Hormones Of Adipose Tissue on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of
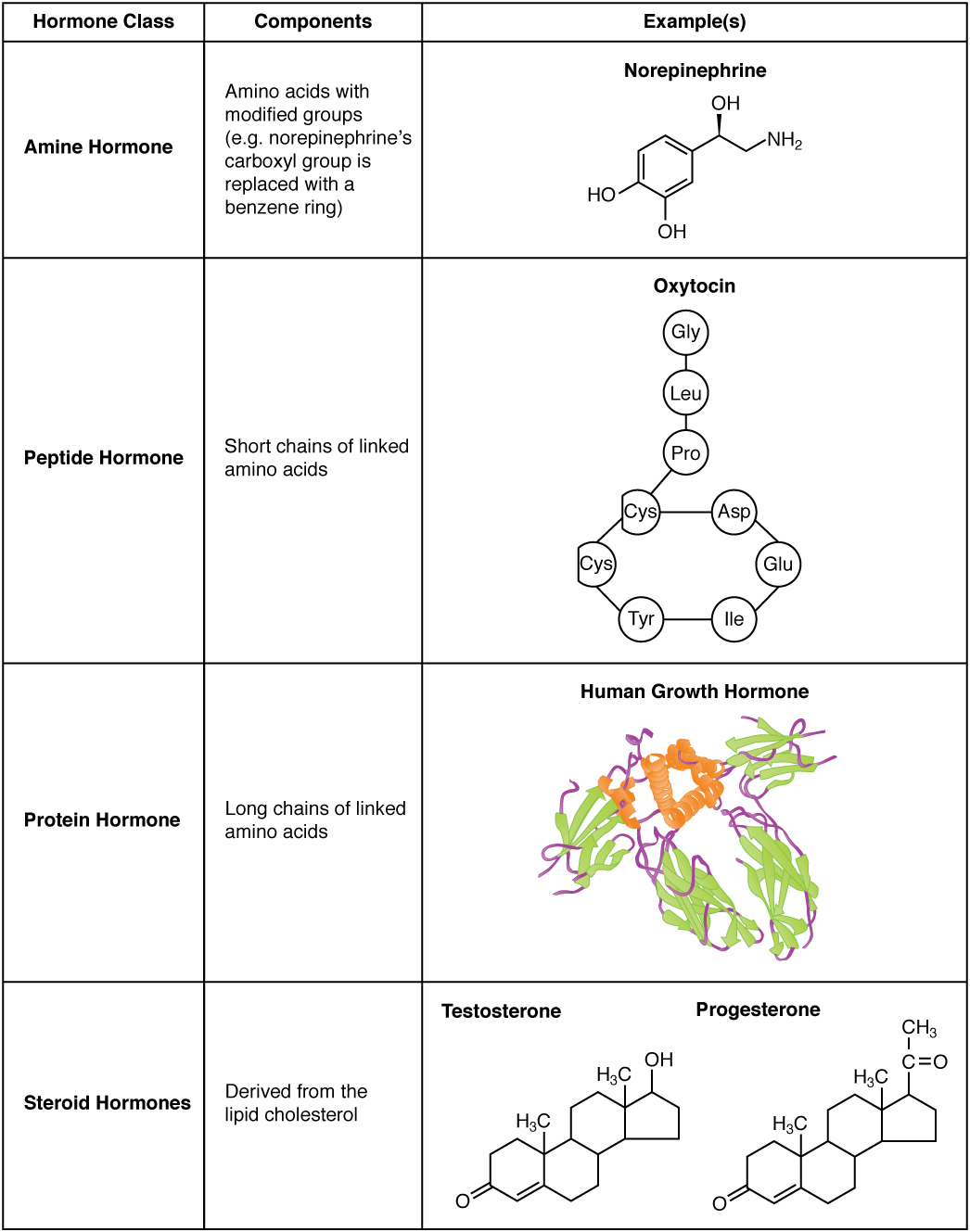
 Most hormones initiate a cellular response by initially binding to either cell membrane associated or intracellular
Most hormones initiate a cellular response by initially binding to either cell membrane associated or intracellular
 Hormone secretion can be stimulated and inhibited by:
* Other hormones (''stimulating''- or ''releasing'' -hormones)
* Plasma concentrations of ions or nutrients, as well as binding globulins
*
Hormone secretion can be stimulated and inhibited by:
* Other hormones (''stimulating''- or ''releasing'' -hormones)
* Plasma concentrations of ions or nutrients, as well as binding globulins
*
HMRbase: A database of hormones and their receptors
* {{Authority control * Physiology Endocrinology Cell signaling Signal transduction Human female endocrine system
 A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellula ...
in multicellular organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- ...
s that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
and behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as wel ...
. Hormones are required for the correct development of animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s, plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
s and fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandin
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derive ...
s and thromboxanes), steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
s (e.g. oestrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal activ ...
and brassinosteroid), amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
derivatives (e.g. epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and ...
and auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essenti ...
), protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
or peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A ...
s (e.g. insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
and CLE peptides), and gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
es (e.g. ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene i ...
and nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its che ...
).
Hormones are used to communicate between organs
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a fu ...
and tissues. In vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, ...
s, hormones are responsible for regulating a variety of physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
processes and behavioral
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as well ...
activities such as digestion, metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
, respiration, sensory perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system ...
, sleep
Sleep is a sedentary state of mind and body. It is characterized by altered consciousness, relatively inhibited sensory activity, reduced muscle activity and reduced interactions with surroundings. It is distinguished from wakefulness by a de ...
, excretion
Excretion is a process in which metabolic waste
is eliminated from an organism. In vertebrates this is primarily carried out by the lungs, kidneys, and skin. This is in contrast with secretion, where the substance may have specific tasks after lea ...
, lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The proces ...
, stress induction, growth and development, movement
Movement may refer to:
Common uses
* Movement (clockwork), the internal mechanism of a timepiece
* Motion, commonly referred to as movement
Arts, entertainment, and media
Literature
* "Movement" (short story), a short story by Nancy Fu ...
, reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual or ...
, and mood manipulation. In plants, hormones modulate almost all aspects of development, from germination
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, fer ...
to senescence
Senescence () or biological aging is the gradual deterioration of functional characteristics in living organisms. The word ''senescence'' can refer to either cellular senescence or to senescence of the whole organism. Organismal senescence inv ...
.
Hormones affect distant cells by binding to specific receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any structure which, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a ...
proteins in the target cell, resulting in a change in cell function. When a hormone binds to the receptor, it results in the activation of a signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
pathway that typically activates gene transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
, resulting in increased expression of target protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s. Hormones can also act in non-genomic pathways that synergize with genomic effects. Water-soluble hormones (such as peptides and amines) generally act on the surface of target cells via second messengers
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form or cell signaling, encompassing both first me ...
. Lipid soluble hormones, (such as steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
s) generally pass through the plasma membranes of target cells (both cytoplasmic
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. Th ...
and nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
* Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
) to act within their nuclei. Brassinosteroids, a type of polyhydroxysteroids, are a sixth class of plant hormones and may be useful as an anticancer drug for endocrine-responsive tumors to cause apoptosis and limit plant growth. Despite being lipid soluble, they nevertheless attach to their receptor at the cell surface.
In vertebrates, endocrine gland
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid ...
s are specialized organs that secrete 440px
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical ...
hormones into the endocrine signaling system. Hormone secretion occurs in response to specific biochemical signals and is often subject to negative feedback regulation. For instance, high blood sugar
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
(serum glucose concentration) promotes insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
synthesis. Insulin then acts to reduce glucose levels and maintain homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis) Help:IPA/English, (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physics, physical, and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. Thi ...
, leading to reduced insulin levels. Upon secretion, water-soluble hormones are readily transported through the circulatory system. Lipid-soluble hormones must bond to carrier plasma glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycos ...
s (e.g., thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG)) to form ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electr ...
-protein complexes. Some hormones, such as insulin and growth hormones, can be released into the bloodstream already fully active. Other hormones, called prohormones, must be activated in certain cells through a series of steps that are usually tightly controlled. The endocrine system
The endocrine system is a messenger system comprising feedback loops of the hormones released by internal glands of an organism directly into the circulatory system, regulating distant target organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neu ...
secrete 440px
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical ...
s hormones directly into the bloodstream, typically via fenestrated capillaries, whereas the exocrine system
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances on to an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of two ...
secretes its hormones indirectly using ducts. Hormones with paracrine Paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse ove ...
function diffuse through the interstitial space
An interstitial space or interstice is a space between structures or objects.
In particular, interstitial may refer to:
Biology
* Interstitial cell tumor
* Interstitial cell, any cell that lies between other cells
* Interstitial collagenase, ...
s to nearby target tissue.
Plants lack specialized organs for the secretion of hormones, although there is spatial distribution of hormone production. For example, the hormone auxin is produced mainly at the tips of young leaves
A leaf (plural, : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant plant stem, stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", wh ...
and in the shoot apical meristem. The lack of specialised glands means that the main site of hormone production can change throughout the life of a plant, and the site of production is dependent on the plant's age and environment.
Introduction and overview
Hormonal signaling involves the following steps: #Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. ...
of a particular hormone in a particular tissue.
# Storage and secretion 440px
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical ...
of the hormone.
# Transport of the hormone to the target cell(s).
# Recognition of the hormone by an associated cell membrane or intracellular receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any structure which, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a ...
protein.
# Relay and amplification of the received hormonal signal via a signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
process: This then leads to a cellular response. The reaction of the target cells may then be recognized by the original hormone-producing cells, leading to a downregulation
In the biological context of organisms' production of gene products, downregulation is the process by which a cell decreases the quantity of a cellular component, such as RNA or protein, in response to an external stimulus. The complementary proc ...
in hormone production. This is an example of a homeostatic
In biology, homeostasis (British also homoeostasis) (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physical, and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and i ...
negative feedback loop
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other ...
.
# Breakdown of the hormone.
Hormone producing cells are found in the endocrine glands
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid g ...
, such as the thyroid gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobe (anatomy), lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of Connective tissue, tissue cal ...
, ovaries
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. T ...
, and testes
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testoster ...
. Exocytosis
Exocytosis () is a form of active transport and bulk transport in which a cell transports molecules (e.g., neurotransmitters and proteins) out of the cell ('' exo-'' + ''cytosis''). As an active transport mechanism, exocytosis requires the use o ...
and other methods of membrane transport
In cellular biology, membrane transport refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such as ions and small molecules through biological membranes, which are lipid bilayers that contain proteins embedded in them. Th ...
are used to secrete hormones when the endocrine glands are signaled. The hierarchical model is an oversimplification
The fallacy of the single cause, also known as complex cause, causal oversimplification, causal reductionism, and reduction fallacy, is an informal fallacy of questionable cause that occurs when it is assumed that there is a single, simple cause of ...
of the hormonal signaling process. Cellular recipients of a particular hormonal signal may be one of several cell types that reside within a number of different tissues, as is the case for insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
, which triggers a diverse range of systemic physiological effects. Different tissue types may also respond differently to the same hormonal signal.
Discovery
Arnold Adolph Berthold (1849)
Arnold Adolph Berthold
Arnold Adolph Berthold (also Arnold Adolf Berthold) (26 February 1803, in Soest – 3 January 1861, in Göttingen) was a German scientist, most notably a physiologist and zoologist . He is best known in modern science for his pioneering experim ...
was a German physiologist
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical a ...
and zoologist
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the Animal, animal kingdom, including the anatomy, structure, embryology, evolution, Biological clas ...
, who, in 1849, had a question about the function of the testes
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testoster ...
. He noticed in castrated roosters that they did not have the same sexual behaviors as roosters with their testes intact. He decided to run an experiment on male roosters to examine this phenomenon. He kept a group of roosters with their testes intact, and saw that they had normal sized wattles and combs (secondary sexual organs
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female, a ...
), a normal crow, and normal sexual and aggressive behaviors. He also had a group with their testes surgically removed, and noticed that their secondary sexual organs were decreased in size, had a weak crow, did not have sexual attraction towards females, and were not aggressive. He realized that this organ was essential for these behaviors, but he did not know how. To test this further, he removed one testis and placed it in the abdominal cavity. The roosters acted and had normal physical anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its ...
. He was able to see that location of the testes does not matter. He then wanted to see if it was a genetic factor that was involved in the testes that provided these functions. He transplanted a testis from another rooster to a rooster with one testis removed, and saw that they had normal behavior and physical anatomy as well. Berthold determined that the location or genetic factors of the testes do not matter in relation to sexual organs and behaviors, but that some chemical in the testes being secreted is causing this phenomenon. It was later identified that this factor was the hormone testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondar ...
.
Charles and Francis Darwin (1880)
Although known primarily for his work on theTheory of Evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation t ...
, Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended fr ...
was also keenly interested in plants. Through the 1870s, he and his son Francis
Francis may refer to:
People
*Pope Francis, the head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State and Bishop of Rome
*Francis (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
*Francis (surname)
Places
* Rural M ...
studied the movement of plants towards light. They were able to show that light is perceived at the tip of a young stem (the coleoptile), whereas the bending occurs lower down the stem. They proposed that a 'transmissible substance' communicated the direction of light from the tip down to the stem. The idea of a 'transmissible substance' was initially dismissed by other plant biologists, but their work later led to the discovery of the first plant hormone. In the 1920s Dutch scientist Frits Warmolt Went and Russian scientist Nikolai Cholodny
Mykola Hryhorovych Kholodny ( ukr, Микола Григорович Холодний ; 22 June 1882 – 4 May 1953) was an influential microbiologist who worked at the University of Kyiv, Ukraine in the USSR during the 1930s.
He is known for the ...
(working independently of each other) conclusively showed that asymmetric accumulation of a growth hormone was responsible for this bending. In 1933 this hormone was finally isolated by Kögl, Haagen-Smit and Erxleben and given the name 'auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essenti ...
'.
Bayliss and Starling (1902)
William Bayliss
Sir William Maddock Bayliss (2 May 1860 – 27 August 1924) was an English physiologist.
Life
He was born in Wednesbury, Staffordshire but shortly thereafter his father, a successful merchant of ornamental ironwork, moved his family to a ...
and Ernest Starling
Ernest Henry Starling (17 April 1866 – 2 May 1927) was a British physiologist who contributed many fundamental ideas to this subject. These ideas were important parts of the British contribution to physiology, which at that time led the world. ...
, a physiologist
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical a ...
and biologist
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual Cell (biology), cell, a multicellular organism, or a Community (ecology), community of Biological inter ...
, respectively, wanted to see if the nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes th ...
had an impact on the digestive system
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller compone ...
. They knew that the pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an end ...
was involved in the secretion of digestive fluid
Gastric acid, gastric juice, or stomach acid is a digestive fluid formed within the stomach lining. With a pH between 1 and 3, gastric acid plays a key role in digestion of proteins by activating digestive enzymes, which together break down the ...
s after the passage of food from the stomach to the intestines, which they believed to be due to the nervous system. They cut the nerves to the pancreas in an animal model and discovered that it was not nerve impulses that controlled secretion from the pancreas. It was determined that a factor secreted from the intestines into the bloodstream was stimulating the pancreas to secrete digestive fluids. This factor was named secretin
Secretin is a hormone that regulates water homeostasis throughout the body and influences the environment of the duodenum by regulating secretions in the stomach, pancreas, and liver. It is a peptide hormone produced in the S cells of the duode ...
: a hormone, although the term hormone was not coined until 1905 by Starling.
Types of signaling
Hormonal effects are dependent on where they are released, as they can be released in different manners. Not all hormones are released from a cell and into the blood until it binds to a receptor on a target. The major types of hormone signaling are:Chemical classes
As hormones are defined functionally, not structurally, they may have diverse chemical structures. Hormones occur inmulticellular organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- ...
s (plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
s, animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s, fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
, brown algae, and red algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority ...
). These compounds occur also in unicellular organism
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and ...
s, and may act as signaling molecules however there is no agreement that these molecules can be called hormones.
Vertebrates

Invertebrates
Compared with vertebrates,insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs ...
s and crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group ...
s possess a number of structurally unusual hormones such as the juvenile hormone, a sesquiterpenoid.
Plants
Examples includeabscisic acid
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a plant hormone. ABA functions in many plant developmental processes, including seed and bud dormancy, the control of organ size and stomatal closure. It is especially important for plants in the response to environmental s ...
, auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essenti ...
, cytokinin
Cytokinins (CK) are a class of plant hormones that promote cell division, or cytokinesis, in plant roots and shoots. They are involved primarily in cell growth and differentiation, but also affect apical dominance, axillary bud growth, and lea ...
, ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene i ...
, and gibberellin.
Receptors
receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any structure which, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a ...
s. A cell may have several different receptor types that recognize the same hormone but activate different signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
pathways, or a cell may have several different receptors that recognize different hormones and activate the same biochemical pathway.
Receptors for most peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A ...
as well as many eicosanoid hormones are embedded in the plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
at the surface of the cell and the majority of these receptors belong to the G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related p ...
(GPCR) class of seven alpha helix
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid located four residues e ...
transmembrane
A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequentl ...
proteins. The interaction of hormone and receptor typically triggers a cascade of secondary effects within the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
of the cell, described as signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
, often involving phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, wh ...
or dephosphorylation of various other cytoplasmic proteins, changes in ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of io ...
permeability, or increased concentrations of intracellular molecules that may act as secondary messengers (e.g., cyclic AMP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal transd ...
). Some protein hormone
Peptide hormones or protein hormones are hormones whose molecules are peptide, or proteins, respectively. The latter have longer amino acid chain lengths than the former. These hormones have an effect on the endocrine system of animals, including h ...
s also interact with intracellular receptors located in the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
or nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
by an intracrine mechanism.
For steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
or thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thy ...
hormones, their receptors are located inside the cell within the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
of the target cell. These receptors belong to the nuclear receptor
In the field of molecular biology, nuclear receptors are a class of proteins responsible for sensing steroids, thyroid hormones, vitamins, and certain other molecules. These receptors work with other proteins to regulate the expression of speci ...
family of ligand-activated transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The fu ...
s. To bind their receptors, these hormones must first cross the cell membrane. They can do so because they are lipid-soluble. The combined hormone-receptor complex then moves across the nuclear membrane into the nucleus of the cell, where it binds to specific DNA sequences, regulating the expression of certain genes
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
, and thereby increasing the levels of the proteins encoded by these genes. However, it has been shown that not all steroid receptors are located inside the cell. Some are associated with the plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
.
Effects in humans
Hormones have the following effects on the body: * stimulation or inhibition of growth * wake-sleep cycle and othercircadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogeno ...
s
* mood swings
* induction or suppression of apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes incl ...
(programmed cell death)
* activation or inhibition of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
* regulation of metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
* preparation of the body for mating, fighting
Combat ( French for ''fight'') is a purposeful violent conflict meant to physically harm or kill the opposition. Combat may be armed (using weapons) or unarmed ( not using weapons). Combat is sometimes resorted to as a method of self-defense, or ...
, fleeing, and other activity
* preparation of the body for a new phase of life, such as puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy. ...
, parenting
Parenting or child rearing promotes and supports the physical, emotional, social, spiritual and intellectual development of a child from infancy to adulthood. Parenting refers to the intricacies of raising a child and not exclusively for a ...
, and menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often d ...
* control of the reproductive cycle
* hunger cravings
A hormone may also regulate the production and release of other hormones. Hormone signals control the internal environment of the body through homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis) Help:IPA/English, (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physics, physical, and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. Thi ...
.
Regulation
The rate of hormone biosynthesis and secretion is often regulated by ahomeostatic
In biology, homeostasis (British also homoeostasis) (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physical, and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and i ...
negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by ...
control mechanism. Such a mechanism depends on factors that influence the metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
and excretion
Excretion is a process in which metabolic waste
is eliminated from an organism. In vertebrates this is primarily carried out by the lungs, kidneys, and skin. This is in contrast with secretion, where the substance may have specific tasks after lea ...
of hormones. Thus, higher hormone concentration alone cannot trigger the negative feedback mechanism. Negative feedback must be triggered by overproduction of an "effect" of the hormone.
 Hormone secretion can be stimulated and inhibited by:
* Other hormones (''stimulating''- or ''releasing'' -hormones)
* Plasma concentrations of ions or nutrients, as well as binding globulins
*
Hormone secretion can be stimulated and inhibited by:
* Other hormones (''stimulating''- or ''releasing'' -hormones)
* Plasma concentrations of ions or nutrients, as well as binding globulins
* Neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. N ...
s and mental activity
* Environmental changes, e.g., of light or temperature
One special group of hormones is the tropic hormone
Tropic hormones are hormones that have other endocrine glands as their target. Most tropic hormones are produced and secreted by the anterior pituitary. The hypothalamus secretes tropic hormones that target the anterior pituitary, and the thyroid ...
s that stimulate the hormone production of other endocrine glands
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid g ...
. For example, thyroid-stimulating hormone
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (also known as thyrotropin, thyrotropic hormone, or abbreviated TSH) is a pituitary hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine (T4), and then triiodothyronine (T3) which stimulates the metabolism of ...
(TSH) causes growth and increased activity of another endocrine gland, the thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thy ...
, which increases output of thyroid hormone
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4
rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone
rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus
rect 66 216 386 25 ...
s.
To release active hormones quickly into the circulation, hormone biosynthetic cells may produce and store biologically inactive hormones in the form of pre- or prohormones. These can then be quickly converted into their active hormone form in response to a particular stimulus.
Eicosanoids are considered to act as local hormones. They are considered to be "local" because they possess specific effects on target cells close to their site of formation. They also have a rapid degradation cycle, making sure they do not reach distant sites within the body.
Hormones are also regulated by receptor agonists. Hormones are ligands, which are any kinds of molecules that produce a signal by binding to a receptor site on a protein. Hormone effects can be inhibited, thus regulated, by competing ligands that bind to the same target receptor as the hormone in question. When a competing ligand is bound to the receptor site, the hormone is unable to bind to that site and is unable to elicit a response from the target cell. These competing ligands are called antagonists of the hormone.
Therapeutic use
Many hormones and their structural and functional analogs are used asmedication
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and re ...
. The most commonly prescribed hormones are estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal acti ...
s and progestogen
Progestogens, also sometimes written progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the body. ...
s (as methods of hormonal contraception
Hormonal contraception refers to birth control methods that act on the endocrine system. Almost all methods are composed of steroid hormones, although in India one selective estrogen receptor modulator is marketed as a contraceptive. The origin ...
and as HRT), thyroxine (as levothyroxine
Levothyroxine, also known as -thyroxine, is a manufactured form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4). It is used to treat hypothyroidism, thyroid hormone deficiency (hypothyroidism), including a severe form known as myxedema coma. It may also ...
, for hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as po ...
) and steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
s (for autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly a ...
s and several respiratory disorders). Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
is used by many diabetics. Local preparations for use in otolaryngology often contain pharmacologic
Pharmacology is a branch of medicine, biology and pharmaceutical sciences concerned with drug or medication action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemic ...
equivalents of adrenaline, while steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
and vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (c ...
creams are used extensively in dermatological
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical ...
practice.
A "pharmacologic dose" or "supraphysiological dose" of a hormone is a medical usage referring to an amount of a hormone far greater than naturally occurs in a healthy body. The effects of pharmacologic doses of hormones may be different from responses to naturally occurring amounts and may be therapeutically useful, though not without potentially adverse side effects. An example is the ability of pharmacologic doses of glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebr ...
s to suppress inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
.
Hormone-behavior interactions
At the neurological level, behavior can be inferred based on hormone concentration, which in turn are influenced by hormone-release patterns; the numbers and locations of hormone receptors; and the efficiency of hormone receptors for those involved in gene transcription. Hormone concentration does not incite behavior, as that would undermine other external stimuli; however, it influences the system by increasing the probability of a certain event to occur. Not only can hormones influence behavior, but also behavior and the environment can influence hormone concentration. Thus, a feedback loop is formed, meaning behavior can affect hormone concentration, which in turn can affect behavior, which in turn can affect hormone concentration, and so on. For example, hormone-behavior feedback loops are essential in providing constancy to episodic hormone secretion, as the behaviors affected by episodically secreted hormones directly prevent the continuous release of said hormones. Three broad stages of reasoning may be used to determine if a specific hormone-behavior interaction is present within a system: * The frequency of occurrence of a hormonally dependent behavior should correspond to that of its hormonal source. * A hormonally dependent behavior is not expected if the hormonal source (or its types of action) is non-existent. * The reintroduction of a missing behaviorally dependent hormonal source (or its types of action) is expected to bring back the absent behavior.Comparison with neurotransmitters
There are various clear distinctions between hormones andneurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neuro ...
s:
* A hormone can perform functions over a larger spatial and temporal scale than can a neurotransmitter, which often acts in micrometer-scale distances.
* Hormonal signals can travel virtually anywhere in the circulatory system, whereas neural signals are restricted to pre-existing nerve tract
A nerve tract is a bundle of nerve fibers (axons) connecting nuclei of the central nervous system. In the peripheral nervous system this is known as a nerve, and has associated connective tissue. The main nerve tracts in the central nervous syste ...
s.
* Assuming the travel distance is equivalent, neural signals can be transmitted much more quickly (in the range of milliseconds) than can hormonal signals (in the range of seconds, minutes, or hours). Neural signals can be sent at speeds up to 100 meters per second.
* Neural signalling is an all-or-nothing (digital) action, whereas hormonal signalling is an action that can be continuously variable as it is dependent upon hormone concentration.
Neurohormones are a type of hormone that share a commonality with neurotransmitters. They are produced by endocrine cells that receive input from neurons, or neuroendocrine cells. Both classic hormones and neurohormones are secreted by endocrine tissue; however, neurohormones are the result of a combination between endocrine reflexes and neural reflexes, creating a neuroendocrine pathway. While endocrine pathways produce chemical signals in the form of hormones, the neuroendocrine pathway involves the electrical signals of neurons. In this pathway, the result of the electrical signal produced by a neuron is the release of a chemical, which is the neurohormone. Finally, like a classic hormone, the neurohormone is released into the bloodstream to reach its target.
Binding proteins
Hormone transport and the involvement of binding proteins is an essential aspect when considering the function of hormones. The formation of a complex with a binding protein has several benefits: the effective half-life of the bound hormone is increased, and a reservoir of bound hormones is created, which evens the variations in concentration of unbound hormones (bound hormones will replace the unbound hormones when these are eliminated). An example of the usage of hormone-binding proteins is in the thyroxine-binding protein which carries up to 80% of all thyroxine in the body, a crucial element in regulating the metabolic rate.See also
* Autocrine signaling *Adipokine
The adipokines, or adipocytokines (Greek ', fat; ', cell; and ', movement) are cytokines (cell signaling proteins) secreted by adipose tissue. Some contribute to an obesity-related low-grade state of inflammation or to the development of metabolic ...
* Cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
* Hepatokine
* Endocrine disease
* Endocrine system
The endocrine system is a messenger system comprising feedback loops of the hormones released by internal glands of an organism directly into the circulatory system, regulating distant target organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neu ...
* Endocrinology
Endocrinology (from '' endocrine'' + '' -ology'') is a branch of biology and medicine dealing with the endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions known as hormones. It is also concerned with the integration of developmental event ...
* Environmental hormones
Xenohormones or environmental hormones produced outside of the human body which exhibit endocrine hormone-like properties. They may be either of natural origin, such as phytoestrogens, which are derived from plants, or of synthetic origin. These co ...
* Growth factor
* Intracrine
* List of investigational sex-hormonal agents
* Metabolomics
* Myokine
* Neohormone
Neohormones are a group of recently evolved hormones primarily associated to the success of mammalian development. These hormones are specific to mammals and are not found in other vertebrates—this is because neohormones are evolved to enhance s ...
* Neuroendocrinology
* Paracrine signaling
* Plant hormone
Plant hormone (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, from embryogenesis, the regulation of organ size, pa ...
s, a.k.a. plant growth regulators
* Semiochemical
* Sex-hormonal agent
* Sexual motivation and hormones Sexual motivation is influenced by hormones such as testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, oxytocin, and vasopressin. In most mammalian species, sex hormones control the ability and motivation to engage in sexual behaviours.
Measuring sexual motiv ...
* Xenohormone
Xenohormones or environmental hormones produced outside of the human body which exhibit endocrine hormone-like properties. They may be either of natural origin, such as phytoestrogens, which are derived from plants, or of synthetic origin. These co ...
* List of human hormones
The following is a list of hormones found in ''Homo sapiens''. Spelling is not uniform for many hormones. For example, current North American and international usage uses estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsib ...
References
External links
HMRbase: A database of hormones and their receptors
* {{Authority control * Physiology Endocrinology Cell signaling Signal transduction Human female endocrine system