Hydrosilanes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hydrosilanes are tetravalent silicon compounds containing one or more Si-H bond. The parent hydrosilane is silane (SiH4). Commonly, hydrosilane refers to

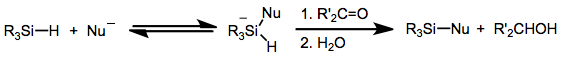
 The reaction is stoichiometric.
The reaction is stoichiometric.
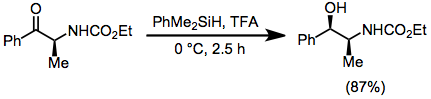
organosilicon
Organosilicon compounds are organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds. Organosilicon chemistry is the corresponding science of their preparation and properties. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic co ...
derivatives. Examples include phenylsilane (PhSiH3) and triethoxysilane
Triethoxysilane is an organosilicon compound with the formula HSi(OC2H5)3. It is a colourless liquid used in precious metal-catalysed hydrosilylation reactions. The resulting triethoxysilyl groups are often valued for attachment to silica surfac ...
((C2H5O)3SiH). Polymers and oligomers terminated with hydrosilanes are resins that are used to make useful materials like caulks.
Synthesis
Trichlorosilane is produced commercially by the reaction of hydrogen chloride with silicon: :Si + 3 HCl → HSiCl3 + H2 Many alkoxy hydrosilanes are generated by alcoholysis of trichlorosilane. One example istriethoxysilane
Triethoxysilane is an organosilicon compound with the formula HSi(OC2H5)3. It is a colourless liquid used in precious metal-catalysed hydrosilylation reactions. The resulting triethoxysilyl groups are often valued for attachment to silica surfac ...
:
:HSiCl3 + 3EtOH → HSi(OEt)3 + 3 HCl
Organohydrosilanes can be prepared by partial hydrosilation of silane itself:
:SiH4 + 3 C2H4 → HSi(C2H5)3
In the laboratory, hydrosilanes classically are prepared by treating chlorosilanes with hydride reagents, such as lithium aluminium hydride
Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li Al H4. It is a white solid, discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947. This compound is used as a reducing agent in organic ...
:
:4ClSi(C2H5)3 + LiAlH4 → 4HSi(C2H5)3 + LiAlCl4
Structure
The silicon-to-hydrogen bond is longer than the C–H bond (148 compared to 105 pm). The Si-H bond is about 10% weaker compared to C-H bonds. Hydrogen is more electronegative than silicon (hence the naming convention of silyl hydrides), which results in the polarization of the Si-H bond to be the reverse of that for the C-H bond. Generally silyl hydrides are colourless with physical properties (solubility, volatility) comparable to hydrocarbons. They can be pyrophoric, reflecting the great driving force for replacing Si-H bonds with Si-O bonds.Reactions and applications
Setting aside silane itself, for which is used mainly in the microelectronics industry as a source of Si, hydrosilanes participate in many reactions. Hydrosilanes are mainly used for diverse styles of reduction in both industrial and laboratory-scale reactions. These including deoxygenation, hydrosilylation, and ionic hydrogenation.Hydrosilylation
SIn hydrosilylation, the Si-H bond adds across multiple bonds in alkenes,alkyne
\ce
\ce
Acetylene
\ce
\ce
\ce
Propyne
\ce
\ce
\ce
\ce
1-Butyne
In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and n ...
s, imines, and carbonyls. The reaction of alkenes is commercially significant. Many organosilicon compounds and materials are prepared in this way. Illustrative is the crosslinking of vinyl-terminated siloxanes:

Conversion to silanols
In the presence of platinum-based catalysts, hydrosilanes react with water to give silanols: :R3SiH + H2O → R3SiOH + H2 The same transformation can be effected with oxygen in the presence of catalysts.Fluoride complexes
In the presence of fluoride ions, hydrosilanes reversibly form hypervalent fluorosilicates with the formula R3Si(F)H−). These species are reducing agents, akin to borohydride.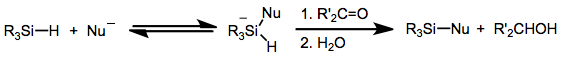
Ionic hydrogenation
Reductions with hydrosilanes Reductions with hydrosilanes are methods used for hydrogenations and hydrogenolysis of organic compounds. The approach is a subset of Ionic hydrogenations. In this particular method, the substrate is treated with a hydrosilane and auxiliary reagent ...
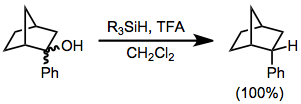
are a subset of ionic hydrogenations. In this type of reaction, carbocations are generated by the action of strong Lewis or Brønsted acids in the presence of hydrosilanes, which then transfer hydride. A typical acid is trifluoroacetic acid (TFA).
: The reaction is stoichiometric.
The reaction is stoichiometric.
Deoxygenation and ionic hydrogenation
Hydrosilanes are used for the deoxygenation of phosphine oxides and sulfoxides. Hydrosilanes serve as hydride donors in some ionic hydrogenations.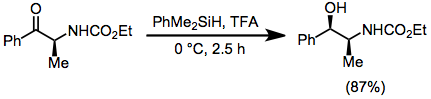
Coordination the metals
Hydrosilanes formsigma complex
In chemistry, a sigma complex or σ-complex usually refers to a family of coordination complexes where one or more ligand interacts with the metal using the bonding electrons in a sigma bond. Dihydrogen complexes are examples. Transition metal ...
es with unsaturated metals. The bonding is similar to that in dihydrogen complexes but stronger. One example is (CH3C5H4)Mn(CO)2(H2SiPh2). Such adducts represent models for and competitors with the oxidative addition of the Si-H bond.
Reduction of or addition to organic substrates
Akin to the hydrosilylation of alkenes, hydrosilanes add to a variety of unsaturated substrates. In one example, PMHS. In one study triethylsilane is used in the conversion of a phenyl azide to an aniline: : In this reactionACCN
ACC Network (ACCN) is an American multinational multichannel television, subscription-television television network, channel owned and operated by ESPN Inc. Dedicated to coverage of the Atlantic Coast Conference, it was announced in July 2016 and ...
is a radical initiator and an aliphatic thiol transfers radical character to the silylhydride. The triethylsilyl free radical then reacts with the azide with expulsion of nitrogen to a N-silylarylaminyl radical which grabs a proton from a thiol completing the catalytic cycle:
:
Further reading
*Hydrogen-terminated silicon surface Hydrogen-terminated silicon surface is a chemically passivated silicon substrate where the surface Si atoms are bonded to hydrogen. The hydrogen-terminated surfaces are hydrophobic, luminescent, and amenable to chemical modification. Hydrogen-ter ...
Selective reading
*References
{{reflist Silanes