Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Heilongjiang () formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is the northernmost and easternmost province of the country and contains China's northernmost point (in Mohe City along the Amur) and easternmost point (at the junction of the Amur and Ussuri rivers).
The province is bordered by Jilin to the south and Inner Mongolia to the west. It also shares a border with Russia ( Amur Oblast, Jewish Autonomous Oblast,
 Ancient Chinese records and other sources state that Heilongjiang was inhabited by people such as the Sushen, Buyeo, the Mohe, and the Khitan. Mongolic Donghu people lived in Inner Mongolia and the western part of Heilongjiang. Some names are Manchu or Mongolian. The eastern portion of Heilongjiang was ruled by the
Ancient Chinese records and other sources state that Heilongjiang was inhabited by people such as the Sushen, Buyeo, the Mohe, and the Khitan. Mongolic Donghu people lived in Inner Mongolia and the western part of Heilongjiang. Some names are Manchu or Mongolian. The eastern portion of Heilongjiang was ruled by the  Heilongjiang as an administrative entity was created in 1683, during the
Heilongjiang as an administrative entity was created in 1683, during the 
 A humid continental climate ( Köppen ''Dwa'' or ''Dwb'') predominates in the province, though areas in the far north are
A humid continental climate ( Köppen ''Dwa'' or ''Dwb'') predominates in the province, though areas in the far north are
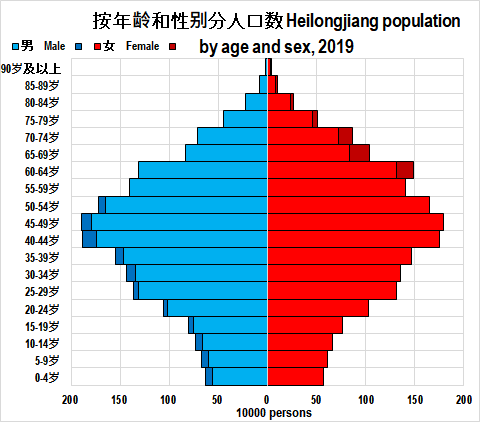 The majority of Heilongjiang's population is Han Chinese, while other List of Chinese nationalities, ethnic minorities include the
The majority of Heilongjiang's population is Han Chinese, while other List of Chinese nationalities, ethnic minorities include the
Source:
 Harbin, the provincial capital, is a city of contrasts, with Chinese, Russian, and eclectic worldwide influences clearly apparent. Bukui Mosque, a national heritage site, is the largest glazed-tile building in the province. Eastern Orthodox, Roman Catholic, and Protestant churches as well as synagogues dot the city.
The long, cold winter is the backdrop for its famed ice sculpture exhibitions. In 2007 already the 8th Ice and Snow World opened to visitors in Harbin. More than 2,000 ice sculptures were on display at the annual event.
Wudalianchi Lakes are a series of five lakes formed between 1719 and 1721 when volcanic eruption shaped one section of a tributary of the Amur into five interconnected lakes. The second lake in particular is renowned for its irregular geological sights. Lake Jingbo, in Ning'an County, is a section of the Mudan River that has been narrowed and shaped by volcanic eruption into a series of sights, including the Diaoshuilou Falls.
The province has a zoological park called "Harbin Siberian Tiger Park".
Harbin, the provincial capital, is a city of contrasts, with Chinese, Russian, and eclectic worldwide influences clearly apparent. Bukui Mosque, a national heritage site, is the largest glazed-tile building in the province. Eastern Orthodox, Roman Catholic, and Protestant churches as well as synagogues dot the city.
The long, cold winter is the backdrop for its famed ice sculpture exhibitions. In 2007 already the 8th Ice and Snow World opened to visitors in Harbin. More than 2,000 ice sculptures were on display at the annual event.
Wudalianchi Lakes are a series of five lakes formed between 1719 and 1721 when volcanic eruption shaped one section of a tributary of the Amur into five interconnected lakes. The second lake in particular is renowned for its irregular geological sights. Lake Jingbo, in Ning'an County, is a section of the Mudan River that has been narrowed and shaped by volcanic eruption into a series of sights, including the Diaoshuilou Falls.
The province has a zoological park called "Harbin Siberian Tiger Park".
Heilongjiang Province Promotes Bandy as Olympic Sport!
/ref>
Heilongjiang Government website
*
at Hong Kong Trade Development Council, HKTDC
Heilongjiang International University
{{Authority control Heilongjiang, Provinces of the People's Republic of China States and territories established in 1954 1954 establishments in China Manchuria
Khabarovsk Krai
Khabarovsk Krai ( rus, Хабаровский край, r=Khabarovsky kray, p=xɐˈbarəfskʲɪj kraj) is a federal subject (a krai) of Russia. It is geographically located in the Russian Far East and is a part of the Far Eastern Federal District ...
, Primorsky Krai and Zabaykalsky Krai) to the north and east. The capital and the largest city of the province is Harbin
Harbin (; mnc, , v=Halbin; ) is a sub-provincial city and the provincial capital and the largest city of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, as well as the second largest city by urban population after Shenyang and largest ...
. Among Chinese provincial-level administrative divisions, Heilongjiang is the sixth-largest by total area, the 15th-most populous, and the second-poorest by GDP per capita.
The province takes its name from the Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's List of longest rivers, tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China, Northeastern China (Inne ...
(see the etymology section below for details) which marks the border between the People's Republic of China and Russia.
Heilongjiang has significant agricultural production, and raw materials, such as timber, oil and coal.
Etymology
The province takes its name from theAmur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's List of longest rivers, tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China, Northeastern China (Inne ...
, whose Mandarin name is ''Heilongjiang'' which is a literal and same-word-order translation of "black dragon
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as ...
river". ''Hei'' comes from qara/hara/har, a common Altaic language cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words in different languages that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymology, etymological ancestor in a proto-language, common parent language. Because language c ...
meaning "black". ''Long'' comes from the Mandarin word for "dragon". ''Jiang'' means "river" in Mandarin.
History
 Ancient Chinese records and other sources state that Heilongjiang was inhabited by people such as the Sushen, Buyeo, the Mohe, and the Khitan. Mongolic Donghu people lived in Inner Mongolia and the western part of Heilongjiang. Some names are Manchu or Mongolian. The eastern portion of Heilongjiang was ruled by the
Ancient Chinese records and other sources state that Heilongjiang was inhabited by people such as the Sushen, Buyeo, the Mohe, and the Khitan. Mongolic Donghu people lived in Inner Mongolia and the western part of Heilongjiang. Some names are Manchu or Mongolian. The eastern portion of Heilongjiang was ruled by the Bohai Kingdom
Balhae ( ko, 발해, zh, c=渤海, p=Bóhǎi, russian: Бохай, translit=Bokhay, ), also rendered as Bohai, was a multi-ethnic kingdom whose land extends to what is today Northeast China, the Korean Peninsula and the Russian Far East. It wa ...
between the 7th and 10th centuries, followed by the Khitan Liao dynasty. The Jurchen Jin dynasty (1115–1234)
The Jin dynasty (,
; ) or Jin State (; Jurchen: Anchun Gurun), officially known as the Great Jin (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 1115 and 1234. Its name is sometimes written as Kin, Jurchen Jin, Jinn, or Chin
in ...
that subsequently ruled much of north China arose within the borders of modern Heilongjiang.
 Heilongjiang as an administrative entity was created in 1683, during the
Heilongjiang as an administrative entity was created in 1683, during the Kangxi
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 1654– 20 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, born Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1661 to 1 ...
era of the Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
Qing Dynasty, from the northwestern part of the Jilin province. This Heilongjiang Province only included the western part of today's Heilongjiang Province, and was under the supervision of the General of Heilongjiang (Sahaliyan Ula i Jiyanggiyūn) (the title is also translated as the Military Governor of Heilongjiang; ''jiyanggiyūn'' is the Manchu reading of the Chinese word ; "military leader, general" and is cognate with Japanese '' shōgun''), whose power extended, according to the Treaty of Nerchinsk, as far north as the Stanovoy Mountains. The eastern part of what's today Heilongjiang remained under the supervision of the General of Jilin (Girin i Jiyanggiyūn), whose power reached the Sea of Japan. These areas deep in Manchuria were closed off to Han Chinese migration.
The original seat of the Military Governor of Heilongjiang, as established in 1683, was in Heilongjiang City (also known as Aigun or Heihe, or, in Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
, Saghalien Ula), located on the Amur River. However, already in 1690 the seat of the governor was transferred to Nenjiang (Mergen) on the Nen River
The Nen River or Nenjiang (), or Nonni () is a river in Northeast China. The Nen River flows through the northern part of Heilongjiang Province and the northeastern section of Inner Mongolia, some parts of the river forming the border between the ...
, and, in 1699, further south to Qiqihar. According to modern historians, the moves may have been driven by supply considerations: Nenjiang and Qiqihar are connected by a convenient waterway (Nen River) with southern Manchuria, whereas accessing Aigun (Heihe) would require either sailing all the way down the Sungari River until its confluence with the Amur and then up the Amur to Heihe, or using a portage
Portage or portaging (Canada: ; ) is the practice of carrying water craft or cargo over land, either around an obstacle in a river, or between two bodies of water. A path where items are regularly carried between bodies of water is also called a ...
over the Lesser Xing'an Mountains between the Nen River valley and the Amur valley. An additional advantage of Qiqihar may have been its location at the junction of a northbound road (to Nenjiang) and a westbound one (to Mongolia), enabling its garrison to defend both against the Russians and the Ölöt Mongols.
Little Qing Military presence existed north of Aigun. According to the 18th- and early-20th-century European sources and the reports of the Russians in the 1850s, the farthest Qing "advance guard" post was at Ulusu-Modon (Ulussu-Mudan) ( ''Wūlǔsūmùdān''), near the Amur River's famous S-shaped meander. (The post was on the left (north) bank of the river, lost to the Russians in 1860.)
In 1858 and 1860, the Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
government was forced to give up all land beyond the Amur and Ussuri Rivers to the Russian Empire, cutting off the Qing Empire from the Sea of Japan and giving Heilongjiang its present northern and eastern borders. At the same time, Manchuria was opened to Han Chinese migration by the Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
government. By the early twentieth century, due to the '' Chuang Guandong'', the Han Chinese had become the dominant ethnic group in the region.
In 1931, Japanese forces invaded
An invasion is a military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitical entity aggressively enter territory owned by another such entity, generally with the objective of either: conquering; liberating or re-establishing con ...
Heilongjiang. In 1932, the Japanese completed their conquest of the province, which became part of the Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
ese puppet state of Manchukuo
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Northeast China, Manchuria from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 afte ...
.
In 1945, Japanese forces in Manchuria were defeated by the Soviet Army. During the Chinese Civil War, Soviet forces aided the Chinese communists. Heilongjiang became the first province to be completely controlled by the communists and Harbin
Harbin (; mnc, , v=Halbin; ) is a sub-provincial city and the provincial capital and the largest city of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, as well as the second largest city by urban population after Shenyang and largest ...
the first major city to be controlled by them.
At the beginning of communist rule, Heilongjiang included only the western portion of the present-day province, and had its capital at Qiqihar. The remaining area was the province of Songjiang; its capital was Harbin. In 1954, these two provinces were merged into present-day Heilongjiang. During the Cultural Revolution, Heilongjiang was also expanded to include Hulunbuir League
Hulunbuir or Hulun Buir ( mn, , ''Kölün buyir'', Mongolian Cyrillic: Хөлөнбуйр, ''Khölönbuir''; zh, s=呼伦贝尔, ''Hūlúnbèi'ěr'') is a region that is governed as a prefecture-level city in northeastern Inner Mongolia, China. ...
and some other areas previously in Inner Mongolia; this has since mostly been reversed.

Geography
Heilongjiang is a land of varied topographies. Much of the province is dominated by mountain ranges such as the Greater Khingan Range and Lesser Khingan Range, Zhangguangcai Mountains, Laoye Mountains, andWanda Mountains
The Wanda Mountains () are located in the Heilongjiang Province of China.
The forests on the mountains are home to many rare species of plants and fungi. Among these include: black fungus, zhenmo, and wei or cinnamon fern (Osmunda cinnamomea).
...
. The highest peak is Datudingzi Mountain
Datudingzi Mountain or Datudingzi Shan (), also known as Mount Datudingzi, abbreviated as "Mt. Datudingzi", is the highest point of Heilongjiang province , located about 170 kilometers southeast of Wuchang County, Harbin City, Heilongjiang Prov ...
at , located on the border with Jilin province. The Greater Khingan Range contains China's largest remaining virgin forest and is an important area for China's forestry industry.
The east and southwest of the province, which are relatively flat and low in altitude, feature the Muling River Muling or Muren () is a river in Northeast China, a left tributary of the Ussuri.
Its length is , and its basin area is approximately . Jixi and Hulin are located on Muling River.
The area of the river is known by Sino-Soviet conflict (1929) and ...
, the Naoli River, the Songhua River, the Nen River
The Nen River or Nenjiang (), or Nonni () is a river in Northeast China. The Nen River flows through the northern part of Heilongjiang Province and the northeastern section of Inner Mongolia, some parts of the river forming the border between the ...
, and the Mudan River, all tributaries of the Amur, while the northern border forms part of the Amur valley. Xingkai Lake (or Khanka Lake) is found on the border with Russia's Primorsky Krai.
Climate
 A humid continental climate ( Köppen ''Dwa'' or ''Dwb'') predominates in the province, though areas in the far north are
A humid continental climate ( Köppen ''Dwa'' or ''Dwb'') predominates in the province, though areas in the far north are subarctic
The subarctic zone is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the true Arctic, north of humid continental regions and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Scandinavia, Siberia, and the Cairngorms. Generally, ...
(Köppen ''Dwc''). Winters are long and bitter, with an average of in January, and summers are short and warm to very warm with an average of in July. The annual average rainfall is , concentrated heavily in summer. Clear weather is prevalent throughout the year, and in the spring, the Songnen Plain
The Songnen Plain () in Northeast China is named after the Songhua and Nenjiang Rivers and is connected to the Sanjiang Plain through the Songhua River Valley; a small plain lies north of Xingkai Lake
Lake Khanka (russian: о́зеро Ха́� ...
and the Sanjiang Plain The Sanjiang Plain includes the Amur River (also known as the Heilong, or literally, "Black Dragon" or River), Songhua and Ussuri (also known as the Wusuli) rivers and covers 23 counties in Heilongjiang Province, China encompassing about 109,000&nb ...
provide abundant sources of wind energy.
The province's largest cities include Harbin
Harbin (; mnc, , v=Halbin; ) is a sub-provincial city and the provincial capital and the largest city of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, as well as the second largest city by urban population after Shenyang and largest ...
, Qiqihar, Mudanjiang, Jiamusi, Daqing
Daqing (; alternately romanized as Taching) is a prefecture-level city in the west of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China. The name literally means "Great Celebration". Daqing is known as the "Oil Capital of China" and has experi ...
, Jixi, Shuangyashan
Shuangyashan () is a coal mining prefecture-level city located in the eastern part Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, bordering Russia's Khabarovsk and Primorsky Krais to the east. The city's name means a pair-of-ducks mountains ...
, Hegang, Qitaihe
Qitaihe () is a prefecture-level city in eastern Heilongjiang province, China. Covering an area , it is geographically the smallest prefecture-level division of the province. Qitaihe also has the second smallest population of the cities in Heil ...
, Yichun, and Heihe.
Transport
Roads
Heilongjiang boasts an extensive road network. As of October 2020, it has 165,989 km of expressways, highways and other roads. The Beijing - Harbin Expressway is the most significant expressway corridor to the province, which begins at the Heilongjiang - Jilin border and ends within the Harbin Ring Expressway. The Harbin - Tongjiang Expressway runs northeast and it links far-flung counties within the jurisdiction of Harbin, Jiamusi and other major counties in Northeast Heilongjiang. Near the end of Harbin - Tongjiang Expressway, Jiansanjiang–Heixiazi Island Expressway branches off the main expressway at Jiansanjiang and connects many state-owned farms at the far east of the province before ending near the Sino-Russian border. The Suifenhe - Manzhouli Expressway is another major corridor, it runs southeast to northwest and connects some of the most significant population centers of the province, including Mudanjiang, Harbin, Daqing and Qiqihar, before ending at the Heilongjiang - Inner Mongolia border. The Hegang - Dalian Expressway runs between Hegang and the Heilongjiang - Jilin border in East Heilongjiang, is another major expressway that facilitates the transportation of lumber and coal.Railways
There are 60 railway lines of around including a section of the Asia-Europe Continental Bridge. The Harbin–Dalian High-Speed Railway, completed in 2012, stretches from Harbin, Heilongjiang's capital, toDalian
Dalian () is a major sub-provincial port city in Liaoning province, People's Republic of China, and is Liaoning's second largest city (after the provincial capital Shenyang) and the third-most populous city of Northeast China. Located on the ...
in Liaoning province via Changchun and Shenyang comprising 23 stops. It is expected to transport 37 million passengers per year by 2020 and 51 million by 2030.
Airports
Major airports include Harbin Taiping International Airport, Qiqihar Airport, Mudanjiang Airport, Jiamusi Airport and Heihe Airport. Harbin International Airport is capable of handling six million passengers every year and connects to over 70 domestic and international cities.Waterways
Tongjiang-Nizhneleninskoye railway bridge
The Tongjiang-Nizhneleninskoye railway bridge was proposed in 2007 by Valery Solomonovich Gurevich, the vice-chairman of the Jewish Autonomous Oblast in Russia. The railway bridge over theAmur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's List of longest rivers, tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China, Northeastern China (Inne ...
will connect Tongjiang with Nizhneleninskoye, a village in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast.
The Chinese portion of the bridge was finished in July 2016. In December 2016, work began on the Russian portion of the bridge. Completion of structural link between the two sides of the bridge was completed in March 2019. Opening to rail traffic has been repeatedly delayed, with the December 2019 estimate being "the end of 2020", and then 3rd quarter of 2021.
Administrative divisions
Heilongjiang is divided into thirteen Administrative divisions of China#Prefectural level, prefecture-level divisions: twelve Prefecture-level city, prefecture-level cities (including a Sub-provincial divisions in the People's Republic of China, sub-provincial city) and one Prefectures of the People's Republic of China, prefecture: (Additional information regarding the last prefecture can be found at Greater Khingan.) These 13 prefecture-level divisions are subdivided into 128 Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China#County level, county-level divisions (65 District of China, districts, 20 county-level cities, 42 County (People's Republic of China), counties, and one autonomous county). Those are in turn divided into 1,284 Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China#Township level, township-level divisions (473 town of China, towns, 400 Townships of the People's Republic of China, townships, 58 ethnic townships, and 353 Subdistricts of China, subdistricts).Urban areas
Politics
List of Secretaries of the Chinese Communist Party Heilongjiang Committee: #Zhang Qilong (; 1949–1950) #Zhao Dezun (; 1950–1953) #Feng Jixin (; 1953–1954) #Ouyang Qin (; 1954–1965) #Pan Fusheng (; 1965–1971) #Wang Jiadao (; 1971–1974) #Liu Guangtao (; 1977) #Yang Yichen (1914–1997), Yang Yichen (; 1977–1983) #Li Li'an (; 1983–1985) #Sun Weiben (; 1985–1994) #Yue Qifeng (; 1994–1997) #Xu Youfang (; 1997–2003) #Song Fatang (; 2003–2005) #Qian Yunlu (; 2005–2008) #Ji Bingxuan (; 2008–2013) #Wang Xiankui (; March 2013 – April 2017) #Zhang Qingwei (; April 2017 – October 2021) #Xu Qin (; October 2021 - present) List of Governors: #Yu Yifu (; 1949–1952) #Zhao Dezun (; 1952–1953) #Chen Lei (Heilongjiang), Chen Lei (; 1953–1954) #Han Guang (; 1954–1956) #Ouyang Qin (; 1956–1958) #Li Fanwu (; 1958–1966) #Pan Fusheng (; 1967–1971) #Wang Jiadao (; 1971–1974) #Liu Guangtao (; February 1977 – December 1977) #Yang Yichen (1914–1997), Yang Yichen (; December 1977 – 1979) #Chen Lei (Heilongjiang), Chen Lei (; 1979–1985) #Hou Jie (; 1985–1989) #Shao Qihui (; 1989–1994) #Tian Fengshan (; 1994–2000) #Song Fatang (; 2000–2003) #Zhang Zuoji (; 2003 – December 2007) #Li Zhanshu (; December 2007 – August 2010) #Wang Xiankui (; August 2010 – March 2013) #Lu Hao (born 1967), Lu Hao (; March 2013 – March 2018) #Wang Wentao (; March 2018 – December 2020) #Hu Changsheng (; February 2021 – present)Economy
Heilongjiang's GDP has been rising steadily since 2003, growing 37% from 2003 to 2007. The value of the private economy reached RMB234 billion in 2006 and accounted for 37.6 percent of the GDP. In that year, the tax revenue from private enterprises hit RMB20.5 billion. Private enterprises in Heilongjiang led the overall economic growth of the province. Many leading private enterprises have begun to emerge. The province's three major private enterprises, namely the Heilongjiang Sunflower Medicine Ltd, Qitaihe Yidaxin Coal Co., and Heilongjiang Yiyang Group, each contributed more than RMB100 million in tax revenue in 2007. During the first decade of this century, many private investors were involved in large construction projects in Heilongjiang. In 2006, 928 large projects absorbed private capital of RMB5 million each, and 101 projects attracted RMB100 million each within the province. In line with the central government's policy to revitalize the Northeast, Heilongjiang also restructured its six pillar industries, namely equipment manufacturing, petrochemicals, food processing, energy, pharmaceuticals, and forest and timber processing. In 2017, Heilongjiang's nominal GDP was 1.62 trillion yuan (ca. US$240 billion), with an annual growth rate of 12.2%. Its per capita GDP was 42,699 yuan (US$6,324). In 2006 the per capita disposable income of urban residents in Heilongjiang reached 11,581 yuan (US$1,667), a rise of 13% from the previous year. The per capita net income of rural residents in the province reached 4,856 yuan (US$700), a rise of 17.5% from 2007.Agriculture
Heilongjiang is home to China's largest plantations of rice, maize, corn and soybeans, with a total of of grain plantation area, including of rice plantation and of corn. Heilongjiang has vast tracts of black soil (chernozem), one of the most fertile soil types. Since the early 20th century, cultivation in the black soil belt has expanded by almost 100-fold, and after the 1960s agriculture in the region transformed to modern agriculture with heavy mechanization and an increase of fertilizer use. Heilongjiang is one of the Asia's leading production areas for japonica rice, known for high quality brand rice varieties. The introduction of cold-resistant varieties, favorable policies and climate change have all contributed to a significant increase in rice production in recent years. Commercial crops grown include beets, flax, sunflowers. Heilongjiang is also an important source of lumber for China. Pine, especially the Korean pine and larch are the most important forms of lumber produced in Heilongjiang. Forests are mostly found in the Greater Khingan Mountains and Lesser Khingan Mountains, which are also home to protected animal species such as the Siberian tiger, the red-crowned crane, and the lynx. Herding in Heilongjiang is centered upon horses and cattle; the province has the largest number of milk cows and the highest production of milk among all the province-level divisions of China.Industry
Heilongjiang is part of northeast China, the country's traditional industrial base. Industry is focused upon coal, petroleum, lumber, machinery, and food. Due to its location, Heilongjiang is also an important gateway for trade with Russia. Since a wave of privatization led to the closure of uncompetitive factories in the 1990s, Manchuria has suffered from stagnation. As a result, the government has started the Northeast Area Revitalization Plan, Revitalize Northeast China campaign to deal with this problem, promoting the private sectors as the preferred method of Chinese economic reform, economic reform. Petroleum is of great importance in Heilongjiang, and the Daqing oilfields are an important source of petroleum for China. Coal, gold, and graphite are other important minerals to be found in Heilongjiang. Heilongjiang also has great potential for wind power, with potential capacity for 134 gigawatts of power production.Development zones
*Daqing
Daqing (; alternately romanized as Taching) is a prefecture-level city in the west of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China. The name literally means "Great Celebration". Daqing is known as the "Oil Capital of China" and has experi ...
New & Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone
:Daqing New & Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone was constructed in April 1992 and was then approved as a national high-tech zone by the State Council later that year. Its initial zone area is , and it recently expanded the area by .
* Heihe Border Economic Cooperation Area
* Harbin
Harbin (; mnc, , v=Halbin; ) is a sub-provincial city and the provincial capital and the largest city of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, as well as the second largest city by urban population after Shenyang and largest ...
Economic and Technological Development Zone
* Harbin
Harbin (; mnc, , v=Halbin; ) is a sub-provincial city and the provincial capital and the largest city of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, as well as the second largest city by urban population after Shenyang and largest ...
New & Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone
:Harbin High-tech Zone was set up in 1988 and was approved by the State Council as a national development zone in 1991. It has a total area of in the centralized parks, subdivided into Nangang, Haping Road and Yingbin Road Centralized Parks. The Nangang Centralized Park is designated for the incubation of high-tech projects and research and development base of enterprises as well as tertiary industries such as finance, insurance, services, catering, tourism, culture, recreation and entertainment, where the headquarters of major well-known companies and their branches in Harbin are located; the Haping Road Centralized Park is a comprehensive industrial basis for the investment projects of automobile and automobile parts manufacturing, medicines, foodstuffs, electronics, textile; the Yingbin Road Centralized Park is mainly for high-tech incubation projects, high-tech industrial development.
* Sino-Russia Dongning-Piurtaphca Trade Zone
:Sino-Russia Dongning-Piurtaphca Trade Zone was approved by the State Council in 2000 and was completed in 2005. The zone has a planned area of 275.4 hectares. The Chinese part of the zone has a 22-hectare trade center with four subsidiary areas, A, B, C, and D, in which more than 6,000 stalls are already set up, mainly dealing with clothes, household appliances, food, construction materials, etc.
* Suifenhe Border Economic Cooperation Area
:Suifenhe Border Economic Cooperation District (Suifenhe BECD) is located in the north of Suifenhe City, and borders Russia to the east. Suifenhe BECD is the largest among the three state-level border-trade zones of Heilongjiang, in terms of investor numbers. Suifenhe BECD has a convenient transport network. The Binzhou-Suifenhe Railway, which connects the Russian Far East Railway, is an important port for export. The railway distance between Suifenhe and Harbin is . Buguranikinai, the corresponding Russian port city, is away.
Demographics
 The majority of Heilongjiang's population is Han Chinese, while other List of Chinese nationalities, ethnic minorities include the
The majority of Heilongjiang's population is Han Chinese, while other List of Chinese nationalities, ethnic minorities include the Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
s, Koreans, Mongols, Hui people, Hui, Xibe people, Xibe, and Hezhen.
Excludes members of the People's Liberation Army in active service.Source:
Religion
Most of Heilongjiang's residents are either non-religious or practice Chinese folk religions, including Taoism. Manchu shamanism is practiced by many Manchu people. Chinese Buddhism and Tibetan Buddhism have an important presence in the province.Culture
Heilongjiang's culture is part of a Northeast China#Culture, culture of Northeast China that is relatively homogeneous across this region, known in Mandarin Chinese as "Dongbei" (the northeast).Media
Heilongjiang Television and Harbin Economy Radio serve as broadcasters.Tourism
Colleges and universities
*Northeast Forestry University *Harbin Institute of Technology *Harbin Engineering University *Northeast Agricultural University *Harbin University of Science and Technology *Heilongjiang University *Heilongjiang International University *Heilongjiang Institute of Technology *Harbin Medical University *Daqing Staff and Workers University *Northeast Petroleum University *Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine *Heilongjiang Commercial University *Harbin Normal University *Heilongjiang August First Land Reclamation University *Qiqihar UniversitySports
Heilongjiang is in the forefront of promoting winter sports and winter-featured sports industry in China. For example, it is promoting bandy as an Winter Olympic Games, Olympic sport./ref>
Events and leagues
* 2009 Winter Universiade * 2018 Bandy World Championship, 2018 Bandy World Championship, Division B * Asia League Ice HockeySee also
* Major national historical and cultural sites (Heilongjiang), Major national historical and cultural sites in HeilongjiangReferences
External links
Heilongjiang Government website
*
at Hong Kong Trade Development Council, HKTDC
Heilongjiang International University
{{Authority control Heilongjiang, Provinces of the People's Republic of China States and territories established in 1954 1954 establishments in China Manchuria