Human Rights In Niger on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread
 The genus ''Homo'' evolved from ''
The genus ''Homo'' evolved from ''
 Until about 12,000 years ago, all humans lived as hunter-gatherers. The Neolithic Revolution (the invention of
Until about 12,000 years ago, all humans lived as hunter-gatherers. The Neolithic Revolution (the invention of  Following the
Following the
 Estimates of the population at the time agriculture emerged in around 10,000 BC have ranged between 1 million and 15 million. Around 50–60 million people lived in the combined eastern and western
Estimates of the population at the time agriculture emerged in around 10,000 BC have ranged between 1 million and 15 million. Around 50–60 million people lived in the combined eastern and western
 Most aspects of human physiology are closely homologous to corresponding aspects of animal physiology. The human body consists of the legs, the
Most aspects of human physiology are closely homologous to corresponding aspects of animal physiology. The human body consists of the legs, the
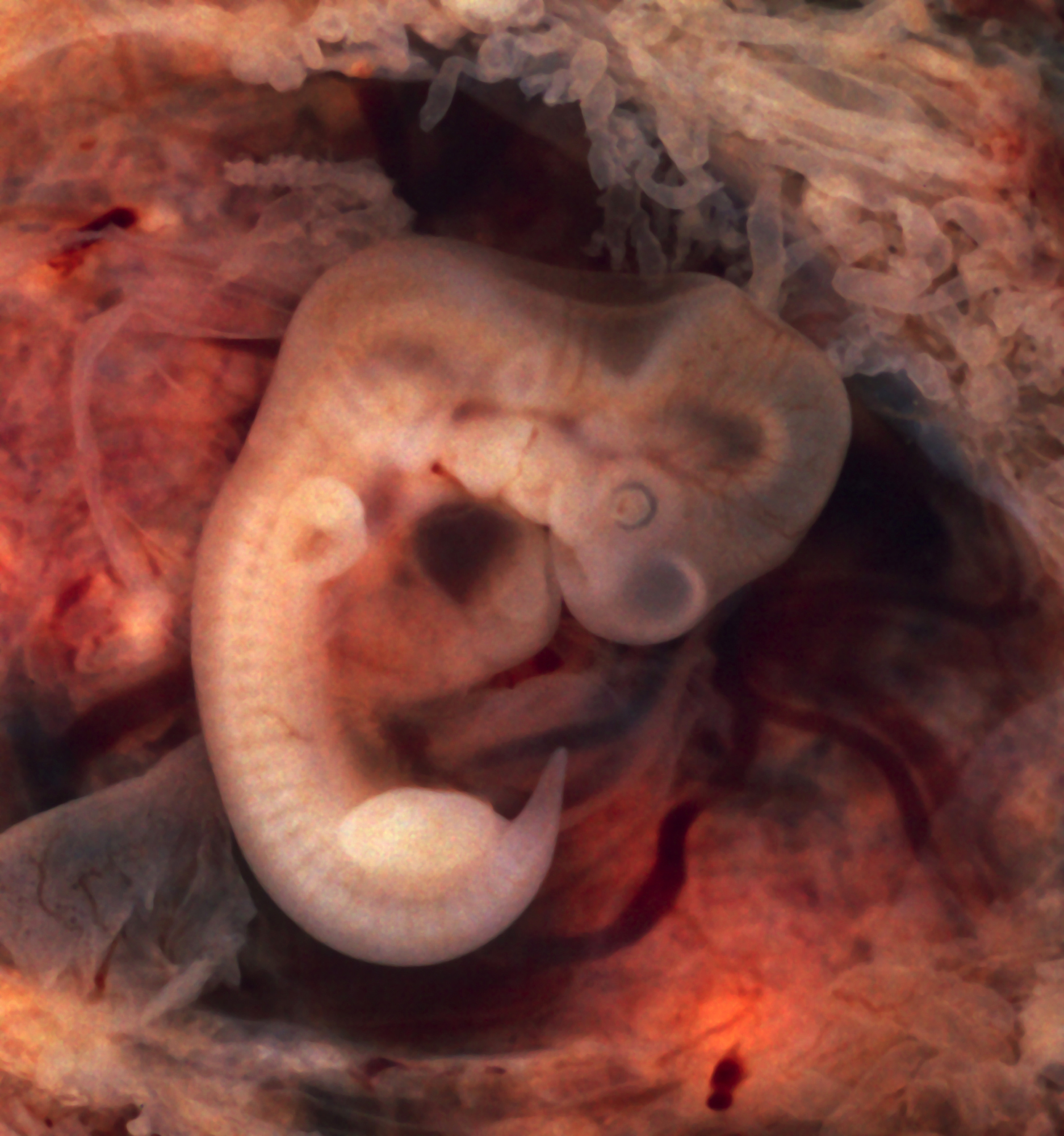
 Like most animals, humans are a diploid and
Like most animals, humans are a diploid and
 Most
Most
 Humans are
Humans are
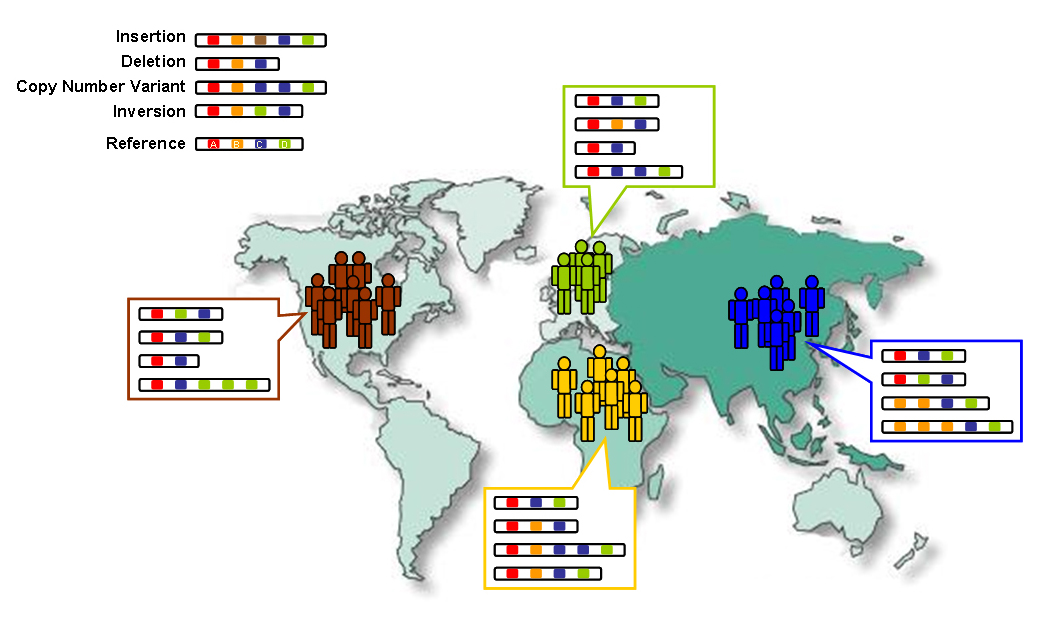 There is biological variation in the human species—with traits such as blood type,
There is biological variation in the human species—with traits such as blood type,  There is relatively little variation between human geographical populations, and most of the variation that occurs is at the individual level. Much of human variation is continuous, often with no clear points of demarcation. Genetic data shows that no matter how population groups are defined, two people from the same population group are almost as different from each other as two people from any two different population groups. Dark-skinned populations that are found in Africa, Australia, and South Asia are not closely related to each other.
Genetic research has demonstrated that human populations native to the African continent are the most genetically diverse and genetic diversity decreases with migratory distance from Africa, possibly the result of bottlenecks during human migration. These non-African populations acquired new genetic inputs from local admixture with archaic populations and have much greater variation from Neanderthals and Denisovans than is found in Africa, though Neanderthal admixture into African populations may be underestimated. Furthermore, recent studies have found that populations in sub-Saharan Africa, and particularly
There is relatively little variation between human geographical populations, and most of the variation that occurs is at the individual level. Much of human variation is continuous, often with no clear points of demarcation. Genetic data shows that no matter how population groups are defined, two people from the same population group are almost as different from each other as two people from any two different population groups. Dark-skinned populations that are found in Africa, Australia, and South Asia are not closely related to each other.
Genetic research has demonstrated that human populations native to the African continent are the most genetically diverse and genetic diversity decreases with migratory distance from Africa, possibly the result of bottlenecks during human migration. These non-African populations acquired new genetic inputs from local admixture with archaic populations and have much greater variation from Neanderthals and Denisovans than is found in Africa, though Neanderthal admixture into African populations may be underestimated. Furthermore, recent studies have found that populations in sub-Saharan Africa, and particularly
 The
The
 Human motivation is not yet wholly understood. From a psychological perspective, Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a well-established theory that can be defined as the process of satisfying certain needs in ascending order of complexity. From a more general, philosophical perspective, human motivation can be defined as a commitment to, or withdrawal from, various goals requiring the application of human ability. Furthermore,
Human motivation is not yet wholly understood. From a psychological perspective, Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a well-established theory that can be defined as the process of satisfying certain needs in ascending order of complexity. From a more general, philosophical perspective, human motivation can be defined as a commitment to, or withdrawal from, various goals requiring the application of human ability. Furthermore,
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
of primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter including ...
, characterized by bipedalism
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' ...
and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
, and language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structure
In the social sciences, social structure is the aggregate of patterned social arrangements in society that are both emergent from and determinant of the actions of individuals. Likewise, society is believed to be grouped into structurally rel ...
s composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideal ...
and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms
Social norms are shared standards of acceptable behavior by groups. Social norms can both be informal understandings that govern the behavior of members of a society, as well as be codified into rules and laws. Social normative influences or soci ...
, and ritual
A ritual is a sequence of activities involving gestures, words, actions, or objects, performed according to a set sequence. Rituals may be prescribed by the traditions of a community, including a religious community. Rituals are characterized ...
s, which bolster human society
A society is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction, or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Soci ...
. Its intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can be des ...
and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
, philosophy, mythology
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narra ...
, religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, ...
, and other fields of study
Fields may refer to:
Music
* Fields (band), an indie rock band formed in 2006
* Fields (progressive rock band), a progressive rock band formed in 1971
* ''Fields'' (album), an LP by Swedish-based indie rock band Junip (2010)
* "Fields", a song b ...
.
Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus '' Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' ( modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely relat ...
'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically modern human
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its ...
s emerged around 300,000 years ago in Africa, evolving from ''Homo heidelbergensis
''Homo heidelbergensis'' (also ''H. sapiens heidelbergensis''), sometimes called Heidelbergs, is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human which existed during the Middle Pleistocene. It was subsumed as a subspecies of '' H. erectus'' i ...
'' or a similar species and migrating out of Africa
''Out of Africa'' is a memoir by the Danish author Karen Blixen. The book, first published in 1937, recounts events of the seventeen years when Blixen made her home in Kenya, then called British East Africa. The book is a lyrical meditation on ...
, gradually replacing or interbreeding
In biology, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different breeds, varieties, species or genera through sexual reproduction. Hybrids are not always intermediates between their parents (such as in ...
with local populations of archaic humans. For most of history, humans were nomadic
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the popu ...
hunter-gatherers. Humans began exhibiting behavioral modernity
Behavioral modernity is a suite of behavioral and cognitive traits that distinguishes current '' Homo sapiens'' from other anatomically modern humans, hominins, and primates. Most scholars agree that modern human behavior can be characterize ...
about 160,000–60,000 years ago. The Neolithic Revolution, which began in Southwest Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
around 13,000 years ago (and separately in a few other places), saw the emergence of agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
and permanent human settlement
In geography, statistics and archaeology, a settlement, locality or populated place is a community in which people live. The complexity of a settlement can range from a minuscule number of dwellings grouped together to the largest of ci ...
. As populations became larger and denser, forms of governance developed within and between communities, and a number of civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
...
s have risen and fallen. Humans have continued to expand, with a global population of over 8 billion .
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s and the environment
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
influence human biological variation in visible characteristics, physiology, disease susceptibility, mental abilities, body size, and life span. Though humans vary in many traits (such as genetic predispositions and physical features), any two humans are at least 99% genetically similar. Humans are sexually dimorphic: generally, males have greater body strength and females have a higher body fat
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular e ...
percentage. At puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a bo ...
, humans develop secondary sex characteristic
Secondary sex characteristics are features that appear during puberty in humans, and at sexual maturity in other animals. These characteristics are particularly evident in the sexually dimorphic phenotypic traits that distinguish the sexes of a s ...
s. Females are capable of pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occur ...
, usually between puberty, at around 12 years, and menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often ...
, around the age of 50.
Humans are omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nut ...
, capable of consuming a wide variety of plant and animal material, and have used fire and other forms of heat to prepare and cook
Cook or The Cook may refer to:
Food preparation
* Cooking, the preparation of food
* Cook (domestic worker), a household staff member who prepares food
* Cook (professional), an individual who prepares food for consumption in the food industry
* ...
food since the time of ''H. erectus''. Humans can survive for up to eight weeks without food and three or four days without water. Humans are generally diurnal, sleeping on average seven to nine hours per day. Childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births glob ...
is dangerous, with a high risk of complications and death. Often, both the mother and the father provide care for their children, who are helpless at birth.
Humans have a large and highly developed prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46 ...
, the region of the brain associated with higher cognition. They are highly intelligent, capable of episodic memory
Episodic memory is the memory of everyday events (such as times, location geography, associated emotions, and other contextual information) that can be explicitly stated or conjured. It is the collection of past personal experiences that occurred ...
, have flexible facial expressions, self-awareness, and a theory of mind
In psychology, theory of mind refers to the capacity to understand other people by ascribing mental states to them (that is, surmising what is happening in their mind). This includes the knowledge that others' mental states may be different fro ...
. The human mind is capable of introspection
Introspection is the examination of one's own conscious thoughts and feelings. In psychology, the process of introspection relies on the observation of one's mental state, while in a spiritual context it may refer to the examination of one's sou ...
, private thought, imagination, volition, and forming views on existence
Existence is the ability of an entity to interact with reality. In philosophy, it refers to the ontological property of being.
Etymology
The term ''existence'' comes from Old French ''existence'', from Medieval Latin ''existentia/exsistentia' ...
. This has allowed great technological advancements and complex tool development possible through complex reasoning and the transmission of knowledge to subsequent generations. Language, art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
, and trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct excha ...
are defining characteristics of humans. Long-distance trade routes might have led to cultural explosions and resource distribution that gave humans an advantage over other similar species.
Etymology and definition
All modern humans are classified into thespecies
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
''Homo sapiens'', coined by Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his Nobility#Ennoblement, ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalise ...
in his 1735 work '' Systema Naturae''. The generic name "''Homo
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus '' Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' ( modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely relat ...
''" is a learned 18th-century derivation from Latin , which refers to humans of either sex. The word ''human'' can refer to all members of the ''Homo'' genus, although in common usage it generally just refers to ''Homo sapiens,'' the only extant species. The name "''Homo'' ''sapiens''" means 'wise man' or 'knowledgeable man'. There is disagreement if certain extinct members of the genus, namely Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the ...
s, should be included as a separate species of humans or as a subspecies of ''H. sapiens''.
''Human'' is a loanword
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because t ...
of Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English ...
from Old French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intellig ...
, ultimately from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, the adjectival form of ('man' — in the sense of humankind). The native English term ''man
A man is an adult male human. Prior to adulthood, a male human is referred to as a boy (a male child or adolescent). Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromo ...
'' can refer to the species generally (a synonym for ''humanity'') as well as to human males. It may also refer to individuals of either sex, though this form is less common in contemporary English.
Despite the fact that the word ''animal'' is colloquially used as an antonym for ''human'', and contrary to a common biological misconception, humans are animals. The word ''person
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of prope ...
'' is often used interchangeably with ''human'', but philosophical debate exists as to whether personhood applies to all humans or all sentient beings, and further if one can lose personhood (such as by going into a persistent vegetative state
A persistent vegetative state (PVS) or post-coma unresponsiveness (PCU) is a disorder of consciousness in which patients with severe brain damage are in a state of partial arousal rather than true awareness. After four weeks in a vegetative stat ...
).
Evolution
Humans are apes ( superfamily Hominoidea). The lineage of apes that eventually gave rise to humans first split from gibbons (family Hylobatidae) andorangutan
Orangutans are great apes native to the rainforests of Indonesia and Malaysia. They are now found only in parts of Borneo and Sumatra, but during the Pleistocene they ranged throughout Southeast Asia and South China. Classified in the genu ...
s (genus ''Pongo''), then gorilla
Gorillas are herbivorous, predominantly ground-dwelling great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or fi ...
s (genus ''Gorilla''), and finally, chimpanzees and bonobos (genus '' Pan''). The last split, between the human and chimpanzee–bonobo lineages, took place around 8–4 million years ago, in the late Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
epoch. During this split, chromosome 2
Chromosome 2 is one of the twenty-three pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 2 is the second-largest human chromosome, spanning more than 242 million base pairs and representing almost e ...
was formed from the joining of two other chromosomes, leaving humans with only 23 pairs of chromosomes, compared to 24 for the other apes. Following their split with chimpanzees and bonobos, the hominins
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas).
The t ...
diversified into many species and at least two distinct genera. All but one of these lineages—representing the genus ''Homo
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus '' Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' ( modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely relat ...
'' and its sole extant species ''Homo sapiens''—are now extinct.
 The genus ''Homo'' evolved from ''
The genus ''Homo'' evolved from ''Australopithecus
''Australopithecus'' (, ; ) is a genus of early hominins that existed in Africa during the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene. The genus ''Homo'' (which includes modern humans) emerged within ''Australopithecus'', as sister to e.g. ''Austral ...
''. Though fossils from the transition are scarce, the earliest members of ''Homo'' share several key traits with ''Australopithecus''. The earliest record of ''Homo'' is the 2.8 million-year-old specimen LD 350-1
LD 350-1 is the earliest known specimen of the genus ''Homo'', dating to 2.8–2.75 million years ago (mya), found in the Ledi-Geraru site in the Afar Region of Ethiopia. The specimen was discovered in silts above the Gurumaha Tuff section of th ...
from Ethiopia, and the earliest named species are '' Homo habilis'' and ''Homo rudolfensis
''Homo rudolfensis'' is an extinct species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East Africa about 2 million years ago (mya). Because ''H. rudolfensis'' coexisted with several other hominins, it is debated what specimens can be confide ...
'' which evolved by 2.3 million years ago. ''H. erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor' ...
'' (the African variant is sometimes called '' H. ergaster'') evolved 2 million years ago and was the first archaic human
A number of varieties of '' Homo'' are grouped into the broad category of archaic humans in the period that precedes and is contemporary to the emergence of the earliest early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') around 300 ka. Omo-Kibish I (Omo I) f ...
species to leave Africa and disperse across Eurasia. ''H. erectus'' also was the first to evolve a characteristically human body plan
A body plan, ( ), or ground plan is a set of morphological features common to many members of a phylum of animals. The vertebrates share one body plan, while invertebrates have many.
This term, usually applied to animals, envisages a "blueprin ...
. ''Homo sapiens'' emerged in Africa around 300,000 years ago from a species commonly designated as either '' H. heidelbergensis'' or '' H. rhodesiensis'', the descendants of ''H. erectus'' that remained in Africa. ''H. sapiens'' migrated out of the continent, gradually replacing or interbreeding with local populations of archaic humans. Humans began exhibiting behavioral modernity
Behavioral modernity is a suite of behavioral and cognitive traits that distinguishes current '' Homo sapiens'' from other anatomically modern humans, hominins, and primates. Most scholars agree that modern human behavior can be characterize ...
about 160,000-70,000 years ago, and possibly earlier.
The "out of Africa" migration took place in at least two waves, the first around 130,000 to 100,000 years ago, the second (Southern Dispersal
In the context of the recent African origin of modern humans, the Southern Dispersal scenario (also the coastal migration or great coastal migration hypothesis) refers to the early migration along the southern coast of Asia, from the Arabian Pen ...
) around 70,000 to 50,000 years ago. ''H. sapiens'' proceeded to colonize all the continents and larger islands, arriving in Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
60,000 years ago, Australia around 65,000 years ago, the Americas around 15,000 years ago, and remote islands such as Hawaii, Easter Island
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its ne ...
, Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
between the years 300 and 1280 CE.
Human evolution was not a simple linear or branched progression but involved interbreeding between related species. Genomic research has shown that hybridization between substantially diverged lineages was common in human evolution. DNA evidence suggests that several genes of Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the ...
origin are present among all non sub-Saharan African populations, and Neanderthals and other hominins, such as Denisovan
The Denisovans or Denisova hominins ) are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human that ranged across Asia during the Lower and Middle Paleolithic. Denisovans are known from few physical remains and consequently, most of what is known ...
s, may have contributed up to 6% of their genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
to present-day non sub-Saharan African humans.
Human evolution is characterized by a number of morphological, developmental
Development of the human body is the process of growth to maturity. The process begins with fertilization, where an egg released from the ovary of a female is penetrated by a sperm cell from a male. The resulting zygote develops through mitosi ...
, physiological, and behavioral
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as we ...
changes that have taken place since the split between the last common ancestor of humans and chimpanzees. The most significant of these adaptations are obligate bipedalism, increased brain size and decreased sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most an ...
(neoteny
Neoteny (), also called juvenilization,Montagu, A. (1989). Growing Young. Bergin & Garvey: CT. is the delaying or slowing of the physiological, or somatic, development of an organism, typically an animal. Neoteny is found in modern humans compa ...
). The relationship between all these changes is the subject of ongoing debate.
History
agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
) first took place in Southwest Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
and spread through large parts of the Old World over the following millennia. It also occurred independently in Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica ...
(about 6,000 years ago), China, Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
, and the Sahel and West Savanna regions of Africa. Access to food surplus led to the formation of permanent human settlement
In geography, statistics and archaeology, a settlement, locality or populated place is a community in which people live. The complexity of a settlement can range from a minuscule number of dwellings grouped together to the largest of ci ...
s, the domestication
Domestication is a sustained multi-generational relationship in which humans assume a significant degree of control over the reproduction and care of another group of organisms to secure a more predictable supply of resources from that group. ...
of animals and the use of metal tools for the first time in history. Agriculture and sedentary lifestyle led to the emergence of early civilizations
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
Civi ...
.
An urban revolution took place in the 4th millennium BC
The 4th millennium BC spanned the years 4000 BC to 3001 BC. Some of the major changes in human culture during this time included the beginning of the Bronze Age and the invention of writing, which played a major role in starting recorded history. ...
E with the development of city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
s, particularly Sumerian cities located in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
. It was in these cities that the earliest known form of writing, cuneiform script, appeared around 3000 BCE. Other major civilizations to develop around this time were Ancient Egypt and the Indus Valley Civilization. They eventually traded with each other and invented technology such as wheels, plows and sails. Astronomy and mathematics were also developed and the Great Pyramid of Giza
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the biggest Egyptian pyramid and the tomb of Fourth Dynasty pharaoh Khufu. Built in the early 26th century BC during a period of around 27 years, the pyramid is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient Worl ...
was built. There is evidence of a severe drought lasting about a hundred years that may have caused the decline of these civilizations, with new ones appearing in the aftermath. Babylonians came to dominate Mesopotamia while others, such as Poverty Point culture
The Poverty Point culture is the archaeological culture of a prehistoric indigenous peoples who inhabited a portion of North America's lower Mississippi Valley and surrounding Gulf coast from about 1730 – 1350 BC.
Archeologists have identified ...
s, Minoans and the Shang dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and ...
, rose to prominence in new areas. The Bronze Age suddenly collapsed around 1200 BCE, resulting in the disappearance of a number of civilizations and the beginning of the Greek Dark Ages. During this period iron started replacing bronze, leading to the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
.
In the 5th century BCE, history started being recorded as a discipline, which provided a much clearer picture of life at the time. Between the 8th and 6th century BCE, Europe entered the classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
age, a period when ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of Classical Antiquity, classical antiquity ( AD 600), th ...
and ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC ...
flourished. Around this time other civilizations also came to prominence. The Maya civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, a ...
started to build cities and create complex calendars. In Africa, the Kingdom of Aksum overtook the declining Kingdom of Kush
The Kingdom of Kush (; Egyptian: 𓎡𓄿𓈙𓈉 ''kꜣš'', Assyrian: ''Kûsi'', in LXX grc, Κυς and Κυσι ; cop, ''Ecōš''; he, כּוּשׁ ''Kūš'') was an ancient kingdom in Nubia, centered along the Nile Valley in wh ...
and facilitated trade between India and the Mediterranean. In West Asia, the Achaemenid Empire's system of centralized governance became the precursor to many later empires, while the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gold ...
in India and the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
in China have been described as golden ages
A golden age is a period considered the apotheosis in the history of a country or people, a time period when the greatness, greatest achievements were made. The term originated from early ancient Greece, Greek and ancient Rome, Roman poets, who ...
in their respective regions.
 Following the
Following the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vas ...
in 476, Europe entered the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. During this period, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
and the Church
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a building for Christian religious activities
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship
* C ...
would provide centralized authority and education. In the Middle East, Islam became the prominent religion and expanded into North Africa. It led to an Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
, inspiring achievements in architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
, the revival of old advances in science and technology, and the formation of a distinct way of life. The Christian and Islamic worlds would eventually clash, with the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, ...
, the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period ...
and the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
declaring a series of holy wars
A religious war or a war of religion, sometimes also known as a holy war ( la, sanctum bellum), is a war which is primarily caused or justified by differences in religion. In the modern period, there are frequent debates over the extent to wh ...
to regain control of the Holy Land from Muslims. In the Americas, complex Mississippian societies would arise starting around 800 CE, while further south, the Aztecs and Incas
The Inca Empire (also known as the Incan Empire and the Inka Empire), called ''Tawantinsuyu'' by its subjects, ( Quechua for the "Realm of the Four Parts", "four parts together" ) was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The adm ...
would become the dominant powers. The Mongol Empire would conquer much of Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
in the 13th and 14th centuries. Over this same time period, the Mali Empire in Africa grew to be the largest empire on the continent, stretching from Senegambia to Ivory Coast. Oceania would see the rise of the Tuʻi Tonga Empire
The Tui Tonga Empire, or Tongan Empire, are descriptions sometimes given to Tongan expansionism and projected hegemony in Oceania which began around 950 CE, reaching its peak during the period 1200–1500.
It was centred in Tonga on the island o ...
which expanded across many islands in the South Pacific.
The early modern period in Europe and the Near East (c.1450–1800) began with the final defeat of the Byzantine Empire, and the rise of the Ottoman Empire
The rise of the Ottoman Empire is a period of history that started with the emergence of the Ottoman principality (Osmanlı Beyliği) in , and ended circa 1453. This period witnessed the foundation of a political entity ruled by the Ottoman D ...
. Meanwhile, Japan entered the Edo period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characte ...
, the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
rose in China and the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
ruled much of India. Europe underwent the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
, starting in the 15th century, and the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafarin ...
began with the exploring and colonizing of new regions. This includes the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
expanding to become the world's largest empire and the colonization of the Americas. This expansion led to the Atlantic slave trade and the genocide of Native American peoples. This period also marked the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology (including human anatomy) and chemistry transfo ...
, with great advances in mathematics, mechanics
Mechanics (from Ancient Greek: μηχανική, ''mēkhanikḗ'', "of machines") is the area of mathematics and physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among physical objects. Forces applied to object ...
, astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
and physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
.
The late modern period (1800–present) saw the Technological
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, ...
and Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
bring such discoveries as imaging technology
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
, major innovations in transport and energy development. The United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
underwent great change, going from a small group of colonies to one of the global superpower
A superpower is a state with a dominant position characterized by its extensive ability to exert influence or project power on a global scale. This is done through the combined means of economic, military, technological, political and cultural s ...
s. The Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
raged through Europe in the early 1800s, Spain lost most of its colonies in the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
, while Europeans continued expansion into Africa—where European control went from 10% to almost 90% in less than 50 years—and Oceania. A tenuous balance of power among European nations collapsed in 1914 with the outbreak of the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, one of the deadliest conflicts in history. In the 1930s, a worldwide economic crisis led to the rise of authoritarian regimes and a Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, involving almost all of the world's countries. Following its conclusion in 1945, the Cold War between the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
and the United States saw a struggle for global influence, including a nuclear arms race
The nuclear arms race was an arms race competition for supremacy in nuclear warfare between the United States, the Soviet Union, and their respective allies during the Cold War. During this same period, in addition to the American and Soviet nuc ...
and a space race
The Space Race was a 20th-century competition between two Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between the t ...
. The current Information Age
The Information Age (also known as the Computer Age, Digital Age, Silicon Age, or New Media Age) is a historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during ...
sees the world becoming increasingly globalized
Globalization, or globalisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is the process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide. The term ''globalization'' first appeared in the early 20t ...
and interconnected.
Habitat and population
Early human settlements were dependent on proximity towater
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
and—depending on the lifestyle—other natural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. ...
s used for subsistence
A subsistence economy is an economy directed to basic subsistence (the provision of food, clothing, shelter) rather than to the market. Henceforth, "subsistence" is understood as supporting oneself at a minimum level. Often, the subsistence econo ...
, such as populations of animal prey for hunting
Hunting is the human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products ( fur/ hide, bone/tusks, horn/antler, ...
and arable land
Arable land (from the la, arabilis, "able to be ploughed") is any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops.''Oxford English Dictionary'', "arable, ''adj''. and ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2013. Alternatively, for th ...
for growing crops and grazing livestock. Modern humans, however, have a great capacity for altering their habitats by means of technology, irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
, urban planning
Urban planning, also known as town planning, city planning, regional planning, or rural planning, is a technical and political process that is focused on the development and design of land use and the built environment, including air, water, ...
, construction, deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated ...
and desertification. Human settlements
In geography, statistics and archaeology, a settlement, locality or populated place is a community in which people live. The complexity of a settlement can range from a minuscule number of dwellings grouped together to the largest of cities ...
continue to be vulnerable to natural disasters, especially those placed in hazardous locations and with low quality of construction. Grouping and deliberate habitat alteration is often done with the goals of providing protection, accumulating comforts or material wealth, expanding the available food, improving aesthetics
Aesthetics, or esthetics, is a branch of philosophy that deals with the nature of beauty and taste, as well as the philosophy of art (its own area of philosophy that comes out of aesthetics). It examines aesthetic values, often expressed t ...
, increasing knowledge or enhancing the exchange of resources.
Humans are one of the most adaptable species, despite having a low or narrow tolerance for many of the earth's extreme environments. Through advanced tools, humans have been able to extend their tolerance to a wide variety of temperatures, humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity dep ...
, and altitudes. As a result, humans are a cosmopolitan
Cosmopolitan may refer to:
Food and drink
* Cosmopolitan (cocktail), also known as a "Cosmo"
History
* Rootless cosmopolitan, a Soviet derogatory epithet during Joseph Stalin's anti-Semitic campaign of 1949–1953
Hotels and resorts
* Cosmopoli ...
species found in almost all regions of the world, including tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equa ...
, arid desert, extremely cold arctic region
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
s, and heavily polluted cities; in comparison, most other species are confined to a few geographical areas by their limited adaptability. The human population is not, however, uniformly distributed on the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
's surface, because the population density varies from one region to another, and large stretches of surface are almost completely uninhabited, like Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
and vast swathes of the ocean. Most humans (61%) live in Asia; the remainder live in the Americas (14%), Africa (14%), Europe (11%), and Oceania (0.5%).
Within the last century, humans have explored challenging environments such as Antarctica, the deep sea
The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of 200 metres (656 feet) or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combin ...
, and outer space
Outer space, commonly shortened to space, is the expanse that exists beyond Earth and its atmosphere and between celestial bodies. Outer space is not completely empty—it is a near-perfect vacuum containing a low density of particles, pred ...
. Human habitation within these hostile environments is restrictive and expensive, typically limited in duration, and restricted to scientific
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
, military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
, or industrial
Industrial may refer to:
Industry
* Industrial archaeology, the study of the history of the industry
* Industrial engineering, engineering dealing with the optimization of complex industrial processes or systems
* Industrial city, a city dominate ...
expeditions. Humans have briefly visited the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
and made their presence felt on other celestial bodies through human-made robotic spacecraft. Since the early 20th century, there has been continuous human presence in Antarctica through research stations
Research stations are facilities where scientific investigation, collection, analysis and experimentation occurs. A research station is a facility that is built for the purpose of conducting scientific research. There are also many types of resea ...
and, since 2000, in space
''In Space'' is the fourth and final studio album by American rock group Big Star, released in 2005. It was the first new studio recording by the band since '' Third/Sister Lovers'', which was recorded in 1974.
The album featured original Big ...
through habitation on the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ( ...
.
 Estimates of the population at the time agriculture emerged in around 10,000 BC have ranged between 1 million and 15 million. Around 50–60 million people lived in the combined eastern and western
Estimates of the population at the time agriculture emerged in around 10,000 BC have ranged between 1 million and 15 million. Around 50–60 million people lived in the combined eastern and western Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
in the 4th century AD. Bubonic plagues, first recorded in the 6th century AD, reduced the population by 50%, with the Black Death killing 75–200 million people in Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
and North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
alone. Human population was believed to have reached one billion in 1800. It has since then increased exponentially, reaching two billion in 1930 and three billion in 1960, four in 1975, five in 1987 and six billion in 1999. It passed seven billion in 2011 and was expected to pass eight billion in November 2022. It took over two million years of human prehistory
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of ...
and history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
for the human population to reach one billion
Billion is a word for a large number, and it has two distinct definitions:
*1,000,000,000, i.e. one thousand million, or (ten to the ninth power), as defined on the short scale. This is its only current meaning in English.
* 1,000,000,000,000, i. ...
and only 207 years more to grow to 7 billion. The combined biomass of the carbon of all the humans on Earth in 2018 was estimated at 60 million tons, about 10 times larger than that of all non-domesticated mammals.
In 2018, 4.2 billion humans (55%) lived in urban areas, up from 751 million in 1950. The most urbanized regions are Northern America (82%), Latin America (81%), Europe (74%) and Oceania (68%), with Africa and Asia having nearly 90% of the world's 3.4 billion rural population. Problems for humans living in cities include various forms of pollution and crime, especially in inner city and suburban slums. Humans have had a dramatic effect on the environment. They are apex predator
An apex predator, also known as a top predator, is a predator at the top of a food chain, without natural predators of its own.
Apex predators are usually defined in terms of trophic dynamics, meaning that they occupy the highest trophic lev ...
s, being rarely preyed upon by other species. Human population growth, industrialization, land development, overconsumption
Overconsumption describes a situation where a consumer overuses their available goods and services to where they can't, or don't want to, replenish or reuse them. In microeconomics, this may be described as the point where the marginal cost of ...
and combustion of fossil fuels have led to environmental destruction
Environmental degradation is the deterioration of the environment through depletion of resources such as quality of air, water and soil; the destruction of ecosystems; habitat destruction; the extinction of wildlife; and pollution. It is defined ...
and pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the ...
that significantly contributes to the ongoing mass extinction
An extinction event (also known as a mass extinction or biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp change in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. I ...
of other forms of life. They are the main contributor to global climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
, which may accelerate the Holocene extinction.
Biology
Anatomy and physiology
 Most aspects of human physiology are closely homologous to corresponding aspects of animal physiology. The human body consists of the legs, the
Most aspects of human physiology are closely homologous to corresponding aspects of animal physiology. The human body consists of the legs, the torso
The torso or trunk is an anatomical term for the central part, or the core, of the body of many animals (including humans), from which the head, neck, limbs, tail and other appendages extend. The tetrapod torso — including that of a huma ...
, the arms, the neck, and the head. An adult human body consists of about 100 trillion (1014) cells. The most commonly defined body systems
A biological system is a complex network which connects several biologically relevant entities. Biological organization spans several scales and are determined based different structures depending on what the system is. Examples of biological syst ...
in humans are the nervous, the cardiovascular
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
, the digestive, the endocrine, the immune
In biology, immunity is the capability of multicellular organisms to resist harmful microorganisms. Immunity involves both specific and nonspecific components. The nonspecific components act as barriers or eliminators of a wide range of pathogens ...
, the integumentary
The integumentary system is the set of organs forming the outermost layer of an animal's body. It comprises the skin and its appendages, which act as a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment that it serves ...
, the lymphatic
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to ...
, the musculoskeletal
The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their muscular and skeletal systems. The musculoskeletal system prov ...
, the reproductive, the respiratory
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies gre ...
, and the urinary system
The urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, c ...
. The dental formula
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiolog ...
of humans is: . Humans have proportionately shorter palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separ ...
s and much smaller teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, t ...
than other primates. They are the only primates to have short, relatively flush canine teeth
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dog teeth, or (in the context of the upper jaw) fangs, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or vampire fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. They can appear more flattened howeve ...
. Humans have characteristically crowded teeth, with gaps from lost teeth usually closing up quickly in young individuals. Humans are gradually losing their third molars, with some individuals having them congenitally absent.
Humans share with chimpanzees a vestigial
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on co ...
tail, appendix, flexible shoulder joints, grasping fingers and opposable thumb
The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thumb ...
s. Apart from bipedalism and brain size, humans differ from chimpanzees mostly in smelling
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, it ...
, hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is audit ...
and digesting proteins. While humans have a density of hair follicles comparable to other apes, it is predominantly vellus hair
Vellus hair is short, thin, light-colored, and barely noticeable hair that develops on most of a human’s body during childhood. Exceptions include the lips, the back of the ear, the palm of the hand, the sole of the foot, some external genital ...
, most of which is so short and wispy as to be practically invisible. Humans have about 2 million sweat glands spread over their entire bodies, many more than chimpanzees, whose sweat glands are scarce and are mainly located on the palm of the hand and on the soles of the feet.
It is estimated that the worldwide average height for an adult human male is about , while the worldwide average height for adult human females is about . Shrinkage of stature may begin in middle age in some individuals but tends to be typical in the extremely aged
Ageing ( BE) or aging ( AE) is the process of becoming older. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi, whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal. In ...
. Throughout history, human populations have universally become taller, probably as a consequence of better nutrition, healthcare, and living conditions. The average mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different eleme ...
of an adult human is for females and for males. Like many other conditions, body weight and body type are influenced by both genetic susceptibility and environment and varies greatly among individuals.
Humans have a far faster and more accurate throw
Throwing is an action which consists in accelerating a projectile and then releasing it so that it follows a ballistic trajectory, usually with the aim of impacting a remote target. This action is best characterized for animals with prehensil ...
than other animals. Humans are also among the best long-distance runners in the animal kingdom, but slower over short distances. Humans' thinner body hair and more productive sweat glands help avoid heat exhaustion Heat exhaustion is a severe form of heat illness. It is a medical emergency. Heat exhaustion is caused by the loss of water and electrolytes through sweating.
The United States Department of Labor makes the following recommendation, "Heat illness ...
while running for long distances.
Genetics
 Like most animals, humans are a diploid and
Like most animals, humans are a diploid and eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the ...
species. Each somatic cell has two sets of 23 chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ...
s, each set received from one parent; gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce ...
s have only one set of chromosomes, which is a mixture of the two parental sets. Among the 23 pairs of chromosomes, there are 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes
A sex chromosome (also referred to as an allosome, heterotypical chromosome, gonosome, heterochromosome, or idiochromosome) is a chromosome that differs from an ordinary autosome in form, size, and behavior. The human sex chromosomes, a typical ...
. Like other mammals, humans have an XY sex-determination system
The XY sex-determination system is a sex-determination system used to classify many mammals, including humans, some insects (''Drosophila''), some snakes, some fish ( guppies), and some plants ('' Ginkgo'' tree). In this system, the sex of an i ...
, so that females have the sex chromosomes XX and males have XY. Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s and environment
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
influence human biological variation in visible characteristics, physiology, disease susceptibility and mental abilities. The exact influence of genes and environment on certain traits is not well understood.
While no humans—not even monozygotic twins
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of TwinLast Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two em ...
—are genetically identical, two humans on average will have a genetic similarity of 99.5%-99.9%. This makes them more homogeneous than other great apes, including chimpanzees. This small variation in human DNA compared to many other species suggests a population bottleneck during the Late Pleistocene (around 100,000 years ago), in which the human population was reduced to a small number of breeding pairs. The forces of natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
have continued to operate on human populations, with evidence that certain regions of the genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
display directional selection
In population genetics, directional selection, is a mode of negative natural selection in which an extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, causing the allele frequency to shift over time in the direction of that phenotype. Under dir ...
in the past 15,000 years.
The human genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the ...
was first sequenced in 2001 and by 2020 hundreds of thousands of genomes had been sequenced. In 2012 the International HapMap Project
The International HapMap Project was an organization that aimed to develop a haplotype map (HapMap) of the human genome, to describe the common patterns of human genetic variation. HapMap is used to find genetic variants affecting health, disease ...
had compared the genomes of 1,184 individuals from 11 populations and identified 1.6 million single nucleotide polymorphisms. African populations harbor the highest number of private genetic variants. While many of the common variants found in populations outside of Africa are also found on the African continent, there are still large numbers that are private to these regions, especially Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
and the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
. By 2010 estimates, humans have approximately 22,000 genes. By comparing mitochondrial DNA, which is inherited only from the mother, geneticists have concluded that the last female common ancestor whose genetic marker A genetic marker is a gene or DNA sequence with a known location on a chromosome that can be used to identify individuals or species. It can be described as a variation (which may arise due to mutation or alteration in the genomic loci) that can be ...
is found in all modern humans, the so-called mitochondrial Eve
In human genetics, the Mitochondrial Eve (also ''mt-Eve, mt-MRCA'') is the matrilineal most recent common ancestor (MRCA) of all living humans. In other words, she is defined as the most recent woman from whom all living humans descend in an ...
, must have lived around 90,000 to 200,000 years ago.
Life cycle
 Most
Most human reproduction
Human reproduction is sexual reproduction that results in human fertilization to produce a human offspring. It typically involves sexual intercourse between a sexually mature human male and female. During sexual intercourse, the interaction ...
takes place by internal fertilization
Internal fertilization is the union of an egg and sperm cell during sexual reproduction inside the female body. Internal fertilization, unlike its counterpart, external fertilization, brings more control to the female with reproduction. For inte ...
via sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. The average gestation period is 38 weeks, but a normal pregnancy can vary by up to 37 days. Embryonic development in the human covers the first eight weeks of development; at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal dev ...
. Humans are able to induce early labor or perform a caesarean section if the child needs to be born earlier for medical reasons. In developed countries, infants are typically in weight and in height at birth. However, low birth weight
Low birth weight (LBW) is defined by the World Health Organization as a birth weight of an
infant of or less, regardless of gestational age. Infants born with LBW have added health risks which require close management, often in a neonatal inten ...
is common in developing countries, and contributes to the high levels of infant mortality in these regions.
Compared with other species, human childbirth is dangerous, with a much higher risk of complications and death. The size of the fetus's head is more closely matched to the pelvis than other primates. The reason for this is not completely understood, but it contributes to a painful labor that can last 24 hours or more. The chances of a successful labor increased significantly during the 20th century in wealthier countries with the advent of new medical technologies. In contrast, pregnancy and natural childbirth
Natural childbirth is childbirth without routine medical interventions, particularly anesthesia. Natural childbirth arose in opposition to the techno-medical model of childbirth that has recently gained popularity in industrialized societies. Natur ...
remain hazardous ordeals in developing regions of the world, with maternal death rates
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to pre ...
approximately 100 times greater than in developed countries.
Both the mother and the father provide care for human offspring, in contrast to other primates, where parental care is mostly done by the mother. Helpless at birth, humans continue to grow for some years, typically reaching sexual maturity
Sexual maturity is the capability of an organism to reproduce. In humans it might be considered synonymous with adulthood, but here puberty is the name for the process of biological sexual maturation, while adulthood is based on cultural definit ...
at 15 to 17 years of age. The human life span has been split into various stages ranging from three to twelve. Common stages include infancy, childhood
A child (plural, : children) is a human being between the stages of childbirth, birth and puberty, or between the Development of the human body, developmental period of infancy and puberty. The legal definition of ''child'' generally refers ...
, adolescence, adulthood and old age. The lengths of these stages have varied across cultures and time periods but is typified by an unusually rapid growth spurt during adolescence. Human females undergo menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often ...
and become infertile at around the age of 50. It has been proposed that menopause increases a woman's overall reproductive success by allowing her to invest more time and resources in her existing offspring, and in turn their children (the grandmother hypothesis
The grandmother hypothesis is a hypothesis to explain the existence of menopause in human life history by identifying the adaptive value of extended kin networking. It builds on the previously postulated " mother hypothesis" which states that as m ...
), rather than by continuing to bear children into old age.
The life span of an individual depends on two major factors, genetics and lifestyle choices. For various reasons, including biological/genetic causes, women live on average about four years longer than men. , the global average life expectancy at birth
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for growth, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, energy t ...
of a girl is estimated to be 74.9 years compared to 70.4 for a boy. There are significant geographical variations in human life expectancy, mostly correlated with economic development—for example, life expectancy at birth in Hong Kong is 87.6 years for girls and 81.8 for boys, while in the Central African Republic
The Central African Republic (CAR; ; , RCA; , or , ) is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Chad to the north, Sudan to the northeast, South Sudan to the southeast, the DR Congo to the south, the Republic of th ...
, it is 55.0 years for girls and 50.6 for boys. The developed world is generally aging, with the median age around 40 years. In the developing world, the median age is between 15 and 20 years. While one in five Europeans is 60 years of age or older, only one in twenty Africans is 60 years of age or older. In 2012, the United Nations estimated that there were 316,600 living centenarians
A centenarian is a person who has reached the age of 100 years. Because life expectancies worldwide are below 100 years, the term is invariably associated with longevity. In 2012, the United Nations estimated that there were 316,600 living centen ...
(humans of age 100 or older) worldwide.
Diet
 Humans are
Humans are omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nut ...
, capable of consuming a wide variety of plant and animal material. Human groups have adopted a range of diets from purely vegan
Veganism is the practice of abstaining from the use of animal product—particularly in diet—and an associated philosophy that rejects the commodity status of animals. An individual who follows the diet or philosophy is known as a vegan. ...
to primarily carnivorous. In some cases, dietary restrictions in humans can lead to deficiency diseases
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues ...
; however, stable human groups have adapted to many dietary patterns through both genetic specialization and cultural conventions to use nutritionally balanced food sources. The human diet is prominently reflected in human culture and has led to the development of food science
Food science is the basic science and applied science of food; its scope starts at overlap with agricultural science and nutritional science and leads through the scientific aspects of food safety and food processing, informing the development ...
.
Until the development of agriculture approximately 10,000 years ago, ''Homo sapiens'' employed a hunter-gatherer method as their sole means of food collection. This involved combining stationary food sources (such as fruits, grains, tubers, and mushrooms, insect larvae and aquatic mollusks) with wild game
Game or quarry is any wild animal hunted for animal products (primarily meat), for recreation (" sporting"), or for trophies. The species of animals hunted as game varies in different parts of the world and by different local jurisdictions, th ...
, which must be hunted and captured in order to be consumed. It has been proposed that humans have used fire to prepare and cook
Cook or The Cook may refer to:
Food preparation
* Cooking, the preparation of food
* Cook (domestic worker), a household staff member who prepares food
* Cook (professional), an individual who prepares food for consumption in the food industry
* ...
food since the time of '' Homo erectus''. Around ten thousand years ago, humans developed agriculture, which substantially altered their diet. This change in diet may also have altered human biology; with the spread of dairy farming
Dairy farming is a class of agriculture for long-term production of milk, which is processed (either on the farm or at a dairy plant, either of which may be called a dairy) for eventual sale of a dairy product. Dairy farming has a history th ...
providing a new and rich source of food, leading to the evolution of the ability to digest lactose in some adults. The types of food consumed, and how they are prepared, have varied widely by time, location, and culture.
In general, humans can survive for up to eight weeks without food, depending on stored body fat. Survival without water is usually limited to three or four days, with a maximum of one week. In 2020 it is estimated 9 million humans die every year from causes directly or indirectly related to starvation. Childhood malnutrition is also common and contributes to the global burden of disease. However, global food distribution is not even, and obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
among some human populations has increased rapidly, leading to health complications and increased mortality in some developed and a few developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
. Worldwide, over one billion people are obese, while in the United States 35% of people are obese, leading to this being described as an "obesity epidemic
Obesity has been observed throughout human history. Many early depictions of the human form in art and sculpture appear obese. However, it was not until the 20th century that obesity became common — so much so that, in 1997, the World Heal ...
." Obesity is caused by consuming more calories than are expended, so excessive weight gain is usually caused by an energy-dense diet.
Biological variation
 There is biological variation in the human species—with traits such as blood type,
There is biological variation in the human species—with traits such as blood type, genetic diseases
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders ...
, cranial features, facial features, organ systems
An organ system is a biological system consisting of a group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions. Each organ has a specialized role in a plant or animal body, and is made up of distinct tissues.
Plants
Plants have ...
, eye color
Eye color is a polygenic phenotypic character determined by two distinct factors: the pigmentation of the eye's iris and the frequency-dependence of the scattering of light by the turbid medium in the stroma of the iris.
In humans, the ...
, hair color
Human hair color is the pigmentation of human hair follicles due to two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. Generally, if more melanin is present, the color of the hair is darker; if less melanin is present, the hair is lighter. The t ...
and texture
Texture may refer to:
Science and technology
* Surface texture, the texture means smoothness, roughness, or bumpiness of the surface of an object
* Texture (roads), road surface characteristics with waves shorter than road roughness
* Texture ...
, height
Height is measure of vertical distance, either vertical extent (how "tall" something or someone is) or vertical position (how "high" a point is).
For example, "The height of that building is 50 m" or "The height of an airplane in-flight is ab ...
and build, and skin color
Human skin color ranges from the darkest brown to the lightest hues. Differences in skin color among individuals is caused by variation in pigmentation, which is the result of genetics (inherited from one's biological parents and or individu ...
varying across the globe. The typical height of an adult human is between , although this varies significantly depending on sex, ethnic origin
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
, and family bloodlines. Body size is partly determined by genes and is also significantly influenced by environmental factors such as diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
, exercise, and sleep pattern
Sleep is a sedentary state of mind and body. It is characterized by altered consciousness, relatively inhibited sensory activity, reduced muscle activity and reduced interactions with surroundings. It is distinguished from wakefulness by a de ...
s.
There is evidence that populations have adapted genetically to various external factors. The genes that allow adult humans to digest lactose are present in high frequencies in populations that have long histories of cattle domestication and are more dependent on cow milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digest solid food. Immune factors and immune-modulati ...
. Sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited from a person's parents. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia. It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red bl ...
, which may provide increased resistance to malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
, is frequent in populations where malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
is endemic. Populations that have for a very long time inhabited specific climates tend to have developed specific phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological pr ...
s that are beneficial for those environments— short stature and stocky build in cold regions, tall and lanky in hot regions, and with high lung capacities or other adaptations at high altitudes. Some populations have evolved highly unique adaptations to very specific environmental conditions, such as those advantageous to ocean-dwelling lifestyles and freediving
Freediving, free-diving, free diving, breath-hold diving, or skin diving is a form of underwater diving that relies on breath-holding until resurfacing rather than the use of breathing apparatus such as scuba gear.
Besides the limits of breath-h ...
in the Bajau
The Sama-Bajau include several Austronesian ethnic groups of Maritime Southeast Asia. The name collectively refers to related people who usually call themselves the Sama or Samah (formally A'a Sama, "Sama people"); or are known by the exonym ...
.
Human hair ranges in color from red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
to blond to brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model us ...
to black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ...
, which is the most frequent. Hair color depends on the amount of melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
, with concentrations fading with increased age, leading to grey
Grey (more common in British English) or gray (more common in American English) is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning literally that it is "without color", because it can be composed o ...
or even white hair. Skin color can range from darkest brown to lightest peach, or even nearly white or colorless in cases of albinism
Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albino.
Varied use and interpretation of the term ...
. It tends to vary clinally and generally correlates with the level of ultraviolet radiation in a particular geographic area, with darker skin mostly around the equator. Skin darkening may have evolved as protection against ultraviolet solar radiation. Light skin pigmentation protects against depletion of vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (c ...
, which requires sunlight to make. Human skin also has a capacity to darken (tan) in response to exposure to ultraviolet radiation. There is relatively little variation between human geographical populations, and most of the variation that occurs is at the individual level. Much of human variation is continuous, often with no clear points of demarcation. Genetic data shows that no matter how population groups are defined, two people from the same population group are almost as different from each other as two people from any two different population groups. Dark-skinned populations that are found in Africa, Australia, and South Asia are not closely related to each other.
Genetic research has demonstrated that human populations native to the African continent are the most genetically diverse and genetic diversity decreases with migratory distance from Africa, possibly the result of bottlenecks during human migration. These non-African populations acquired new genetic inputs from local admixture with archaic populations and have much greater variation from Neanderthals and Denisovans than is found in Africa, though Neanderthal admixture into African populations may be underestimated. Furthermore, recent studies have found that populations in sub-Saharan Africa, and particularly
There is relatively little variation between human geographical populations, and most of the variation that occurs is at the individual level. Much of human variation is continuous, often with no clear points of demarcation. Genetic data shows that no matter how population groups are defined, two people from the same population group are almost as different from each other as two people from any two different population groups. Dark-skinned populations that are found in Africa, Australia, and South Asia are not closely related to each other.
Genetic research has demonstrated that human populations native to the African continent are the most genetically diverse and genetic diversity decreases with migratory distance from Africa, possibly the result of bottlenecks during human migration. These non-African populations acquired new genetic inputs from local admixture with archaic populations and have much greater variation from Neanderthals and Denisovans than is found in Africa, though Neanderthal admixture into African populations may be underestimated. Furthermore, recent studies have found that populations in sub-Saharan Africa, and particularly West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
, have ancestral genetic variation which predates modern humans and has been lost in most non-African populations. Some of this ancestry is thought to originate from admixture with an unknown archaic hominin that diverged before the split of Neanderthals and modern humans.
Humans are a gonochoric
In biology, gonochorism is a sexual system where there are only two sexes and each individual organism is either male or female. The term gonochorism is usually applied in animal species, the vast majority of which are gonochoric.
Gonochorism c ...
species, meaning they are divided into male and female sex
Sex is the trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing animal or plant produces male or female gametes. Male plants and animals produce smaller mobile gametes (spermatozoa, sperm, pollen), while females produce larger ones ( ova, of ...
es. The greatest degree of genetic variation exists between males and females. While the nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecule ...
genetic variation of individuals of the same sex across global populations is no greater than 0.1%–0.5%, the genetic difference between males
Male (symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilization.
A male organism cannot reproduce sexually without access to ...
and females
Female (symbol: ♀) is the sex of an organism that produces the large non-motile ova (egg cells), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Females ...
is between 1% and 2%. Males on average are 15% heavier and taller than females. On average, men have about 40–50% more upper body strength and 20–30% more lower body strength than women at the same weight, due to higher amounts of muscle and larger muscle fibers. Women generally have a higher body fat
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular e ...
percentage than men. Women have lighter skin than men of the same population; this has been explained by a higher need for vitamin D in females during pregnancy and lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The proces ...
. As there are chromosomal differences between females and males, some X and Y chromosome-related conditions and disorders only affect either men or women. After allowing for body weight and volume, the male voice is usually an octave deeper than the female voice. Women have a longer life span in almost every population around the world.
Psychology
 The
The human brain
The human brain is the central organ (anatomy), organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the act ...
, the focal point of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
in humans, controls the peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain ...
. In addition to controlling "lower," involuntary, or primarily autonomic activities such as respiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellul ...
and digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intest ...
, it is also the locus of "higher" order functioning such as thought, reason
Reason is the capacity of consciously applying logic by drawing conclusions from new or existing information, with the aim of seeking the truth. It is closely associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, science, ...
ing, and abstraction. These cognitive processes
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, ...
constitute the mind, and, along with their behavioral consequences, are studied in the field of psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between ...
.
Humans have a larger and more developed prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46 ...
than other primates, the region of the brain associated with higher cognition. This has led humans to proclaim themselves to be more intelligent than any other known species. Objectively defining intelligence is difficult, with other animals adapting senses and excelling in areas that humans are unable to.
There are some traits that, although not strictly unique, do set humans apart from other animals. Humans may be the only animals who have episodic memory
Episodic memory is the memory of everyday events (such as times, location geography, associated emotions, and other contextual information) that can be explicitly stated or conjured. It is the collection of past personal experiences that occurred ...
and who can engage in "mental time travel
In psychology, mental time travel is the capacity to mentally reconstruct personal events from the past (episodic memory) as well as to imagine possible scenarios in the future (episodic foresight / episodic future thinking). The term was coine ...
". Even compared with other social animals, humans have an unusually high degree of flexibility in their facial expressions. Humans are the only animals known to cry emotional tears. Humans are one of the few animals able to self-recognize in mirror test
The mirror test—sometimes called the mark test, mirror self-recognition (MSR) test, red spot technique, or rouge test—is a behavioral technique developed in 1970 by American psychologist Gordon Gallup Jr. as an attempt to determine whether an ...
s and there is also debate over to what extent humans are the only animals with a theory of mind
In psychology, theory of mind refers to the capacity to understand other people by ascribing mental states to them (that is, surmising what is happening in their mind). This includes the knowledge that others' mental states may be different fro ...
.
Sleep and dreaming
Humans are generally diurnal. The average sleep requirement is between seven and nine hours per day for an adult and nine to ten hours per day for a child; elderly people usually sleep for six to seven hours. Having less sleep than this is common among humans, even though sleep deprivation can have negative health effects. A sustained restriction of adult sleep to four hours per day has been shown to correlate with changes in physiology and mental state, including reduced memory, fatigue, aggression, and bodily discomfort. During sleep humans dream, where they experience sensory images and sounds. Dreaming is stimulated by thepons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other bipeds lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Va ...
and mostly occurs during the REM phase of sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep in mammals and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream viv ...
. The length of a dream can vary, from a few seconds up to 30 minutes. Humans have three to five dreams per night, and some may have up to seven; however most dreams are immediately or quickly forgotten. They are more likely to remember the dream if awakened during the REM phase. The events in dreams are generally outside the control of the dreamer, with the exception of lucid dream
A lucid dream is a type of dream in which the dreamer becomes aware that they are dreaming while dreaming. During a lucid dream, the dreamer may gain some amount of control over the dream characters, narrative, or environment; however, this is ...
ing, where the dreamer is self-aware
In philosophy of self, self-awareness is the experience of one's own personality or individuality. It is not to be confused with consciousness in the sense of qualia. While consciousness is being aware of one's environment and body and lifest ...
. Dreams can at times make a creative thought occur or give a sense of inspiration.
Consciousness and thought
Human consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience orawareness
Awareness is the state of being conscious of something. More specifically, it is the ability to directly know and perceive, to feel, or to be cognizant of events. Another definition describes it as a state wherein a subject is aware of some infor ...
of internal or external existence. Despite centuries of analyses, definitions, explanations and debates by philosophers and scientists, consciousness remains puzzling and controversial, being "at once the most familiar and most mysterious aspect of our lives". The only widely agreed notion about the topic is the intuition that it exists. Opinions differ about what exactly needs to be studied and explained as consciousness. Some philosophers divide consciousness into phenomenal consciousness, which is sensory experience itself, and access consciousness, which can be used for reasoning or directly controlling actions. It is sometimes synonymous with 'the mind', and at other times, an aspect of it. Historically it is associated with introspection
Introspection is the examination of one's own conscious thoughts and feelings. In psychology, the process of introspection relies on the observation of one's mental state, while in a spiritual context it may refer to the examination of one's sou ...
, private thought, imagination and volition. It now often includes some kind of experience
Experience refers to conscious events in general, more specifically to perceptions, or to the practical knowledge and familiarity that is produced by these conscious processes. Understood as a conscious event in the widest sense, experience involv ...
, cognition, feeling or perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system ...
. It may be 'awareness', or ' awareness of awareness', or self-awareness. There might be different levels or orders of consciousness, or different kinds of consciousness, or just one kind with different features.
The process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses is known as cognition. The human brain perceives the external world through the sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system re ...
s, and each individual human is influenced greatly by his or her experiences, leading to subjective views of existence
Existence is the ability of an entity to interact with reality. In philosophy, it refers to the ontological property of being.
Etymology
The term ''existence'' comes from Old French ''existence'', from Medieval Latin ''existentia/exsistentia' ...
and the passage of time. The nature of thought is central to psychology and related fields. Cognitive psychology studies cognition, the mental processes
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, ...
underlying behavior. Largely focusing on the development of the human mind through the life span, developmental psychology seeks to understand how people come to perceive, understand, and act within the world and how these processes change as they age. This may focus on intellectual, cognitive, neural, social, or moral development
Moral Development focuses on the emergence, change and understanding of morality from infancy through adulthood. Morality develops across a life span in a variety of ways and is influenced by an individual's experiences and behavior when faced ...
. Psychologists
A psychologist is a professional who practices psychology and studies mental states, perceptual, cognitive, emotional, and social processes and behavior. Their work often involves the experimentation, observation, and interpretation of how indi ...
have developed intelligence tests and the concept of intelligence quotient
An intelligence quotient (IQ) is a total score derived from a set of standardized tests or subtests designed to assess human intelligence. The abbreviation "IQ" was coined by the psychologist William Stern for the German term ''Intelligen ...
in order to assess the relative intelligence of human beings and study its distribution among population.
Motivation and emotion
 Human motivation is not yet wholly understood. From a psychological perspective, Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a well-established theory that can be defined as the process of satisfying certain needs in ascending order of complexity. From a more general, philosophical perspective, human motivation can be defined as a commitment to, or withdrawal from, various goals requiring the application of human ability. Furthermore,
Human motivation is not yet wholly understood. From a psychological perspective, Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a well-established theory that can be defined as the process of satisfying certain needs in ascending order of complexity. From a more general, philosophical perspective, human motivation can be defined as a commitment to, or withdrawal from, various goals requiring the application of human ability. Furthermore, incentive
In general, incentives are anything that persuade a person to alter their behaviour. It is emphasised that incentives matter by the basic law of economists and the laws of behaviour, which state that higher incentives amount to greater levels of ...
and preference are both factors, as are any perceived links between incentives and preferences. Volition may also be involved, in which case willpower is also a factor. Ideally, both motivation and volition ensure the selection, striving for, and realization of goals in an optimal manner, a function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-oriente ...
beginning in childhood and continuing throughout a lifetime in a process known as socialization
In sociology, socialization or socialisation (see spelling differences) is the process of internalizing the norms and ideologies of society. Socialization encompasses both learning and teaching and is thus "the means by which social and cul ...
.
Emotions are biological states associated with the nervous system brought on by neurophysiological
Neurophysiology is a branch of physiology and neuroscience that studies nervous system function rather than nervous system architecture. This area aids in the diagnosis and monitoring of neurological diseases. Historically, it has been dominated b ...
changes variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or displeasure
{{Short pages monitor