Hyena Bestiary on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Hyenas, or hyaenas (from
Hyenas, or hyaenas (from
 The descendants of ''Plioviverrops'' reached their peak 15 million years ago, with more than 30 species having been identified. Unlike most modern hyena species, which are specialised bone-crushers, these dog-like hyenas were nimble-bodied, wolfish animals; one species among them was ''
The descendants of ''Plioviverrops'' reached their peak 15 million years ago, with more than 30 species having been identified. Unlike most modern hyena species, which are specialised bone-crushers, these dog-like hyenas were nimble-bodied, wolfish animals; one species among them was ''
 The four extant species are the striped hyena (''Hyaena hyaena''), the brown hyena (''Parahyaena brunnea''), the spotted hyena (''Crocuta crocuta''), and the aardwolf (''Proteles cristata'').
The
The four extant species are the striped hyena (''Hyaena hyaena''), the brown hyena (''Parahyaena brunnea''), the spotted hyena (''Crocuta crocuta''), and the aardwolf (''Proteles cristata'').
The
 The list follows McKenna and Bell's ''Classification of Mammals'' for prehistoric genera (1997)Malcolm C. McKenna, Susan K. Bell: ''Classification of Mammals: Above the Species Level'', Columbia University Press, New York 1997, 631 Seiten, and Wozencraft (2005) in Wilson and Reeders ''
The list follows McKenna and Bell's ''Classification of Mammals'' for prehistoric genera (1997)Malcolm C. McKenna, Susan K. Bell: ''Classification of Mammals: Above the Species Level'', Columbia University Press, New York 1997, 631 Seiten, and Wozencraft (2005) in Wilson and Reeders ''
 Hyenas have relatively short torsos and are fairly massive and
Hyenas have relatively short torsos and are fairly massive and
Sketches of Indian Field Sports: With Observations on the Animals; Also an Account of Some of the Customs of the Inhabitants; with a Description of the Art of Catching Serpents, as Practiced by the Conjoors and Their Method of Curing Themselves when Bitten: with Remarks on Hydrophobia and Rabid Animals
' p. 45-46, R. Jennings, 1827Stevenson-Hamilton, James (1917)
Animal life in Africa
Vol. 1'', p.95, London : William Heinemann The spotted hyena is renowned for its strong bite proportional to its size, but a number of other animals (including the

 Hyenas groom themselves often like
Hyenas groom themselves often like

 Spotted hyenas vary in their folkloric and mythological depictions, depending on the ethnic group from which the tales originate. It is often difficult to know whether spotted hyenas are the specific hyena species featured in such stories, particularly in West Africa, as both spotted and striped hyenas are often given the same names. In western African tales, spotted hyenas are sometimes depicted as bad
Spotted hyenas vary in their folkloric and mythological depictions, depending on the ethnic group from which the tales originate. It is often difficult to know whether spotted hyenas are the specific hyena species featured in such stories, particularly in West Africa, as both spotted and striped hyenas are often given the same names. In western African tales, spotted hyenas are sometimes depicted as bad
 Hyenas, or hyaenas (from
Hyenas, or hyaenas (from Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
, ), are feliform
Feliformia is a suborder within the order Carnivora consisting of "cat-like" carnivorans, including cats (large and small), hyenas, mongooses, viverrids, and related taxa. Feliformia stands in contrast to the other suborder of Carnivora, Caniform ...
carnivora
Carnivora is a Clade, monophyletic order of Placentalia, placental mammals consisting of the most recent common ancestor of all felidae, cat-like and canidae, dog-like animals, and all descendants of that ancestor. Members of this group are f ...
n mammals of the family Hyaenidae . With only four extant species (each in its own genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
), it is the fifth-smallest family
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its ...
in the Carnivora and one of the smallest in the class Mammalia
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur o ...
. Despite their low diversity, hyenas are unique and vital components of most Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
n ecosystems.
Although phylogenetically
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
closer to felines
The Felinae are a subfamily of the family Felidae. This subfamily comprises the small cats having a bony hyoid, because of which they are able to purr but not roar.
Other authors have proposed an alternative definition for this subfamily: as c ...
and viverrid
Viverridae is a family of small to medium-sized, feliform mammals. The viverrids () comprise 33 species placed in 14 genera. This family was named and first described by John Edward Gray in 1821. Viverrids occur all over Africa, southern Europe, ...
s, as part of suborder Feliformia, hyenas are behaviourally and morphologically similar to canids
Canidae (; from Latin, ''canis'', "dog") is a biological family of dog-like carnivorans, colloquially referred to as dogs, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a canid (). There are three subfamilies found within th ...
in several elements due to convergent evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last com ...
; both hyenas and canines are non-arboreal
Arboreal locomotion is the Animal locomotion, locomotion of animals in trees. In habitats in which trees are present, animals have evolved to move in them. Some animals may scale trees only occasionally, but others are exclusively arboreal. Th ...
, cursorial
A cursorial organism is one that is adapted specifically to run. An animal can be considered cursorial if it has the ability to run fast (e.g. cheetah) or if it can keep a constant speed for a long distance (high endurance). "Cursorial" is often u ...
hunters that catch prey with their teeth rather than claws. Both eat food quickly and may store it, and their calloused feet with large, blunt, nonretractable claws are adapted for running and making sharp turns. However, hyenas' grooming, scent marking
In ethology, territory is the sociographical area that an animal consistently defends against conspecific competition (or, occasionally, against animals of other species) using agonistic behaviors or (less commonly) real physical aggression. ...
, defecation habits, mating and parental behavior are consistent with the behavior of other feliforms.
Hyenas feature prominently in the folklore and mythology of human cultures that live alongside them. Hyenas are commonly viewed as frightening and worthy of contempt. In some cultures, hyenas are thought to influence people's spirits, rob graves, and steal livestock and children. Other cultures associate them with witchcraft, using their body parts in traditional African medicine
Traditional African medicine is a range of traditional medicine disciplines involving Indigenous peoples of Africa, indigenous herbalism and Traditional African religions, African spirituality, typically including divination, diviners, midwives, ...
.
Evolution
Origins
Hyenas originated in the jungles ofMiocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
Eurasia 22 million years ago, when most early feliform species were still largely arboreal
Arboreal locomotion is the Animal locomotion, locomotion of animals in trees. In habitats in which trees are present, animals have evolved to move in them. Some animals may scale trees only occasionally, but others are exclusively arboreal. Th ...
. The first ancestral hyenas were likely similar to the modern African civet
The African civet (''Civettictis civetta'') is a large viverrid native to sub-Saharan Africa, where it is considered common and widely distributed in woodlands and secondary forests. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List since 2008 ...
; one of the earliest hyena species described, ''Plioviverrops
''Plioviverrops'' is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivore of the family Hyaenidae, endemic to Southern Europe during the Late Miocene
The Late Miocene (also known as Upper Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch made ...
'', was a lithe, civet-like animal that inhabited Eurasia 20–22 million years ago, and is identifiable as a hyaenid by the structure of the middle ear
The middle ear is the portion of the ear medial to the eardrum, and distal to the oval window of the cochlea (of the inner ear).
The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles, which transfer the vibrations of the eardrum into waves in the ...
and dentition. The lineage of ''Plioviverrops'' prospered, and gave rise to descendants with longer legs and more pointed jaws, a direction similar to that taken by canids in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
.
Hyenas then diversified into two distinct types: lightly built dog-like hyenas and robust bone-crushing hyenas. Although the dog-like hyenas thrived 15 million years ago (with one taxon
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ...
having colonised North America), they became extinct after a change in climate, along with the arrival of canids into Eurasia. Of the dog-like hyena lineage, only the insectivorous aardwolf
The aardwolf (''Proteles cristata'') is an insectivorous species of hyena, native to East and Southern Africa. Its name means "earth-wolf" in Afrikaans and Dutch. It is also called maanhaar-jackal (Afrikaans for " mane-jackal"), termite-eatin ...
survived, while the bone-crushing hyenas (including the extant
Extant is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Extant taxon, a taxon which is not extinct, ...
spotted, brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model used ...
and striped hyenas) became the undisputed top scavengers of Eurasia and Africa.
Rise and fall of the dog-like hyenas
Ictitherium
''Ictitherium'' is an extinct genus belonging to the family (biology), family Hyaenidae and the subfamily Ictitheriinae erected by Trouessart in 1897. ''Ictitherium'' species were endemic to Eurasia and Africa during the Middle Miocene through th ...
viverrinum'', which was similar to a jackal
Jackals are medium-sized canids native to Africa and Eurasia. While the word "jackal" has historically been used for many canines of the subtribe canina, in modern use it most commonly refers to three species: the closely related black-backed ...
. The dog-like hyenas were numerous; in some Miocene fossil sites, the remains of ''Ictitherium'' and other dog-like hyenas outnumber those of all other carnivores combined. The decline of the dog-like hyenas began 5–7 million years ago during a period of climate change, exacerbated by canid
Canidae (; from Latin, ''canis'', "dog") is a biological family of dog-like carnivorans, colloquially referred to as dogs, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a canid (). There are three subfamilies found within the ...
s crossing the Bering land bridge
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of ...
to Eurasia. One species, '' Chasmaporthetes ossifragus'', managed to cross the land bridge into North America, being the only hyena to do so. ''Chasmaporthetes'' managed to survive for some time in North America by deviating from the endurance-running and bone-crushing niches monopolized by canids, and developing into a cheetah
The cheetah (''Acinonyx jubatus'') is a large cat native to Africa and central Iran. It is the fastest land animal, estimated to be capable of running at with the fastest reliably recorded speeds being , and as such has evolved specialized ...
-like sprinter. Most of the dog-like hyenas had died off by 1.5 million years ago.
Bone-crushing hyenas
By 10–14 million years ago, the hyena family had split into two distinct groups: dog-like hyenas and bone-crushing hyenas. The arrival of the ancestral bone-crushing hyenas coincided with the decline of the similarly built familyPercrocutidae
Percrocutidae is an extinct family of hyena-like feliform carnivores endemic to Asia, Africa, and Southern Europe from the Middle Miocene through the Pliocene, existing for about .
The first percrocutids are known from the middle Miocene of Eur ...
. The bone-crushing hyenas survived the changes in climate and the arrival of canids, which wiped out the dog-like hyenas, though they never crossed into North America, as their niche there had already been taken by the dog subfamily Borophaginae
The extinct Borophaginae form one of three subfamilies found within the canid family. The other two canid subfamilies are the extinct Hesperocyoninae and extant Caninae. Borophaginae, called "bone-crushing dogs", were endemic to North America du ...
. By 5 million years ago, the bone-crushing hyenas had become the dominant scavengers of Eurasia, primarily feeding on large herbivore carcasses felled by sabre-toothed cat
Machairodontinae is an extinct subfamily of carnivoran mammals of the family Felidae (true cats). They were found in Asia, Africa, North America, South America, and Europe from the Miocene to the Pleistocene, living from about 16 million until ...
s. One genus, ''Pachycrocuta
''Pachycrocuta'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric hyenas. The largest and most well-researched species is ''Pachycrocuta brevirostris'', colloquially known as the giant short-faced hyena as it stood about at the shoulder and it is estimated to ...
'', was a 200 kg (440 lb) mega-scavenger that could splinter the bones of elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae an ...
s. With the decline of large herbivores by the late ice age, ''Pachycrocuta'' was replaced by the smaller ''Crocuta''.
Rise of modern hyenas
 The four extant species are the striped hyena (''Hyaena hyaena''), the brown hyena (''Parahyaena brunnea''), the spotted hyena (''Crocuta crocuta''), and the aardwolf (''Proteles cristata'').
The
The four extant species are the striped hyena (''Hyaena hyaena''), the brown hyena (''Parahyaena brunnea''), the spotted hyena (''Crocuta crocuta''), and the aardwolf (''Proteles cristata'').
The aardwolf
The aardwolf (''Proteles cristata'') is an insectivorous species of hyena, native to East and Southern Africa. Its name means "earth-wolf" in Afrikaans and Dutch. It is also called maanhaar-jackal (Afrikaans for " mane-jackal"), termite-eatin ...
can trace its lineage directly back to ''Plioviverrops'' 15 million years ago, and is the only survivor of the dog-like hyena lineage. Its success is partly attributed to its insectivorous diet, for which it faced no competition from canids crossing from North America. It is likely that its unrivaled ability to digest the terpene
Terpenes () are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n > 1. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predominantly by plants, particularly conifers. Terpenes ar ...
excretions from soldier termite
Termites are small insects that live in colonies and have distinct castes (eusocial) and feed on wood or other dead plant matter. Termites comprise the infraorder Isoptera, or alternatively the epifamily Termitoidae, within the order Blattode ...
s is a modification of the strong digestive system its ancestors used to consume fetid carrion.
The striped hyena may have evolved from ''Hyaenictitherium namaquensis'' of Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. Striped hyena fossils are common in Africa, with records going back as far as the Villafranchian
Villafranchian age ( ) is a period of geologic time (3.5–1.0 Ma) spanning the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene used more specifically with European Land Mammal Ages. Named by Italian geologist Lorenzo Pareto for a sequence of terrestrial s ...
. As fossil striped hyenas are absent from the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
region, it is likely that the species is a relatively late invader to Eurasia, having likely spread outside Africa only after the extinction of spotted hyena
The spotted hyena (''Crocuta crocuta''), also known as the laughing hyena, is a hyena species, currently classed as the sole extant member of the genus ''Crocuta'', native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is listed as being of least concern by the IUC ...
s in Asia at the end of the Ice Age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
. The striped hyena occurred for some time in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
during the Pleistocene, having been particularly widespread in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
. It also occurred in Montmaurin
Montmaurin () is a commune in the Haute-Garonne department of southwestern France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territori ...
, Hollabrunn
Hollabrunn () is a district capital town in the Austrian States of Austria, state of Lower Austria, on the Göllersbach river. It is situated in the heart of the biggest wine region of Austria, the Weinviertel.
History
The surroundings of Ho ...
in Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, the Furninha Cave in Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
and the Genista Caves in Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
. The European form was similar in appearance to modern populations, but was larger, being comparable in size to the brown hyena
The brown hyena (''Parahyaena brunnea''), also called strandwolf, is a species of hyena found in Namibia, Botswana, western and southern Zimbabwe, southern Mozambique and South Africa. It is the only extant species in the genus ''Parahyaena''. It ...
.
The spotted hyena
The spotted hyena (''Crocuta crocuta''), also known as the laughing hyena, is a hyena species, currently classed as the sole extant member of the genus ''Crocuta'', native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is listed as being of least concern by the IUC ...
(''Crocuta crocuta'') diverged from the striped and brown hyena 10 million years ago. Its direct ancestor was the Indian ''Crocuta sivalensis'', which lived during the Villafranchian. Ancestral spotted hyenas probably developed social behaviours in response to increased pressure from rivals on carcasses, thus forcing them to operate in teams. Spotted hyenas evolved sharp carnassial
Carnassials are paired upper and lower teeth modified in such a way as to allow enlarged and often self-sharpening edges to pass by each other in a shearing manner. This adaptation is found in carnivorans, where the carnassials are the modified f ...
s behind their crushing premolars, therefore they did not need to wait for their prey to die, and thus became pack hunters as well as scavengers. They began forming increasingly larger territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or an ...
, necessitated by the fact that their prey was often migratory, and long chases in a small territory would have caused them to encroach into another clan's turf. Spotted hyenas spread from their original homeland during the Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, widely known by its previous designation of Middle Pleistocene, is an age in the international geologic timescale or a stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. The ...
, and quickly colonised a very wide area from Europe, to southern Africa and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. With the decline of grasslands 12,500 years ago, Europe experienced a massive loss of lowland habitats favoured by spotted hyenas, and a corresponding increase in mixed woodlands. Spotted hyenas, under these circumstances, would have been outcompeted by wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; plural, : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large Canis, canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of Canis lupus, subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been reco ...
and human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
s, who were as much at home in forests as in open lands—and in highlands as in lowlands. Spotted hyena populations began to shrink after roughly 20,000 years ago, completely disappearing from Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
between 11 and 14 thousand years ago, and earlier in some areas.
Genera of the Hyaenidae (extinct and recent)
 The list follows McKenna and Bell's ''Classification of Mammals'' for prehistoric genera (1997)Malcolm C. McKenna, Susan K. Bell: ''Classification of Mammals: Above the Species Level'', Columbia University Press, New York 1997, 631 Seiten, and Wozencraft (2005) in Wilson and Reeders ''
The list follows McKenna and Bell's ''Classification of Mammals'' for prehistoric genera (1997)Malcolm C. McKenna, Susan K. Bell: ''Classification of Mammals: Above the Species Level'', Columbia University Press, New York 1997, 631 Seiten, and Wozencraft (2005) in Wilson and Reeders ''Mammal Species of the World
''Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference'' is a standard reference work in mammalogy giving descriptions and bibliographic data for the known species of mammals. It is now in its third edition, published in late 2005, ...
'' for extant genera. The percrocutids are, in contrast to McKenna and Bell's classification, not included as a subfamily into the Hyaenidae, but as the separate family Percrocutidae
Percrocutidae is an extinct family of hyena-like feliform carnivores endemic to Asia, Africa, and Southern Europe from the Middle Miocene through the Pliocene, existing for about .
The first percrocutids are known from the middle Miocene of Eur ...
(though they are generally grouped as sister-taxa to hyenas). Furthermore, the living brown hyena and its closest extinct relatives are not included in the genus ''Pachycrocuta'', but in the genus ''Parahyaena''. The Protelinae (aardwolves) are not treated as a separate subfamily, but included in the Hyaeninae.
* Family Hyaenidae
** Subfamily ''Incertae sedis''
*** †'' Tongxinictis'' (Middle Miocene of Asia)
** †Subfamily Ictitheriinae
*** †'' Herpestides'' (Early Miocene of Africa and Eurasia)
*** †''Plioviverrops
''Plioviverrops'' is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivore of the family Hyaenidae, endemic to Southern Europe during the Late Miocene
The Late Miocene (also known as Upper Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch made ...
'' (including ''Jordanictis'', ''Protoviverrops'', ''Mesoviverrops''; Early Miocene to Early Pliocene of Europe, Late Miocene of Asia)
*** †''Ictitherium
''Ictitherium'' is an extinct genus belonging to the family (biology), family Hyaenidae and the subfamily Ictitheriinae erected by Trouessart in 1897. ''Ictitherium'' species were endemic to Eurasia and Africa during the Middle Miocene through th ...
'' (=''Galeotherium''; including ''Lepthyaena'', ''Sinictitherium'', ''Paraictitherium''; Middle Miocene of Africa, Late Miocene to Early Pliocene of Eurasia)
*** †''Thalassictis
''Thalassictis'' is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivore in the family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose ...
'' (including ''Palhyaena'', ''Miohyaena'', ''Hyaenictitherium'', ''Hyaenalopex''; Middle to Late Miocene of Asia, Late Miocene of Africa and Europe)
*** †'' Hyaenotherium'' (Late Miocene to Early Pliocene of Eurasia)
*** †'' Miohyaenotherium''(Late Miocene of Europe)
*** †''Lycyaena
''Lycyaena'' is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivore in the family Hyaenidae.
''Lycyaena'' was a cursorial hunting hyaena as opposed to full-time scavenger. It has been suggested by R. F. EwerR. F. Ewer, ''The Carnivores'' (1973) that ''Lyc ...
'' (Late Miocene of Eurasia)
*** †'' Tungurictis'' (Middle Miocene of Africa and Eurasia)
*** †''Protictitherium
''Protictitherium'' ( gr. first striking beast) is an extinct genus of hyaena that lived across Europe and Asia during the Middle and Late Miocene, it is often considered to be the first hyaena since it contains some of the oldest fossils of th ...
'' (Middle Miocene of Africa and Asia, Middle to Late Miocene of Europe)
** Subfamily Hyaeninae
*** †'' Palinhyaena'' (Late Miocene of Asia)
*** †'' Ikelohyaena'' (Early Pliocene of Africa)
*** '' Hyaena'' (=''Euhyaena'',=''Parahyaena''; including striped hyena, ''Pliohyaena'', ''Pliocrocuta'', ''Anomalopithecus'') Early Pliocene (?Middle Miocene) to Recent of Africa, Late Pliocene (?Late Miocene) to Late Pleistocene of Europe, Late Pliocene to recent in Asia
*** ''Parahyaena
The brown hyena (''Parahyaena brunnea''), also called strandwolf, is a species of hyena found in Namibia, Botswana, western and southern Zimbabwe, southern Mozambique and South Africa. It is the only extant species in the genus ''Parahyaena''. It ...
'' (=''Hyaena''; brown hyena
The brown hyena (''Parahyaena brunnea''), also called strandwolf, is a species of hyena found in Namibia, Botswana, western and southern Zimbabwe, southern Mozambique and South Africa. It is the only extant species in the genus ''Parahyaena''. It ...
Pliocene to Europe)
*** †'' Hyaenictis'' (Late Miocene of Asia?, Late Miocene of Europe, Early Pliocene (?Early Pleistocene) of Africa)
*** †'' Leecyaena'' (Late Miocene and/or Early Pliocene of Asia)
*** †''Chasmaporthetes
''Chasmaporthetes'', also known as hunting or running hyena, is an extinct genus of hyenas distributed in Eurasia, North America, and Africa during the Pliocene-Pleistocene epochs, living from 4.9 million to 780,000 years ago, existing for about ...
'' (=''Ailuriaena''; including ''Lycaenops'', ''Euryboas''; Late Miocene to Early Pleistocene of Eurasia, Early Pliocene to Late Pliocene or Early Pleistocene of Africa, Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene of North America)
*** †''Pachycrocuta
''Pachycrocuta'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric hyenas. The largest and most well-researched species is ''Pachycrocuta brevirostris'', colloquially known as the giant short-faced hyena as it stood about at the shoulder and it is estimated to ...
'' (Pliocene and Pleistocene of Eurasia and Africa)
*** †'' Adcrocuta'' (Late Miocene of Eurasia)
*** ''Crocuta
''Crocuta'' is a genus of hyena containing the largest living member of the family, the spotted hyena ''(Crocuta crocuta)''. Several fossil species are known as well.
Taxonomy
It is still unclear whether the genus evolved in Africa or Asia, altho ...
'' (=''Crocotta''; including ''Eucrocuta''; spotted hyena
The spotted hyena (''Crocuta crocuta''), also known as the laughing hyena, is a hyena species, currently classed as the sole extant member of the genus ''Crocuta'', native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is listed as being of least concern by the IUC ...
and cave hyena
The cave hyena (''Crocuta crocuta spelaea''), also known as the Ice Age spotted hyena, was a paleosubspecies of spotted hyena which ranged from the Iberian Peninsula to eastern Siberia. It is one of the best known mammals of the Ice Age and is w ...
. Late Pliocene to recent of Africa, Late Pliocene to Late Pleistocene of Eurasia)
** Subfamily Protelinae
*** ''Proteles
''Proteles'' is a genus of distinctive hyenas which contain the aardwolf ''(Proteles cristatus)'' and its close fossil relatives. It is the only genus of the subfamily Protelinae.
While the oldest fossils definitely belonging to ''Proteles'' date ...
'' (=''Geocyon''; aardwolf
The aardwolf (''Proteles cristata'') is an insectivorous species of hyena, native to East and Southern Africa. Its name means "earth-wolf" in Afrikaans and Dutch. It is also called maanhaar-jackal (Afrikaans for " mane-jackal"), termite-eatin ...
. Pleistocene to Recent of Africa)
Phylogeny
The following cladogram illustrates the phylogenetic relationships between extant and extinct hyaenids based on the morphological analysis by Werdelin & Solounias (1991), as updated by Turner et al. (2008). A more recent molecular analysis agrees on the phylogenetic relationship between the four extant hyaenidae species (Koepfli ''et al'', 2006).Characteristics
Build

 Hyenas have relatively short torsos and are fairly massive and
Hyenas have relatively short torsos and are fairly massive and wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly u ...
-like in build, but have lower hind quarters, high withers and their backs slope noticeably downward towards their rumps. The forelegs are high, while the hind legs are very short and their necks are thick and short. Their skulls superficially resemble those of large canids, but are much larger and heavier, with shorter facial portions. Hyenas are digitigrade
In terrestrial vertebrates, digitigrade () locomotion is walking or running on the toes (from the Latin ''digitus'', 'finger', and ''gradior'', 'walk'). A digitigrade animal is one that stands or walks with its toes (metatarsals) touching the groun ...
, with the fore and hind paws having four digits each and sporting bulging pawpads. Like canids, hyenas have short, blunt, non-retractable claws. Their pelage
Fur is a thick growth of hair that covers the skin of mammals. It consists of a combination of oily #Guard hair, guard hair on top and thick #Down hair, underfur beneath. The guard hair keeps moisture from reaching the skin; the underfur acts as ...
is sparse and coarse with poorly developed or absent underfur. Most species have a rich mane of long hair running from the withers or from the head. With the exception of the spotted hyena, hyaenids have striped coats, which they likely inherited from their viverrid ancestors. Their ears are large and have simple basal ridges and no marginal bursa. Their vertebral column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordata, ...
, including the cervical region are of limited mobility. Hyenas have no baculum
The baculum (also penis bone, penile bone, or ''os penis'', ''os genitale'' or ''os priapi'') is a bone found in the penis of many placental mammals. It is absent from the human penis, but present in the penises of some primates, such as the ...
. Hyenas have one more pair of ribs than canids do, and their tongues are rough like those of felids and viverrids. Males in most hyena species are larger than females, though the spotted hyena is exceptional, as it is the female of the species that outweighs and dominates the male. Also, unlike other hyenas, the female spotted hyena's external genitalia closely resembles that of the male.
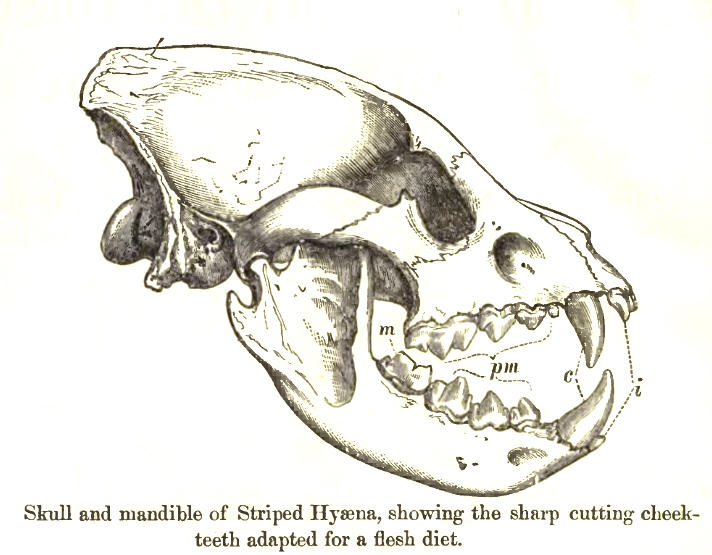
Their dentition
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiolo ...
is similar to that of the canid
Canidae (; from Latin, ''canis'', "dog") is a biological family of dog-like carnivorans, colloquially referred to as dogs, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a canid (). There are three subfamilies found within the ...
, but is more specialised for consuming coarse food and crushing bones. The carnassial
Carnassials are paired upper and lower teeth modified in such a way as to allow enlarged and often self-sharpening edges to pass by each other in a shearing manner. This adaptation is found in carnivorans, where the carnassials are the modified f ...
s, especially the upper, are very powerful and are shifted far back to the point of exertion of peak pressure on the jaws. The other teeth, save for the underdeveloped upper molars
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone to ...
, are powerful, with broad bases and cutting edges. The canines
Canine may refer to:
Zoology and anatomy
* a dog-like Canid animal in the subfamily Caninae
** ''Canis'', a genus including dogs, wolves, coyotes, and jackals
** Dog, the domestic dog
* Canine tooth, in mammalian oral anatomy
People with the surn ...
are short, but thick and robust. Labiolingually, their mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movabl ...
s are much stronger at the canine teeth than in canids, reflecting the fact that hyenas crack bones with both their anterior dentition and premolars
The premolars, also called premolar teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per quadrant in the permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth ...
, unlike canids, which do so with their post-carnassial molars. The strength of their jaws is such that both striped and spotted hyenas have been recorded to kill dogs with a single bite to the neck without breaking the skin. Daniel Johnson (1827) Sketches of Indian Field Sports: With Observations on the Animals; Also an Account of Some of the Customs of the Inhabitants; with a Description of the Art of Catching Serpents, as Practiced by the Conjoors and Their Method of Curing Themselves when Bitten: with Remarks on Hydrophobia and Rabid Animals
' p. 45-46, R. Jennings, 1827Stevenson-Hamilton, James (1917)
Animal life in Africa
Vol. 1'', p.95, London : William Heinemann The spotted hyena is renowned for its strong bite proportional to its size, but a number of other animals (including the
Tasmanian devil
The Tasmanian devil (''Sarcophilus harrisii'') (palawa kani: purinina) is a carnivorous marsupial of the family Dasyuridae. Until recently, it was only found on the island state of Tasmania, but it has been reintroduced to New South Wales in ...
) are proportionately stronger. The aardwolf has greatly reduced cheek teeth, sometimes absent in the adult, but otherwise has the same dentition as the other three species. The dental formula
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiolo ...
for all hyena species is:
Although hyenas lack perineal scent glands, they have a large pouch of naked skin located at the anal opening. Large anal gland
Anal may refer to:
Related to the anus
*Related to the anus of animals:
** Anal fin, in fish anatomy
** Anal vein, in insect anatomy
** Anal scale, in reptile anatomy
*Related to the human anus:
** Anal sex, a type of sexual activity involving s ...
s above the anus open into this pouch. Several sebaceous gland
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number ...
s are present between the openings of the anal glands and above them. These glands produce a white, creamy secretion that the hyenas paste onto grass stalks. The odor of this secretion is very strong, smelling of boiling cheap soap
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are use ...
or burning, and can be detected by humans several meters downwind. The secretions are primarily used for territorial marking
In ethology, territory is the sociographical area that an animal consistently defends against conspecific competition (or, occasionally, against animals of other species) using agonistic behaviors or (less commonly) real physical aggression. ...
, though both the aardwolf and the striped hyena will spray
Spray or spraying commonly refer to:
* Spray (liquid drop)
** Aerosol spray
** Blood spray
** Hair spray
** Nasal spray
** Pepper spray
** PAVA spray
** Road spray or tire spray, road debris kicked up from a vehicle tire
** Sea spray, refers to ...
them when attacked.
Behavior

felids
Felidae () is the family of mammals in the order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a felid (). The term "cat" refers both to felids in general and specifically to the do ...
and viverrids
Viverridae is a family (biology), family of small to medium-sized, feliform mammals. The viverrids () comprise 33 species placed in 14 genera. This family was named and first described by John Edward Gray in 1821. Viverrids occur all over Africa, ...
, and their way of licking their genitals is very cat-like (sitting on the lower back, legs spread with one leg pointing vertically upward). However, unlike other feliforms, they do not "wash" their faces. They defecate in the same manner as other Carnivora, though they never raise their legs as canids do when urinating, as urination serves no territorial function for them. Instead, hyenas mark their territories using their anal glands, a trait found also in viverrids and mustelid
The Mustelidae (; from Latin ''mustela'', weasel) are a family of carnivorous mammals, including weasels, badgers, otters, ferrets, martens, minks and wolverines, among others. Mustelids () are a diverse group and form the largest family in ...
s, but not canids and felid
Felidae () is the family of mammals in the order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a felid (). The term "cat" refers both to felids in general and specifically to the dom ...
s. When attacked by lions or dogs, striped and brown hyenas will feign death, though the spotted hyena will defend itself ferociously. The spotted hyena is very vocal, producing a number of different sounds consisting of whoops, grunts, groans, lows, giggles, yells, growls, laughs and whines. The striped hyena is comparatively silent, its vocalizations being limited to a chattering laugh and howling.
left, Whoop of a spotted hyena in Umfolosi Game Park, South Africa.
Mating
In biology, mating is the pairing of either opposite-sex or hermaphroditic organisms for the purposes of sexual reproduction. ''Fertilization'' is the fusion of two gametes. ''Copulation'' is the union of the sex organs of two sexually reproduc ...
between hyenas involves a number of short copulations with brief intervals, unlike canids, who generally engage in a single, drawn out copulation. Spotted hyena cubs are born almost fully developed, with their eyes open and erupting incisors and canines, though lacking adult markings. In contrast, striped hyena cubs are born with adult markings, closed eyes and small ears. Hyenas do not regurgitate food for their young and male spotted hyenas play no part in raising their cubs, though male striped hyenas do so.
The striped hyena is primarily a scavenger, though it will also attack and kill any animals it can overcome, and will supplement its diet with fruit. The spotted hyena, though it also scavenges occasionally, is an active pack hunter of medium to large sized ungulates
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, cam ...
, which it catches by wearing them down in long chases and dismembering them in a canid-like manner. The aardwolf is primarily an insectivore, specialised for feeding on termite
Termites are small insects that live in colonies and have distinct castes (eusocial) and feed on wood or other dead plant matter. Termites comprise the infraorder Isoptera, or alternatively the epifamily Termitoidae, within the order Blattode ...
s of the genus ''Trinervitermes
''Trinervitermes'' is a termite genus belonging to family Termitidae. Members are native to the Old World. They inhabit grasslands and store grass in their nests or mounds, just below the ground surface. Their grass-collecting activities are main ...
'' and ''Hodotermes
''Hodotermes'' (from Greek ὁδός (hodós), travelling; Latin '' termes'', woodworm) is a genus of African harvester termites in the Hodotermitidae. They range from Palaearctic North Africa, through the East African savannas to the karroid ...
'', which it consumes by licking them up with its long, broad tongue. An aardwolf can eat 300,000 ''Trinervitermes'' on a single outing.
Spotted hyena
The spotted hyena (''Crocuta crocuta''), also known as the laughing hyena, is a hyena species, currently classed as the sole extant member of the genus ''Crocuta'', native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is listed as being of least concern by the IUC ...
s may kill as many as 95% of the animals they eat, while striped hyenas are largely scavenger
Scavengers are animals that consume dead organisms that have died from causes other than predation or have been killed by other predators. While scavenging generally refers to carnivores feeding on carrion, it is also a herbivorous feeding b ...
s. Generally, hyenas are known to drive off larger predators, like lions, from their kills, despite having a reputation in popular culture for being cowardly. Hyenas are primarily nocturnal animals, but sometimes venture from their lairs in the early-morning hours. With the exception of the highly social spotted hyena, hyenas are generally not gregarious animals, though they may live in family groups and congregate at kills.
Spotted hyenas are one of the few mammals other than bats known to survive infection with rabies virus and have showed little or no disease-induced mortality during outbreaks in sympatric carnivores. Despite this perceived unique disease resistance, little is known about the immune system of spotted hyenas, and even less is known about other Hyaenidae species.
Relationships with humans
Folklore, mythology and literature

 Spotted hyenas vary in their folkloric and mythological depictions, depending on the ethnic group from which the tales originate. It is often difficult to know whether spotted hyenas are the specific hyena species featured in such stories, particularly in West Africa, as both spotted and striped hyenas are often given the same names. In western African tales, spotted hyenas are sometimes depicted as bad
Spotted hyenas vary in their folkloric and mythological depictions, depending on the ethnic group from which the tales originate. It is often difficult to know whether spotted hyenas are the specific hyena species featured in such stories, particularly in West Africa, as both spotted and striped hyenas are often given the same names. In western African tales, spotted hyenas are sometimes depicted as bad Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s who challenge the local animism
Animism (from Latin: ' meaning 'breath, Soul, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct Spirituality, spiritual essence. Potentially, animism perceives all things—Animal, animals, Plant, plants, Ro ...
that exists among the Beng in Côte d’Ivoire
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
. In East Africa, Tabwa
The Lungu people (also known as Rungu or Tabwa) are a Bantu ethnic group living primarily on the southwestern shores of Lake Tanganyika, on the Marungu massif in eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, and in southwestern Tanzania and northeas ...
mythology portrays the spotted hyena as a solar animal that first brought the sun to warm the cold earth, while West African folklore generally shows the hyena as symbolizing immorality, dirty habits, the reversal of normal activities, and other negative traits. In Tanzania, there is a belief that witch
Witchcraft traditionally means the use of Magic (supernatural), magic or supernatural powers to harm others. A practitioner is a witch. In Middle Ages, medieval and early modern Europe, where the term originated, accused witches were usually ...
es use spotted hyenas as mounts. In the Mtwara Region
Mtwara Region (''Mkoa wa Mtwara'' in Swahili) is one of Tanzania's 31 administrative regions. The regional capital is the municipality of Mtwara. Mtwara Region is home to one of the most infuluencial people in Tanzania, the Makonde. Mtwara is ...
of Tanzania, it is believed that a child born at night while a hyena is crying will be likely to grow up to be a thief. In the same area, hyena feces are believed to enable a child to walk at an early age, thus it is not uncommon in that area to see children with hyena dung wrapped in their clothes. The Kaguru
The Kaguru, or Kagulu, are a Bantu ethno-linguistic group based in central Tanzania. The population of Kaguru was predicted to be 217,000 in 1987.
Geography
Ukagura (Kaguraland, about 3,600 square miles) is located around 200 miles west of the ...
of Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and ...
and the Kujamaat of Southern Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 � ...
view hyenas as inedible
{{Short pages monitor Cases of children being taken by hyenas by night are known in southeast Turkmenistan's
IUCN Conservation Union Hyaena Specialist Group
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hyena Mammals of Asia Scavengers Extant Miocene first appearances Taxa named by John Edward Gray eo:Hieno
Bathyz Nature Reserve
The Badhyz State Nature Reserve is a protected area (zapovednik) in south-western Turkmenistan that was established in 1941 and extends over in the Mary and Akhal Provinces. It is located south of the Karakum Desert, and the Tejen River forms i ...
. A further attack on a child was reported around Serakhs
Sarahs (, also written Saraghs, Serahs, Sarakhs, Saragt, or Serakhs, the last a backformation of russian: Серахс) is an oasis city in Ahal Province, Turkmenistan, and the administrative center of Sarahs district ( tk, Sarahs etraby). It is ...
in 1948. Several attacks have occurred in India; in 1962, 9 children were thought to have been taken by hyenas in the town of Bhagalpur
Bhagalpur is a city in the Indian state of Bihar, situated on the southern banks of the river Ganges. It is the 2nd largest city of Bihar by population and also the headquarters of Bhagalpur district and Bhagalpur division. Known as the Silk ...
in the Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West Be ...
State in a six-week period, and 19 children up to the age of four were killed by hyenas in Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
in 1974. A survey of wild animal attacks during a five-year period in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the seco ...
reported that hyenas had attacked three people, causing fewer deaths than wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; plural, : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large Canis, canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of Canis lupus, subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been reco ...
, gaur
The gaur (''Bos gaurus''; ), also known as the Indian bison, is a bovine native to South Asia and Southeast Asia, and has been listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List since 1986. The global population was estimated at a maximum of 21,000 m ...
, boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is no ...
, elephants
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and ...
, tigers
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is the largest living cat species and a member of the genus ''Panthera''. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily preys on un ...
, leopards
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, ...
and sloth bear
The sloth bear (''Melursus ursinus'') is a myrmecophagous bear species native to the Indian subcontinent. It feeds on fruits, ants and termites. It is listed as Vulnerable species, vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, mainly because of habitat loss ...
s.
Hyenas as food and medicine
Hyenas are used for food and medicinal purposes inSomalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
although they are considered haraam
''Haram'' (; ar, حَرَام, , ) is an Arabic term meaning 'Forbidden'. This may refer to either something sacred to which access is not allowed to the people who are not in a state of purity or who are not initiated into the sacred knowle ...
in Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
. This practice dates back to the times of the Ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cultu ...
and Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, who believed that different parts of the hyena's body were effective means to ward off evil and to ensure love and fertility.
References
Citations
General and cited references
* * * * * * * *Further reading
* Funk, Holdger (2010) ''Hyaena: On the Naming and Localisation of an Enigmatic Animal'', GRIN Verlag, * Lawick, Hugo & Goodall, Jane (1971) ''Innocent Killers'', Houghton Mifflin Company Boston * Mills, M. G. L. (2003) ''Kalahari Hyenas: Comparative Behavioral Ecology of Two Species'', The Blackburn PressExternal links
IUCN Conservation Union Hyaena Specialist Group
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hyena Mammals of Asia Scavengers Extant Miocene first appearances Taxa named by John Edward Gray eo:Hieno