Hospital Corpsman Dental Assistant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A hospital corpsman (HM r corpsman is an enlisted medical specialist of the United States Navy, who may also serve in a

 Hospital corpsmen work in a wide variety of capacities and locations, including shore establishments such as naval hospitals and clinics, aboard ships, and as the primary medical caregivers for sailors while underway. Hospital corpsmen are frequently the only medical care-giver available in many fleet or
Hospital corpsmen work in a wide variety of capacities and locations, including shore establishments such as naval hospitals and clinics, aboard ships, and as the primary medical caregivers for sailors while underway. Hospital corpsmen are frequently the only medical care-giver available in many fleet or
 Still, there existed pressure to reform the enlisted component of the Navy's medical department—medicine as a science was advancing rapidly, foreign navies had begun training medically skilled sailors, and the U.S. Army had established an enlisted hospital corps in 1887. Navy Surgeon General J.R. Tryon and subordinate physicians lobbied the Navy administration to take action. With the Spanish–American War looming, Congress passed a bill authorizing establishment of the U.S. Navy Hospital Corps, signed into law by President William McKinley on 17 June 1898. Three ratings were created therein—hospital apprentice, hospital apprentice first class (a petty officer third class), and hospital steward, which was a chief petty officer.
A revision in 1916 established a new rate structure. With the introduction of a second junior rate there were now hospital apprentice second class (HA2c) and hospital apprentice first class (HA1c). The rating title for petty officers was established as pharmacist's mate (PhM), following the pattern of some of the Navy's other ratings (boatswain's mate, gunner's mate, etc.). Pharmacist's mate third class (PhM3c), second class (PhM2c), and first class (PhM1c) were now the petty officers, and chief pharmacist's mate (CPhM) was the chief petty officer. This structure remained in place until 1947.
A total of 684 personal awards were awarded to hospital corpsmen, including 23
Still, there existed pressure to reform the enlisted component of the Navy's medical department—medicine as a science was advancing rapidly, foreign navies had begun training medically skilled sailors, and the U.S. Army had established an enlisted hospital corps in 1887. Navy Surgeon General J.R. Tryon and subordinate physicians lobbied the Navy administration to take action. With the Spanish–American War looming, Congress passed a bill authorizing establishment of the U.S. Navy Hospital Corps, signed into law by President William McKinley on 17 June 1898. Three ratings were created therein—hospital apprentice, hospital apprentice first class (a petty officer third class), and hospital steward, which was a chief petty officer.
A revision in 1916 established a new rate structure. With the introduction of a second junior rate there were now hospital apprentice second class (HA2c) and hospital apprentice first class (HA1c). The rating title for petty officers was established as pharmacist's mate (PhM), following the pattern of some of the Navy's other ratings (boatswain's mate, gunner's mate, etc.). Pharmacist's mate third class (PhM3c), second class (PhM2c), and first class (PhM1c) were now the petty officers, and chief pharmacist's mate (CPhM) was the chief petty officer. This structure remained in place until 1947.
A total of 684 personal awards were awarded to hospital corpsmen, including 23  Following the war, the hospital corps changed its rating title to the generic term it had used all along—hospital corpsman. The rates of hospital corpsman third class (HM3), second class (HM2), and first class (HM1), and chief hospital corpsman (HMC) were supplemented by senior chief hospital corpsman (HMCS) and master chief hospital corpsman (HMCM) in 1958.
Hospital corpsmen continued to serve at sea and ashore, and accompanied marines and Marine units into battle during the Korean and Vietnam wars. Fifteen hospital corpsmen were counted among the dead following the bombing of the Marine barracks in Beirut in 1983. Hospital corpsmen also served in the Iraq and Afghanistan wars providing corpsmen for convoys, patrols, and hospital or clinic treatment.
Whether they are assigned to hospital ships, reservist installations, recruiter offices, or Marine Corps combat units, the rating of hospital corpsman is the most decorated in the United States Navy and the most decorated job in the U.S. military, with 22 Medals of Honor, 179 Navy Crosses since World War I, 31
Following the war, the hospital corps changed its rating title to the generic term it had used all along—hospital corpsman. The rates of hospital corpsman third class (HM3), second class (HM2), and first class (HM1), and chief hospital corpsman (HMC) were supplemented by senior chief hospital corpsman (HMCS) and master chief hospital corpsman (HMCM) in 1958.
Hospital corpsmen continued to serve at sea and ashore, and accompanied marines and Marine units into battle during the Korean and Vietnam wars. Fifteen hospital corpsmen were counted among the dead following the bombing of the Marine barracks in Beirut in 1983. Hospital corpsmen also served in the Iraq and Afghanistan wars providing corpsmen for convoys, patrols, and hospital or clinic treatment.
Whether they are assigned to hospital ships, reservist installations, recruiter offices, or Marine Corps combat units, the rating of hospital corpsman is the most decorated in the United States Navy and the most decorated job in the U.S. military, with 22 Medals of Honor, 179 Navy Crosses since World War I, 31
 As of April 2011, training to become a hospital corpsman began at Basic Medical Technician Corpsman Program (BMTCP) located at Joint Base Fort Sam Houston in San Antonio, Texas.
Because of the need for hospital corpsmen in a vast array of foreign, domestic, and shipboard duty stations, as well as with United States Marine Corps units, the hospital corps is the largest occupational rating (Navy Enlisted Classification-HM) in the United States Navy, with about 25,000 members active duty and reserve.
The basic training for hospital corpsmen is conducted at the
As of April 2011, training to become a hospital corpsman began at Basic Medical Technician Corpsman Program (BMTCP) located at Joint Base Fort Sam Houston in San Antonio, Texas.
Because of the need for hospital corpsmen in a vast array of foreign, domestic, and shipboard duty stations, as well as with United States Marine Corps units, the hospital corps is the largest occupational rating (Navy Enlisted Classification-HM) in the United States Navy, with about 25,000 members active duty and reserve.
The basic training for hospital corpsmen is conducted at the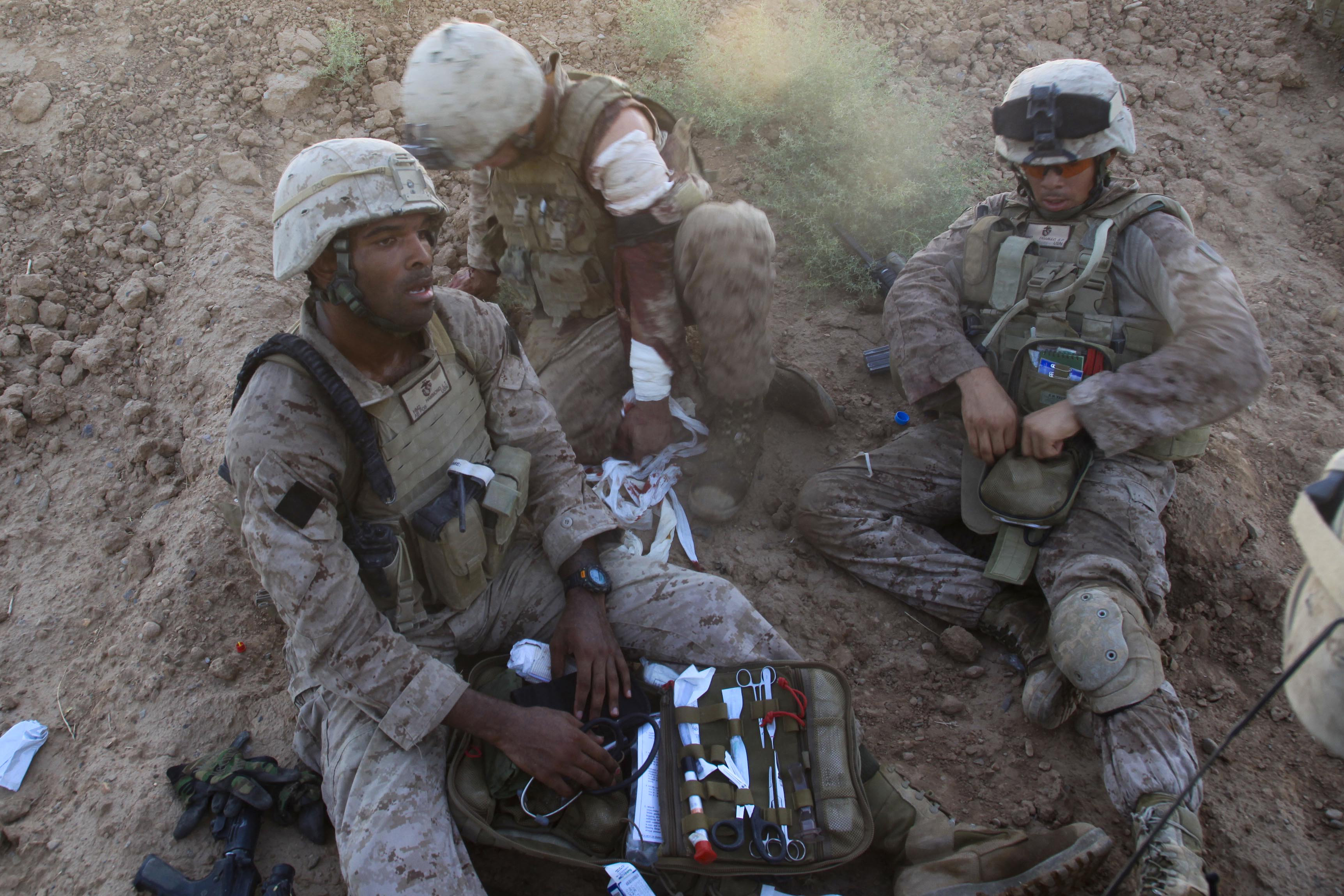  Hospital corpsmen who have received the warfare designator of enlisted fleet marine force warfare specialist are highly trained members of the Hospital Corps who specialize in all aspects of working with the United States Marine Corps operating forces. Attainment of this designation is highly prized among all corpsmen. The enlisted fleet marine force warfare designation for hospital corpsmen is the only U.S. Navy warfare device awarded solely by a U.S. Marine Corps general officer. This awarding authority cannot be delegated to U.S. Navy officers. However, obtaining the title of "FMF" is a rigorous procedure and not every hospital corpsman who has been with a Marine Corps unit will wear the FMF warfare device. U.S. Navy officers in the medical community (Medical Corps (doctor), Nurse Corps, Dental Corps, Medical Service Corps) can earn and wear the officer equivalent to this insignia. Additionally any sailor attached to a USMC unit can earn and wear an FMF warfare device. (e.g., administrative rates such as logistic specialists) provided they complete all the qualifications for the FMF warfare specialist.
Hospital corpsmen who have received the warfare designator of enlisted fleet marine force warfare specialist are highly trained members of the Hospital Corps who specialize in all aspects of working with the United States Marine Corps operating forces. Attainment of this designation is highly prized among all corpsmen. The enlisted fleet marine force warfare designation for hospital corpsmen is the only U.S. Navy warfare device awarded solely by a U.S. Marine Corps general officer. This awarding authority cannot be delegated to U.S. Navy officers. However, obtaining the title of "FMF" is a rigorous procedure and not every hospital corpsman who has been with a Marine Corps unit will wear the FMF warfare device. U.S. Navy officers in the medical community (Medical Corps (doctor), Nurse Corps, Dental Corps, Medical Service Corps) can earn and wear the officer equivalent to this insignia. Additionally any sailor attached to a USMC unit can earn and wear an FMF warfare device. (e.g., administrative rates such as logistic specialists) provided they complete all the qualifications for the FMF warfare specialist.
Corpsman.com, A Site run by Corpsmen for Corpsmen
* {{US Navy navbox Navy, Hospital Corpsman Health care occupations United States Navy ratings
U.S. Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through comb ...
unit. The corresponding rating within the United States Coast Guard is health services technician (HS).
Overview

 Hospital corpsmen work in a wide variety of capacities and locations, including shore establishments such as naval hospitals and clinics, aboard ships, and as the primary medical caregivers for sailors while underway. Hospital corpsmen are frequently the only medical care-giver available in many fleet or
Hospital corpsmen work in a wide variety of capacities and locations, including shore establishments such as naval hospitals and clinics, aboard ships, and as the primary medical caregivers for sailors while underway. Hospital corpsmen are frequently the only medical care-giver available in many fleet or Marine
Marine is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the sea or ocean.
Marine or marines may refer to:
Ocean
* Maritime (disambiguation)
* Marine art
* Marine biology
* Marine debris
* Marine habitats
* Marine life
* Marine pollution
Military
* ...
units on extended deployment. In addition, hospital corpsmen perform duties as assistants in the prevention and treatment of disease and injury and assist health care professionals in providing medical care to sailors and their families.
They may function as clinical or specialty technicians, medical administrative personnel and health care providers at medical treatment facilities. They also serve as battlefield corpsmen with the Marine Corps, rendering emergency medical treatment to include initial treatment in a combat environment. Qualified hospital corpsmen may be assigned the responsibility of independent duty aboard ships and submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
s; Fleet Marine Force, SEAL and Seabee units, and at isolated duty stations where no medical officer is available.
Hospital corpsmen were previously trained at Naval Hospital Corps School, Great Lakes, Illinois, and the U.S. Naval Hospital Corps School San Diego, California, until the 2011 Base Realignment and Closure Bill caused Hospital Corps School to be relocated to the Medical Education and Training Campus
The Medical Education and Training Campus (METC) is a United States Department of Defense (DoD) integrated campus under a single university-style administration, with nearly 50 programs of study available to U.S. military enlisted students and a ...
(METC) at Joint Base San Antonio, Texas. Naval Hospital Corps School was also located at NRMC Balboa in San Diego, California.
During the Vietnam War, many of the 16-week Naval Hospital Corps school graduates went directly to 8404 Field Medical Service School (FMSS) at Camp Lejeune, North Carolina, or Camp Pendleton, California, for nine weeks of field training, before deployment to a Marine Corps unit in South Vietnam.
The colloquial form of address for a hospital corpsman is "Doc". In the United States Marine Corps, this term is generally used as a sign of respect.
History
Prior to the establishment of the hospital corps, enlisted medical support in the U.S. Navy was limited in scope. In theContinental Navy
The Continental Navy was the navy of the United States during the American Revolutionary War and was founded October 13, 1775. The fleet cumulatively became relatively substantial through the efforts of the Continental Navy's patron John Adams ...
and the early U.S. Navy, medical assistants were assigned at random out of the ship's company. Their primary duties were to keep the irons hot and buckets of sand at the ready for the operating area. It was commonplace during battle for the surgeons to conduct amputations and irons were used to close lacerations and wounds. Sand was used to keep the surgeon from slipping on the bloody ship deck. Previously, corpsmen were commonly referred to as loblolly boys, a term borrowed from the Royal Navy, and a reference to the daily ration of porridge fed to the sick. The nickname was in common use for so many years that it was finally officially recognized by the Navy Regulations of 1814. In coming decades, the title of the enlisted medical assistant would change several times—from loblolly boy, to nurse (1861), and finally to bayman (1876). A senior enlisted medical rating, surgeon's steward, was introduced in 1841 and remained through the Civil War. Following the war, the title surgeon's steward was abolished in favor of apothecary, a position requiring completion of a course in pharmacy.
 Still, there existed pressure to reform the enlisted component of the Navy's medical department—medicine as a science was advancing rapidly, foreign navies had begun training medically skilled sailors, and the U.S. Army had established an enlisted hospital corps in 1887. Navy Surgeon General J.R. Tryon and subordinate physicians lobbied the Navy administration to take action. With the Spanish–American War looming, Congress passed a bill authorizing establishment of the U.S. Navy Hospital Corps, signed into law by President William McKinley on 17 June 1898. Three ratings were created therein—hospital apprentice, hospital apprentice first class (a petty officer third class), and hospital steward, which was a chief petty officer.
A revision in 1916 established a new rate structure. With the introduction of a second junior rate there were now hospital apprentice second class (HA2c) and hospital apprentice first class (HA1c). The rating title for petty officers was established as pharmacist's mate (PhM), following the pattern of some of the Navy's other ratings (boatswain's mate, gunner's mate, etc.). Pharmacist's mate third class (PhM3c), second class (PhM2c), and first class (PhM1c) were now the petty officers, and chief pharmacist's mate (CPhM) was the chief petty officer. This structure remained in place until 1947.
A total of 684 personal awards were awarded to hospital corpsmen, including 23
Still, there existed pressure to reform the enlisted component of the Navy's medical department—medicine as a science was advancing rapidly, foreign navies had begun training medically skilled sailors, and the U.S. Army had established an enlisted hospital corps in 1887. Navy Surgeon General J.R. Tryon and subordinate physicians lobbied the Navy administration to take action. With the Spanish–American War looming, Congress passed a bill authorizing establishment of the U.S. Navy Hospital Corps, signed into law by President William McKinley on 17 June 1898. Three ratings were created therein—hospital apprentice, hospital apprentice first class (a petty officer third class), and hospital steward, which was a chief petty officer.
A revision in 1916 established a new rate structure. With the introduction of a second junior rate there were now hospital apprentice second class (HA2c) and hospital apprentice first class (HA1c). The rating title for petty officers was established as pharmacist's mate (PhM), following the pattern of some of the Navy's other ratings (boatswain's mate, gunner's mate, etc.). Pharmacist's mate third class (PhM3c), second class (PhM2c), and first class (PhM1c) were now the petty officers, and chief pharmacist's mate (CPhM) was the chief petty officer. This structure remained in place until 1947.
A total of 684 personal awards were awarded to hospital corpsmen, including 23 Medals of Honor
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the United States Armed Forces' highest military decoration and is awarded to recognize American soldiers, sailors, marines, airmen, guardians and coast guardsmen who have distinguished themselves by acts of valor. Th ...
, 55 Navy Crosses, and 237 Silver Star
The Silver Star Medal (SSM) is the United States Armed Forces' third-highest military decoration for valor in combat. The Silver Star Medal is awarded primarily to members of the United States Armed Forces for gallantry in action against an e ...
s. During World War I, hospital corpsmen served throughout the fleet, earning particular distinction on the Western Front Western Front or West Front may refer to:
Military frontiers
*Western Front (World War I), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (World War II), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (Russian Empire), a majo ...
with the Marine Corps.
In the United States Navy in World War II, hospital corpsmen assigned to Marine units made beach assaults with the marines in every battle in the Pacific. Corpsmen also served on thousands of ships and submarines. Three unassisted emergency appendectomies were performed by hospital corpsmen serving undersea and beyond hope of medical evacuation. The hospital corps has the distinction of being the only corps in the U.S. Navy to be commended, in a famous speech by Secretary of the Navy James Forrestal after the conclusion of the war.
 Following the war, the hospital corps changed its rating title to the generic term it had used all along—hospital corpsman. The rates of hospital corpsman third class (HM3), second class (HM2), and first class (HM1), and chief hospital corpsman (HMC) were supplemented by senior chief hospital corpsman (HMCS) and master chief hospital corpsman (HMCM) in 1958.
Hospital corpsmen continued to serve at sea and ashore, and accompanied marines and Marine units into battle during the Korean and Vietnam wars. Fifteen hospital corpsmen were counted among the dead following the bombing of the Marine barracks in Beirut in 1983. Hospital corpsmen also served in the Iraq and Afghanistan wars providing corpsmen for convoys, patrols, and hospital or clinic treatment.
Whether they are assigned to hospital ships, reservist installations, recruiter offices, or Marine Corps combat units, the rating of hospital corpsman is the most decorated in the United States Navy and the most decorated job in the U.S. military, with 22 Medals of Honor, 179 Navy Crosses since World War I, 31
Following the war, the hospital corps changed its rating title to the generic term it had used all along—hospital corpsman. The rates of hospital corpsman third class (HM3), second class (HM2), and first class (HM1), and chief hospital corpsman (HMC) were supplemented by senior chief hospital corpsman (HMCS) and master chief hospital corpsman (HMCM) in 1958.
Hospital corpsmen continued to serve at sea and ashore, and accompanied marines and Marine units into battle during the Korean and Vietnam wars. Fifteen hospital corpsmen were counted among the dead following the bombing of the Marine barracks in Beirut in 1983. Hospital corpsmen also served in the Iraq and Afghanistan wars providing corpsmen for convoys, patrols, and hospital or clinic treatment.
Whether they are assigned to hospital ships, reservist installations, recruiter offices, or Marine Corps combat units, the rating of hospital corpsman is the most decorated in the United States Navy and the most decorated job in the U.S. military, with 22 Medals of Honor, 179 Navy Crosses since World War I, 31 Navy Distinguished Service Medal
The Navy Distinguished Service Medal is a military decoration of the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps which was first created in 1919 and is presented to sailors and Marines to recognize distinguished and exceptionally meritoriou ...
s, 959 Silver Stars, and more than 1,600 Bronze Star Medal
The Bronze Star Medal (BSM) is a United States Armed Forces decoration awarded to members of the United States Armed Forces for either heroic achievement, heroic service, meritorious achievement, or meritorious service in a combat zone.
Wh ...
's with combat V's for heroism since World War II (as of 2016). Twenty naval ships have been named after hospital corpsmen. Prior to selection to the command master chief program, the 11th MCPON, Joe R. Campa
Joe R. Campa Jr. is a retired United States Navy sailor who served as the 11th Master Chief Petty Officer of the Navy.
Early life and education
Campa was born in Lynwood, California and grew up in Southern California. Campa is a distinguished h ...
, was a hospital corpsman.
On 29 September 2016, the Secretary of the Navy Ray Mabus terminated the corpsman rating along with all other U.S. Navy enlisted ratings. However, in late December 2016, the usage of ratings were restored by the Navy after much backlash by many in the enlisted naval ranks.
Navy and Marine Corps training
 As of April 2011, training to become a hospital corpsman began at Basic Medical Technician Corpsman Program (BMTCP) located at Joint Base Fort Sam Houston in San Antonio, Texas.
Because of the need for hospital corpsmen in a vast array of foreign, domestic, and shipboard duty stations, as well as with United States Marine Corps units, the hospital corps is the largest occupational rating (Navy Enlisted Classification-HM) in the United States Navy, with about 25,000 members active duty and reserve.
The basic training for hospital corpsmen is conducted at the
As of April 2011, training to become a hospital corpsman began at Basic Medical Technician Corpsman Program (BMTCP) located at Joint Base Fort Sam Houston in San Antonio, Texas.
Because of the need for hospital corpsmen in a vast array of foreign, domestic, and shipboard duty stations, as well as with United States Marine Corps units, the hospital corps is the largest occupational rating (Navy Enlisted Classification-HM) in the United States Navy, with about 25,000 members active duty and reserve.
The basic training for hospital corpsmen is conducted at the Medical Education and Training Campus
The Medical Education and Training Campus (METC) is a United States Department of Defense (DoD) integrated campus under a single university-style administration, with nearly 50 programs of study available to U.S. military enlisted students and a ...
, located in Texas at a joint military base. Originally one of the Navy's "A" schools (primary rating training). Upon graduation, the hospital corpsman is given the Navy Enlisted Classification (NEC) code of HM-0000, or "quad-zero" in common usage. Students go through a 14-week course that provides in-depth and extensive training into the application of emergency medical techniques, disease and pathologies, and nursing techniques.
NECs are not as analogous to MOS in the United States Army and Marine Corps, or AFSC in the Air Force as the rating in the Navy. There are primary NECs, and secondary NECs. For example, a hospital corpsman who completes Field Medical Training Battalion (FMTB) and earns the NEC HM-L03A, moves that NEC to primary and has a secondary NEC of HM-0000. If that hospital corpsman attends a "C" School, then the NEC earned at the "C" School becomes their primary and HM-L03A becomes the secondary. Some hospital corpsmen go on to receive more specialized training in roles such as medical laboratory technician
A medical laboratory or clinical laboratory is a laboratory where tests are conducted out on clinical specimens to obtain information about the health of a patient to aid in diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease. Clinical Medical la ...
, optometry technician, radiology technician
Radiographers, also known as radiologic technologists, diagnostic radiographers and medical radiation technologists are healthcare professionals who specialize in the imaging of human anatomy for the diagnosis and treatment of pathology. Radi ...
, aerospace medicine specialist, pharmacy technician, operating room technician
A surgical technologist, also called a scrub, scrub tech, surgical technician, or operating room technician, is an allied health professional working as a part of the team delivering surgical care. Surgical technologists are members of the sur ...
, etc. This advanced education is done through "C" schools, which confer 39 additional NECs. Additionally, hospital corpsmen (E-5 and above) may attend independent duty corpsman training, qualifying for independent duty in surface ships and submarines, with diving teams, and Fleet Marine Force Recon teams, as well as at remote shore installations. In addition to advanced medical training, these hospital corpsmen receive qualification in sanitation and public health.
Of note is the Field Medical Training Battalion (FMTB), with locations at Camp Del Mar
Marine Corps Base Camp Pendleton is the major West Coast base of the United States Marine Corps and is one of the largest Marine Corps bases in the United States. It is on the Southern California coast in San Diego County and is bordered by Oc ...
and Camp Johnson, where sailors bound for service with USMC operating forces earn the NEC HM-L03A (formerly 8404), Field Medical Service Technician. FMTB provides specialized training in advanced emergency medicine and the fundamentals of Marine Corps life, while emphasizing physical conditioning, small arms familiarity, and basic battlefield tactics. , this rigorous training is 8 weeks. Training for the Fleet Marine Force (FMF) familiarizes navy corpsmen with the Marines. A bond and mutual respect is often formed between Marines and their assigned hospital corpsmen, earning respect apart from their Navy shipmates. FMF hospital corpsmen are issued the Marine Corps service uniforms and camouflage uniforms (MARPAT) while assigned to the Marine Corps and also have the option to go Marine Corps Regulations. They are then issued a new seabag containing the Marine uniforms (except dress blues) with uniform matching Navy rate chevrons instead of the Marine rank chevrons, and collar rank insignias, and wear those instead of traditional Navy uniforms. The Navy's new digitized camouflage working uniform are worn by sailors stationed at other naval facilities. Note that hospital corpsmen going to units within NECC (Navy Expeditionary Combat Command) such as Seabees, Riverines (Now called MSRON), and Explosive Ordinance Disposal (EOD) also have to go to FMTB.
Hospital corpsmen can further specialize; they may undergo further training to become Special Amphibious Reconnaissance Corpsmen
A Special Amphibious Reconnaissance Corpsman (SARC) is a United States Navy hospital corpsman who provides MARSOC and other USSOCOM units advanced trauma management associated with combatant diving and parachute entry. Traditionally, they are a ...
, or ''SARC''. They are usually found in both the FMF Recon, Marine Division Recon and MARSOC units. They are trained and skilled in combat, including combatant swimming, opened/closed circuit scuba diving, military free-fall and amphibious operations. They act as advisers regarding health and injury prevention, and treat illnesses from decompression sickness as well as other conditions requiring hyperbaric treatment.
 Hospital corpsmen who have received the warfare designator of enlisted fleet marine force warfare specialist are highly trained members of the Hospital Corps who specialize in all aspects of working with the United States Marine Corps operating forces. Attainment of this designation is highly prized among all corpsmen. The enlisted fleet marine force warfare designation for hospital corpsmen is the only U.S. Navy warfare device awarded solely by a U.S. Marine Corps general officer. This awarding authority cannot be delegated to U.S. Navy officers. However, obtaining the title of "FMF" is a rigorous procedure and not every hospital corpsman who has been with a Marine Corps unit will wear the FMF warfare device. U.S. Navy officers in the medical community (Medical Corps (doctor), Nurse Corps, Dental Corps, Medical Service Corps) can earn and wear the officer equivalent to this insignia. Additionally any sailor attached to a USMC unit can earn and wear an FMF warfare device. (e.g., administrative rates such as logistic specialists) provided they complete all the qualifications for the FMF warfare specialist.
Hospital corpsmen who have received the warfare designator of enlisted fleet marine force warfare specialist are highly trained members of the Hospital Corps who specialize in all aspects of working with the United States Marine Corps operating forces. Attainment of this designation is highly prized among all corpsmen. The enlisted fleet marine force warfare designation for hospital corpsmen is the only U.S. Navy warfare device awarded solely by a U.S. Marine Corps general officer. This awarding authority cannot be delegated to U.S. Navy officers. However, obtaining the title of "FMF" is a rigorous procedure and not every hospital corpsman who has been with a Marine Corps unit will wear the FMF warfare device. U.S. Navy officers in the medical community (Medical Corps (doctor), Nurse Corps, Dental Corps, Medical Service Corps) can earn and wear the officer equivalent to this insignia. Additionally any sailor attached to a USMC unit can earn and wear an FMF warfare device. (e.g., administrative rates such as logistic specialists) provided they complete all the qualifications for the FMF warfare specialist.
Independent Duty Corpsman
The firstphysician assistant
A physician assistant or physician associate (PA) is a type of Mid-level practitioner, mid-level health care provider. In North America PAs may diagnose illnesses, develop and manage treatment plans, prescribe medications, and may serve as a pri ...
s were selected from Navy corpsmen who had combat experience in Vietnam. They made up members of the first PA class at Duke University. The Navy trained its own physician assistants drawing from the ranks of qualified petty officer second class corpsman, as well as independent duty hospital corpsmen at the Naval School of Health Sciences in Portsmouth, VA until 1985, then at San Diego, CA and current the Interservice Physician Assistant Program (IPAP) with a university affiliation of the University of Nebraska Medical Center (UNMC). It is conducted in two phases the first phase at the Graduate School and Academy of Health Sciences at AMEDDC&S, Ft. Sam Houston, TX and the second phase at various medical facilities and specialties. When training completed they become officers in the Medical Service Corps (MSC). Former Navy hospital corpsmen are also represented in many medical disciplines, as physicians, nurses, medical administrators and other walks of life. After completing their training, a physician assistant is promoted to the rank of lieutenant junior grade (O-2). Previously after graduating from civilian PA school, they had only been given the rank of warrant officer 2 (CWO2).
Rate/rating structure
*HR: Hospitalman Recruit (E-1) *HA: Hospitalman Apprentice (E-2) *HN: Hospitalman (E-3) (See USN apprenticeships) *HM3: Hospital Corpsman Third Class (E-4) *HM2: Hospital Corpsman Second Class (E-5) *HM1: Hospital Corpsman First Class (E-6) *HMC: Chief Hospital Corpsman (E-7) *HMCS: Senior Chief Hospital Corpsman (E-8) *HMCM: Master Chief Hospital Corpsman (E-9)Badges
Effective 2 April 1948 the Navy changed the names and insignia of the hospital corps. The new titles were Hospitalman Recruit, Hospitalman Apprentice, Hospitalman, Hospital Corpsman Third, Second, and First Class, and Chief Hospital Corpsman. The red Geneva cross, which had marked corpsmen for 50 years, was replaced in the rating badge with the misattributed mark of the wingedcaduceus
The caduceus (☤; ; la, cādūceus, from grc-gre, κηρύκειον "herald's wand, or staff") is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology and consequently by Hermes Trismegistus in Greco-Egyptian mythology. The same staff was also ...
. The rates of Senior Chief and Master Chief Hospital Corpsman were added in 1958.
:''See:
Ships named in honor of hospital corpsmen
Reference: '' Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships'' * USS ''Benfold'' (DDG-65) * USS ''Caron'' (DD-970) * USS ''De Wert'' (FFG-45) * USS ''Durant'' (DER-389) *Also sailed as USCGC ''Durant'' (WDE-489) * USS ''Frament'' (APD-77) * USS ''Halyburton'' (FFG-40) * USS ''Francis Hammond'' (FF-1067) * USS ''Jobb'' (DE-707) * USS ''Daniel A. Joy'' (DE-585) * USS ''Lester'' (DE-1022) * USS ''Liddle'' (DE-206) * USS ''Litchfield'' (AG-95) * USS ''Thaddeus Parker'' (DE-369) * USS ''David R. Ray'' (DD-971) * USS ''Henry W. Tucker'' (DD-875) * USS ''Valdez'' (FF-1096) * USS ''Walter C. Wann'' (DE-412) * USS ''Jack Williams'' (FFG-24) * USS ''John Willis'' (DE-1027) * USS ''Don O. Woods'' (APD-118) * USS ''William Charette'' (DDG-130) * USS ''John E. Kilmer'' (DDG-134)U.S. Navy enlisted medical personnel killed in action
* American Civil War (1861–1865), 6 * Spanish–American War (1898), 3 * World War I (1917–1918), 20 * Nicaragua (1932), 1 * World War II (1941–1945), 1,170 * Korean War (1950–1953), 109 * Dominican Republic (1965), 1 * Vietnam War (1962–1975), 639 * Beirut, (1983), 15 * Gulf War (1990–1991), 0 * Afghanistan (2001–2021), 14 * Iraq War (2003–2010), 29 * Total in all conflicts: 2,013Decorations of valor awarded to Hospital Corpsmen
* Medal of Honor, 23 * Navy Cross, 179 *Distinguished Service Cross (United States Army)
The Distinguished Service Cross (DSC) is the United States Army's second highest military decoration for soldiers who display extraordinary heroism in combat with an armed enemy force. Actions that merit the Distinguished Service Cross must be ...
, 31
* Silver Star Medal, 959
*Bronze Star Medal
The Bronze Star Medal (BSM) is a United States Armed Forces decoration awarded to members of the United States Armed Forces for either heroic achievement, heroic service, meritorious achievement, or meritorious service in a combat zone.
Wh ...
with Combat "V" for heroism, 1,600
Medal of Honor recipients
Pre- World War I * Hospital ApprenticeRobert H. Stanley
Robert Henry Stanley (May 2, 1881 – July 15, 1942) was a 40-year member of the United States Navy. He was the first hospital corpsman to receive the nation's highest military decoration for valor, the Medal of Honor. He was awarded the medal f ...
, USN (Boxer Rebellion
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an anti-foreign, anti-colonial, and anti-Christian uprising in China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by ...
)
* Hospital Apprentice First Class William Zuiderveld
William Zuiderveld (January 8, 1888 – February 5, 1978) was a United States Navy Hospital Apprentice First Class. He received the Medal of Honor for actions during the United States occupation of Veracruz.
Service during United States occu ...
, USN (Veracruz Incursion)
* Hospital Apprentice Fred H. McGuire
Fred Henry McGuire (November 7, 1890 – February 4, 1958) was a Hospital Apprentice in the United States Navy and a Medal of Honor recipient for his role in the Philippine–American War.
He died February 4, 1958, and is buried in Springfie ...
, USN (Philippine Insurrection)
* Hospital Steward William S. Shacklette
William Sidney Shacklette (May 18, 1880 - February 12, 1945) was a hospital steward serving in the United States Navy who received the Medal of Honor for bravery.
Biography
Shacklette was born May 18, 1880, in Delaplane, Virginia and when he was t ...
, USN (Boiler Explosion in San Diego)
World War I
* Pharmacist's Mate First Class John H. Balch
John Henry Balch (January 2, 1896 – October 15, 1980) was a United States Naval Reserve officer. He received the Medal of Honor for his actions in World War I.
Education
Balch enlisted in the Navy in Kansas City, Missouri under an officers train ...
, USN
* Hospital Apprentice First Class David E. Hayden
David Ephraim Hayden (October 2, 1897 – March 18, 1974) was a United States Navy Hospital Corpsman who served during World War I and earned the Medal of Honor for valiant actions in France.
Biography
Hayden was born in Florence, Texas and enlis ...
, USN
World War II
* Hospital Apprentice First Class Robert Eugene Bush, USN
* Pharmacist's Mate Second Class William D. Halyburton, Jr.
William David Halyburton Jr. (October 2, 1924 – May 10, 1945) was a United States Navy hospital corpsman who was killed in action during World War II while assigned to a Marine Corps rifle company. He was posthumously awarded the nation's highest ...
, USNR
* Hospital Apprentice First Class Fred F. Lester, USN
* Pharmacist's Mate First Class Francis J. Pierce
Francis Junior Pierce (December 7, 1924 – December 21, 1986) was a United States Navy hospital corpsman in World War II who received the nation's highest military decoration for valor, the Medal of Honor. He was awarded the medal for heroic act ...
, USN
* Pharmacist's Mate Second Class George E. Wahlen
George E. Wahlen (August 8, 1924 – June 5, 2009) was a United States Army major who served with the United States Navy as a hospital corpsman attached to a Marine Corps rifle company in World War II and was awarded the U.S. military's highest de ...
, USN
* Pharmacist's Mate Third Class Jack Williams, USN
* Pharmacist's Mate First Class John H. Willis, USN
Korean War
* Hospital Corpsman Third Class Edward C. Benfold, USN
* Hospital Corpsman Third Class William R. Charette
William Richard Charette (March 29, 1932 – March 18, 2012) was a United States Navy master chief hospital corpsman who received the nation's highest military decoration for valor, the Medal of Honor. He was awarded the medal for heroic actions ...
, USN
* Hospitalman Richard D. Dewert
Richard David De Wert (November 17, 1931 – April 5, 1951) was a United States Navy hospital corpsman who was killed in action during the Korean War while serving with a Marine Corps rifle company. He was posthumously awarded the nation's highest ...
, USN
* Hospitalman Francis C. Hammond
Francis Colton Hammond (November 9, 1931 – March 26, 1953) was a United States Navy hospital corpsman who was killed in action in Korea while serving with a Marine Corps rifle company during the Korean War. He posthumously received the Medal of ...
, USN
* Hospitalman John E. Kilmer
John Edward Kilmer (August 15, 1930 – August 13, 1952) was a United States Navy hospitalman who was killed in action during the Battle of Bunker Hill (1952) while attached to a Marine Corps rifle company in the Korean War. He was posthumously ...
, USN
Vietnam War
* Hospital Corpsman Second Class Donald E. Ballard
Donald Everett Ballard (born December 5, 1945) is a retired colonel of the Kansas National Guard and former member of the United States Navy. As a hospital corpsman in the Vietnam War, he received the Medal of Honor for his heroic actions on May 1 ...
, USN
* Hospital Corpsman Third Class Wayne M. Caron
Wayne Maurice Caron (November 2, 1946 – July 28, 1968) was a United States Navy hospital corpsman who was killed in action while serving with a Marine Corps rifle company in the Vietnam War. For heroic actions above and beyond the call of duty o ...
, USN
* Hospital Corpsman Third Class Robert R. Ingram
Robert Roland Ingram (born January 20, 1945) is a retired United States Navy hospital corpsman third class and a recipient of the United States' highest military decoration, the Medal of Honor, for heroism during the Vietnam War.
Military career
...
, USN
* Hospital Corpsman Second Class David R. Ray
David Robert "Bobby" Ray (February 14, 1945 – March 19, 1969) was a United States Navy hospital corpsman second class who was killed in action during the Vietnam War while assigned to an artillery battery of the United States Marine Corps. He ...
, USN
Afghanistan War
War in Afghanistan, Afghan war, or Afghan civil war may refer to:
*Conquest of Afghanistan by Alexander the Great (330 BC – 327 BC)
*Muslim conquests of Afghanistan (637–709)
*Conquest of Afghanistan by the Mongol Empire (13th century), see als ...
* Command Master Chief, SEAL Edward Byers, USN
United States Maritime Service hospital corpsmen
During World War II, the United States Maritime Service created a Hospital Corps similar to the U.S. Navy's and sent pursers through this hospital corpsman training, to serve in a combined administrative and medical role on civiliantanker
Tanker may refer to:
Transportation
* Tanker, a tank crewman (US)
* Tanker (ship), a ship designed to carry bulk liquids
** Chemical tanker, a type of tanker designed to transport chemicals in bulk
** Oil tanker, also known as a petroleum ta ...
s, freighters, and oilers. Prior to this, there were no competent trained personnel to perform first aid aboard these vessels. The purser-corpsman was trained in anatomy, physiology, pharmacy
Pharmacy is the science and practice of discovering, producing, preparing, dispensing, reviewing and monitoring medications, aiming to ensure the safe, effective, and affordable use of medicines. It is a miscellaneous science as it links heal ...
, clinical laboratory, hygiene and sanitation, emergency treatment
Emergency medicine is the medical speciality concerned with the care of illnesses or injuries requiring immediate medical attention. Emergency physicians (often called “ER doctors” in the United States) continuously learn to care for unsche ...
, first aid, and nursing. They were taught how to administer injections, treat compound fractures, administer blood plasma, and suture wounds.
The Maritime Service's Hospital Corps School was founded at the Sheepshead Bay Maritime Service Training Station on 7 December 1942. Surgeon S.S. Heilwell (R), United States Uniformed Public Health Service, was placed in charge of training. The course was taught over four months, with a 12-week period of didactic classroom experience and four weeks of practical experience at a Marine hospital. The original class of 331 students resulted in 239 graduates on 12 March 1943, but demand saw an increase in the class to 600 students, to cycle in 50 student classes starting on a weekly basis. Training stations were instructed to provide careful scrutiny by examining boards for all candidates. Pursers on sea duty started arriving at the station on 10 August 1943. By 1 January 1944, there were 600 purser-corpsmen at sea, with 1,324 graduates in the Maritime Service. Selection required an above average mark on the General Classification Test
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED ...
and interest in both administration and health care.''Mast Magazine
Mast, MAST or MASt may refer to:
Engineering
* Mast (sailing), a vertical spar on a sailing ship
* Flagmast, a pole for flying a flag
* Guyed mast, a structure supported by guy-wires
* Mooring mast, a structure for docking an airship
* Radio mast ...
'' May 1944, August 1944, May 1945
See also
* 68W (U.S. Army Combat Medic MOS code) * * Battlefield medicine * Combat medic * Combat Medical Technician (British Army) * Enlisted Medics (U.S. Air Force) * Fleet Marine Force * Fleet Marine Force insignia * Flight medic *Medical assistant
A medical assistant, also known as a "clinical assistant" or healthcare assistant in the USA is an allied health professional who supports the work of physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants and other health professionals, usually ...
* Medical Assistant (Royal Navy)
* Military medicine
* Medical Corps (United States Navy)
*Nurse Corps (United States Navy)
The United States Navy Nurse Corps was officially established by United States Congress, Congress in 1908; however, unofficially, women had been working as nurses aboard Navy ships and in Navy hospitals for nearly 100 years. The Corps was all-fem ...
* Navy Medical Service Corps
*Dental Corps (United States Navy)
The Dental Corps of the United States Navy consists of naval officers who have a doctorate in either dental surgery (DDS) or dental medicine (DMD) and who practice dentistry for Sailors and Marines to ensure optimal oral health.
The U.S. Navy ...
* Special Amphibious Reconnaissance Corpsman
* Special Warfare Combatant-craft Crewmen (SWCC)
*Pharmacist's Mate First Class Wheeler Bryson Lipes
In September 1942, Pharmacist's Mate Wheeler Lipes performed an emergency appendectomy aboard a United States Navy submarine. Although he did not have proper medical equipment or formal surgical training, the operation was a success. After the war, ...
References
Further reading
* Cowdrey, Albert E. ''Fighting for Life: American Military Medicine in World War II'' (1994), pp 51–72External links
Corpsman.com, A Site run by Corpsmen for Corpsmen
* {{US Navy navbox Navy, Hospital Corpsman Health care occupations United States Navy ratings