Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky halogenation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky halogenation reaction is a chemical transformation that involves the 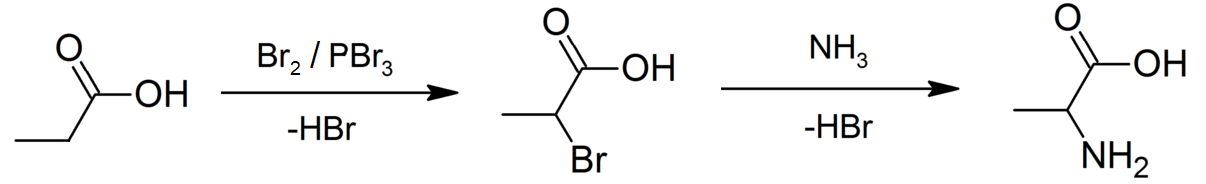
halogenation
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction that entails the introduction of one or more halogens into a compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, ...
of a carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic ...
at the α carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
. For this reaction to occur the α carbon must bear at least one proton. The reaction is named after the German chemists Carl Magnus von Hell
Carl Magnus von Hell (8 September 1849 – 11 December 1926) was the German chemist who discovered, together with Jacob Volhard and the Russian chemist Nikolay Zelinsky, the Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky halogenation reaction.
Life
He studied chemist ...
(1849–1926) and Jacob Volhard
Jacob Volhard (4 June 1834 – 14 January 1910) was the German chemist who discovered, together with his student Hugo Erdmann, the Volhard–Erdmann cyclization reaction. He was also responsible for the improvement of the Hell–Volhard–Ze ...
(1834–1910) and the Russian chemist Nikolay Zelinsky (1861–1953).
:
An example of the Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky reaction can be seen in the preparation of alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side c ...
from propionic acid
Propionic acid (, from the Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula CH3CH2CO2H. It is a liq ...
. In the first step, a combination of bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table (halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simila ...
and phosphorus tribromide
Phosphorus tribromide is a colourless liquid with the formula P Br3. The liquid fumes in moist air due to hydrolysis and has a penetrating odour. It is used in the laboratory for the conversion of alcohols to alkyl bromides.
Preparation
PBr3 ...
(catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
) is used in the Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky reaction to prepare 2-bromopropanoic acid, which in the second step is converted to a racemic mixture
In chemistry, a racemic mixture, or racemate (), is one that has equal amounts of left- and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule or salt. Racemic mixtures are rare in nature, but many compounds are produced industrially as racemates. ...
of the amino acid product by ammonolysis
In chemistry, ammonolysis (/am·mo·nol·y·sis/) is the process of splitting ammonia into NH2- + H+. Ammonolysis reactions can be conducted with organic compounds to produce amines (molecules containing a nitrogen atom with a lone pair, :N), o ...
.
::
Mechanism
The reaction is initiated by addition of a catalytic amount of PBr3, after which one molar equivalent of Br2 is added. : PBr3 replaces the carboxylic OH with a bromide, resulting in a carboxylic acid bromide. Theacyl bromide
In organic chemistry, an acyl halide (also known as an acid halide) is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with a halide group (, where X is a halogen).
If the acid is a carboxylic acid (), the compoun ...
tautomer
Tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert.
The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hydr ...
izes to an enol
In organic chemistry, alkenols (shortened to enols) are a type of reactive structure or intermediate in organic chemistry that is represented as an alkene ( olefin) with a hydroxyl group attached to one end of the alkene double bond (). The te ...
, which reacts with the Br2 to brominate at the α position.
In neutral to slightly acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
ic aqueous
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be rep ...
solution, hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
of the α-bromo acyl bromide occurs spontaneously, yielding the α-bromo carboxylic acid in an example of a nucleophilic acyl substitution
Nucleophilic acyl substitution describe a class of substitution reactions involving nucleophiles and acyl compounds. In this type of reaction, a nucleophile – such as an alcohol, amine, or enolate – displaces the leaving group of an acyl deriv ...
. If an aqueous solution is desirable, a full molar equivalent of PBr3 must be used as the catalytic chain is disrupted.
If little nucleophilic
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are ...
solvent is present, reaction of the α-bromo acyl bromide with the carboxylic acid yields the α-bromo carboxylic acid and regenerates the acyl bromide intermediate. In practice a molar equivalent of PBr3 is often used anyway to overcome the slow reaction kinetics
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the branch of physical chemistry that is concerned with understanding the rates of chemical reactions. It is to be contrasted with chemical thermodynamics, which deals with the direction in w ...
.
The mechanism for the exchange between an alkanoyl bromide and a carboxylic acid is below.
The α-bromoalkanoyl bromide has a strongly electrophilic carbonyl carbon because of the electron-withdrawing effects of the two bromides.
By quenching the reaction with an alcohol, instead of water, the α-bromo ester can be obtained.
See also
*Reformatsky reaction
The Reformatsky reaction (sometimes misspelled Reformatskii reaction) is an organic reaction which condenses aldehydes or ketones with α-halo esters using metallic zinc to form β-hydroxy-esters:
The organozinc reagent, also called a 'Reforma ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky halogenation Halogenation reactions Substitution reactions Name reactions