however, was short-lived after the Crusader army was routed by list of Bulgarian monarchs, Bulgarian Emperor Kaloyan of Bulgaria, Kaloyan in the Battle of Adrianople (1205).
Climate and agriculture
The Medieval Warm Period, the period from the 10th century to about the 14th century in Europe, was a relatively warm and gentle interval ended by the generally colder Little Ice Age. Farmers grew wheat well north into Scandinavia, and wine grapes in northern England, although the maximum expansion of vineyards appears to occur within the Little Ice Age period. During this time, a high demand for wine and steady volume of Alcoholic drink, alcohol consumption inspired a viticulture revolution of progress. This protection from famine allowed Europe's population to increase, despite the famine in 1315 that killed 1.5 million people. This increased population contributed to the founding of new towns and an increase in industrial and economic activity during the period. They also established trade and a comprehensive production of alcohol. Food production also increased during this time as new ways of farming were introduced, including the use of a heavier plow, horses instead of oxen, and a three-field system that allowed the cultivation of a greater variety of crops than the earlier two-field system—notably legumes, the growth of which prevented the depletion of important nitrogen from the soil.The rise of chivalry
During the High Middle Ages, the idea of a Christian warrior started to change as Christianity grew more prominent in Medieval Europe. The Chivalry, Codes of Chivalry promoted the ideal knight to be selfless, faithful, and fierce against those who threaten the weak. Household heavy cavalry (knights) became common in the 11th century across Europe, and Tournament (medieval), tournaments were invented. Tournaments allowed knights to establish their family name while being able to gather vast wealth and renown through victories. In the 12th century, the Cluny monks promoted ethical warfare and inspired the formation of order of chivalry, orders of chivalry, such as the Knights Templar, Templar Knights. Inherited titles of nobility were established during this period. In 13th-century Germany, knighthood became another inheritance, inheritable title, although one of the less prestigious, and the trend spread to other countries.Religion
Christian Church
The East–West Schism of 1054 formally separated the Christian church into two parts: Roman Catholicism in Western Europe and Eastern Orthodoxy in the east. It occurred when Pope Leo IX and Michael Cerularius, Patriarch Michael I excommunication, excommunicated each other, mainly over disputes as to the use of unleavened bread in the liturgy and fasting days, existence of papal authority over the four Eastern patriarchs, as well as disagreement over the filioque.Crusades
 The Catholic Crusades occurred between the 11th and 13th centuries. They were conducted under papal authority, initially with the intent of reestablishing Christian rule in ''The Holy Land'' by taking the area from the Muslim Fatimid Caliphate. The Fatimids had captured Palestine in AD 970, lost it to the
The Catholic Crusades occurred between the 11th and 13th centuries. They were conducted under papal authority, initially with the intent of reestablishing Christian rule in ''The Holy Land'' by taking the area from the Muslim Fatimid Caliphate. The Fatimids had captured Palestine in AD 970, lost it to the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
in 1073 and recaptured it in 1098, just before they lost it again in 1099 as a result of the First Crusade.
Military orders
In the context of the crusades, monastic military orders were founded that would become the template for the late medieval chivalric orders. The Knights Templar were a Christian military order founded after the First Crusade to help protect Christian pilgrimage, Christian pilgrims from hostile locals and highway bandits. The order was deeply involved in banking, and in 1307 Philip IV of France, Philip the Fair (Philippine le Bel) had the entire order arrested in France and dismantled on charges of heresy. The Knights Hospitaller were originally a Christianity, Christian organization founded in Jerusalem in 1080 to provide care for poor, sick, or injured pilgrimage, pilgrims to theHoly Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
. After Jerusalem was taken in the First Crusade, it became a religious order, religious/Military order (society), military order that was charged with the care and defence of the Crusader states. After the Holy Lands were eventually taken by Muslim forces, it moved its operations to Rhodes, and later Malta.
The Teutonic Knights were a German religious order formed in 1190, in the city of Acre,, Acre, to aid Christian pilgrims on their way to the Holy Lands and to operate hospitals for the sick and injured in Outremer. After Muslim forces captured the Holy Lands, the order moved to Transylvania in 1211 and later, after being expelled, invaded pagan Prussia with the intention of Christianizing the Baltic region. Yet, both before and after the Order's main pagan opponent, Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuania, Christianization of Lithuania, converted to Christianity, the Order had already attacked other Christian nations such as Novgorod Republic, Novgorod and Kingdom of Poland (1025–1385), Poland. The Teutonic Knights' power hold, which became considerable, was broken in 1410, at the Battle of Grunwald, where the Order suffered a devastating defeat against a joint Polish-Lithuanian army. After Grunwald, the Order declined in power until 1809 when it was officially dissolved. There were ten crusades in total.
Scholasticism
The new Christianity, Christian method of learning was influenced by Anselm of Canterbury (1033–1109) from the rediscovery of the works ofAristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
, at first indirectly through Medieval Jewish and Muslim Philosophy (Maimonides
Musa ibn Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (); la, Moses Maimonides and also referred to by the acronym Rambam ( he, רמב״ם), was a Sephardic Jewish philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah ...
, Avicenna, and Averroes) and then through Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
's own works brought back from Byzantine and Muslim libraries; and those whom he influenced, most notably Albertus Magnus, Bonaventure and Peter Abelard, Abélard. Many scholastics believed in empiricism and supporting Roman Catholic doctrines through secular study, reason, and logic. They opposed Christian mysticism, and the Platonist-Augustinian belief that the Dualism (philosophy of mind), mind is an immaterial substance. The most famous of the Scholasticism, scholastics was Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas, OP (; it, Tommaso d'Aquino, lit=Thomas of Aquino; 1225 – 7 March 1274) was an Italian Dominican friar and priest who was an influential philosopher, theologian and jurist in the tradition of scholasticism; he is known wi ...
(later declared a "Doctor of the Church"), who led the move away from the Platonism, Platonic and Augustine of Hippo, Augustinian and towards Aristotelianism. Aquinas developed a philosophy of mind by writing that the mind was at birth a ''tabula rasa'' ("blank slate") that was given the ability to think and recognize forms or ideas through a divine spark. Other notable scholastics included Averroes, Muhammad Averroes, Roscellinus, Roscelin, Abélard, Peter Lombard, and Francisco Suárez. One of the main questions during this time was the problem of universals. Prominent opponents of various aspects of the scholastic mainstream included Duns Scotus, William of Ockham, Peter Damian, Bernard of Clairvaux, and the Victorines.
Golden age of monasticism
* The late 11th century/early-mid 12th century was the height of the golden age of Christian monasticism (8th-12th centuries). ** Benedictine Order – black-robed monks ** Cistercian Order – white-robed monks *** Bernard of ClairvauxMendicant orders
* The 13th century saw the rise of the Mendicant orders such as the: ** Franciscans (Friars Minor, commonly known as the Grey Friars), founded 1209 ** Carmelites (Hermits of the Blessed Virgin Mary of Carmel, commonly known as the White Friars), founded 1206–1214 ** Dominican Order, Dominicans (Order of Preachers, commonly called the Black Friars), founded 1215 ** Augustinians (Hermits of St. Augustine, commonly called the Austin Friars), founded 1256Heretical movements
Christian Heresy, heresies existed in Europe before the 11th century but only in small numbers and of local character: in most cases, a rogue priest, or a village returning to pagan traditions. Beginning in the 11th century, however mass-movement heresies appeared. The roots of this can be partially sought in the rise of urban cities, free merchants, and a new money-based economy. The rural values of monasticism held little appeal to urban people who began to form sects more in tune with urban culture. The first large-scale heretical movements in Western Europe originated in the newly urbanized areas such as southern France and northern Italy and were probably influenced by the Bogomilism, Bogomils and other Dualistic cosmology, dualist movements. These heresies were on a scale the Catholic Church had never seen before; the response was one of elimination for some (such as the Cathars), and acceptance and integration of others (such as the veneration of Francis of Assisi, the son of an urban merchant who renounced money).Cathars
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
.
The Bogomilism, Bogomils were strong in the Balkans, and became the Bosnian Church, official religion supported by the Bosnian kings.
* Dualistic cosmology, Dualists believed that historical events were the result of struggle between a good force and an evil force and that evil ruled the world, though it could be controlled or defeated through asceticism and good works.
* Albigensian Crusade, Simon de Montfort, 5th Earl of Leicester, Simon de Montfort, Montségur, Château de Quéribus
Waldensians
Peter Waldo of Lyon was a wealthy merchant who gave up his riches around 1175 after a religious experience and became a preacher. He founded the Waldensians which became a Christian sect believing that all religious practices should have scriptural basis. Waldo was denied the right to preach his sermons by the Third Lateran Council in 1179, which he did not obey and continued to speak freely until he was excommunicated in 1184. Waldo was critical of the Christian clergy saying they did not live according to the word. He rejected the practice of selling indulgences, as well as the common saint cult practices of the day. Waldensians are considered a forerunner to the Protestant Reformation, and they melted into Protestantism with the outbreak of the Reformation and became a part of the wider Reformed tradition after the views of John Calvin and his theological successors in Geneva proved very similar to their own theological thought. Waldensian churches still exist, located on several continents.Trade and commerce
In Northern Europe, the Hanseatic League, a federation of free cities to advance trade by sea, was founded in the 12th century, with the foundation of the city of Lübeck, which would later dominate the League, in 1158–1159. Many northern cities of theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
became Hanseatic cities, including Amsterdam, Cologne, Bremen, Hanover and Berlin. Hanseatic cities outside the Holy Roman Empire were, for instance, Bruges and the Polish city of Gdańsk (Danzig), as well as Königsberg, capital of the monastic state of the Teutonic Knights. In Bergen, Norway and Veliky Novgorod, Russia the league had factories and middlemen. In this period the Germans started colonising Europe beyond the Empire, into Prussia and Silesia.
In the late 13th century, a Venice, Venetian explorer named Marco Polo became one of the first Europeans to travel the Silk Road to China. Westerners became more aware of the Far East when Polo documented his travels in ''The Travels of Marco Polo, Il Milione''. He was followed by numerous Christian missionaries to the East, such as William of Rubruck, Giovanni da Pian del Carpine, André de Longjumeau, Odoric of Pordenone, Giovanni de' Marignolli, John of Montecorvino, Giovanni di Monte Corvino, and other travellers such as Niccolò de' Conti.
Science
 Philosophical and scientific teaching of the
Philosophical and scientific teaching of the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
was based upon few copies and commentaries of ancient Greek texts that remained in Western Europe after the collapse of the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
. Most of them were studied only in Latin as knowledge of Greek was very limited.
This scenario changed during the Renaissance of the 12th century. The intellectual revitalization of Europe started with the birth of Medieval university, medieval universities. The increased contact with the Islamic world in Al-Andalus, Spain and History of Islam in southern Italy, Sicily during the Reconquista, and the Byzantine world and Muslim Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
during the Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
, allowed Europeans access to scientific Arabic and Greek texts, including the works of Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
, Ibn al-Haytham, Alhazen, and Averroes. The European universities aided materially in the Latin translations of the 12th century, translation and propagation of these texts and started a new infrastructure which was needed for science, scientific communities.
 At the beginning of the 13th century there were reasonably accurate Latin translations of the main works of almost all the intellectually crucial ancient authors, allowing a sound transfer of scientific ideas via both the universities and the monasteries. By then, the natural science contained in these texts began to be extended by notable scholastics such as Robert Grosseteste, Roger Bacon, Albertus Magnus and Duns Scotus. Precursors of the modern scientific method can be seen already in Grosseteste's emphasis on mathematics as a way to understand nature, and in the empirical approach admired by Bacon, particularly in his ''Opus Majus''.
At the beginning of the 13th century there were reasonably accurate Latin translations of the main works of almost all the intellectually crucial ancient authors, allowing a sound transfer of scientific ideas via both the universities and the monasteries. By then, the natural science contained in these texts began to be extended by notable scholastics such as Robert Grosseteste, Roger Bacon, Albertus Magnus and Duns Scotus. Precursors of the modern scientific method can be seen already in Grosseteste's emphasis on mathematics as a way to understand nature, and in the empirical approach admired by Bacon, particularly in his ''Opus Majus''.
Technology
During the 12th and 13th century in Europe there was a radical change in the rate of new inventions, innovations in the ways of managing traditional means of production, and economic growth. In less than a century there were more inventions developed and applied usefully than in the previous thousand years of human history all over the globe. The period saw major technology, technological advances, including the adoption or invention of windmills, watermills, printing (though not yet with movable type), gunpowder, the astrolabe, glasses, scissors of the modern shape, a better clock, and greatly improved ships. The latter two advances made possible the dawn of the Age of Discovery. These inventions were influenced by foreign culture and society. Alfred W. Crosby described some of this technological revolution in ''The Measure of Reality: Quantification in Western Europe, 1250-1600'' and other major historians of technology have also noted it. * The earliest written record of a windmill is from Yorkshire, England, dated 1185.
* Paper manufacture began in Italy around 1270.
* The spinning wheel was brought to Europe (probably from India) in the 13th century.
* The magnetic compass aided navigation, first reaching Europe some time in the late 12th century.
* Eye glasses were invented in Italy in the late 1280s.
* The astrolabe returned to Europe via Islamic Spain.
* Fibonacci introduces Hindu-Arabic numerals to Europe with his book ''Liber Abaci'' in 1202.
* The West's oldest known depiction of a stern-mounted rudder can be found on church carvings dating to around 1180.
* The earliest written record of a windmill is from Yorkshire, England, dated 1185.
* Paper manufacture began in Italy around 1270.
* The spinning wheel was brought to Europe (probably from India) in the 13th century.
* The magnetic compass aided navigation, first reaching Europe some time in the late 12th century.
* Eye glasses were invented in Italy in the late 1280s.
* The astrolabe returned to Europe via Islamic Spain.
* Fibonacci introduces Hindu-Arabic numerals to Europe with his book ''Liber Abaci'' in 1202.
* The West's oldest known depiction of a stern-mounted rudder can be found on church carvings dating to around 1180.
Arts
Visual arts
 Art in the High Middle Ages includes these important movements:
* Anglo-Saxon art was influential on the British Isles until the Norman Invasion of 1066
* Romanesque art continued traditions from the Classical world (not to be confused with Romanesque architecture)
* Gothic art developed a distinct Germanic flavor (not to be confused with Gothic architecture).
* Indo-Islamic architecture begins when Muhammad of Ghor made Delhi a Muslim capital
*
Art in the High Middle Ages includes these important movements:
* Anglo-Saxon art was influential on the British Isles until the Norman Invasion of 1066
* Romanesque art continued traditions from the Classical world (not to be confused with Romanesque architecture)
* Gothic art developed a distinct Germanic flavor (not to be confused with Gothic architecture).
* Indo-Islamic architecture begins when Muhammad of Ghor made Delhi a Muslim capital
* Byzantine art
Byzantine art comprises the body of Christian Greek artistic products of the Eastern Roman Empire, as well as the nations and states that inherited culturally from the empire. Though the empire itself emerged from the decline of Rome and lasted ...
continued earlier Byzantine traditions, influencing much of Eastern Europe.
* Illuminated manuscripts gained prominence both in the Catholic and Orthodox churches
Architecture

 Gothic architecture superseded the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque style by combining flying buttresses, gothic (or pointed) arches and ribbed vaults. It was influenced by the spiritual background of the time, being religious in essence: thin horizontal lines and grates made the building strive towards the sky. Architecture was made to appear light and weightless, as opposed to the dark and bulky forms of the previous Romanesque architecture, Romanesque style. Saint Augustine of Hippo taught that light was an expression of God. Architectural techniques were adapted and developed to build churches that reflected this teaching. Colorful glass windows enhanced the spirit of lightness. As color was much rarer at medieval times than today, it can be assumed that these virtuoso works of art had an awe-inspiring impact on the common man from the street. High-rising intricate ribbed, and later fan vaultings demonstrated movement toward heaven. Veneration of God was also expressed by the relatively large size of these buildings. A gothic cathedral therefore not only invited the visitors to elevate themselves spiritually, it was also meant to demonstrate the greatness of God. The floor plan of a gothic cathedral corresponded to the rules of scholasticism: According to Erwin Panofsky's ''Gothic Architecture and Scholasticism'', the plan was divided into sections and uniform subsections. These characteristics are exhibited by the most famous sacral building of the time: Notre Dame de Paris.
Gothic architecture superseded the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque style by combining flying buttresses, gothic (or pointed) arches and ribbed vaults. It was influenced by the spiritual background of the time, being religious in essence: thin horizontal lines and grates made the building strive towards the sky. Architecture was made to appear light and weightless, as opposed to the dark and bulky forms of the previous Romanesque architecture, Romanesque style. Saint Augustine of Hippo taught that light was an expression of God. Architectural techniques were adapted and developed to build churches that reflected this teaching. Colorful glass windows enhanced the spirit of lightness. As color was much rarer at medieval times than today, it can be assumed that these virtuoso works of art had an awe-inspiring impact on the common man from the street. High-rising intricate ribbed, and later fan vaultings demonstrated movement toward heaven. Veneration of God was also expressed by the relatively large size of these buildings. A gothic cathedral therefore not only invited the visitors to elevate themselves spiritually, it was also meant to demonstrate the greatness of God. The floor plan of a gothic cathedral corresponded to the rules of scholasticism: According to Erwin Panofsky's ''Gothic Architecture and Scholasticism'', the plan was divided into sections and uniform subsections. These characteristics are exhibited by the most famous sacral building of the time: Notre Dame de Paris.
Literature
 A variety of cultures influenced the literature of the High Middle Ages, one of the strongest among them being Christianity. The connection to Christianity was greatest in Latin literature, which influenced the vernacular languages in the Literature cycle, literary cycle of the Matter of Rome. Other literary cycles, or interrelated groups of stories, included the Matter of France (stories about Charlemagne and his court), the Acritic songs dealing with the chivalry of Byzantine Empire, Byzantium's frontiersmen, and perhaps the best known cycle, the Matter of Britain, which featured tales about King Arthur, his court, and related stories from Brittany, Cornwall,
A variety of cultures influenced the literature of the High Middle Ages, one of the strongest among them being Christianity. The connection to Christianity was greatest in Latin literature, which influenced the vernacular languages in the Literature cycle, literary cycle of the Matter of Rome. Other literary cycles, or interrelated groups of stories, included the Matter of France (stories about Charlemagne and his court), the Acritic songs dealing with the chivalry of Byzantine Empire, Byzantium's frontiersmen, and perhaps the best known cycle, the Matter of Britain, which featured tales about King Arthur, his court, and related stories from Brittany, Cornwall, Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
and Ireland. An anonymous German poet tried to bring the Germanic myths from the Migration Period to the level of the French and British epics, producing the Nibelungenlied. There was also a quantity of poetry and historical writings which were written during this period, such as ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' by Geoffrey of Monmouth.
Despite political decline during the late 12th and much of the 13th centuries, the Byzantine scholarly tradition remained particularly fruitful over the time period. One of the most prominent philosophers of the 11th century, Michael Psellos, reinvigorated Neoplatonism on Christian foundations and bolstered the study of Ancient Greek philosophy, ancient philosophical texts, along with contributing to history, grammar, and rhetorics. His pupil and successor at the head of Philosophy at the University of Constantinople John Italus, Ioannes Italos continued the Platonic line in Byzantine thought and was criticized by the Church for holding opinions it considered heretical, such as the doctrine of Reincarnation, transmigration. Two Orthodox theologians important in the dialogue between the eastern and western churches were Nikephoros Blemmydes and Maximus Planudes. Byzantine historical tradition also flourished with the works of the brothers Niketas Choniates, Niketas and Michael Choniates in the beginning of the 13th century and George Akropolites a generation later. Dating from 12th century Byzantine Empire is also Timarion, an Orthodox Christian anticipation of Divine Comedy. Around the same time the so-called Byzantine novel rose in popularity with its synthesis of ancient pagan and contemporaneous Christian themes.
At the same time southern France gave birth to Occitan literature, which is best known for troubadours who sang of courtly love. It included elements from Latin literature and Arab-influenced Spain and North Africa. Later its influence spread to several cultures in Western Europe, notably in Portugal and the Minnesänger in Germany. Provençal literature also reached Sicily and Northern Italy laying the foundation of the Dolce Stil Nuovo, "sweet new style" of Dante Alighieri, Dante and later Petrarch, Petrarca. Indeed, the most important poem of the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the Periodization, period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Eur ...
, the allegorical ''Divine Comedy,'' is to a large degree a product of both the Summa Theologica, theology of Thomas Aquinas and the largely secular Occitan literature.
Music

 The surviving music of the High Middle Ages is primarily religious in nature, since music notation developed in religious institutions, and the application of notation to secular music was a later development. Early in the period, Gregorian chant was the dominant form of church music; other forms, beginning with organum, and later including Clausula (music), clausulae, conductus, and the motet, developed using the chant as source material.
During the 11th century, Guido of Arezzo was one of the first to develop musical notation, which made it easier for singers to remember Gregorian chants.
It was during the 12th and 13th centuries that Gregorian plainchant gave birth to polyphony, which appeared in the works of French Notre Dame School (Léonin and Pérotin). Later it evolved into the ''ars nova'' (Philippe de Vitry, Guillaume de Machaut) and the musical genres of late Middle Ages. An important composer during the 12th century was the nun Hildegard of Bingen.
The most significant secular movement was that of the troubadours, who arose in Occitania (Southern France) in the late 11th century. The troubadours were often itinerant entertainer, itinerant, came from all classes of society, and wrote songs on a variety of topics, though with a particular focus on courtly love. Their style went on to influence the trouvères of northern France, the minnesingers of Germany, and the composers of secular music of the Trecento in northern Italy.
The surviving music of the High Middle Ages is primarily religious in nature, since music notation developed in religious institutions, and the application of notation to secular music was a later development. Early in the period, Gregorian chant was the dominant form of church music; other forms, beginning with organum, and later including Clausula (music), clausulae, conductus, and the motet, developed using the chant as source material.
During the 11th century, Guido of Arezzo was one of the first to develop musical notation, which made it easier for singers to remember Gregorian chants.
It was during the 12th and 13th centuries that Gregorian plainchant gave birth to polyphony, which appeared in the works of French Notre Dame School (Léonin and Pérotin). Later it evolved into the ''ars nova'' (Philippe de Vitry, Guillaume de Machaut) and the musical genres of late Middle Ages. An important composer during the 12th century was the nun Hildegard of Bingen.
The most significant secular movement was that of the troubadours, who arose in Occitania (Southern France) in the late 11th century. The troubadours were often itinerant entertainer, itinerant, came from all classes of society, and wrote songs on a variety of topics, though with a particular focus on courtly love. Their style went on to influence the trouvères of northern France, the minnesingers of Germany, and the composers of secular music of the Trecento in northern Italy.
Theatre
Economic and political changes in the High Middle Ages led to the formation of guilds and the growth of towns, and this would lead to significant changes for theatre starting in this time and continuing into theLate Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the Periodization, period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Eur ...
. Trade guilds began to perform plays, usually religiously based, and often dealing with a biblical story that referenced their profession. For instance, a baker's guild would perform a reenactment of the Last Supper. In the British Isles, plays were produced in some 127 different towns during the Middle Ages. These vernacular Mystery plays were written in cycles of a large number of plays: York Mystery Plays, York (48 plays), Chester Mystery Plays, Chester (24), Wakefield Mystery Plays, Wakefield (32) and N-Town Plays, Unknown (42). A larger number of plays survive from France and Germany in this period and some type of religious dramas were performed in nearly every European country in the Late Middle Ages. Many of these plays contained comedy, devils, villains and clowns.
There were also a number of secular performances staged in the Middle Ages, the earliest of which is ''The Play of the Greenwood'' by Adam de la Halle in 1276. It contains satirical scenes and Folk culture, folk material such as faeries and other supernatural occurrences. Farces also rose dramatically in popularity after the 13th century. The majority of these plays come from France and Germany and are similar in tone and form, emphasizing sex and bodily excretions.Brockett and Hildy (2003, 96)
Timeline
* 1003 – death of Pope Sylvester II * 1018 – the First Bulgarian Empire is conquered by theByzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
under Basil II.
* 1027 – the Salian Conrad II, Holy Roman Emperor, Conrad II succeeds the last Ottonian Henry II the Saint
* 1054 – East–West Schism
* 1066 – Battle of Hastings
* 1073–1085 – Pope Gregory VII
* 1071 – Battle of Manzikert
* 1077 – Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Henry IV's Walk to Canossa
* 1086 – Domesday Book
* 1086 – Battle of az-Zallaqah
* 1088 – University of Bologna founded
* 1091 – Battle of Levounion
* 1096 – University of Oxford founded
* 1096–1099 – First Crusade
* 1123 – First Lateran Council
* 1139 – Second Lateran Council
* 1145–1149 – Second Crusade
* 1147 – Wendish Crusade
* – University of Paris founded
* 1155–1190 – Frederick I Barbarossa
* 1159 – foundation of the Hanseatic League
* 1169 – Norman invasion of Ireland
* 1185 – reestablishment of the Second Bulgarian Empire, Bulgarian Empire
* 1189–1192 – Third Crusade
* 1200–1204 – Fourth Crusade
* 1205 – Battle of Adrianople (1205), Battle of Adrianople
* 1209 – University of Cambridge founded
* 1209 – foundation of the Franciscan Order
* 1209–1229 – Albigensian Crusade
* 1212 – Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa
* 1215 – Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the ...
* 1216 – recognition of the Dominican Order
* 1215 – Fourth Lateran Council
* 1217–1221 – Fifth Crusade
* 1218 – University of Salamanca founded
* 1220–1250 – Frederick II
* 1222 – University of Padua founded
* 1223 – approval of the Franciscan Rule of Life
* 1228–1229 – Sixth Crusade
* 1230 – Prussian Crusade
* 1230 – Battle of Klokotnitsa
* 1237–1242 – Mongol invasion of Europe
* 1241 – Battle of Legnica and Battle of Mohi
* 1242 – Battle of the Ice
* 1248–1254 – Seventh Crusade
* 1257 – foundation of the Collège de Sorbonne
* 1261 – the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
reconquers Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
.
* 1274 – death of Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas, OP (; it, Tommaso d'Aquino, lit=Thomas of Aquino; 1225 – 7 March 1274) was an Italian Dominican friar and priest who was an influential philosopher, theologian and jurist in the tradition of scholasticism; he is known wi ...
; ''Summa Theologica'' published
* 1277-1280 – Uprising of Ivaylo – Medieval Europe's only successful peasant uprising
* 1280 – death of Albertus Magnus
* 1291 – Akko, Acre, the last European outpost in the Near East, is captured by the Mamluks under Al-Ashraf Khalil, Khalil.
* 1299 – Peak of Mongol supremacy in Southeastern Europe with Chaka of Bulgaria
* 1299 – Osman I founds the Ottoman Empire.
See also
*Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
* Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the Periodization, period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Eur ...
* Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
Notes
Further reading
* Fuhrmann, Horst. ''Germany in the High Middle Ages: c. 1050-1200'' (Cambridge UP, 1986). * Jordan, William C. ''Europe in the High Middle Ages'' (2nd ed. Penguin, 2004). * Mundy, John H. ''Europe in the High Middle Ages, 1150–1309'' (2014)online
* Power, Daniel, ed. ''The Central Middle Ages: Europe 950–1320'' (Oxford UP, 2006).
External links
in the ''Columbia Encyclopedia'' at Infoplease
Provençal literature
in the ''Columbia Encyclopedia'' at Infoplease {{Authority control High Middle Ages, Middle Ages, .02 11th century in Europe, . 12th century in Europe, . 13th century in Europe, . 11th-century establishments in Europe, . 13th-century disestablishments in Europe, . pt:Idade Média#Alta Idade Média