Hylaeosaurus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Hylaeosaurus'' ( ;
 The first ''Hylaeosaurus''
The first ''Hylaeosaurus''  On 30 November Mantell sent the piece to the
On 30 November Mantell sent the piece to the  ''Hylaeosaurus'' is the most obscure of the three animals used by Sir Richard Owen to first define the new group
''Hylaeosaurus'' is the most obscure of the three animals used by Sir Richard Owen to first define the new group  Additional remains have been referred to ''Hylaeosaurus'', from the
Additional remains have been referred to ''Hylaeosaurus'', from the
 ''Hylaeosaurus armatus'' Mantell 1833 is currently considered the only valid
''Hylaeosaurus armatus'' Mantell 1833 is currently considered the only valid
 Gideon Mantell originally estimated that ''Hylaeosaurus'' was about long, or about half the size of the other two original dinosaurs, ''
Gideon Mantell originally estimated that ''Hylaeosaurus'' was about long, or about half the size of the other two original dinosaurs, ''

 ''Hylaeosaurus'' was the first ankylosaur discovered. Until well into the twentieth century its exact affinities would remain uncertain. In 1978 Coombs assigned it to the
''Hylaeosaurus'' was the first ankylosaur discovered. Until well into the twentieth century its exact affinities would remain uncertain. In 1978 Coombs assigned it to the
Paper Dinosaurs, 1824–1969, from Linda Hall Library.illustration
{{Taxonbar, from=Q131770 Nodosaurids Valanginian life Early Cretaceous dinosaurs of Europe Cretaceous England Fossils of England Fossil taxa described in 1833 Taxa named by Gideon Mantell Ornithischian genera
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
: / "belonging to the forest" and / "lizard") is a herbivorous ankylosaurian
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the order Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs. ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
that lived about 136 million years ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago). ...
, in the late Valanginian
In the geologic timescale, the Valanginian is an age or stage of the Early or Lower Cretaceous. It spans between 139.8 ± 3.0 Ma and 132.9 ± 2.0 Ma (million years ago). The Valanginian Stage succeeds the Berriasian Stage of the Lower Cretaceou ...
stage
Stage or stages may refer to:
Acting
* Stage (theatre), a space for the performance of theatrical productions
* Theatre, a branch of the performing arts, often referred to as "the stage"
* ''The Stage'', a weekly British theatre newspaper
* Sta ...
of the early Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
of England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
. It was found in the Grinstead Clay Formation.
''Hylaeosaurus'' was one of the first dinosaurs to be discovered, in 1832 by Gideon Mantell
Gideon Algernon Mantell MRCS FRS (3 February 1790 – 10 November 1852) was a British obstetrician, geologist and palaeontologist. His attempts to reconstruct the structure and life of ''Iguanodon'' began the scientific study of dinosaurs: in ...
. In 1842 it was one of the three dinosaurs Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen (20 July 1804 – 18 December 1892) was an English biologist, comparative anatomist and paleontologist. Owen is generally considered to have been an outstanding naturalist with a remarkable gift for interpreting fossils.
Owe ...
based the Dinosauria on, the others being ''Iguanodon
''Iguanodon'' ( ; meaning 'iguana-tooth'), named in 1825, is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur. While many species have been classified in the genus ''Iguanodon'', dating from the late Jurassic Period to the early Cretaceous Period of Asia, Eu ...
'' and ''Megalosaurus
''Megalosaurus'' (meaning "great lizard", from Greek , ', meaning 'big', 'tall' or 'great' and , ', meaning 'lizard') is an extinct genus of large carnivorous theropod dinosaurs of the Middle Jurassic period (Bathonian stage, 166 million years ...
''. Four species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
were named in the genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
, but only the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ...
''Hylaeosaurus armatus'' is today considered valid. Only limited remains have been found of ''Hylaeosaurus'' and much of its anatomy is unknown. It might have been a basal nodosaurid
Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs, from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous period in what is now North America, South America, Europe, and Asia.
Description
Nodosaurids, like their close relatives the ankylosaurids, we ...
, although a recent cladistic analysis recovers it as a basal ankylosaurid
Ankylosauridae () is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to Nodosauridae. The oldest known Ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Pal ...
.
''Hylaeosaurus'' was about five metres long. It was an armoured dinosaur that carried at least three long spines on its shoulder.
History of discovery
 The first ''Hylaeosaurus''
The first ''Hylaeosaurus'' fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s were discovered in the Grinstead Clay Formation, West Sussex
West Sussex is a county in South East England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the shire districts of Adur, Arun, Chichester, Horsham, and Mid Sussex, and the boroughs of Crawley and Worthing. Covering an ar ...
. On 20 July 1832, fossil collector Gideon Mantell
Gideon Algernon Mantell MRCS FRS (3 February 1790 – 10 November 1852) was a British obstetrician, geologist and palaeontologist. His attempts to reconstruct the structure and life of ''Iguanodon'' began the scientific study of dinosaurs: in ...
wrote to Professor Benjamin Silliman
Benjamin Silliman (August 8, 1779 – November 24, 1864) was an early American chemist and science educator. He was one of the first American professors of science, at Yale College, the first person to use the process of fractional distillation ...
that when a gunpowder explosion had demolished a quarry rock face in Tilgate Forest
Tilgate Forest is a Local Nature Reserve in Crawley in West Sussex. It is owned and managed by Crawley Borough Council and is part of Tilgate Park.
This site has woods, tall herb and fern, and heathland. The most common trees in areas of natural ...
, several of the boulders freed showed the bones of a saurian. A local fossil dealer had assembled the about fifty pieces, described by him as a "great consarn of bites and boanes". Having doubts about the value of the fragments, Mantell had nevertheless purchased the pieces and soon discovered they could be united into a single skeleton, partially articulated. Mantell was delighted with the find because previous specimens of ''Megalosaurus
''Megalosaurus'' (meaning "great lizard", from Greek , ', meaning 'big', 'tall' or 'great' and , ', meaning 'lizard') is an extinct genus of large carnivorous theropod dinosaurs of the Middle Jurassic period (Bathonian stage, 166 million years ...
'' and ''Iguanodon
''Iguanodon'' ( ; meaning 'iguana-tooth'), named in 1825, is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur. While many species have been classified in the genus ''Iguanodon'', dating from the late Jurassic Period to the early Cretaceous Period of Asia, Eu ...
'' had consisted of single bone elements. The discovery in fact represented the most complete non-avian dinosaur skeleton known at the time. He was strongly inclined to describe the find as belonging to the latter genus, but during a visit by William Clift
William Clift FRS (14 February 1775 – 20 June 1849) was a British illustrator and conservator.
Early life
Clift was born in Burcombe near Bodmin in Cornwall. He was the youngest of seven children and grew up in poverty following his fat ...
, the curator of the Royal College of Surgeons of England
The Royal College of Surgeons of England (RCS England) is an independent professional body and registered charity that promotes and advances standards of surgical care for patients, and regulates surgery and dentistry in England and Wales. The ...
museum, and his assistant John Edward Gray
John Edward Gray, FRS (12 February 1800 – 7 March 1875) was a British zoologist. He was the elder brother of zoologist George Robert Gray and son of the pharmacologist and botanist Samuel Frederick Gray (1766–1828). The same is used for ...
, he began to doubt the identification. Clift was the first to point out that several plates and spikes were probably part of a body armour, attached to the back or sides of the rump.Dennis R. Dean, 1999, ''Gideon Mantell and the Discovery of Dinosaurs'', Cambridge University Press, 315 pp In November 1832 Mantell decided to create a new generic name: ''Hylaeosaurus''. It is derived from the Greek ὑλαῖος, ''hylaios'', "of the wood". Mantell originally claimed the name ''Hylaeosaurus'' meant "forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
lizard", after the Tilgate Forest in which it was discovered. Later, he claimed that it meant "Weald
The Weald () is an area of South East England between the parallel chalk escarpments of the North and the South Downs. It crosses the counties of Hampshire, Surrey, Sussex and Kent. It has three separate parts: the sandstone "High Weald" in the ...
en lizard" ("wealden" being another word for ''forest''), in reference to the Wealden Group, the name for the early Cretaceous geological
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Eart ...
formation in which the dinosaur was first found.
 On 30 November Mantell sent the piece to the
On 30 November Mantell sent the piece to the Geological Society of London
The Geological Society of London, known commonly as the Geological Society, is a learned society based in the United Kingdom. It is the oldest national geological society in the world and the largest in Europe with more than 12,000 Fellows.
Fe ...
. Shortly afterwards he himself went to London and on 5 December during a meeting of the Society, in which he for the first time personally met Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen (20 July 1804 – 18 December 1892) was an English biologist, comparative anatomist and paleontologist. Owen is generally considered to have been an outstanding naturalist with a remarkable gift for interpreting fossils.
Owe ...
, reported on the find to large acclaim. However, he was also informed that a paper he had already prepared, was a third too long. On advice of his friend Charles Lyell
Sir Charles Lyell, 1st Baronet, (14 November 1797 – 22 February 1875) was a Scottish geologist who demonstrated the power of known natural causes in explaining the earth's history. He is best known as the author of ''Principles of Geolo ...
, Mantell decided instead of rewriting the paper, to publish an entire book on his fossil finds and dedicate a chapter to ''Hylaeosaurus''. Within three weeks Mantell composed the volume from earlier notes. On 17 December Henry De la Beche
Sir Henry Thomas De la Beche KCB, FRS (10 February 179613 April 1855) was an English geologist and palaeontologist, the first director of the Geological Survey of Great Britain, who helped pioneer early geological survey methods. He was the ...
warned him that the changed conventions in nomenclature implied that only he who provided a full species name was recognised as the author: to ''Hylaeosaurus'' a specific name needed to be added. Mantell on 19 December chose ''armatus'', Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
for "armed" or "armoured", in reference to the spikes and armour plates. As Mantell himself put it: "there appears every reason to conclude that either its back was armed with a formidable row of spines, constituting a dermal fringe, or that its tail possessed the same appendage". In May 1833 his ''The Geology of the South-East of England'' appeared, hereby validly naming the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ...
''Hylaeosaurus armatus''. Mantell published a lithograph
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone (lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German a ...
of his find in ''The Geology of the South-East of England''; and another drawing in the fourth edition of ''The Wonders of Geology'', in 1840.
 ''Hylaeosaurus'' is the most obscure of the three animals used by Sir Richard Owen to first define the new group
''Hylaeosaurus'' is the most obscure of the three animals used by Sir Richard Owen to first define the new group Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
ia, in 1842, the other genera being ''Megalosaurus'' and ''Iguanodon''. Not only has ''Hylaeosaurus'' received less public attention, despite being included in the life-sized models by Benjamin Waterhouse Hawkins
Benjamin Waterhouse Hawkins (8 February 1807 – 27 January 1894) was an English sculptor and natural history artist renowned for his work on the life-size models of dinosaurs in the Crystal Palace Park in south London. The models, accurately ...
placed in the Crystal Palace
Crystal Palace may refer to:
Places Canada
* Crystal Palace Complex (Dieppe), a former amusement park now a shopping complex in Dieppe, New Brunswick
* Crystal Palace Barracks, London, Ontario
* Crystal Palace (Montreal), an exhibition building ...
Park, it also never functioned as a "wastebasket taxon". Owen in 1840 developed a new hypothesis about the spikes; noting they were asymmetrical he correctly rejected the notion they formed a row on the back but incorrectly assumed they were gastralia
Gastralia (singular gastralium) are dermal bones found in the ventral body wall of modern crocodilians and tuatara, and many prehistoric tetrapods. They are found between the sternum and pelvis, and do not articulate with the vertebrae. In these ...
or belly-ribs.
The original specimen, recovered by Gideon Mantell from the Tilgate
Tilgate is one of 14 neighbourhoods within the town of Crawley in West Sussex, England. The area contains a mixture of privately developed housing, self-build groups and ex-council housing. It is bordered by the districts of Furnace Green to the ...
Forest, was in 1838 acquired by the Natural History Museum
A natural history museum or museum of natural history is a scientific institution with natural history collections that include current and historical records of animals, plants, fungi, ecosystems, geology, paleontology, climatology, and more. ...
of London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
. It has the inventory number NHMUK 3775 (earlier BMNH R3775). It was found in a layer of the Tunbridge Wells Sand Formation
The Tunbridge Wells Sand Formation is a geological unit which forms part of the Wealden Group and the uppermost and youngest part of the unofficial Hastings Beds. These geological units make up the core of the geology of the Weald in the English c ...
dating from the Valanginian
In the geologic timescale, the Valanginian is an age or stage of the Early or Lower Cretaceous. It spans between 139.8 ± 3.0 Ma and 132.9 ± 2.0 Ma (million years ago). The Valanginian Stage succeeds the Berriasian Stage of the Lower Cretaceou ...
, about 137 million years old. This holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several ...
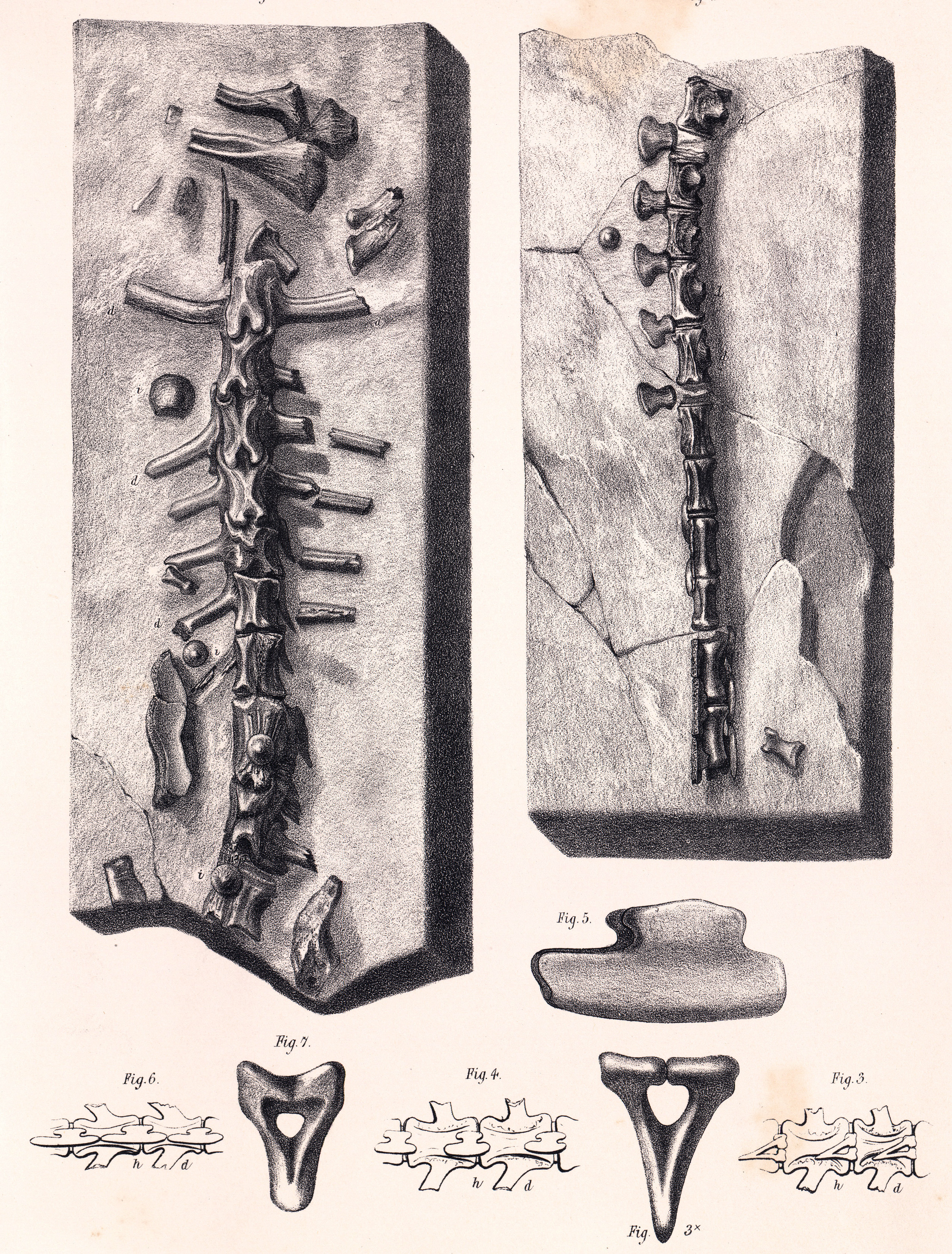
is the best specimen and is composed of the front end of a skeleton minus most of the head and the forelimbs, though only the parts on the face of the stone block are easily studied. The block measures about 135 by 75 centimetres. The holotype consists of the rear of the skull and perhaps lower jaws, ten vertebrae, both scapulae, both coracoids and several spikes and armour plates. The skeleton is viewed from below. For a long time no further preparation had taken place, beyond the assembly and chiselling out by Mantell himself, but in the early twenty-first century the museum began to further free the bones by both chemical and mechanical means. This has proven difficult because the acids used tended to dissolve the glue and gypsum with which the fossils had been repaired, causing the blocks to fall apart. The limited information gained by the preparations by Mark Graham since 2003, was published in 2020, together with a revised description.
Several finds from the mainland of Britain have been referred to ''Hylaeosaurus armatus''. However, in 2011 Paul Barrett
Paul Franklyn "Legs" Barrett (14 December 1940 – 20 January 2019) was a UK agent and manager of 1950s style Rock and Roll artistes, an author and previously a singer, songwriter and film actor. Barrett is the discoverer, mentor and first ma ...
and Susannah Maidment Susannah Catherine Rose Maidment is a British palaeontologist at the Natural History Museum, London. She is internationally recognised for her research on ornithischian dinosaur evolution, and was awarded the 2016 Hodson Award of the Palaeontologic ...
concluded that only the holotype could with certainty be associated with the species, in view of the presence of ''Polacanthus
''Polacanthus'', deriving its name from the Ancient Greek polys-/πολύς- "many" and akantha/ἄκανθα "thorn" or "prickle", is an early armoured, spiked, plant-eating ankylosaurian dinosaur from the early Cretaceous period of England.
I ...
'' in the same layers.Barrett, P.M. and Maidment, S.C.R., 2011, "Wealden armoured dinosaurs". In: Batten, D.J. (ed.). ''English Wealden fossils''. Palaeontological Association, London, Field Guides to Fossils 14, 769 pp
 Additional remains have been referred to ''Hylaeosaurus'', from the
Additional remains have been referred to ''Hylaeosaurus'', from the Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the largest and second-most populous island of England. Referred to as 'The Island' by residents, the Isle of ...
, (the Ardennes
The Ardennes (french: Ardenne ; nl, Ardennen ; german: Ardennen; wa, Årdene ; lb, Ardennen ), also known as the Ardennes Forest or Forest of Ardennes, is a region of extensive forests, rough terrain, rolling hills and ridges primarily in Be ...
of) France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Bückeberg Formation
The Bückeberg Formation is a geologic formation and LagerstätteHornung et al., in Reitner et al., 2013, p.75 in Germany. It preserves fossils dating back to the Berriasian of the Cretaceous period.Hornung et al., 2012 The Bückeberg Formation ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
. The remains from France may actually belong to ''Polacanthus
''Polacanthus'', deriving its name from the Ancient Greek polys-/πολύς- "many" and akantha/ἄκανθα "thorn" or "prickle", is an early armoured, spiked, plant-eating ankylosaurian dinosaur from the early Cretaceous period of England.
I ...
'' and the other references are today also considered dubious. However, possible remains were reported from Germany in 2013: a spike, specimen DLM 537 and the lower end of a humerus, specimen GPMM A3D.3, which were referred to a ''Hylaeosaurus'' sp.
Later species
 ''Hylaeosaurus armatus'' Mantell 1833 is currently considered the only valid
''Hylaeosaurus armatus'' Mantell 1833 is currently considered the only valid species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
in the genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
. However, three others have been named. In 1844, Mantell named ''Hylaeosaurus oweni'' based on the same specimen as ''H. armatus'', wanting to honour Richard Owen. This has been sunk as a junior objective synonym
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently.
* In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnae ...
of ''H. armatus''. In 1956 Alfred Romer
Alfred Sherwood Romer (December 28, 1894 – November 5, 1973) was an American paleontologist and biologist and a specialist in vertebrate evolution.
Biography
Alfred Romer was born in White Plains, New York, the son of Harry Houston Romer an ...
renamed ''Regnosaurus
''Regnosaurus'' (meaning "Sussex lizard") is a genus of herbivorous stegosaurian dinosaur that lived during the Early Cretaceous Period in what is now England. It was one of the first stegosaurs disvovered.
Discovery and species
The fossil re ...
'' into ''Hylaeosaurus northhamptoni''. ''Polacanthus
''Polacanthus'', deriving its name from the Ancient Greek polys-/πολύς- "many" and akantha/ἄκανθα "thorn" or "prickle", is an early armoured, spiked, plant-eating ankylosaurian dinosaur from the early Cretaceous period of England.
I ...
'' Owen 1865 was by Walter Coombs in 1971 renamed into ''Hylaeosaurus foxii''. These last two names have found no acceptance; ''H. foxii'' remained an invalid ''nomen ex dissertatione''. It has also been suggested that ''Polacanthus
''Polacanthus'', deriving its name from the Ancient Greek polys-/πολύς- "many" and akantha/ἄκανθα "thorn" or "prickle", is an early armoured, spiked, plant-eating ankylosaurian dinosaur from the early Cretaceous period of England.
I ...
'' is simply the same species as ''Hylaeosaurus armatus'' and thus a junior synonym, but there are a number of differences in their osteology
Osteology () is the scientific study of bones, practised by osteologists. A subdiscipline of anatomy, anthropology, and paleontology, osteology is the detailed study of the structure of bones, skeletal elements, teeth, microbone morphology, funct ...
.
Sometimes bones from the ''Hylaeosaurus'' material have later been made separate species. In 1928 Franz Nopcsa Franz may refer to:
People
* Franz (given name)
* Franz (surname)
Places
* Franz (crater), a lunar crater
* Franz, Ontario, a railway junction and unorganized town in Canada
* Franz Lake, in the state of Washington, United States – see ...
made specimen BMNH 2584, a left scapula referred by Mantell to ''H. armatus'', part of the type material of ''Polacanthoides ponderosus''. Though in 1978 synonymised with ''Hylaeosaurus'', ''Polacanthoides'' is today considered a ''nomen dubium
In binomial nomenclature, a ''nomen dubium'' (Latin for "doubtful name", plural ''nomina dubia'') is a scientific name that is of unknown or doubtful application.
Zoology
In case of a ''nomen dubium'' it may be impossible to determine whether a s ...
'', an indeterminate member of the Thyreophora
Thyreophora ("shield bearers", often known simply as "armored dinosaurs") is a group of armored ornithischian dinosaurs that lived from the Early Jurassic until the end of the Cretaceous.
Thyreophorans are characterized by the presence of body ...
.
Description
 Gideon Mantell originally estimated that ''Hylaeosaurus'' was about long, or about half the size of the other two original dinosaurs, ''
Gideon Mantell originally estimated that ''Hylaeosaurus'' was about long, or about half the size of the other two original dinosaurs, ''Iguanodon
''Iguanodon'' ( ; meaning 'iguana-tooth'), named in 1825, is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur. While many species have been classified in the genus ''Iguanodon'', dating from the late Jurassic Period to the early Cretaceous Period of Asia, Eu ...
'' and ''Megalosaurus
''Megalosaurus'' (meaning "great lizard", from Greek , ', meaning 'big', 'tall' or 'great' and , ', meaning 'lizard') is an extinct genus of large carnivorous theropod dinosaurs of the Middle Jurassic period (Bathonian stage, 166 million years ...
''. At the time, he modelled the animal after a modern lizard. Modern estimates range up to in length. Gregory S. Paul
Gregory Scott Paul (born December 24, 1954) is an American freelance researcher, author and illustrator who works in paleontology, and more recently has examined sociology and theology. He is best known for his work and research on theropod dino ...
in 2010 estimated the length at , the weight at . Some estimates are considerably lower: in 2001 Darren Naish
Darren William Naish is a British vertebrate palaeontologist, author and science communicator.
As a researcher, he is best known for his work describing and reevaluating dinosaurs and other Mesozoic reptiles, including '' Eotyrannus'', '' Xenop ...
e.a. gave a length of .Naish, D. and Martill, D.M., 2001, "Armoured Dinosaurs: Thyreophorans". In: Martill, D.M., Naish, D., (editors). ''Dinosaurs of the Isle of Wight''. Palaeontological Association Field Guides to Fossils 10. pp. 147–184
Many details about the build of ''Hylaeosaurus'' are unknown, especially if the material is strictly limited to the holotype. Maidment gave two autapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an autapomorphy is a distinctive feature, known as a derived trait, that is unique to a given taxon. That is, it is found only in one taxon, but not found in any others or outgroup taxa, not even those most closely related to t ...
, unique derived traits: the scapula did not fuse with the coracoid, even when the animal was of a considerable size; there were three long spines on its shoulder. Even these traits are not very distinctive: Mantell and Owen had attributed the lack of fusion to ontogeny
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the stu ...
and the total number of spines cannot be observed. ''Hylaeosaurus'' is often styled as a fairly typical nodosaur, with rows of armour plating on the back and tail combined with a relatively long head, equipped with a beak
The beak, bill, or rostrum is an external anatomical structure found mostly in birds, but also in turtles, non-avian dinosaurs and a few mammals. A beak is used for eating, preening, manipulating objects, killing prey, fighting, probing for food ...
used to crop low-lying vegetation.
In 2001 the skull and lower jaws remains were described by Kenneth Carpenter
Kenneth Carpenter (born September 21, 1949, in Tokyo, Japan) is a paleontologist. He is the former director of the USU Eastern Prehistoric Museum and author or co-author of books on dinosaurs and Mesozoic life. His main research interests ...
. The damaged and shifted skull elements provided little information. The quadrate is laterally bowed. The quadratojugal The quadratojugal is a skull bone present in many vertebrates, including some living reptiles and amphibians.
Anatomy and function
In animals with a quadratojugal bone, it is typically found connected to the jugal (cheek) bone from the front and ...
has a high attachment point on the shaft of the quadrate. A triangular postorbital
The ''postorbital'' is one of the bones in vertebrate skulls which forms a portion of the dermal skull roof and, sometimes, a ring about the orbit. Generally, it is located behind the postfrontal and posteriorly to the orbital fenestra. In some ve ...
horn was present. In 2020, it was concluded that the presumed quadrate was in fact the jugal.
Several distinguishing traits were established in 2020. On the shoulder blade, there is a sharp angle of 120° between the acromion and the proximal plate. The acromial process is shelf-shaped instead of thumb-like or folded, from a point positioned at a third from the top edge projecting obliquely to below and sideways instead of strictly laterally. The top edge of the proximal plate is curved sideways. The sides of the centra of the neck vertebrae show a horizontal ridge. Apart from these autapomorphies, the undersides of the side processes of the back vertebrae are exceptionally concave.
The spines at the shoulder are curved to the rear, long, flattened, narrow and pointed. Their underside shows a shallow trough. The front spine is the longest at 42.5 centimetres; to the rear the spines become gradually shorter and wider. A fourth spine, of about the same build but more forward-pointing, is present immediately behind the skull. In 2013 Sven Sachs and Jahn Hornung suggested a configuration in which there were five lateral neck spines, the new German spine having a morphology adapted to fit in the third position.
Phylogeny

 ''Hylaeosaurus'' was the first ankylosaur discovered. Until well into the twentieth century its exact affinities would remain uncertain. In 1978 Coombs assigned it to the
''Hylaeosaurus'' was the first ankylosaur discovered. Until well into the twentieth century its exact affinities would remain uncertain. In 1978 Coombs assigned it to the Nodosauridae
Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs, from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous period in what is now North America, South America, Europe, and Asia.
Description
Nodosaurids, like their close relatives the ankylosaurids, wer ...
within the Ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the order Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs. ...
. This is still a usual classification, ''Hylaeosaurus'' being recovered as a basal nodosaurid in most exact cladistic
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups (" clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived char ...
analyses, sometimes more precisely as a member of the Polacanthinae
Polacanthinae is a subfamily of ankylosaurs, most often nodosaurids, from the Late Jurassic through Early Cretaceous of Europe and potentially North America and Asia. The group is defined as the largest clade closer to '' Polacanthus foxii'' tha ...
, and thus being related to '' Gastonia'' and ''Polacanthus''. However, in the 1990s, the polacanthines were sometimes seen as basal ankylosaurid
Ankylosauridae () is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to Nodosauridae. The oldest known Ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Pal ...
s, because they were mistakenly believed to have small tail-clubs. A more popular alternative today is that they formed a Polacanthidae, a basal group outside of the nodosaurids + ankylosaurids clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
.
A 2012 study finding ''Hylaeosaurus'' to be a basal nodosaurid but not a polacanthine is shown in this cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ...
:
See also
*Timeline of ankylosaur research
This timeline of ankylosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the history of paleontology focused on the ankylosaurs, quadrupedal herbivorous dinosaurs who were protected by a covering bony plates and spikes and sometimes by a club ...
References
External links
Paper Dinosaurs, 1824–1969, from Linda Hall Library.
{{Taxonbar, from=Q131770 Nodosaurids Valanginian life Early Cretaceous dinosaurs of Europe Cretaceous England Fossils of England Fossil taxa described in 1833 Taxa named by Gideon Mantell Ornithischian genera