Hemoglobin variants on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
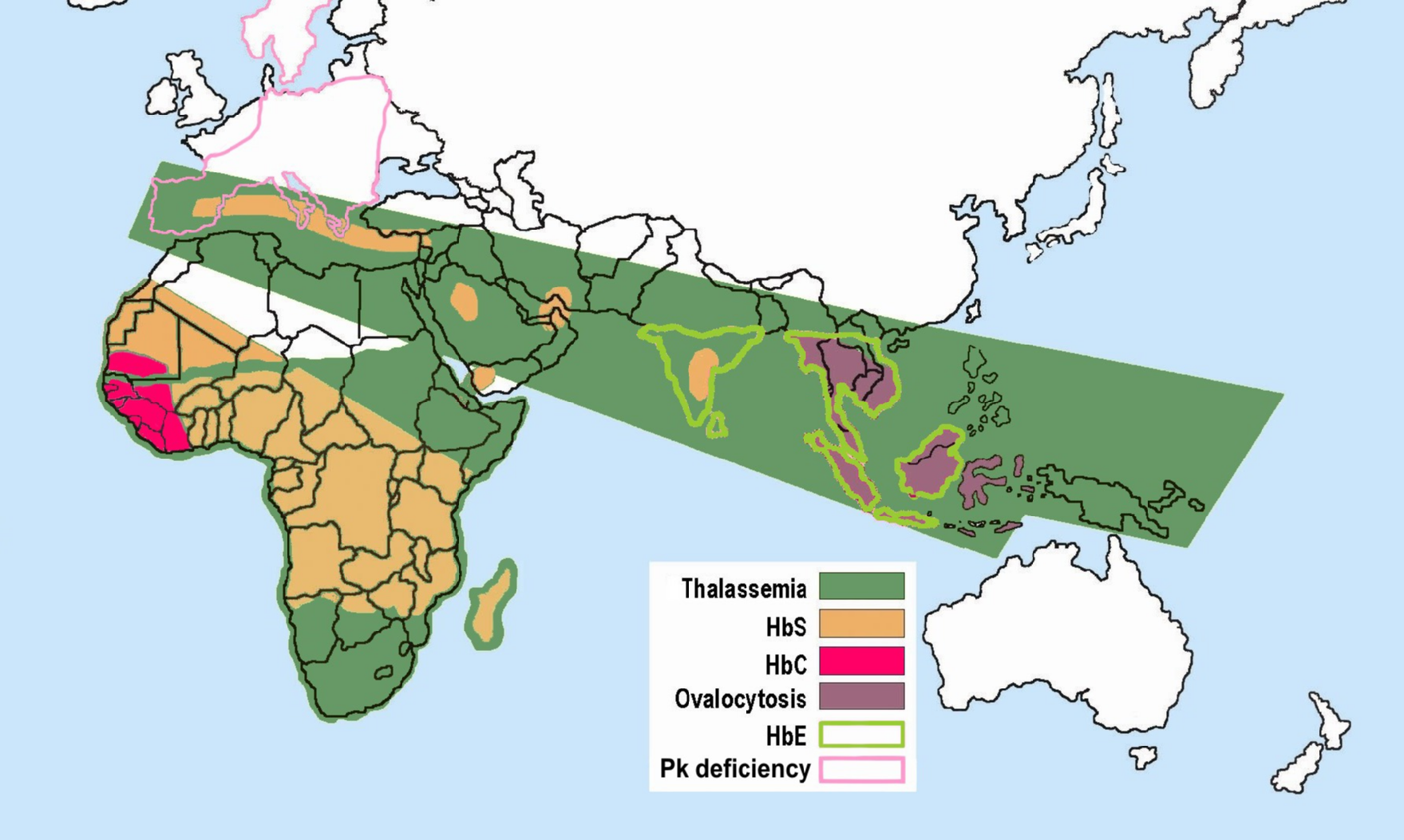
A syllabus of hemoglobin variants
{{Hemeproteins Red blood cell disorders Genetic disorders with no OMIM Hemoglobins Respiratory physiology

Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
is a protein that transports oxygen in the blood. Genetic differences lead to structural variants in the hemoglobin protein structure. Some variants can cause disease while others have little to no effect.
The normal hemoglobin types are Hemoglobin A (HbA), which makes up 95–98% of total hemoglobin in adults, Hemoglobin A2 (HbA2), which constitutes 2–3% of total hemoglobin in adults, and Hemoglobin F (HbF), which is the predominant hemoglobin in the fetus during pregnancy, and may persist in small amounts in adults.
Hemoglobin variants occur when there are mutations in specific genes that code for the protein chains, known as globins, which make up the hemoglobin molecule. This leads to amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
substitutions in the hemoglobin molecule that could affect the structure, properties, and/or the stability of the hemoglobin molecule. There are over 1,000 naturally occurring structural variants of hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
in humans.
Effects of variants
The physiological effects of these variants can range from minor to severe. Mutations can caused impaired production of hemoglobin (thalassemia
Thalassemias are a group of Genetic disorder, inherited blood disorders that manifest as the production of reduced hemoglobin. Symptoms depend on the type of thalassemia and can vary from none to severe, including death. Often there is mild to ...
) or produce structurally altered hemoglobins. Some hemoglobin variants, such as HbS which causes sickle-cell anemia, are responsible for severe diseases and are considered hemoglobinopathies. Other variants cause no detectable pathology
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatme ...
, and are thus considered non-pathological variants.
Discovery of variants
Hemoglobin variants can be discovered through examination, routine laboratory testing, or evaluation of patients with severe anemia. In some countries, all newborns are tested for hemoglobinopathies, thalassemias, and HbS. Isoelectric focusing orhigh-performance liquid chromatography
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), formerly referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography, is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify specific components in mixtures. The mixtures can origin ...
are used to identify structural abnormalities in hemoglobin.
Examples of variants
There are in excess of 1,000 known hemoglobin variants. A research database of hemoglobin variants is maintained byPenn State University
The Pennsylvania State University (Penn State or PSU) is a Public university, public Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related Land-grant university, land-grant research university with campuses and facilities throughout Pennsyl ...
. A few of these variants are listed below.
Normal hemoglobins
;Embryonic * HbE Gower 1 (ζ2ε2) * HbE Gower 2 (α2ε2) * HbE Portland I (ζ2γ2) * HbE Portland II (ζ2β2) ;Fetal * HbF/Fetal (α2γ2) * HbA (α2β2) ;Adult * HbA (α2β2) * HbA2 (α2δ2) * HbF/Fetal (α2γ2)Pathologic/abnormal hemoglobins
Relatively common
Source: * HbS (α2βS2) * HbC (α2βC2) * HbE (α2βE2)Less frequent
* HbH (β4) * Hb Barts (γ4) *HbO
Home Box Office (HBO) is an American pay television service, which is the flagship property of namesake parent-subsidiary Home Box Office, Inc., itself a unit owned by Warner Bros. Discovery. The overall Home Box Office business unit is based a ...
(α2βO2)
* Hb Bassett
* Hb Kansas
* Hb D-Punjab
* Hb O-Arab
* Hb G-Philadelphia
* Hb Hasharon
* Hb Kirklareli
* Hb Lepore
* Hb M
* Hb Hope
* Hb Pisa
* Hb J
* Hb N-Baltimore
* Hemoglobin Chesapeake
* Hemoglobin Louisville
* Hemoglobin Vanvitelli
References
External links
A syllabus of hemoglobin variants
{{Hemeproteins Red blood cell disorders Genetic disorders with no OMIM Hemoglobins Respiratory physiology