|
Electronegative
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity, the more an atom or a substituent group attracts electrons. Electronegativity serves as a simple way to quantitatively estimate the bond energy, and the sign and magnitude of a bond's chemical polarity, which characterizes a bond along the continuous scale from covalent to ionic bonding. The loosely defined term electropositivity is the opposite of electronegativity: it characterizes an element's tendency to donate valence electrons. On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more "pull" it will have on electrons) and the number and locatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
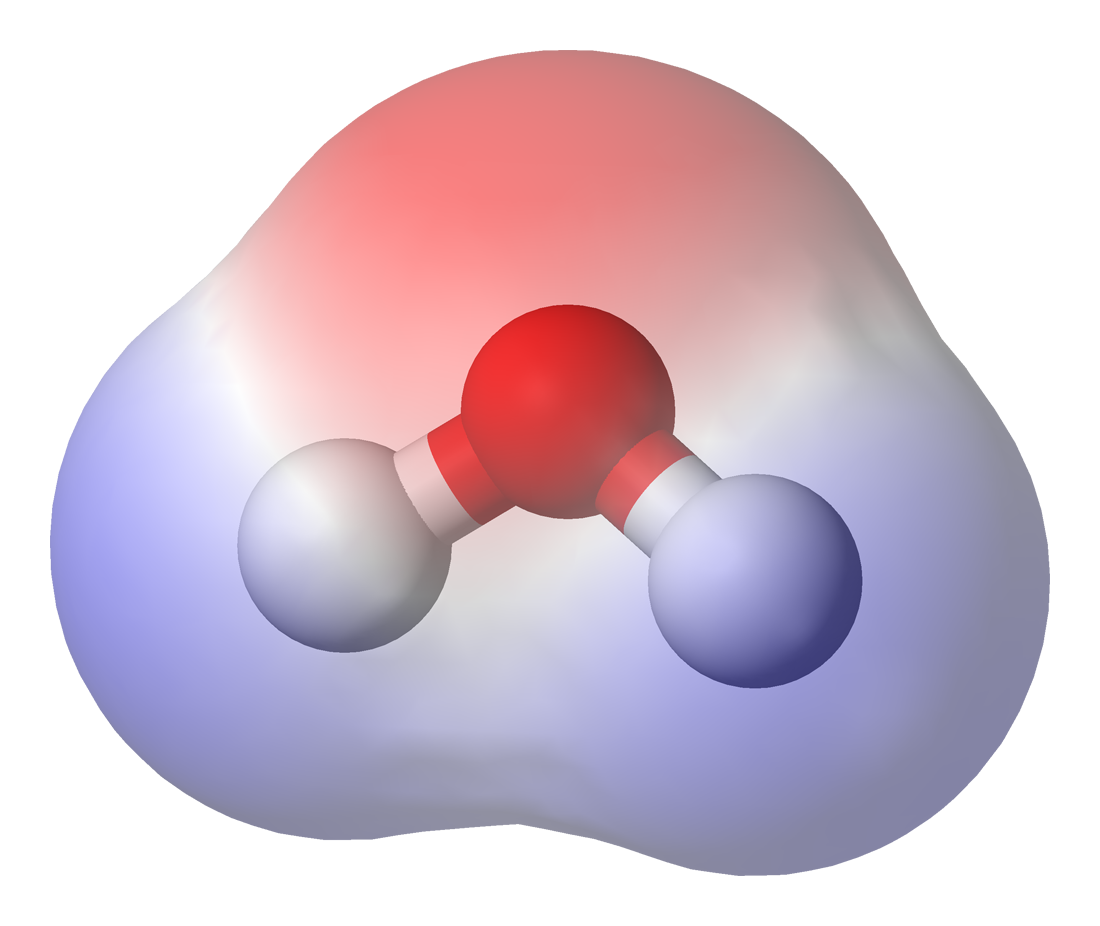
Chemical Polarity
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole-dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alkaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Bonding
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the Coulomb's law, electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, or between two atoms with sharply different electronegativities, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. It is one of the main types of bonding, along with covalent bonding and metallic bonding. Ions are atoms (or groups of atoms) with an electrostatic charge. Atoms that gain electrons make negatively charged ions (called anions). Atoms that lose electrons make positively charged ions (called cations). This transfer of electrons is known as electrovalence in contrast to covalent bond, covalence. In the simplest case, the cation is a metal atom and the anion is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal atom, but these ions can be more complex, e.g. polyatomic ions, polyatomic ions like or . In simpler words, an ionic bond results from the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal to obtain a full valence shell for both atoms. '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodic Trends
In chemistry, periodic trends are specific patterns present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of certain Chemical element, elements when grouped by period (periodic table), period and/or Group (periodic table), group. They were discovered by the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1863. Major periodic trends include atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity, nucleophilicity, electrophilicity, Valence (chemistry), valency, nuclear charge, and metal#Chemical, metallic character. Dmitri Mendeleev, Mendeleev built the foundation of the periodic table. Mendeleev organized the elements based on atomic weight, leaving empty spaces where he believed undiscovered elements would take their places. Mendeleev's discovery of this trend allowed him to predict the existence and properties of three unknown elements, which were later discovered by other chemists and named gallium, scandium, and germanium. English physicist Henry Moseley discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Bond
A chemical bond is the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals, and other structures. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds, or some combination of these effects. Chemical bonds are described as having different strengths: there are "strong bonds" or "primary bonds" such as covalent, ionic and metallic bonds, and "weak bonds" or "secondary bonds" such as dipole–dipole interactions, the London dispersion force, and hydrogen bonding. Since opposite electric charges attract, the negatively charged electrons surrounding the nucleus and the positively charged protons within a nucleus attract each other. Electrons shared between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them. "Constructive quantum mechanical wavefunction interference" stabilizes the paired nuclei (see Theories of chemical bonding). Bonded nuclei maintain an optima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter. Under standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules with the chemical formula, formula , called dihydrogen, or sometimes hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen, or simply hydrogen. Dihydrogen is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Stars, including the Sun, mainly consist of hydrogen in a plasma state, while on Earth, hydrogen is found as the gas (dihydrogen) and in molecular forms, such as in water and organic compounds. The most common isotope of hydrogen (H) consists of one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the 17th century by the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, in 1766–1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance and discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Chemical Education
The ''Journal of Chemical Education'' is a monthly peer-reviewed academic journal available in both print and electronic versions. It is published by the Division of Chemical Education of the American Chemical Society The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a scientific society based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of chemistry. Founded in 1876 at New York University, the ACS currently has more than 155,000 members at all ... and was established in 1924 by Neil Gordon. The journal covers research on chemical education, and its target audience includes instructors of chemistry from middle school through graduate school and some scientists in commerce, industry, and government. References External links * Chemical education journals American Chemical Society academic journals Monthly journals Academic journals established in 1924 English-language journals {{chemistry-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amadeo Avogadro
Lorenzo Romano Amedeo Carlo Avogadro, Count of Quaregna and Cerreto (, also , ; 9 August 17769 July 1856) was an Italian scientist, most noted for his contribution to molecular theory now known as Avogadro's law, which states that equal volumes of gases under the same conditions of temperature and pressure will contain equal numbers of molecules. In tribute to him, the ratio of the number of elementary entities (atoms, molecules, ions or other particles) in a substance to its amount of substance (the latter having the unit mole), , is known as the Avogadro constant. This constant is denoted ''N''A, and is one of the seven defining constants of the SI. Biography Amedeo Avogadro was born in Turin to a noble family of the Kingdom of Sardinia (now part of Italy) in the year 1776. He graduated in ecclesiastical law at the late age of 20 and began to practice. Soon after, he dedicated himself to physics and mathematics (then called ''positive philosophy''), and in 1809 sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linus Pauling
Linus Carl Pauling ( ; February 28, 1901August 19, 1994) was an American chemist and peace activist. He published more than 1,200 papers and books, of which about 850 dealt with scientific topics. ''New Scientist'' called him one of the 20 greatest scientists of all time. For his scientific work, Pauling was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1954. For his peace activism, he was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1962. He is one of five people to have Nobel Prize#Multiple laureates, won more than one Nobel Prize. Of these, he is the only person to have been awarded two unshared Nobel Prizes, and one of two people to be awarded Nobel Prizes in different fields, the other being Marie Curie. Pauling was one of the founders of the fields of quantum chemistry and molecular biology. His contributions to the theory of the chemical bond include the concept of orbital hybridisation and the first accurate scale of electronegativity, electronegativities of the elements. Pauling also wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valence Bond Theory
In chemistry, valence bond (VB) theory is one of the two basic theories, along with molecular orbital (MO) theory, that were developed to use the methods of quantum mechanics to explain chemical bonding. It focuses on how the atomic orbitals of the dissociated atoms combine to give individual chemical bonds when a molecule is formed. In contrast, molecular orbital theory has orbitals that cover the whole molecule. History In 1916, G. N. Lewis proposed that a chemical bond forms by the interaction of two shared bonding electrons, with the representation of molecules as Lewis structures. The chemist Charles Rugeley Bury suggested in 1921 that eight and eighteen electrons in a shell form stable configurations. Bury proposed that the electron configurations in transitional elements depended upon the valence electrons in their outer shell. In 1916, Kossel put forth his theory of the ionic chemical bond (octet rule), also independently advanced in the same year by Gilbert N. Lew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostatic Potential
Electric potential (also called the ''electric field potential'', potential drop, the electrostatic potential) is defined as electric potential energy per unit of electric charge. More precisely, electric potential is the amount of work needed to move a test charge from a reference point to a specific point in a static electric field. The test charge used is small enough that disturbance to the field is unnoticeable, and its motion across the field is supposed to proceed with negligible acceleration, so as to avoid the test charge acquiring kinetic energy or producing radiation. By definition, the electric potential at the reference point is zero units. Typically, the reference point is earth or a point at infinity, although any point can be used. In classical electrostatics, the electrostatic field is a vector quantity expressed as the gradient of the electrostatic potential, which is a scalar quantity denoted by or occasionally , equal to the electric potential energy of any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The American Chemical Society
The ''Journal of the American Chemical Society'' (also known as JACS) is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1879 by the American Chemical Society. The journal has absorbed two other publications in its history, the ''Journal of Analytical and Applied Chemistry'' (July 1893) and the ''American Chemical Journal'' (January 1914). It covers all fields of chemistry. Since 2021, the editor-in-chief is Erick M. Carreira (ETH Zurich). In 2014, the journal moved to a hybrid open access publishing model. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 14.4. Editors-in-chief The following people are or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shielding Effect
In chemistry, the shielding effect sometimes referred to as atomic shielding or electron shielding describes the attraction between an electron and the nucleus in any atom with more than one electron. The shielding effect can be defined as a reduction in the effective nuclear charge on the electron cloud, due to a difference in the attraction forces on the electrons in the atom. It is a special case of electric-field screening. This effect also has some significance in many projects in material sciences. Strength per electron shell or orbital The wider the electron shells are in space, the weaker is the electric interaction between the electrons and the nucleus due to screening. Further, because of differences in orbital penetration, we can order the screening strength, ''S'', that electrons in a given orbital (s, p, d, or f) provide to the rest of the electrons thus: S(\mathrm) > S(\mathrm) > S(\mathrm) > S(\mathrm) . Description In hydrogen, or any other atom in group 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |