History of the Indo-Greek Kingdom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The History of the Indo-Greek Kingdom covers a period from the 2nd century BCE to the beginning of the 1st century CE in northern and northwestern 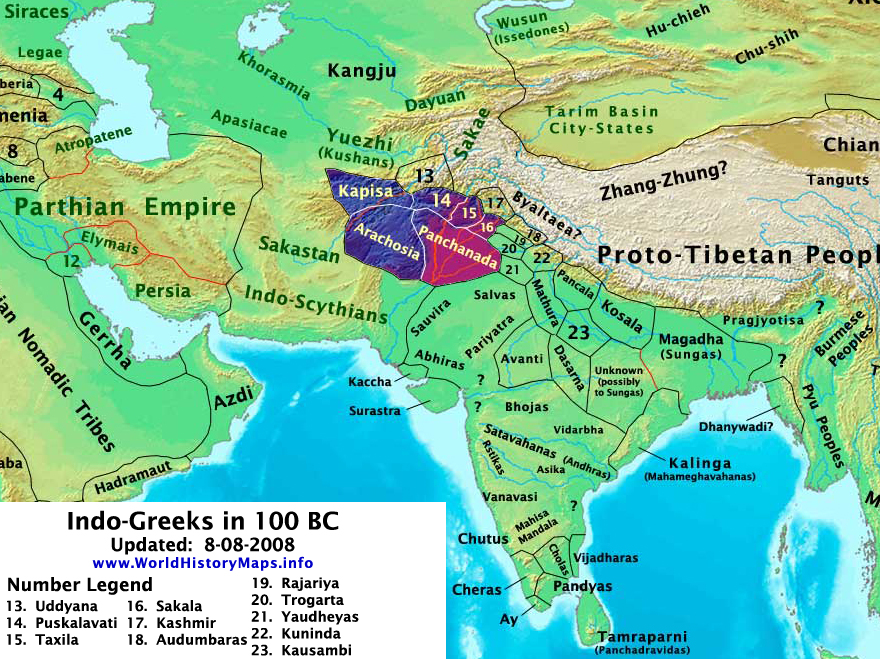
 Written evidence of the initial Greek invasion survives in the Greek writings of
Written evidence of the initial Greek invasion survives in the Greek writings of
 The 1st century BCE Greek historian
The 1st century BCE Greek historian  To the south, the Greeks occupied the areas of the
To the south, the Greeks occupied the areas of the
 Several Hellenistic artifacts have been found, in particular coins of Indo-Greek kings, stone palettes representing Greek mythological scenes, and small statuettes. Some of them are purely Hellenistic, others indicate an evolution of the
Several Hellenistic artifacts have been found, in particular coins of Indo-Greek kings, stone palettes representing Greek mythological scenes, and small statuettes. Some of them are purely Hellenistic, others indicate an evolution of the
 When the Indo-Greeks settled in the area of Taxila, large Buddhist structures were already present, such as the stupa of
When the Indo-Greeks settled in the area of Taxila, large Buddhist structures were already present, such as the stupa of
 There may also have been setbacks in the east. The
There may also have been setbacks in the east. The
 Menander is considered as probably the most successful Indo-Greek king, and the conqueror of the vastest territory. The finds of his coins are the most numerous and the most widespread of all the Indo-Greek kings. In Antiquity, from at least the 1st century CE, the "Menander Mons", or "Mountains of Menander", came to designate the mountain chain at the extreme east of the Indian subcontinent, today's Naga hills and
Menander is considered as probably the most successful Indo-Greek king, and the conqueror of the vastest territory. The finds of his coins are the most numerous and the most widespread of all the Indo-Greek kings. In Antiquity, from at least the 1st century CE, the "Menander Mons", or "Mountains of Menander", came to designate the mountain chain at the extreme east of the Indian subcontinent, today's Naga hills and

 The Indo-Greeks may have ruled as far as the area of
The Indo-Greeks may have ruled as far as the area of

 Around 80 BCE, an
Around 80 BCE, an
 The Parthians, represented by the Suren, a noble Parthian family of Arsacid descent, started to make inroads into the territories which had been occupied by the
The Parthians, represented by the Suren, a noble Parthian family of Arsacid descent, started to make inroads into the territories which had been occupied by the
 The Yuezhi expanded to the east during the 1st century CE, to found the
The Yuezhi expanded to the east during the 1st century CE, to found the
Coins
Demetrius was the first Indo-Greek king to gain territories in India. It is possible that he made his first conquests as general for his father, a view supported by the Heliodorus inscription. Territories of Paropamisadae, Gandhara
*
Territories of Paropamisadae, Gandhara
*
Coins
These two Bactrian kings, likely father and son, ruled between c. 190–175 BCE. Territories of Gandhara, western Punjab *
Coins
R.C Senior (2004) has suggested that this king was possibly identical with Antimachus I, but an Antimachus, who was the co-regent (and presumably son) of Antimachus I is known from a preserved tax-receipt. Territories of Gandhara, western and eastern Punjab *
Coins
Territories of Arachosia, Paropamisadae, Gandhara * Eucratides managed to eradicate the Euthydemid dynasty and occupy territory as far as he
Coin
* Philoxenus Territories of Arachosia, Paropamisadae, Gandhara, western and eastern Punjab *
Coins
and *
Coins
were the most important successors of Menander. They ruled most of the Indo-Greek kingdom, though perhaps as co-rulers, c. 130–110 BCE. * Philoxenus (c. 115–105 or 100–95 BCE
Coins
Philoxenus temporarily united the major kingdom with the smaller state in the Kabul valley. Territories of Arachosia and the Paropamisadae *
Coin
*
Coins
*
Coin
The territory of
Coins
*
Coins
*
Coins
The following minor kings ruled parts of the kingdom: * Polyxenos (c. 80 BCE - possibly in Gandhara) *
Coins
Territories of the Paropamisadae and Gandhara During the 1st century BCE, the Indo-Greeks progressively lost ground against the invasion of the
Coins
*
Coins
* Telephos (c. 65–60 BCE
Coins
Despite his Greek name, Artemidoros was the son of Maues and therefore formally a Scythian king, and the ethnicity of Telephus is unknown as well. Territories of Gandhara, western and eastern Punjab
*
Territories of Gandhara, western and eastern Punjab
*
Coins
Apollodotus II temporarily united most of the Indo-Greek kingdom, but after his death it fragmented again. Territories of Gandhara and western Punjab *
Coins
who was defeated by the
Coin
with Strato III, who was overthrown by * (
 *
* Senior, R. C, ''New Indo Greek Coins'', Journal of the Oriental Numismatic Society 186
* Senior, R. C. and MacDonald, D, ''The decline of the Indo-Greeks'', Monographs of the Hellenic Numismatic Society, Athens, 1998
* Senior, R. C., ''Indo-Greek–The Indo-Greek and Indo-Scythian King Sequences in the Second and First Centuries BC'', 2004, Supplement to Oriental Numismatic Society Newsletter, no. 179
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of The Indo-Greek Kingdom
Indo-Greeks
*
* Senior, R. C, ''New Indo Greek Coins'', Journal of the Oriental Numismatic Society 186
* Senior, R. C. and MacDonald, D, ''The decline of the Indo-Greeks'', Monographs of the Hellenic Numismatic Society, Athens, 1998
* Senior, R. C., ''Indo-Greek–The Indo-Greek and Indo-Scythian King Sequences in the Second and First Centuries BC'', 2004, Supplement to Oriental Numismatic Society Newsletter, no. 179
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of The Indo-Greek Kingdom
Indo-Greeks
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
. There were over 30 Indo-Greek
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern r ...
kings, often in competition on different territories. Many of them are only known through their coins.
Many of the dates, territories, and relationships between Indo-Greek kings are tentative and essentially based on numismatic
Numismatics is the study or collection of currency, including coins, tokens, paper money, medals and related objects.
Specialists, known as numismatists, are often characterized as students or collectors of coins, but the discipline also includ ...
analysis (find places, overstrikes, monograms, metallurgy, styles), a few Classical writings, and Indian writings and epigraphic evidence. The following list of kings, dates and territories after the reign of Demetrius is derived from the latest and most extensive analysis on the subject, by Osmund Bopearachchi
Osmund Bopearachchi (born 1949) is a Sri Lankan historian and numismatist who has specialized notably standardized the coinage of the Indo-Greek and Greco-Bactrian kingdoms. He is currently Emeritus Director of the CNRS at the École Normale Supé ...
and R. C. Senior.
The invasion of northern India, and the establishment of what would be known as the "Indo-Greek kingdom", started around 200 BCE when Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning “Demetris” - "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, Dimitri, Dimitrie, Dimitar, Dumit ...
, son of the Greco-Bactrian king Euthydemus I
Euthydemus I (Greek: , ''Euthydemos'') c. 260 BC – 200/195 BC) was a Greco-Bactrian king and founder of the Euthydemid dynasty. He is thought to have originally been a governor (Satrap) of Sogdia, who seized the throne by force from Diodotus II ...
, led his troops across the Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Provinc ...
. Apollodotus
Apollodotus I (Greek: ) Prakrit in the Kharoshti script: ''maharajasa apaladatasa tratarasa'') was an Indo-Greek king between 180 BC and 160 BC or between 174 and 165 BC (first dating Osmund Bopearachchi and R. C. Senior, second dating ...
, may have made advances in the south, while Menander
Menander (; grc-gre, Μένανδρος ''Menandros''; c. 342/41 – c. 290 BC) was a Greek dramatist and the best-known representative of Athenian New Comedy. He wrote 108 comedies and took the prize at the Lenaia festival eight times. His rec ...
, led later invasions further east. Following his conquests, Demetrius received the title ''ανικητος'' ("Anicetus", lit. ''invincible''), a title never given to any king before.

 Written evidence of the initial Greek invasion survives in the Greek writings of
Written evidence of the initial Greek invasion survives in the Greek writings of Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
and Justin
Justin may refer to: People
* Justin (name), including a list of persons with the given name Justin
* Justin (historian), a Latin historian who lived under the Roman Empire
* Justin I (c. 450–527), or ''Flavius Iustinius Augustus'', Eastern Rom ...
, and in Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
in the records of Patanjali
Patanjali ( sa, पतञ्जलि, Patañjali), also called Gonardiya or Gonikaputra, was a Hindu author, mystic and philosopher. Very little is known about him, and while no one knows exactly when he lived; from analysis of his works it i ...
, Kālidāsa
Kālidāsa (''fl.'' 4th–5th century CE) was a Classical Sanskrit author who is often considered ancient India's greatest poet and playwright. His plays and poetry are primarily based on the Vedas, the Rāmāyaṇa, the Mahābhārata and t ...
, and in the ''Yuga Purana
The ''Yuga Purana'' is a Sanskrit text and the last chapter of a ''Jyotisha'' (astrology) text '' Vriddhagargiya Samhita''. It is also considered a minor text in the Puranic literature.
Contents
The Yuga Purana is structured as a chronicle, and ...
'', among others. Coins and architectural evidence also attest to the extent of the initial Greek campaign.
Evidence of the initial invasion
Greco-Roman sources
The Greco-Bactrians went over theHindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Provinc ...
and also started to re-occupy the area of Arachosia
Arachosia () is the Hellenized name of an ancient satrapy situated in the eastern parts of the Achaemenid empire. It was centred around the valley of the Arghandab River in modern-day southern Afghanistan, and extended as far east as the In ...
, where Greek populations had been living since before the acquisition of the territory by Chandragupta from Seleucus. Isidore of Charax
Isidore of Charax (; grc, Ἰσίδωρος ὁ Χαρακηνός, ''Isídōros o Charakēnós''; la, Isidorus Characenus) was a Greco-Roman geographer of the 1st century BC and 1st century AD, a citizen of the Parthian Empire, about whom noth ...
describes Greek cities there, one of them called Demetrias, probably in honour of the conqueror Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning “Demetris” - "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, Dimitri, Dimitrie, Dimitar, Dumit ...
.
According to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
, Greek advances temporarily went as far as the Shunga capital Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at the ...
(today Patna
Patna (
), historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. ...
) in eastern India:
 The 1st century BCE Greek historian
The 1st century BCE Greek historian Apollodorus
Apollodorus (Ancient Greek, Greek: Ἀπολλόδωρος ''Apollodoros'') was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to: ...
, quoted by Strabo, affirms that the Bactrian Greeks, led by Demetrius I and Menander
Menander (; grc-gre, Μένανδρος ''Menandros''; c. 342/41 – c. 290 BC) was a Greek dramatist and the best-known representative of Athenian New Comedy. He wrote 108 comedies and took the prize at the Lenaia festival eight times. His rec ...
, conquered India and occupied a larger territory than the Greeks under Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
, going beyond the Hypanis towards the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ...
:
The Roman historian Justin
Justin may refer to: People
* Justin (name), including a list of persons with the given name Justin
* Justin (historian), a Latin historian who lived under the Roman Empire
* Justin I (c. 450–527), or ''Flavius Iustinius Augustus'', Eastern Rom ...
also mentioned the Indo-Greek kingdom, describing a "Demetrius, King of the Indians" ("''Regis Indorum''"), and explaining that after vanquishing him Eucratides in turn "put India under his rule" ("''Indiam in potestatem redegit''") (since the time of the embassies of Megasthenes
Megasthenes ( ; grc, Μεγασθένης, c. 350 BCE– c. 290 BCE) was an ancient Greek historian, diplomat and Indian ethnographer and explorer in the Hellenistic period. He described India in his book '' Indica'', which is now lost, but has ...
in the 3rd century BCE "India" was understood as the entire subcontinent, and was mapped by geographers such as Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; grc-gre, Ἐρατοσθένης ; – ) was a Greek polymath: a mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of Alexandria ...
). Justin also mentions Apollodotus and Menander as kings of the Indians.
Greek and Indian sources tend to indicate that the Greeks campaigned as far as Pataliputra until they were forced to retreat. This advance probably took place under the reign of Menander, the most important Indo-Greek king (A.K. Narain and Keay 2000) and was likely only of a military advance of temporary nature, perhaps in alliance with native Indian states. The permanent Indo-Greek dominions extended only from the Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
Valley to the eastern Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
or slightly further east.
Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
and Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
down to the region of Surat
Surat is a city in the western Indian state of Gujarat. The word Surat literally means ''face'' in Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of the river Tapti near its confluence with the Arabian Sea, it used to be a large seaport. It is now ...
(Greek: ''Saraostus
Saraostus also called Syrastrene(also ''Surastrene'', modern Saurashtra in India) was the name given by the Greeks to the area of Saurashtra and parts of south-western Gujarat.
:"The Greeks ... took possession, not only of Patalena, but also, ...
'') near Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second- ...
(Bombay), including the strategic harbour of Barigaza (Bharuch
Bharuch (), formerly known as Broach, is a city at the mouth of the river Narmada in Gujarat in western India. Bharuch is the administrative headquarters of Bharuch District.
The city of Bharuch and surroundings have been settled since tim ...
), as attested by several writers (Strabo 11; Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, Chap. 41/47) and as evidenced by coins dating from the Indo-Greek ruler Apollodotus I
Apollodotus I (Greek: ) Prakrit in the Kharoshti script: ''maharajasa apaladatasa tratarasa'') was an Indo-Greek king between 180 BC and 160 BC or between 174 and 165 BC (first dating Osmund Bopearachchi and R. C. Senior, second dating ...
:
The 1st century CE Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' ( grc, Περίπλους τῆς Ἐρυθρᾶς Θαλάσσης, ', modern Greek '), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and ...
describes numerous Greek buildings and fortifications in Barigaza
Bharuch (), formerly known as Broach, is a city at the mouth of the river Narmada in Gujarat in western India. Bharuch is the administrative headquarters of Bharuch District.
The city of Bharuch and surroundings have been settled since time ...
, although mistakenly attributing them to Alexander, and testifies to the circulation of Indo-Greek coinage in the region:
From ancient authors (Pliny, Arrian, Ptolemy and Strabo), a list of provinces, satrapies, or simple regional designations, and Greek cities from within the Indo-Greek Kingdom can be discerned (though others have been lost), ranging from the Indus basin to the upper valley of the Ganges.
Indian sources
Various Indian records describe ''Yavana
The word Yona in Pali and the Prakrits, and the analogue Yavana in Sanskrit and Yavanar in Tamil, were words used in Ancient India to designate Greek speakers. "Yona" and "Yavana" are transliterations of the Greek word for "Ionians" ( grc, � ...
'' attacks on Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. ...
, Panchala, Saketa, and Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at the ...
. The term ''Yavana'' is thought to be a transliteration of "Ionians" and is known to have designated Hellenistic Greeks (starting with the Edicts of Ashoka
The Edicts of Ashoka are a collection of more than thirty inscriptions on the Pillars of Ashoka, as well as boulders and cave walls, attributed to Emperor Ashoka of the Maurya Empire who reigned from 268 BCE to 232 BCE. Ashoka used the expres ...
, where Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, ...
writes about "the ''Yavana'' king Antiochus
Antiochus is a Greek male first name, which was a dynastic name for rulers of the Seleucid Empire and the Kingdom of Commagene.
In Jewish historical memory, connected with the Maccabean Revolt and the holiday of Hanukkah, "Antiochus" refers spec ...
"), but may have sometimes referred to other foreigners as well, especially in later centuries.
Patanjali
Patanjali ( sa, पतञ्जलि, Patañjali), also called Gonardiya or Gonikaputra, was a Hindu author, mystic and philosopher. Very little is known about him, and while no one knows exactly when he lived; from analysis of his works it i ...
, a grammarian and commentator on Pāṇini
, era = ;;6th–5th century BCE
, region = Indian philosophy
, main_interests = Grammar, linguistics
, notable_works = ' (Sanskrit#Classical Sanskrit, Classical Sanskrit)
, influenced=
, notable_ideas=Descript ...
around 150 BCE, describes in the '' Mahābhāsya'', the invasion in two examples using the imperfect tense of Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
, denoting a recent event:
* "''Arunad Yavanah Sāketam''" ("The Yavana
The word Yona in Pali and the Prakrits, and the analogue Yavana in Sanskrit and Yavanar in Tamil, were words used in Ancient India to designate Greek speakers. "Yona" and "Yavana" are transliterations of the Greek word for "Ionians" ( grc, � ...
s (Greeks) besieged Saketa")
* "''Arunad Yavano Madhyamikām''" ("The Yavanas were besieged Madhyamika" (the "Middle country")).
The '' Anushasanaparava'' of the Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the Kuruk ...
affirms that the country of Mathura, the heartland of India, was under the joint control of the Yavanas and the Kambojas
Kamboja ( sa, कम्बोज) was a kingdom of Iron Age India that spanned parts of South and Central Asia, frequently mentioned in Sanskrit and Pali literature. Eponymous with the kingdom name, the Kambojas were an Indo-Iranian people o ...
. The ''Vayupurana'' asserts that Mathura was ruled by seven Greek kings over a period of 82 years.
Accounts of battles between the Greeks and the Shunga in Central India are also found in the ''Mālavikāgnimitram
The ''Mālavikāgnimitram'' (Sanskrit, meaning ''Mālavikā and Agnimitra'') is a Sanskrit play by Kālidāsa. Based on some events of the reign of Pushyamitra Shunga, it is his first play.
''Mālavikāgnimitram'' tells the story of the love of A ...
'', a play by Kālidāsa
Kālidāsa (''fl.'' 4th–5th century CE) was a Classical Sanskrit author who is often considered ancient India's greatest poet and playwright. His plays and poetry are primarily based on the Vedas, the Rāmāyaṇa, the Mahābhārata and t ...
which describes an encounter between Greek forces and Vasumitra, the grandson of Pushyamitra
Pushyamitra Shunga (IAST: ) or Pushpamitra Shunga (IAST: ) (ruled ) was the co-founder and the first or second ruler of the Shunga Empire which he and Gopāla established against the Maurya Empire. His original name was Puṣpaka or Puṣpami ...
, during the latter's reign.
Also the Brahmanical text of the ''Yuga Purana
The ''Yuga Purana'' is a Sanskrit text and the last chapter of a ''Jyotisha'' (astrology) text '' Vriddhagargiya Samhita''. It is also considered a minor text in the Puranic literature.
Contents
The Yuga Purana is structured as a chronicle, and ...
'', which describes Indian historical events in the form of a prophecy, relates the attack of the Indo-Greeks on the capital Pataliputra, a magnificent fortified city with 570 towers and 64 gates according to Megasthenes
Megasthenes ( ; grc, Μεγασθένης, c. 350 BCE– c. 290 BCE) was an ancient Greek historian, diplomat and Indian ethnographer and explorer in the Hellenistic period. He described India in his book '' Indica'', which is now lost, but has ...
, and describes the ultimate destruction of the city's walls:
According to the Yuga Purana a situation of complete social disorder follows, in which the Yavanas rule and mingle with the people, and the position of the Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests (purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru ...
s and the Sudras is inverted:
Epigraphic remains
Several depictions of Greeks in Central India dated to the 2nd-1st century BCE are known, such as the Greek soldier inBharhut
Bharhut is a village located in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh, central India. It is known for its famous relics from a Buddhist stupa. What makes Bharhut panels unique is that each panel is explicitly labelled in Brahmi characters mentioni ...
, or a frieze in Sanchi
Sanchi is a Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometres from Raisen, Raisen town, dist ...
which describes Greek-looking foreigners honouring the Sanchi stupa with gifts, prayers and music (image above). They wear the chlamys
The chlamys (Ancient Greek: χλαμύς : chlamýs, genitive: χλαμύδος : chlamydos) was a type of an ancient Greek cloak.
cape over short chiton
Chitons () are marine molluscs of varying size in the class Polyplacophora (), formerly known as Amphineura. About 940 extant and 430 fossil species are recognized.
They are also sometimes known as gumboots or sea cradles or coat-of-mail s ...
tunic
A tunic is a garment for the body, usually simple in style, reaching from the shoulders to a length somewhere between the hips and the knees. The name derives from the Latin ''tunica'', the basic garment worn by both men and women in Ancient Rome ...
s without trousers, and have high-laced sandal
Sandals are an open type of footwear, consisting of a sole held to the wearer's foot by straps going over the instep and around the ankle. Sandals can also have a heel. While the distinction between sandals and other types of footwear can some ...
s. They are beardless with short curly hair and headbands, and two men wear the conical pilos
The pileus (, ; also or in Latin) was a brimless felt cap worn in Ancient Greece, Etruria, Illyria (Pannonia), later also introduced in Ancient Rome. The pileus also appears on Apulian red-figure pottery.
The pilos together with the petasos we ...
hat. They play various instruments, including two carnyx
The ancient carnyx was a wind instrument of the Iron Age Celts, used between c. 200 BC and c. AD 200. It was a type of bronze trumpet with an elongated S shape, held so that the long straight central portion was vertical and the short mouthpiec ...
es, and one aulos
An ''aulos'' ( grc, αὐλός, plural , ''auloi'') or ''tibia'' (Latin) was an ancient Greek wind instrument, depicted often in art and also attested by archaeology.
Though ''aulos'' is often translated as "flute" or "double flute", it was usu ...
double-flute. This is near Vidisa
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar in ancient times) is a city in central Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located 62.5 km northeast of the state capital, Bhopal. The name "Vidisha" is derived from th ...
, where an Indo-Greek monument, the Heliodorus pillar
The Heliodorus pillar is a stone column that was erected around 113 BCE in central India in Besnagar (near Vidisha, Madhya Pradesh). The pillar was called the ''Garuda-standard'' by Heliodorus, referring to the deity Garuda. The pillar is commonly ...
, is known.
A pillar discovered in Reh, in the Ganges valley
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
350 km south-east of Mathura mentions Menander:
Another inscription 17mk from Mathura, the Maghera inscription, contains the phrase "In the 116th year of the Greek kings...", suggesting Greek rule in the area until around 70 BCE, as the "Greek era" is thought to have started around 186 BCE.
Archaeological remains
Urban remains
The city ofSirkap
Sirkap (Urdu and pnb, ) is the name of an archaeological site on the bank opposite to the city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan.
The city of Sirkap was built by the Greco-Bactrian king Demetrius after he invaded modern-day Pakistan around 180 BC. ...
, today in northwestern Pakistan near Taxila
Taxila or Takshashila (; sa, तक्षशिला; pi, ; , ; , ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and ...
, was built according to the "Hippodamian
Hippodamus of Miletus (; Greek: Ἱππόδαμος ὁ Μιλήσιος, ''Hippodamos ho Milesios''; 498 – 408 BC) was an ancient Greek architect, urban planner, physician, mathematician, meteorologist and philosopher, who is considered to b ...
" grid-plan characteristic of Greek cities, and was a Hellenistic fortress of considerable proportions, with a 6,000 meter wall on the circumference, of a height of about 10 meters. The houses of the Indo-Greek level are "the best planned of all the six strata, and the rubble masonry of which its walls are built is also the most solid and compact". It is thought that the city was built by Demetrius.
Artifacts
Greco-Bactrian
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic-era Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world in Central Asia and the India ...
styles found at Ai-Khanoum
Ai-Khanoum (, meaning ''Lady Moon''; uz, Oyxonim) is the archaeological site of a Hellenistic city in Takhar Province, Afghanistan. The city, whose original name is unknown, was probably founded by an early ruler of the Seleucid Empire and s ...
towards more indianized styles.
For example, accessories such as Indian ankle bracelets can be found on some representations of Greek mythological figures such as Artemis
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Artemis (; grc-gre, Ἄρτεμις) is the goddess of the hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, nature, vegetation, childbirth, care of children, and chastity. She was heavily identified wit ...
.
The excavations of the Greek levels at Sirkap were however very limited and made in peripheral areas, out of respect for the more recent archeological strata (those of the Indo-Scythian
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centur ...
and especially Indo-Parthian
The Indo-Parthian Kingdom was a Parthian kingdom founded by Gondophares, and active from 19 CE to c. 226 CE. At their zenith, they ruled an area covering parts of eastern Iran, various parts of Afghanistan and the northwest regions of the Indian s ...
levels) and the remaining religious buildings, and due to the difficulty of excavating extensively to a depth of about 6 meters. The results, although interesting, are partial and cannot be considered as exhaustive. Beyond this, no extensive archaeological excavation of an Indo-Greek city has ever essentially been done.
Quantities of Hellenistic artifacts and ceramics can also be found throughout Northern India. Clay seals depicting Greek deities, and the depiction of an Indo-Greek king thought to be Demetrius were found at Benares
Varanasi (; ; also Banaras or Benares (; ), and Kashi.) is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.
*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic tr ...
.
Stupas
 When the Indo-Greeks settled in the area of Taxila, large Buddhist structures were already present, such as the stupa of
When the Indo-Greeks settled in the area of Taxila, large Buddhist structures were already present, such as the stupa of Dharmarajika
The Dharmarajika Stupa ( ur, ), also referred to as the Great Stupa of Taxila, is a Buddhist stupa near Taxila, Pakistan. It was built over the relics of the Buddha by Ashoka in the 3rd century BCE. The stupa, along with the large monastic ...
built by Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, ...
in the 3rd century BCE. These structures were reinforced in the following centuries, by building rings of smaller stupas and constructions around the original ones. Numerous coins of the Indo-Greek king Zoilos II
Zoilus II Soter ( grc, Ζωΐλος Σωτήρ, Zōïlos Sōtēr; epithet means "the Saviour") was an Indo-Greek king who ruled in eastern Punjab. Bopearachchi dates his reign to c. 55–35 BC, a date approximately supported by R. C. Senior. ...
were found under the foundation of a 1st-century BCE rectangular chapel near the Dharmarajika stupa.
Also, various Buddhist structures, such as the Butkara Stupa
The Butkara Stupa (Pashto: بت کړه سټوپا) is an important Buddhist stupa near Mingora, in the area of Swat, Pakistan. It may have been built by the Mauryan emperor Ashoka, but it is generally dated slightly later to the 2nd century BCE ...
in the area of Swat
In the United States, a SWAT team (special weapons and tactics, originally special weapons assault team) is a police tactical unit that uses specialized or military equipment and tactics. Although they were first created in the 1960s to ...
were enlarged and decorated with Hellenistic architectural elements in the 2nd century BCE, especially during the rule of Menander
Menander (; grc-gre, Μένανδρος ''Menandros''; c. 342/41 – c. 290 BC) was a Greek dramatist and the best-known representative of Athenian New Comedy. He wrote 108 comedies and took the prize at the Lenaia festival eight times. His rec ...
. Stupas were just round mounds when the Indo-Greeks settled in India, possibly with some top decorations, but soon they added various structural and decorative elements, such as reinforcement belts, niches, architectural decorations such as plinth
A pedestal (from French ''piédestal'', Italian ''piedistallo'' 'foot of a stall') or plinth is a support at the bottom of a statue, vase, column, or certain altars. Smaller pedestals, especially if round in shape, may be called socles. In c ...
es, torus
In geometry, a torus (plural tori, colloquially donut or doughnut) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space about an axis that is coplanar with the circle.
If the axis of revolution does not tou ...
es and cavetto
A cavetto is a concave moulding with a regular curved profile that is part of a circle, widely used in architecture as well as furniture, picture frames, metalwork and other decorative arts. In describing vessels and similar shapes in pottery, ...
s, plaster painted with decorative scrolls. The niches were probably designed to place statues or friezes, an indication of early Buddhist descriptive art during the time of the Indo-Greeks. Coins of Menander
Menander (; grc-gre, Μένανδρος ''Menandros''; c. 342/41 – c. 290 BC) was a Greek dramatist and the best-known representative of Athenian New Comedy. He wrote 108 comedies and took the prize at the Lenaia festival eight times. His rec ...
were found within these constructions dating them to around 150 BCE. By the end of Indo-Greek rule and during the Indo-Scythian
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centur ...
period (1st century BCE), stupas were highly decorated with colonnaded flights of stairs and Hellenistic scrolls of Acanthus leaves.
Consolidation
The end of the first conquests
Back in Bactria a king named Eucratides managed to topple the Euthydemid dynasty around 170 BCE and some years later made himself ruler of the westernmost Indian territories as well, thus weakening the Indo-Greek kingdom and putting a stop to their expansion. There may also have been setbacks in the east. The
There may also have been setbacks in the east. The Hathigumpha inscription
The Hathigumpha Inscription is a seventeen line inscription in Prakrit language incised in Brahmi script in a cavern called Hathigumpha in Udayagiri hills, near Bhubaneswar in Odisha, India. Dated between 2nd-century BCE and 1st-century CE, it ...
, written by the king of Kalinga Kalinga may refer to:
Geography, linguistics and/or ethnology
* Kalinga (historical region), a historical region of India
** Kalinga (Mahabharata), an apocryphal kingdom mentioned in classical Indian literature
** Kalinga script, an ancient writin ...
, Kharavela
Kharavela (also transliterated Khārabēḷa) was a monarch of Kalinga in present-day Odisha, India, who ruled during the second or first century BCE. The primary source for Kharavela is his rock-cut Hathigumpha inscription. The inscription is ...
, also describes the presence of the ''Yavana'' king whose name has been identified as "Demetrius" with his army in eastern India, apparently as far as the city of Rajagriha
Rajgir, meaning "The City of Kings," is a historic town in the district of Nalanda in Bihar, India. As the ancient seat and capital of the Haryanka dynasty, the Pradyota dynasty, the Brihadratha dynasty and the Mauryan Empire, as well as the d ...
about 70 km southeast of Pataliputra and one of the foremost Buddhist sacred cities, but claims that this Demetrius ultimately retreated to Mathura on hearing of Kharavela's military successes further south:
The interpretation has been challenged, and a presence this far east seems difficult to attest to Demetrius I, who issued no Indian coins whatsoever.
In any case, Eucratides seems to have occupied territory as far as the Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
, between c. 170 BCE and 150 BCE. His advances were ultimately checked by the Indo-Greek king Menander I
Menander I Soter ( grc, Μένανδρος Σωτήρ, Ménandros Sōtḗr, Menander the Saviour; pi, मिलिन्दो, Milinda), was a Greco-Bactrian and later Indo-Greek King (reigned c.165/155Bopearachchi (1998) and (1991), respectivel ...
who asserted himself in the Indian part of the empire, and began the last expansions eastwards.
Consolidation and rise of Menander I
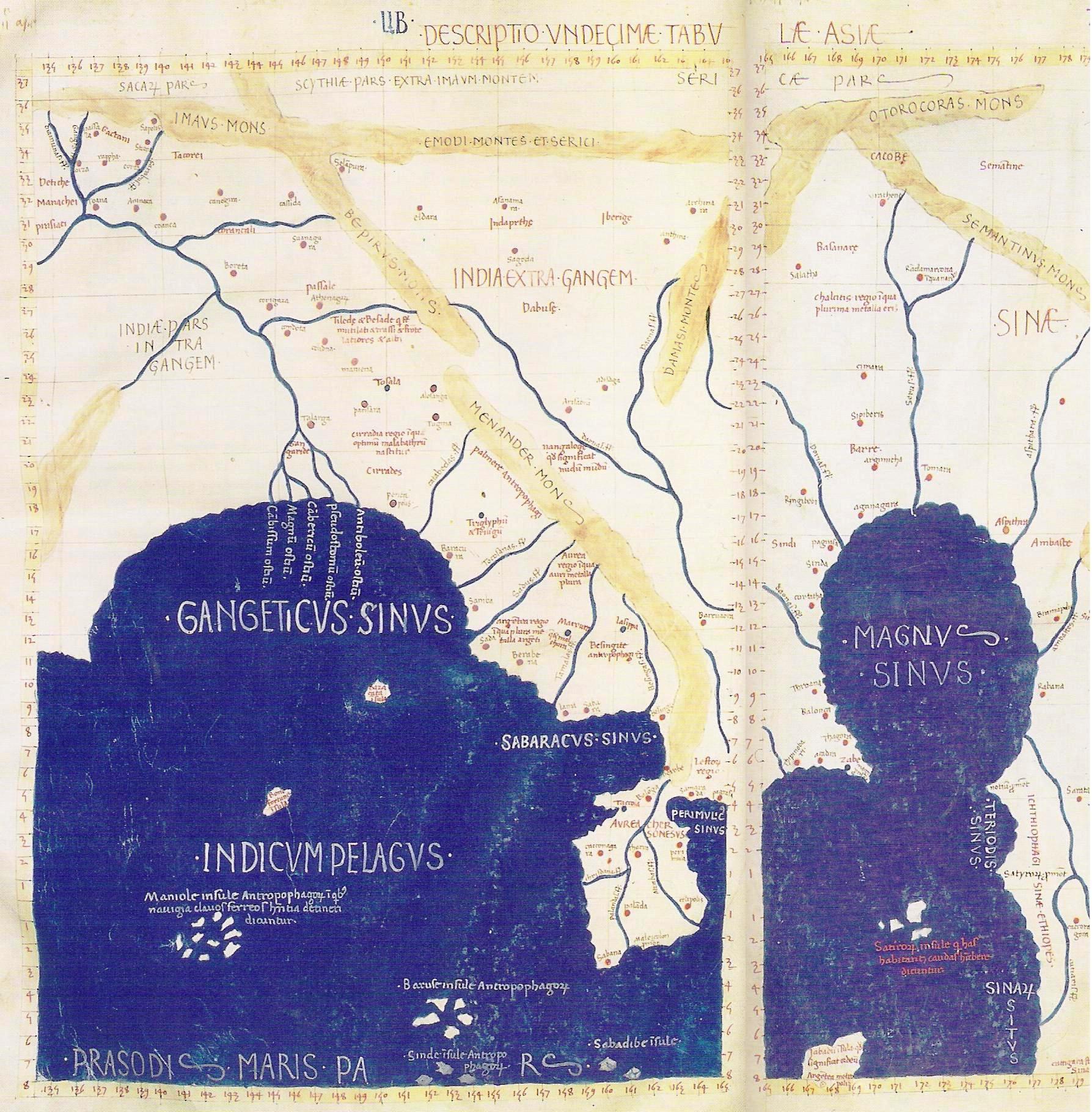
 Menander is considered as probably the most successful Indo-Greek king, and the conqueror of the vastest territory. The finds of his coins are the most numerous and the most widespread of all the Indo-Greek kings. In Antiquity, from at least the 1st century CE, the "Menander Mons", or "Mountains of Menander", came to designate the mountain chain at the extreme east of the Indian subcontinent, today's Naga hills and
Menander is considered as probably the most successful Indo-Greek king, and the conqueror of the vastest territory. The finds of his coins are the most numerous and the most widespread of all the Indo-Greek kings. In Antiquity, from at least the 1st century CE, the "Menander Mons", or "Mountains of Menander", came to designate the mountain chain at the extreme east of the Indian subcontinent, today's Naga hills and Arakan
Arakan ( or ) is a historic coastal region in Southeast Asia. Its borders faced the Bay of Bengal to its west, the Indian subcontinent to its north and Burma proper to its east. The Arakan Mountains isolated the region and made it accessi ...
, as indicated in Ptolemy's world map
The Ptolemy world map is a map of the world known to Greco-Roman societies in the 2nd century. It is based on the description contained in Ptolemy's book ''Geography'', written . Based on an inscription in several of the earliest surviving manusc ...
of the 1st century CE geographer Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
. Menander is also remembered in Buddhist literature, where he called Milinda, and is described in the Milinda Panha
The ''Milinda Pañha'' () is a Buddhist text which dates from sometime between 100 BC and 200 AD. It purports to record a dialogue between the Indian Buddhist sage Nāgasena, and the 2nd century BC Indo-Greek king Menander I (Pali: ''Milinda'') ...
as a convert to Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
: he became an arhat
In Buddhism, an ''arhat'' (Sanskrit: अर्हत्) or ''arahant'' (Pali: अरहन्त्, 𑀅𑀭𑀳𑀦𑁆𑀢𑁆) is one who has gained insight into the true nature of existence and has achieved ''Nirvana'' and liberated ...
whose relics were enshrined in a manner reminiscent of the Buddha. He also introduced numismatic reforms, such as issuing coins with portraits, which had hitherto been unknown in India. His most common coin reverse Athena
Athena or Athene, often given the epithet Pallas, is an ancient Greek goddess associated with wisdom, warfare, and handicraft who was later syncretized with the Roman goddess Minerva. Athena was regarded as the patron and protectress of ...
Alkidemos ("Protector of the people") became a common type for his successors in the East.
Conquests east of the Punjab region
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
were most likely made during the second half of the century by the king Menander I
Menander I Soter ( grc, Μένανδρος Σωτήρ, Ménandros Sōtḗr, Menander the Saviour; pi, मिलिन्दो, Milinda), was a Greco-Bactrian and later Indo-Greek King (reigned c.165/155Bopearachchi (1998) and (1991), respectivel ...
, but his eastern conquests were brief. The following passage may allude to the return of Menander to his home territories, perhaps due to a civil war with the competing king Zoilos I
Zoilus I Dicaeus ( grc, Ζωΐλος Δίκαιος, Zōïlos Dikaios; epithet means "the Just") was an Indo-Greek king who ruled in Afghanistan and Pakistan and occupied the areas of the Paropamisade and Arachosia previously held by Menander I ...
, or the nomad invasion of Bactria:
Following Menander's reign, about twenty Indo-Greek kings are known to have ruled in succession in the eastern parts of the Indo-Greek territory. Upon his death, Menander was succeeded by his infant son Thraso
Thraso (Greek: ), latinized as Thrason, was an Indo-Greek king in Central and Western Punjab, unknown until the 1982 discovery of one of his coins by R. C. Senior in the Surana hoard. The coin is in a style similar to those of Menander I, has the s ...
, but he was apparently murdered and further civil wars ensued. Judging from their coins, many of the later kings claimed descendance from either the Euthydemids or Menander, but the details remain uncertain due to the lack of sources.
The fall of Bactria
From 130 BCE, theScythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved f ...
and then the Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat ...
, following a long migration from the border of China, started to invade Bactria from the north. Around 125 BCE, the Greco-Bactrian king Heliocles
Heliocles I ( grc, Ἡλιοκλῆς, Helioklēs; reigned 145–120 BCE) was a Greco-Bactrian king, brother and successor of Eucratides the Great, and considered (along with his co-ruler and son/nephew Heliocles II) the last Greek king to reig ...
, was probably killed during the invasion and the Greco-Bactrian kingdom proper ceased to exist. The Indo-Greek kingdom, now entirely isolated from the Hellenistic world, did nevertheless maintain itself, if we can judge from the vast number of coins issued from the following kings, such as Lysias
Lysias (; el, Λυσίας; c. 445 – c. 380 BC) was a logographer (speech writer) in Ancient Greece. He was one of the ten Attic orators included in the "Alexandrian Canon" compiled by Aristophanes of Byzantium and Aristarchus of Samothrace i ...
and Antialcidas
Antialcidas Nikephoros ( grc, Ἀντιαλκίδας ὁ Νικηφόρος; epithet means "the Victorious", Brahmi: 𑀅𑀁𑀢𑀮𑀺𑀓𑀺𑀢𑀲 ''Aṃtalikitasa'', in the Heliodorus Pillar) was a king of the Indo-Greek Kingdom, who re ...
.
During this time, the Indo-Greek territory seems to have extended from the Paropamisadae
Paropamisadae or Parapamisadae (Greek: Παροπαμισάδαι) was a satrapy of the Alexandrian Empire in modern Afghanistan and Pakistan, which largely coincided with the Achaemenid province of Parupraesanna. It consisted of the districts o ...
and Arachosia
Arachosia () is the Hellenized name of an ancient satrapy situated in the eastern parts of the Achaemenid empire. It was centred around the valley of the Arghandab River in modern-day southern Afghanistan, and extended as far east as the In ...
in the west, to eastern Punjab, perhaps even with further eastern strongholds such as Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. ...
(see below). It is uncertain when the coastal provinces along the mouth of the Indus and further east were lost, or how tightly they were ever integrated with the kingdom.
Later history
Throughout the 1st century BCE, the Indo-Greeks progressively lost ground to the Indians in the east, and theScythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
s, the Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat ...
, and the Parthians Parthian may be:
Historical
* A demonym "of Parthia", a region of north-eastern of Greater Iran
* Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD)
* Parthian language, a now-extinct Middle Iranian language
* Parthian shot, an archery skill famously employed by ...
in the West. About 20 Indo-Greek king are known during this period, down to the last known Indo-Greek king Strato II
Strato II Soter ( grc, Στράτων B΄ ὁ Σωτήρ, ''Strátōn B΄ ho Sotḗr''; epithet means "the Saviour") also known as Stratha, was an Indo-Greek king. He ruled c. 25 BCE to 10 CE according to Bopearachchi. R. C. Senior suggests ...
, who ruled in the Punjab region
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
until around 10 CE.
Loss of Mathura and eastern territories (after 100 BCE)

Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. ...
until sometime in the 1st century BCE: the Maghera inscription, from a village near Mathura, records the dedication of a well "in the one hundred and sixteenth year of the reign of the Yavanas", which could be as late as 70 BCE. Soon however Indian kings recovered the area of Mathura and south-eastern Punjab, west of the Yamuna River
The Yamuna ( Hindustani: ), also spelt Jumna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Ban ...
, and started to mint their own coins. The Arjunayana
Arjunayana, Arjunavana, Arjunavayana or Arjunayanaka was an ancient republican people located in Punjab or north-eastern Rajasthan. They emerged as a political power during the Shunga period (). In the Allahabad Pillar Inscription of Samudragupta ...
s (area of Mathura) and Yaudheya
Yaudheya (Brahmi script: 𑀬𑁅𑀥𑁂𑀬) or Yoddheya Gana (Yoddheya Republic) was an ancient militant confederation. The word Yaudheya is a derivative of the word from yodha meaning warriors.“Yaudheyas.” Ancient Communities of the Himal ...
s mention military victories on their coins ("Victory of the Arjunayanas", "Victory of the Yaudheyas"). During the 1st century BCE, the Trigartas, Audumbaras
The Audumbras, or Audumbaras (Hindi;ओदुम्बर) were a north Indian tribal nation east of the Punjab region, Punjab, in the Western Himalaya region. They were the most important tribe of the Himachal Pradesh, Himachal, and lived in the ...
and finally the Kuninda
The Kingdom of Kuninda (or Kulinda in ancient literature) was an ancient central Himalayan kingdom documented from around the 2nd century BCE to the 3rd century, located in the southern areas of modern Himachal Pradesh and far western areas of U ...
s (closest to Punjab) also started to mint their own coins, usually in a style highly reminiscent of Indo-Greek coinage.
The Western king Philoxenus briefly occupied most of the remaining Greek territory from the Paropamisadae to Western Punjab c. 100 BCE, after which the territories fragmented again. The following decades saw fierce internal fighting between several kings, such as Heliokles II
Heliocles II Dicaeus (Greek: ; epithet means "the just") is thought to have been one of the later Indo-Greek kings and a relative of the Bactrian king Heliocles I. Current scholarly consensus is that he ruled ca 95–80 BCE.
Heliocles II seem ...
, Strato I
Straton or Strato may refer to:
* Strato I, Indo-Greek king
* Strato II, Indo-Greek king
* Strato of Lampsacus (c. 335 – c. 269 BC), Greek philosopher
* Straton of Sardis, Greek poet and anthologist
* Abdashtart I (Straton I, 365–352 BC), kin ...
and Hermaeus
Hermaeus Soter or Hermaios Soter ( grc, Ἑρμαῖος ὁ Σωτήρ; epithet means "the Saviour") was a Western Indo-Greek king of the Eucratid Dynasty, who ruled the territory of Paropamisade in the Hindu-Kush region, with his capital in Alex ...
, which contributed to the downfall in a manner perhaps reminiscent of how the Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
and Ptolemaic Ptolemaic is the adjective formed from the name Ptolemy, and may refer to:
Pertaining to the Ptolemaic dynasty
* Ptolemaic dynasty, the Macedonian Greek dynasty that ruled Egypt founded in 305 BC by Ptolemy I Soter
* Ptolemaic Kingdom
Pertaining ...
states were torn apart by dynastic wars at the same period.
The Yuezhi expansion (70 BCE–)
Philoxenus was succeeded byDiomedes
Diomedes (Jones, Daniel; Roach, Peter, James Hartman and Jane Setter, eds. ''Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary''. 17th edition. Cambridge UP, 2006.) or Diomede (; grc-gre, Διομήδης, Diomēdēs, "god-like cunning" or "advised by ...
, probably his son or younger brother, in the west, but his reign was short and he was succeeded by
Hermaeus
Hermaeus Soter or Hermaios Soter ( grc, Ἑρμαῖος ὁ Σωτήρ; epithet means "the Saviour") was a Western Indo-Greek king of the Eucratid Dynasty, who ruled the territory of Paropamisade in the Hindu-Kush region, with his capital in Alex ...
, a king married to the princess Calliope who was likely a daughter of Philoxenus. After a reign of at least one decade, Hermaeus was overthrown by nomad tribes, either the Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat ...
or Sakas When Hermaeus is depicted on his coins riding a horse, he is equipped with the recurve bow
In archery, a recurve bow is one of the main shapes a bow can take, with limbs that curve away from the archer when unstrung. A recurve bow stores more energy and delivers energy more efficiently than the equivalent straight-limbed bow, giving a ...
and bow-case of the steppes.
In any case, these nomads became the new rulers of the Paropamisadae, and minted vast quantities of posthumous issues of Hermaeus
Hermaeus Soter or Hermaios Soter ( grc, Ἑρμαῖος ὁ Σωτήρ; epithet means "the Saviour") was a Western Indo-Greek king of the Eucratid Dynasty, who ruled the territory of Paropamisade in the Hindu-Kush region, with his capital in Alex ...
up to around 40 CE, when they blend with the coinage of the Kushan
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, i ...
king Kujula Kadphises
Kujula Kadphises (Kushan language: Κοζουλου Καδφιζου, also Κοζολα Καδαφες; Kharosthi: 𐨐𐨂𐨗𐨂𐨫 𐨐𐨯, IAST: ', '; Ancient Chinese: 丘就卻, ''Qiujiuque''; reigned 30–80 CE, or 40-90 CE according to ...
. The first documented Yuezhi prince, Sapalbizes, ruled around 20 BCE, and minted in Greek and in the same style as the western Indo-Greek kings, probably depending on Greek mints and .
Scythian invasions (80 BCE – 50 CE)

 Around 80 BCE, an
Around 80 BCE, an Indo-Scythian
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centur ...
king named Maues
Maues (Greek: ; (epigraphic); Kharosthi: , , called , on the Taxila copper plate; also called , in the Mathura lion capital inscription,) was the first Indo-Scythian king, ruling from 98/85 to 60/57 BCE. He invaded India and establishe ...
, possibly an ally of some of the Indo-Greeks kings, captured Taxila and ruled Gandhara for a few years. The king he dethroned was probably Archebius
Archebius Dikaios Nikephoros (Greek: ; epithets mean respectively, "the Just", "the Victorious"; formerly read as "Archelius") was an Indo-Greek king who ruled in the area of Taxila. Osmund Bopearachchi dates him to c. 90–80 BCE, and R. C. ...
. After Maues' death, the Indo-Greeks were able to regain control of Taxila, but at this time the line between Greeks and Sakas may not have been that clear. Among the kings who emerged in Gandhara after Maues' death, Artemidoros
Artemidoros Aniketos (Greek: ; epithet means "the Invincible") was a king who ruled in the area of Gandhara and Pushkalavati in modern northern Pakistan and Afghanistan.
A son of Maues?
Artemidoros has a Greek name and has traditionally been ...
who was seemingly a regular Indo-Greek king, presents himself as "son of Maues" on a bronze. This discovery caused a small sensation and has led scholars such as Senior to assume that also Hermaeus may have been of partly Saka origin.
Another important king during this period was Amyntas, who issued the last Attic coins found in Bactria and may have attempted to reunite the Indo-Greek territories. It was however the king Apollodotus II
Apollodotus II (Greek: ) was an Indo-Greek king who ruled in the western and eastern parts of Punjab. Bopearachchi dates him to c. 80–65 BC, and R. C. Senior to c. 85–65 BC. Apollodotos II was an important ruler who seems to have re-establis ...
, seemingly a descendant of Menander, who managed to regain Gandhara from remaining Greek strongholds in eastern Punjab. After the death of Apollodotus II the kingdom fragmented once more.
In the west, he was succeeded by Hippostratos
Hippostratus ( grc, Ἱππόστρατος, Hippostratos) was an Indo-Greek king who ruled central and north-western Punjab and Pushkalavati. Bopearachchi dates Hippostratus to 65 to 55 BCE whereas R. C. Senior suggests 60 to 50 BCE.
Rule
In B ...
who was initially a successful ruler, but he was the last western ruler: around 55–50 BCE he was defeated by the Indo-Scythian Azes I
Azes I (Greek: , epigraphically ; Kharosthi: , ) was an Indo-Scythian ruler who ruled around c. 48/47 BCE – 25 BCE with a dynastic empire based in the Punjab and Indus Valley, completed the domination of the Scythians in the northwestern In ...
, who established his own Indo-Scythian dynasty.
Although the Indo-Scythians clearly ruled militarily and politically, they remained respectful of Greek and Indian cultures. Their coins were minted in Greek mints, continued using Greek and Kharoshthi scripts, and incorporated depictions of Greek deities, particularly Zeus. The Mathura lion capital
The Mathura lion capital is an Indo-Scythian sandstone capital (a part of a pillar) from Mathura in Northern India, dated to the first decade of the 1st century CE (1–10 CE). It was consecrated under the rule of Rajuvula, one of the Norther ...
inscription attests that they adopted the Buddhist faith, as do the depictions of deities forming the vitarka mudra on their coins. Greek communities, far from being exterminated, probably persisted under Indo-Scythian rule. The Buner reliefs show Indo-Greeks and Indo-Scythians reveling in a Buddhist context.
The last eastern kingdom (50 BCE – 10 CE)
The Indo-Greeks continued to maintain themselves in the eastern Punjab for several decades, until the kingdom of the last Indo-Greek kingStrato II
Strato II Soter ( grc, Στράτων B΄ ὁ Σωτήρ, ''Strátōn B΄ ho Sotḗr''; epithet means "the Saviour") also known as Stratha, was an Indo-Greek king. He ruled c. 25 BCE to 10 CE according to Bopearachchi. R. C. Senior suggests ...
was taken over by the Indo-Scythian ruler Rajuvula
Rajuvula (Greek alphabet, Greek ; Brahmi script, Brahmi: , ; Kharosthi: , ; , ; , ) was an Indo-Scythian Great Satrap (''Mahākṣatrapa''), one of the "Northern Satraps" who ruled in the area of Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, Mathura in the northe ...
around 10 CE. The coins of these Indo-Greek rulers deteriorated constantly, both in terms of artistic quality (due to the long isolation) and in silver content. Still, the last Strato had the honour of ruling the last pocket of an independent Hellenistic state; when he disappeared, Cleopatra
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a ...
, usually seen as the last of the rulers who followed Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
, was already gone.
Indo-Parthian rule (10–60 CE)
Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centur ...
and the Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat ...
, until the demise of the last Indo-Scythian emperor Azes II
Azes II (Greek: , epigraphically ; Kharosthi: , ), may have been the last Indo-Scythian king, speculated to have reigned circa 35–12 BCE, in the northern Indian subcontinent (modern day Pakistan). His existence has been questioned; if he did ...
around 12 BCE. The Parthians ended up controlling all of Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
and extensive territories in Northern India, after fighting many local rulers such as the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, i ...
ruler Kujula Kadphises
Kujula Kadphises (Kushan language: Κοζουλου Καδφιζου, also Κοζολα Καδαφες; Kharosthi: 𐨐𐨂𐨗𐨂𐨫 𐨐𐨯, IAST: ', '; Ancient Chinese: 丘就卻, ''Qiujiuque''; reigned 30–80 CE, or 40-90 CE according to ...
, in the Gandhara
Gandhāra is the name of an ancient region located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, more precisely in present-day north-west Pakistan and parts of south-east Afghanistan. The region centered around the Peshawar Vall ...
region. Around 20, Gondophares
Gondophares I (Greek: Γονδοφαρης ''Gondopharēs'', Υνδοφερρης ''Hyndopherrēs''; Kharosthi: 𐨒𐨂𐨡𐨥𐨪 ', '; 𐨒𐨂𐨡𐨥𐨪𐨿𐨣 ', '; 𐨒𐨂𐨡𐨂𐨵𐨪 ', ') was the founder of the Indo-Parthian K ...
, one of the Parthian conquerors, declared his independence from the Parthian empire and established the Indo-Parthian kingdom
The Indo-Parthian Kingdom was a Parthian kingdom founded by Gondophares, and active from 19 CE to c. 226 CE. At their zenith, they ruled an area covering parts of eastern Iran, various parts of Afghanistan and the northwest regions of the Indian ...
in the conquered territories, with his capital in ancient Taxila.
Kushan supremacy
Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, i ...
. The first Kushan emperor Kujula Kadphises
Kujula Kadphises (Kushan language: Κοζουλου Καδφιζου, also Κοζολα Καδαφες; Kharosthi: 𐨐𐨂𐨗𐨂𐨫 𐨐𐨯, IAST: ', '; Ancient Chinese: 丘就卻, ''Qiujiuque''; reigned 30–80 CE, or 40-90 CE according to ...
ostensibly associated himself with Hermaeus
Hermaeus Soter or Hermaios Soter ( grc, Ἑρμαῖος ὁ Σωτήρ; epithet means "the Saviour") was a Western Indo-Greek king of the Eucratid Dynasty, who ruled the territory of Paropamisade in the Hindu-Kush region, with his capital in Alex ...
on his coins, suggesting that he may have been one of his descendants by alliance, or at least wanted to claim his legacy. The Yuezhi (future Kushan
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, i ...
s) were in many ways the cultural and political heirs to the Indo-Greeks, as suggested by their adoption of the Greek culture (writing system, Greco-Buddhist art
The Greco-Buddhist art or Gandhara art of the north Indian subcontinent is the artistic manifestation of Greco-Buddhism, a cultural syncretism between Ancient Greek art and Buddhism. It had mainly evolved in the ancient region of Gandhara.
The s ...
) and their claim to a lineage with the last western Indo-Greek king Hermaeus.
The last known mention of an Indo-Greek ruler is suggested by an inscription on a signet ring of the 1st century CE in the name of a king Theodamas
Theodamas ( ''fl.'' 1st century) seems to have been an Indo-Greek ruler in the Bajaur area of Gandhara, in modern Pakistan.
No coins of him are known, but he has left a signet bearing his name in kharoshthi script, which was found in the region o ...
, from the Bajaur
Bajaur District ( ps, باجوړ ولسوالۍ, ur, ) is a district in Malakand Division of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province in Pakistan. Until 2018, it was an agency of the Federally Administered Tribal Areas, then during restructuring that merged ...
area of Gandhara
Gandhāra is the name of an ancient region located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, more precisely in present-day north-west Pakistan and parts of south-east Afghanistan. The region centered around the Peshawar Vall ...
, in modern Pakistan. No coins of him are known, but the signet bears in kharoshthi
The Kharoṣṭhī script, also spelled Kharoshthi (Kharosthi: ), was an ancient Indo-Iranian script used by various Aryan peoples in north-western regions of the Indian subcontinent, more precisely around present-day northern Pakistan and ...
script the inscription ''"Su Theodamasa"'', ''"Su"'' being explained as the Greek transliteration of the ubiquitous Kushan
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, i ...
royal title ''"Shau"'' ("Shah
Shah (; fa, شاه, , ) is a royal title that was historically used by the leading figures of Iranian monarchies.Yarshater, EhsaPersia or Iran, Persian or Farsi, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII no. 1 (1989) It was also used by a variety of ...
", "King").
The Indo-Greek rulers
"Indo-Greek" kings are distinguished from "Bactrian" kings in that they issued dominantly bilingual coinage, meant for circulation outside the Hindu Kush. However, Demetrius I is usually included (though he issued no such coins) and some mainly Bactrian kings who also held Indian territories. The chronology is tentative, as are the territories. This overview largely gives the chronology of Senior (2004) while most of the territories are adapted from Bopearachchi (1991). The views of both authors, as well as other alternatives, are given under each king.The Bactrian period (c. 200–130 BCE)
Territories of Arachosia, Paropamisadae, Gandhara?Euthydemus I
Euthydemus I (Greek: , ''Euthydemos'') c. 260 BC – 200/195 BC) was a Greco-Bactrian king and founder of the Euthydemid dynasty. He is thought to have originally been a governor (Satrap) of Sogdia, who seized the throne by force from Diodotus II ...
and Demetrius I (c. 200–175 BCECoins
Demetrius was the first Indo-Greek king to gain territories in India. It is possible that he made his first conquests as general for his father, a view supported by the Heliodorus inscription.
 Territories of Paropamisadae, Gandhara
*
Territories of Paropamisadae, Gandhara
* Pantaleon
Pantaleon, also known as Panteleimon, (Greek: ) was a Greek king who reigned some time between 190–180 BC in Bactria and India. He was a younger contemporary or successor of the Greco-Bactrian king Demetrius, and is sometimes believed to hav ...
* Agathocles Agathocles (Greek: ) is a Greek name, the most famous of which is Agathocles of Syracuse, the tyrant of Syracuse. The name is derived from , ''agathos'', i.e. "good" and , ''kleos'', i.e. "glory".
Other personalities named Agathocles:
*Agathocles, ...
''Coins
These two Bactrian kings, likely father and son, ruled between c. 190–175 BCE. Territories of Gandhara, western Punjab *
Apollodotus I
Apollodotus I (Greek: ) Prakrit in the Kharoshti script: ''maharajasa apaladatasa tratarasa'') was an Indo-Greek king between 180 BC and 160 BC or between 174 and 165 BC (first dating Osmund Bopearachchi and R. C. Senior, second dating ...
(c. 180–160 BCE)
* Antimachus II
Antimachus II Nikephoros (Greek: ; the epithet means "the Victorious") was an Indo-Greek king. He ruled a vast territory from the Hindu-Kush to the Punjab around 170 BCE. He was almost certainly the eponymous son of Antimachus I, who is known from ...
(c. 174–165 BCE or 160–155 BCE)Coins
R.C Senior (2004) has suggested that this king was possibly identical with Antimachus I, but an Antimachus, who was the co-regent (and presumably son) of Antimachus I is known from a preserved tax-receipt. Territories of Gandhara, western and eastern Punjab *
Menander I
Menander I Soter ( grc, Μένανδρος Σωτήρ, Ménandros Sōtḗr, Menander the Saviour; pi, मिलिन्दो, Milinda), was a Greco-Bactrian and later Indo-Greek King (reigned c.165/155Bopearachchi (1998) and (1991), respectivel ...
(reigned c. 165/155 – 135/130 BCE), though with some interruption in the western territories. Legendary for the size of his kingdom, and his support of the Buddhist faithCoins
Territories of Arachosia, Paropamisadae, Gandhara * Eucratides managed to eradicate the Euthydemid dynasty and occupy territory as far as he
Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
, between c. 160–145 BCE. Eucratides was then murdered by his son, thereafter Menander I
Menander I Soter ( grc, Μένανδρος Σωτήρ, Ménandros Sōtḗr, Menander the Saviour; pi, मिलिन्दो, Milinda), was a Greco-Bactrian and later Indo-Greek King (reigned c.165/155Bopearachchi (1998) and (1991), respectivel ...
seems to have regained all of the territory as far west as the Hindu-Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Province ...
.
* Zoilos I
Zoilus I Dicaeus ( grc, Ζωΐλος Δίκαιος, Zōïlos Dikaios; epithet means "the Just") was an Indo-Greek king who ruled in Afghanistan and Pakistan and occupied the areas of the Paropamisade and Arachosia previously held by Menander I ...
This king may have fought against Menander I around 150–140 BCE.
* ( Demetrius III possibly c. 150 BCE). This ephemeral ruler was possibly identical with the Demetrius, king of the Indians, who fought with Eucratides.Jakobsson, J. Relations between the Indo-Greek kings after Menander I, part 1, Journal of the Oriental Numismatic Society 191, 2007
Civil wars and nomad invasions (c. 130 BCE – 50 CE)
Territories of Gandhara or western Punjab A smaller kingdom seems to have emerged in the Kabul valley, between c. 130–115/110 BCE. *Thrason
Thraso (Greek: ), latinized as Thrason, was an Indo-Greek king in Central and Western Punjab, unknown until the 1982 discovery of one of his coins by R. C. Senior in the Surana hoard. The coin is in a style similar to those of Menander I, has the s ...
Son of Menander, ruled very briefly c. 130 BCE.
* Nicias
Nicias (; Νικίας ''Nikias''; c. 470–413 BC) was an Athenian politician and general during the period of the Peloponnesian War. Nicias was a member of the Athenian aristocracy and had inherited a large fortune from his father, which was inve ...
* Theophilos''Coin
* Philoxenus Territories of Arachosia, Paropamisadae, Gandhara, western and eastern Punjab *
Lysias
Lysias (; el, Λυσίας; c. 445 – c. 380 BC) was a logographer (speech writer) in Ancient Greece. He was one of the ten Attic orators included in the "Alexandrian Canon" compiled by Aristophanes of Byzantium and Aristarchus of Samothrace i ...
''Coins
and *
Antialcidas
Antialcidas Nikephoros ( grc, Ἀντιαλκίδας ὁ Νικηφόρος; epithet means "the Victorious", Brahmi: 𑀅𑀁𑀢𑀮𑀺𑀓𑀺𑀢𑀲 ''Aṃtalikitasa'', in the Heliodorus Pillar) was a king of the Indo-Greek Kingdom, who re ...
''Coins
were the most important successors of Menander. They ruled most of the Indo-Greek kingdom, though perhaps as co-rulers, c. 130–110 BCE. * Philoxenus (c. 115–105 or 100–95 BCE
Coins
Philoxenus temporarily united the major kingdom with the smaller state in the Kabul valley. Territories of Arachosia and the Paropamisadae *
Diomedes
Diomedes (Jones, Daniel; Roach, Peter, James Hartman and Jane Setter, eds. ''Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary''. 17th edition. Cambridge UP, 2006.) or Diomede (; grc-gre, Διομήδης, Diomēdēs, "god-like cunning" or "advised by ...
(c. 105–95 BCECoin
*
Hermaeus
Hermaeus Soter or Hermaios Soter ( grc, Ἑρμαῖος ὁ Σωτήρ; epithet means "the Saviour") was a Western Indo-Greek king of the Eucratid Dynasty, who ruled the territory of Paropamisade in the Hindu-Kush region, with his capital in Alex ...
(reigned c. 95–80 BCE).
* ( Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat ...
or Saka
The Saka ( Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who hist ...
rulers)
Territories of Gandhara, western and eastern Punjab
A number of kings fought for hegemony during the period after Philoxenus' death to the advent of Maues.
* Agathokleia (c. 110–105 BCE), Probably widow of another king, she was presumably regent for her son Strato I
Straton or Strato may refer to:
* Strato I, Indo-Greek king
* Strato II, Indo-Greek king
* Strato of Lampsacus (c. 335 – c. 269 BC), Greek philosopher
* Straton of Sardis, Greek poet and anthologist
* Abdashtart I (Straton I, 365–352 BC), kin ...
Coins
*
Strato I
Straton or Strato may refer to:
* Strato I, Indo-Greek king
* Strato II, Indo-Greek king
* Strato of Lampsacus (c. 335 – c. 269 BC), Greek philosopher
* Straton of Sardis, Greek poet and anthologist
* Abdashtart I (Straton I, 365–352 BC), kin ...
(c. 110–85 BCECoin
The territory of
Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. ...
and eastern Punjab may have been lost after Strato's death.
* Heliokles II
Heliocles II Dicaeus (Greek: ; epithet means "the just") is thought to have been one of the later Indo-Greek kings and a relative of the Bactrian king Heliocles I. Current scholarly consensus is that he ruled ca 95–80 BCE.
Heliocles II seem ...
(c. 95–80 BCECoins
*
Archebios
Archebius Dikaios Nikephoros (Greek: ; epithets mean respectively, "the Just", "the Victorious"; formerly read as "Archelius") was an Indo-Greek king who ruled in the area of Taxila. Osmund Bopearachchi dates him to c. 90–80 BCE, and R. C. Se ...
(c. 90–80 BCECoins
*
Amyntas Nikator
Amyntas Nicator ( grc, Ἀμύντας Νικάτωρ, Amyntas Nikatōr; epithet means "the Conqueror") was an Indo-Greek king. His coins have been found both in eastern Punjab and Afghanistan, indicating that he ruled a considerable territory. ...
(c. 80–65 BCECoins
The following minor kings ruled parts of the kingdom: * Polyxenos (c. 80 BCE - possibly in Gandhara) *
Peukolaos
Peucolaus Soter Dicaeus ( grc, Πευκόλαος Σωτήρ Δίκαιος, Peukolaos Sōtēr Dikaios; epithets mean respectively, "the Saviour", "the Just") was an Indo-Greek king who ruled in the area of Gandhara c. 90 BCE. His reign was proba ...
(c. 90 BCE)
* Demetrius III Aniketos (possibly c. 75 BCE)
* Epander
Epander (Greek: ) was one of the Indo-Greek kings. He may have been a relative of Menander I, and the findplaces of his coins seem to indicate that he ruled in the area of Punjab.
Time of reign
Bopearachchi dates Epander to c. 95–90 BC and R. ...
(c. 95–90 BCECoins
Territories of the Paropamisadae and Gandhara During the 1st century BCE, the Indo-Greeks progressively lost ground against the invasion of the
Indo-Scythian
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centur ...
s. After the invasion of (Maues
Maues (Greek: ; (epigraphic); Kharosthi: , , called , on the Taxila copper plate; also called , in the Mathura lion capital inscription,) was the first Indo-Scythian king, ruling from 98/85 to 60/57 BCE. He invaded India and establishe ...
), the following kings maintained themselves in the Paropamisadae or Gandhara:
* Menander II
Menander II Dikaios (Greek: ; epithet means "the Just") may have been an Indo-Greek King who ruled in the areas of Arachosia and Gandhara in the north of modern Pakistan. However, since he is entirely known through his coins, this may have just ...
(c. 70–65 BCECoins
*
Artemidoros
Artemidoros Aniketos (Greek: ; epithet means "the Invincible") was a king who ruled in the area of Gandhara and Pushkalavati in modern northern Pakistan and Afghanistan.
A son of Maues?
Artemidoros has a Greek name and has traditionally been ...
(c. 75–65 BCECoins
* Telephos (c. 65–60 BCE
Coins
Despite his Greek name, Artemidoros was the son of Maues and therefore formally a Scythian king, and the ethnicity of Telephus is unknown as well.
 Territories of Gandhara, western and eastern Punjab
*
Territories of Gandhara, western and eastern Punjab
* Apollodotus II
Apollodotus II (Greek: ) was an Indo-Greek king who ruled in the western and eastern parts of Punjab. Bopearachchi dates him to c. 80–65 BC, and R. C. Senior to c. 85–65 BC. Apollodotos II was an important ruler who seems to have re-establis ...
(c. 65–55 BCECoins
Apollodotus II temporarily united most of the Indo-Greek kingdom, but after his death it fragmented again. Territories of Gandhara and western Punjab *
Hippostratos
Hippostratus ( grc, Ἱππόστρατος, Hippostratos) was an Indo-Greek king who ruled central and north-western Punjab and Pushkalavati. Bopearachchi dates Hippostratus to 65 to 55 BCE whereas R. C. Senior suggests 60 to 50 BCE.
Rule
In B ...
(c. 60–50 BCCoins
who was defeated by the
Indo-Scythian
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centur ...
King Azes I
Azes I (Greek: , epigraphically ; Kharosthi: , ) was an Indo-Scythian ruler who ruled around c. 48/47 BCE – 25 BCE with a dynastic empire based in the Punjab and Indus Valley, completed the domination of the Scythians in the northwestern In ...
.
* (Azes I
Azes I (Greek: , epigraphically ; Kharosthi: , ) was an Indo-Scythian ruler who ruled around c. 48/47 BCE – 25 BCE with a dynastic empire based in the Punjab and Indus Valley, completed the domination of the Scythians in the northwestern In ...
). Indo-Scythian
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centur ...
king.
Last eastern kingdom
Territories of eastern Punjab The last Indo-Greek kings ruled in eastern Punjab from around 55 BCE – 10 CE *Dionysios
The name Dionysius (; el, Διονύσιος ''Dionysios'', "of Dionysus"; la, Dionysius) was common in classical and post-classical times. Etymologically it is a nominalized adjective formed with a -ios suffix from the stem Dionys- of the name ...
* Zoilos II
Zoilus II Soter ( grc, Ζωΐλος Σωτήρ, Zōïlos Sōtēr; epithet means "the Saviour") was an Indo-Greek king who ruled in eastern Punjab. Bopearachchi dates his reign to c. 55–35 BC, a date approximately supported by R. C. Senior. ...
* Apollophanes
Apollophanes Soter (Greek: ; epithet means "the Saviour"; reigned c. 35 – 25 BCE) was an Indo-Greek king in the area of eastern and central Punjab in modern India and Pakistan.
Rule
Little is known about him, except for some of his remaining ...
* Strato II
Strato II Soter ( grc, Στράτων B΄ ὁ Σωτήρ, ''Strátōn B΄ ho Sotḗr''; epithet means "the Saviour") also known as Stratha, was an Indo-Greek king. He ruled c. 25 BCE to 10 CE according to Bopearachchi. R. C. Senior suggests ...
'Coin
with Strato III, who was overthrown by * (
Rajuvula
Rajuvula (Greek alphabet, Greek ; Brahmi script, Brahmi: , ; Kharosthi: , ; , ; , ) was an Indo-Scythian Great Satrap (''Mahākṣatrapa''), one of the "Northern Satraps" who ruled in the area of Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, Mathura in the northe ...
), Indo-Scythian
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centur ...
king.
Indo-Greek princelets (Gandhara)
After theIndo-Scythian
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centur ...
Kings became the rulers of northern India, remaining Greek communities were probably governed by lesser Greek rulers, without the right of coinage, into the 1st century CE, in the areas of the Paropamisadae and Gandhara:
* Theodamas
Theodamas ( ''fl.'' 1st century) seems to have been an Indo-Greek ruler in the Bajaur area of Gandhara, in modern Pakistan.
No coins of him are known, but he has left a signet bearing his name in kharoshthi script, which was found in the region o ...
(c. 1st century CE) Indo-Greek ruler of the Bajaur area, northern Gandhara.
The Indo-Greeks may have kept a significant military role towards the 2nd century CE as suggested by the inscriptions of the Satavahana
The Satavahanas (''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan region. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the late ...
kings.
References
Sources
* *
* Senior, R. C, ''New Indo Greek Coins'', Journal of the Oriental Numismatic Society 186
* Senior, R. C. and MacDonald, D, ''The decline of the Indo-Greeks'', Monographs of the Hellenic Numismatic Society, Athens, 1998
* Senior, R. C., ''Indo-Greek–The Indo-Greek and Indo-Scythian King Sequences in the Second and First Centuries BC'', 2004, Supplement to Oriental Numismatic Society Newsletter, no. 179
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of The Indo-Greek Kingdom
Indo-Greeks
*
* Senior, R. C, ''New Indo Greek Coins'', Journal of the Oriental Numismatic Society 186
* Senior, R. C. and MacDonald, D, ''The decline of the Indo-Greeks'', Monographs of the Hellenic Numismatic Society, Athens, 1998
* Senior, R. C., ''Indo-Greek–The Indo-Greek and Indo-Scythian King Sequences in the Second and First Centuries BC'', 2004, Supplement to Oriental Numismatic Society Newsletter, no. 179
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of The Indo-Greek Kingdom
Indo-Greeks