Hurricanes In Colombia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Tropical cyclones tend to develop during the summer, but have been noted in nearly every month in most tropical cyclone basins. Tropical cyclones on either side of the Equator generally have their origins in the
Tropical cyclones tend to develop during the summer, but have been noted in nearly every month in most tropical cyclone basins. Tropical cyclones on either side of the Equator generally have their origins in the
 There are a number of ways a tropical cyclone can weaken, dissipate, or lose its tropical characteristics. These include making landfall, moving over cooler water, encountering dry air, or interacting with other weather systems; however, once a system has dissipated or lost its tropical characteristics, its remnants could regenerate a tropical cyclone if environmental conditions become favorable.
A tropical cyclone can dissipate when it moves over waters significantly cooler than . This will deprive the storm of such tropical characteristics as a warm core with thunderstorms near the center, so that it becomes a remnant low-pressure area. Remnant systems may persist for several days before losing their identity. This dissipation mechanism is most common in the eastern North Pacific. Weakening or dissipation can also occur if a storm experiences vertical wind shear which causes the convection and heat engine to move away from the center; this normally ceases the development of a tropical cyclone. In addition, its interaction with the main belt of the Westerlies, by means of merging with a nearby frontal zone, can cause tropical cyclones to evolve into extratropical cyclones. This transition can take 1–3 days.
Should a tropical cyclone make landfall or pass over an island, its circulation could start to break down, especially if it encounters mountainous terrain. When a system makes landfall on a large landmass, it is cut off from its supply of warm moist maritime air and starts to draw in dry continental air. This, combined with the increased friction over land areas, leads to the weakening and dissipation of the tropical cyclone. Over a mountainous terrain, a system can quickly weaken; however, over flat areas, it may endure for two to three days before circulation breaks down and dissipates.
Over the years, there have been a number of techniques considered to try to artificially modify tropical cyclones. These techniques have included using
There are a number of ways a tropical cyclone can weaken, dissipate, or lose its tropical characteristics. These include making landfall, moving over cooler water, encountering dry air, or interacting with other weather systems; however, once a system has dissipated or lost its tropical characteristics, its remnants could regenerate a tropical cyclone if environmental conditions become favorable.
A tropical cyclone can dissipate when it moves over waters significantly cooler than . This will deprive the storm of such tropical characteristics as a warm core with thunderstorms near the center, so that it becomes a remnant low-pressure area. Remnant systems may persist for several days before losing their identity. This dissipation mechanism is most common in the eastern North Pacific. Weakening or dissipation can also occur if a storm experiences vertical wind shear which causes the convection and heat engine to move away from the center; this normally ceases the development of a tropical cyclone. In addition, its interaction with the main belt of the Westerlies, by means of merging with a nearby frontal zone, can cause tropical cyclones to evolve into extratropical cyclones. This transition can take 1–3 days.
Should a tropical cyclone make landfall or pass over an island, its circulation could start to break down, especially if it encounters mountainous terrain. When a system makes landfall on a large landmass, it is cut off from its supply of warm moist maritime air and starts to draw in dry continental air. This, combined with the increased friction over land areas, leads to the weakening and dissipation of the tropical cyclone. Over a mountainous terrain, a system can quickly weaken; however, over flat areas, it may endure for two to three days before circulation breaks down and dissipates.
Over the years, there have been a number of techniques considered to try to artificially modify tropical cyclones. These techniques have included using
 Around the world, tropical cyclones are classified in different ways, based on the location ( tropical cyclone basins), the structure of the system and its intensity. For example, within the Northern Atlantic and Eastern Pacific basins, a tropical cyclone with wind speeds of over is called a hurricane, while it is called a typhoon or a severe cyclonic storm within the Western Pacific or North Indian Oceans. Within the Southern Hemisphere, it is either called a hurricane, tropical cyclone or a severe tropical cyclone, depending on if it is located within the South Atlantic, South-West Indian Ocean, Australian region or the South Pacific Ocean.
Around the world, tropical cyclones are classified in different ways, based on the location ( tropical cyclone basins), the structure of the system and its intensity. For example, within the Northern Atlantic and Eastern Pacific basins, a tropical cyclone with wind speeds of over is called a hurricane, while it is called a typhoon or a severe cyclonic storm within the Western Pacific or North Indian Oceans. Within the Southern Hemisphere, it is either called a hurricane, tropical cyclone or a severe tropical cyclone, depending on if it is located within the South Atlantic, South-West Indian Ocean, Australian region or the South Pacific Ocean.
 At the center of a mature tropical cyclone, air sinks rather than rises. For a sufficiently strong storm, air may sink over a layer deep enough to suppress cloud formation, thereby creating a clear "
At the center of a mature tropical cyclone, air sinks rather than rises. For a sufficiently strong storm, air may sink over a layer deep enough to suppress cloud formation, thereby creating a clear "
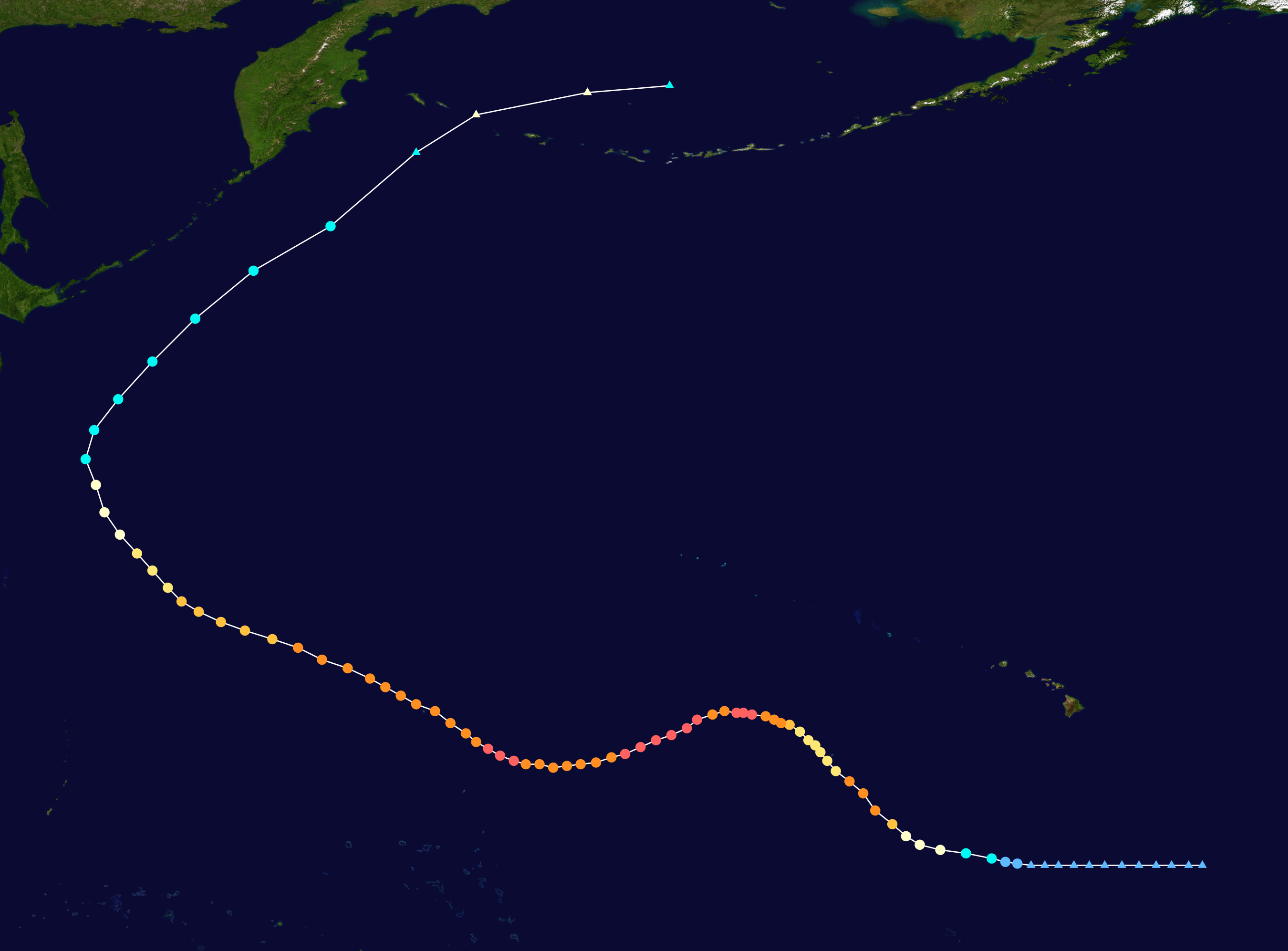 Though a tropical cyclone typically moves from east to west in the tropics, its track may shift poleward and eastward either as it moves west of the subtropical ridge axis or else if it interacts with the mid-latitude flow, such as the
Though a tropical cyclone typically moves from east to west in the tropics, its track may shift poleward and eastward either as it moves west of the subtropical ridge axis or else if it interacts with the mid-latitude flow, such as the

 Tropical cyclones regularly affect the coastlines of most of Earth's major bodies of water along the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian oceans. Tropical cyclones have caused significant destruction and loss of human life, resulting in about 2 million deaths since the 19th century. Large areas of standing water caused by flooding lead to infection, as well as contributing to mosquito-borne illnesses. Crowded evacuees in shelters increase the risk of disease propagation. Tropical cyclones significantly interrupt infrastructure, leading to power outages, bridge and road destruction, and the hampering of reconstruction efforts. Winds and water from storms can damage or destroy homes, buildings, and other manmade structures. Tropical cyclones destroy agriculture, kill livestock, and prevent access to marketplaces for both buyers and sellers; both of these result in financial losses. Powerful cyclones that make landfall – moving from the ocean to over land – are some of the most impactful, although that is not always the case. An average of 86 tropical cyclones of tropical storm intensity form annually worldwide, with 47 reaching hurricane or typhoon strength, and 20 becoming intense tropical cyclones, super typhoons, or major hurricanes (at least of Category 3 intensity).
In Africa, tropical cyclones can originate from
Tropical cyclones regularly affect the coastlines of most of Earth's major bodies of water along the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian oceans. Tropical cyclones have caused significant destruction and loss of human life, resulting in about 2 million deaths since the 19th century. Large areas of standing water caused by flooding lead to infection, as well as contributing to mosquito-borne illnesses. Crowded evacuees in shelters increase the risk of disease propagation. Tropical cyclones significantly interrupt infrastructure, leading to power outages, bridge and road destruction, and the hampering of reconstruction efforts. Winds and water from storms can damage or destroy homes, buildings, and other manmade structures. Tropical cyclones destroy agriculture, kill livestock, and prevent access to marketplaces for both buyers and sellers; both of these result in financial losses. Powerful cyclones that make landfall – moving from the ocean to over land – are some of the most impactful, although that is not always the case. An average of 86 tropical cyclones of tropical storm intensity form annually worldwide, with 47 reaching hurricane or typhoon strength, and 20 becoming intense tropical cyclones, super typhoons, or major hurricanes (at least of Category 3 intensity).
In Africa, tropical cyclones can originate from
2005 Tropical Eastern North Pacific Hurricane Outlook.
. Retrieved May 2, 2006. Their precipitation may also alleviate drought conditions by restoring soil moisture, though one study focused on the Southeastern United States suggested tropical cyclones did not offer significant drought recovery. Tropical cyclones also help maintain the global heat balance by moving warm, moist tropical air to the middle latitudes and polar regions, and by regulating the thermohaline circulation through upwelling. The storm surge and winds of hurricanes may be destructive to human-made structures, but they also stir up the waters of coastal estuaries, which are typically important fish breeding locales. Ecosystems, such as saltmarshes and
 Hurricane response is the disaster response after a hurricane. Activities performed by hurricane responders include assessment, restoration, and demolition of buildings; removal of debris and waste; repairs to land-based and maritime
Hurricane response is the disaster response after a hurricane. Activities performed by hurricane responders include assessment, restoration, and demolition of buildings; removal of debris and waste; repairs to land-based and maritime
 Climate change can affect tropical cyclones in a variety of ways: an intensification of rainfall and wind speed, a decrease in overall frequency, an increase in the frequency of very intense storms and a poleward extension of where the cyclones reach maximum intensity are among the possible consequences of human-induced climate change. Tropical cyclones use warm, moist air as their fuel. As climate change is warming ocean temperatures, there is potentially more of this fuel available. Between 1979 and 2017, there was a global increase in the proportion of tropical cyclones of Category 3 and higher on the Saffir–Simpson scale. The trend was most clear in the North Atlantic and in the Southern Indian Ocean. In the North Pacific, tropical cyclones have been moving poleward into colder waters and there was no increase in intensity over this period. With warming, a greater percentage (+13%) of tropical cyclones are expected to reach Category 4 and 5 strength. A 2019 study indicates that climate change has been driving the observed trend of rapid intensification of tropical cyclones in the Atlantic basin. Rapidly intensifying cyclones are hard to forecast and therefore pose additional risk to coastal communities.
Warmer air can hold more water vapor: the theoretical maximum water vapor content is given by the
Climate change can affect tropical cyclones in a variety of ways: an intensification of rainfall and wind speed, a decrease in overall frequency, an increase in the frequency of very intense storms and a poleward extension of where the cyclones reach maximum intensity are among the possible consequences of human-induced climate change. Tropical cyclones use warm, moist air as their fuel. As climate change is warming ocean temperatures, there is potentially more of this fuel available. Between 1979 and 2017, there was a global increase in the proportion of tropical cyclones of Category 3 and higher on the Saffir–Simpson scale. The trend was most clear in the North Atlantic and in the Southern Indian Ocean. In the North Pacific, tropical cyclones have been moving poleward into colder waters and there was no increase in intensity over this period. With warming, a greater percentage (+13%) of tropical cyclones are expected to reach Category 4 and 5 strength. A 2019 study indicates that climate change has been driving the observed trend of rapid intensification of tropical cyclones in the Atlantic basin. Rapidly intensifying cyclones are hard to forecast and therefore pose additional risk to coastal communities.
Warmer air can hold more water vapor: the theoretical maximum water vapor content is given by the

 Intense tropical cyclones pose a particular observation challenge, as they are a dangerous oceanic phenomenon, and weather stations, being relatively sparse, are rarely available on the site of the storm itself. In general, surface observations are available only if the storm is passing over an island or a coastal area, or if there is a nearby ship. Real-time measurements are usually taken in the periphery of the cyclone, where conditions are less catastrophic and its true strength cannot be evaluated. For this reason, there are teams of meteorologists that move into the path of tropical cyclones to help evaluate their strength at the point of landfall.
Tropical cyclones are tracked by weather satellites capturing
Intense tropical cyclones pose a particular observation challenge, as they are a dangerous oceanic phenomenon, and weather stations, being relatively sparse, are rarely available on the site of the storm itself. In general, surface observations are available only if the storm is passing over an island or a coastal area, or if there is a nearby ship. Real-time measurements are usually taken in the periphery of the cyclone, where conditions are less catastrophic and its true strength cannot be evaluated. For this reason, there are teams of meteorologists that move into the path of tropical cyclones to help evaluate their strength at the point of landfall.
Tropical cyclones are tracked by weather satellites capturing 
online review
* Vecchi, Gabriel A., et al. "Changes in Atlantic major hurricane frequency since the late-19th century." ''Nature communications'' 12.1 (2021): 1-9
online
* Weinkle, Jessica, et al. "Normalized hurricane damage in the continental United States 1900–2017." ''Nature Sustainability'' 1.12 (2018): 808-813
online
United States National Hurricane Center
nbsp;– North Atlantic, Eastern Pacific
United States Central Pacific Hurricane Center
nbsp;– Central Pacific
Japan Meteorological Agency
nbsp;– Western Pacific
India Meteorological Department
nbsp;– Indian Ocean
Météo-France – La Reunion
nbsp;– South Indian Ocean from 30°E to 90°E
Indonesian Meteorological Department
nbsp;– South Indian Ocean from 90°E to 125°E, north of 10°S
Australian Bureau of Meteorology
nbsp;– South Indian Ocean and South Pacific Ocean from 90°E to 160°E
Papua New Guinea National Weather Service
nbsp;– South Pacific east of 160°E, north of 10°S
Fiji Meteorological Service
nbsp;– South Pacific west of 160°E, north of 25° S
MetService New Zealand
nbsp;– South Pacific west of 160°E, south of 25°S {{DEFAULTSORT:Tropical Cyclone Articles containing video clips Climate change and hurricanes Meteorological phenomena Types of cyclone Vortices Weather hazards Storm
strong winds
''Strong Winds'' (German: ''Windstärke 9. Die Geschichte einer reichen Erbin'') is a 1924 German silent film directed by Reinhold Schünzel and starring Maria Kamradek, Alwin Neuss and Albert Bennefeld.Das Ufa-Buch p.126
The film's sets were d ...
, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by different names, including hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean, and a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean, South Pacific, or (rarely) South Atlantic, comparable storms are referred to simply as "tropical cyclones", and such storms in the Indian Ocean can also be called "severe cyclonic storms".
"Tropical" refers to the geographical origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively over tropical seas. "Cyclone" refers to their winds moving in a circle, whirling round their central clear eye
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and conv ...
, with their surface winds blowing counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. The opposite direction of circulation is due to the Coriolis effect. Tropical cyclones typically form over large bodies of relatively warm water. They derive their energy through the evaporation of water from the ocean surface, which ultimately condenses into clouds and rain when moist air rises and cools to saturation. This energy source differs from that of mid-latitude cyclonic storms, such as nor'easters and European windstorm
European windstorms are powerful extratropical cyclones which form as cyclonic windstorms associated with areas of low atmospheric pressure. They can occur throughout the year, but are most frequent between October and March, with peak intensit ...
s, which are powered primarily by horizontal temperature contrasts. Tropical cyclones are typically between in diameter. Every year tropical cyclones impact various regions of the globe including the Gulf Coast of North America, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, India, and Bangladesh.
The strong rotating winds of a tropical cyclone are a result of the conservation of angular momentum imparted by the Earth's rotation
Earth's rotation or Earth's spin is the rotation of planet Earth around its own Rotation around a fixed axis, axis, as well as changes in the orientation (geometry), orientation of the rotation axis in space. Earth rotates eastward, in retrograd ...
as air flows inwards toward the axis of rotation. As a result, they rarely form within 5° of the equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
. Tropical cyclones are very rare in the South Atlantic (although occasional examples do occur) due to consistently strong wind shear and a weak Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal e ...
. Conversely, the African easterly jet and areas of atmospheric instability give rise to cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea, while cyclones near Australia owe their genesis to the Asian monsoon and Western Pacific Warm Pool The Tropical Warm Pool (TWP) or Indo-Pacific Warm Pool is a mass of ocean water located in the western Pacific Ocean and eastern Indian Ocean which consistently exhibits the highest water temperatures over the largest expanse of the Earth's surface. ...
.
The primary energy source for these storms is warm ocean waters. These storms are therefore typically strongest when over or near water, and they weaken quite rapidly over land. This causes coastal regions to be particularly vulnerable to tropical cyclones, compared to inland regions. Coastal damage may be caused by strong winds and rain, high waves (due to winds), storm surge
A storm surge, storm flood, tidal surge, or storm tide is a coastal flood or tsunami-like phenomenon of rising water commonly associated with low-pressure weather systems, such as cyclones. It is measured as the rise in water level above the n ...
s (due to wind and severe pressure changes), and the potential of spawning tornadoes. Tropical cyclones draw in air from a large area and concentrate the water content of that air (from atmospheric moisture and moisture evaporated from water) into precipitation over a much smaller area. This replenishing of moisture-bearing air after rain may cause multi-hour or multi-day extremely heavy rain up to from the coastline, far beyond the amount of water that the local atmosphere holds at any one time. This in turn can lead to river flooding, overland flooding, and a general overwhelming of local water control structures across a large area. Although their effects on human populations can be devastating, tropical cyclones may play a role in relieving drought conditions, though this claim is disputed. They also carry heat and energy away from the tropics and transport it towards temperate latitudes, which plays an important role in regulating global climate.
Background
A tropical cyclone is the generic term for a warm-cored, non-frontal synoptic-scale low-pressure system over tropical orsubtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Geographical z ...
waters around the world. The systems generally have a well-defined center which is surrounded by deep atmospheric convection and a closed wind circulation at the surface.
Historically, tropical cyclones have occurred around the world for thousands of years, with one of the earliest tropical cyclones on record estimated to have occurred in Western Australia in around 4000 BC. However, before satellite imagery became available during the 20th century, there was no way to detect a tropical cyclone unless it impacted land or a ship encountered it by chance.
These days, on average around 80 to 90 named tropical cyclones form each year around the world, over half of which develop hurricane-force winds of or more. Around the world, a tropical cyclone is generally deemed to have formed once mean surface winds in excess of are observed. It is assumed at this stage that a tropical cyclone has become self-sustaining and can continue to intensify without any help from its environment.
A study review article published in 2021 in '' Nature Geoscience'' concluded that the geographic range of tropical cyclones will probably expand poleward in response to climate warming of the Hadley circulation.
Intensity
Tropical cyclone intensity is based on wind speeds and pressure; relationships between winds and pressure are often used in determining the intensity of a storm. Tropical cyclone scales such as the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale and Australia's scale (Bureau of Meteorology) only use wind speed for determining the category of a storm. The most intense storm on record is Typhoon Tip in the northwestern Pacific Ocean in 1979, which reached a minimum pressure of and maximum sustained wind speeds of . The highest maximum sustained wind speed ever recorded was in Hurricane Patricia in 2015—the most intense cyclone ever recorded in the Western Hemisphere.Factors that influence intensity
Warm sea surface temperatures are required in order for tropical cyclones to form and strengthen. The commonly-accepted minimum temperature range for this to occur is , however, multiple studies have proposed a lower minimum of . Higher sea surface temperatures result in faster intensification rates and sometimes even rapid intensification. Highocean heat content
In oceanography and climatology, ocean heat content (OHC) is a term for the energy absorbed by the ocean, where it is stored for indefinite time periods as internal energy or enthalpy. The rise in OHC accounts for over 90% of Earth’s excess the ...
, also known as Tropical Cyclone Heat Potential
Tropical Cyclone Heat Potential (TCHP) is one of such non-conventional oceanographic parameters influencing the tropical cyclone intensity. The relationship between Sea Surface Temperature
Sea surface temperature (SST), or ocean surface tempera ...
, allows storms to achieve a higher intensity. Most tropical cyclones that experience rapid intensification are traversing regions of high ocean heat content rather than lower values. High ocean heat content values can help to offset the oceanic cooling caused by the passage of a tropical cyclone, limiting the effect this cooling has on the storm. Faster-moving systems are able to intensify to higher intensities with lower ocean heat content values. Slower-moving systems require higher values of ocean heat content to achieve the same intensity.
The passage of a tropical cyclone over the ocean causes the upper layers of the ocean to cool substantially, a process known as upwelling, which can negatively influence subsequent cyclone development. This cooling is primarily caused by wind-driven mixing of cold water from deeper in the ocean with the warm surface waters. This effect results in a negative feedback process that can inhibit further development or lead to weakening. Additional cooling may come in the form of cold water from falling raindrops (this is because the atmosphere is cooler at higher altitudes). Cloud cover may also play a role in cooling the ocean, by shielding the ocean surface from direct sunlight before and slightly after the storm passage. All these effects can combine to produce a dramatic drop in sea surface temperature over a large area in just a few days. Conversely, the mixing of the sea can result in heat being inserted in deeper waters, with potential effects on global climate.
Vertical wind shear negatively impacts tropical cyclone intensification by displacing moisture and heat from a system's center. Low levels of vertical wind shear are most optimal for strengthening, while stronger wind shear induces weakening. Dry air entraining into a tropical cyclone's core has a negative effect on its development and intensity by diminishing atmospheric convection and introducing asymmetries in the storm's structure. Symmetric, strong outflow
Outflow may refer to:
*Capital outflow, the capital leaving a particular economy
*Bipolar outflow, in astronomy, two continuous flows of gas from the poles of a star
*Outflow (hydrology), the discharge of a lake or other reservoir system
* Outflow ...
leads to a faster rate of intensification than observed in other systems by mitigating local wind shear. Weakening outflow is associated with the weakening of rainbands within a tropical cyclone.
The size of tropical cyclones plays a role in how quickly they intensify. Smaller tropical cyclones are more prone to rapid intensification than larger ones. The Fujiwhara effect, which involves interaction between two tropical cyclones, can weaken and ultimately result in the dissipation of the weaker of two tropical cyclones by reducing the organization of the system's convection and imparting horizontal wind shear. Tropical cyclones typically weaken while situated over a landmass because conditions are often unfavorable as a result of the lack of oceanic forcing. The Brown ocean effect can allow a tropical cyclone to maintain or increase its intensity following landfall, in cases where there has been copious rainfall, through the release of latent heat from the saturated soil. Orographic lift can cause an significant increase in the intensity of the convection of a tropical cyclone when its eye moves over a mountain, breaking the capped boundary layer that had been restraining it. Jet streams can both enhance and inhibit tropical cyclone intensity by influencing the storm's outflow as well as vertical wind shear.
Formation
Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal e ...
, where winds blow from either the northeast or southeast. Within this broad area of low-pressure, air is heated over the warm tropical ocean and rises in discrete parcels, which causes thundery showers to form. These showers dissipate quite quickly; however, they can group together into large clusters of thunderstorms. This creates a flow of warm, moist, rapidly rising air, which starts to rotate cyclonically as it interacts with the rotation of the earth.
Several factors are required for these thunderstorms to develop further, including sea surface temperatures of around and low vertical wind shear surrounding the system, atmospheric instability, high humidity in the lower to middle levels of the troposphere, enough Coriolis force
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
to develop a low-pressure center, a pre-existing low-level focus or disturbance,
There is a limit on tropical cyclone intensity which is strongly related to the water temperatures along its path. and upper-level divergence.
An average of 86 tropical cyclones of tropical storm intensity form annually worldwide. Of those, 47 reach strength higher than , and 20 become intense tropical cyclones (at least Category 3 intensity on the Saffir–Simpson scale).
Climate cycles such as ENSO and the Madden–Julian oscillation modulate the timing and frequency of tropical cyclone development. Rossby waves can aid in the formation of a new tropical cyclone by disseminating the energy of an existing, mature storm. Kelvin waves can contribute to tropical cyclone formation by regulating the development of the westerlies. Cyclone formation is usually reduced 3 days prior to the wave's crest and increased during the 3 days after.
Rapid intensification
On occasion, tropical cyclones may undergo a process known as rapid intensification, a period in which the maximum sustained winds of a tropical cyclone increase by or more within 24 hours. Similarly, rapid deepening in tropical cyclones is defined as a minimum sea surface pressure decrease of per hour or within a 24-hour period; explosive deepening occurs when the surface pressure decreases by per hour for at least 12 hours or per hour for at least 6 hours. For rapid intensification to occur, several conditions must be in place. Water temperatures must be extremely high (near or above ), and water of this temperature must be sufficiently deep such that waves do not upwell cooler waters to the surface. On the other hand,Tropical Cyclone Heat Potential
Tropical Cyclone Heat Potential (TCHP) is one of such non-conventional oceanographic parameters influencing the tropical cyclone intensity. The relationship between Sea Surface Temperature
Sea surface temperature (SST), or ocean surface tempera ...
is one of such non-conventional subsurface oceanographic parameters influencing the cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anti ...
intensity. Wind shear must be low; when wind shear is high, the convection and circulation in the cyclone will be disrupted. Usually, an anticyclone in the upper layers of the troposphere above the storm must be present as well—for extremely low surface pressures to develop, air must be rising very rapidly in the eyewall of the storm, and an upper-level anticyclone helps channel this air away from the cyclone efficiently. However, some cyclones such as Hurricane Epsilon have rapidly intensified despite relatively unfavorable conditions.
Dissipation
 There are a number of ways a tropical cyclone can weaken, dissipate, or lose its tropical characteristics. These include making landfall, moving over cooler water, encountering dry air, or interacting with other weather systems; however, once a system has dissipated or lost its tropical characteristics, its remnants could regenerate a tropical cyclone if environmental conditions become favorable.
A tropical cyclone can dissipate when it moves over waters significantly cooler than . This will deprive the storm of such tropical characteristics as a warm core with thunderstorms near the center, so that it becomes a remnant low-pressure area. Remnant systems may persist for several days before losing their identity. This dissipation mechanism is most common in the eastern North Pacific. Weakening or dissipation can also occur if a storm experiences vertical wind shear which causes the convection and heat engine to move away from the center; this normally ceases the development of a tropical cyclone. In addition, its interaction with the main belt of the Westerlies, by means of merging with a nearby frontal zone, can cause tropical cyclones to evolve into extratropical cyclones. This transition can take 1–3 days.
Should a tropical cyclone make landfall or pass over an island, its circulation could start to break down, especially if it encounters mountainous terrain. When a system makes landfall on a large landmass, it is cut off from its supply of warm moist maritime air and starts to draw in dry continental air. This, combined with the increased friction over land areas, leads to the weakening and dissipation of the tropical cyclone. Over a mountainous terrain, a system can quickly weaken; however, over flat areas, it may endure for two to three days before circulation breaks down and dissipates.
Over the years, there have been a number of techniques considered to try to artificially modify tropical cyclones. These techniques have included using
There are a number of ways a tropical cyclone can weaken, dissipate, or lose its tropical characteristics. These include making landfall, moving over cooler water, encountering dry air, or interacting with other weather systems; however, once a system has dissipated or lost its tropical characteristics, its remnants could regenerate a tropical cyclone if environmental conditions become favorable.
A tropical cyclone can dissipate when it moves over waters significantly cooler than . This will deprive the storm of such tropical characteristics as a warm core with thunderstorms near the center, so that it becomes a remnant low-pressure area. Remnant systems may persist for several days before losing their identity. This dissipation mechanism is most common in the eastern North Pacific. Weakening or dissipation can also occur if a storm experiences vertical wind shear which causes the convection and heat engine to move away from the center; this normally ceases the development of a tropical cyclone. In addition, its interaction with the main belt of the Westerlies, by means of merging with a nearby frontal zone, can cause tropical cyclones to evolve into extratropical cyclones. This transition can take 1–3 days.
Should a tropical cyclone make landfall or pass over an island, its circulation could start to break down, especially if it encounters mountainous terrain. When a system makes landfall on a large landmass, it is cut off from its supply of warm moist maritime air and starts to draw in dry continental air. This, combined with the increased friction over land areas, leads to the weakening and dissipation of the tropical cyclone. Over a mountainous terrain, a system can quickly weaken; however, over flat areas, it may endure for two to three days before circulation breaks down and dissipates.
Over the years, there have been a number of techniques considered to try to artificially modify tropical cyclones. These techniques have included using nuclear weapons
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
, cooling the ocean with icebergs, blowing the storm away from land with giant fans, and seeding selected storms with dry ice or silver iodide
Silver iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula Ag I. The compound is a bright yellow solid, but samples almost always contain impurities of metallic silver that give a gray coloration. The silver contamination arises because AgI is hig ...
. These techniques, however, fail to appreciate the duration, intensity, power or size of tropical cyclones.
Methods for assessing intensity
A variety of methods or techniques, including surface, satellite, and aerial, are used to assess the intensity of a tropical cyclone. Reconnaissance aircraft fly around and through tropical cyclones, outfitted with specialized instruments, to collect information that can be used to ascertain the winds and pressure of a system. Tropical cyclones possess winds of different speeds at different heights. Winds recorded at flight level can be converted to find the wind speeds at the surface. Surface observations, such as ship reports, land stations, mesonets, coastal stations, and buoys, can provide information on a tropical cyclone's intensity or the direction it is traveling. Wind-pressure relationships (WPRs) are used as a way to determine the pressure of a storm based on its wind speed. Several different methods and equations have been proposed to calculate WPRs. Tropical cyclones agencies each use their own, fixed WPR, which can result in inaccuracies between agencies that are issuing estimates on the same system. The ASCAT is a scatterometer used by the MetOp satellites to map the wind field vectors of tropical cyclones. The SMAP uses an L-bandradiometer
A radiometer or roentgenometer is a device for measuring the radiant flux (power) of electromagnetic radiation. Generally, a radiometer is an infrared radiation detector or an ultraviolet detector. Microwave radiometers operate in the microwave w ...
channel to determine the wind speeds of tropical cyclones at the ocean surface, and has been shown to be reliable at higher intensities and under heavy rainfall conditions, unlike scatterometer-based and other radiometer-based instruments.
The Dvorak technique plays a large role in both the classification of a tropical cyclone and the determination of its intensity. Used in warning centers, the method was developed by Vernon Dvorak
Vernon Francis Dvorak (November 15, 1928 – September 19, 2022) was an American meteorologist. He studied meteorology at the University of California, Los Angeles and wrote his Master thesis ''An investigation of the inversion-cloud regime over ...
in the 1970s, and uses both visible and infrared satellite imagery in the assessment of tropical cyclone intensity. The Dvorak technique uses a scale of "T-numbers", scaling in increments of 0.5 from T1.0 to T8.0. Each T-number has an intensity assigned to it, with larger T-numbers indicating a stronger system. Tropical cyclones are assessed by forecasters according to an array of patterns, including curved banding features, shear, central dense overcast, and eye, in order to determine the T-number and thus assess the intensity of the storm. The Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies works to develop and improve automated satellite methods, such as the Advanced Dvorak Technique (ADT) and SATCON. The ADT, used by a large number of forecasting centers, uses infrared geostationary satellite imagery and an algorithm based upon the Dvorak technique to assess the intensity of tropical cyclones. The ADT has a number of differences from the conventional Dvorak technique, including changes to intensity constraint rules and the usage of microwave imagery to base a system's intensity upon its internal structure, which prevents the intensity from leveling off before an eye emerges in infrared imagery. The SATCON weights estimates from various satellite-based systems and microwave sounders, accounting for the strengths and flaws in each individual estimate, to produce a consensus estimate of a tropical cyclone's intensity which can be more reliable than the Dvorak technique at times.
Intensity metrics
Multiple intensity metrics are used, includingaccumulated cyclone energy
Accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) is a metric used by various agencies to express the energy released by a tropical cyclone during its lifetime. It is calculating by summing the square of a tropical cyclone's maximum sustained winds, measured ever ...
(ACE), the Hurricane Surge Index
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm, storm system characterized by a Low-pressure area, low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, Beaufort scale, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms tha ...
, the Hurricane Severity Index The Hurricane Severity Index (or HSI) is a hurricane rating system which defines the strength and destructive capability of a storm. The HSI uses equations which incorporate the intensity of the winds and the size of the area covered by the winds. T ...
, the Power Dissipation Index
Power most often refers to:
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
** Abusive power
Power may a ...
(PDI), and integrated kinetic energy
Integration may refer to:
Biology
*Multisensory integration
*Path integration
* Pre-integration complex, viral genetic material used to insert a viral genome into a host genome
*DNA integration, by means of site-specific recombinase technology, ...
(IKE). ACE is a metric of the total energy a system has exerted over its lifespan. ACE is calculated by summing the squares of a cyclone's sustained wind speed, every six hours as long as the system is at or above tropical storm intensity and either tropical or subtropical. The calculation of the PDI is similar in nature to ACE, with the major difference being that wind speeds are cubed rather than squared. The Hurricane Surge Index is a metric of the potential damage a storm may inflict via storm surge. It is calculated by squaring the dividend of the storm's wind speed and a climatological value (), and then multiplying that quantity by the dividend of the radius of hurricane-force winds and its climatological value (). This can be represented in equation form as:
:
where v is the storm's wind speed and r is the radius of hurricane-force winds. The Hurricane Severity Index is a scale that can assign up to 50 points to a system; up to 25 points come from intensity, while the other 25 come from the size of the storm's wind field. The IKE model measures the destructive capability of a tropical cyclone via winds, waves, and surge. It is calculated as:
:
where p is the density of air, u is a sustained surface wind speed value, and d is the volume element.
Classification and naming
Intensity classifications
 Around the world, tropical cyclones are classified in different ways, based on the location ( tropical cyclone basins), the structure of the system and its intensity. For example, within the Northern Atlantic and Eastern Pacific basins, a tropical cyclone with wind speeds of over is called a hurricane, while it is called a typhoon or a severe cyclonic storm within the Western Pacific or North Indian Oceans. Within the Southern Hemisphere, it is either called a hurricane, tropical cyclone or a severe tropical cyclone, depending on if it is located within the South Atlantic, South-West Indian Ocean, Australian region or the South Pacific Ocean.
Around the world, tropical cyclones are classified in different ways, based on the location ( tropical cyclone basins), the structure of the system and its intensity. For example, within the Northern Atlantic and Eastern Pacific basins, a tropical cyclone with wind speeds of over is called a hurricane, while it is called a typhoon or a severe cyclonic storm within the Western Pacific or North Indian Oceans. Within the Southern Hemisphere, it is either called a hurricane, tropical cyclone or a severe tropical cyclone, depending on if it is located within the South Atlantic, South-West Indian Ocean, Australian region or the South Pacific Ocean.
Naming
The practice of using names to identify tropical cyclones goes back many years, with systems named after places or things they hit before the formal start of naming. The system currently used provides positive identification of severe weather systems in a brief form, that is readily understood and recognized by the public. The credit for the first usage of personal names for weather systems is generally given to the Queensland Government MeteorologistClement Wragge
Clement Lindley Wragge (18 September 185210 December 1922) was a meteorologist born in Stourbridge, Worcestershire, England, but moved to Oakamoor, Staffordshire as a child. He set up the Wragge Museum in Stafford following a trip around the wor ...
who named systems between 1887 and 1907. This system of naming weather systems subsequently fell into disuse for several years after Wragge retired, until it was revived in the latter part of World War II for the Western Pacific. Formal naming schemes have subsequently been introduced for the North and South Atlantic, Eastern, Central, Western and Southern Pacific basins as well as the Australian region and Indian Ocean.
At present, tropical cyclones are officially named by one of twelve meteorological services and retain their names throughout their lifetimes to provide ease of communication between forecasters and the general public regarding forecasts, watches, and warnings. Since the systems can last a week or longer and more than one can be occurring in the same basin at the same time, the names are thought to reduce the confusion about what storm is being described. Names are assigned in order from predetermined lists
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
with one, three, or ten-minute sustained wind speeds of more than depending on which basin it originates. However, standards vary from basin to basin with some tropical depressions named in the Western Pacific, while tropical cyclones have to have a significant amount of gale-force winds occurring around the center before they are named within the Southern Hemisphere. The names of significant tropical cyclones in the North Atlantic Ocean, Pacific Ocean, and Australian region are retired from the naming lists and replaced with another name. Tropical cyclones that develop around the world are assigned an identification code consisting of a two-digit number and suffix letter by the warning centers that monitor them.
Structure
Eye and center
 At the center of a mature tropical cyclone, air sinks rather than rises. For a sufficiently strong storm, air may sink over a layer deep enough to suppress cloud formation, thereby creating a clear "
At the center of a mature tropical cyclone, air sinks rather than rises. For a sufficiently strong storm, air may sink over a layer deep enough to suppress cloud formation, thereby creating a clear "eye
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and conv ...
". Weather in the eye is normally calm and free of convective clouds, although the sea may be extremely violent. The eye is normally circular and is typically in diameter, though eyes as small as and as large as have been observed.
The cloudy outer edge of the eye is called the "eyewall". The eyewall typically expands outward with height, resembling an arena football stadium; this phenomenon is sometimes referred to as the "stadium effect
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather at the center of tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area, typically in diameter. It is surrounded by the ''eyewall'', a ring of towering thunderstorms where the most severe wea ...
". The eyewall is where the greatest wind speeds are found, air rises most rapidly, clouds reach their highest altitude, and precipitation is the heaviest. The heaviest wind damage occurs where a tropical cyclone's eyewall passes over land.
In a weaker storm, the eye may be obscured by the central dense overcast, which is the upper-level cirrus shield that is associated with a concentrated area of strong thunderstorm activity near the center of a tropical cyclone.
The eyewall may vary over time in the form of eyewall replacement cycles
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather at the center of tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area, typically in diameter. It is surrounded by the ''eyewall'', a ring of towering thunderstorms where the most severe weat ...
, particularly in intense tropical cyclones. Outer rainbands can organize into an outer ring of thunderstorms that slowly moves inward, which is believed to rob the primary eyewall of moisture and angular momentum. When the primary eyewall weakens, the tropical cyclone weakens temporarily. The outer eyewall eventually replaces the primary one at the end of the cycle, at which time the storm may return to its original intensity.
Size
There are a variety of metrics commonly used to measure storm size. The most common metrics include the radius of maximum wind, the radius of wind (i.e. gale force), the radius of outermost closed isobar ( ROCI), and the radius of vanishing wind. An additional metric is the radius at which the cyclone's relative vorticity field decreases to 1×10−5 s−1. On Earth, tropical cyclones span a large range of sizes, from as measured by the radius of vanishing wind. They are largest on average in the northwest Pacific Ocean basin and smallest in the northeastern Pacific Ocean basin. If the radius of outermost closed isobar is less than two degrees of latitude (), then the cyclone is "very small" or a "midget". A radius of 3–6 latitude degrees () is considered "average sized". "Very large" tropical cyclones have a radius of greater than 8 degrees (). Observations indicate that size is only weakly correlated to variables such as storm intensity (i.e. maximum wind speed), radius of maximum wind, latitude, and maximum potential intensity. Typhoon Tip is the largest cyclone on record, with tropical storm-force winds in diameter. The smallest storm on record isTropical Storm Marco (2008)
Tropical Storm Marco was the smallest tropical cyclone on record by radius of winds from center. The thirteenth named storm of the 2008 Atlantic hurricane season, Marco developed out of a broad area of low pressure over the northwestern Caribbean ...
, which generated tropical storm-force winds only in diameter.
Movement
The movement of a tropical cyclone (i.e. its "track") is typically approximated as the sum of two terms: "steering" by the background environmental wind and "beta drift". Some tropical cyclones can move across large distances, such as Hurricane John, the longest-lasting tropical cyclone on record, which traveled , the longest track of any Northern Hemisphere tropical cyclone, over its 31-day lifespan in1994
File:1994 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1994 Winter Olympics are held in Lillehammer, Norway; The Kaiser Permanente building after the 1994 Northridge earthquake; A model of the MS Estonia, which Sinking of the MS Estonia, sank in ...
.
Environmental steering
Environmental steering is the primary influence on the motion of tropical cyclones. It represents the movement of the storm due to prevailing winds and other wider environmental conditions, similar to "leaves carried along by a stream". Physically, the winds, orflow field
Flow may refer to:
Science and technology
* Fluid flow, the motion of a gas or liquid
* Flow (geomorphology), a type of mass wasting or slope movement in geomorphology
* Flow (mathematics), a group action of the real numbers on a set
* Flow (psych ...
, in the vicinity of a tropical cyclone may be treated as having two parts: the flow associated with the storm itself, and the large-scale background flow of the environment. Tropical cyclones can be treated as local maxima of vorticity suspended within the large-scale background flow of the environment. In this way, tropical cyclone motion may be represented to first-order as advection
In the field of physics, engineering, and earth sciences, advection is the transport of a substance or quantity by bulk motion of a fluid. The properties of that substance are carried with it. Generally the majority of the advected substance is al ...
of the storm by the local environmental flow. This environmental flow is termed the "steering flow" and is the dominant influence on tropical cyclone motion. The strength and direction of the steering flow can be approximated as a vertical integration of the winds blowing horizontally in the cyclone's vicinity, weighted by the altitude at which those winds are occurring. Because winds can vary with height, determining the steering flow precisely can be difficult.
The pressure altitude at which the background winds are most correlated with a tropical cyclone's motion is known as the "steering level". The motion of stronger tropical cyclones is more correlated with the background flow averaged across a thicker portion of troposphere compared to weaker tropical cyclones whose motion is more correlated with the background flow averaged across a narrower extent of the lower troposphere. When wind shear and latent heat release is present, tropical cyclones tend to move towards regions where potential vorticity
In fluid mechanics, potential vorticity (PV) is a quantity which is proportional to the dot product of vorticity and stratification. This quantity, following a parcel of air or water, can only be changed by diabatic or frictional processes. It i ...
is increasing most quickly.
Climatologically, tropical cyclones are steered primarily westward by the east-to-west trade winds on the equatorial side of the subtropical ridge
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as Subtropics, subtropical ridges, or highs. It is a h ...
—a persistent high-pressure area over the world's subtropical oceans. In the tropical North Atlantic and Northeast Pacific oceans, the trade winds steer tropical easterly waves westward from the African coast toward the Caribbean Sea, North America, and ultimately into the central Pacific Ocean before the waves dampen out. These waves are the precursors to many tropical cyclones within this region. In contrast, in the Indian Ocean and Western Pacific in both hemispheres, tropical cyclogenesis is influenced less by tropical easterly waves and more by the seasonal movement of the Intertropical Convergence Zone and the monsoon trough. Other weather systems such as mid-latitude trough
Trough may refer to:
In science
* Trough (geology), a long depression less steep than a trench
* Trough (meteorology), an elongated region of low atmospheric pressure
* Trough (physics), the lowest point on a wave
* Trough level (medicine), the l ...
s and broad monsoon gyres can also influence tropical cyclone motion by modifying the steering flow.
Beta drift
In addition to environmental steering, a tropical cyclone will tend to drift poleward and westward, a motion known as "beta drift". This motion is due to the superposition of a vortex, such as a tropical cyclone, onto an environment in which theCoriolis force
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
varies with latitude, such as on a sphere or beta plane. The magnitude of the component of tropical cyclone motion associated with the beta drift ranges between and tends to be larger for more intense tropical cyclones and at higher latitudes. It is induced indirectly by the storm itself as a result of feedback between the cyclonic flow of the storm and its environment.
Physically, the cyclonic circulation of the storm advects environmental air poleward east of center and equatorial west of center. Because air must conserve its angular momentum, this flow configuration induces a cyclonic gyre equatorward and westward of the storm center and an anticyclonic gyre poleward and eastward of the storm center. The combined flow of these gyres acts to advect the storm slowly poleward and westward. This effect occurs even if there is zero environmental flow. Due to a direct dependence of the beta drift on angular momentum, the size of a tropical cyclone can impact the influence of beta drift on its motion; beta drift imparts a greater influence on the movement of larger tropical cyclones than that of smaller ones.
Multiple storm interaction
A third component of motion that occurs relatively infrequently involves the interaction of multiple tropical cyclones. When two cyclones approach one another, their centers will begin orbiting cyclonically about a point between the two systems. Depending on their separation distance and strength, the two vortices may simply orbit around one another, or else may spiral into the center point and merge. When the two vortices are of unequal size, the larger vortex will tend to dominate the interaction, and the smaller vortex will orbit around it. This phenomenon is called the Fujiwhara effect, after Sakuhei Fujiwhara.Interaction with the mid-latitude westerlies
 Though a tropical cyclone typically moves from east to west in the tropics, its track may shift poleward and eastward either as it moves west of the subtropical ridge axis or else if it interacts with the mid-latitude flow, such as the
Though a tropical cyclone typically moves from east to west in the tropics, its track may shift poleward and eastward either as it moves west of the subtropical ridge axis or else if it interacts with the mid-latitude flow, such as the jet stream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow, meandering thermal wind, air currents in the Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheres of some planets, including Earth. On Earth, the main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are west ...
or an extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of ...
. This motion, termed "recurvature
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes and trend to ...
", commonly occurs near the western edge of the major ocean basins, where the jet stream typically has a poleward component and extratropical cyclones are common. An example of tropical cyclone recurvature was Typhoon Ioke
Hurricane Ioke, also referred to as Typhoon Ioke, had the highest Accumulated cyclone energy, accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) of any tropical cyclone on record. The first and only storm to form in the Central Pacific in the 2006 Pacific hurrica ...
in 2006.
Formation regions and warning centers
The majority of tropical cyclones each year form in one of seven tropical cyclone basins, which are monitored by a variety of meteorological services and warning centres. Ten of these warning centres worldwide are designated as either a Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre or aTropical Cyclone Warning Centre
A Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre (RSMC) is responsible for the distribution of information, advisories, and warnings regarding the specific program they have a part of, agreed by consensus at the World Meteorological Organization as p ...
by the World Meteorological Organisation's (WMO) tropical cyclone programme. These warning centres issue advisories which provide basic information and cover a systems present, forecast position, movement and intensity, in their designated areas of responsibility. Meteorological services around the world are generally responsible for issuing warnings for their own country, however, there are exceptions, as the United States National Hurricane Center and Fiji Meteorological Service issue alerts, watches and warnings for various island nations in their areas of responsibility. The United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center and Fleet Weather Center also publicly issue warnings, about tropical cyclones on behalf of the United States Government. The Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center names South Atlantic tropical cyclones, however the South Atlantic is not a major basin, and not an official basin according to the WMO.
Preparations
Ahead of the formal season starting, people are urged to prepare for the effects of a tropical cyclone by politicians and weather forecasters, amongst others. They prepare by determining their risk to the different types of weather, tropical cyclones cause, checking their insurance coverage and emergency supplies, as well as determining where to evacuate to if needed. When a tropical cyclone develops and is forecast to impact land, each member nation of the World Meteorological Organization issues various watches and warnings to cover the expected impacts. However, there are some exceptions with the United States National Hurricane Center and Fiji Meteorological Service responsible for issuing or recommending warnings for other nations in their area of responsibility.Impacts
Natural phenomena caused or worsened by tropical cyclones
Tropical cyclones out at sea cause large waves, heavy rain, floods and high winds, disrupting international shipping and, at times, causing shipwrecks. Tropical cyclones stir up water, leaving a cool wake behind them, which causes the region to be less favorable for subsequent tropical cyclones. On land, strong winds can damage or destroy vehicles, buildings, bridges, and other outside objects, turning loose debris into deadly flying projectiles. Thestorm surge
A storm surge, storm flood, tidal surge, or storm tide is a coastal flood or tsunami-like phenomenon of rising water commonly associated with low-pressure weather systems, such as cyclones. It is measured as the rise in water level above the n ...
, or the increase in sea level due to the cyclone, is typically the worst effect from landfalling tropical cyclones, historically resulting in 90% of tropical cyclone deaths. Cyclone Mahina
Cyclone Mahina was the deadliest cyclone in recorded Australian history, and also likely the most intense tropical cyclone ever recorded in the Southern Hemisphere. Mahina struck Bathurst Bay, Cape York Peninsula, Queensland, on 4 March 1899, ...
produced the highest storm surge on record, , at Bathurst Bay
Bathurst Bay is a bay in the localities of Lakefield and Starcke in the Shire of Cook, Queensland, Australia. In the 19th century it was the base for the pearling fleet. It is now a tourist attraction on Cape York Peninsula in northern Que ...
, Queensland, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, in March 1899. Other ocean-based hazards that tropical cyclones produce are rip currents and undertow. These hazards can occur hundreds of kilometers (hundreds of miles) away from the center of a cyclone, even if other weather conditions are favorable.
The broad rotation of a landfalling tropical cyclone, and vertical wind shear at its periphery, spawns tornadoes. Tornadoes can also be spawned as a result of eyewall mesovortices, which persist until landfall. Hurricane Ivan produced 120 tornadoes, more than any other tropical cyclone. Lightning activity is produced within tropical cyclones; this activity is more intense within stronger storms and closer to and within the storm's eyewall. Tropical cyclones can increase the amount of snowfall a region experiences by delivering additional moisture. Wildfires can be worsened when a nearby storm fans their flames with its strong winds.
Impact on property and human life

tropical wave
A tropical wave (also called easterly wave, tropical easterly wave, and African easterly wave), in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which ...
s generated over the Sahara Desert, or otherwise strike the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
and Southern Africa. Cyclone Idai in March 2019 hit central Mozambique, becoming the deadliest tropical cyclone on record in Africa, with 1,302 fatalities, and damage estimated at US$2.2 billion. Réunion
Réunion (; french: La Réunion, ; previously ''Île Bourbon''; rcf, label= Reunionese Creole, La Rényon) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas department and region of France. It is located approximately east of the island ...
island, located east of Southern Africa, experiences some of the wettest tropical cyclones on record. In January 1980, Cyclone Hyacinthe produced 6,083 mm (239.5 in) of rain over 15 days, which was the largest rain total recorded from a tropical cyclone on record. In Asia, tropical cyclones from the Indian and Pacific oceans regularly affect some of the most populated countries on Earth. In 1970, a cyclone struck Bangladesh, then known as East Pakistan, producing a storm surge that killed at least 300,000 people; this made it the deadliest tropical cyclone on record. In October 2019, Typhoon Hagibis struck the Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
ese island of Honshu and inflicted US$15 billion in damage, making it the costliest storm on record in Japan. The islands that comprise Oceania, from Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
to French Polynesia
)Territorial motto: ( en, "Great Tahiti of the Golden Haze")
, anthem =
, song_type = Regional anthem
, song = " Ia Ora 'O Tahiti Nui"
, image_map = French Polynesia on the globe (French Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of Frenc ...
, are routinely affected by tropical cyclones. In Indonesia, a cyclone struck the island of Flores
Flores is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, a group of islands in the eastern half of Indonesia. Including the Komodo Islands off its west coast (but excluding the Solor Archipelago to the east of Flores), the land area is 15,530.58 km2, and th ...
in April 1973, killing 1,653 people, making it the deadliest tropical cyclone recorded in the Southern Hemisphere.
Atlantic and Pacific hurricanes regularly affect North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
. In the United States, hurricanes Katrina
Katrina or Katrine may refer to:
People
* Katrina (given name)
* Katrine (given name)
Meteorology
* List of storms named Katrina, a list of tropical cyclones designated as Katrina
** Hurricane Katrina, an exceptionally powerful Atlantic hurrican ...
in 2005 and Harvey in 2017 are the country's costliest ever natural disasters, with monetary damage estimated at US$125 billion. Katrina struck Louisiana and largely destroyed the city of New Orleans, while Harvey caused significant flooding in southeastern Texas after it dropped of rainfall; this was the highest rainfall total on record in the country. Europe is rarely affected by tropical cyclones; however, the continent regularly encounters storms after they transitioned into extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of ...
s. Only one tropical depression – Vince in 2005 – struck Spain, and only one subtropical cyclone – Subtropical Storm Alpha The name Alpha or Alfa has been used for three subtropical cyclones and one tropical cyclone in the Atlantic Ocean:
* Subtropical Storm Alpha (1972), pre-season storm that made landfall in Georgia
* Subtropical Storm Alfa (1973), briefly threatened ...
in 2020 – struck Portugal. Occasionally, there are tropical-like cyclones in the Mediterranean Sea. The northern portion of South America experiences occasional tropical cyclones, with 173 fatalities from Tropical Storm Bret in August 1993. The South Atlantic Ocean is generally inhospitable to the formation of a tropical storm. However, in March 2004, Hurricane Catarina
Hurricane Catarina, or Cyclone Catarina () was an extraordinarily rare South Atlantic tropical cyclone, the only recorded hurricane strength storm on record in the South Atlantic Ocean. Catarina made landfall on South Brazil at peak intensity, ...
struck southeastern Brazil as the first hurricane on record in the South Atlantic Ocean.
Environmental impact
Although cyclones take an enormous toll in lives and personal property, they may be important factors in the precipitation regimes of places they impact, as they may bring much-needed precipitation to otherwise dry regions. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration2005 Tropical Eastern North Pacific Hurricane Outlook.
. Retrieved May 2, 2006. Their precipitation may also alleviate drought conditions by restoring soil moisture, though one study focused on the Southeastern United States suggested tropical cyclones did not offer significant drought recovery. Tropical cyclones also help maintain the global heat balance by moving warm, moist tropical air to the middle latitudes and polar regions, and by regulating the thermohaline circulation through upwelling. The storm surge and winds of hurricanes may be destructive to human-made structures, but they also stir up the waters of coastal estuaries, which are typically important fish breeding locales. Ecosystems, such as saltmarshes and
Mangrove forest
Mangrove forests, also called mangrove swamps, mangrove thickets or mangals, are productive wetlands that occur in coastal intertidal zones. Mangrove forests grow mainly at tropical and subtropical latitudes because mangroves cannot withstand fr ...
s, can be severely damaged or destroyed by tropical cyclones, which erode land and destroy vegetation. Tropical cyclones can cause harmful algae blooms
An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in freshwater or marine water systems. It is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from the algae's pigments. The term ''algae'' encompa ...
to form in bodies of water by increasing the amount of nutrients available. Insect populations can decrease in both quantity and diversity after the passage of storms. Strong winds associated with tropical cyclones and their remnants are capable of felling thousands of trees, causing damage to forests.
When hurricanes surge upon shore from the ocean, salt is introduced to many freshwater areas and raises the salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
levels too high for some habitats to withstand. Some are able to cope with the salt and recycle it back into the ocean, but others can not release the extra surface water quickly enough or do not have a large enough freshwater source to replace it. Because of this, some species of plants and vegetation die due to the excess salt. In addition, hurricanes can carry toxins
A toxin is a naturally occurring organic poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. Toxins occur especially as a protein or conjugated protein. The term toxin was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1 ...
and acids onshore when they make landfall. The floodwater can pick up the toxins from different spills and contaminate the land that it passes over. These toxins are harmful to the people and animals in the area, as well as the environment around them. Tropical cyclones can cause oil spills by damaging or destroying pipelines and storage facilities. Similarly, chemical spills have been reported when chemical and processing facilities were damaged. Waterways have become contaminated with toxic levels of metals such as nickel, chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardne ...
, and mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
during tropical cyclones.
Tropical cyclones can have an extensive effect on geography, such as creating or destroying land. Cyclone Bebe increased the size of Tuvalu island, Funafuti Atoll
Funafuti is the capital of the island nation of Tuvalu. It has a population of 6,320 people (2017 census), and so it has more people than the rest of Tuvalu combined, with approximately 60% of the population. It consists of a narrow sweep of lan ...
, by nearly 20%. Hurricane Walaka destroyed the small East Island in 2018, which destroyed the habitat for the endangered Hawaiian monk seal, as well as, threatened sea turtles and seabirds. Landslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, deep-seated grade (slope), slope failures, mudflows, and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of ...
s frequently occur during tropical cyclones and can vastly alter landscapes; some storms are capable of causing hundreds to tens of thousands of landslides. Storms can erode coastlines over an extensive area and transport the sediment to other locations.
Response
 Hurricane response is the disaster response after a hurricane. Activities performed by hurricane responders include assessment, restoration, and demolition of buildings; removal of debris and waste; repairs to land-based and maritime
Hurricane response is the disaster response after a hurricane. Activities performed by hurricane responders include assessment, restoration, and demolition of buildings; removal of debris and waste; repairs to land-based and maritime infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and priv ...
; and public health services including search and rescue
Search and rescue (SAR) is the search for and provision of aid to people who are in distress or imminent danger. The general field of search and rescue includes many specialty sub-fields, typically determined by the type of terrain the search ...
operations. Hurricane response requires coordination between federal, tribal, state, local, and private entities. According to the National Voluntary Organizations Active in Disaster, potential response volunteers should affiliate with established organizations and should not self-deploy, so that proper training and support can be provided to mitigate the danger and stress of response work.
Hurricane responders face many hazards. Hurricane responders may be exposed to chemical and biological contaminants including stored chemicals, sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged from residenc ...
, human remains Human remains may refer to:
A corpse or skeleton
* A deceased human body
** A cadaver
** A Human skeleton, skeleton
Music
* Human Remains (band), an American grindcore band
* Human Remains (Hell album), ''Human Remains'' (Hell album), 2011
* Huma ...
, and mold growth encouraged by flooding, as well as asbestos
Asbestos () is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere b ...
and lead that may be present in older buildings. Common injuries arise from falls
Falls may refer to:
Places
* Waterfalls or rapids
* Falls, North Carolina, USA
* Falls, West Virginia, USA
Other uses
* The ropes or wires, fed through davits, that are used to secure and lower a ship's lifeboats.
* Falls (surname)
* The sepa ...
from heights, such as from a ladder or from level surfaces; from electrocution in flooded areas, including from backfeed from portable generators; or from motor vehicle accidents. Long and irregular shifts may lead to sleep deprivation
Sleep deprivation, also known as sleep insufficiency or sleeplessness, is the condition of not having adequate duration and/or quality of sleep to support decent alertness, performance, and health. It can be either chronic or acute and may vary ...
and fatigue
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve ...
, increasing the risk of injuries, and workers may experience mental stress associated with a traumatic incident. Additionally, heat stress is a concern as workers are often exposed to hot and humid temperatures, wear protective clothing and equipment, and have physically difficult tasks.
Climatology
Tropical cyclones have occurred around the world for millennia. Reanalyses and research are being undertaken to extend the historical record, through the usage of proxy data such as overwash deposits, beach ridges and historical documents such as diaries. Major tropical cyclones leave traces in overwash records and shell layers in some coastal areas, which have been used to gain insight into hurricane activity over the past thousands of years. Sediment records in Western Australia suggest an intense tropical cyclone in the4th millennium BC
The 4th millennium BC spanned the years 4000 BC to 3001 BC. Some of the major changes in human culture during this time included the beginning of the Bronze Age and the invention of writing, which played a major role in starting recorded history. ...
. Proxy records based on paleotempestological research have revealed that major hurricane activity along the Gulf of Mexico coast varies on timescales of centuries to millennia. In the year 957, a powerful typhoon struck southern China, killing around 10,000 people due to flooding. The Spanish colonization of Mexico described "tempestades" in 1730, although the official record for Pacific hurricanes only dates to 1949. In the south-west Indian Ocean, the tropical cyclone record goes back to 1848. In 2003, the Atlantic hurricane reanalysis project examined and analyzed the historical record of tropical cyclones in the Atlantic back to 1851, extending the existing database from 1886.
Before satellite imagery became available during the 20th century, many of these systems went undetected unless it impacted land or a ship encountered it by chance. Often in part because of the threat of hurricanes, many coastal regions had sparse population between major ports until the advent of automobile tourism; therefore, the most severe portions of hurricanes striking the coast may have gone unmeasured in some instances. The combined effects of ship destruction and remote landfall severely limit the number of intense hurricanes in the official record before the era of hurricane reconnaissance aircraft and satellite meteorology. Although the record shows a distinct increase in the number and strength of intense hurricanes, therefore, experts regard the early data as suspect. The ability of climatologists to make a long-term analysis of tropical cyclones is limited by the amount of reliable historical data. During the 1940s, routine aircraft reconnaissance started in both the Atlantic and Western Pacific basin during the mid-1940s, which provided ground truth data, however, early flights were only made once or twice a day. Polar-orbiting weather satellites were first launched by the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding th ...
in 1960 but were not declared operational until 1965. However, it took several years for some of the warning centres to take advantage of this new viewing platform and develop the expertise to associate satellite signatures with storm position and intensity.
Each year on average, around 80 to 90 named tropical cyclones form around the world, of which over half develop hurricane-force winds of or more. Worldwide, tropical cyclone activity peaks in late summer, when the difference between temperatures aloft and sea surface temperatures is the greatest. However, each particular basin has its own seasonal patterns. On a worldwide scale, May is the least active month, while September is the most active month. November is the only month in which all the tropical cyclone basins are in season. In the Northern Atlantic Ocean, a distinct cyclone season occurs from June 1 to November 30, sharply peaking from late August through September. The statistical peak of the Atlantic hurricane season is September 10. The Northeast Pacific Ocean has a broader period of activity, but in a similar time frame to the Atlantic. The Northwest Pacific sees tropical cyclones year-round, with a minimum in February and March and a peak in early September. In the North Indian basin, storms are most common from April to December, with peaks in May and November. In the Southern Hemisphere, the tropical cyclone year begins on July 1 and runs all year-round encompassing the tropical cyclone seasons, which run from November 1 until the end of April, with peaks in mid-February to early March.
Of various modes of variability in the climate system, El Niño–Southern Oscillation has the largest impact on tropical cyclone activity. Most tropical cyclones form on the side of the subtropical ridge closer to the equator, then move poleward past the ridge axis before recurving into the main belt of the Westerlies. When the subtropical ridge
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as Subtropics, subtropical ridges, or highs. It is a h ...
position shifts due to El Niño, so will the preferred tropical cyclone tracks. Areas west of Japan and Korea tend to experience much fewer September–November tropical cyclone impacts during El Niño and neutral years. During La Niña years, the formation of tropical cyclones, along with the subtropical ridge position, shifts westward across the western Pacific Ocean, which increases the landfall threat to China and much greater intensity in the Philippines. The Atlantic Ocean experiences depressed activity due to increased vertical wind shear across the region during El Niño years. Tropical cyclones are further influenced by the Atlantic Meridional Mode, the Quasi-biennial oscillation and the Madden–Julian oscillation.
Influence of climate change
Clausius–Clapeyron relation
The Clausius–Clapeyron relation, named after Rudolf Clausius and Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron, specifies the temperature dependence of pressure, most importantly vapor pressure, at a discontinuous phase transition between two phases of matter ...
, which yields ≈7% increase in water vapor in the atmosphere per warming. All models that were assessed in a 2019 review paper show a future increase of rainfall rates. Additional sea level rise will increase storm surge levels. It is plausible that extreme wind wave
In fluid dynamics, a wind wave, water wave, or wind-generated water wave, is a surface wave that occurs on the free surface of bodies of water as a result from the wind blowing over the water surface. The contact distance in the direction of t ...
s see an increase as a consequence of changes in tropical cyclones, further exacerbating storm surge dangers to coastal communities. The compounding effects from floods, storm surge, and terrestrial flooding (rivers) are projected to increase due to global warming.
There is currently no consensus on how climate change will affect the overall frequency of tropical cyclones. A majority of climate models show a decreased frequency in future projections. For instance, a 2020 paper comparing nine high-resolution climate models found robust decreases in frequency in the Southern Indian Ocean and the Southern Hemisphere more generally, while finding mixed signals for Northern Hemisphere tropical cyclones. Observations have shown little change in the overall frequency of tropical cyclones worldwide, with increased frequency in the North Atlantic and central Pacific, and significant decreases in the southern Indian Ocean and western North Pacific. There has been a poleward expansion of the latitude at which the maximum intensity of tropical cyclones occurs, which may be associated with climate change. In the North Pacific, there may also have been an eastward expansion. Between 1949 and 2016, there was a slowdown in tropical cyclone translation speeds. It is unclear still to what extent this can be attributed to climate change: climate models do not all show this feature.
Observation and forecasting
Observation

 Intense tropical cyclones pose a particular observation challenge, as they are a dangerous oceanic phenomenon, and weather stations, being relatively sparse, are rarely available on the site of the storm itself. In general, surface observations are available only if the storm is passing over an island or a coastal area, or if there is a nearby ship. Real-time measurements are usually taken in the periphery of the cyclone, where conditions are less catastrophic and its true strength cannot be evaluated. For this reason, there are teams of meteorologists that move into the path of tropical cyclones to help evaluate their strength at the point of landfall.
Tropical cyclones are tracked by weather satellites capturing
Intense tropical cyclones pose a particular observation challenge, as they are a dangerous oceanic phenomenon, and weather stations, being relatively sparse, are rarely available on the site of the storm itself. In general, surface observations are available only if the storm is passing over an island or a coastal area, or if there is a nearby ship. Real-time measurements are usually taken in the periphery of the cyclone, where conditions are less catastrophic and its true strength cannot be evaluated. For this reason, there are teams of meteorologists that move into the path of tropical cyclones to help evaluate their strength at the point of landfall.
Tropical cyclones are tracked by weather satellites capturing visible
Visibility, in meteorology, is a measure of the distance at which an object or light can be seen.
Visibility may also refer to:
* A measure of turbidity in water quality control
* Interferometric visibility, which quantifies interference contrast ...
and infrared images from space, usually at half-hour to quarter-hour intervals. As a storm approaches land, it can be observed by land-based Doppler weather radar. Radar plays a crucial role around landfall by showing a storm's location and intensity every several minutes. Other satellites provide information from the perturbations of GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
signals, providing thousands of snapshots per day and capturing atmospheric temperature, pressure, and moisture content.
In situ measurements, in real-time, can be taken by sending specially equipped reconnaissance flights into the cyclone. In the Atlantic basin, these flights are regularly flown by United States government hurricane hunters. These aircraft fly directly into the cyclone and take direct and remote-sensing measurements. The aircraft also launch GPS dropsonde
A dropsonde is an expendable weather reconnaissance device created by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), designed to be dropped from an aircraft at altitude over water to measure (and therefore track) storm conditions as the devi ...
s inside the cyclone. These sondes measure temperature, humidity, pressure, and especially winds between flight level and the ocean's surface. A new era in hurricane observation began when a remotely piloted Aerosonde, a small drone aircraft, was flown through Tropical Storm Ophelia as it passed Virginia's eastern shore during the 2005 hurricane season
During 2005, tropical cyclones formed within seven different tropical cyclone basins, located within various parts of the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. During the year, a total of 141 systems formed with 94 of these developing further and ...
. A similar mission was also completed successfully in the western Pacific Ocean.

Forecasting
High-speed computers and sophisticated simulation software allow forecasters to produce computer models that predict tropical cyclone tracks based on the future position and strength of high- and low-pressure systems. Combining forecast models with increased understanding of the forces that act on tropical cyclones, as well as with a wealth of data from Earth-orbitingsatellites
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotop ...
and other sensors, scientists have increased the accuracy of track forecasts over recent decades. However, scientists are not as skillful at predicting the intensity of tropical cyclones. The lack of improvement in intensity forecasting is attributed to the complexity of tropical systems and an incomplete understanding of factors that affect their development. New tropical cyclone position and forecast information is available at least every six hours from the various warning centers.Geopotential height
In meteorology, geopotential heights are used when creating forecasts and analyzing pressure systems. Geopotential heights represent the estimate of the real height of a pressure system above the average sea level. Geopotential heights for weather are divided up into several levels. The lowest geopotential height level is , which represents the lowest of the atmosphere. The moisture content, gained by using either the relative humidity or the precipitable water value, is used in creating forecasts for precipitation. The next level, , is at a height of ; 700 hPa is regarded as the highest point in the lower atmosphere. At this layer, both vertical movement and moisture levels are used to locate and create forecasts for precipitation. The middle level of the atmosphere is at or a height of . The 500 hPa level is used for measuring atmospheric vorticity, commonly known as the spin of air. The relative humidity is also analyzed at this height in order to establish where precipitation is likely to materialize. The next level occurs at or a height of . The top-most level is located at , which corresponds to a height of . Both the 200 and 300 hPa levels are mainly used to locate the jet stream.Related cyclone types
In addition to tropical cyclones, there are two other classes of cyclones within the spectrum of cyclone types. These kinds of cyclones, known asextratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of ...
s and subtropical cyclones, can be stages a tropical cyclone passes through during its formation or dissipation. An ''extratropical cyclone'' is a storm that derives energy from horizontal temperature differences, which are typical in higher latitudes. A tropical cyclone can become extratropical as it moves toward higher latitudes if its energy source changes from heat released by condensation to differences in temperature between air masses; although not as frequently, an extratropical cyclone can transform into a subtropical storm, and from there into a tropical cyclone. From space, extratropical storms have a characteristic "comma
The comma is a punctuation mark that appears in several variants in different languages. It has the same shape as an apostrophe or single closing quotation mark () in many typefaces, but it differs from them in being placed on the baseline ...
-shaped" cloud pattern. Extratropical cyclones can also be dangerous when their low-pressure centers cause powerful winds and high seas.
A ''subtropical cyclone'' is a weather system that has some characteristics of a tropical cyclone and some characteristics of an extratropical cyclone. They can form in a wide band of latitudes, from the equator to 50°. Although subtropical storms rarely have hurricane-force winds, they may become tropical in nature as their cores warm.
See also
*Tropical cyclones in
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
* Atlantic hurricane season
* Pacific hurricane season
* Pacific typhoon season
* North Indian Ocean cyclone season
* South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season
* Australian region cyclone season
* South Pacific cyclone season
References
Further reading
* Barnes, Jay. ''Fifteen Hurricanes That Changed the Carolinas: Powerful Storms, Climate Change, and What We Do Next'' (University of North Carolina Press, 2022online review
* Vecchi, Gabriel A., et al. "Changes in Atlantic major hurricane frequency since the late-19th century." ''Nature communications'' 12.1 (2021): 1-9
online
* Weinkle, Jessica, et al. "Normalized hurricane damage in the continental United States 1900–2017." ''Nature Sustainability'' 1.12 (2018): 808-813
online
External links
United States National Hurricane Center
nbsp;– North Atlantic, Eastern Pacific
United States Central Pacific Hurricane Center
nbsp;– Central Pacific
Japan Meteorological Agency
nbsp;– Western Pacific
India Meteorological Department
nbsp;– Indian Ocean
Météo-France – La Reunion
nbsp;– South Indian Ocean from 30°E to 90°E
Indonesian Meteorological Department
nbsp;– South Indian Ocean from 90°E to 125°E, north of 10°S
Australian Bureau of Meteorology
nbsp;– South Indian Ocean and South Pacific Ocean from 90°E to 160°E
Papua New Guinea National Weather Service
nbsp;– South Pacific east of 160°E, north of 10°S
Fiji Meteorological Service
nbsp;– South Pacific west of 160°E, north of 25° S
MetService New Zealand
nbsp;– South Pacific west of 160°E, south of 25°S {{DEFAULTSORT:Tropical Cyclone Articles containing video clips Climate change and hurricanes Meteorological phenomena Types of cyclone Vortices Weather hazards Storm