Hospitals In Simcoe County on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A hospital is a
A hospital is a
 During the Middle Ages, hospitals served different functions from modern institutions in that they were
During the Middle Ages, hospitals served different functions from modern institutions in that they were
 A specialty hospital is primarily and exclusively dedicated to one or a few related medical specialties. Subtypes include rehabilitation hospitals, children's hospitals, seniors' ( geriatric) hospitals, long-term acute care facilities, and hospitals for dealing with specific medical needs such as psychiatric problems (see psychiatric hospital), cancer treatment, certain disease categories such as cardiac, oncology, or orthopedic problems, and so forth.
In Germany specialised hospitals are called ''Fachkrankenhaus''; an example is Fachkrankenhaus Coswig (thoracic surgery). In India, specialty hospitals are known as ''super-specialty hospitals'' and are distinguished from multispecialty hospitals which are composed of several specialties.
Specialised hospitals can help reduce health care costs compared to general hospitals. For example, Narayana Health's cardiac unit in Bangalore specialises in cardiac surgery and allows for a significantly greater number of patients. It has 3,000 beds and performs 3,000 in paediatric cardiac operations annually, the largest number in the world for such a facility. Surgeons are paid on a fixed salary instead of per operation, thus when the number of procedures increases, the hospital is able to take advantage of economies of scale and reduce its cost per procedure. Each specialist may also become more efficient by working on one procedure like a production line.
A specialty hospital is primarily and exclusively dedicated to one or a few related medical specialties. Subtypes include rehabilitation hospitals, children's hospitals, seniors' ( geriatric) hospitals, long-term acute care facilities, and hospitals for dealing with specific medical needs such as psychiatric problems (see psychiatric hospital), cancer treatment, certain disease categories such as cardiac, oncology, or orthopedic problems, and so forth.
In Germany specialised hospitals are called ''Fachkrankenhaus''; an example is Fachkrankenhaus Coswig (thoracic surgery). In India, specialty hospitals are known as ''super-specialty hospitals'' and are distinguished from multispecialty hospitals which are composed of several specialties.
Specialised hospitals can help reduce health care costs compared to general hospitals. For example, Narayana Health's cardiac unit in Bangalore specialises in cardiac surgery and allows for a significantly greater number of patients. It has 3,000 beds and performs 3,000 in paediatric cardiac operations annually, the largest number in the world for such a facility. Surgeons are paid on a fixed salary instead of per operation, thus when the number of procedures increases, the hospital is able to take advantage of economies of scale and reduce its cost per procedure. Each specialist may also become more efficient by working on one procedure like a production line.
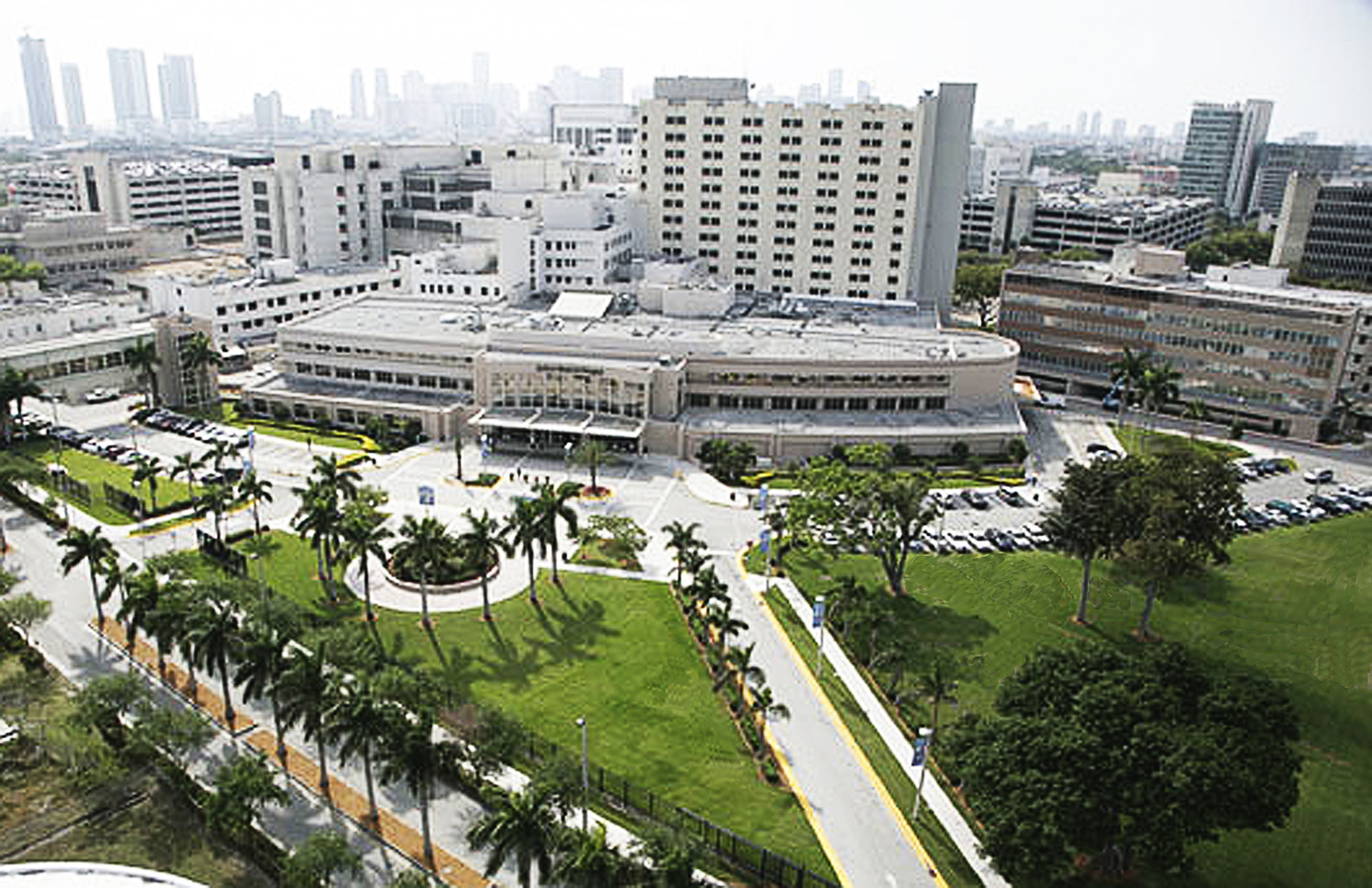 A teaching hospital delivers healthcare to patients as well as training to prospective medical professionals such as medical students and student nurses. It may be linked to a
A teaching hospital delivers healthcare to patients as well as training to prospective medical professionals such as medical students and student nurses. It may be linked to a

 A hospital contains one or more wards that house hospital beds for inpatients. It may also have acute services such as an
A hospital contains one or more wards that house hospital beds for inpatients. It may also have acute services such as an
 In early India, Fa Xian, a Chinese Buddhist monk who travelled across India c. AD 400, recorded examples of healing institutions. According to the '' Mahavamsa'', the ancient chronicle of Sinhalese royalty, written in the sixth century AD, King
In early India, Fa Xian, a Chinese Buddhist monk who travelled across India c. AD 400, recorded examples of healing institutions. According to the '' Mahavamsa'', the ancient chronicle of Sinhalese royalty, written in the sixth century AD, King 
 The earliest general hospital in the Islamic world was built in 805 in Baghdad by Harun Al-Rashid. By the 10th century, Baghdad had five more hospitals, while
The earliest general hospital in the Islamic world was built in 805 in Baghdad by Harun Al-Rashid. By the 10th century, Baghdad had five more hospitals, while
United States National Library of Medicine Hospitals in this era were the first to require medical diplomas to license doctors, and compensation for negligence could be made. Hospitals were forbidden by law to turn away patients who were unable to pay. These hospitals were financially supported by waqfs, as well as state funds.
 In Europe the medieval concept of Christian care evolved during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries into a secular one. In England, after the dissolution of the monasteries in 1540 by King
In Europe the medieval concept of Christian care evolved during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries into a secular one. In England, after the dissolution of the monasteries in 1540 by King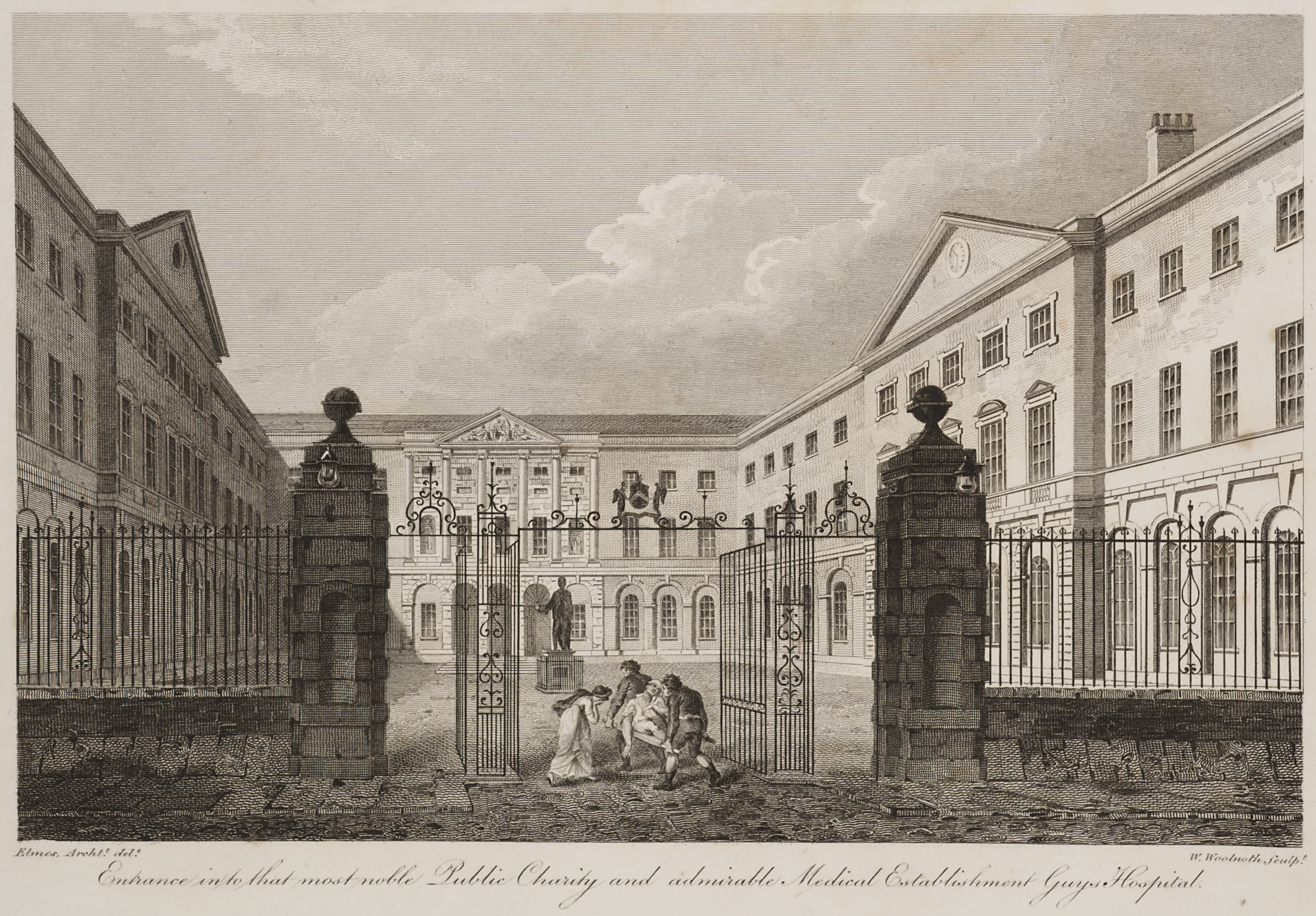 
 The voluntary hospital movement began in the early 18th century, with hospitals being founded in London by the 1720s, including Westminster Hospital (1719) promoted by the private bank C. Hoare & Co and Guy's Hospital (1724) funded from the bequest of the wealthy merchant, Thomas Guy.
Other hospitals sprang up in London and other British cities over the century, many paid for by private subscriptions. St Bartholomew's in London was rebuilt from 1730 to 1759, and the London Hospital, Whitechapel, opened in 1752.
These hospitals represented a turning point in the function of the institution; they began to evolve from being basic places of care for the sick to becoming centres of medical innovation and discovery and the principal place for the education and training of prospective practitioners. Some of the era's greatest
The voluntary hospital movement began in the early 18th century, with hospitals being founded in London by the 1720s, including Westminster Hospital (1719) promoted by the private bank C. Hoare & Co and Guy's Hospital (1724) funded from the bequest of the wealthy merchant, Thomas Guy.
Other hospitals sprang up in London and other British cities over the century, many paid for by private subscriptions. St Bartholomew's in London was rebuilt from 1730 to 1759, and the London Hospital, Whitechapel, opened in 1752.
These hospitals represented a turning point in the function of the institution; they began to evolve from being basic places of care for the sick to becoming centres of medical innovation and discovery and the principal place for the education and training of prospective practitioners. Some of the era's greatest
 Modern hospitals derive funding from a variety of sources. They may be funded by private payment and
Modern hospitals derive funding from a variety of sources. They may be funded by private payment and
Hospitals in New Orleans see surge in uninsured patients but not public funds
' – '' USA Today'', Wednesday 26 April 2006
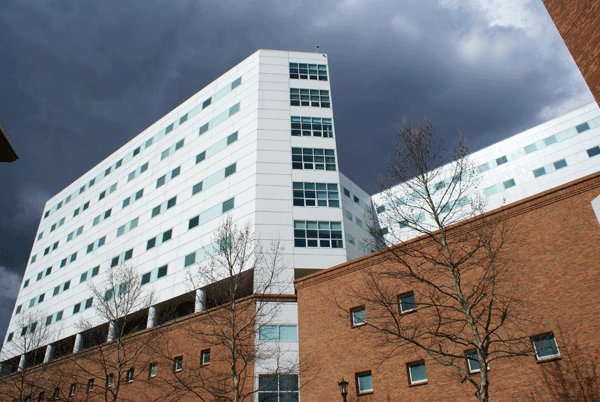

 Modern hospital buildings are designed to minimise the effort of medical personnel and the possibility of contamination while maximising the efficiency of the whole system. Travel time for personnel within the hospital and the transportation of patients between units is facilitated and minimised. The building also should be built to accommodate heavy departments such as radiology and operating rooms while space for special wiring, plumbing, and waste disposal must be allowed for in the design.
However, many hospitals, even those considered "modern", are the product of continual and often badly managed growth over decades or even centuries, with utilitarian new sections added on as needs and finances dictate. As a result, Dutch architectural historian Cor Wagenaar has called many hospitals:
:''"... built catastrophes, anonymous institutional complexes run by vast bureaucracies, and totally unfit for the purpose they have been designed for ... They are hardly ever functional, and instead of making patients feel at home, they produce stress and anxiety."
Modern hospital buildings are designed to minimise the effort of medical personnel and the possibility of contamination while maximising the efficiency of the whole system. Travel time for personnel within the hospital and the transportation of patients between units is facilitated and minimised. The building also should be built to accommodate heavy departments such as radiology and operating rooms while space for special wiring, plumbing, and waste disposal must be allowed for in the design.
However, many hospitals, even those considered "modern", are the product of continual and often badly managed growth over decades or even centuries, with utilitarian new sections added on as needs and finances dictate. As a result, Dutch architectural historian Cor Wagenaar has called many hospitals:
:''"... built catastrophes, anonymous institutional complexes run by vast bureaucracies, and totally unfit for the purpose they have been designed for ... They are hardly ever functional, and instead of making patients feel at home, they produce stress and anxiety."
Healing by design
'' – ''Ode Magazine'', July/August 2006 issue. Accessed 10 February 2008. Some newer hospitals now try to re-establish design that takes the patient's psychological needs into account, such as providing more fresh air, better views and more pleasant colour schemes. These ideas harken back to the late eighteenth century, when the concept of providing fresh air and access to the 'healing powers of nature' were first employed by hospital architects in improving their buildings. The research of
Health administrators go shopping for new hospital designs
'' – '' National Review of Medicine'', Monday 15 November 2004, Volume 1 No. 21
File:Hinduja Hospital, Mahim, Mumbai.jpg, Hinduja National Hospital, Mumbai
File:Intensivstation (01) 2007-03-03.jpg, An intensive care unit (ICU) within a hospital
File:KlinikumAachen.jpg,
Bibliography of Histories of Canadian hospitals and schools of nursing
* Gorsky, Martin. "The British National Health Service 1948–2008: A Review of the Historiography," ''Social History of Medicine'', December 2008, Vol. 21 Issue 3, pp. 437–60 * Harrison, Mar, et al. eds. ''From Western Medicine to Global Medicine: The Hospital Beyond the West'' (2008) * Horden, Peregrine. ''Hospitals and Healing From Antiquity to the Later Middle Ages'' (2008) * McGrew, Roderick E. ''Encyclopedia of Medical History'' (1985) * * Porter, Roy. ''The Hospital in History'', with Lindsay Patricia Granshaw (1989) * Risse, Guenter B. ''Mending Bodies, Saving Souls: A History of Hospitals'' (1999); world coverage * Rosenberg, Charles E. ''The Care of Strangers: The Rise of America's Hospital System'' (1995); history to 1920 * Scheutz, Martin et al. eds. ''Hospitals and Institutional Care in Medieval and Early Modern Europe'' (2009) * Wall, Barbra Mann. ''American Catholic Hospitals: A Century of Changing Markets and Missions'' (Rutgers University Press, 2011).
 A hospital is a
A hospital is a health care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to health sciences:
Health sciences are those sciences which focus on health, or health care, as core parts of their subject matter. Health sciences relate to multiple acad ...
and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emergency department
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the acute care of pati ...
to treat urgent health problems ranging from fire and accident victims to a sudden illness. A district hospital typically is the major health care facility in its region, with many beds for intensive care and additional beds for patients who need long-term care. Specialized hospitals include trauma centers, rehabilitation hospitals, children's hospitals, seniors' ( geriatric) hospitals, and hospitals for dealing with specific medical needs such as psychiatric treatment (see psychiatric hospital) and certain disease categories. Specialized hospitals can help reduce health care costs compared to general hospitals. Hospitals are classified as general, specialty, or government depending on the sources of income received.
A teaching hospital combines assistance to people with teaching to health science
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to health sciences:
Health sciences are those sciences which focus on health, or health care, as core parts of their subject matter. Health sciences relate to multiple acad ...
students and auxiliary healthcare students. A health science facility smaller than a hospital is generally called a clinic. Hospitals have a range of departments (e.g. surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
and urgent care) and specialist units such as cardiology. Some hospitals have outpatient departments and some have chronic treatment units. Common support units include a pharmacy
Pharmacy is the science and practice of discovering, producing, preparing, dispensing, reviewing and monitoring medications, aiming to ensure the safe, effective, and affordable use of medicines. It is a miscellaneous science as it links heal ...
, pathology, and radiology.
Hospitals are typically funded by public funding, health organisations ( for-profit or nonprofit
A nonprofit organization (NPO) or non-profit organisation, also known as a non-business entity, not-for-profit organization, or nonprofit institution, is a legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public or social benefit, in co ...
), health insurance
Health insurance or medical insurance (also known as medical aid in South Africa) is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among ma ...
companies, or charities
A charitable organization or charity is an organization whose primary objectives are philanthropy and social well-being (e.g. educational, religious or other activities serving the public interest or common good).
The legal definition of a cha ...
, including direct charitable donations. Historically, hospitals were often founded and funded by religious orders, or by charitable individuals and leaders.
Currently, hospitals are largely staffed by professional physicians, surgeon
In modern medicine, a surgeon is a medical professional who performs surgery. Although there are different traditions in different times and places, a modern surgeon usually is also a licensed physician or received the same medical training as ...
s, nurses, and allied health practitioners, whereas in the past, this work was usually performed by the members of founding religious orders or by volunteers. However, there are various Catholic religious orders, such as the Alexians and the Bon Secours Sisters that still focus on hospital ministry in the late 1990s, as well as several other Christian denominations, including the Methodists and Lutherans, which run hospitals. In accordance with the original meaning of the word, hospitals were original "places of hospitality", and this meaning is still preserved in the names of some institutions such as the Royal Hospital Chelsea, established in 1681 as a retirement and nursing home for veteran soldiers.
Etymology
almshouses
An almshouse (also known as a bede-house, poorhouse, or hospital) was charitable housing provided to people in a particular community, especially during the medieval era. They were often targeted at the poor of a locality, at those from certain ...
for the poor, hostel
A hostel is a form of low-cost, short-term shared sociable lodging where guests can rent a bed, usually a bunk bed in a dormitory, with shared use of a lounge and sometimes a kitchen. Rooms can be mixed or single-sex and have private or shared b ...
s for pilgrims, or hospital school
A hospital school is a school operated in a hospital, generally a children's hospital which provides instruction to all primary and secondary grade levels. These schools help children regain academic progress during periods of hospitalization or ...
s. The word "hospital" comes from the Latin , signifying a stranger or foreigner, hence a guest. Another noun derived from this, came to signify hospitality, that is the relation between guest and shelterer, hospitality, friendliness, and hospitable reception. By metonymy
Metonymy () is a figure of speech in which a concept is referred to by the name of something closely associated with that thing or concept.
Etymology
The words ''metonymy'' and ''metonym'' come from grc, μετωνυμία, 'a change of name' ...
, the Latin word then came to mean a guest-chamber, guest's lodging, an inn. is thus the root for the English words ''host'' (where the ''p'' was dropped for convenience of pronunciation) '' hospitality'', ''hospice
Hospice care is a type of health care that focuses on the palliation of a terminally ill patient's pain and symptoms and attending to their emotional and spiritual needs at the end of life. Hospice care prioritizes comfort and quality of life by ...
'', ''hostel
A hostel is a form of low-cost, short-term shared sociable lodging where guests can rent a bed, usually a bunk bed in a dormitory, with shared use of a lounge and sometimes a kitchen. Rooms can be mixed or single-sex and have private or shared b ...
,'' and '' hotel''. The latter modern word derives from Latin via the Old French romance word , which developed a silent ''s'', which letter was eventually removed from the word, the loss of which is signified by a circumflex
The circumflex () is a diacritic in the Latin and Greek scripts that is also used in the written forms of many languages and in various romanization and transcription schemes. It received its English name from la, circumflexus "bent around"a ...
in the modern French word . The German word shares similar roots.
Types
Some patients go to a hospital just for diagnosis, treatment, or therapy and then leave (" outpatients") without staying overnight; while others are "admitted" and stay overnight or for several days or weeks or months (" inpatients"). Hospitals are usually distinguished from other types of medical facilities by their ability to admit and care for inpatients whilst the others, which are smaller, are often described as clinics.General and acute care
The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, also known as an acute-care hospital. These facilities handle many kinds of disease and injury, and normally have an emergency department (sometimes known as "accident & emergency") or trauma center to deal with immediate and urgent threats to health. Larger cities may have several hospitals of varying sizes and facilities. Some hospitals, especially in the United States and Canada, have their own ambulance service.District
A district hospital typically is the major health care facility in its region, with large numbers of beds for intensive care, critical care, and long-term care. In California, "district hospital" refers specifically to a class of healthcare facility created shortly after World War II to address a shortage of hospital beds in many local communities. Even today, district hospitals are the sole public hospitals in 19 of California's counties, and are the sole locally-accessible hospital within nine additional counties in which one or more other hospitals are present at a substantial distance from a local community. Twenty-eight of California's rural hospitals and 20 of its critical-access hospitals are district hospitals. They are formed by local municipalities, have boards that are individually elected by their local communities, and exist to serve local needs. They are a particularly important provider of healthcare to uninsured patients and patients with Medi-Cal (which is California's Medicaid program, serving low-income persons, some senior citizens, persons withdisabilities
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be cognitive, developmental, intellectual, mental, physical, se ...
, children in foster care, and pregnant women). In 2012, district hospitals provided $54 million in uncompensated care in California.
Specialized
 A specialty hospital is primarily and exclusively dedicated to one or a few related medical specialties. Subtypes include rehabilitation hospitals, children's hospitals, seniors' ( geriatric) hospitals, long-term acute care facilities, and hospitals for dealing with specific medical needs such as psychiatric problems (see psychiatric hospital), cancer treatment, certain disease categories such as cardiac, oncology, or orthopedic problems, and so forth.
In Germany specialised hospitals are called ''Fachkrankenhaus''; an example is Fachkrankenhaus Coswig (thoracic surgery). In India, specialty hospitals are known as ''super-specialty hospitals'' and are distinguished from multispecialty hospitals which are composed of several specialties.
Specialised hospitals can help reduce health care costs compared to general hospitals. For example, Narayana Health's cardiac unit in Bangalore specialises in cardiac surgery and allows for a significantly greater number of patients. It has 3,000 beds and performs 3,000 in paediatric cardiac operations annually, the largest number in the world for such a facility. Surgeons are paid on a fixed salary instead of per operation, thus when the number of procedures increases, the hospital is able to take advantage of economies of scale and reduce its cost per procedure. Each specialist may also become more efficient by working on one procedure like a production line.
A specialty hospital is primarily and exclusively dedicated to one or a few related medical specialties. Subtypes include rehabilitation hospitals, children's hospitals, seniors' ( geriatric) hospitals, long-term acute care facilities, and hospitals for dealing with specific medical needs such as psychiatric problems (see psychiatric hospital), cancer treatment, certain disease categories such as cardiac, oncology, or orthopedic problems, and so forth.
In Germany specialised hospitals are called ''Fachkrankenhaus''; an example is Fachkrankenhaus Coswig (thoracic surgery). In India, specialty hospitals are known as ''super-specialty hospitals'' and are distinguished from multispecialty hospitals which are composed of several specialties.
Specialised hospitals can help reduce health care costs compared to general hospitals. For example, Narayana Health's cardiac unit in Bangalore specialises in cardiac surgery and allows for a significantly greater number of patients. It has 3,000 beds and performs 3,000 in paediatric cardiac operations annually, the largest number in the world for such a facility. Surgeons are paid on a fixed salary instead of per operation, thus when the number of procedures increases, the hospital is able to take advantage of economies of scale and reduce its cost per procedure. Each specialist may also become more efficient by working on one procedure like a production line.
Teaching
 A teaching hospital delivers healthcare to patients as well as training to prospective medical professionals such as medical students and student nurses. It may be linked to a
A teaching hospital delivers healthcare to patients as well as training to prospective medical professionals such as medical students and student nurses. It may be linked to a medical school
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, or part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS, M ...
or nursing school
Nursing is a profession within the health care sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other health ca ...
, and may be involved in medical research
Medical research (or biomedical research), also known as experimental medicine, encompasses a wide array of research, extending from "basic research" (also called ''bench science'' or ''bench research''), – involving fundamental scientif ...
. Students may also observe clinical work in the hospital.
Clinics
Clinics generally provide only outpatient services, but some may have a few inpatient beds and a limited range of services that may otherwise be found in typical hospitals.Departments or wards

 A hospital contains one or more wards that house hospital beds for inpatients. It may also have acute services such as an
A hospital contains one or more wards that house hospital beds for inpatients. It may also have acute services such as an emergency department
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the acute care of pati ...
, operating theatre, and intensive care unit, as well as a range of medical specialty departments. A well-equipped hospital may be classified as a trauma center. They may also have other services such as a hospital pharmacy, radiology, pathology, and medical laboratories
A medical laboratory or clinical laboratory is a laboratory where tests are conducted out on clinical specimens to obtain information about the health of a patient to aid in diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease. Clinical Medical la ...
. Some hospitals have outpatient departments such as behavioral health services, dentistry
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions o ...
, and rehabilitation services.
A hospital may also have a department of nursing, headed by a chief nursing officer
Nursing management consists of the performance of the leadership functions of governance and decision-making within organizations employing nurses. It includes processes common to all management like planning, organizing, staffing, directing and ...
or director of nursing. This department is responsible for the administration of professional nursing practice, research, and policy for the hospital.
Many units have both a nursing and a medical director that serve as administrators for their respective disciplines within that unit. For example, within an intensive care nursery, a medical director is responsible for physicians and medical care, while the nursing manager is responsible for all the nurses and nursing care.
Support units may include a medical records department, release of information department
A release of information (ROI) department or division is found in the majority of hospitals. In the United States, HIPAA and state guidelines strongly direct the rules and regulations of patient information. ROI departments perform such tasks as o ...
, technical support, clinical engineering, facilities management, plant operations
Physical plant, mechanical plant or industrial plant (and where context is given, often just plant) refers to the necessary infrastructure used in operation and maintenance of a given facility. The operation of these facilities, or the department o ...
, dining services, and security departments.
Remote monitoring
The COVID-19 pandemic stimulated the development of virtual wards across the British NHS. Patients are managed at home, monitoring their own oxygen levels using an oxygen saturation probe if necessary and supported by telephone. West Hertfordshire Hospitals NHS Trust managed around 1200 patients at home between March and June 2020 and planned to continue the system after COVID-19, initially for respiratory patients. Mersey Care NHS Foundation Trust started a COVID Oximetry@Home service in April 2020. This enables them to monitor more than 5000 patients a day in their own homes. The technology allows nurses, carers, or patients to record and monitor vital signs such as blood oxygen levels.History
Early examples
 In early India, Fa Xian, a Chinese Buddhist monk who travelled across India c. AD 400, recorded examples of healing institutions. According to the '' Mahavamsa'', the ancient chronicle of Sinhalese royalty, written in the sixth century AD, King
In early India, Fa Xian, a Chinese Buddhist monk who travelled across India c. AD 400, recorded examples of healing institutions. According to the '' Mahavamsa'', the ancient chronicle of Sinhalese royalty, written in the sixth century AD, King Pandukabhaya of Sri Lanka
Pandukabhaya (474 BC – 367 BC) was King of Kingdom of Upatissa Nuwara, Upatissa Nuwara and the first monarch of the Anuradhapura Kingdom and 6th over all of the island of Sri Lanka since the arrival of the Vijaya of Sri Lanka, Vijaya; he reign ...
(r. 437–367 BC) had lying-in-homes and hospitals (Sivikasotthi-Sala). A hospital and medical training centre also existed at Gundeshapur, a major city in southwest of the Sassanid Persian Empire founded in AD 271 by Shapur I. In ancient Greece, temples dedicated to the healer-god Asclepius, known as Asclepeion
Asclepieia ( grc, Ἀσκληπιεῖον ''Asklepieion''; Ἀσκλαπιεῖον in Doric dialect; Latin ''aesculapīum'') were healing temples located in ancient Greece (and in the wider Hellenistic and Roman world), dedicated to Asclepius ...
functioned as centres of medical advice, prognosis, and healing. The Asclepeia spread to the Roman Empire. While public healthcare was non-existent in the Roman Empire, military hospitals called ''valetudinaria'' did exist stationed in military barracks and would serve the soldiers and slaves within the fort.Ziegler, Tiffany A., Tiffany A. Ziegler, and Troyanos. Medieval Healthcare and the Rise of Charitable Institutions. Springer International Publishing, 2018, 33. Evidence exists that some civilian hospitals, while unavailable to the Roman population, were occasionally privately built in extremely wealthy Roman households located in the countryside for that family, although this practice seems to have ended in 80 AD.

Middle Ages
The declaration of Christianity as an accepted religion in the Roman Empire drove an expansion of the provision of care. Following the First Council of Nicaea in AD 325 construction of a hospital in every cathedral town was begun, including among the earliest hospitals by Saint Sampson in Constantinople and by Basil, bishop of Caesarea in modern-day Turkey. By the twelfth century, Constantinople had two well-organised hospitals, staffed by doctors who were both male and female. Facilities included systematic treatment procedures and specialised wards for various diseases. The earliest general hospital in the Islamic world was built in 805 in Baghdad by Harun Al-Rashid. By the 10th century, Baghdad had five more hospitals, while
The earliest general hospital in the Islamic world was built in 805 in Baghdad by Harun Al-Rashid. By the 10th century, Baghdad had five more hospitals, while Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
had six hospitals by the 15th century, and Córdoba alone had 50 major hospitals , many exclusively for the military. The Islamic ''bimaristan
A bimaristan (; ), also known as ''dar al-shifa'' (also ''darüşşifa'' in Turkish) or simply maristan, is a hospital in the historic Islamic world.
Etymology
''Bimaristan'' is a Persian word ( ''bīmārestān'') meaning "hospital", with '' ...
'' served as a center of medical treatment, as well nursing home and lunatic asylum. It typically treated the poor, as the rich would have been treated in their own homes.Islamic Culture and the Medical Arts: HospitalsUnited States National Library of Medicine Hospitals in this era were the first to require medical diplomas to license doctors, and compensation for negligence could be made. Hospitals were forbidden by law to turn away patients who were unable to pay. These hospitals were financially supported by waqfs, as well as state funds.
Early modern and Enlightenment Europe
 In Europe the medieval concept of Christian care evolved during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries into a secular one. In England, after the dissolution of the monasteries in 1540 by King
In Europe the medieval concept of Christian care evolved during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries into a secular one. In England, after the dissolution of the monasteries in 1540 by King Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
, the church abruptly ceased to be the supporter of hospitals, and only by direct petition from the citizens of London, were the hospitals St Bartholomew's, St Thomas's
St Thomas' Hospital is a large NHS teaching hospital in Central London, England. It is one of the institutions that compose the King's Health Partners, an academic health science centre. Administratively part of the Guy's and St Thomas' NHS F ...
and St Mary of Bethlehem's (Bedlam) endowed directly by the crown; this was the first instance of secular support being provided for medical institutions.

 The voluntary hospital movement began in the early 18th century, with hospitals being founded in London by the 1720s, including Westminster Hospital (1719) promoted by the private bank C. Hoare & Co and Guy's Hospital (1724) funded from the bequest of the wealthy merchant, Thomas Guy.
Other hospitals sprang up in London and other British cities over the century, many paid for by private subscriptions. St Bartholomew's in London was rebuilt from 1730 to 1759, and the London Hospital, Whitechapel, opened in 1752.
These hospitals represented a turning point in the function of the institution; they began to evolve from being basic places of care for the sick to becoming centres of medical innovation and discovery and the principal place for the education and training of prospective practitioners. Some of the era's greatest
The voluntary hospital movement began in the early 18th century, with hospitals being founded in London by the 1720s, including Westminster Hospital (1719) promoted by the private bank C. Hoare & Co and Guy's Hospital (1724) funded from the bequest of the wealthy merchant, Thomas Guy.
Other hospitals sprang up in London and other British cities over the century, many paid for by private subscriptions. St Bartholomew's in London was rebuilt from 1730 to 1759, and the London Hospital, Whitechapel, opened in 1752.
These hospitals represented a turning point in the function of the institution; they began to evolve from being basic places of care for the sick to becoming centres of medical innovation and discovery and the principal place for the education and training of prospective practitioners. Some of the era's greatest surgeon
In modern medicine, a surgeon is a medical professional who performs surgery. Although there are different traditions in different times and places, a modern surgeon usually is also a licensed physician or received the same medical training as ...
s and doctors worked and passed on their knowledge at the hospitals. They also changed from being mere homes of refuge to being complex institutions for the provision of medicine and care for sick. The Charité
The Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin (Charité – Berlin University of Medicine) is one of Europe's largest university hospitals, affiliated with Humboldt University and Free University Berlin. With numerous Collaborative Research Cen ...
was founded in Berlin in 1710 by King Frederick I of Prussia as a response to an outbreak of plague.
The concept of voluntary hospitals also spread to Colonial America
The colonial history of the United States covers the history of European colonization of North America from the early 17th century until the incorporation of the Thirteen Colonies into the United States after the Revolutionary War. In the ...
; the Bellevue Hospital opened in 1736 (as a workhouse, then later becoming a hospital); the Pennsylvania Hospital opened in 1752, New York Hospital
Weill Cornell Medical Center (previously known as New York Hospital or Old New York Hospital or City Hospital) is a research hospital in New York City. It is part of NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital and the teaching hospital for Cornell University.
...
(now Weill Cornell Medical Center) in 1771, and Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General or MGH) is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School located in the West End neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. It is the third oldest general hospital in the United Stat ...
in 1811.
When the Vienna General Hospital opened in 1784 (instantly becoming the world's largest hospital), physicians acquired a new facility that gradually developed into one of the most important research centres.
Another Enlightenment
Enlightenment or enlighten may refer to:
Age of Enlightenment
* Age of Enlightenment, period in Western intellectual history from the late 17th to late 18th century, centered in France but also encompassing (alphabetically by country or culture): ...
era charitable innovation was the dispensary; these would issue the poor with medicines free of charge. The London Dispensary opened its doors in 1696 as the first such clinic in the British Empire. The idea was slow to catch on until the 1770s, when many such organisations began to appear, including the Public Dispensary of Edinburgh
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öffentlichkei ...
(1776), the Metropolitan Dispensary and Charitable Fund (1779) and the Finsbury Dispensary (1780). Dispensaries were also opened in New York 1771, Philadelphia 1786, and Boston 1796.
The Royal Naval Hospital, Stonehouse
The Royal Naval Hospital, Stonehouse was a medical facility for naval officers and other ranks at Stonehouse, Plymouth.
History
The naval hospital was built between 1758 and 1765 to a design by the little-known Alexander Rovehead. The design was ...
, Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymouth ...
, was a pioneer of hospital design in having "pavilions" to minimize the spread of infection. John Wesley
John Wesley (; 2 March 1791) was an English people, English cleric, Christian theology, theologian, and Evangelism, evangelist who was a leader of a Christian revival, revival movement within the Church of England known as Methodism. The soci ...
visited in 1785, and commented "I never saw anything of the kind so complete; every part is so convenient, and so admirably neat. But there is nothing superfluous, and nothing purely ornamented, either within or without." This revolutionary design was made more widely known by John Howard, the philanthropist. In 1787 the French government sent two scholar administrators, Coulomb
The coulomb (symbol: C) is the unit of electric charge in the International System of Units (SI).
In the present version of the SI it is equal to the electric charge delivered by a 1 ampere constant current in 1 second and to elementary char ...
and Tenon, who had visited most of the hospitals in Europe. They were impressed and the "pavilion" design was copied in France and throughout Europe.
19th century
English physician Thomas Percival (1740–1804) wrote a comprehensive system of medical conduct, '' Medical Ethics; or, a Code of Institutes and Precepts, Adapted to the Professional Conduct of Physicians and Surgeons'' (1803) that set the standard for many textbooks. In the mid-19th century, hospitals and the medical profession became more professionalised, with a reorganisation of hospital management along more bureaucratic and administrative lines. The Apothecaries Act 1815 made it compulsory for medical students to practise for at least half a year at a hospital as part of their training. Florence Nightingale pioneered the modern profession of nursing during the Crimean War when she set an example of compassion, commitment to patient care and diligent and thoughtful hospital administration. The first official nurses' training programme, the Nightingale School for Nurses, was opened in 1860, with the mission of training nurses to work in hospitals, to work with the poor and to teach. Nightingale was instrumental in reforming the nature of the hospital, by improving sanitation standards and changing the image of the hospital from a place the sick would go to die, to an institution devoted to recuperation and healing. She also emphasised the importance ofstatistical measurement
Statistics (from German: ''Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industria ...
for determining the success rate of a given intervention and pushed for administrative reform at hospitals.
By the late 19th century, the modern hospital was beginning to take shape with a proliferation of a variety of public and private hospital systems. By the 1870s, hospitals had more than trebled their original average intake of 3,000 patients. In continental Europe the new hospitals generally were built and run from public funds. The National Health Service, the principal provider of health care in the United Kingdom, was founded in 1948. During the nineteenth century, the Second Viennese Medical School emerged with the contributions of physicians such as Carl Freiherr von Rokitansky, Josef Škoda, Ferdinand Ritter von Hebra, and Ignaz Philipp Semmelweis. Basic medical science expanded and specialisation advanced. Furthermore, the first dermatology, eye, as well as ear, nose, and throat clinics in the world were founded in Vienna, being considered as the birth of specialised medicine.
20th century and beyond
By the late 19th and early 20th centuries, medical advancements such asanesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), ...
and sterile techniques that could make surgery less risky, and the availability of more advanced diagnostic devices such as X-rays, continued to make hospitals a more attractive option for treatment.
Modern hospitals measure various efficiency metrics such as occupancy rates, the average length of stay, time to service, patient satisfaction, physician performance, patient readmission rate, inpatient mortality rate, and case mix index
Case mix index (CMI) within health care and medicine, is a relative value assigned to a diagnosis-related group of patients in a medical care environment. The CMI value is used in determining the allocation of resources to care for and/or treat the ...
.
In the United States, the number of hospitalizations continued to grow and reached its peak in 1981 with 171 admissions per 1,000 Americans and 6,933 hospitals. This trend subsequently reversed, with the rate of hospitalization falling by more than 10% and the number of US hospitals shrinking from 6,933 in 1981 to 5,534 in 2016. Occupancy rates also dropped from 77% in 1980 to 60% in 2013. Among the reasons for this are the increasing availability of more complex care elsewhere such as at home or the physicians' offices and also the less therapeutic and more life-threatening image of the hospitals in the eyes of the public.https://www.cdc.gov/hai/pdfs/hai/infections_deaths.pdf In the US, a patient may sleep in a hospital bed, but be considered outpatient and "under observation" if not formally admitted. In the US, inpatient stays are covered under Medicare Part A, but a hospital might keep a patient under observation which is only covered under Medicare Part B, and subjects the patient to additional coinsurance costs. In 2013, the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) introduced a "two-midnight" rule for inpatient admissions, intended to reduce an increasing number of long-term "observation" stays being used for reimbursement. This rule was later dropped in 2018. In 2016 and 2017, healthcare reform and a continued decline in admissions resulted in US hospital-based healthcare systems performing poorly financially. Microhospitals, with bed capacities of between eight and fifty, are expanding in the United States. Similarly, freestanding emergency rooms
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the acute care of pati ...
, which transfer patients that require inpatient care to hospitals, were popularised in the 1970s and have since expanded rapidly across the United States.
Funding
 Modern hospitals derive funding from a variety of sources. They may be funded by private payment and
Modern hospitals derive funding from a variety of sources. They may be funded by private payment and health insurance
Health insurance or medical insurance (also known as medical aid in South Africa) is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among ma ...
or public expenditure, charitable donation
The practice of charity is the voluntary giving of help to those in need, as a humanitarian act, unmotivated by self-interest. There are a number of philosophies about charity, often associated with religion.
Etymology
The word ''charity'' ori ...
s.
In the United Kingdom, the National Health Service delivers health care to legal residents funded by the state "free at the point of delivery", and emergency care free to anyone regardless of nationality or status. Due to the need for hospitals to prioritise their limited resources, there is a tendency in countries with such systems for 'waiting lists' for non-crucial treatment, so those who can afford it may take out private health care to access treatment more quickly.
In the United States, hospitals typically operate privately and in some cases on a for-profit basis, such as HCA Healthcare. The list of procedures and their prices are billed with a chargemaster
In the United States, the chargemaster, also known as charge master, or charge description master (CDM), is a comprehensive listing of items billable to a hospital patient or a patient's health insurance provider. In practice, it usually contains ...
; however, these prices may be lower for health care obtained within healthcare networks. Legislation requires hospitals to provide care to patients in life-threatening emergency situations regardless of the patient's ability to pay. Privately funded hospitals which admit uninsured patients in emergency situations incur direct financial losses, such as in the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina was a destructive Category 5 Atlantic hurricane that caused over 1,800 fatalities and $125 billion in damage in late August 2005, especially in the city of New Orleans and the surrounding areas. It was at the time the cost ...
.Hospitals in New Orleans see surge in uninsured patients but not public funds
' – '' USA Today'', Wednesday 26 April 2006
Quality and safety
As the quality of health care has increasingly become an issue around the world, hospitals have increasingly had to pay serious attention to this matter. Independent external assessment of quality is one of the most powerful ways to assess this aspect of health care, and hospital accreditation is one means by which this is achieved. In many parts of the world such accreditation is sourced from other countries, a phenomenon known as international healthcare accreditation, by groups such as Accreditation Canada from Canada, the Joint Commission from the US, the Trent Accreditation Scheme from Great Britain, and the '' Haute Autorité de santé'' (HAS) from France. In England hospitals are monitored by the Care Quality Commission. In 2020 they turned their attention to hospital food standards after seven patient deaths from listeria linked to pre-packaged sandwiches and salads in 2019, saying "Nutrition and hydration is part of a patient’s recovery." The World Health Organization noted in 2011 that going into hospital was far riskier than flying. Globally the chance of a patient being subject to an error was about 10% and the chance of death resulting from an error was about 1 in 300 according to Liam Donaldson. 7% of hospitalised patients in developed countries, and 10% in developing countries, acquire at least one health care-associated infection. In the USA 1.7 million infections are acquired in hospital each year, leading to 100,000 deaths, figures much worse than in Europe where there were 4.5 million infections and 37,000 deaths.Architecture

 Modern hospital buildings are designed to minimise the effort of medical personnel and the possibility of contamination while maximising the efficiency of the whole system. Travel time for personnel within the hospital and the transportation of patients between units is facilitated and minimised. The building also should be built to accommodate heavy departments such as radiology and operating rooms while space for special wiring, plumbing, and waste disposal must be allowed for in the design.
However, many hospitals, even those considered "modern", are the product of continual and often badly managed growth over decades or even centuries, with utilitarian new sections added on as needs and finances dictate. As a result, Dutch architectural historian Cor Wagenaar has called many hospitals:
:''"... built catastrophes, anonymous institutional complexes run by vast bureaucracies, and totally unfit for the purpose they have been designed for ... They are hardly ever functional, and instead of making patients feel at home, they produce stress and anxiety."
Modern hospital buildings are designed to minimise the effort of medical personnel and the possibility of contamination while maximising the efficiency of the whole system. Travel time for personnel within the hospital and the transportation of patients between units is facilitated and minimised. The building also should be built to accommodate heavy departments such as radiology and operating rooms while space for special wiring, plumbing, and waste disposal must be allowed for in the design.
However, many hospitals, even those considered "modern", are the product of continual and often badly managed growth over decades or even centuries, with utilitarian new sections added on as needs and finances dictate. As a result, Dutch architectural historian Cor Wagenaar has called many hospitals:
:''"... built catastrophes, anonymous institutional complexes run by vast bureaucracies, and totally unfit for the purpose they have been designed for ... They are hardly ever functional, and instead of making patients feel at home, they produce stress and anxiety."Healing by design
'' – ''Ode Magazine'', July/August 2006 issue. Accessed 10 February 2008. Some newer hospitals now try to re-establish design that takes the patient's psychological needs into account, such as providing more fresh air, better views and more pleasant colour schemes. These ideas harken back to the late eighteenth century, when the concept of providing fresh air and access to the 'healing powers of nature' were first employed by hospital architects in improving their buildings. The research of
British Medical Association
The British Medical Association (BMA) is a registered trade union for doctors in the United Kingdom. The association does not regulate or certify doctors, a responsibility which lies with the General Medical Council. The association's headquar ...
is showing that good hospital design can reduce patient's recovery time. Exposure to daylight is effective in reducing depression. Single-sex accommodation help ensure that patients are treated in privacy and with dignity. Exposure to nature and hospital gardens is also important – looking out windows improves patients' moods and reduces blood pressure and stress level. Open windows in patient rooms have also demonstrated some evidence of beneficial outcomes by improving airflow and increased microbial diversity. Eliminating long corridors can reduce nurses' fatigue and stress.
Another ongoing major development is the change from a ward-based system (where patients are accommodated in communal rooms, separated by movable partitions) to one in which they are accommodated in individual rooms. The ward-based system has been described as very efficient, especially for the medical staff, but is considered to be more stressful for patients and detrimental to their privacy. A major constraint on providing all patients with their own rooms is however found in the higher cost of building and operating such a hospital; this causes some hospitals to charge for private rooms.Health administrators go shopping for new hospital designs
'' – '' National Review of Medicine'', Monday 15 November 2004, Volume 1 No. 21
Uniklinikum Aachen
The Uniklinikum Aachen, full German name ''Universitätsklinikum Aachen'' ("University Hospital Aachen", abbreviated ''UKA''), formerly known as ''Neues Klinikum'' ("New Clinic"), is the university hospital of the city of Aachen, Germany ...
in Germany
File:TAYS,TAMPERE 1.12-09 aamulla n.klo 8 - panoramio.jpg, Tampere University Hospital in Tampere, Finland
File:AIIMS central lawn.jpg, All India Institute of Medical Sciences in Delhi, India
File:Lehigh-Valley-Hospital.x.jpg, Lehigh Valley Hospital–Cedar Crest in Allentown, Pennsylvania
Allentown (Pennsylvania Dutch language, Pennsylvania Dutch: ''Allenschteddel'', ''Allenschtadt'', or ''Ellsdaun'') is a city in Lehigh County, Pennsylvania, Lehigh County, Pennsylvania. The city has a population of 125,845 as of the 2020 United ...
See also
* Burn center * History of hospitals * History of medicine * Hospital network * Lists of hospitals * Hospital information system * Trauma center * The Waiting Room *Hospice
Hospice care is a type of health care that focuses on the palliation of a terminally ill patient's pain and symptoms and attending to their emotional and spiritual needs at the end of life. Hospice care prioritizes comfort and quality of life by ...
* Walk-in clinic
Notes
References
* *Bibliography
History of hospitals
* Brockliss, Lawrence, and Colin Jones. "The Hospital in the Enlightenment," in ''The Medical World of Early Modern France'' (Oxford UP, 1997), pp. 671–729; covers France 1650–1800 * Chaney, Edward (2000),"'Philanthropy in Italy': English Observations on Italian Hospitals 1545–1789", in: ''The Evolution of the Grand Tour: Anglo-Italian Cultural Relations since the Renaissance'', 2nd ed. London, Routledge, 2000. https://books.google.com/books/about/The_evolution_of_the_grand_tour.html?id=rYB_HYPsa8gC * Connor, J.T.H. "Hospital History in Canada and the United States," ''Canadian Bulletin of Medical History'', 1990, Vol. 7 Issue 1, pp. 93–104 * Crawford, D.SBibliography of Histories of Canadian hospitals and schools of nursing
* Gorsky, Martin. "The British National Health Service 1948–2008: A Review of the Historiography," ''Social History of Medicine'', December 2008, Vol. 21 Issue 3, pp. 437–60 * Harrison, Mar, et al. eds. ''From Western Medicine to Global Medicine: The Hospital Beyond the West'' (2008) * Horden, Peregrine. ''Hospitals and Healing From Antiquity to the Later Middle Ages'' (2008) * McGrew, Roderick E. ''Encyclopedia of Medical History'' (1985) * * Porter, Roy. ''The Hospital in History'', with Lindsay Patricia Granshaw (1989) * Risse, Guenter B. ''Mending Bodies, Saving Souls: A History of Hospitals'' (1999); world coverage * Rosenberg, Charles E. ''The Care of Strangers: The Rise of America's Hospital System'' (1995); history to 1920 * Scheutz, Martin et al. eds. ''Hospitals and Institutional Care in Medieval and Early Modern Europe'' (2009) * Wall, Barbra Mann. ''American Catholic Hospitals: A Century of Changing Markets and Missions'' (Rutgers University Press, 2011).
External links
* WHO Hospitals https://www.who.int/hospitals/en/ * * * {{cite web, url= https://ayurvedakidneydoctor.wordpress.com/2022/11/01/karma-ayurveda-kidney-specialist-negetive-reviews-dr-puneet-dhawan-patient-bunty-rana-review, title= karma ayurveda hospital, website= ayurvedakidneydoctor.wordpress.com
The domain name .com is a top-level domain (TLD) in the Domain Name System (DNS) of the Internet. Added at the beginning of 1985, its name is derived from the word ''commercial'', indicating its original intended purpose for domains registere ...
, language= en