Hydraulic Reclamation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and
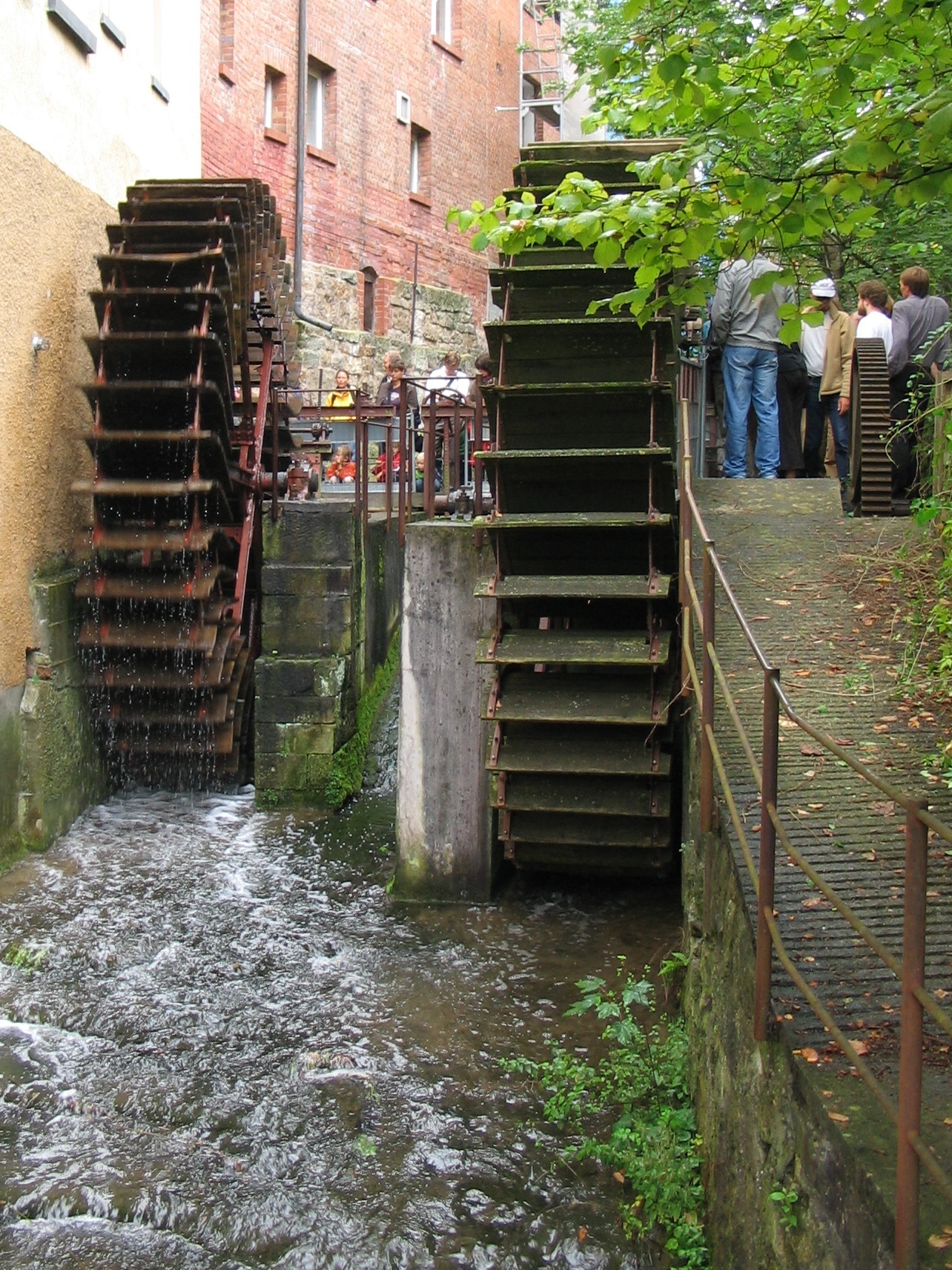 Early uses of water power date back to
Early uses of water power date back to
 In ancient Sri Lanka, hydraulics were widely used in the ancient kingdoms of Anuradhapura and Polonnaruwa. The discovery of the principle of the valve tower, or valve pit, (Bisokotuwa in Sinhalese) for regulating the escape of water is credited to ingenuity more than 2,000 years ago. By the first century AD, several large-scale irrigation works had been completed. Macro- and micro-hydraulics to provide for domestic horticultural and agricultural needs, surface drainage and erosion control, ornamental and recreational water courses and retaining structures and also cooling systems were in place in Sigiriya, Sri Lanka. The coral on the massive rock at the site includes
In ancient Sri Lanka, hydraulics were widely used in the ancient kingdoms of Anuradhapura and Polonnaruwa. The discovery of the principle of the valve tower, or valve pit, (Bisokotuwa in Sinhalese) for regulating the escape of water is credited to ingenuity more than 2,000 years ago. By the first century AD, several large-scale irrigation works had been completed. Macro- and micro-hydraulics to provide for domestic horticultural and agricultural needs, surface drainage and erosion control, ornamental and recreational water courses and retaining structures and also cooling systems were in place in Sigiriya, Sri Lanka. The coral on the massive rock at the site includes
 In the Roman Empire, different hydraulic applications were developed, including public water supplies, innumerable aqueducts, power using watermills and
In the Roman Empire, different hydraulic applications were developed, including public water supplies, innumerable aqueducts, power using watermills and
Transfer Of Islamic Technology To The West, Part II: Transmission Of Islamic Engineering
A 13th Century Programmable Robot (Archive)
University of Sheffield. The castle clock, a hydro-powered mechanical astronomical clock invented by Al-Jazari, was the first programmable analog computer. Donald Routledge Hill, "Mechanical Engineering in the Medieval Near East", ''Scientific American'', May 1991, pp. 64–9 ( cf. Donald Routledge Hill
Mechanical Engineering
)
Pascal's Principle and Hydraulics
The principle of hydraulics
IAHR media library Web resource of photos, animation & video
Basic hydraulic equations
MIT hydraulics course notes
{{Authority control Ancient inventions Hellenistic engineering Hydraulic engineering Mechanical engineering

 Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science
Applied science is the use of the scientific method and knowledge obtained via conclusions from the method to attain practical goals. It includes a broad range of disciplines such as engineering and medicine. Applied science is often contrasted ...
using engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad rang ...
, chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions ...
, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, a ...
s. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counterpart of pneumatics
Pneumatics (from Greek ‘wind, breath’) is a branch of engineering that makes use of gas or pressurized air.
Pneumatic systems used in industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A centrally located and elec ...
, which concerns gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
es. Fluid mechanics
Fluid mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the mechanics of fluids ( liquids, gases, and plasmas) and the forces on them.
It has applications in a wide range of disciplines, including mechanical, aerospace, civil, chemical and bio ...
provides the theoretical foundation for hydraulics, which focuses on the applied engineering using the properties of fluids. In its fluid power applications, hydraulics is used for the generation, control, and transmission of power by the use of pressurized
{{Wiktionary
Pressurization or pressurisation is the application of pressure in a given situation or environment.
Industrial
Industrial equipment is often maintained at pressures above or below atmospheric.
Atmospheric
This is the process by ...
liquids. Hydraulic topics range through some parts of science and most of engineering modules, and cover concepts such as pipe flow
Flow may refer to:
Science and technology
* Fluid flow, the motion of a gas or liquid
* Flow (geomorphology), a type of mass wasting or slope movement in geomorphology
* Flow (mathematics), a group action of the real numbers on a set
* Flow (psych ...
, dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, a ...
design, fluidics
Fluidics, or fluidic logic, is the use of a fluid to perform analog signal, analog or Digital data, digital operations similar to those performed with electronics.
The physical basis of fluidics is pneumatics and hydraulics, based on the theoret ...
and fluid control circuitry. The principles of hydraulics are in use naturally in the human body within the vascular system and erectile tissue.
Free surface hydraulics is the branch of hydraulics dealing with free surface flow, such as occurring in river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
s, canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow un ...
s, lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much large ...
s, estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environment ...
and sea
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, ...
s. Its sub-field open-channel flow studies the flow in open channels.
The word "hydraulics" originates from the Greek word (''hydraulikos'') which in turn originates from (''hydor'', Greek for water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a ...
) and (''aulos'', meaning pipe).
History
Ancient and medieval eras
 Early uses of water power date back to
Early uses of water power date back to Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
and ancient Egypt, where irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow Crop, crops, Landscape plant, landscape plants, and Lawn, lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,00 ...
has been used since the 6th millennium BC and water clock
A water clock or clepsydra (; ; ) is a timepiece by which time is measured by the regulated flow of liquid into (inflow type) or out from (outflow type) a vessel, and where the amount is then measured.
Water clocks are one of the oldest time-m ...
s had been used since the early 2nd millennium BC. Other early examples of water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a ...
power include the Qanat system in ancient Persia and the Turpan water system
The Turpan water system or Turfan karez system ug, كارىز, kariz, 6=кариз) in Turpan, located in the Turpan Depression, Xinjiang, China, is a vertical tunnel system adapted by the Uyghur people. The word ''karez'' means "well" in the l ...
in ancient Central Asia.
Persian Empire
In thePersian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
, the Persians constructed an intricate system of water mills, canals and dams known as the Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System. The project, commenced by Achaemenid king Darius the Great
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his d ...
and finished by a group of Roman engineers captured by Sassanian king Shapur I, has been referred to by UNESCO as "a masterpiece of creative genius". They were also the inventors of the Qanat, an underground aqueduct. Several of Iran's large, ancient gardens were irrigated thanks to Qanats.
The earliest evidence of water wheels and watermills date back to the ancient Near East in the 4th century BC, specifically in the Persian Empire before 350 BCE, in the regions of Iraq, Iran, and Egypt.
China
Inancient China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapte ...
there was Sunshu Ao
Sunshu Ao (孫叔敖, c. 630 – c. 593 BCE) was a Chinese hydraulic engineer and politician. He was a court minister serving the administration of King Zhuang of Chu during the Eastern Zhou Dynasty. During his governmental career, Sunshu Ao was ...
(6th century BC), Ximen Bao
Ximen Bao was a Chinese hydraulic engineer, philosopher, and politician. He was a government minister and court advisor to Marquis Wen of Wei (reigned 445–396 BC) during the Warring States period of ancient China. He was known as an early ratio ...
(5th century BC), Du Shi (circa 31 AD), Zhang Heng
Zhang Heng (; AD 78–139), formerly romanized as Chang Heng, was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman who lived during the Han dynasty. Educated in the capital cities of Luoyang and Chang'an, he achieved success as an astronomer, ma ...
(78 – 139 AD), and Ma Jun Ma Jun, may refer to:
*Ma Jun (historian) (born 1953), Chinese historian.
*Ma Jun (footballer) (born 1989), Chinese footballer.
*Ma Jun (environmentalist) (born 1968), Chinese environmentalist.
*Ma Jun (engineer) (born 1962), Chinese environmental ...
(200 – 265 AD), while medieval China had Su Song
Su Song (, 1020–1101), courtesy name Zirong (), was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman. Excelling in a variety of fields, he was accomplished in mathematics, Chinese astronomy, astronomy, History of cartography#China, cartography, ...
(1020 – 1101 AD) and Shen Kuo
Shen Kuo (; 1031–1095) or Shen Gua, courtesy name Cunzhong (存中) and pseudonym Mengqi (now usually given as Mengxi) Weng (夢溪翁),Yao (2003), 544. was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman of the Song dynasty (960–1279). Shen wa ...
(1031–1095). Du Shi employed a waterwheel
A water wheel is a machine for converting the energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power, often in a watermill. A water wheel consists of a wheel (usually constructed from wood or metal), with a number of blades or buckets ...
to power the bellows of a blast furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being "forced" or supplied above atmospheric ...
producing cast iron. Zhang Heng was the first to employ hydraulics to provide motive power in rotating an armillary sphere
An armillary sphere (variations are known as spherical astrolabe, armilla, or armil) is a model of objects in the sky (on the celestial sphere), consisting of a spherical framework of rings, centered on Earth or the Sun, that represent lines of ...
for astronomical observation.
Sri Lanka
 In ancient Sri Lanka, hydraulics were widely used in the ancient kingdoms of Anuradhapura and Polonnaruwa. The discovery of the principle of the valve tower, or valve pit, (Bisokotuwa in Sinhalese) for regulating the escape of water is credited to ingenuity more than 2,000 years ago. By the first century AD, several large-scale irrigation works had been completed. Macro- and micro-hydraulics to provide for domestic horticultural and agricultural needs, surface drainage and erosion control, ornamental and recreational water courses and retaining structures and also cooling systems were in place in Sigiriya, Sri Lanka. The coral on the massive rock at the site includes
In ancient Sri Lanka, hydraulics were widely used in the ancient kingdoms of Anuradhapura and Polonnaruwa. The discovery of the principle of the valve tower, or valve pit, (Bisokotuwa in Sinhalese) for regulating the escape of water is credited to ingenuity more than 2,000 years ago. By the first century AD, several large-scale irrigation works had been completed. Macro- and micro-hydraulics to provide for domestic horticultural and agricultural needs, surface drainage and erosion control, ornamental and recreational water courses and retaining structures and also cooling systems were in place in Sigiriya, Sri Lanka. The coral on the massive rock at the site includes cistern
A cistern (Middle English ', from Latin ', from ', "box", from Greek ', "basket") is a waterproof receptacle for holding liquids, usually water. Cisterns are often built to catch and store rainwater. Cisterns are distinguished from wells by t ...
s for collecting water. Large ancient reservoirs of Sri Lanka are Kalawewa (King Dhatusena), Parakrama Samudra (King Parakrama Bahu), Tisa Wewa (King Dutugamunu), Minneriya (King Mahasen)
Greco-Roman world
In Ancient Greece, the Greeks constructed sophisticated water and hydraulic power systems. An example is a construction by Eupalinos, under a public contract, of a watering channel for Samos, the Tunnel of Eupalinos. An early example of the usage of hydraulic wheel, probably the earliest in Europe, is the Perachora wheel (3rd century BC). InGreco-Roman Egypt
The history of Egypt has been long and wealthy, due to the flow of the Nile River with its fertile banks and delta, as well as the accomplishments of Egypt's native inhabitants and outside influence. Much of Egypt's ancient history was a myster ...
, the construction of the first hydraulic machine automata by Ctesibius (flourished c. 270 BC) and Hero of Alexandria (c. 10 – 80 AD) is notable. Hero describes several working machines using hydraulic power, such as the force pump, which is known from many Roman sites as having been used for raising water and in fire engines.
hydraulic mining
Hydraulic mining is a form of mining that uses high-pressure jets of water to dislodge rock material or move sediment.Paul W. Thrush, ''A Dictionary of Mining, Mineral, and Related Terms'', US Bureau of Mines, 1968, p.560. In the placer mining of ...
. They were among the first to make use of the siphon
A siphon (from grc, σίφων, síphōn, "pipe, tube", also spelled nonetymologically syphon) is any of a wide variety of devices that involve the flow of liquids through tubes. In a narrower sense, the word refers particularly to a tube in a ...
to carry water across valleys, and used hushing on a large scale to prospect for and then extract metal ores. They used lead widely in plumbing systems for domestic and public supply, such as feeding thermae.
Hydraulic mining was used in the gold-fields of northern Spain, which was conquered by Augustus in 25 BC. The alluvial gold-mine of Las Medulas was one of the largest of their mines. At least seven long aqueducts worked it, and the water streams were used to erode the soft deposits, and then wash the tailings for the valuable gold content.
Arabic-Islamic world
In the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age and Arab Agricultural Revolution (8th–13th centuries), engineers made wide use of hydropower as well as early uses of tidal power, and large hydraulic factory complexes. A variety of water-powered industrial mills were used in the Islamic world, including fulling mills, gristmills,paper mill
A paper mill is a factory devoted to making paper from vegetable fibres such as wood pulp, old rags, and other ingredients. Prior to the invention and adoption of the Fourdrinier machine and other types of paper machine that use an endless belt, ...
s, hullers, sawmills, ship mills, stamp mill
A stamp mill (or stamp battery or stamping mill) is a type of mill machine that crushes material by pounding rather than grinding, either for further processing or for extraction of metallic ores. Breaking material down is a type of unit operatio ...
s, steel mill
A steel mill or steelworks is an industrial plant for the manufacture of steel. It may be an integrated steel works carrying out all steps of steelmaking from smelting iron ore to rolled product, but may also be a plant where steel semi-finish ...
s, sugar mills
A sugar cane mill is a factory that processes sugar cane to produce raw or white sugar.
The term is also used to refer to the equipment that crushes the sticks of sugar cane to extract the juice.
Processing
There are a number of steps in prod ...
, and tide mills. By the 11th century, every province throughout the Islamic world had these industrial mills in operation, from Al-Andalus and North Africa to the Middle East and Central Asia.Adam Robert Lucas (2005), "Industrial Milling in the Ancient and Medieval Worlds: A Survey of the Evidence for an Industrial Revolution in Medieval Europe," ''Technology and Culture'' 46 (1), pp. 1–30 0 Muslim engineers also used water turbines, employed gears in watermills and water-raising machines, and pioneered the use of dams as a source of water power, used to provide additional power to watermills and water-raising machines. Ahmad Y. al-HassanTransfer Of Islamic Technology To The West, Part II: Transmission Of Islamic Engineering
Al-Jazari
Badīʿ az-Zaman Abu l-ʿIzz ibn Ismāʿīl ibn ar-Razāz al-Jazarī (1136–1206, ar, بديع الزمان أَبُ اَلْعِزِ إبْنُ إسْماعِيلِ إبْنُ الرِّزاز الجزري, ) was a polymath: a scholar, ...
(1136–1206) described designs for 50 devices, many of them water-powered, in his book, ''The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices'', including water clocks, a device to serve wine, and five devices to lift water from rivers or pools. These include an endless belt with jugs attached and a reciprocating device with hinged valves.
The earliest programmable machines were water-powered devices developed in the Muslim world. A music sequencer
A music sequencer (or audio sequencer or simply sequencer) is a device or application software that can record, edit, or play back music, by handling note and performance information in several forms, typically CV/Gate, MIDI, or Open Sound Cont ...
, a programmable musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person who pl ...
, was the earliest type of programmable machine. The first music sequencer was an automated water-powered flute
The flute is a family of classical music instrument in the woodwind group. Like all woodwinds, flutes are aerophones, meaning they make sound by vibrating a column of air. However, unlike woodwind instruments with reeds, a flute is a reedless ...
player invented by the Banu Musa brothers, described in their '' Book of Ingenious Devices'', in the 9th century. In 1206, Al-Jazari invented water-powered programmable automata/ robots. He described four automaton musicians, including drummers operated by a programmable drum machine, where they could be made to play different rhythms and different drum patterns.Professor Noel SharkeyA 13th Century Programmable Robot (Archive)
University of Sheffield. The castle clock, a hydro-powered mechanical astronomical clock invented by Al-Jazari, was the first programmable analog computer. Donald Routledge Hill, "Mechanical Engineering in the Medieval Near East", ''Scientific American'', May 1991, pp. 64–9 ( cf. Donald Routledge Hill
Mechanical Engineering
)
Modern era (c. 1600–1870)
Benedetto Castelli
In 1619 Benedetto Castelli, a student of Galileo Galilei, published the book ''Della Misura dell'Acque Correnti'' or "On the Measurement of Running Waters," one of the foundations of modern hydrodynamics. He served as a chief consultant to the Pope on hydraulic projects, i.e., management of rivers in the Papal States, beginning in 1626.Blaise Pascal
Blaise Pascal
Blaise Pascal ( , , ; ; 19 June 1623 – 19 August 1662) was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, and Catholic Church, Catholic writer.
He was a child prodigy who was educated by his father, a tax collector in Rouen. Pa ...
(1623–1662) studied fluid hydrodynamics and hydrostatics, centered on the principles of hydraulic fluids. His discovery on the theory behind hydraulics led to his invention of the hydraulic press, which multiplied a smaller force acting on a smaller area into the application of a larger force totaled over a larger area, transmitted through the same pressure (or exact change of pressure) at both locations. Pascal's law or principle states that for an incompressible fluid at rest, the difference in pressure is proportional to the difference in height, and this difference remains the same whether or not the overall pressure of the fluid is changed by applying an external force. This implies that by increasing the pressure at any point in a confined fluid, there is an equal increase at every other end in the container, i.e., any change in pressure applied at any point of the liquid is transmitted undiminished throughout the fluids.
Jean Léonard Marie Poiseuille
A French physician, Poiseuille (1797–1869) researched the flow of blood through the body and discovered an important law governing the rate of flow with the diameter of the tube in which flow occurred.In the UK
Several cities developed citywidehydraulic power network
A hydraulic power network is a system of interconnected pipes carrying pressurized liquid used to transmit mechanical power from a power source, like a pump, to hydraulic equipment like lifts or motors. The system is analogous to an electrical gri ...
s in the 19th century, to operate machinery such as lifts, cranes, capstans and the like. Joseph Bramah
Joseph Bramah (13 April 1748 – 9 December 1814), born Stainborough Lane Farm, Stainborough, in Barnsley, Yorkshire, was an English inventor and locksmith. He is best known for having improved the flush toilet and inventing the hydraulic pr ...
(1748–1814) was an early innovator and William Armstrong (1810–1900) perfected the apparatus for power delivery on an industrial scale. In London, the London Hydraulic Power Company was a major supplier its pipes serving large parts of the West End of London, City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
and the Docks, but there were schemes restricted to single enterprises such as docks and railway goods yards.
Hydraulic models
After students understand the basic principles of hydraulics, some teachers use a hydraulicanalogy
Analogy (from Greek ''analogia'', "proportion", from ''ana-'' "upon, according to" lso "against", "anew"+ ''logos'' "ratio" lso "word, speech, reckoning" is a cognitive process of transferring information or meaning from a particular subject ( ...
to help students learn other things.
For example:
* The MONIAC Computer
The MONIAC (Monetary National Income Analogue Computer), also known as the Phillips Hydraulic Computer and the Financephalograph, was created in 1949 by the New Zealand economist Bill Phillips to model the national economic processes of the Uni ...
uses water flowing through hydraulic components to help students learn about economics.
* The thermal-hydraulic analogy uses hydraulic principles to help students learn about thermal circuits.
* The electronic– hydraulic analogy uses hydraulic principles to help students learn about electronics.
The conservation of mass requirement combined with fluid compressibility yields a fundamental relationship between pressure, fluid flow, and volumetric expansion, as shown below:
:
Assuming an incompressible fluid or a "very large" ratio of compressibility to contained fluid volume, a finite rate of pressure rise requires that any net flow into the collected fluid volume create a volumetric change.
See also
* Affinity laws * Bernoulli's principle * Fluid power *Hydraulic brake
A hydraulic brake is an arrangement of braking mechanism which uses brake fluid, typically containing glycol ethers or diethylene glycol, to transfer pressure from the controlling mechanism to the braking mechanism.
History
During 1904, Frederick ...
* Hydraulic cylinder
* Hydraulic engineering
* Hydraulic machinery
* Hydraulic mining
Hydraulic mining is a form of mining that uses high-pressure jets of water to dislodge rock material or move sediment.Paul W. Thrush, ''A Dictionary of Mining, Mineral, and Related Terms'', US Bureau of Mines, 1968, p.560. In the placer mining of ...
* Hydrology
* International Association for Hydro-Environment Engineering and Research
* Miniature hydraulics
Miniature Hydraulics are copies or models that represent and reproduce regular or standard sized hydraulic systems and components, but in a reduced state, on a small scale, or in a greatly reduced size. True working and functional miniature hydraul ...
* Open-channel flow
* Pneumatics
Pneumatics (from Greek ‘wind, breath’) is a branch of engineering that makes use of gas or pressurized air.
Pneumatic systems used in industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A centrally located and elec ...
Notes
References
*External links
Pascal's Principle and Hydraulics
The principle of hydraulics
IAHR media library Web resource of photos, animation & video
Basic hydraulic equations
MIT hydraulics course notes
{{Authority control Ancient inventions Hellenistic engineering Hydraulic engineering Mechanical engineering