HaloTag on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 HaloTag is a self-labeling protein tag. It is a 297 residue protein (33 kDa) derived from a bacterial
HaloTag is a self-labeling protein tag. It is a 297 residue protein (33 kDa) derived from a bacterial
 The HaloTag is a hydrolase, which has a genetically modified active site, which specifically binds the reactive chloroalkane linker and has an increased rate of ligand binding. The reaction that forms the bond between the protein tag and chloroalkane linker is fast and essentially irreversible under physiological conditions due to the terminal chlorine of the linker portion. In the aforementioned reaction, nucleophilic attack of the chloroalkane reactive linker causes displacement of the halogen with an amino acid residue, which results in the formation of a covalent alkyl-enzyme intermediate. This intermediate would then be hydrolyzed by an amino acid residue within the wild-type hydrolase. This would lead to regeneration of the enzyme following the reaction. However, in the modified haloalkane dehalogenase (HaloTag), the reaction intermediate cannot proceed through a subsequent reaction because it cannot be hydrolyzed due to the mutation in the enzyme. This causes the intermediate to persist as a stable covalent adduct with which there is no associated back reaction.
The HaloTag is a hydrolase, which has a genetically modified active site, which specifically binds the reactive chloroalkane linker and has an increased rate of ligand binding. The reaction that forms the bond between the protein tag and chloroalkane linker is fast and essentially irreversible under physiological conditions due to the terminal chlorine of the linker portion. In the aforementioned reaction, nucleophilic attack of the chloroalkane reactive linker causes displacement of the halogen with an amino acid residue, which results in the formation of a covalent alkyl-enzyme intermediate. This intermediate would then be hydrolyzed by an amino acid residue within the wild-type hydrolase. This would lead to regeneration of the enzyme following the reaction. However, in the modified haloalkane dehalogenase (HaloTag), the reaction intermediate cannot proceed through a subsequent reaction because it cannot be hydrolyzed due to the mutation in the enzyme. This causes the intermediate to persist as a stable covalent adduct with which there is no associated back reaction.
 HaloTagged
HaloTagged
"> Since bacterial dehalogenases are relatively small and the reactions described above are foreign to mammalian cells, there is no interference by endogenous mammalian metabolic reactions. Once the fusion protein has been expressed, there is a wide range of potential areas of experimentation including enzymatic assays, cellular imaging, protein arrays, determination of sub-cellular localization, and many additional possibilities.
Recently, HaloTag has been engineered to create hybrid protein + small molecule biosensors of neuronal activity. These sensors undergo a conformational change in response to calcium concentration spikes during neuronal firing; this conformational change modulates the conformation of a HaloTag-bound dye molecule.
 HaloTag is a self-labeling protein tag. It is a 297 residue protein (33 kDa) derived from a bacterial
HaloTag is a self-labeling protein tag. It is a 297 residue protein (33 kDa) derived from a bacterial enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
, designed to covalently bind to a synthetic ligand. The bacterial enzyme can be fused to various proteins of interest. The synthetic ligand is chosen from a number of available ligands in accordance with the type of experiments to be performed. This bacterial enzyme is a haloalkane dehalogenase
In enzymology, a haloalkane dehalogenase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
:1-haloalkane + H2O \rightleftharpoons a primary alcohol + halide
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are 1-haloalkane and H2O, whereas its two ...
, which acts as a hydrolase
Hydrolase is a class of enzyme that commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond, which typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are este ...
and is designed to facilitate visualization of the subcellular localization of a protein of interest, immobilization of a protein of interest, or capture of the binding partners of a protein of interest within its biochemical environment. The HaloTag is composed of two covalently bound segments including a haloalkane dehalogenase and a synthetic ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electr ...
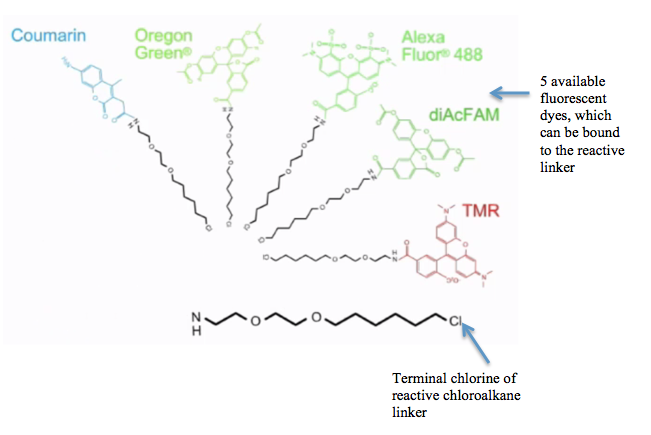
of choice. These synthetic ligands consist of a reactive chloroalkane linker bound to a functional group. Functional groups can either be biotin (can be used as an affinity tag) or can be chosen from five available fluorescent dyes including Coumarin, Oregon Green, Alexa Fluor 488, diAcFAM, and TMR. These fluorescent dyes can be used in the visualization of either living or chemically fixed cells.
Mechanism
 The HaloTag is a hydrolase, which has a genetically modified active site, which specifically binds the reactive chloroalkane linker and has an increased rate of ligand binding. The reaction that forms the bond between the protein tag and chloroalkane linker is fast and essentially irreversible under physiological conditions due to the terminal chlorine of the linker portion. In the aforementioned reaction, nucleophilic attack of the chloroalkane reactive linker causes displacement of the halogen with an amino acid residue, which results in the formation of a covalent alkyl-enzyme intermediate. This intermediate would then be hydrolyzed by an amino acid residue within the wild-type hydrolase. This would lead to regeneration of the enzyme following the reaction. However, in the modified haloalkane dehalogenase (HaloTag), the reaction intermediate cannot proceed through a subsequent reaction because it cannot be hydrolyzed due to the mutation in the enzyme. This causes the intermediate to persist as a stable covalent adduct with which there is no associated back reaction.
The HaloTag is a hydrolase, which has a genetically modified active site, which specifically binds the reactive chloroalkane linker and has an increased rate of ligand binding. The reaction that forms the bond between the protein tag and chloroalkane linker is fast and essentially irreversible under physiological conditions due to the terminal chlorine of the linker portion. In the aforementioned reaction, nucleophilic attack of the chloroalkane reactive linker causes displacement of the halogen with an amino acid residue, which results in the formation of a covalent alkyl-enzyme intermediate. This intermediate would then be hydrolyzed by an amino acid residue within the wild-type hydrolase. This would lead to regeneration of the enzyme following the reaction. However, in the modified haloalkane dehalogenase (HaloTag), the reaction intermediate cannot proceed through a subsequent reaction because it cannot be hydrolyzed due to the mutation in the enzyme. This causes the intermediate to persist as a stable covalent adduct with which there is no associated back reaction.
Uses
 HaloTagged
HaloTagged fusion proteins
Fusion proteins or chimeric (kī-ˈmir-ik) proteins (literally, made of parts from different sources) are proteins created through the joining of two or more genes that originally coded for separate proteins. Translation of this ''fusion gene'' r ...
can be expressed using standard recombinant protein
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be fou ...
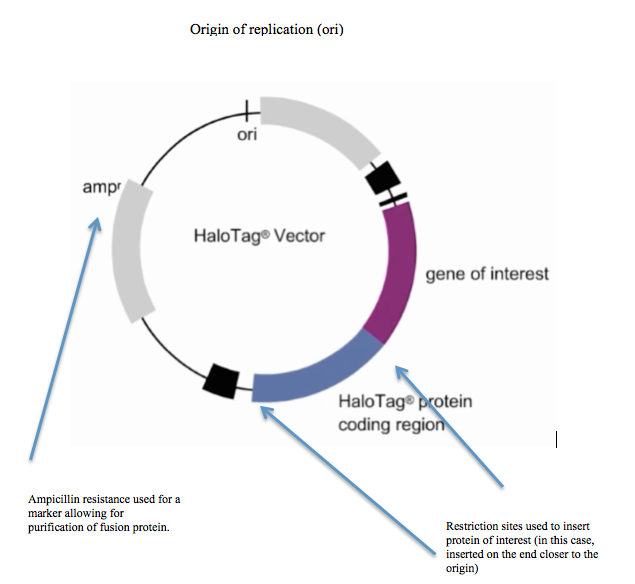
expression techniques. Furthermore, there are several commercial vectors available that just require insertion of a gene of interest.Promega
Promega Corporation is a Madison, Wisconsin-based manufacturer of enzymes and other products for biotechnology and molecular biology with a portfolio covering the fields of genomics, protein analysis and expression, cellular analysis, drug disc ...See also
*Protein tag
Protein tags are peptide sequences genetically grafted onto a recombinant protein. Tags are attached to proteins for various purposes. They can be added to either end of the target protein, so they are either C-terminus or N-terminus specific or a ...
* SNAP tag
* SpyTag
*Fluorescent proteins
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, tha ...
References
{{Reflist, 32em Bacterial enzymes