|
Electronegative
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity, the more an atom or a substituent group attracts electrons. Electronegativity serves as a simple way to quantitatively estimate the bond energy, and the sign and magnitude of a bond's chemical polarity, which characterizes a bond along the continuous scale from covalent to ionic bonding. The loosely defined term electropositivity is the opposite of electronegativity: it characterizes an element's tendency to donate valence electrons. On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more "pull" it will have on electrons) and the number and location ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
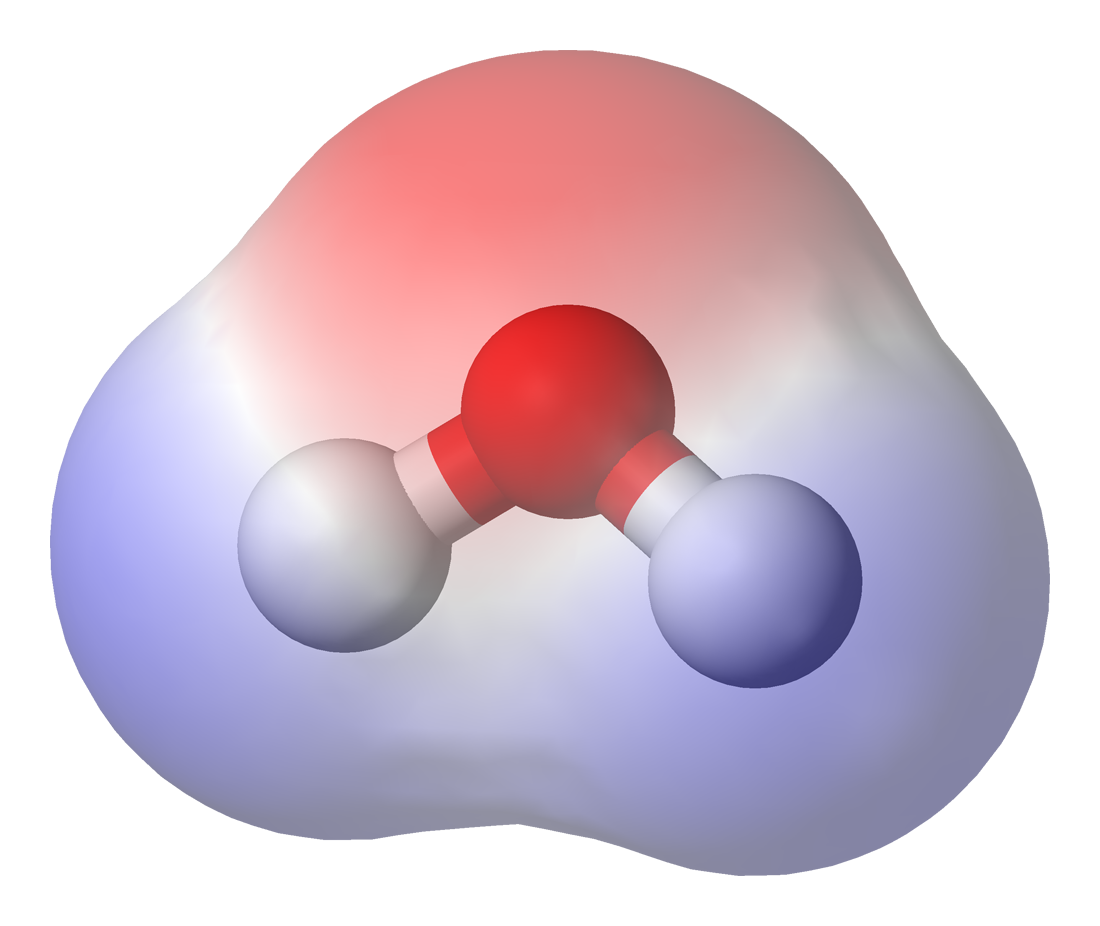
Chemical Polarity
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alkaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurred about 370,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Bonding
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, or between two atoms with sharply different electronegativities, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. It is one of the main types of bonding along with covalent bonding and metallic bonding. Ions are atoms (or groups of atoms) with an electrostatic charge. Atoms that gain electrons make negatively charged ions (called anions). Atoms that lose electrons make positively charged ions (called cations). This transfer of electrons is known as electrovalence in contrast to covalence. In the simplest case, the cation is a metal atom and the anion is a nonmetal atom, but these ions can be of a more complex nature, e.g. molecular ions like or . In simpler words, an ionic bond results from the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal in order to obtain a full valence shell for both atoms. It is important to recognize that ''clean'' ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Bond
A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that enables the formation of molecules and crystals. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds, or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are "strong bonds" or "primary bonds" such as covalent, ionic and metallic bonds, and "weak bonds" or "secondary bonds" such as dipole–dipole interactions, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding. Strong chemical bonding arises from the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. Since opposite electric charges attract, the negatively charged electrons surrounding the nucleus and the positively charged protons within a nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodic Trends
Periodic trends are specific patterns that are present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of a certain element. They were discovered by the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in the year 1863. Major periodic trends include atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity, valency and metallic character. These trends exist because of the similar electronic configuration of the elements within their respective groups or periods and because of the periodic nature of the elements. These give a qualitative assessment of the properties of each element. Summary Atomic radius The atomic radius is the distance from the atomic nucleus to the outermost electron orbital in an atom. In general, the atomic radius decreases as we move from left to right in a period, and it increases when we go down a group. This is because in periods, the valence electrons are in the same outermost shell. The atomic number increases within the same period whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Chemical Education
The ''Journal of Chemical Education'' is a monthly peer-reviewed academic journal available in both print and electronic versions. It is published by the Division of Chemical Education of the American Chemical Society and was established in 1924 by Neil Gordon. The journal covers research on chemical education Chemistry education (or chemical education) is the study of teaching and learning chemistry. It is one subset of STEM education or discipline-based education research (DBER). Topics in chemistry education include understanding how students learn ..., and its target audience includes instructors of chemistry from middle school through graduate school and some scientists in commerce, industry, and government. References External links * Chemical education journals American Chemical Society academic journals Monthly journals Publications established in 1924 English-language journals {{chemistry-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amadeo Avogadro
Lorenzo Romano Amedeo Carlo Avogadro, Count of Quaregna and Cerreto (, also , ; 9 August 17769 July 1856) was an Italian scientist, most noted for his contribution to molecular theory now known as Avogadro's law, which states that equal volumes of gases under the same conditions of temperature and pressure will contain equal numbers of molecules. In tribute to him, the ratio of the number of elementary entities (atoms, molecules, ions or other particles) in a substance to its amount of substance (the latter having the unit mole), , is known as the Avogadro constant. This constant is denoted ''N''A, and is one of the seven defining constants of the SI. Biography Amedeo Avogadro was born in Turin to a noble family of the Kingdom of Sardinia (now part of Italy) in the year 1776. He graduated in ecclesiastical law at the late age of 20 and began to practice. Soon after, he dedicated himself to physics and mathematics (then called ''positive philosophy''), and in 1809 started t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linus Pauling
Linus Carl Pauling (; February 28, 1901August 19, 1994) was an American chemist, biochemist, chemical engineer, peace activist, author, and educator. He published more than 1,200 papers and books, of which about 850 dealt with scientific topics. ''New Scientist'' called him one of the 20 greatest scientists of all time, and as of 2000, he was rated the 16th most important scientist in history. For his scientific work, Pauling was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1954. For his peace activism, he was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1962. He is one of five people to have won more than one Nobel Prize (the others being Marie Curie, John Bardeen, Frederick Sanger and Karl Barry Sharpless). Of these, he is the only person to have been awarded two unshared Nobel Prizes, and one of two people to be awarded Nobel Prizes in different fields, the other being Marie Curie. Pauling was one of the founders of the fields of quantum chemistry and molecular biology. His contributions t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valence Bond Theory
In chemistry, valence bond (VB) theory is one of the two basic theories, along with molecular orbital (MO) theory, that were developed to use the methods of quantum mechanics to explain chemical bonding. It focuses on how the atomic orbitals of the dissociated atoms combine to give individual chemical bonds when a molecule is formed. In contrast, molecular orbital theory has orbitals that cover the whole molecule. History Lothar Meyer in his 1864 book, ''Die modernen Theorien der Chemie'', contained an early version of the periodic table containing 28 elements, classified elements into six families by their valence—for the first time, elements had been grouped according to their valence. Works on organizing the elements by atomic weight, until then had been stymied by the widespread use of equivalent weights for the elements, rather than atomic weights. In 1916, G. N. Lewis proposed that a chemical bond forms by the interaction of two shared bonding electrons, with the repr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostatic Potential
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies electric charges at rest (static electricity). Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber, (), was thus the source of the word 'electricity'. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law. Even though electrostatically induced forces seem to be rather weak, some electrostatic forces are relatively large. The force between an electron and a proton, which together make up a hydrogen atom, is about 36 orders of magnitude stronger than the gravitational force acting between them. There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of plastic wrap to one's hand after it is removed from a package, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The American Chemical Society
The ''Journal of the American Chemical Society'' is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1879 by the American Chemical Society. The journal has absorbed two other publications in its history, the ''Journal of Analytical and Applied Chemistry'' (July 1893) and the ''American Chemical Journal'' (January 1914). It covers all fields of chemistry. Since 2021, the editor-in-chief is Erick M. Carreira (ETH Zurich). In 2014, the journal moved to a hybrid open access publishing model. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Chemical Abstracts Service, Scopus, EBSCO databases, ProQuest databases, Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed, and the Science Citation Index Expanded. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 16.383. Editors-in-chief The following people are or have been editor-in-chief: * 1879–1880 – Hermann Endemann * 1880–1881 – Gideon E. Moore * 1881–1882 – Hermann Endemann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shielding Effect
In chemistry, the shielding effect sometimes referred to as atomic shielding or electron shielding describes the attraction between an electron and the nucleus in any atom with more than one electron. The shielding effect can be defined as a reduction in the effective nuclear charge on the electron cloud, due to a difference in the attraction forces on the electrons in the atom. It is a special case of electric-field screening. This effect also has some significance in many projects in material sciences. Strength per electron shell The wider the electron shells are in space, the weaker is the electric interaction between the electrons and the nucleus due to screening. In general we can order the electron shells (s,p,d,f) as such S(\mathrm) > S(\mathrm) > S(\mathrm) > S(\mathrm) , where ''S'' is the screening strength that a given orbital provides to the rest of the electrons. Description In hydrogen, or any other atom in group 1A of the periodic table (those with only one v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |