hydrophobic effect on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The hydrophobic effect is the observed tendency of
The hydrophobic effect is the observed tendency of
 The origin of the hydrophobic effect is not fully understood.
Some argue that the hydrophobic interaction is mostly an
The origin of the hydrophobic effect is not fully understood.
Some argue that the hydrophobic interaction is mostly an
 The hydrophobic effect is the observed tendency of
The hydrophobic effect is the observed tendency of nonpolar
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end.
Polar molecules must contain one or more polar ...
substances to aggregate in an aqueous solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be re ...
and exclude water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a ...
molecules. The word hydrophobic literally means "water-fearing", and it describes the segregation Segregation may refer to:
Separation of people
* Geographical segregation, rates of two or more populations which are not homogenous throughout a defined space
* School segregation
* Housing segregation
* Racial segregation, separation of humans ...
of water and nonpolar substances, which maximizes hydrogen bonding between molecules of water and minimizes the area of contact between water and nonpolar molecules. In terms of thermodynamics, the hydrophobic effect is the free energy change of water surrounding a solute. A positive free energy change of the surrounding solvent indicates hydrophobicity, whereas a negative free energy change implies hydrophilicity.
The hydrophobic effect is responsible for the separation of a mixture of oil and water into its two components. It is also responsible for effects related to biology, including: cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
and vesicle formation, protein folding
Protein folding is the physical process by which a protein chain is translated to its native three-dimensional structure, typically a "folded" conformation by which the protein becomes biologically functional. Via an expeditious and reproduci ...
, insertion of membrane protein
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane ...
s into the nonpolar lipid environment and protein-small molecule
Within the fields of molecular biology and pharmacology, a small molecule or micromolecule is a low molecular weight (≤ 1000 daltons) organic compound that may regulate a biological process, with a size on the order of 1 nm. Many drugs ar ...
associations. Hence the hydrophobic effect is essential to life. Substances for which this effect is observed are known as hydrophobe
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, th ...
s.
Amphiphiles
Amphiphiles
An amphiphile (from the Greek αμφις amphis, both, and φιλíα philia, love, friendship), or amphipath, is a chemical compound possessing both hydrophilic (''water-loving'', polar) and lipophilic (''fat-loving'') properties. Such a compoun ...
are molecules that have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic domains. Detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with cleansing properties when in dilute solutions. There are a large variety of detergents, a common family being the alkylbenzene sulfonates, which are soap-like compounds that are more ...
s are composed of amphiphiles that allow hydrophobic molecules to be solubilized in water by forming micelle
A micelle () or micella () (plural micelles or micellae, respectively) is an aggregate (or supramolecular assembly) of surfactant amphipathic lipid molecules dispersed in a liquid, forming a colloidal suspension (also known as associated collo ...
s and bilayers (as in soap bubbles
A soap bubble is an extremely thin film of soap or detergent and water enclosing air that forms a hollow sphere with an iridescent surface. Soap bubbles usually last for only a few seconds before bursting, either on their own or on contact ...
). They are also important to cell membranes composed of amphiphilic phospholipid
Phospholipids, are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typ ...
s that prevent the internal aqueous environment of a cell from mixing with external water.
Folding of macromolecules
In the case of protein folding, the hydrophobic effect is important to understanding the structure of proteins that have hydrophobicamino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
s (such as glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogeni ...
, alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side c ...
, valine
Valine (symbol Val or V) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonat ...
, leucine
Leucine (symbol Leu or L) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Leucine is an α-amino acid, meaning it contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- ca ...
, isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprot ...
, phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino a ...
, tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α- carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromatic ...
and methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical ro ...
) clustered together within the protein. Structures of water-soluble proteins have a hydrophobic core in which side chains
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called the "main chain" or backbone. The side chain is a hydrocarbon branching element of a molecule that is attached to a ...
are buried from water, which stabilizes the folded state. Charged and polar
Polar may refer to:
Geography
Polar may refer to:
* Geographical pole, either of two fixed points on the surface of a rotating body or planet, at 90 degrees from the equator, based on the axis around which a body rotates
* Polar climate, the c ...
side chains are situated on the solvent-exposed surface where they interact with surrounding water molecules. Minimizing the number of hydrophobic side chains exposed to water is the principal driving force behind the folding process, although formation of hydrogen bonds within the protein also stabilizes protein structure.
The energetics of DNA tertiary structure assembly were determined to be driven by the hydrophobic effect, in addition to Watson-Crick base pairing, which is responsible for sequence selectivity, and stacking interactions between the aromatic bases.
Protein purification
Inbiochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and ...
, the hydrophobic effect can be used to separate mixtures of proteins based on their hydrophobicity. Column chromatography
Column chromatography in chemistry is a chromatography method used to isolate a single chemical compound from a mixture. Chromatography is able to separate substances based on differential adsorption of compounds to the adsorbent; compounds move th ...
with a hydrophobic stationary phase such as phenyl
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6 H5, and is often represented by the symbol Ph. Phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen ...
-sepharose Sepharose is a tradename for a crosslinked, beaded-form of agarose, a polysaccharide polymer material extracted from seaweed. Its brand name is a portmanteau derived from Separation-Pharmacia-Agarose. A common application for the material is in chro ...
will cause more hydrophobic proteins to travel more slowly, while less hydrophobic ones elute from the column sooner. To achieve better separation, a salt may be added (higher concentrations of salt increase the hydrophobic effect) and its concentration decreased as the separation progresses.
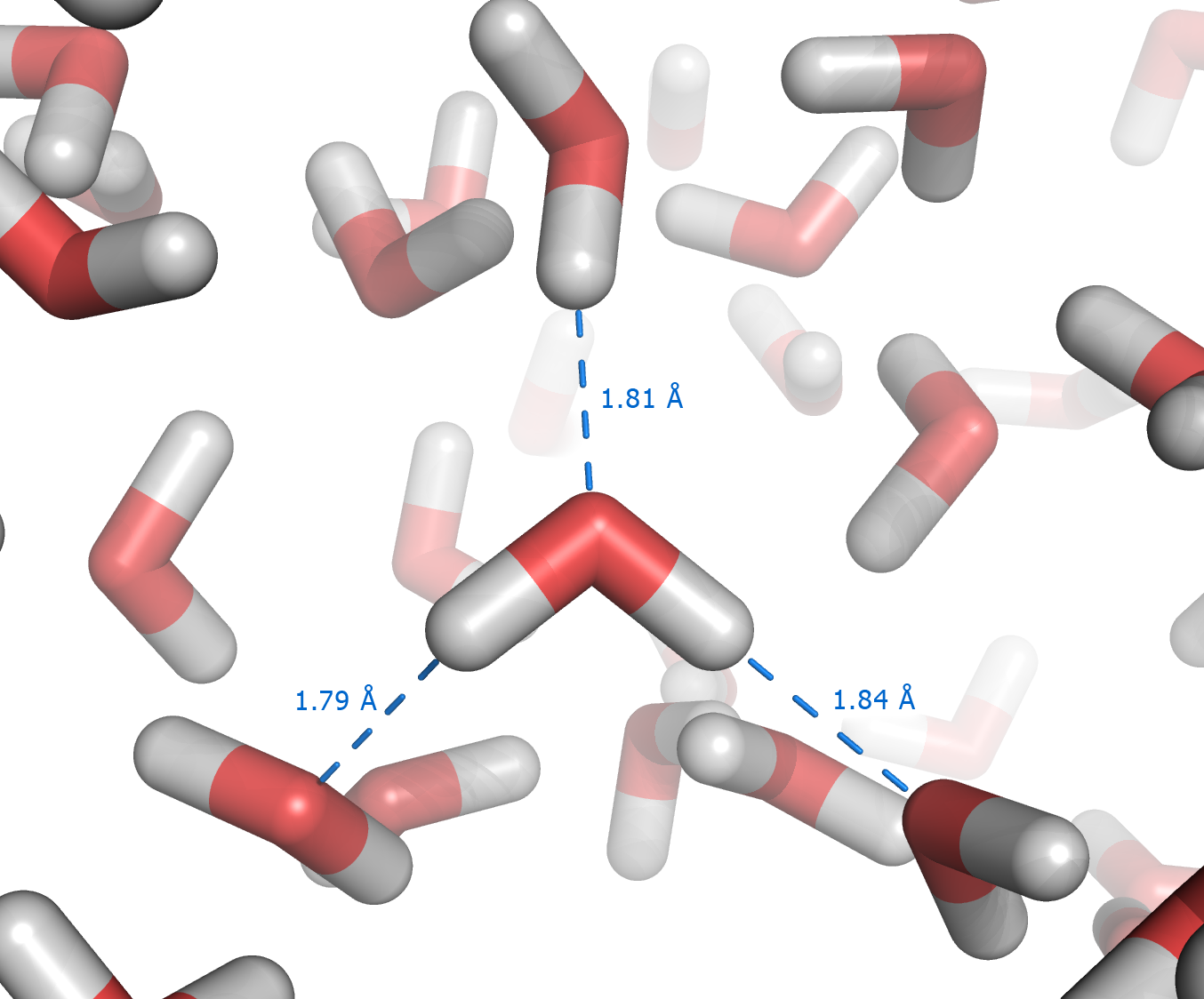
Cause
 The origin of the hydrophobic effect is not fully understood.
Some argue that the hydrophobic interaction is mostly an
The origin of the hydrophobic effect is not fully understood.
Some argue that the hydrophobic interaction is mostly an entropic
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynam ...
effect originating from the disruption of highly dynamic hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a ...
s between molecules of liquid water by the nonpolar solute. A hydrocarbon chain or a similar nonpolar region of a large molecule is incapable of forming hydrogen bonds with water. Introduction of such a non-hydrogen bonding surface into water causes disruption of the hydrogen bonding network between water molecules. The hydrogen bonds are reoriented tangentially to such surface to minimize disruption of the hydrogen bonded 3D network of water molecules, and this leads to a structured water "cage" around the nonpolar surface. The water molecules that form the "cage" (or clathrate
A clathrate is a chemical substance consisting of a lattice that traps or contains molecules. The word ''clathrate'' is derived from the Latin (), meaning ‘with bars, latticed’. Most clathrate compounds are polymeric and completely envelop t ...
) have restricted mobility. In the solvation shell of small nonpolar particles, the restriction amounts to some 10%. For example, in the case of dissolved xenon at room temperature a mobility restriction of 30% has been found. In the case of larger nonpolar molecules, the reorientational and translational motion of the water molecules in the solvation shell may be restricted by a factor of two to four; thus, at 25 °C the reorientational correlation time of water increases from 2 to 4-8 picoseconds. Generally, this leads to significant losses in translational and rotational entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynam ...
of water molecules and makes the process unfavorable in terms of the free energy in the system. By aggregating together, nonpolar molecules reduce the surface area exposed to water and minimize their disruptive effect.
The hydrophobic effect can be quantified by measuring the partition coefficient
In the physical sciences, a partition coefficient (''P'') or distribution coefficient (''D'') is the ratio of concentrations of a compound in a mixture of two immiscible solvents at equilibrium. This ratio is therefore a comparison of the solub ...
s of non-polar molecules between water and non-polar solvents. The partition coefficients can be transformed to free energy of transfer which includes enthalpic
Enthalpy , a property of a thermodynamic system, is the sum of the system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant p ...
and entropic components, ''ΔG = ΔH - TΔS''. These components are experimentally determined by calorimetry
In chemistry and thermodynamics, calorimetry () is the science or act of measuring changes in ''state variables'' of a body for the purpose of deriving the heat transfer associated with changes of its state due, for example, to chemical reacti ...
. The hydrophobic effect was found to be entropy-driven at room temperature because of the reduced mobility of water molecules in the solvation shell of the non-polar solute; however, the enthalpic component of transfer energy was found to be favorable, meaning it strengthened water-water hydrogen bonds in the solvation shell due to the reduced mobility of water molecules. At the higher temperature, when water molecules become more mobile, this energy gain decreases along with the entropic component. The hydrophobic effect depends on the temperature, which leads to "cold denaturation" of proteins.
The hydrophobic effect can be calculated by comparing the free energy of solvation with bulk water. In this way, the hydrophobic effect not only can be localized but also decomposed into enthalpic and entropic contributions.
See also
*Entropic force
In physics, an entropic force acting in a system is an emergent phenomenon resulting from the entire system's statistical tendency to increase its entropy, rather than from a particular underlying force on the atomic scale.
Mathematical form ...
* Hydrophobe
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, th ...
* Hydrophile
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are no ...
* Hydrophobicity scales Hydrophobicity scales are values that define the relative hydrophobicity or hydrophilicity of amino acid residues. The more positive the value, the more hydrophobic are the amino acids located in that region of the protein. These scales are commonly ...
* Interfacial tension
* Superhydrophobe
* Superhydrophobic coating
A superhydrophobic coating is a thin surface layer that repels water. It is made from superhydrophobic ( ultrahydrophobicity) materials. Droplets hitting this kind of coating can fully rebound.Richard, Denis, Christophe Clanet, and David Quéré ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hydrophobic Effect Chemical bonding Supramolecular chemistry Intermolecular forces