Household Cavalry Museum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Horse Guards is a historic building in the
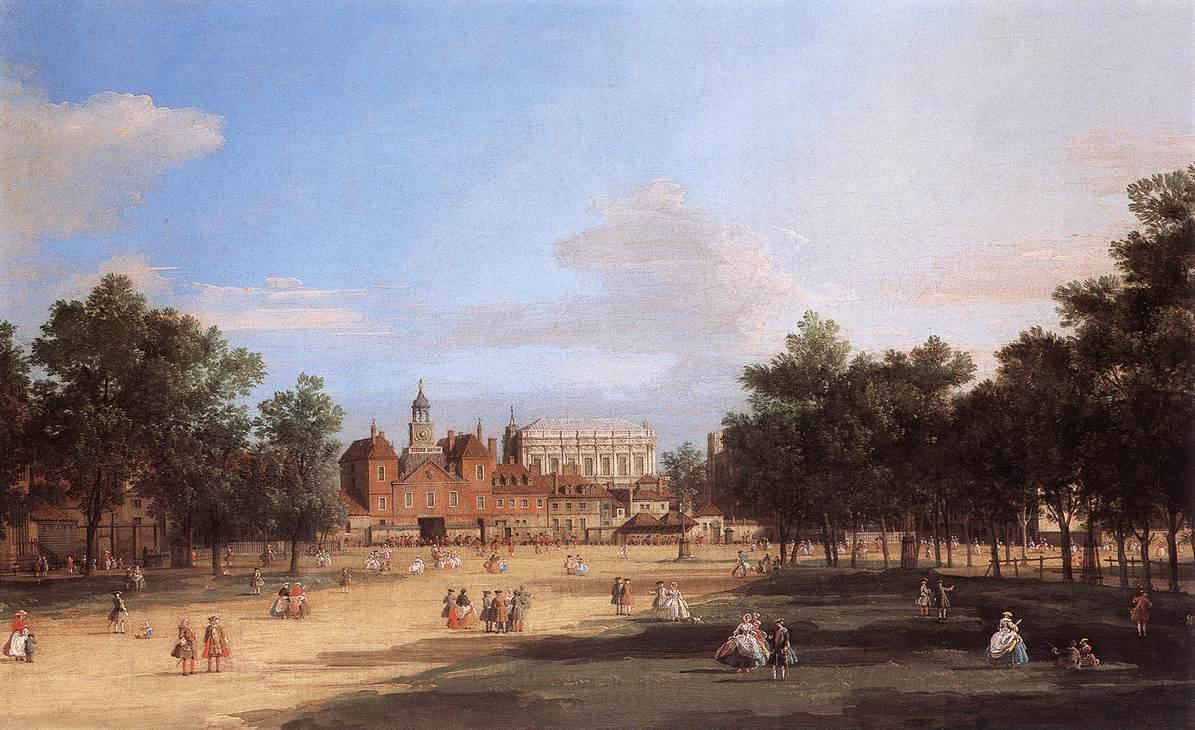 The first Horse Guards building was commissioned by King Charles II in 1663,Tabor, p.18 on the site of a cavalry stables which had been built on the
The first Horse Guards building was commissioned by King Charles II in 1663,Tabor, p.18 on the site of a cavalry stables which had been built on the 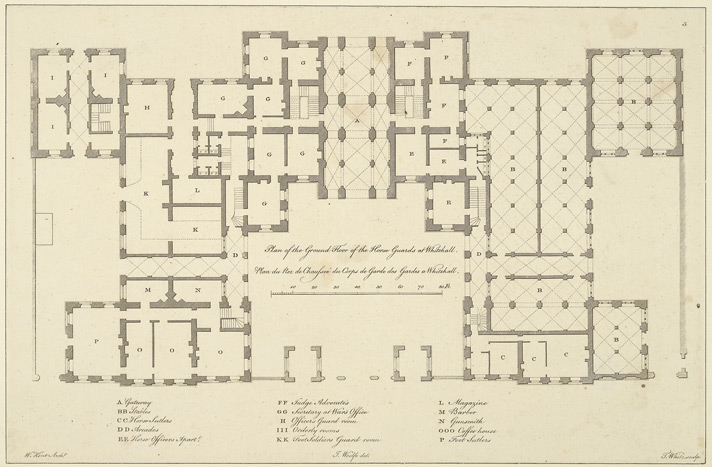 In the following decades, Horse Guards was increasingly used as administrative offices for the growing regular army and soon became overcrowded. The fabric of the building was also allowed to deteriorate; pieces of falling masonry were said to be a danger to the sentries. In 1745, King George II commissioned a new building in the fashionable
In the following decades, Horse Guards was increasingly used as administrative offices for the growing regular army and soon became overcrowded. The fabric of the building was also allowed to deteriorate; pieces of falling masonry were said to be a danger to the sentries. In 1745, King George II commissioned a new building in the fashionable  The building also served as the offices for the various administrative departments responsible to the Secretary at War, which would eventually become formalised as the
The building also served as the offices for the various administrative departments responsible to the Secretary at War, which would eventually become formalised as the
 The Household Cavalry Museum is the official museum of the Household Cavalry and is located in the Horse Guards. Visitors can view the horses in the 18th-century working stables through a glazed partition. Exhibits explain the training and history of the regiment and include ceremonial uniforms, regalia, royal standards, awards, musical instruments, horse furniture and silverware by Fabergé. Visitors to the museum are welcome to watch the afternoon inspection of the guards and horses that happens daily at 4 pm. This routine began in 1894 when Queen Victoria found the guards drinking and gambling in the afternoon instead of tending to their duty. She proclaimed that they would be punished by a four o'clock inspection daily for the next 100 years. This proclamation and punishment officially expired in 1994, but Queen Elizabeth II chose to continue the inspection out of respect for tradition.
The Household Cavalry Museum is the official museum of the Household Cavalry and is located in the Horse Guards. Visitors can view the horses in the 18th-century working stables through a glazed partition. Exhibits explain the training and history of the regiment and include ceremonial uniforms, regalia, royal standards, awards, musical instruments, horse furniture and silverware by Fabergé. Visitors to the museum are welcome to watch the afternoon inspection of the guards and horses that happens daily at 4 pm. This routine began in 1894 when Queen Victoria found the guards drinking and gambling in the afternoon instead of tending to their duty. She proclaimed that they would be punished by a four o'clock inspection daily for the next 100 years. This proclamation and punishment officially expired in 1994, but Queen Elizabeth II chose to continue the inspection out of respect for tradition.
 Every morning, the mounted King's Life Guard rides from Hyde Park Barracks in Knightsbridge, by way of
Every morning, the mounted King's Life Guard rides from Hyde Park Barracks in Knightsbridge, by way of
File:Horseguards Building, London MOD 45152987 (cropped).jpg, Aerial view of Horse Guards from Whitehall
File:Mounted Household Cavalry at the House Guards.jpg, A mounted trooper of the Life Guards on duty at Horse Guards
File:Cavall, city of westminster, londres.JPG, A mounted trooper of the King's Troop, Royal Horse Artillery on duty at Horse Guards
File:State Opening of Parliament 2008 I (3082920424).jpg, Queen Elizabeth II approaches Horse Guards following the
Household Cavalry Museum
– official site {{DEFAULTSORT:Horse Guards (Building) Household Cavalry National government buildings in London War Office Government buildings completed in 1753 Grade I listed buildings in the City of Westminster Grade I listed government buildings Tourist attractions in the City of Westminster William Kent buildings Georgian architecture in London Neoclassical architecture in London Whitehall
City of Westminster
The City of Westminster is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and London boroughs, borough in Inner London. It is the site of the United Kingdom's Houses of Parliament and much of the British government. It occupies a large area of cent ...
, London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, between Whitehall
Whitehall is a road and area in the City of Westminster, Central London. The road forms the first part of the A roads in Zone 3 of the Great Britain numbering scheme, A3212 road from Trafalgar Square to Chelsea, London, Chelsea. It is the main ...
and Horse Guards Parade. It was built in the mid-18th century, replacing an earlier building, as a barracks
Barracks are usually a group of long buildings built to house military personnel or laborers. The English word originates from the 17th century via French and Italian from an old Spanish word "barraca" ("soldier's tent"), but today barracks are u ...
and stable
A stable is a building in which livestock, especially horses, are kept. It most commonly means a building that is divided into separate stalls for individual animals and livestock. There are many different types of stables in use today; the ...
s for the Household Cavalry. It was, between the early 18th century and 1858, the main military headquarters
Headquarters (commonly referred to as HQ) denotes the location where most, if not all, of the important functions of an organization are coordinated. In the United States, the corporate headquarters represents the entity at the center or the to ...
for the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
. Horse Guards originally formed the entrance to the Palace of Whitehall
The Palace of Whitehall (also spelt White Hall) at Westminster was the main residence of the English monarchs from 1530 until 1698, when most of its structures, except notably Inigo Jones's Banqueting House of 1622, were destroyed by fire. H ...
and later St James's Palace
St James's Palace is the most senior royal palace in London, the capital of the United Kingdom. The palace gives its name to the Court of St James's, which is the monarch's royal court, and is located in the City of Westminster in London. Altho ...
; for that reason it is still ceremonially defended by the King's Life Guard
The King's Guard and King's Life Guard (called the Queen's Guard and the Queen's Life Guard when the reigning monarch is female) are the contingents of infantry and cavalry soldiers charged with guarding the official List of British royal res ...
.
Although still in military use, part of the building houses the Household Cavalry Museum which is open to the public. It also functions as a gateway between Whitehall
Whitehall is a road and area in the City of Westminster, Central London. The road forms the first part of the A roads in Zone 3 of the Great Britain numbering scheme, A3212 road from Trafalgar Square to Chelsea, London, Chelsea. It is the main ...
and St James's Park.
History
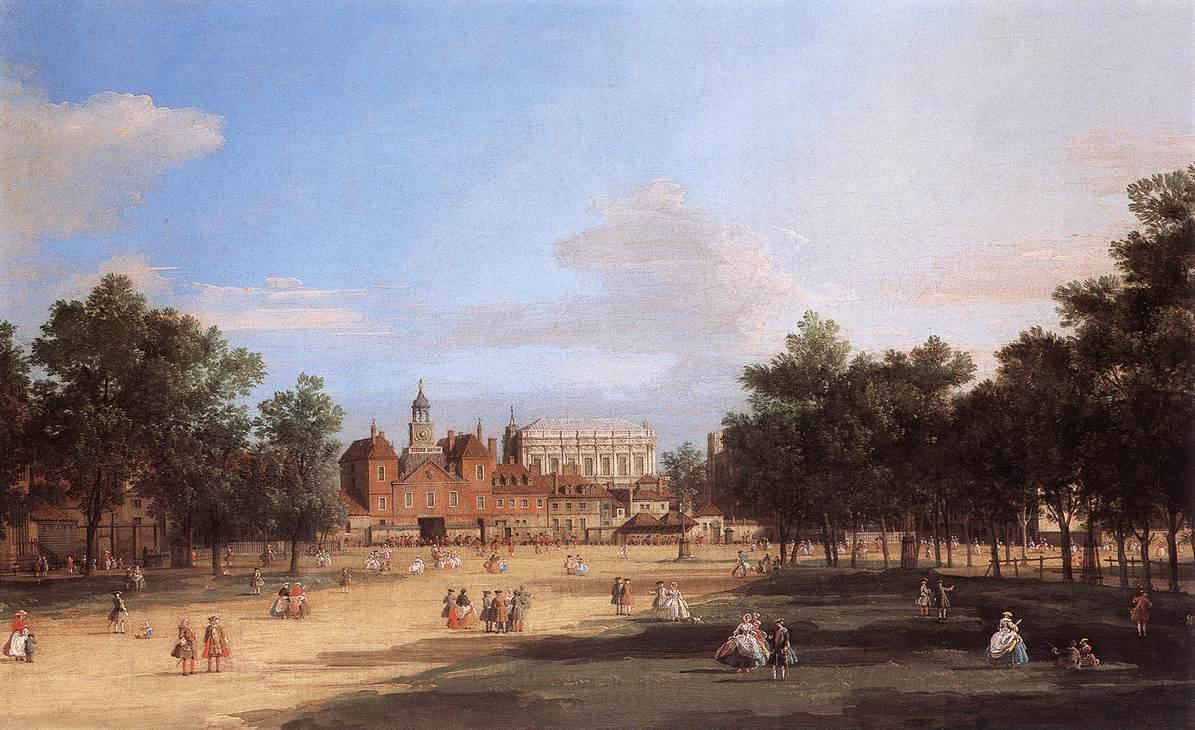 The first Horse Guards building was commissioned by King Charles II in 1663,Tabor, p.18 on the site of a cavalry stables which had been built on the
The first Horse Guards building was commissioned by King Charles II in 1663,Tabor, p.18 on the site of a cavalry stables which had been built on the tiltyard
A tiltyard (or tilt yard or tilt-yard) was an enclosed courtyard for jousting. Tiltyards were a common feature of Tudor era castles and palaces.
The Horse Guards Parade in London was formerly the tiltyard constructed by Henry VIII as an entertainm ...
of the Palace of Whitehall during the Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
. Built of red brick and costing some £4,000, it comprised a central range with a clock tower
Clock towers are a specific type of structure which house a turret clock and have one or more clock faces on the upper exterior walls. Many clock towers are freestanding structures but they can also adjoin or be located on top of another buildi ...
, under which an arch connected Whitehall with St James's Park; two wings enclosed a courtyard with two large sentry box
A sentry box is a small shelter with an open front in which a sentry or person on guard duty may stand to be sheltered from the weather. Many boxes are decorated in national colours.
Compare:
In literature
The sentry box at the entrance to Buck ...
es for mounted troopers on the Whitehall side, facing the palace gate. Entry to the park, then an enclosed private garden, was controlled by special ivory passes issued to favoured courtiers, a tradition which continues to the present, although the modern passes are made of plastic; only the monarch has the right to drive through the arch without a pass. Initially, the building was intended only to accommodate the King's Guard
The King's Guard and King's Life Guard (called the Queen's Guard and the Queen's Life Guard when the reigning monarch is female) are the contingents of infantry and cavalry soldiers charged with guarding the official royal residences in the U ...
and included stabling for more than a hundred cavalry horses on the ground floor, as well as separate barracks for the foot guards. Following a fire at Whitehall in 1698, the court transferred to St James's Palace, therefore the function of Horse Guards changed to controlling the ceremonial approach to St James's from Westminster.
 In the following decades, Horse Guards was increasingly used as administrative offices for the growing regular army and soon became overcrowded. The fabric of the building was also allowed to deteriorate; pieces of falling masonry were said to be a danger to the sentries. In 1745, King George II commissioned a new building in the fashionable
In the following decades, Horse Guards was increasingly used as administrative offices for the growing regular army and soon became overcrowded. The fabric of the building was also allowed to deteriorate; pieces of falling masonry were said to be a danger to the sentries. In 1745, King George II commissioned a new building in the fashionable Palladian
Palladian architecture is a European architectural style derived from the work of the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). What is today recognised as Palladian architecture evolved from his concepts of symmetry, perspective and ...
style by the architect William Kent
William Kent (c. 1685 – 12 April 1748) was an English architect, landscape architect, painter and furniture designer of the early 18th century. He began his career as a painter, and became Principal Painter in Ordinary or court painter, but ...
. Having to reuse the same plot of land, Kent managed to retain essentially the same plan as the original building while doubling the interior space. Kent died in April 1748 before the old Horse Guards had been demolished; work on the new building commenced in 1750 under the direction of Kent's assistant, John Vardy
John Vardy (February 1718 – 17 May 1765) was an English architect attached to the Royal Office of Works from 1736. He was a close follower of the neo-Palladian architect William Kent.
John Vardy was born to a simple working family in Durham. Hi ...
and William Robinson from the Office of Works. The cost of the buildings was £65,000 and took nearly ten years to complete. The Household Cavalry moved into the northern wing of the uncompleted building in 1755; at that time, there was stabling for 62 horses compared to 17 today. Originally, the two wings were connected to the central block by single storey ranges; in 1803-5 a further two floors were added to these, giving the building its present appearance. Kent's decision to retain a Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
clock tower on his new Palladian building resulted in a peculiar blend of styles, perhaps the cause of it being described by Charles Knight as "the ugliest building in the metropolis".
 The building also served as the offices for the various administrative departments responsible to the Secretary at War, which would eventually become formalised as the
The building also served as the offices for the various administrative departments responsible to the Secretary at War, which would eventually become formalised as the War Office
The War Office was a department of the British Government responsible for the administration of the British Army between 1857 and 1964, when its functions were transferred to the new Ministry of Defence (MoD). This article contains text from ...
. Also located at Horse Guards was the office of the Commander-in-Chief of the Forces.Tabor, p.19 Hence, for many decades the term 'Horse Guards' was used as a metonym
Metonymy () is a figure of speech in which a concept is referred to by the name of something closely associated with that thing or concept.
Etymology
The words ''metonymy'' and ''metonym'' come from grc, μετωνυμία, 'a change of name' ...
for British Army headquarters. Two famous occupants of the office, a room originally intended for courts-martial, were Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany
Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany (Frederick Augustus; 16 August 1763 – 5 January 1827) was the second son of George III, King of the United Kingdom and Hanover, and his consort Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz. A soldier by profess ...
(1795–1809), popularly believed to be "The Grand Old Duke of York
"The Grand Old Duke of York" (also sung as The Noble Duke of York) is an English children's nursery rhyme, often performed as an action song. The eponymous duke has been argued to be a number of the bearers of that title, particularly Prince Fre ...
", and the Duke of Wellington
Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, (1 May 1769 – 14 September 1852) was an Anglo-Irish soldier and Tory statesman who was one of the leading military and political figures of 19th-century Britain, serving twice as prime minister of ...
(1827–28 and 1842–1852). The final Commander-in-Chief at Horse Guards was Prince George, Duke of Cambridge
Prince George, Duke of Cambridge (George William Frederick Charles; 26 March 1819 – 17 March 1904) was a member of the British royal family, a grandson of King George III and cousin of Queen Victoria. The Duke was an army officer by professio ...
, who was so reluctant to move to the new War Office building at Cumberland House
Cumberland House was a mansion on the south side of Pall Mall in London, England. It was built in the 1760s by Matthew Brettingham for Prince Edward, Duke of York and Albany and was originally called York House. The Duke of York died in 1767 a ...
in Pall Mall that he had to be ordered to vacate the building by Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 21 ...
in 1858. Wellington's desk is preserved in the same room, which is now the office of the Major-General Commanding the Household Division and General Officer Commanding London District. Horse Guards subsequently became the headquarters of two major Army commands: the London District
London District (LONDIST) is the name given by the British Army to the area of operations encompassing the Greater London area. It was established in 1870 as ''Home District''.
History
In January 1876 a ‘Mobilization Scheme for the forces in ...
and the Household Cavalry.
At the annual Trooping the Colour ceremony in June, members of the Royal Family
A royal family is the immediate family of kings/queens, emirs/emiras, sultans/ sultanas, or raja/ rani and sometimes their extended family. The term imperial family appropriately describes the family of an emperor or empress, and the term ...
who are not participants watch the parade from the windows of Wellington's office over the archway.
Horse Guards Clock
The clock is sited in the turret above the main archway; it has two faces, one facing Whitehall and the other, Horse Guards Parade, each dial being in diameter. It strikes the quarter-hours on two bells. Originally made by Thwaites in 1756, the clock was rebuilt in 1815–16 byBenjamin Lewis Vulliamy
Benjamin Lewis Vulliamy (25 January 1780 – 8 January 1854) was a clockmaker, active in 18th and 19th century Britain. He succeeded his father Benjamin Vulliamy as head of the firm and Clockmaker to the Crown.
Biography
The family was of Sw ...
, the clockmaker to King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
. Prior to the completion of the clock of Big Ben
Big Ben is the nickname for the Great Bell of the Great Clock of Westminster, at the north end of the Palace of Westminster in London, England, and the name is frequently extended to refer also to the clock and the clock tower. The officia ...
in 1859, the Horse Guards Clock was the main public clock in Westminster. A dark stain above the Roman number two on the clock face is supposed to mark the time of the execution of King Charles I
The execution of Charles I by Decapitation, beheading occurred on Tuesday, 30 January 1649 outside the Banqueting House on Whitehall. The execution was the culmination of political and military conflicts between the cavaliers, royalists and the ...
in 1649, which took place in the roadway outside Horse Guards. The annual ceremony of Trooping the Colour commences when the Horse Guards Clock strikes eleven.
Household Cavalry Museum
 The Household Cavalry Museum is the official museum of the Household Cavalry and is located in the Horse Guards. Visitors can view the horses in the 18th-century working stables through a glazed partition. Exhibits explain the training and history of the regiment and include ceremonial uniforms, regalia, royal standards, awards, musical instruments, horse furniture and silverware by Fabergé. Visitors to the museum are welcome to watch the afternoon inspection of the guards and horses that happens daily at 4 pm. This routine began in 1894 when Queen Victoria found the guards drinking and gambling in the afternoon instead of tending to their duty. She proclaimed that they would be punished by a four o'clock inspection daily for the next 100 years. This proclamation and punishment officially expired in 1994, but Queen Elizabeth II chose to continue the inspection out of respect for tradition.
The Household Cavalry Museum is the official museum of the Household Cavalry and is located in the Horse Guards. Visitors can view the horses in the 18th-century working stables through a glazed partition. Exhibits explain the training and history of the regiment and include ceremonial uniforms, regalia, royal standards, awards, musical instruments, horse furniture and silverware by Fabergé. Visitors to the museum are welcome to watch the afternoon inspection of the guards and horses that happens daily at 4 pm. This routine began in 1894 when Queen Victoria found the guards drinking and gambling in the afternoon instead of tending to their duty. She proclaimed that they would be punished by a four o'clock inspection daily for the next 100 years. This proclamation and punishment officially expired in 1994, but Queen Elizabeth II chose to continue the inspection out of respect for tradition.
Ceremonial
Hyde Park Corner
Hyde Park Corner is between Knightsbridge, Belgravia and Mayfair in London, England. It primarily refers to its major road junction at the southeastern corner of Hyde Park, that was designed by Decimus Burton. Six streets converge at the junc ...
, Constitution Hill Constitution Hill may refer to:
*Constitution Hill, New South Wales, Australia
*Constitution Hill, Aberystwyth
* Constitution Hill, Birmingham
* Constitution Hill, London, a road in the City of Westminster in London
* Constitution Hill, Swansea
*Con ...
and The Mall, to take over guard duties in a ceremony at 11:00 am or 10:00 am on Sundays. The guard is usually provided by the Household Cavalry Mounted Regiment
The Household Cavalry Mounted Regiment (HCMR) is a cavalry regiment of the British Army tasked primarily with ceremonial duties. Part of the Household Division, it is classed as a regiment of guards, and carries out mounted (and some dismount ...
, which consists of a squadron from each of the Household Cavalry regiments; the Life Guards who wear red tunics and white helmet-plumes, and the Blues and Royals who wear blue tunics and red plumes. However, some other mounted units from Britain and other Commonwealth realms
A Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state in the Commonwealth of Nations whose monarch and head of state is shared among the other realms. Each realm functions as an independent state, equal with the other realms and nations of the Commonwealt ...
occasionally mount the guard; the King's Troop, Royal Horse Artillery and the Royal Canadian Mounted Police
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP; french: Gendarmerie royale du Canada; french: GRC, label=none), commonly known in English as the Mounties (and colloquially in French as ) is the federal police, federal and national police service of ...
are examples.
When the monarch is in London, the Guard consists of one officer and twelve other ranks including a trumpeter and standard bearer; known as a Long Guard. When the monarch is not in London, the Guard is reduced to two non-commissioned officer
A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is a military officer who has not pursued a commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority by promotion through the enlisted ranks. (Non-officers, which includes most or all enli ...
s and ten troopers; known as a Short Guard.
The ceremony of Changing The King's Life Guard takes place on Horse Guards Parade adjacent to the Horse Guards building. Two mounted sentries guard the entrance to Horse Guards on Whitehall from 10:00 am until 4:00 pm and are changed every hour. There is a dismounted parade at 4:00 pm (described above) and two dismounted sentries remain on duty until 8:00 pm.
Gallery
State Opening of Parliament
The State Opening of Parliament is a ceremonial event which formally marks the beginning of a session of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It includes a speech from the throne known as the King's (or Queen's) Speech. The event takes place ...
in 2008.
File:Horse Guards Building Wide Shot 2013.jpg, View across Horse Guards Parade in 2013.
References
Bibliography
* * Tabor, Paddy, (2010) ''The Household Cavalry Museum'', Ajanta Book PublishingExternal links
Household Cavalry Museum
– official site {{DEFAULTSORT:Horse Guards (Building) Household Cavalry National government buildings in London War Office Government buildings completed in 1753 Grade I listed buildings in the City of Westminster Grade I listed government buildings Tourist attractions in the City of Westminster William Kent buildings Georgian architecture in London Neoclassical architecture in London Whitehall