The
history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
of
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
dates to contact the
pre-Roman peoples of the
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
coast of the
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
made with the
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, Albania, Greeks in Italy, ...
and
Phoenicians
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their hist ...
and the first writing systems known as
Paleohispanic scripts were developed. During
Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations ...
, the peninsula was the site of multiple successive colonizations of Greeks, Carthaginians, and Romans. Native peoples of the peninsula, such as the
Tartessos people, intermingled with the colonizers to create a uniquely Iberian culture. The Romans referred to the entire Peninsula as
Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: His ...
, from where the modern name of Spain originates. The region was divided up, at various times, into different Roman provinces. As was the rest of the
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
, Spain was subject to the numerous invasions of
Germanic tribes during the 4th and 5th centuries CE, resulting in the loss of Roman rule and the establishment of Germanic kingdoms, most notably the
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
and the
Suebi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own name ...
, marking the beginning of the
Middle Ages in Spain.
Various Germanic kingdoms were established on the Iberian peninsula in the early 5th century CE in the wake of the fall of Roman control; germanic control lasted about 200 years until the
Umayyad conquest of Hispania
The Umayyad conquest of Hispania, also known as the Umayyad conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom, was the initial expansion of the Umayyad Caliphate over Hispania (in the Iberian Peninsula) from 711 to 718. The conquest resulted in the decline of t ...
began in 711 and marked the introduction of
Islam to the Iberian Peninsula. The region became known as
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the Mus ...
, and excepting for the small
Kingdom of Asturias
The Kingdom of Asturias ( la, Asturum Regnum; ast, Reinu d'Asturies) was a kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula founded by the Visigothic nobleman Pelagius. It was the first Christian political entity established after the Umayyad conquest of V ...
, a Christian
rump state in the north of Iberia, the region remained under the control of Muslim-lead states for much of the
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the M ...
, a period known as the
Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
. By the time of the
High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD ...
, Christians from the north gradually expanded their control over Iberia, a period known as the
Reconquista
The ' ( Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the Na ...
. As they expanded southward, a number of Christian kingdoms were formed, including the
Kingdom of Navarre
The Kingdom of Navarre (; , , , ), originally the Kingdom of Pamplona (), was a Basque kingdom that occupied lands on both sides of the western Pyrenees, alongside the Atlantic Ocean between present-day Spain and France.
The medieval state took ...
(a Basque kingdom centered on the city of
Pamplona), the
Kingdom of León (in the northwest, originally an offshoot of, and later supplanting, the Kingdom of Asturias), the
Kingdom of Castile
The Kingdom of Castile (; es, Reino de Castilla, la, Regnum Castellae) was a large and powerful state on the Iberian Peninsula during the Middle Ages. Its name comes from the host of castles constructed in the region. It began in the 9th centu ...
(in central Iberia), and the
Kingdom of Aragon
The Kingdom of Aragon ( an, Reino d'Aragón, ca, Regne d'Aragó, la, Regnum Aragoniae, es, Reino de Aragón) was a medieval and early modern kingdom on the Iberian Peninsula, corresponding to the modern-day autonomous community
eu, a ...
(in
Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
and surrounding areas of Eastern Iberia). The history of these kingdoms and other are intertwined and they eventually consolidated into two roughly equivalent polities, the
Crown of Castile and the
Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon ( , ) an, Corona d'Aragón ; ca, Corona d'Aragó, , , ; es, Corona de Aragón ; la, Corona Aragonum . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of ...
, roughly occupying the central and eastern thirds of the Iberian Peninsula respectively. During this period, the southwestern portion of the Peninsula developed into the
Kingdom of Portugal
The Kingdom of Portugal ( la, Regnum Portugalliae, pt, Reino de Portugal) was a monarchy in the western Iberian Peninsula and the predecessor of the modern Portuguese Republic. Existing to various extents between 1139 and 1910, it was also kn ...
, and developed its own distinct national identity separate from that of Spain.
The
early modern period is generally dated from the union of the Crowns of Castile and Aragon under the
Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being bo ...
,
Isabella I of Castile
Isabella I ( es, Isabel I; 22 April 1451 – 26 November 1504), also called Isabella the Catholic (Spanish: ''la Católica''), was Queen of Castile from 1474 until her death in 1504, as well as Queen consort of Aragon from 1479 until 1504 by ...
and
Ferdinand II of Aragon in 1469. This marked what is
historiographically considered the foundation of unified Spain, although technically Castile and Aragon continued to maintain independent institutions for several centuries. The
conquest of Granada, and the
first voyage of Columbus, both in 1492, made that year a critical inflection point in Spanish history. The victory over Granada marked the official end of the Reconquista, as it was the last Muslim-ruled kingdom in Iberia, and the voyages of the various explorers and
Conquistadors of Spain during the subsequent decades helped establish a
Spanish colonial empire which was among the largest the world had ever seen. King
Carlos I, grandson of Ferdinand and Isabella through their daughter Joanna, established the
Spanish Habsburg dynasty. It was under the rule of his son
Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal fro ...
that the
Spanish Golden Age
The Spanish Golden Age ( es, Siglo de Oro, links=no , "Golden Century") is a period of flourishing in arts and literature in Spain, coinciding with the political rise of the Spanish Empire under the Catholic Monarchs of Spain and the Spanish ...
flourished, the Spanish Empire reached its territorial and economic peak, and his palace at
El Escorial
El Escorial, or the Royal Site of San Lorenzo de El Escorial ( es, Monasterio y Sitio de El Escorial en Madrid), or Monasterio del Escorial (), is a historical residence of the King of Spain located in the town of San Lorenzo de El Escorial, ...
became the center of artistic flourishing. However, Philip's rule also saw the calamitous destruction of the
Spanish Armada
The Spanish Armada (a.k.a. the Enterprise of England, es, Grande y Felicísima Armada, links=no, lit=Great and Most Fortunate Navy) was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by the Duke of Medina Sidonia, an a ...
, coupled with financial mismanagement that led to numerous state bankruptcies and independence of the
Northern Netherlands
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
, which marked the beginning of the slow decline of Spanish influence in Europe.
Spain's power was further tested by their participation in the
Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Re ...
, whereby they tried and failed to recapture the newly independent Dutch Republic, and the
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battl ...
, which resulted in continued decline of Habsburg power in favor of French
Bourbon dynasty
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a European dynasty of French origin, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Kingdom of Navarre, Navarre in the 16th century. By the 18th century, memb ...
. Matters came to a head during the reign of
Charles II of Spain, whose mental incapacity and inability to father children left the future of Spain in doubt. Upon his death, the
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phili ...
broke out between the French Bourbons and the Austrian Habsburgs over the right to succeed Charles II. The Bourbons prevailed, resulting in the ascension of
Philip V of Spain. Though himself a French prince, Philip quickly established himself as his own person, taking Spain into the various wars to recapture the Spanish-controlled lands in Southern Italy recently lost. Spain's apparent resurgence was cut short by losses during the
Napoleonic era, when Napoleon placed his own brother,
Joseph Bonaparte
it, Giuseppe-Napoleone Buonaparte es, José Napoleón Bonaparte
, house = Bonaparte
, father = Carlo Buonaparte
, mother = Letizia Ramolino
, birth_date = 7 January 1768
, birth_place = Corte, Corsica, Republic ...
, as King of Spain, turning it into a French puppet state. Concurrent with, and following, the Napoleonic period the
Spanish American wars of independence resulted in the loss of most of Spain's territory in the Americas. During the re-establishment of the Bourbon rule in Spain,
constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies di ...
was introduced in 1813. As with much of Europe, Spain's history during the nineteenth century was tumultuous, and featured alternating periods of republican-liberal and monarchical rule.
The twentieth century began for Spain in foreign and domestic turmoil; the
Spanish-American War
Spanish Americans ( es, españoles estadounidenses, ''hispanoestadounidenses'', or ''hispanonorteamericanos'') are Americans whose ancestry originates wholly or partly from Spain. They are the longest-established European American group in ...
led to losses of Spanish colonial possessions and a series of military dictatorships, first under
Miguel Primo de Rivera
Miguel Primo de Rivera y Orbaneja, 2nd Marquess of Estella (8 January 1870 – 16 March 1930), was a dictator, aristocrat, and military officer who served as Prime Minister of Spain from 1923 to 1930 during Spain's Restoration era. He deep ...
and secondly under
Dámaso Berenguer. During Berenguer's dictatorship, the king,
Alfonso XIII
Alfonso XIII (17 May 1886 – 28 February 1941), also known as El Africano or the African, was King of Spain from 17 May 1886 to 14 April 1931, when the Second Spanish Republic was proclaimed. He was a monarch from birth as his father, A ...
was deposed and a
new Republican government was formed. Ultimately, the political disorder within Spain led to a coup by the military which led to the
Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlism, Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebeli ...
, in which the Republican forces squared off against the
Nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
s. After much foreign intervention on both sides, the Nationalists emerged victorious thanks to the help provided by Nazi Germany and Italy, their leader
Francisco Franco
Francisco Franco Bahamonde (; 4 December 1892 – 20 November 1975) was a Spanish general who led the Nationalist forces in overthrowing the Second Spanish Republic during the Spanish Civil War and thereafter ruled over Spain from 19 ...
, who led a fascist dictatorship for almost four decades. Francisco's death ushered in a return of the monarchy King
Juan Carlos I, which saw a liberalization of Spanish society and a re-engagement with the international community after the oppressive and isolated years under Franco. A new liberal
Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
was established in 1978. Spain entered the
European Economic Community in 1986 (transformed into the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
with the
Maastricht Treaty
The Treaty on European Union, commonly known as the Maastricht Treaty, is the foundation treaty of the European Union (EU). Concluded in 1992 between the then-twelve member states of the European Communities, it announced "a new stage in the p ...
of 1992), and the
Eurozone
The euro area, commonly called eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro ( €) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU polic ...
in 1998. Juan Carlos abdicated in 2014, and was succeeded by his son
Felipe VI
Felipe VI (;,
* eu, Felipe VI.a,
* ca, Felip VI,
* gl, Filipe VI, . Felipe Juan Pablo Alfonso de Todos los Santos de Borbón y Grecia; born 30 January 1968) is King of Spain. He is the son of former King Juan Carlos I and Queen Sofía, an ...
, the current king.
Prehistory
The earliest record of
hominids living in Western Europe has been found in the Spanish cave of
Atapuerca; a flint tool found there dates from 1.4 million years ago, and early human
fossils
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
date to roughly 1.2 million years ago.
Modern humans in the form of
Cro-Magnons began arriving in the Iberian Peninsula from north of the
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
some 35,000 years ago. The most conspicuous sign of prehistoric human settlements are the famous
paintings in the northern Spanish cave of
Altamira, which were done c. 15,000
BC and are regarded as paramount instances of
cave art
In archaeology, Cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric origin, and the oldest known are more than 40,000 ye ...
.
Archeological evidence in places like
Los Millares and
El Argar, both in the
province of Almería, and La Almoloya near
Murcia
Murcia (, , ) is a city in south-eastern Spain, the Capital (political), capital and most populous city of the autonomous community of the Region of Murcia, and the List of municipalities of Spain, seventh largest city in the country. It has a ...
suggests developed cultures existed in the eastern part of the Iberian Peninsula during the late
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
and the
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
.
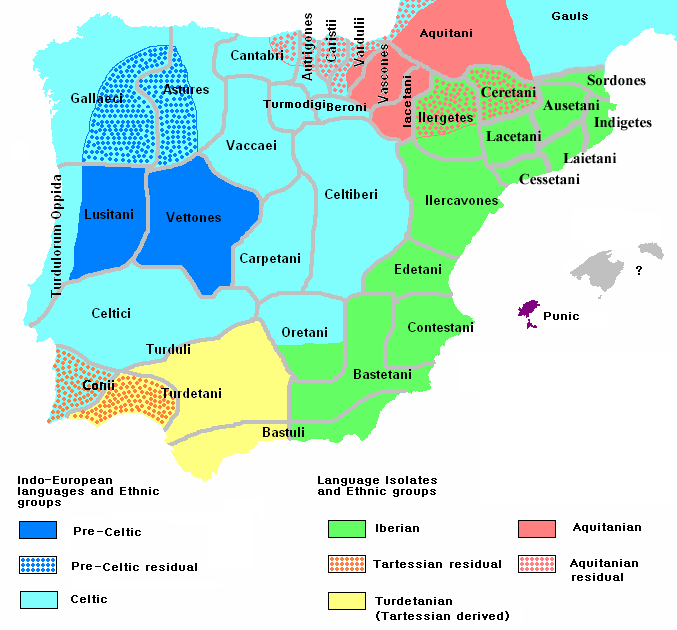
Around 2500 BC, the nomadic shepherds known as the
Yamna or
Pit Grave culture conquered the peninsula using new technologies and horses while killing all local males according to DNA studies. Spanish prehistory extends to the pre-Roman
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
cultures that controlled most of
Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a la ...
: those of the
Iberians
The Iberians ( la, Hibērī, from el, Ἴβηρες, ''Iberes'') were an ancient people settled in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian peninsula, at least from the 6th century BC. They are described in Greek and Roman sources (amo ...
,
Celtiberians
The Celtiberians were a group of Celts and Celticized peoples inhabiting an area in the central-northeastern Iberian Peninsula during the final centuries BCE. They were explicitly mentioned as being Celts by several classic authors (e.g. Strab ...
,
Tartessians,
Lusitanians
The Lusitanians ( la, Lusitani) were an Indo-European speaking people living in the west of the Iberian Peninsula prior to its conquest by the Roman Republic and the subsequent incorporation of the territory into the Roman province of Lusitania ...
, and
Vascones and trading settlements of
Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their his ...
ns,
Carthaginians
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of the ...
, and
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, Albania, Greeks in Italy, ...
on the
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
coast.
Early history of the Iberian Peninsula
Before the
Roman conquest the major cultures along the Mediterranean coast were the
Iberians
The Iberians ( la, Hibērī, from el, Ἴβηρες, ''Iberes'') were an ancient people settled in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian peninsula, at least from the 6th century BC. They are described in Greek and Roman sources (amo ...
, the
Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
in the interior and north-west, the
Lusitanians
The Lusitanians ( la, Lusitani) were an Indo-European speaking people living in the west of the Iberian Peninsula prior to its conquest by the Roman Republic and the subsequent incorporation of the territory into the Roman province of Lusitania ...
in the west, and the
Tartessians in the southwest. The seafaring Phoenicians, Carthaginians, and Greeks successively established trading settlements along the eastern and southern coast. The development of writing in the peninsula (the so-called
paleohispanic scripts) should have taken place after the arrival of early Phoenician settlers and traders (tentatively dated 9th century BC or sometime later).

The south of the peninsula was rich in archaic Phoenician colonies, unmatched by any other region in the central-western Mediterranean. They were small and densely packed settlements. The colony of
Gadir—which sustained strong links with its metropolis of
Tyre—stood out from the rest of the network of colonies, also featuring a more complex sociopolitical organization.
Archaic Greeks arrived to the Peninsula by the late 7th century BC. They founded
Greek colonies
Greek colonization was an organised Colonies in antiquity, colonial expansion by the Archaic Greece, Archaic Greeks into the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea in the period of the 8th–6th centuries BC.
This colonization differed from the Iron Ag ...
such as
Emporion (570 BC).
The Greeks are responsible for the name ''Iberia'', apparently after the river Iber (
Ebro). By the 6th century BC, much of the territory of southern Iberia passed to
Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the clas ...
's overarching influence (featuring two centres of Punic influence in ''Gadir'' and ''Mastia''); the latter grip strengthened from the 4th century BC on. The
Barcids, following their landing in Gadir in 237 BC, militarily conquered the territories that had already belonged to the sphere of influence of Carthage. Up until 219 BC, their presence in the peninsula was underpinned by their control of places such as
Carthago Nova and Akra Leuké (both founded by Punics), as well as the network of old Phoenician settlements.

The peninsula was one of the military theatres of the
Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Ital ...
(218–201 BC) waged between Carthage and the
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingd ...
, the two powers vying for supremacy in the western mediterranean. Romans expelled Carthaginians from the peninsula in 206 BC.
The peoples whom the
Romans met at the time of their invasion in what is now known as Spain were the Iberians, inhabiting an area stretching from the northeast part of the Iberian Peninsula through the southeast. The Celts mostly inhabited the inner and north-west part of the peninsula. To the east of the
Meseta Central, the
Sistema Ibérico area was inhabited by the
Celtiberians
The Celtiberians were a group of Celts and Celticized peoples inhabiting an area in the central-northeastern Iberian Peninsula during the final centuries BCE. They were explicitly mentioned as being Celts by several classic authors (e.g. Strab ...
, reportedly rich in
precious metal
Precious metals are rare, naturally occurring metallic chemical elements of high economic value.
Chemically, the precious metals tend to be less reactive than most elements (see noble metal). They are usually ductile and have a high lu ...
s (which were obtained by Romans in the form of
tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conq ...
s). Celtiberians developed a refined technique of iron-forging, displayed, for example, in their quality weapons.
The
Celtiberian Wars were fought between the advancing
legions of the Roman Republic and the Celtiberian tribes of Hispania Citerior from 181 to 133 BC. The Roman conquest of the peninsula was completed in 19 BC.
Roman Hispania (2nd century BC – 5th century AD)
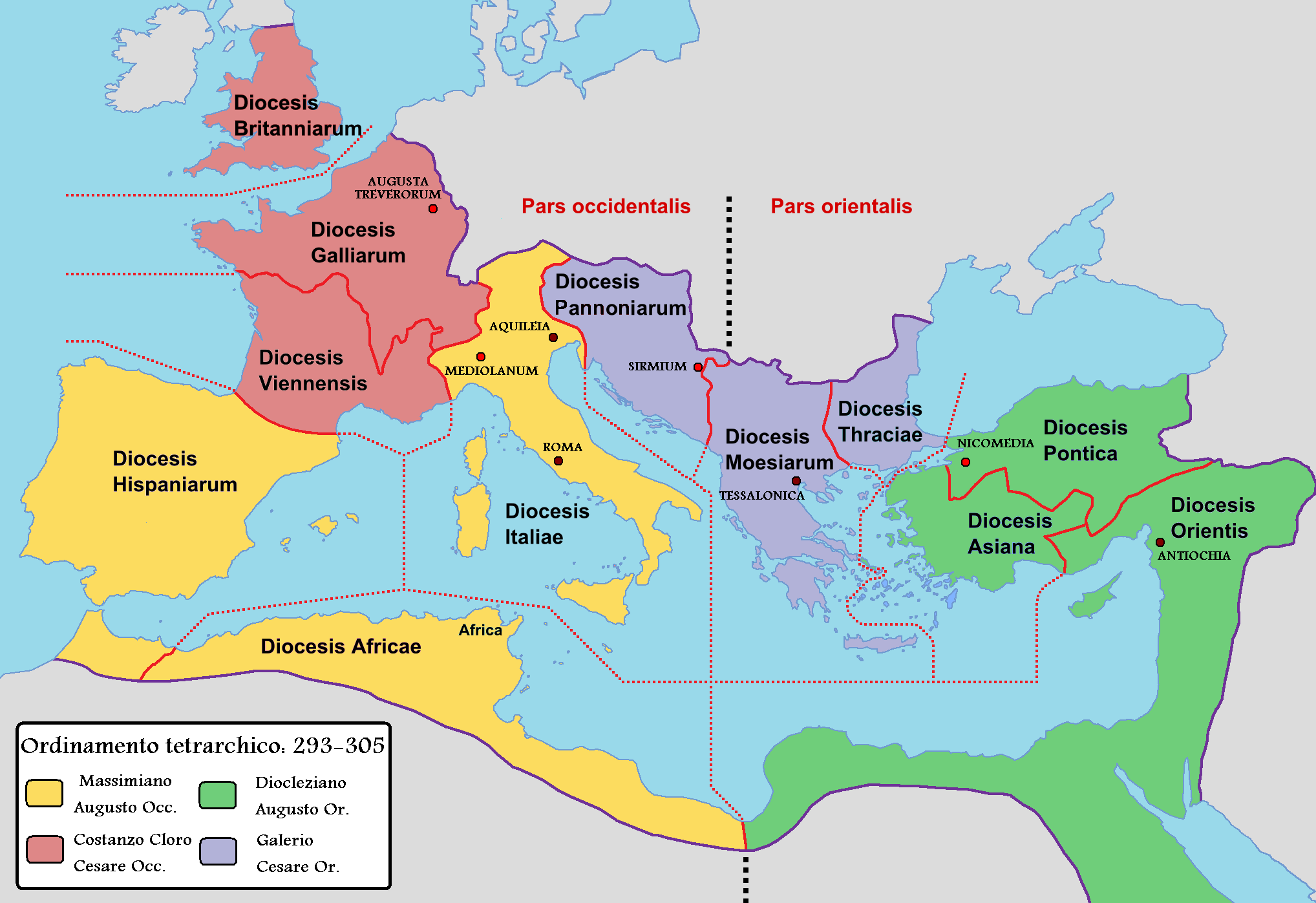
''
Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: His ...
'' was the name used for the Iberian Peninsula under
Roman rule from the 2nd century BC. The populations of the peninsula were gradually culturally
Romanized, and local leaders were admitted into the Roman aristocratic class.
The Romans improved existing cities, such as
Tarragona (''Tarraco''), and established others like
Zaragoza
Zaragoza, also known in English as Saragossa,''Encyclopædia Britannica'"Zaragoza (conventional Saragossa)" is the capital city of the Zaragoza Province and of the autonomous community of Aragon, Spain. It lies by the Ebro river and its tribut ...
(''Caesaraugusta''),
Mérida (''Augusta Emerita''),
Valencia
Valencia ( va, València) is the capital of the autonomous community of Valencia and the third-most populated municipality in Spain, with 791,413 inhabitants. It is also the capital of the province of the same name. The wider urban area al ...
(''Valentia''),
León ("Legio Septima"),
Badajoz
Badajoz (; formerly written ''Badajos'' in English) is the capital of the Province of Badajoz in the autonomous community of Extremadura, Spain. It is situated close to the Portuguese border, on the left bank of the river Guadiana. The populatio ...
("Pax Augusta"), and
Palencia
Palencia () is a city of Spain located in the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is the capital and most populated municipality of the province of Palencia.
Located in the Northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, in the northern half ...
. The peninsula's economy expanded under Roman tutelage. Hispania supplied Rome with food, olive oil, wine and metal. The emperors
Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presid ...
,
Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman '' municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispan ...
, and
Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also called Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. During his reign, he succeeded in a crucial war against the Goths, as well as in two ...
, the philosopher
Seneca, and the poets
Martial
Marcus Valerius Martialis (known in English as Martial ; March, between 38 and 41 AD – between 102 and 104 AD) was a Roman poet from Hispania (modern Spain) best known for his twelve books of ''Epigrams'', published in Rome between AD 86 an ...
,
Quintilian
Marcus Fabius Quintilianus (; 35 – 100 AD) was a Roman educator and rhetorician from Hispania, widely referred to in medieval schools of rhetoric and in Renaissance writing. In English translation, he is usually referred to as Quintili ...
, and
Lucan were born in Hispania. Hispanic bishops held the
Council of Elvira around 306.
After the fall of the
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
in the 5th century, parts of Hispania came under the control of the Germanic tribes of
Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area be ...
,
Suebi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own name ...
, and
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
.
The collapse of the
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
did not lead to the same wholesale destruction of Western classical society as happened in areas like
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered wa ...
,
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only durin ...
and
Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agrippine ...
during the
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the M ...
, although the institutions and infrastructure did decline. Spain's present languages, its religion, and the basis of its laws originate from this period. The centuries of uninterrupted Roman rule and settlement left a deep and enduring imprint upon the culture of Spain.
Gothic Hispania (5th–8th centuries)

The first
Germanic tribes to invade Hispania arrived in the 5th century, as the
Roman Empire decayed.The
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
,
Suebi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own name ...
,
Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area be ...
and
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the ...
arrived in Hispania by crossing the Pyrenees mountain range, leading to the establishment of the
Suebi Kingdom
The Kingdom of the Suebi ( la, Regnum Suevorum), also called the Kingdom of Galicia ( la, Regnum Galicia) or Suebi Kingdom of Galicia ( la, Galicia suevorum regnum), was a Germanic post-Roman kingdom that was one of the first to separate from ...
in
Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia, northern Portugal, Asturias and Leon and the later Kingdom of Gallaecia. The Roman cities include ...
, in the northwest, the
Vandal Kingdom of Vandalusia (Andalusia), and finally the
Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of the Goths ( la, Regnum Gothorum), was a kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic successor states to ...
in Toledo. The
Romanized Visigoths entered Hispania in 415. After the conversion of their monarchy to
Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and after conquering the disordered Suebic territories in the northwest and
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
territories in the southeast, the Visigothic Kingdom eventually encompassed a great part of the Iberian Peninsula.
As the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
declined,
Germanic tribes invaded the former empire. Some were ''
foederati'', tribes enlisted to serve in Roman armies, and given land within the empire as payment, while others, such as the
Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area be ...
, took advantage of the empire's weakening defenses to seek plunder within its borders. Those tribes that survived took over existing Roman institutions, and created successor-kingdoms to the Romans in various parts of Europe. Hispania was taken over by the
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
after 410.
At the same time, there was a process of "Romanization" of the Germanic and
Hunnic tribes settled on both sides of the ''
limes
Limes may refer to:
* the plural form of lime (disambiguation)
* the Latin word for ''limit'' which refers to:
** Limes (Roman Empire)
(Latin, singular; plural: ) is a modern term used primarily for the Germanic border defence or delimitin ...
'' (the fortified frontier of the Empire along the
Rhine
The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label=Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label=Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), including in Alsatian dialect, Al ...
and
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , ...
rivers). The Visigoths, for example, were converted to
Arian Christianity around 360, even before they were pushed into imperial territory by the expansion of the
Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
.
In the winter of 406, taking advantage of the frozen Rhine, refugees from (
Germanic)
Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area be ...
and
Sueves, and the (
Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th ...
)
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the ...
, fleeing the advancing Huns, invaded the empire in force.
The Visigoths, having
sacked Rome two years earlier, arrived in Gaul in 412, founding the Visigothic kingdom of
Toulouse
Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Departments of France, French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania. The city is on t ...
(in the south of modern France) and gradually expanded their influence into Hispania after the battle of Vouillé (507) at the expense of the Vandals and Alans, who moved on into North Africa without leaving much permanent mark on Hispanic culture. The
Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of the Goths ( la, Regnum Gothorum), was a kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic successor states to ...
shifted its capital to
Toledo
Toledo most commonly refers to:
* Toledo, Spain, a city in Spain
* Province of Toledo, Spain
* Toledo, Ohio, a city in the United States
Toledo may also refer to:
Places Belize
* Toledo District
* Toledo Settlement
Bolivia
* Toledo, Orur ...
and reached a high point during the reign of
Leovigild.
Visigothic rule
The
Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of the Goths ( la, Regnum Gothorum), was a kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic successor states to ...
conquered all of Hispania and ruled it until the early 8th century, when the peninsula fell to the
Muslim conquests. The Muslim state in Hispania came to be known as
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the Mus ...
. After a period of Muslim dominance, the
medieval history of Spain is dominated by the long Christian ''
Reconquista
The ' ( Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the Na ...
'' or "reconquest" of the Iberian Peninsula from Muslim rule. The Reconquista gathered momentum during the 12th century, leading to the establishment of the Christian kingdoms of
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, In recognized minority languages of Portugal:
:* mwl, República Pertuesa is a country located on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Macaronesian ...
,
Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to so ...
,
Castile and
Navarre
Navarre (; es, Navarra ; eu, Nafarroa ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre ( es, Comunidad Foral de Navarra, links=no ; eu, Nafarroako Foru Komunitatea, links=no ), is a foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, ...
and by 1250, had reduced Muslim control to the
Emirate of Granada in the south-east of the peninsula. Muslim rule in Granada survived until 1492, when it fell to the
Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being bo ...
.
Hispania never saw a decline in interest in classical culture to the degree observable in Britain, Gaul, Lombardy and Germany. The Visigoths, having assimilated Roman culture and its language during their tenure as ''foederati'', tended to maintain more of the old Roman institutions, and they had a unique respect for legal codes that resulted in continuous frameworks and historical records for most of the period between 415, when Visigothic rule in Hispania began, and 711 when it is traditionally said to end.chap The
''Liber Iudiciorum'' or Lex Visigothorum (654), also known as the Book of Judges, which
Recceswinth promulgated, based on Roman law and Germanic customary laws, brought about legal unification by applying it to the entire population both Goths and Hispano-Romans. According to the historian Joseph F. O'Callaghan, at that time they already considered themselves one people, the process of population unification had been completed, and together with the Hispano-Gothic nobility they called themselves the ''gens Gothorum''.
In the early Middle Ages, the ''Liber Iudiciorum'' was known as the Visigothic Code and also as the ''
Fuero Juzgo The ''Fuero Juzgo'' () was a codex of Spanish laws enacted in Castile in 1241 by Fernando III. It is essentially a translation of the ''Liber Iudiciorum'' that was formulated in 654 by the Visigoths.
The ''Fuero Juzgo'' was first applied legally a ...
''. Its influence on law extends to the present day.
The proximity of the Visigothic kingdoms to the Mediterranean and the continuity of western Mediterranean trade, though in reduced quantity, supported Visigothic culture. The Visigothic ruling class looked to
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
for style and technology.
Spanish Catholic religion also coalesced during this time. The period of rule by the
Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of the Goths ( la, Regnum Gothorum), was a kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic successor states to ...
saw the spread of
Arianism
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by G ...
briefly in Hispania. The
Councils of Toledo
From the 5th century to the 7th century AD, about thirty synods, variously counted, were held at Toledo (''Concilia toletana'') in what would come to be part of Spain. The earliest, directed against Priscillianism, assembled in 400. The "thir ...
debated creed and liturgy in orthodox
Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, and the Council of Lerida in 546 constrained the clergy and extended the power of law over them with the approval of the Pope. In 587, the Visigothic king at Toledo,
Reccared, converted to Catholicism and launched a movement in Hispania to unify the various religious doctrines that existed in the land. This put an end to dissension on the question of Arianism.
The Visigoths inherited from Late Antiquity a sort of
prefeudal system in Hispania,
based in the south on the Roman
villa
A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became s ...
system and in the north drawing on their vassals to supply troops in exchange for protection. The bulk of the Visigothic army was composed of slaves, raised from the countryside. The loose council of nobles that advised Hispania's Visigothic kings and legitimized their rule was responsible for raising the army, and only upon its consent was the king able to summon soldiers.
The economy of the Visigothic kingdom depended primarily on agriculture and animal husbandry; there is little evidence of Visigothic commerce and industry.
The native Hispani maintained the cultural and economic life of Hispania, such as it was, and they were responsible for the relatively prosperous times in the 6th and 7th centuries. Administrative affairs in society were still based on Roman law, and only gradually did Visigothic customs and Roman common law merge.
The Visigoths did not, until the period of Muslim rule, intermarry with the Spanish population, preferring to remain separate, and the Visigothic language left only the faintest mark on the modern languages of Iberia. The historian Joseph F. O'Callaghan says in his book, ''A History of Medieval Spain'', that at the end of the Visigothic era the assimilation of Hispano-Romans and Visigoths was occurring rapidly, and the leaders of society were beginning to see themselves as one people. The old differences were disappearing, there was no longer a separate people, nor a divided nobility.
Little literature in the Gothic language remains from the period of Visigothic rule—only translations of parts of the Greek Bible and a few fragments of other documents have survived.
The Hispano-Romans found Visigothic rule and its early embrace of the Arian heresy more of a threat than Islam, and shed their thralldom to the Visigoths only in the 8th century, with the aid of the Muslims themselves.
The most visible effect of Visigothic rule was the depopulation of the cities as their inhabitanats moved to the countryside. Even while the country enjoyed a degree of prosperity when compared to France and Germany, where the people suffered famines during this period, the Visigoths felt little reason to contribute to the welfare, permanency, and infrastructure of their people and state. This contributed to their downfall, as they could not count on the loyalty of their subjects when the
Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct o ...
arrived in the 8th century.
Goldsmithery in Visigothic Hispania

In Spain, an important collection of Visigothic metalwork was found in
Guadamur, in the
Province of Toledo
Toledo is a province of central Spain, in the western part of the autonomous community of Castile–La Mancha. It is bordered by the provinces of Madrid, Cuenca, Ciudad Real, Badajoz, Cáceres, and Ávila. Its capital is the city of Toledo.
D ...
, known as the
Treasure of Guarrazar. This
archeological find is composed of twenty-six
votive crowns and gold
cross
A cross is a geometrical figure consisting of two intersecting lines or bars, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of the Latin letter X, is termed a s ...
es from the royal workshop in Toledo, with signs of Byzantine influence.
* Two important votive crowns are those of
Recceswinth and of
Suintila, displayed in the National Archaeological Museum of Madrid; both are made of gold, encrusted with sapphires, pearls, and other precious stones. Suintila's crown was stolen in 1921 and never recovered. There are several other small crowns and many votive crosses in the treasure.
* The aquiliform (eagle-shaped)
fibulae that have been discovered in
necropolises such as
Duraton,
Madrona or Castiltierra (cities of
Segovia
Segovia ( , , ) is a city in the autonomous community of Castile and León, Spain. It is the capital and most populated municipality of the Province of Segovia.
Segovia is in the Inner Plateau ('' Meseta central''), near the northern slopes o ...
. These fibulae were used individually or in pairs, as clasps or pins in gold, bronze and glass to join clothes.
* The Visigothic belt buckles, a symbol of rank and status characteristic of Visigothic women's clothing, are also notable as works of goldsmithery. Some pieces contain exceptional
Byzantine-style lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color.
As early as the 7th millennium BC, lapis lazuli was mined in the Sar-i Sang mine ...
inlays and are generally rectangular in shape, with copper alloy, garnets and glass.
The architecture of Visigothic Hispania
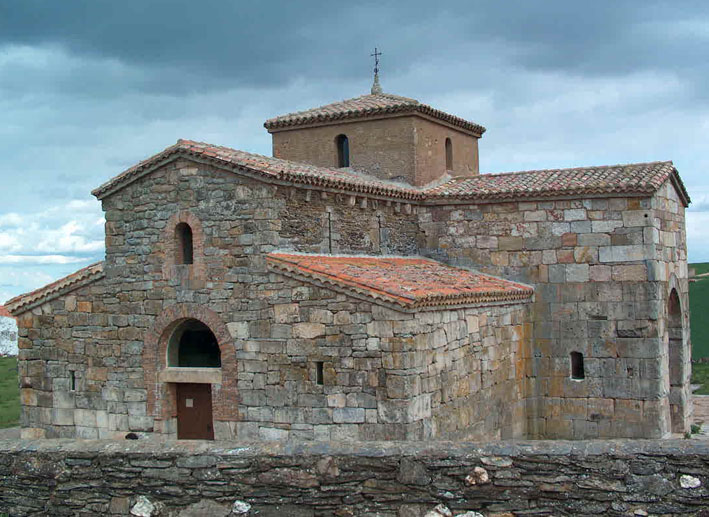

* During their governance of Hispania, the Visigoths built several churches in the
basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name ...
l or
cruciform style that survive, including the churches of
San Pedro de la Nave in El Campillo,
Santa María de Melque in
San Martín de Montalbán, Santa Lucía del Trampal in Alcuéscar, Santa Comba in Bande, and
Santa María de Lara in Quintanilla de las Viñas. The Visigothic
crypt
A crypt (from Latin '' crypta'' " vault") is a stone chamber beneath the floor of a church or other building. It typically contains coffins, sarcophagi, or religious relics.
Originally, crypts were typically found below the main apse of a ...
(the Crypt of San Antolín) in the
Palencia Cathedral
Palencia Cathedral (''Catedral de Palencia'') is a Roman Catholic church architecture, church located in Palencia, Spain. It is dedicated to Saint Antoninus of Pamiers (''San Antolín'').
The cathedral was built from 1172 to 1504 stands over a lo ...
is a Visigothic chapel from the mid 7th century, built during the reign of
Wamba to preserve the remains of the martyr
Saint Antoninus of Pamiers
Saint Antoninus of Pamiers (french: Saint Antonin, oc, Sant Antoní, and es, San Antolín) was an early Christian missionary and martyr, called the "Apostle of the Rouergue". His life is dated to the first, second, fourth, and fifth century by va ...
, a Visigothic-Gallic nobleman brought from Narbonne to Visigothic Hispania in 672 or 673 by Wamba himself. These are the only remains of the Visigothic cathedral of Palencia.
*
Reccopolis
Reccopolis ( es, link=no, Recópolis; la, Reccopolis), located near the tiny modern village of Zorita de los Canes in the province of Guadalajara, Castile-La Mancha, Spain, is an archaeological site of one of at least four cities founded in Hisp ...
, located near the tiny modern village of
Zorita de los Canes in the
province of Guadalajara, Castile-La Mancha, Spain, is an archaeological site of one of at least four cities founded in
Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: His ...
by the Visigoths. It is the only city in Western Europe to have been founded between the fifth and eighth centuries. The city's construction was ordered by the Visigothic king
Liuvigild
Liuvigild, Leuvigild, Leovigild, or ''Leovigildo'' ( Spanish and Portuguese), ( 519 – 586) was a Visigothic King of Hispania and Septimania from 568 to 586. Known for his Codex Revisus or Code of Leovigild, a law allowing equal rights between ...
to honor his son
Reccared and to serve as Reccared's seat as co-king in the Visigothic province of
Celtiberia, to the west of
Carpetania, where the main capital, Toledo, lay.
Religion
At the beginning of the
Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of the Goths ( la, Regnum Gothorum), was a kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic successor states to ...
,
Arianism
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by G ...
was the official religion in Hispania, but only for a brief time, according to historian Rhea Marsh Smith (1905–1991). In 587,
Reccared, the Visigothic king at Toledo, converted to Catholicism and launched a movement to unify the various religious doctrines that existed in the Iberian Peninsula. The
Councils of Toledo
From the 5th century to the 7th century AD, about thirty synods, variously counted, were held at Toledo (''Concilia toletana'') in what would come to be part of Spain. The earliest, directed against Priscillianism, assembled in 400. The "thir ...
debated the creed and liturgy of orthodox
Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, and the Council of Lerida in 546 constrained the clergy and extended the power of law over them with the approval of the pope.
While the Visigoths clung to their Arian faith, the
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
were well-tolerated. Previous Roman and Byzantine law determined their status, and already sharply discriminated against them. Historian Jane Gerber relates that some of the Jews "held ranking posts in the government or the army; others were recruited and organized for garrison service; still others continued to hold senatorial rank". In general, then, they were well-respected and well-treated by the Visigothic kings, that is, until their transition from Arianism to Catholicism. Conversion to Catholicism across Visigothic society reduced the friction between the Visigoths and the Hispano-Roman population. However, the Visigothic conversion negatively impacted the Jews, who came under scrutiny for their religious practices.
Islamic ''al-Andalus'' and the Christian ''Reconquest'' (8th–15th centuries)


The
Arab Islamic conquest
The spread of Islam spans about 1,400 years. Muslim conquests following Muhammad's death led to the creation of the caliphates, occupying a vast geographical area; conversion to Islam was boosted by Arab Muslim forces conquering vast territories ...
dominated most of North Africa by 710 AD. In 711 an Islamic
Berber conquering party, led by
Tariq ibn Ziyad, was sent to Hispania to intervene in a civil war in the
Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of the Goths ( la, Regnum Gothorum), was a kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic successor states to ...
. Tariq's army contained about 7,000 Berber horsemen, and
Musa bin Nusayr
Musa ibn Nusayr ( ar, موسى بن نصير ''Mūsá bin Nuṣayr''; 640 – c. 716) served as a Umayyad governor and an Arab general under the Umayyad caliph Al-Walid I. He ruled over the Muslim provinces of North Africa (Ifriqiya), and dir ...
is said to have sent an additional 5,000 reinforcements after the conquest. Crossing the
Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar ( ar, مضيق جبل طارق, Maḍīq Jabal Ṭāriq; es, Estrecho de Gibraltar, Archaism, Archaic: Pillars of Hercules), also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, they won a decisive victory in the summer of 711 when the Visigothic King
Roderic was defeated and killed on July 19 at the
Battle of Guadalete
The Battle of Guadalete was the first major battle of the Umayyad conquest of Hispania, fought in 711 at an unidentified location in what is now southern Spain between the Christian Visigoths under their king, Roderic, and the invading forces o ...
. Tariq's commander, Musa, quickly crossed with Arab reinforcements, and by 718 the
Muslims were in control of nearly the whole
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
. The advance into
Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
was only stopped in what is now north-central France by the
West Germanic
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages). The West Germanic branch is classically subdivided into ...
Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
under
Charles Martel
Charles Martel ( – 22 October 741) was a Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of Francia from 718 until his death. He was a son of the Frankish state ...
at the
Battle of Tours in 732.
The Muslim conquerors (also known as "Moors") were
Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
and
Berbers; following the conquest, conversion and arabization of the Hispano-Roman population took place, (''muwalladum'' or ''
Muwallad'').
After a long process, spurred on in the 9th and 10th centuries, the majority of the population in Al-Andalus eventually converted to Islam. The Muslim population was divided per ethnicity (Arabs, Berbers, Muwallad), and the supremacy of Arabs over the rest of group was a recurrent causal for strife, rivalry and hatred, particularly between Arabs and Berbers. Arab elites could be further divided in the Yemenites (first wave) and the Syrians (second wave). Male Muslim rulers were often the offspring of female Christian slaves.
Christians and Jews were allowed to live as subordinate groups of a stratified society under the
''dhimmah'' system, although Jews became very important in certain fields. Some Christians migrated to the Northern Christian kingdoms, while those who stayed in Al-Andalus progressively arabised and became known as ''musta'arab'' (
mozarab
The Mozarabs ( es, mozárabes ; pt, moçárabes ; ca, mossàrabs ; from ar, مستعرب, musta‘rab, lit=Arabized) is a modern historical term for the Iberian Christians, including Christianized Iberian Jews, who lived under Muslim rule in ...
s). Besides slaves of Iberian origin,
the slave population also comprised the ''
Ṣaqāliba
Saqaliba ( ar, صقالبة, ṣaqāliba, singular ar, صقلبي, ṣaqlabī) is a term used in medieval Arabic sources to refer to Slavs and other peoples of Central, Southern, and Eastern Europe, or in a broad sense to European slaves. The te ...
'' (literally meaning "slavs", although they were slaves of generic European origin) as well as
Sudanese
Sudanese or Sudanic may refer to:
*pertaining to the country of Sudan
**the people of Sudan, see Demographics of Sudan
*pertaining to Sudan (region)
**Sudanic languages
**Sudanic race, subtype of the Africoid racial category
See also
*Sudanese Civ ...
slaves. The frequent raids in Christian lands provided Al-Andalus with continuous slave stock, including women who often became part of the harems of the Muslim elite.
Slaves were also shipped from Spain to elsewhere in the
Ummah
' (; ar, أمة ) is an Arabic word meaning "community". It is distinguished from ' ( ), which means a nation with common ancestry or geography. Thus, it can be said to be a supra-national community with a common history.
It is a synonym for ' ...
.
In what should not have amounted to much more than a skirmish (later magnified by
Spanish nationalism), a Muslim force sent to put down the Christian rebels in the northern mountains was defeated by a force reportedly led by the legendary
Pelagius
Pelagius (; c. 354–418) was a British theologian known for promoting a system of doctrines (termed Pelagianism by his opponents) which emphasized human choice in salvation and denied original sin. Pelagius and his followers abhorred the moral ...
, this is known as the
Battle of Covadonga. The figure of Pelagius, a by-product of the Asturian chronicles of
Alfonso III (written more than a century after the alleged battle), has been later reconstructed in conflicting historiographical theories, most notably that of a refuged Visigoth noble or an autochthonous
Astur chieftain. The consolidation of a Christian polity that came to be known as the
Kingdom of Asturias
The Kingdom of Asturias ( la, Asturum Regnum; ast, Reinu d'Asturies) was a kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula founded by the Visigothic nobleman Pelagius. It was the first Christian political entity established after the Umayyad conquest of V ...
ensued later. At the end of Visigothic rule, the assimilation of Hispano-Romans and Visigoths was occurring at a fast pace. An unknown number of them fled and took refuge in Asturias or Septimania. In Asturias they supported Pelagius's uprising, and joining with the indigenous leaders, formed a new aristocracy. The population of the mountain region consisted of native
Astures
The Astures or Asturs, also named Astyrs, were the Hispano-Celtic inhabitants of the northwest area of Hispania that now comprises almost the entire modern autonomous community of Principality of Asturias, the modern province of León, and the ...
,
Galicians,
Cantabri
The Cantabri ( grc-gre, Καντάβροι, ''Kantabroi'') or Ancient Cantabrians, were a pre-Roman people and large tribal federation that lived in the northern coastal region of ancient Iberia in the second half of the first millennium BC. Thes ...
,
Basques and other groups unassimilated into Hispano-Gothic society.
In 739, a rebellion in Galicia, assisted by the Asturians, drove out Muslim forces and it joined the Asturian kingdom. In the northern Christian kingdoms, lords and religious organizations often owned Muslim slaves who were employed as day laborers and household servants.
Caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
Al-Walid I
Al-Walid ibn Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan ( ar, الوليد بن عبد الملك بن مروان, al-Walīd ibn ʿAbd al-Malik ibn Marwān; ), commonly known as al-Walid I ( ar, الوليد الأول), was the sixth Umayyad caliph, ruling from ...
had paid great attention to the expansion of an organized military, building the strongest navy in the
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
era (the second major Arab dynasty after Mohammad and the first Arab dynasty of
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the Mus ...
). It was this tactic that supported the ultimate expansion to Hispania. Islamic power in Spain specifically climaxed in the 10th century under
Abd-ar-Rahman III. The rulers of
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the Mus ...
were granted the rank of
Emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
by the Umayyad Caliph Al-Walid I in
Damascus. When the
Abbasids
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
overthrew the Umayyad Caliphate,
Abd al-Rahman I managed to escape to al-Andalus. Once arrived, he declared al-Andalus independent. It is not clear if Abd al-Rahman considered himself to be a rival caliph, perpetuating the Umayyad Caliphate, or merely an independent Emir. The state founded by him is known as the
Emirate of Cordoba. Al-Andalus was rife with internal conflict between the Islamic Umayyad rulers and people and the Christian Visigoth-Roman leaders and people.

The Vikings invaded Galicia in 844, but were heavily defeated by
Ramiro I at
A Coruña
A Coruña (; es, La Coruña ; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and ...
.
[ Many of the Vikings' casualties were caused by the Galicians' ]ballista
The ballista (Latin, from Greek βαλλίστρα ''ballistra'' and that from βάλλω ''ballō'', "throw"), plural ballistae, sometimes called bolt thrower, was an ancient missile weapon that launched either bolts or stones at a distant ...
s – powerful torsion-powered projectile weapons that looked rather like giant crossbows.[ 70 Viking ships were captured and burned.]Caliphate of Córdoba
The Caliphate of Córdoba ( ar, خلافة قرطبة; transliterated ''Khilāfat Qurṭuba''), also known as the Cordoban Caliphate was an Islamic state ruled by the Umayyad dynasty from 929 to 1031. Its territory comprised Iberia and part ...
, effectively breaking all ties with the Egyptian and Syrian caliphs. The Caliphate was mostly concerned with maintaining its power base in North Africa, but these possessions eventually dwindled to the Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ar, سَبْتَة, Sabtah) is a Spanish autonomous city on the north coast of Africa.
Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of several Spanish territo ...
province. The first navy of the Emir of Córdoba was built after the Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and s ...
ascent of the Guadalquivir
The Guadalquivir (, also , , ) is the fifth-longest river in the Iberian Peninsula and the second-longest river with its entire length in Spain. The Guadalquivir is the only major navigable river in Spain. Currently it is navigable from the Gu ...
in 844 when they sacked Seville.Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
, took place, according to Ibn Hayyan's work.Golden age of Jewish culture in the Iberian Peninsula
The golden age of Jewish culture in Spain, which coincided with the Middle Ages in Europe, was a period of Muslim rule during which, intermittently, Jews were generally accepted in society and Jewish religious, cultural, and economic life flou ...
. Muslim interest in the peninsula returned in force around the year 1000 when Almanzor, Al-Mansur (also known as ''Almanzor'') sacked Barcelona in 985, and he assaulted Zamora, Spain, Zamora, Toro, Spain, Toro, León, Spain, Leon and Astorga, Spain, Astorga in 988 and 989, which controlled access to Galicia (Spain), Galicia. Under his son, other Christian cities were subjected to numerous raids. After his son's death, the caliphate plunged into a civil war and splintered into the so-called "Taifa Kingdoms". The Taifa kings competed against each other not only in war but also in the protection of the arts, and culture enjoyed a brief renaissance. The ''aceifas'' (Muslim military expeditions made in summer in medieval Spain) were the continuation of a policy from the times of the emirate: the capture of numerous contingents of Christian slaves, the ''saqáliba'' (plural of ''siqlabi'', "slave"). These were the most lucrative part of the booty, and constituted an excellent method of payment for the troops, so much so that many ''aceifas'' were real hunts for people.
The Almohads, who had taken control of the Almoravids' Maghribi and al-Andalus territories by 1147, surpassed the Almoravides in fundamentalist Islamic outlook, and they treated the non-believer ''dhimmis'' harshly. Faced with the choice of death, conversion, or emigration, many Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
and Christians left.
By the mid-13th century, the Emirate of Granada was the only independent Muslim realm in Spain, which survived Granada War, until 1492 by becoming a vassal state to Castile, to which it paid parias, tribute.
Warfare between Muslims and Christians
 Spain in the Middle Ages, Medieval Spain was the scene of almost constant warfare between Muslims and Christians.
The Taifa kingdoms lost ground to the Christian realms in the north. After the loss of Toledo in 1085, the Muslim rulers reluctantly invited the Almoravides, who invaded Al-Andalus from North Africa and established an empire. In the 12th century the Almoravid empire broke up again, only to be taken over by the Almohad invasion, who were defeated by an alliance of the Christian kingdoms in the decisive Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in 1212. By 1250, nearly all of Hispania was back under Christian rule with the exception of the Muslim kingdom of Granada.
Spain in the Middle Ages, Medieval Spain was the scene of almost constant warfare between Muslims and Christians.
The Taifa kingdoms lost ground to the Christian realms in the north. After the loss of Toledo in 1085, the Muslim rulers reluctantly invited the Almoravides, who invaded Al-Andalus from North Africa and established an empire. In the 12th century the Almoravid empire broke up again, only to be taken over by the Almohad invasion, who were defeated by an alliance of the Christian kingdoms in the decisive Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in 1212. By 1250, nearly all of Hispania was back under Christian rule with the exception of the Muslim kingdom of Granada.
The Spanish language and universities
 In the 13th century, many languages were spoken in the Christian kingdoms of Hispania. These were the Latin-based Romance languages of Spanish language, Castilian, Aragonese language, Aragonese, Catalan language, Catalan, Galician language, Galician, Aranese language, Aranese, Asturian language, Asturian, Leonese language, Leonese, and Portuguese language, Portuguese, and the ancient language isolate of Basque language, Basque. Throughout the century, Castilian (what is also known today as Spanish) gained a growing prominence in the Kingdom of Castile as the language of culture and communication, at the expense of Leonese and of other close dialects.
One example of this is the oldest preserved Castilian epic poem, ''Cantar de Mio Cid'', written about the military leader ''El Cid''. In the last years of the reign of Ferdinand III of Castile, Castilian began to be used for certain types of documents, and it was during the reign of Alfonso X of Castile, Alfonso X that it became the official language. Henceforth all public documents were written in Castilian; likewise all translations were made into Castilian instead of Latin.
At the same time, Catalan and Galician became the standard languages in their respective territories, developing important literary traditions and being the normal languages in which public and private documents were issued: Galician from the 13th to the 16th century in Galicia and nearby regions of Asturias and Leon,
In the 13th century, many languages were spoken in the Christian kingdoms of Hispania. These were the Latin-based Romance languages of Spanish language, Castilian, Aragonese language, Aragonese, Catalan language, Catalan, Galician language, Galician, Aranese language, Aranese, Asturian language, Asturian, Leonese language, Leonese, and Portuguese language, Portuguese, and the ancient language isolate of Basque language, Basque. Throughout the century, Castilian (what is also known today as Spanish) gained a growing prominence in the Kingdom of Castile as the language of culture and communication, at the expense of Leonese and of other close dialects.
One example of this is the oldest preserved Castilian epic poem, ''Cantar de Mio Cid'', written about the military leader ''El Cid''. In the last years of the reign of Ferdinand III of Castile, Castilian began to be used for certain types of documents, and it was during the reign of Alfonso X of Castile, Alfonso X that it became the official language. Henceforth all public documents were written in Castilian; likewise all translations were made into Castilian instead of Latin.
At the same time, Catalan and Galician became the standard languages in their respective territories, developing important literary traditions and being the normal languages in which public and private documents were issued: Galician from the 13th to the 16th century in Galicia and nearby regions of Asturias and Leon,Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being bo ...
, the first edition of the ''Grammar of the Castilian Language'' by Antonio de Nebrija was published.
Early Modern Spain
Dynastic union of the Catholic Monarchs
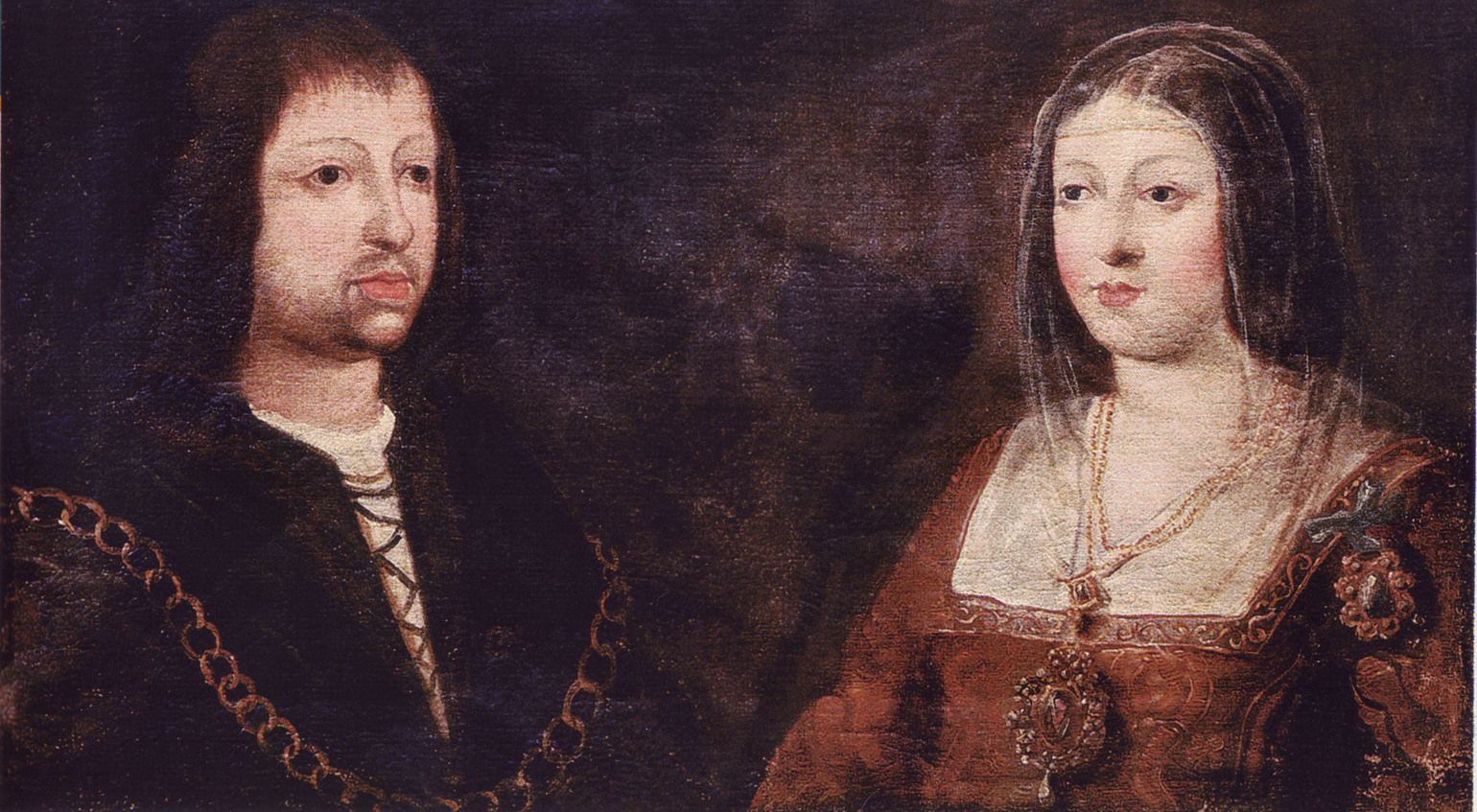 In the 15th century, the most important among all of the separate Christian kingdoms that made up the old
In the 15th century, the most important among all of the separate Christian kingdoms that made up the old Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: His ...
were the Kingdom of Castile
The Kingdom of Castile (; es, Reino de Castilla, la, Regnum Castellae) was a large and powerful state on the Iberian Peninsula during the Middle Ages. Its name comes from the host of castles constructed in the region. It began in the 9th centu ...
(occupying northern and central portions of the Iberian Peninsula), the Kingdom of Aragon
The Kingdom of Aragon ( an, Reino d'Aragón, ca, Regne d'Aragó, la, Regnum Aragoniae, es, Reino de Aragón) was a medieval and early modern kingdom on the Iberian Peninsula, corresponding to the modern-day autonomous community
eu, a ...
(occupying northeastern portions of the peninsula), and the Kingdom of Portugal
The Kingdom of Portugal ( la, Regnum Portugalliae, pt, Reino de Portugal) was a monarchy in the western Iberian Peninsula and the predecessor of the modern Portuguese Republic. Existing to various extents between 1139 and 1910, it was also kn ...
occupying the far western Iberian Peninsula. The rulers of the kingdoms of Castile and Aragon were allied with dynastic families in Portugal, France, and other neighboring kingdoms.
The death of King Henry IV of Castile in 1474 set off a struggle for power called the War of the Castilian Succession (1475–1479). Contenders for the throne of Castile were Henry's one-time heir Joanna la Beltraneja, supported by Portugal and France, and Henry's half-sister Queen Isabella I of Castile
Isabella I ( es, Isabel I; 22 April 1451 – 26 November 1504), also called Isabella the Catholic (Spanish: ''la Católica''), was Queen of Castile from 1474 until her death in 1504, as well as Queen consort of Aragon from 1479 until 1504 by ...
, supported by the Kingdom of Aragon and by the Castilian nobility.
Isabella retained the throne and ruled jointly with her husband, Ferdinand II of Aragon, King Ferdinand II. Isabella and Ferdinand had married in 1469 in Valladolid. Their marriage united both crowns and set the stage for the creation of the Kingdom of Spain, at the dawn of the modern era. That union, however, was a union in title only, as each region retained its own political and judicial structure. Pursuant to an agreement signed by Isabella and Ferdinand on January 15, 1474, Isabella held more authority over the newly unified Spain than her husband, although their rule was shared. Together, Isabella of Crown of Castile, Castile and Ferdinand of Crown of Aragon, Aragon were known as the "Catholic Monarchs" ( es, los Reyes Católicos, links=no), a title bestowed on them by Pope Alexander VI.
Conclusion of the Reconquista and expulsions of Jews and Muslims
The monarchs oversaw the final stages of the Reconquista
The ' ( Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the Na ...
of Iberian Peninsula, Iberian territory from the Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct o ...
with the conquest of Granada, conquered the Canary Islands, and expelled the Jews from Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
under the Alhambra Decree.
Although until the 13th century religious minorities (Jews and Muslims) had enjoyed considerable tolerance in Castile and Aragon – the only Christian kingdoms where Jews were not restricted from any professional occupation – the situation of the Jews collapsed over the 14th century, reaching a climax in 1391 with large scale massacres in every major city except Ávila, Spain, Ávila.
The Catholic Monarchs ordered the remaining Jews to convert or face expulsion from Spain in 1492, and extended the expulsion decrees to their territories on the Italian peninsula, including Sicily (1493), Naples (1542), and Milan (1597).
Over the following decades, Muslims faced the same fate; and about 60 years after the Jews, they were also compelled to convert ("Moriscos") or be expelled. In the early 17th century, the converts were also expelled. Jews and Muslims were not the only people to be persecuted during this time period.
Isabella ensured long-term political stability in Spain by arranging strategic marriages for each of her five children. Her firstborn, a daughter named Isabella of Asturias, Isabella, married Afonso, Prince of Portugal, Afonso of Portugal, forging important ties between these two neighboring countries and hopefully ensuring future alliance, but Isabella soon died before giving birth to an heir. Joanna of Castile, Juana, Isabella's second daughter, married into the Habsburg dynasty when she wed Philip the Handsome, Philip the Fair, the son of Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, Maximilian I, King of Bohemia (Austria) and likely heir to the crown of the Holy Roman Emperor.
This ensured an alliance with the Habsburgs and the Holy Roman Empire, a powerful, far-reaching territory that assured Spain's future political security. Isabella's only son, Juan, Prince of Asturias, Juan, married Margaret of Austria, Duchess of Savoy, Margaret of Austria, further strengthening ties with the Habsburg dynasty. Isabella's fourth child, Maria of Aragon, Queen of Portugal, Maria, married Manuel I of Portugal, strengthening the link forged by her older sister's marriage. Her fifth child, Catherine of Aragon, Catherine, married King Henry VIII of England and was mother to Queen Mary I of England.
Conquest of the Canary Islands, Columbian expeditions to the New World and African expansion

 The Castilian conquest of the Canary Islands, inhabited by Guanche people, took place between 1402 (with the conquest of Lanzarote) and 1496 (with the conquest of Tenerife). Two periods can be distinguished in this process: the noble conquest, carried out by the nobility in exchange for a pact of vassalage, and the royal conquest, carried out directly by the Crown, during the reign of the Catholic Monarchs.
The Castilian conquest of the Canary Islands, inhabited by Guanche people, took place between 1402 (with the conquest of Lanzarote) and 1496 (with the conquest of Tenerife). Two periods can be distinguished in this process: the noble conquest, carried out by the nobility in exchange for a pact of vassalage, and the royal conquest, carried out directly by the Crown, during the reign of the Catholic Monarchs.Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ar, سَبْتَة, Sabtah) is a Spanish autonomous city on the north coast of Africa.
Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of several Spanish territo ...
was annexed from the Portuguese in 1668. Today, both Ceuta and Melilla still remain under Spanish control, together with smaller islets known as the ''presidios menores'' (Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, Alhucemas Islands, las Islas de Alhucemas, Chafarinas Islands, las Islas de Chafarinas).
Spanish empire
 The Spanish Empire was one of the first Global Empire, global empires. It was also one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in world history. In the 16th century, Spain and Portugal were in the vanguard of European global exploration and colonial expansion. The two kingdoms on the conquest and Iberian Peninsula competed with each other in opening of trade routes across the oceans. Spanish imperial conquest and colonization began with the Canary Islands in 1312 and 1402. which began the Canary Islands#Castilian conquest, Castilian conquest of the Canary Islands, completed in 1495.
The Spanish Empire was one of the first Global Empire, global empires. It was also one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in world history. In the 16th century, Spain and Portugal were in the vanguard of European global exploration and colonial expansion. The two kingdoms on the conquest and Iberian Peninsula competed with each other in opening of trade routes across the oceans. Spanish imperial conquest and colonization began with the Canary Islands in 1312 and 1402. which began the Canary Islands#Castilian conquest, Castilian conquest of the Canary Islands, completed in 1495.
 In the 15th and 16th centuries, trade flourished across the Atlantic between Spain and the Americas and across the Pacific between East Asia and Mexico via the Philippines. Spanish Conquistadors, operating privately, deposed the Aztec, Inca Empire, Inca and Maya civilization, Maya governments with extensive help from local factions and took control of vast stretches of land. In the Philippines, the Spanish, using Mexican Conquistadors like Juan de Salcedo, conquered the History of the Philippines (900–1565), kingdoms and sultanates of the islands by pitting Pagans and Muslims against each other, thus employing the principle of "Divide and Conquer". They considered their war against the native Muslims of the Southeast Asia an extension of the Spanish
In the 15th and 16th centuries, trade flourished across the Atlantic between Spain and the Americas and across the Pacific between East Asia and Mexico via the Philippines. Spanish Conquistadors, operating privately, deposed the Aztec, Inca Empire, Inca and Maya civilization, Maya governments with extensive help from local factions and took control of vast stretches of land. In the Philippines, the Spanish, using Mexican Conquistadors like Juan de Salcedo, conquered the History of the Philippines (900–1565), kingdoms and sultanates of the islands by pitting Pagans and Muslims against each other, thus employing the principle of "Divide and Conquer". They considered their war against the native Muslims of the Southeast Asia an extension of the Spanish Reconquista
The ' ( Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the Na ...
.
This New World empire was at first a disappointment, as the natives had little to trade. Diseases such as smallpox and measles that arrived with the colonizers devastated the native populations, especially in the densely populated regions of the Aztec, Maya and Inca civilizations, and this reduced the economic potential of conquered areas. Estimates of the pre-Columbian population of the Americas vary but possibly stood at 100 million—one fifth of humanity in 1492. Between 1500 and 1600 the population of the Americas was halved. In Mexico alone, it has been estimated that the pre-conquest population of around 25 million people was reduced within 80 years to about 1.3 million.
In the 1520s, large-scale extraction of silver from the rich deposits of Mexico's Guanajuato began to be greatly augmented by the silver mines in Mexico's Zacatecas and Bolivia's Potosí from 1546. These silver shipments re-oriented the Spanish economy, leading to the importation of luxuries and grain. The resource-rich colonies of Spain thus caused large cash inflows for the country. They also became indispensable in financing the military capability of Habsburg Spain in its long series of European and North African wars, though, with the exception of a few years in the 17th century, Taxes in Castile were the most important source of revenue.
 Spain enjoyed a Spanish Golden Age, cultural golden age in the 16th and 17th centuries. For a time, the Spanish Empire dominated the oceans with its experienced Spanish navy, navy and ruled the European battlefield with its fearsome and well trained infantry, the famous '.
The financial burden within the peninsula was on the backs of the peasant class while the nobility enjoyed an increasingly lavish lifestyle. From the time beginning with the incorporation of the Portuguese Empire in 1580 (lost in 1640) until the loss of its American colonies in the 19th century, Spain maintained one of the largest empires in the world even though it suffered military and economic misfortunes from the 1640s.
Religion played a very strong role in the spread of the Spanish empire. The thought that Spain could bring Christianity to the New World and protect Catholicism in Europe certainly played a strong role in the expansion of Spain's empire.
Spain enjoyed a Spanish Golden Age, cultural golden age in the 16th and 17th centuries. For a time, the Spanish Empire dominated the oceans with its experienced Spanish navy, navy and ruled the European battlefield with its fearsome and well trained infantry, the famous '.
The financial burden within the peninsula was on the backs of the peasant class while the nobility enjoyed an increasingly lavish lifestyle. From the time beginning with the incorporation of the Portuguese Empire in 1580 (lost in 1640) until the loss of its American colonies in the 19th century, Spain maintained one of the largest empires in the world even though it suffered military and economic misfortunes from the 1640s.
Religion played a very strong role in the spread of the Spanish empire. The thought that Spain could bring Christianity to the New World and protect Catholicism in Europe certainly played a strong role in the expansion of Spain's empire.
Spanish Kingdoms under the 'Great' Habsburgs (16th century)
Charles I, Holy Emperor
 Spain's world empire reached its greatest territorial extent in the late 18th century but it was under the Habsburg dynasty in the 16th and 17th centuries it reached the peak of its power and declined. The Iberian Union with Portugal meant that the monarch of Castile was also the monarch of Portugal, but they were ruled as separate entities both on the peninsula and in Spanish America and Brazil. In 1640, the House of Braganza revolted against Spanish rule and reasserted Portugal's independence.
When Spain's first Habsburg ruler Charles I of Spain, Charles I became king of Spain in 1516 (with his mother and co-monarch Queen Juana I effectively powerless and kept imprisoned till her death in 1555), Spain became central to the dynastic struggles of Europe. After he became king of Spain, Charles also became Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor and because of his widely scattered domains was not often in Spain.
In 1556 Charles abdicated from his positions, giving his Spanish empire to his only surviving son,
Spain's world empire reached its greatest territorial extent in the late 18th century but it was under the Habsburg dynasty in the 16th and 17th centuries it reached the peak of its power and declined. The Iberian Union with Portugal meant that the monarch of Castile was also the monarch of Portugal, but they were ruled as separate entities both on the peninsula and in Spanish America and Brazil. In 1640, the House of Braganza revolted against Spanish rule and reasserted Portugal's independence.
When Spain's first Habsburg ruler Charles I of Spain, Charles I became king of Spain in 1516 (with his mother and co-monarch Queen Juana I effectively powerless and kept imprisoned till her death in 1555), Spain became central to the dynastic struggles of Europe. After he became king of Spain, Charles also became Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor and because of his widely scattered domains was not often in Spain.
In 1556 Charles abdicated from his positions, giving his Spanish empire to his only surviving son, Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal fro ...
, and the Holy Roman Empire to his brother, Ferdinand. Philip treated Castile as the foundation of his empire, but the population of Castile (about a third of France's) was never large enough to provide the soldiers needed to support the Empire. His marriage to Mary I of England, Mary Tudor allied England with Spain.
Philip II and the wars of religion
 In the 1560s, plans to consolidate control of the Netherlands led to unrest, which gradually led to the Calvinism, Calvinist leadership of the revolt and the
In the 1560s, plans to consolidate control of the Netherlands led to unrest, which gradually led to the Calvinism, Calvinist leadership of the revolt and the Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Re ...
. The Dutch armies waged a war of maneuver warfare, maneuver and siege, successfully avoiding pitched battle, set piece battles. This conflict consumed much Spanish expenditure during the later 16th century. Other extremely expensive failures included an attempt to invade Protestant England in 1588 that produced the worst military disaster in Spanish history when the Spanish Armada
The Spanish Armada (a.k.a. the Enterprise of England, es, Grande y Felicísima Armada, links=no, lit=Great and Most Fortunate Navy) was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by the Duke of Medina Sidonia, an a ...
—costing 10 million ducats—was scattered by a freak storm. Over 8,000 English sailors died from diseases such as dysentery and typhus while the Spanish Armada was at sea.
Economic and administrative problems multiplied in Castile (historical region), Castile, and the weakness of the native economy became evident in the following century. Rising price revolution, inflation, financially draining wars in Europe, the ongoing aftermath of the Expulsion of Jews from Spain, expulsion of the Jews and Moors from Spain, and Spain's growing dependency on the silver imports, combined to cause several bankruptcies that caused economic crisis in the country, especially in heavily burdened Castile. The Great Plague of Seville, great plague of 1596–1602 killed 600,000 to 700,000 people, or about 10% of the population. Altogether more than 1,250,000 deaths resulted from the extreme incidence of plague in 17th-century Spain. Economically, the plague destroyed the labor force as well as creating a psychological blow to an already problematic Spain.

The cultural Golden Age (''Siglo de Oro'')
 The Spanish Golden Age (in Spanish, ''Siglo de Oro'') was a period of flourishing arts and letters in the Spanish Empire (now Spain and the Spanish-speaking countries of Latin America), coinciding with the political decline and fall of the Habsburgs (Philip III of Spain, Philip III, Philip IV of Spain, Philip IV and Charles II of Spain, Charles II). Arts during the Golden Age flourished despite the decline of the empire in the 17th century. The last great writer of the age, Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz, died in New Spain in 1695.
The Habsburgs, both in Spain and Austria, were great patrons of art in their countries. ''
The Spanish Golden Age (in Spanish, ''Siglo de Oro'') was a period of flourishing arts and letters in the Spanish Empire (now Spain and the Spanish-speaking countries of Latin America), coinciding with the political decline and fall of the Habsburgs (Philip III of Spain, Philip III, Philip IV of Spain, Philip IV and Charles II of Spain, Charles II). Arts during the Golden Age flourished despite the decline of the empire in the 17th century. The last great writer of the age, Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz, died in New Spain in 1695.
The Habsburgs, both in Spain and Austria, were great patrons of art in their countries. ''El Escorial
El Escorial, or the Royal Site of San Lorenzo de El Escorial ( es, Monasterio y Sitio de El Escorial en Madrid), or Monasterio del Escorial (), is a historical residence of the King of Spain located in the town of San Lorenzo de El Escorial, ...
'', the great royal monastery built by King Philip II of Spain, Philip II, invited the attention of some of Europe's greatest architects and painters. Diego Velázquez, regarded as one of the most influential painters of European history and a greatly respected artist in his own time, cultivated a relationship with King Philip IV and his chief minister, the Count-Duke of Olivares, leaving us several portraits that demonstrate his style and skill. El Greco, a respected Greek artist from the period, settled in Spain, and infused Spanish art with the styles of the Italian renaissance and helped create a uniquely Spanish style of painting.
Some of Spain's greatest music is regarded as having been written in the period. Such composers as Tomás Luis de Victoria, Luis de Milán and Alonso Lobo helped to shape Renaissance music and the styles of counterpoint and polychoral music, and their influence lasted far into the Baroque music, Baroque period.
Spanish literature blossomed as well, most famously demonstrated in the work of Miguel de Cervantes, the author of ''Don Quixote, Don Quixote de la Mancha''. Spain's most prolific playwright, Lope de Vega, wrote possibly as many as one thousand plays over his lifetime, over four hundred of which survive to the present day.
Decline under the 'Minor' Habsburgs (17th century)
Spain's severe financial difficulties began in the middle 16th century, and continued for the remainder of Habsburg rule. Despite the successes of Spanish armies, at home the period was marked by monetary inflation, mercantilism, and a variety of government monopolies and interventions. Spanish kings were forced to declare sovereign defaults nine times between 1557 and 1666.
Philip II died in 1598, and was succeeded by his son Philip III of Spain, Philip III. In his reign (1598–1621) a ten-year truce with the Dutch was overshadowed in 1618 by Spain's involvement in the European-wide Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battl ...
. Government policy was dominated by favorites, but it was also the period in which the geniuses of Miguel de Cervantes, Cervantes and El Greco flourished. Philip III was succeeded in 1621 by his son Philip IV of Spain (reigned 1621–65). Much of the policy was conducted by the Gaspar de Guzmán, Count-Duke of Olivares, Count-Duke of Olivares. The Count-Duke of Olivares was the inept prime minister from 1621 to 1643. He over-exerted Spain in foreign affairs and unsuccessfully attempted domestic reform. His policy of committing Spain to recapture Holland led to a renewal of the Eighty Years' War while Spain was also embroiled in the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648). His attempts to centralise power and increase wartime taxation led to revolts in Catalonia and in Portugal, which brought about his downfall. The Spanish "Golden Age" politically ends no later than 1659, with the Treaty of the Pyrenees, ratified between France and Habsburg Spain.
During the long regency for Charles II of Spain, Charles II, the last of the Spanish Habsburgs, favouritism milked Spain's treasury, and Spain's government operated principally as a dispenser of patronage. Plague, famine, floods, drought, and renewed war with France wasted the country. The Peace of the Pyrenees (1659) had ended fifty years of warfare with France, whose king, Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV, found the temptation to exploit a weakened Spain too great. Louis instigated the War of Devolution (1667–68) to acquire the Spanish Netherlands.
By the 17th century, the Catholic Church and Spain had showcased a close bond to one another, attesting to the fact that Spain was virtually free of Protestantism during the 16th century. In 1620, there were 100,000 Spaniards in the clergy; by 1660 the number had grown to about 200,000, and the Church owned 20% of all the land in Spain. The Spanish bureaucracy in this period was highly centralized, and totally reliant on the king for its efficient functioning. Under Charles II, the councils became the sinecures of wealthy aristocrats despite various attempt at reform. Political commentators in Spain, known as arbitristas, proposed a number of measures to reverse the decline of the Spanish economy, with limited success. In rural areas of Spain, heavy taxation of peasants reduced agricultural output as peasants in the countryside migrated to the cities. The influx of silver from the Americas has been cited as the cause of inflation, although only one fifth of the precious metal, i.e. the ''quinto real'' (royal fifth), actually went to Spain. A prominent internal factor was the Spanish economy's dependence on the export of luxurious Merino wool, which had its markets in northern Europe reduced by war and growing competition from cheaper textiles.
The once proud Spanish army was falling far behind its foes. It did badly at Bergen op Zoom in 1622, and finance was not to blame. The Dutch won very easily at Hertogenbosch and Wesel in 1629. In 1632 the Dutch captured the strategic fortress town of Maastricht, repulsing three relief armies and dooming the Spanish to defeat.
While Spain built a rich American Empire that exported a silver treasure fleet every year, it was unable to focus its financial, military, and diplomatic power on building up its Spanish base. The Crown's dedication to destroying Protestantism through almost constant warfare created a cultural ethos among Spanish leaders that undermined the opportunity for economic modernization or industrialization. When Philip II died in 1598, his treasury spent most of its income on funding the huge deficit, which continued to grow. In peninsular Spain, the productive forces were undermined by steady inflation, heavy taxation, immigration of ambitious youth to the colonies, and by depopulation. Industry went into reverse – Seville in 1621 operated 400 looms, where it had 16,000 a century before. Religiosity led by saints and mystics, missionaries and crusaders, theologians and friars dominated Spanish culture, with the psychology of a reward in the next world. Palmer and Colton argue:
: the generations of crusading against infidels, even, heathens and heretics had produced an exceptionally large number of minor aristocrats, chevaliers, dons, and hidalgos, who as a class were contemptuous of work and who were numerous enough and close enough to the common people to impress their haughty indifference upon the country as a whole. Elliott cites the achievements of Castille in many areas, especially high culture. He finds:
:A certain paradox in the fact that the achievement of the two most outstanding creative artists of Castile – Cervantes and Velázquez – was shot through with a deep sense of disillusionment and failure; but the paradox was itself a faithful reflection of the paradox of sixteenth-and seventeenth-century Castile. For here was a country which had climbed to the heights and sunk to the depths; which had achieved everything and lost everything; which had conquered the world only to be vanquished itself. The Spanish achievement of the sixteenth century was essentially the work of Castile, but so also was the Spanish disaster of the seventeenth; and it was José Ortega y Gasset, Ortega y Gasset who expressed the paradox most clearly when he wrote what may serve as an epitaph on the Spain of the House of Austria: ‘Castile has made Spain, and Castile has destroyed it.’
The Habsburg dynasty became extinct in Spain with Charles II's death in 1700, and the
The Spanish "Golden Age" politically ends no later than 1659, with the Treaty of the Pyrenees, ratified between France and Habsburg Spain.
During the long regency for Charles II of Spain, Charles II, the last of the Spanish Habsburgs, favouritism milked Spain's treasury, and Spain's government operated principally as a dispenser of patronage. Plague, famine, floods, drought, and renewed war with France wasted the country. The Peace of the Pyrenees (1659) had ended fifty years of warfare with France, whose king, Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV, found the temptation to exploit a weakened Spain too great. Louis instigated the War of Devolution (1667–68) to acquire the Spanish Netherlands.
By the 17th century, the Catholic Church and Spain had showcased a close bond to one another, attesting to the fact that Spain was virtually free of Protestantism during the 16th century. In 1620, there were 100,000 Spaniards in the clergy; by 1660 the number had grown to about 200,000, and the Church owned 20% of all the land in Spain. The Spanish bureaucracy in this period was highly centralized, and totally reliant on the king for its efficient functioning. Under Charles II, the councils became the sinecures of wealthy aristocrats despite various attempt at reform. Political commentators in Spain, known as arbitristas, proposed a number of measures to reverse the decline of the Spanish economy, with limited success. In rural areas of Spain, heavy taxation of peasants reduced agricultural output as peasants in the countryside migrated to the cities. The influx of silver from the Americas has been cited as the cause of inflation, although only one fifth of the precious metal, i.e. the ''quinto real'' (royal fifth), actually went to Spain. A prominent internal factor was the Spanish economy's dependence on the export of luxurious Merino wool, which had its markets in northern Europe reduced by war and growing competition from cheaper textiles.
The once proud Spanish army was falling far behind its foes. It did badly at Bergen op Zoom in 1622, and finance was not to blame. The Dutch won very easily at Hertogenbosch and Wesel in 1629. In 1632 the Dutch captured the strategic fortress town of Maastricht, repulsing three relief armies and dooming the Spanish to defeat.
While Spain built a rich American Empire that exported a silver treasure fleet every year, it was unable to focus its financial, military, and diplomatic power on building up its Spanish base. The Crown's dedication to destroying Protestantism through almost constant warfare created a cultural ethos among Spanish leaders that undermined the opportunity for economic modernization or industrialization. When Philip II died in 1598, his treasury spent most of its income on funding the huge deficit, which continued to grow. In peninsular Spain, the productive forces were undermined by steady inflation, heavy taxation, immigration of ambitious youth to the colonies, and by depopulation. Industry went into reverse – Seville in 1621 operated 400 looms, where it had 16,000 a century before. Religiosity led by saints and mystics, missionaries and crusaders, theologians and friars dominated Spanish culture, with the psychology of a reward in the next world. Palmer and Colton argue:
: the generations of crusading against infidels, even, heathens and heretics had produced an exceptionally large number of minor aristocrats, chevaliers, dons, and hidalgos, who as a class were contemptuous of work and who were numerous enough and close enough to the common people to impress their haughty indifference upon the country as a whole. Elliott cites the achievements of Castille in many areas, especially high culture. He finds:
:A certain paradox in the fact that the achievement of the two most outstanding creative artists of Castile – Cervantes and Velázquez – was shot through with a deep sense of disillusionment and failure; but the paradox was itself a faithful reflection of the paradox of sixteenth-and seventeenth-century Castile. For here was a country which had climbed to the heights and sunk to the depths; which had achieved everything and lost everything; which had conquered the world only to be vanquished itself. The Spanish achievement of the sixteenth century was essentially the work of Castile, but so also was the Spanish disaster of the seventeenth; and it was José Ortega y Gasset, Ortega y Gasset who expressed the paradox most clearly when he wrote what may serve as an epitaph on the Spain of the House of Austria: ‘Castile has made Spain, and Castile has destroyed it.’
The Habsburg dynasty became extinct in Spain with Charles II's death in 1700, and the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phili ...
ensued in which the other European powers tried to assume control of the Spanish monarchy. King Louis XIV of France eventually lost the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phili ...
. The victors were Britain, the Dutch Republic and Austria. They allowed the crown of Spain to pass to the Bourbon dynasty
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a European dynasty of French origin, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Kingdom of Navarre, Navarre in the 16th century. By the 18th century, memb ...
, provided that Spain and France never merged.
After the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phili ...
, the assimilation of the Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon ( , ) an, Corona d'Aragón ; ca, Corona d'Aragó, , , ; es, Corona de Aragón ; la, Corona Aragonum . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of ...
by the Crown of Castile, Castilian Crown, through the Nueva Planta decrees, Nueva Planta Decrees, was the first step in the creation of the Spanish nation state. And like other European nation-states in formation, it was not on a uniform Ethnic group, ethnic basis, but by imposing the political and cultural characteristics of the dominant ethnic group, in this case the Castilian, on those of the other ethnic groups, become national minorities to be assimilated through nationalist policies. These nationalist policies, sometimes very aggressive,
Spain under the Bourbons, 1715–1808
 Charles II of Spain, Charles II died in 1700, and having no direct heir, was succeeded by his great-nephew Philip V of Spain, Philippe d'Anjou, a French prince. The
Charles II of Spain, Charles II died in 1700, and having no direct heir, was succeeded by his great-nephew Philip V of Spain, Philippe d'Anjou, a French prince. The War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phili ...
(1700–1714) pitted proponents of the Bourbon succession against those for the Hapsburg. Concern among other European powers that Spain and France united under a single Bourbon monarch would upset the Balance of power in international relations, balance of power, the war pitted powerful France and fairly strong Spain against the Grand Alliance of England, Portugal, Savoy, the Netherlands and Austria. After an extended conflict, especially in Spain, the treaty of Utrecht recognized Philip V of Spain, Philip, Duke of Anjou, Louis XIV's grandson, as King of Spain (as Philip V), thus confirming the succession stipulated in the will of the Charles II of Spain. However, Philip was compelled to renounce for himself and his descendants any right to the French throne, despite some doubts as to the lawfulness of such an act. Spain's Italian territories were apportioned.
 Philip V of Spain, Philip V signed the ''Nueva Planta decrees, Decreto de Nueva Planta'' in 1715. This new law revoked most of the historical rights and privileges of the different kingdoms that formed the Spanish Crown, especially the
Philip V of Spain, Philip V signed the ''Nueva Planta decrees, Decreto de Nueva Planta'' in 1715. This new law revoked most of the historical rights and privileges of the different kingdoms that formed the Spanish Crown, especially the Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon ( , ) an, Corona d'Aragón ; ca, Corona d'Aragó, , , ; es, Corona de Aragón ; la, Corona Aragonum . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of ...
, unifying them under the laws of Castile, where the Castilian Cortes Generales had been more receptive to the royal wish. Spain became culturally and politically a follower of Absolutism (European history), absolutist France. Lynch says Philip V advanced the government only marginally over that of his predecessors and was more of a liability than the incapacitated Charles II; when a conflict came up between the interests of Spain and France, he usually favored France.
War of Spanish Independence and American wars of independence
War of Spanish Independence (1808–1814)
 In the late 18th century, Bourbon-ruled Spain had an alliance with Bourbon-ruled France, and therefore did not have to fear a land war. Its only serious enemy was Britain, which had a powerful navy; Spain therefore concentrated its resources on its navy. When the French Revolution overthrew the Bourbons, a land war with France became a threat which the king tried to avoid. The Spanish army was ill-prepared. The officer corps was selected primarily on the basis of royal patronage, rather than merit. About a third of the junior officers had been promoted from the ranks, and while they did have talent they had few opportunities for promotion or leadership. The rank-and-file were poorly trained peasants. Elite units included foreign regiments of Irishmen, Italians, Swiss, and Walloons, in addition to elite artillery and engineering units. Equipment was old-fashioned and in disrepair. The army lacked its own horses, oxen and mules for transportation, so these auxiliaries were operated by civilians, who might run away if conditions looked bad. In combat, small units fought well, but their old-fashioned tactics were hardly of use against the Napoleonic forces, despite repeated desperate efforts at last-minute reform. When war broke out with France in 1808, the army was deeply unpopular. Leading generals were assassinated, and the army proved incompetent to handle command-and-control. Junior officers from peasant families deserted and went over to the insurgents; many units disintegrated. Spain was unable to mobilize its artillery or cavalry. In the war, there was one victory at the Battle of Bailén, and many humiliating defeats. Conditions steadily worsened, as the insurgents increasingly took control of Spain's battle against Napoleon. Napoleon ridiculed the army as "the worst in Europe"; the British who had to work with it agreed. It was not the Army that defeated Napoleon, but the insurgent peasants whom Napoleon ridiculed as packs of "bandits led by monks" (they in turn believed Napoleon was the devil). By 1812, the army controlled only scattered enclaves, and could only harass the French with occasional raids. The morale of the army had reached a nadir, and reformers stripped the aristocratic officers of most of their legal privileges.
Spain initially sided against France in the Napoleonic Wars, but the defeat of her army early in the war led to Charles IV of Spain, Charles IV's pragmatic decision to align with the revolutionary French. Spain was put under a British blockade, and her colonies began to trade independently with Britain, but Britain invaded and was the defeat in the British invasions of the Río de la Plata in South America (1806 and 1807) without help from mainland Spain, which emboldened independence and revolutionary hopes in Spain's vast American colonies. A major Franco-Spanish fleet was lost at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805, prompting the vacillating king of Spain to reconsider his difficult alliance with Napoleon. Spain temporarily broke off from the Continental System, and Napoleon – irritated with the Bourbon kings of Spain – invaded Spain in 1808 and deposed Ferdinand VII of Spain, Ferdinand VII, who had been on the throne only forty-eight days after his father's abdication in March 1808. On July 20, 1808,
In the late 18th century, Bourbon-ruled Spain had an alliance with Bourbon-ruled France, and therefore did not have to fear a land war. Its only serious enemy was Britain, which had a powerful navy; Spain therefore concentrated its resources on its navy. When the French Revolution overthrew the Bourbons, a land war with France became a threat which the king tried to avoid. The Spanish army was ill-prepared. The officer corps was selected primarily on the basis of royal patronage, rather than merit. About a third of the junior officers had been promoted from the ranks, and while they did have talent they had few opportunities for promotion or leadership. The rank-and-file were poorly trained peasants. Elite units included foreign regiments of Irishmen, Italians, Swiss, and Walloons, in addition to elite artillery and engineering units. Equipment was old-fashioned and in disrepair. The army lacked its own horses, oxen and mules for transportation, so these auxiliaries were operated by civilians, who might run away if conditions looked bad. In combat, small units fought well, but their old-fashioned tactics were hardly of use against the Napoleonic forces, despite repeated desperate efforts at last-minute reform. When war broke out with France in 1808, the army was deeply unpopular. Leading generals were assassinated, and the army proved incompetent to handle command-and-control. Junior officers from peasant families deserted and went over to the insurgents; many units disintegrated. Spain was unable to mobilize its artillery or cavalry. In the war, there was one victory at the Battle of Bailén, and many humiliating defeats. Conditions steadily worsened, as the insurgents increasingly took control of Spain's battle against Napoleon. Napoleon ridiculed the army as "the worst in Europe"; the British who had to work with it agreed. It was not the Army that defeated Napoleon, but the insurgent peasants whom Napoleon ridiculed as packs of "bandits led by monks" (they in turn believed Napoleon was the devil). By 1812, the army controlled only scattered enclaves, and could only harass the French with occasional raids. The morale of the army had reached a nadir, and reformers stripped the aristocratic officers of most of their legal privileges.
Spain initially sided against France in the Napoleonic Wars, but the defeat of her army early in the war led to Charles IV of Spain, Charles IV's pragmatic decision to align with the revolutionary French. Spain was put under a British blockade, and her colonies began to trade independently with Britain, but Britain invaded and was the defeat in the British invasions of the Río de la Plata in South America (1806 and 1807) without help from mainland Spain, which emboldened independence and revolutionary hopes in Spain's vast American colonies. A major Franco-Spanish fleet was lost at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805, prompting the vacillating king of Spain to reconsider his difficult alliance with Napoleon. Spain temporarily broke off from the Continental System, and Napoleon – irritated with the Bourbon kings of Spain – invaded Spain in 1808 and deposed Ferdinand VII of Spain, Ferdinand VII, who had been on the throne only forty-eight days after his father's abdication in March 1808. On July 20, 1808, Joseph Bonaparte
it, Giuseppe-Napoleone Buonaparte es, José Napoleón Bonaparte
, house = Bonaparte
, father = Carlo Buonaparte
, mother = Letizia Ramolino
, birth_date = 7 January 1768
, birth_place = Corte, Corsica, Republic ...
, eldest brother of Napoleon Bonaparte, entered Madrid and established a government by which he became King of Spain, serving as a surrogate for Napoleon.
 The former Spanish king was dethroned by Napoleon, who put his own brother on the throne. Spaniards revolted. Thompson says the Spanish revolt was, "a reaction against new institutions and ideas, a movement for loyalty to the old order: to the hereditary crown of the Most Catholic kings, which Napoleon, an excommunicated enemy of the Pope, had put on the head of a Frenchman; to the Catholic Church persecuted by republicans who had desecrated churches, murdered priests, and enforced a "loi des cultes"; and to local and provincial rights and privileges threatened by an efficiently centralized government. ''Junta (Peninsular War), Juntas'' were formed all across Spain that pronounced themselves in favor of Ferdinand VII. On September 26, 1808, a Central Junta was formed in the town of Aranjuez to coordinate the nationwide struggle against the French. Initially, the Central Junta declared support for Ferdinand VII, and convened a "Cortes Generales, General and Extraordinary Cortes" for all the kingdoms of the Spanish Monarchy. On February 22 and 23, 1809, a popular insurrection against the French occupation broke out all over Spain.
The peninsular campaign was a disaster for France. Napoleon did well when he was in direct command, but that followed severe losses, and when he left in 1809 conditions grew worse for France. Vicious reprisals, famously portrayed by Goya in "The Disasters of War", only made the Spanish guerrillas angrier and more active; the war in Spain proved to be a major, long-term drain on French money, manpower and prestige.
The former Spanish king was dethroned by Napoleon, who put his own brother on the throne. Spaniards revolted. Thompson says the Spanish revolt was, "a reaction against new institutions and ideas, a movement for loyalty to the old order: to the hereditary crown of the Most Catholic kings, which Napoleon, an excommunicated enemy of the Pope, had put on the head of a Frenchman; to the Catholic Church persecuted by republicans who had desecrated churches, murdered priests, and enforced a "loi des cultes"; and to local and provincial rights and privileges threatened by an efficiently centralized government. ''Junta (Peninsular War), Juntas'' were formed all across Spain that pronounced themselves in favor of Ferdinand VII. On September 26, 1808, a Central Junta was formed in the town of Aranjuez to coordinate the nationwide struggle against the French. Initially, the Central Junta declared support for Ferdinand VII, and convened a "Cortes Generales, General and Extraordinary Cortes" for all the kingdoms of the Spanish Monarchy. On February 22 and 23, 1809, a popular insurrection against the French occupation broke out all over Spain.
The peninsular campaign was a disaster for France. Napoleon did well when he was in direct command, but that followed severe losses, and when he left in 1809 conditions grew worse for France. Vicious reprisals, famously portrayed by Goya in "The Disasters of War", only made the Spanish guerrillas angrier and more active; the war in Spain proved to be a major, long-term drain on French money, manpower and prestige.
 In March 1812, the Cortes of Cádiz created the first modern Spanish constitution, the Spanish Constitution of 1812, Constitution of 1812 (informally named ''La Pepa''). This constitution provided for a separation of the powers of the executive and the legislative branches of government. The Cortes was to be elected by universal suffrage, albeit by an indirect method. Each member of the Cortes was to represent 70,000 people. Members of the Cortes were to meet in annual sessions. The King was prevented from either convening or proroguing the Cortes. Members of the Cortes were to serve single two-year terms. They could not serve consecutive terms; a member could serve a second term only by allowing someone else to serve a single intervening term in office. This attempt at the development of a modern constitutional government lasted from 1808 until 1814. Leaders of the liberals or reformist forces during this revolution were José Moñino, 1st Count of Floridablanca, José Moñino, Count of Floridablanca, Gaspar Melchor de Jovellanos and Pedro Rodríguez, Conde de Campomanes. Born in 1728, Floridablanca was eighty years of age at the time of the revolutionary outbreak in 1808. He had served as Prime Minister under King Charles III of Spain from 1777 until 1792; However, he tended to be suspicious of the popular spontaneity and resisted a revolution. Born in 1744, Jovellanos was somewhat younger than Floridablanco. A writer and follower of the philosophers of the Enlightenment tradition of the previous century, Jovellanos had served as Minister of Justice from 1797 to 1798 and now commanded a substantial and influential group within the Central Junta. However, Jovellanos had been imprisoned by Manuel Godoy, Prince of the Peace, Manuel de Godoy, Duke of Alcudia, who had served as the prime minister, virtually running the country as a dictator from 1792 until 1798 and from 1801 until 1808. Accordingly, even Jovellanos tended to be somewhat overly cautious in his approach to the revolutionary upsurge that was sweeping Spain in 1808.
The Spanish army was stretched as it fought Napoleon's forces because of a lack of supplies and too many untrained recruits, but at Battle of Bailén, Bailén in June 1808, the Spanish army inflicted the first major defeat suffered by a Napoleonic army; this resulted in the collapse of French power in Spain. Napoleon took personal charge and with fresh forces, defeating the Spanish and British armies in a campaigns of attrition. After this the Spanish armies lost every battle they fought against the French imperial forces, but were never annihilated; after battles they retreated into the mountains to regroup and launch new attacks and raids on unsuspecting French forces. Guerrilla forces sprang up all over Spain and, with the army, tied down huge numbers of Napoleon's troops, making it difficult to sustain concentrated attacks on Spanish forces. The attacks and raids of the Spanish army and guerrillas became a massive drain on Napoleon's military and economic resources. In this war, Spain was aided by the British and Portuguese, led by the Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Duke of Wellington. The Duke of Wellington fought Napoleon's forces in the Peninsular War, with Joseph Bonaparte playing a minor role as king at Madrid. The brutal war was one of the first guerrilla warfare, guerrilla wars in modern Western history. French supply lines stretching across Spain were mauled repeatedly by the Spanish armies and guerrilla forces; thereafter, Napoleon's armies were never able to control much of the country and ending in French defeat. The war fluctuated, with Wellington spending several years behind his fortresses in Portugal while launching occasional campaigns into Spain.
After Napoleon's disastrous 1812 campaign in Russia, Napoleon began to recall his forces for the defence of France against the advancing Russian and other coalition forces, leaving his forces in Spain increasingly undermanned and on the defensive against the advancing Spanish, British and Portuguese armies. At the Battle of Vitoria in 1813, an allied army under the Duke of Wellington decisively defeated the French and in 1814 Ferdinand VII was restored as King of Spain.
In March 1812, the Cortes of Cádiz created the first modern Spanish constitution, the Spanish Constitution of 1812, Constitution of 1812 (informally named ''La Pepa''). This constitution provided for a separation of the powers of the executive and the legislative branches of government. The Cortes was to be elected by universal suffrage, albeit by an indirect method. Each member of the Cortes was to represent 70,000 people. Members of the Cortes were to meet in annual sessions. The King was prevented from either convening or proroguing the Cortes. Members of the Cortes were to serve single two-year terms. They could not serve consecutive terms; a member could serve a second term only by allowing someone else to serve a single intervening term in office. This attempt at the development of a modern constitutional government lasted from 1808 until 1814. Leaders of the liberals or reformist forces during this revolution were José Moñino, 1st Count of Floridablanca, José Moñino, Count of Floridablanca, Gaspar Melchor de Jovellanos and Pedro Rodríguez, Conde de Campomanes. Born in 1728, Floridablanca was eighty years of age at the time of the revolutionary outbreak in 1808. He had served as Prime Minister under King Charles III of Spain from 1777 until 1792; However, he tended to be suspicious of the popular spontaneity and resisted a revolution. Born in 1744, Jovellanos was somewhat younger than Floridablanco. A writer and follower of the philosophers of the Enlightenment tradition of the previous century, Jovellanos had served as Minister of Justice from 1797 to 1798 and now commanded a substantial and influential group within the Central Junta. However, Jovellanos had been imprisoned by Manuel Godoy, Prince of the Peace, Manuel de Godoy, Duke of Alcudia, who had served as the prime minister, virtually running the country as a dictator from 1792 until 1798 and from 1801 until 1808. Accordingly, even Jovellanos tended to be somewhat overly cautious in his approach to the revolutionary upsurge that was sweeping Spain in 1808.
The Spanish army was stretched as it fought Napoleon's forces because of a lack of supplies and too many untrained recruits, but at Battle of Bailén, Bailén in June 1808, the Spanish army inflicted the first major defeat suffered by a Napoleonic army; this resulted in the collapse of French power in Spain. Napoleon took personal charge and with fresh forces, defeating the Spanish and British armies in a campaigns of attrition. After this the Spanish armies lost every battle they fought against the French imperial forces, but were never annihilated; after battles they retreated into the mountains to regroup and launch new attacks and raids on unsuspecting French forces. Guerrilla forces sprang up all over Spain and, with the army, tied down huge numbers of Napoleon's troops, making it difficult to sustain concentrated attacks on Spanish forces. The attacks and raids of the Spanish army and guerrillas became a massive drain on Napoleon's military and economic resources. In this war, Spain was aided by the British and Portuguese, led by the Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Duke of Wellington. The Duke of Wellington fought Napoleon's forces in the Peninsular War, with Joseph Bonaparte playing a minor role as king at Madrid. The brutal war was one of the first guerrilla warfare, guerrilla wars in modern Western history. French supply lines stretching across Spain were mauled repeatedly by the Spanish armies and guerrilla forces; thereafter, Napoleon's armies were never able to control much of the country and ending in French defeat. The war fluctuated, with Wellington spending several years behind his fortresses in Portugal while launching occasional campaigns into Spain.
After Napoleon's disastrous 1812 campaign in Russia, Napoleon began to recall his forces for the defence of France against the advancing Russian and other coalition forces, leaving his forces in Spain increasingly undermanned and on the defensive against the advancing Spanish, British and Portuguese armies. At the Battle of Vitoria in 1813, an allied army under the Duke of Wellington decisively defeated the French and in 1814 Ferdinand VII was restored as King of Spain.
Independence of Spanish America
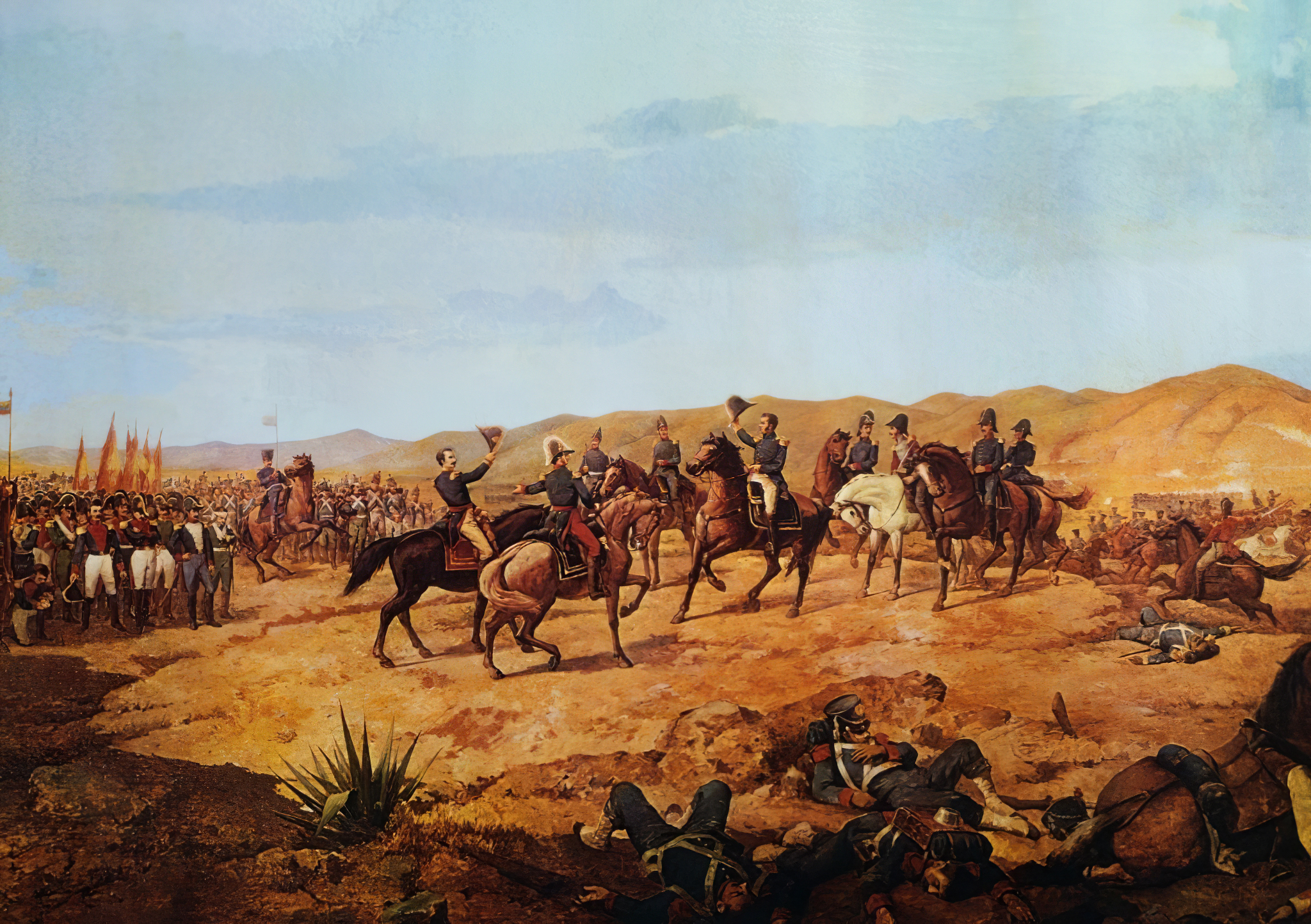 Spain lost all of its North and South American territories, except Cuba and Puerto Rico, in a complex series of revolts 1808–26. Spain was at war with Britain 1798–1808, and the British blockade cut Spain's ties to the overseas empire. Trade was handled by American and Dutch traders. The colonies thus had achieved economic independence from Spain, and set up temporary governments or juntas which were generally out of touch with the mother country. After 1814, as Napoleon was defeated and Ferdinand VII was back on the throne, the king sent armies to regain control and reimpose autocratic rule. In the next phase 1809–16, Spain defeated all the uprising. A second round 1816–25 was successful and drove the Spanish out of all of its mainland holdings. Spain had no help from European powers. Indeed, Britain (and the United States) worked against it. When they were cut off from Spain, the colonies saw a struggle for power between Spaniards who were born in Spain (called "peninsulares") and those of Spanish descent born in New Spain (called "creoles"). The creoles were the activists for independence. Multiple revolutions enabled the colonies to break free of the mother country. In 1824 the armies of generals José de San Martín of Argentina and Simón Bolívar of Venezuela defeated the last Spanish forces; the final defeat came at the Battle of Ayacucho in southern History of Peru, Peru. After that Spain played a minor role in international affairs. Business and trade in the ex-colonies were under British control. Spain kept only Cuba and Puerto Rico in the New World.
Spain lost all of its North and South American territories, except Cuba and Puerto Rico, in a complex series of revolts 1808–26. Spain was at war with Britain 1798–1808, and the British blockade cut Spain's ties to the overseas empire. Trade was handled by American and Dutch traders. The colonies thus had achieved economic independence from Spain, and set up temporary governments or juntas which were generally out of touch with the mother country. After 1814, as Napoleon was defeated and Ferdinand VII was back on the throne, the king sent armies to regain control and reimpose autocratic rule. In the next phase 1809–16, Spain defeated all the uprising. A second round 1816–25 was successful and drove the Spanish out of all of its mainland holdings. Spain had no help from European powers. Indeed, Britain (and the United States) worked against it. When they were cut off from Spain, the colonies saw a struggle for power between Spaniards who were born in Spain (called "peninsulares") and those of Spanish descent born in New Spain (called "creoles"). The creoles were the activists for independence. Multiple revolutions enabled the colonies to break free of the mother country. In 1824 the armies of generals José de San Martín of Argentina and Simón Bolívar of Venezuela defeated the last Spanish forces; the final defeat came at the Battle of Ayacucho in southern History of Peru, Peru. After that Spain played a minor role in international affairs. Business and trade in the ex-colonies were under British control. Spain kept only Cuba and Puerto Rico in the New World.
Reign of Ferdinand VII (1813–1833)
Aftermath of the Napoleonic wars
The Napoleonic wars had severe negative effects on Spain's long-term economic development. The Peninsular war ravaged towns and countryside alike, and the demographic impact was the worst of any Spanish war, with a sharp decline in population in many areas caused by casualties, outmigration, and disruption of family life. The marauding armies seized farmers' crops, and more importantly, farmers lost much of their livestock, their main capital asset. Severe poverty became widespread, reducing market demand, while the disruption of local and international trade, and the shortages of critical inputs, seriously hurt industry and services. The loss of a vast colonial empire reduced Spain's overall wealth, and by 1820 it had become one of Europe's poorest and least-developed societies; three-fourths of the people were illiterate. There was little industry beyond the production of textiles in Catalonia. Natural resources, such as coal and iron, were available for exploitation, but the transportation system was rudimentary, with few canals or navigable rivers, and road travel was slow and expensive. British railroad builders were pessimistic about the potential for freight and passenger traffic and did not invest. Eventually a small railway system was built, radiating from Madrid and bypassing the natural resources. The government relied on high tariffs, especially on grain, which further slowed economic development. For example, eastern Spain was unable to import inexpensive Italian wheat, and had to rely on expensive homegrown products carted in over poor roads. The export market collapsed apart from some agricultural products. Catalonia had some industry, but Castile remained the political and cultural center, and was not interested in promoting industry.
''Trienio liberal'' (1820–23)
The tumultuous three years of liberal rule that followed (1820–23) were marked by various absolutist conspiracies. The liberal government, which reminded European statesmen entirely too much of the governments of the French Revolution, was viewed with hostility by the Congress of Verona in 1822, and France was authorized to intervene. France crushed the liberal government with massive force in the so-called "Hundred Thousand Sons of Saint Louis" expedition, and Ferdinand was restored as absolute monarch in 1823. In Spain proper, this marked the end of the second Spanish bourgeois revolution.
"Ominous Decade" (1823–1833)
 In Spain, the failure of the second bourgeois revolution was followed by a period of uneasy peace for the next decade. Having borne only a female heir presumptive, it appeared that Ferdinand would be succeeded by his brother, Infante Carlos, Count of Molina, Infante Carlos of Spain. While Ferdinand aligned with the conservatives, fearing another national insurrection, he did not view Carlos's reactionary policies as a viable option. Ferdinand – resisting the wishes of his brother – decreed the Pragmatic Sanction of 1830, enabling his daughter Isabella to become Queen. Carlos, who made known his intent to resist the sanction, fled to Portugal.
In Spain, the failure of the second bourgeois revolution was followed by a period of uneasy peace for the next decade. Having borne only a female heir presumptive, it appeared that Ferdinand would be succeeded by his brother, Infante Carlos, Count of Molina, Infante Carlos of Spain. While Ferdinand aligned with the conservatives, fearing another national insurrection, he did not view Carlos's reactionary policies as a viable option. Ferdinand – resisting the wishes of his brother – decreed the Pragmatic Sanction of 1830, enabling his daughter Isabella to become Queen. Carlos, who made known his intent to resist the sanction, fled to Portugal.
Reign of Isabella II (1833–1868)
Ferdinand's death in 1833 and the accession of Isabella II of Spain, Isabella II as Queen of Spain sparked the First Carlist War (1833–39). Isabella was only three years old at the time so her mother, Maria Cristina of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, was named regent until her daughter came of age. Carlos invaded the Basque country in the north of Spain and attracted support from absolutist reactionaries and conservatives; these forces were known as the "Carlist" forces. The supporters of reform and of limitations on the absolutist rule of the Spanish throne rallied behind Isabella and the regent, Maria Cristina; these reformists were called "Christinos." Though Christino resistance to the insurrection seemed to have been overcome by the end of 1833, Maria Cristina's forces suddenly drove the Carlist armies from most of the Basque country. Carlos then appointed the Basque general Tomás de Zumalacárregui as his commander-in-chief. Zumalacárregui resuscitated the Carlist cause, and by 1835 had driven the Christino armies to the Ebro River and transformed the Carlist army from a demoralized band into a professional army of 30,000 of superior quality to the government forces. Zumalacárregui's death in 1835 changed the Carlists' fortunes. The Christinos found a capable general in Baldomero Espartero. His victory at the Battle of Luchana (1836) turned the tide of the war, and in 1839, the Convention of Vergara put an end to the first Carlist insurrection.Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
, but it was poorly organized and suppressed by 1849.
Isabella II of Spain, Isabella II took a more active role in government after coming of age, but she was unpopular throughout her reign (1833–68). There was another pronunciamiento in 1854 led General Leopoldo O'Donnell, intending to topple the discredited rule of Luis Sartorius, the Count of San Luis. A popular insurrection followed the coup and the Progressive Party (Spain), Progressive Party obtained widespread support in Spain and came to government in 1854. After 1856, O'Donnell, who had already marched on Madrid that year and ousted another Espartero ministry, attempted to form the Liberal Union (Spain), Liberal Union, his own political project. Following attacks on Ceuta by tribesmen based in Morocco, a Spanish-Moroccan War (1859), war against the latter country was successfully waged by generals O'Donnell and Juan Prim.
Sexenio Democrático (1868–1874)
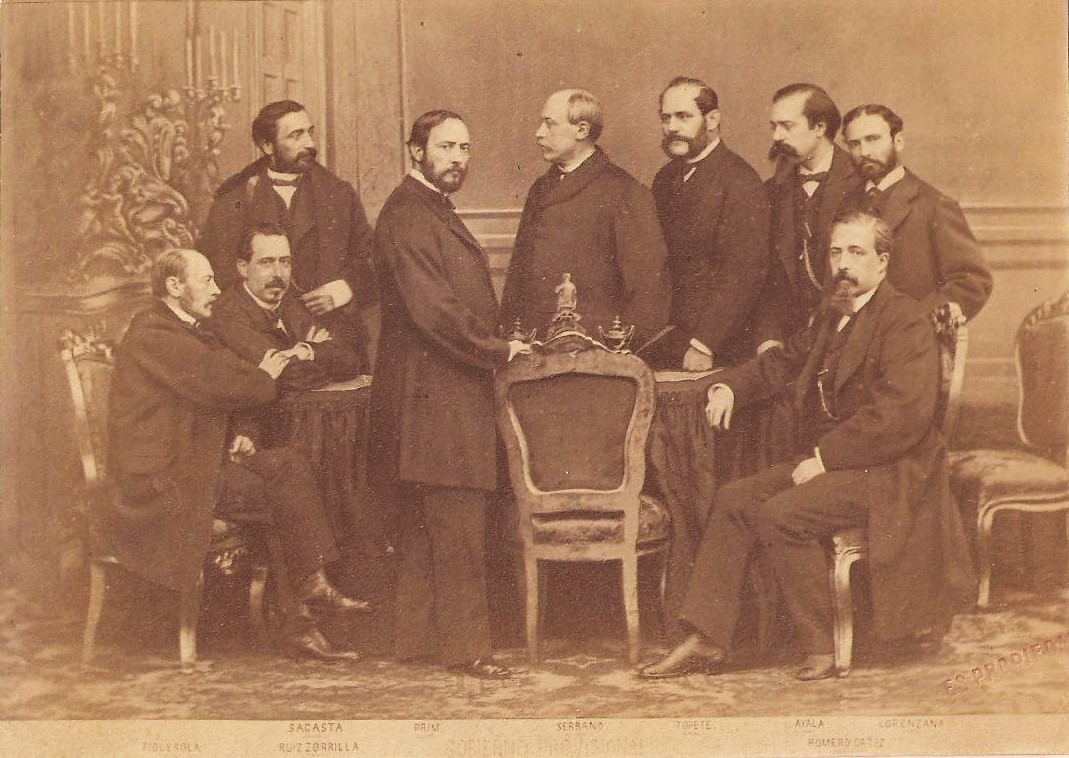 In 1868 another insurgency, known as the Glorious Revolution (Spain), Glorious Revolution took place. The ''progresista'' generals Francisco Serrano y Dominguez, Francisco Serrano and Juan Prim revolted against Isabella and defeated her ''moderado'' generals at the Battle of Alcolea (1868). Isabella was driven into exile in Paris.
Two years later, in 1870, the Cortes declared that Spain would again have a king. Amadeus I of Spain, Amadeus of Savoy, the second son of King Victor Emmanuel II of Italy, was selected and duly crowned King of Spain early the following year. Amadeus – a liberal who swore by the liberal constitution the Cortes promulgated – was faced immediately with the incredible task of bringing the disparate political ideologies of Spain to one table. The country was plagued by internecine strife, not merely between Spaniards but within Spanish parties.
Following the Hidalgo affair and an army rebellion, Amadeus famously declared the people of Spain to be ungovernable, abdicated the throne, and left the country (11 February 1873).
;First Spanish Republic (1873–74)
In the absence of the Monarch, a government of radicals and Republicans was formed and declared Spain a republic. The First Spanish Republic (1873–74) was immediately under siege from all quarters. The Carlists were the most immediate threat, launching a violent insurrection after their poor showing in the 1872 elections. There were calls for socialist revolution from the International Workingmen's Association, revolts and unrest in the autonomous regions of Navarre and
In 1868 another insurgency, known as the Glorious Revolution (Spain), Glorious Revolution took place. The ''progresista'' generals Francisco Serrano y Dominguez, Francisco Serrano and Juan Prim revolted against Isabella and defeated her ''moderado'' generals at the Battle of Alcolea (1868). Isabella was driven into exile in Paris.
Two years later, in 1870, the Cortes declared that Spain would again have a king. Amadeus I of Spain, Amadeus of Savoy, the second son of King Victor Emmanuel II of Italy, was selected and duly crowned King of Spain early the following year. Amadeus – a liberal who swore by the liberal constitution the Cortes promulgated – was faced immediately with the incredible task of bringing the disparate political ideologies of Spain to one table. The country was plagued by internecine strife, not merely between Spaniards but within Spanish parties.
Following the Hidalgo affair and an army rebellion, Amadeus famously declared the people of Spain to be ungovernable, abdicated the throne, and left the country (11 February 1873).
;First Spanish Republic (1873–74)
In the absence of the Monarch, a government of radicals and Republicans was formed and declared Spain a republic. The First Spanish Republic (1873–74) was immediately under siege from all quarters. The Carlists were the most immediate threat, launching a violent insurrection after their poor showing in the 1872 elections. There were calls for socialist revolution from the International Workingmen's Association, revolts and unrest in the autonomous regions of Navarre and Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
, and pressure from the Catholic Church against the fledgling republic.
A coup took place in January 1874, when Manuel Pavía y Rodríguez de Alburquerque, General Pavía broke into the Cortes. This prevented the formation of a federal republican government, forced the dissolution of the Parliament and led to the instauration of a unitary praetorian republic ruled by Francisco Serrano, 1st Duke of la Torre, General Serrano, paving the way for the Restoration (Spain), Restoration of the Monarchy through another ''pronunciamiento'', this time by Arsenio Martínez Campos, in December 1874.
Restoration (1874–1931)
Reign of Alfonso XII and Regency of Maria Christina
 Following the success of a December 1874 military coup the monarchy was restored in the person of Alfonso XII of Spain, Alfonso XII (the son of former queen Isabella II). The ongoing Carlist insurrection was eventually put down. The Restoration (Spain), Restoration period, following the proclamation of the Spanish Constitution of 1876, 1876 Constitution, witnessed the installment of an uncompetitive parliamentary system devised by Antonio Cánovas del Castillo, in which two "dynastic" parties, the conservatism, conservatives and the liberalism, liberals alternated in control of the government (''turnos, turnismo''). Election fraud (materialized in the so-called ''caciquismo'') became ubiquitous, with elections reproducing pre-arranged outcomes struck in the Capital. Voter apathy was no less important.
Following the success of a December 1874 military coup the monarchy was restored in the person of Alfonso XII of Spain, Alfonso XII (the son of former queen Isabella II). The ongoing Carlist insurrection was eventually put down. The Restoration (Spain), Restoration period, following the proclamation of the Spanish Constitution of 1876, 1876 Constitution, witnessed the installment of an uncompetitive parliamentary system devised by Antonio Cánovas del Castillo, in which two "dynastic" parties, the conservatism, conservatives and the liberalism, liberals alternated in control of the government (''turnos, turnismo''). Election fraud (materialized in the so-called ''caciquismo'') became ubiquitous, with elections reproducing pre-arranged outcomes struck in the Capital. Voter apathy was no less important.
Disaster of 1898
 In 1868, Cuba launched a Ten Years' War, war of independence against Spain. On that island, as had been the case in Santo Domingo, the Spanish government found itself embroiled in a difficult campaign against an indigenous rebellion. Dominican Restoration War, Unlike in Santo Domingo, however, Spain initially won this struggle, having learned the lessons of guerrilla warfare well enough to defeat this rebellion. The pacification of the island was temporary, however, as the conflict Cuban War of Independence, revived in 1895 and ended in defeat at the hands of the United States in the Spanish–American War of 1898. Cuba gained its independence and Spain lost its remaining New World colony, Puerto Rico, which together with Guam and the Philippines were ceded to the United States for 20 million dollars. In 1899, Spain sold its remaining Pacific islands – the Northern Mariana Islands, Caroline Islands and Palau – to Germany and Spanish colonial possessions were reduced to Spanish Morocco, Spanish Sahara and Spanish Guinea, all in Africa.
The "disaster" of 1898 created the Generation of '98, a group of statesmen and intellectuals who demanded liberal change from the new government. However both Anarchism on the left and fascism on the right grew rapidly in Spain in the early 20th century. A revolt in 1909 in
In 1868, Cuba launched a Ten Years' War, war of independence against Spain. On that island, as had been the case in Santo Domingo, the Spanish government found itself embroiled in a difficult campaign against an indigenous rebellion. Dominican Restoration War, Unlike in Santo Domingo, however, Spain initially won this struggle, having learned the lessons of guerrilla warfare well enough to defeat this rebellion. The pacification of the island was temporary, however, as the conflict Cuban War of Independence, revived in 1895 and ended in defeat at the hands of the United States in the Spanish–American War of 1898. Cuba gained its independence and Spain lost its remaining New World colony, Puerto Rico, which together with Guam and the Philippines were ceded to the United States for 20 million dollars. In 1899, Spain sold its remaining Pacific islands – the Northern Mariana Islands, Caroline Islands and Palau – to Germany and Spanish colonial possessions were reduced to Spanish Morocco, Spanish Sahara and Spanish Guinea, all in Africa.
The "disaster" of 1898 created the Generation of '98, a group of statesmen and intellectuals who demanded liberal change from the new government. However both Anarchism on the left and fascism on the right grew rapidly in Spain in the early 20th century. A revolt in 1909 in Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
was bloodily suppressed. Jensen (1999) argues that the defeat of 1898 led many military officers to abandon the liberalism that had been strong in the officer corps and turn to the right. They interpreted the American victory in 1898 as well as the Russo-Japanese War, Japanese victory against Russia in 1905 as proof of the superiority of willpower and moral values over technology. Over the next three decades, Jensen argues, these values shaped the outlook of Francisco Franco
Francisco Franco Bahamonde (; 4 December 1892 – 20 November 1975) was a Spanish general who led the Nationalist forces in overthrowing the Second Spanish Republic during the Spanish Civil War and thereafter ruled over Spain from 19 ...
and other Falangists.
Crisis of the Restoration system (1913–1931)
The bipartisan system began to collapse in the later years of the constitutional part of the reign of Alfonso XIII, with the dynastic parties largely disintegrating into factions: the conservatives faced a schism between ''Eduardo Dato, datistas'', ''Maurismo, mauristas'' and ''Ciervists, ciervistas''. The liberal camp split into the mainstream liberals followers of the Count of Romanones (''romanonistas'') and the followers of Manuel García Prieto, the "democrats" (''prietistas''). An additional liberal Santiago Alba, ''albista'' faction was later added to the last two.
Spain's neutrality in World War I spared the country from carnage, yet the conflict caused massive economic disruption, with the country experiencing at the same time an economic boom (the increasing foreign demand of products and the drop of imports brought hefty profits) and widespread social distress (with mounting inflation, shortage of basic goods and extreme income inequality). 1917 Spanish general strike, A major revolutionary strike was called for August 1917, supported by the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party, the Unión General de Trabajadores, UGT and the Confederación Nacional del Trabajo, CNT, seeking to overthrow the government by means of a general strike. The Eduardo Dato, Dato government deployed the army against the workers to brutally quell any threat to social order, sealing in turn the demise of the cabinet and undermining the constitutional order. The strike was one of the three simultaneous developments of a wider Spanish crisis of 1917, three-headed crisis in 1917 that cracked the Restoration regime, that also included a military crisis induced by the cleavage in the Armed Forces between Mainland and Africa-based ranks vis-à-vis the military promotion (and ensuing formation of ''juntas'' of officers that refused to dissolve upon request from the government), and a political crisis brought by the challenge posed by Catalan nationalism, whose bourgeois was emboldened by the economic upswing caused by the profits from exports to Entente powers during World War I.
During the Rif War, the crushing defeat of the Spanish Army in the so-called Battle of Annual, "Disaster of Annual" in the Summer of 1921 brought in a matter of days the catastrophic loss of the lives of about 9,000 Spanish soldiers and the loss of all occupied territory in Morocco that had been gained since 1912. This entailed the greatest defeat suffered by a European power in an African colonial war in the 20th century.
 Alfonso XIII tacitly endorsed the September 1923 coup by General
Alfonso XIII tacitly endorsed the September 1923 coup by General Miguel Primo de Rivera
Miguel Primo de Rivera y Orbaneja, 2nd Marquess of Estella (8 January 1870 – 16 March 1930), was a dictator, aristocrat, and military officer who served as Prime Minister of Spain from 1923 to 1930 during Spain's Restoration era. He deep ...
that installed a dictatorship led by the latter. The regime enforced the Martial law, State of War all over the country from September 1923 to May 1925 and, in permanent violation of the Spanish Constitution of 1876, 1876 Constitution, wrecked with the legal-rational component of the constitutional compromise.
Second Spanish Republic (1931–36)
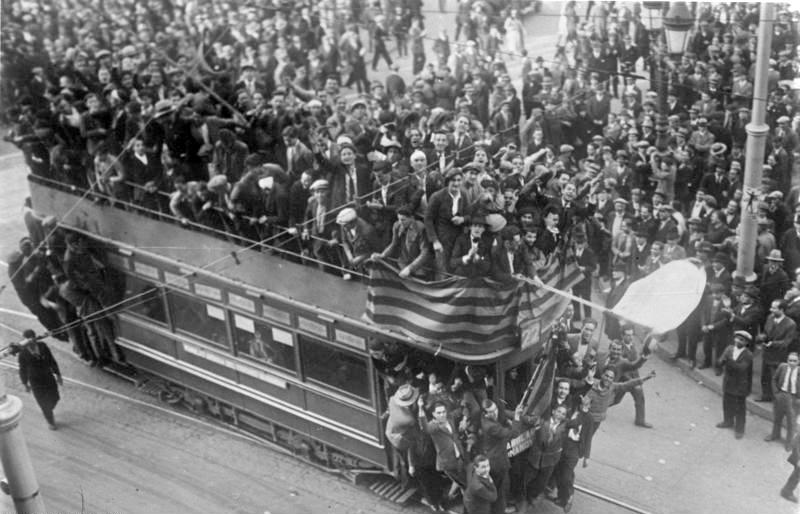 A provisional government presided by Niceto Alcalá Zamora was installed as the Republic, popularly nicknamed as "''la niña bonita''" ('the pretty girl'), was proclaimed on 14 April 1931, a democratic experiment at a time when democracies were beginning to descend into dictatorships elsewhere in the continent. A 1931 Spanish general election, Constituent election was called for June 1931. The dominant bloc emerging from the election, an alliance of liberals and socialists, brought Manuel Azaña (who had undertaken a decisive reform as War minister in the provisional government by trying to democratize the Armed Forces) to premiership, heading from the on a number of coalition cabinets. While the Republican government was able to easily quell the Sanjurjada, first 1932 coup d'etat led by José Sanjurjo, the generals, who felt humiliated because of the military reform privately developed a strong contempt towards Azaña. The new parliament drafted a Spanish Constitution of 1931, new constitution which was approved on 9 December 1931.
Political ideologies were intensely polarized, as both right and left saw vast evil conspiracies on the other side that had to be stopped. Regarding the crux of the role of the Church, within the Left people saw the former as the major enemy of modernity and the Spanish people, and the right saw it as the invaluable protector of Spanish values.
Under the Second Spanish Republic, Women's suffrage, women were allowed to vote in general elections for the first time. The Republic devolved substantial self-government to
A provisional government presided by Niceto Alcalá Zamora was installed as the Republic, popularly nicknamed as "''la niña bonita''" ('the pretty girl'), was proclaimed on 14 April 1931, a democratic experiment at a time when democracies were beginning to descend into dictatorships elsewhere in the continent. A 1931 Spanish general election, Constituent election was called for June 1931. The dominant bloc emerging from the election, an alliance of liberals and socialists, brought Manuel Azaña (who had undertaken a decisive reform as War minister in the provisional government by trying to democratize the Armed Forces) to premiership, heading from the on a number of coalition cabinets. While the Republican government was able to easily quell the Sanjurjada, first 1932 coup d'etat led by José Sanjurjo, the generals, who felt humiliated because of the military reform privately developed a strong contempt towards Azaña. The new parliament drafted a Spanish Constitution of 1931, new constitution which was approved on 9 December 1931.
Political ideologies were intensely polarized, as both right and left saw vast evil conspiracies on the other side that had to be stopped. Regarding the crux of the role of the Church, within the Left people saw the former as the major enemy of modernity and the Spanish people, and the right saw it as the invaluable protector of Spanish values.
Under the Second Spanish Republic, Women's suffrage, women were allowed to vote in general elections for the first time. The Republic devolved substantial self-government to Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
and, for a brief period in wartime, also to the Basque Provinces.
The first cabinets of the Republic were center-left, headed by Niceto Alcalá-Zamora and Manuel Azaña. Economic turmoil, substantial debt, and fractious, rapidly changing governing coalitions led to escalating political violence and attempted coups by right and left.
Following the 1933 election, the right-wing Spanish Confederation of the Autonomous Right (CEDA), based on the Catholic vote, was set to enter the radical government. An armed rising of workers in October 1934, which reached its greatest intensity in Asturias, was forcefully put down by the government. This in turn energized political movements across the spectrum in Spain, including a revived anarchist movement and new reactionary and fascist groups, including the Falange and a revived Carlism, Carlist movement.
A devastating 1936–39 civil war was won in 1939 by the rebel forces under Francisco Franco
Francisco Franco Bahamonde (; 4 December 1892 – 20 November 1975) was a Spanish general who led the Nationalist forces in overthrowing the Second Spanish Republic during the Spanish Civil War and thereafter ruled over Spain from 19 ...
. It was supported by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. The rebels (backed among other by traditionalist Carlists, Fascist falangism, falangists and Far-right alfonsism, alfonsists) defeated the Republican loyalists (with a variable support of Socialists, Liberals, Communists, Anarchists and Catalan and Basque nationalists), who were backed by the Soviet Union.
Spanish Civil War (1936–1939)
 The Spanish Civil War was started by a 1936 Spanish coup d'etat, military coup d'etat in 17–18 July 1936 against the Republican government. The coup, intending to prevent social and economic reforms carried by the new government, had been carefully plotted since the electoral right-wing defeat at the 1936 Spanish general election, February 1936 election. The coup failed everywhere but in the Catholic heartland (Galicia, Old Castile and Navarre), Morocco,
The Spanish Civil War was started by a 1936 Spanish coup d'etat, military coup d'etat in 17–18 July 1936 against the Republican government. The coup, intending to prevent social and economic reforms carried by the new government, had been carefully plotted since the electoral right-wing defeat at the 1936 Spanish general election, February 1936 election. The coup failed everywhere but in the Catholic heartland (Galicia, Old Castile and Navarre), Morocco, Zaragoza
Zaragoza, also known in English as Saragossa,''Encyclopædia Britannica'"Zaragoza (conventional Saragossa)" is the capital city of the Zaragoza Province and of the autonomous community of Aragon, Spain. It lies by the Ebro river and its tribut ...
, Seville and Oviedo, while the rest of the country remained loyal to the Republic, including the main industrial cities (such as Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia
Valencia ( va, València) is the capital of the autonomous community of Valencia and the third-most populated municipality in Spain, with 791,413 inhabitants. It is also the capital of the province of the same name. The wider urban area al ...
and Bilbao), where the putschists were crushed by the combined action of workers and peasants.
The Republic looked to the Western democracies for help, but following an earlier commitment to provide assistance by French premier Léon Blum, by 25 July the latter had already backtracked on it, as to the mounting inner division within his country the British opposition to intervention added up, as the sympathies of the UK lied in the Rebel faction.
The Rebel faction enjoyed direct military support from Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany, while since the very beginning they also enjoyed the support of Estado Novo (Portugal), Salazarist Portugal, the power-base of one of the leading rebels, José Sanjurjo. The Soviet Union sold weapons to the Republican faction, while left-wing sympathizers around the world went to Spain to fight in the International Brigades, set up by the Communist International. The conflict become a worldwide ideological battleground that pitted the left and many liberals against Catholics and conservatives. Worldwide there was a decline in pacifism and a growing sense that another world war was imminent, and that it was worth fighting for.
After the Spanish Civil War, the active agrarian population began to decline in Spain, the provinces with latifundia in Andalusia continued being the ones with the greatest number of day laborers; at the same time this was the region with the lowest literacy share.
Political and military balance
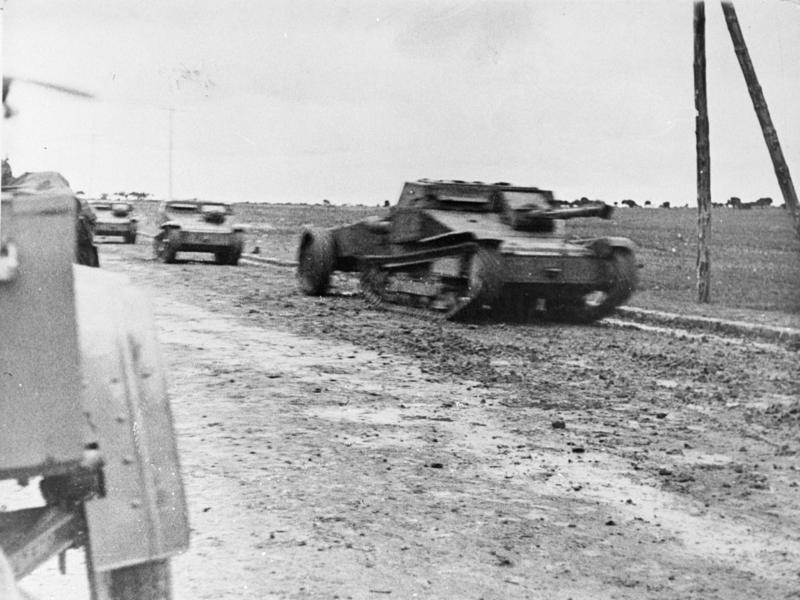 The Spanish Republican government moved to Valencia, to escape Madrid, which was under siege by the Nationalists. It had some military strength in the Air Force and Navy, but it had lost nearly all of the regular Army. After opening the arsenals to give rifles, machine guns and artillery to local militias, it had little control over the Loyalist ground forces. Republican diplomacy proved ineffective, with only two useful allies, the Soviet Union and Mexico. Britain, France and 27 other countries had agreed to an arms embargo on Spain, and the United States went along. Nazi Germany and Kingdom of Italy, Fascist Italy both signed that agreement, but ignored it and sent supplies and vital help, including a powerful air force under German command, the Condor Legion. Tens of thousands of Italians arrived under Italian command. Portugal supported the Nationalists, and allowed the trans-shipment of supplies to Franco's forces. The Soviets sold tanks and other armaments for Spanish gold, and sent well-trained officers and political commissars. It organized the mobilization of tens of thousands of mostly communist volunteers from around the world, who formed the International Brigades.
In 1936, the Left united in the Popular Front and were elected to power. However, this coalition, dominated by the centre-left, was undermined both by the revolutionary groups such as the anarchist Confederación Nacional del Trabajo (CNT) and Federación Anarquista Ibérica (FAI) and by anti-democratic far-right groups such as the Falange and the Carlists. The political violence of previous years began to start again. There were gunfights over strikes; landless labourers began to seize land, church officials were killed and churches burnt. On the other side, right wing militias (such as the Falange) and gunmen hired by employers assassinated left wing activists. The Republican democracy never generated the consensus or mutual trust between the various political groups that it needed to function peacefully. As a result, the country slid into civil war. The right wing of the country and high ranking figures in the army began to plan a coup, and when Falangist politician José Calvo-Sotelo was The Assassination of José Calvo Sotelo, shot by Republican police, they used it as a signal to act while the Republican leadership was confused and inert.
The Spanish Republican government moved to Valencia, to escape Madrid, which was under siege by the Nationalists. It had some military strength in the Air Force and Navy, but it had lost nearly all of the regular Army. After opening the arsenals to give rifles, machine guns and artillery to local militias, it had little control over the Loyalist ground forces. Republican diplomacy proved ineffective, with only two useful allies, the Soviet Union and Mexico. Britain, France and 27 other countries had agreed to an arms embargo on Spain, and the United States went along. Nazi Germany and Kingdom of Italy, Fascist Italy both signed that agreement, but ignored it and sent supplies and vital help, including a powerful air force under German command, the Condor Legion. Tens of thousands of Italians arrived under Italian command. Portugal supported the Nationalists, and allowed the trans-shipment of supplies to Franco's forces. The Soviets sold tanks and other armaments for Spanish gold, and sent well-trained officers and political commissars. It organized the mobilization of tens of thousands of mostly communist volunteers from around the world, who formed the International Brigades.
In 1936, the Left united in the Popular Front and were elected to power. However, this coalition, dominated by the centre-left, was undermined both by the revolutionary groups such as the anarchist Confederación Nacional del Trabajo (CNT) and Federación Anarquista Ibérica (FAI) and by anti-democratic far-right groups such as the Falange and the Carlists. The political violence of previous years began to start again. There were gunfights over strikes; landless labourers began to seize land, church officials were killed and churches burnt. On the other side, right wing militias (such as the Falange) and gunmen hired by employers assassinated left wing activists. The Republican democracy never generated the consensus or mutual trust between the various political groups that it needed to function peacefully. As a result, the country slid into civil war. The right wing of the country and high ranking figures in the army began to plan a coup, and when Falangist politician José Calvo-Sotelo was The Assassination of José Calvo Sotelo, shot by Republican police, they used it as a signal to act while the Republican leadership was confused and inert.
Military operations
 The Nationalists under Franco won the war, and historians continue to debate the reasons. The Nationalists were much better unified and led than the Republicans, who squabbled and fought amongst themselves endlessly and had no clear military strategy. The Army went over to the Nationalists, but it was very poorly equipped – there were no tanks or modern airplanes. The small navy supported the Republicans, but their armies were made up of raw recruits and they lacked both equipment and skilled officers and sergeants. Nationalist senior officers were much better trained and more familiar with modern tactics than the Republicans.
On 17 July 1936, General
The Nationalists under Franco won the war, and historians continue to debate the reasons. The Nationalists were much better unified and led than the Republicans, who squabbled and fought amongst themselves endlessly and had no clear military strategy. The Army went over to the Nationalists, but it was very poorly equipped – there were no tanks or modern airplanes. The small navy supported the Republicans, but their armies were made up of raw recruits and they lacked both equipment and skilled officers and sergeants. Nationalist senior officers were much better trained and more familiar with modern tactics than the Republicans.
On 17 July 1936, General Francisco Franco
Francisco Franco Bahamonde (; 4 December 1892 – 20 November 1975) was a Spanish general who led the Nationalist forces in overthrowing the Second Spanish Republic during the Spanish Civil War and thereafter ruled over Spain from 19 ...
brought the colonial army stationed in Morocco to the mainland, while another force from the north under General Mola moved south from Navarre. Another conspirator, General Sanjurjo, who was in exile in Portugal, was killed in a plane crash while being brought to join the other military leaders. Military units were also mobilised elsewhere to take over government institutions. Franco intended to seize power immediately, but successful resistance by Republicans in the key centers of Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia, the Basque country, and other points meant that Spain faced a prolonged civil war. By 1937 much of the south and west was under the control of the Nationalists, whose Spanish Army of Africa, Army of Africa was the most professional force available to either side. Both sides received foreign military aid: the Nationalists from Nazi Germany and Italy, while the Republicans were supported by organised far-left volunteers from the Soviet Union.
 The Siege of the Alcázar at Toledo (Spain), Toledo early in the war was a turning point, with the Nationalists successfully resisting after a long siege. The Republicans managed to Siege of Madrid, hold out in Madrid, despite a Nationalist assault in November 1936, and frustrated subsequent offensives against the capital at battle of Jarama, Jarama and battle of Guadalajara, Guadalajara in 1937. Soon, though, the Nationalists began to erode their territory, starving Madrid and making inroads into the east. The North, including the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque country fell in late 1937 and the Aragon front collapsed shortly afterwards. The bombing of Guernica on the afternoon of 26 April 1937 – a mission used as a testing ground for the German Luftwaffe's Condor Legion – was probably the most infamous event of the war and inspired Guernica (painting), Picasso's painting. The Battle of the Ebro in July–November 1938 was the final desperate attempt by the Republicans to turn the tide. When this failed and Barcelona fell to the Nationalists in early 1939, it was clear the war was over. The remaining Republican fronts collapsed, as civil war broke out inside the Left, as the Republicans suppressed the Communists. Madrid fell in March 1939.
The Siege of the Alcázar at Toledo (Spain), Toledo early in the war was a turning point, with the Nationalists successfully resisting after a long siege. The Republicans managed to Siege of Madrid, hold out in Madrid, despite a Nationalist assault in November 1936, and frustrated subsequent offensives against the capital at battle of Jarama, Jarama and battle of Guadalajara, Guadalajara in 1937. Soon, though, the Nationalists began to erode their territory, starving Madrid and making inroads into the east. The North, including the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque country fell in late 1937 and the Aragon front collapsed shortly afterwards. The bombing of Guernica on the afternoon of 26 April 1937 – a mission used as a testing ground for the German Luftwaffe's Condor Legion – was probably the most infamous event of the war and inspired Guernica (painting), Picasso's painting. The Battle of the Ebro in July–November 1938 was the final desperate attempt by the Republicans to turn the tide. When this failed and Barcelona fell to the Nationalists in early 1939, it was clear the war was over. The remaining Republican fronts collapsed, as civil war broke out inside the Left, as the Republicans suppressed the Communists. Madrid fell in March 1939.[
The conduct of the war was brutal on both sides, with widespread massacres of civilians and prisoners. After the war, many thousands of Republicans were imprisoned and up to 150,000 were executed between 1939 and 1943. Some 500,000 refugees escaped to France; they remained in exile for years or decades.
]
Francoist Spain (1939–1975)
 The Francoist regime resulted in the deaths and arrests of hundreds of thousands of people who were either supporters of the previous Second Republic of Spain or potential threats to Franco's state. They were executed, sent to prisons or concentration camps. According to Gabriel Jackson, the number of victims of the White Terror (executions and hunger or illness in prisons) just between 1939 and 1943 was 200,000. Child abduction was also a wide-scale practice. The lost children of Francoism may reach 300,000.
The Francoist regime resulted in the deaths and arrests of hundreds of thousands of people who were either supporters of the previous Second Republic of Spain or potential threats to Franco's state. They were executed, sent to prisons or concentration camps. According to Gabriel Jackson, the number of victims of the White Terror (executions and hunger or illness in prisons) just between 1939 and 1943 was 200,000. Child abduction was also a wide-scale practice. The lost children of Francoism may reach 300,000.Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ar, سَبْتَة, Sabtah) is a Spanish autonomous city on the north coast of Africa.
Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of several Spanish territo ...
and Melilla remain under Spanish rule and sovereignty.
The latter years of Franco's rule saw some economic and political liberalization (the Spanish miracle), including the birth of a tourism industry. Spain began to catch up economically with its European neighbors.
Franco ruled until his death on 20 November 1975, when control was given to Juan Carlos I of Spain, King Juan Carlos. In the last few months before Franco's death, the Spanish state went into a paralysis. This was capitalized upon by King Hassan II of Morocco, who ordered the 'Green March' into Western Sahara, Spain's last colonial possession.
History of Spain (1975–present)
Transition to democracy
The Spanish transition to democracy or new Bourbon restoration was the era when Spain moved from the dictatorship of Francisco Franco to a liberal democratic state. The transition started with Franco's death on 20 November 1975, while its completion is marked by the electoral victory of the socialist Spanish Socialist Workers' Party, PSOE on 28 October 1982.
Under its current (1978) constitution, Spain is a constitutional monarchy. It comprises 17 autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous communities (Andalusia, Aragon, Asturias, Balearic Islands, Canary Islands, Cantabria, Castile and León, Castile–La Mancha, Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
, Extremadura, Galicia (Spain), Galicia, La Rioja (Spain), La Rioja, Community of Madrid, Region of Murcia, Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country, Valencian Community, and Navarre) and 2 autonomous cities (Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ar, سَبْتَة, Sabtah) is a Spanish autonomous city on the north coast of Africa.
Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of several Spanish territo ...
and Melilla).
Between 1978 and 1982, Spain was led by the ''Union of the Democratic Centre (Spain), Unión del Centro Democrático'' governments.
In 1981 the 23-F coup d'état attempt took place. On 23 February Antonio Tejero, with members of the Guardia Civil (Spain), Guardia Civil entered the Congress of Deputies, and stopped the session, where Leopoldo Calvo Sotelo was about to be named prime minister of the government. Officially, the coup d'état failed thanks to the intervention of King Juan Carlos of Spain, Juan Carlos. Spain joined NATO before Calvo-Sotelo left office.
Along with political change came Spanish society after the democratic transition, radical change in Spanish society. Spanish society had been extremely conservative under Franco, but the transition to democracy also began a liberalization of values and social customs.
After earning a sweeping majority at the 1982 Spanish general election, October 1982 general election, the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE) governed the country, with Felipe González as prime minister. On 1 January 1986, Spain 1986 enlargement of the European Communities, joined the European Economic Community (EEC). 1986 Spanish NATO membership referendum, A referendum on whether Spain should remain in NATO was held in March 1986. The ruling party, the PSOE, favoured Spain's permanence (a turn from their anti-NATO stance back in 1982, a change of discourse already initiated by 1983 and made explicit in 1984). Meanwhile, the Conservative opposition (People's Coalition (Spain), People's Coalition), called for abstention.
The country hosted the 1992 Summer Olympics in Barcelona and Seville Expo '92.
Spain within the European Union (1993–present)
In 1996, the centre-right ''Partido Popular'' government came to power, led by José María Aznar. On 1 January 1999, Spain exchanged the ''Spanish peseta, peseta'' for the new Euro currency. The peseta continued to be used for cash transactions until January 1, 2002. On 11 March 2004 a number of March 11, 2004 Madrid attacks, terrorist bombs exploded on busy commuter trains in Madrid by Islamic extremists linked to Al-Qaeda, killing 191 persons and injuring thousands.
The election, held three days after the attacks, was won by the PSOE, and José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero replaced Aznar as prime minister. As José María Aznar and his ministers at first accused ETA (separatist group), ETA of the atrocity, it has been argued that the outcome of the election has been influenced by this event.
In the wake of its joining the EEC, Spain experienced an economic boom during two decades, cut painfully short by the 2008–14 Spanish financial crisis, financial crisis of 2008.
During the boom years, Spain attracted a large number of immigration to Spain, immigrants, especially from the United Kingdom, but also including unknown but substantial illegal immigration, mostly from Latin America, eastern Europe and north Africa. Spain had the fourth largest economy in the Eurozone
The euro area, commonly called eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro ( €) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU polic ...
, but after 2008 the global economic recession hit Spain hard, with the bursting of the housing bubble and unemployment reaching over 25%, sharp budget cutbacks were needed to stay in the Euro zone. The GDP shrank 1.2% in 2012.
Although interest rates were historically low, investments were not encouraged sufficiently by entrepreneurs. Losses were especially high in real estate, banking, and construction. Economists concluded in early 2013 that, "Where once Spain's problems were acute, now they are chronic: entrenched unemployment, a large mass of small and medium-sized enterprises with low productivity, and, above all, a constriction in credit."
With the financial crisis and high unemployment, Spain is now suffering from a combination of continued illegal immigration paired with a massive emigration of workers, forced to seek employment elsewhere under the EU's "Free movement of people#European Union, Freedom of Movement", with an estimated 700,000, or 1.5% of total population, leaving the country between 2008 and 2013.
Spain is ranked as a middle power able to exert modest regional power, regional influence. It has a small voice in international organizations; it is not part of the G8 and participates in the G20 only as a guest. Spain is part of the G6 (EU).
Historical population
See also
* Demographics of Spain
* Economic history of Spain
* Foreign relations of Spain
* History of Europe
* List of missing landmarks in Spain
* Monarchy of Spain
* Politics of Spain
* Nation state
Notes
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
excerpt and text search
*
excerpt and text search
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* ; the first book in a trilogy about the Spanish Empire.
** ''The Golden Age: The Spanish Empire of Charles V'' (2010); the second book in the trilogy Published in the United States as ''The Golden Empire: Spain, Charles V, and the Creation of America'' (2011).
** ''World Without End: The Global Empire of Philip II of Spain, Philip II'' (2014); the third volume in the trilogy
*
*
Further reading
* Ida Altman, Altman, Ida. ''Emigrants and Society, Extremadura and America in the Sixteenth Century''. U of California Press 1989.
* Barton, Simon. ''A History of Spain'' (2009
excerpt and text search
* Bertrand, Louis and Charles Petrie. ''The History of Spain'' (2nd ed. 1956
online
* Braudel, Fernand ''The Mediterranean and the Mediterranean World in the Age of Philip II'' (2 vol; 1976
vol 1 free to borrow
* Cortada, James W. ''Spain in the Twentieth-Century World: Essays on Spanish Diplomacy, 1898–1978'' (1980
online
* Edwards, John. ''The Spain of the Catholic Monarchs 1474–1520'' (2001
excerpt and text search
* Elliott, J.H. ''The Old World and the New''. Cambridge 1970.
* Esdaile, Charles J. ''Spain in the Liberal Age: From Constitution to Civil War, 1808–1939'' (2000
excerpt and text search
* Gerli, E. Michael, ed. ''Medieval Iberia: an encyclopedia''. New York 2005.
* Hamilton, Earl J. ''American Treasure and the Price Revolution in Spain, 1501–1650''. Cambridge MA 1934.
* Clarence Haring, Haring, Clarence. ''Trade and Navigation between Spain and the Indies in the Time of the Hapsburgs''. (1918)
online free
* Israel, Jonathan I. "Debate—The Decline of Spain: A Historical Myth," ''Past and Present'' 91 (May 1981), 170–85.
* Kamen, Henry. ''Spain. A Society of Conflict'' (3rd ed.) London and New York: Pearson Longman 2005.
* Lynch, John. ''The Hispanic World in Crisis and Change: 1598–1700'' (1994
excerpt and text search
* Lynch, John C. ''Spain under the Habsburgs''. (2 vols. 2nd ed. Oxford UP, 1981).
* Roger Bigelow Merriman, Merriman, Roger Bigelow. ''The Rise of the Spanish Empire in the Old World and the New''. 4 vols. New York 1918–34
online free
* Norwich, John Julius. ''Four Princes: Henry VIII, Francis I, Charles V, Suleiman the Magnificent and the Obsessions that Forged Modern Europe'' (2017), popular history
excerpt
* Olson, James S. et al. '' Historical Dictionary of the Spanish Empire, 1402–1975'' (1992
online
* O'Callaghan, Joseph F. ''A History of Medieval Spain'' (1983
excerpt and text search
* Paquette, Gabriel B. ''Enlightenment, governance, and reform in Spain and its empire, 1759–1808''. (2008)
* Parker, Geoffrey. ''Emperor: A New Life of Charles V'' (2019
excerpt
* Parker, Geoffrey. ''The Grand Strategy of Philip II'' (Yale UP, 1998)
* J.H. Parry, Parry, J.H. ''The Spanish Seaborne Empire''. New York 1966.
* Payne, Stanley G. ''Spain: A Unique History'' (University of Wisconsin Press; 2011) 304 pages; history since the Visigothic era.
* Payne, Stanley G. ''Politics and Society in Twentieth-Century Spain'' (2012)
* Phillips, William D., Jr. ''Enrique IV and the Crisis of Fifteenth-Century Castile, 1425–1480''. Cambridge MA 1978
* Phillips, William D., Jr., and Carla Rahn Phillips. ''A Concise History of Spain'' (2010
excerpt and text search
* Phillips, Carla Rahn. "Time and Duration: A Model for the Economy of Early Modern Spain," ''American Historical Review'', Vol. 92. No. 3 (June 1987), pp. 531–562.
* Pierson, Peter. ''The History of Spain'' (2nd ed. 2008
excerpt and text search
* Pike, Ruth. ''Enterprise and Adventure: The Genoese in Seville and the Opening of the New World''. Ithaca 1966.
* Pike, Ruth. ''Aristocrats and Traders: Sevillan Society in the Sixteenth Century''. Ithaca 1972.
* Preston, Paul. ''The Spanish Civil War: Reaction, Revolution, and Revenge'' (2nd ed. 2007)
* Reston Jr, James. ''Defenders of the Faith: Charles V, Suleyman the Magnificent, and the Battle for Europe, 1520–1536'' (2009), popular history.
* Ringrose, David. ''Madrid and the Spanish Economy 1560–1850''. Berkeley 1983.
* Shubert, Adrian. ''A Social History of Modern Spain'' (1990
excerpt
* Thompson, I.A.A. ''War and Government in Habsburg Spain, 1560–1620''. London 1976.
* Thompson, I.A.A. ''Crown and Cortes. Government Institutions and Representation in Early-Modern Castile''. Brookfield VT 1993.
* Treasure, Geoffrey. ''The Making of Modern Europe, 1648–1780'' (3rd ed. 2003). pp 332–373.
* Javier Tusell, Tusell, Javier. ''Spain: From Dictatorship to Democracy, 1939 to the Present'' (2007
excerpt and text search
* Vivens Vives, Jaime. ''An Economic History of Spain'', 3d edn. rev. Princeton 1969.
* Walker, Geoffrey. ''Spanish Politics and Imperial Trade, 1700–1789''. Bloomington IN 1979.
* Woodcock, George. "Anarchism in Spain" '' History Today'' (Jan 1962) 12#1 pp 22–32.
Historiography
*
* Cabrera, Miguel A. "Developments in contemporary Spanish historiography: from social history to the new cultural history." ''Journal of Modern History'' 77.4 (2005): 988–1023.
* Cortada, James W. ''A Bibliographic Guide to Spanish Diplomatic History, 1460–1977'' (Greenwood Press, 1977) 390 pages
* Feros, Antonio. "Spain and America: All is One”: Historiography of the Conquest and Colonization of the Americas and National Mythology in Spain c. 1892–c. 1992." in Christopher Schmidt-Nowara and John M. Nieto Phillips, eds. ''Interpreting Spanish Colonialism: Empires, Nations, and Legends'' (2005).
* García-Sanjuán, Alejandro. "Rejecting al-Andalus, exalting the Reconquista: historical memory in contemporary Spain." ''Journal of Medieval Iberian Studies'' 10.1 (2018): 127–145
online
* Herzberger, David K. ''Narrating the past: fiction and historiography in postwar Spain'' (Duke University Press, 1995).
* Herzberger, David K. "Narrating the past: History and the Novel of Memory in Postwar Spain." ''Publications of the Modern Language Association of America'' (1991): 34–45.
in JSTOR
* Jover, José María. "Panorama of current Spanish historiography" ''Cahiers d'Histoire Mondiale''. 1961, Vol. 6 Issue 4, pp 1023–1038.
* Linehan, Peter. ''History and the historians of medieval Spain'' (Oxford UP, 1993)
* Luengo, Jorge, and Pol Dalmau. "Writing Spanish history in the global age: connections and entanglements in the nineteenth century." ''Journal of global history'' 13.3 (2018): 425–445
online
* Payne, Stanley G. “Jaime Vicens Vives and the Writing of Spanish History.” ''Journal of Modern History'' 34#2 (1962), pp. 119–134
online
* Viñao, Antonio. "From dictatorship to democracy: history of education in Spain." ''Paedagogica Historica'' 50#6 (2014): 830–843.
External links
*
*
*
*
* Pereira-Muro, Carmen ''Culturas de España''. Boston and New York: Houghton Mifflin Company 2003.
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Spain
History of Spain,
 The south of the peninsula was rich in archaic Phoenician colonies, unmatched by any other region in the central-western Mediterranean. They were small and densely packed settlements. The colony of Gadir—which sustained strong links with its metropolis of Tyre—stood out from the rest of the network of colonies, also featuring a more complex sociopolitical organization. Archaic Greeks arrived to the Peninsula by the late 7th century BC. They founded
The south of the peninsula was rich in archaic Phoenician colonies, unmatched by any other region in the central-western Mediterranean. They were small and densely packed settlements. The colony of Gadir—which sustained strong links with its metropolis of Tyre—stood out from the rest of the network of colonies, also featuring a more complex sociopolitical organization. Archaic Greeks arrived to the Peninsula by the late 7th century BC. They founded  The first Germanic tribes to invade Hispania arrived in the 5th century, as the Roman Empire decayed.The
The first Germanic tribes to invade Hispania arrived in the 5th century, as the Roman Empire decayed.The  In Spain, an important collection of Visigothic metalwork was found in Guadamur, in the
In Spain, an important collection of Visigothic metalwork was found in Guadamur, in the  * During their governance of Hispania, the Visigoths built several churches in the
* During their governance of Hispania, the Visigoths built several churches in the  The Vikings invaded Galicia in 844, but were heavily defeated by Ramiro I at
The Vikings invaded Galicia in 844, but were heavily defeated by Ramiro I at  Spain in the Middle Ages, Medieval Spain was the scene of almost constant warfare between Muslims and Christians.
The Taifa kingdoms lost ground to the Christian realms in the north. After the loss of Toledo in 1085, the Muslim rulers reluctantly invited the Almoravides, who invaded Al-Andalus from North Africa and established an empire. In the 12th century the Almoravid empire broke up again, only to be taken over by the Almohad invasion, who were defeated by an alliance of the Christian kingdoms in the decisive Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in 1212. By 1250, nearly all of Hispania was back under Christian rule with the exception of the Muslim kingdom of Granada.
Spain in the Middle Ages, Medieval Spain was the scene of almost constant warfare between Muslims and Christians.
The Taifa kingdoms lost ground to the Christian realms in the north. After the loss of Toledo in 1085, the Muslim rulers reluctantly invited the Almoravides, who invaded Al-Andalus from North Africa and established an empire. In the 12th century the Almoravid empire broke up again, only to be taken over by the Almohad invasion, who were defeated by an alliance of the Christian kingdoms in the decisive Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in 1212. By 1250, nearly all of Hispania was back under Christian rule with the exception of the Muslim kingdom of Granada.
 In the 13th century, many languages were spoken in the Christian kingdoms of Hispania. These were the Latin-based Romance languages of Spanish language, Castilian, Aragonese language, Aragonese, Catalan language, Catalan, Galician language, Galician, Aranese language, Aranese, Asturian language, Asturian, Leonese language, Leonese, and Portuguese language, Portuguese, and the ancient language isolate of Basque language, Basque. Throughout the century, Castilian (what is also known today as Spanish) gained a growing prominence in the Kingdom of Castile as the language of culture and communication, at the expense of Leonese and of other close dialects.
One example of this is the oldest preserved Castilian epic poem, ''Cantar de Mio Cid'', written about the military leader ''El Cid''. In the last years of the reign of Ferdinand III of Castile, Castilian began to be used for certain types of documents, and it was during the reign of Alfonso X of Castile, Alfonso X that it became the official language. Henceforth all public documents were written in Castilian; likewise all translations were made into Castilian instead of Latin.
At the same time, Catalan and Galician became the standard languages in their respective territories, developing important literary traditions and being the normal languages in which public and private documents were issued: Galician from the 13th to the 16th century in Galicia and nearby regions of Asturias and Leon, and Catalan from the 12th to the 18th century in Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and Valencia, where it was known as Valencian. Both languages were later substituted in its official status by Castilian Spanish, till the 20th century.
In the 13th century many universities were founded in León and in Castile. Some, such as the Leonese University of Salamanca, Salamanca and the Castilian Palencia, were among the earliest universities in Europe.
In 1492, under the
In the 13th century, many languages were spoken in the Christian kingdoms of Hispania. These were the Latin-based Romance languages of Spanish language, Castilian, Aragonese language, Aragonese, Catalan language, Catalan, Galician language, Galician, Aranese language, Aranese, Asturian language, Asturian, Leonese language, Leonese, and Portuguese language, Portuguese, and the ancient language isolate of Basque language, Basque. Throughout the century, Castilian (what is also known today as Spanish) gained a growing prominence in the Kingdom of Castile as the language of culture and communication, at the expense of Leonese and of other close dialects.
One example of this is the oldest preserved Castilian epic poem, ''Cantar de Mio Cid'', written about the military leader ''El Cid''. In the last years of the reign of Ferdinand III of Castile, Castilian began to be used for certain types of documents, and it was during the reign of Alfonso X of Castile, Alfonso X that it became the official language. Henceforth all public documents were written in Castilian; likewise all translations were made into Castilian instead of Latin.
At the same time, Catalan and Galician became the standard languages in their respective territories, developing important literary traditions and being the normal languages in which public and private documents were issued: Galician from the 13th to the 16th century in Galicia and nearby regions of Asturias and Leon, and Catalan from the 12th to the 18th century in Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and Valencia, where it was known as Valencian. Both languages were later substituted in its official status by Castilian Spanish, till the 20th century.
In the 13th century many universities were founded in León and in Castile. Some, such as the Leonese University of Salamanca, Salamanca and the Castilian Palencia, were among the earliest universities in Europe.
In 1492, under the  In the 15th century, the most important among all of the separate Christian kingdoms that made up the old
In the 15th century, the most important among all of the separate Christian kingdoms that made up the old 
 The Castilian conquest of the Canary Islands, inhabited by Guanche people, took place between 1402 (with the conquest of Lanzarote) and 1496 (with the conquest of Tenerife). Two periods can be distinguished in this process: the noble conquest, carried out by the nobility in exchange for a pact of vassalage, and the royal conquest, carried out directly by the Crown, during the reign of the Catholic Monarchs. By 1520, European military technology combined with the devastating epidemics such as bubonic plague and pneumonia brought by the Castilians and enslavement and deportation of natives led to the extinction of the Guanches.
Isabella and Ferdinand VII of Spain, Ferdinand authorized the 1492 expedition of Christopher Columbus, who became the first known European to reach the New World since Leif Ericson. This and subsequent expeditions led to an influx of wealth into Spain, supplementing income from within Castile for the state that was a dominant power in Europe for the next two centuries.
Spain established colonies in North Africa that ranged from the Atlantic Moroccan coast to Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli in Libya. Melilla was occupied in 1497, Oran in 1509, Larache in 1610, and
The Castilian conquest of the Canary Islands, inhabited by Guanche people, took place between 1402 (with the conquest of Lanzarote) and 1496 (with the conquest of Tenerife). Two periods can be distinguished in this process: the noble conquest, carried out by the nobility in exchange for a pact of vassalage, and the royal conquest, carried out directly by the Crown, during the reign of the Catholic Monarchs. By 1520, European military technology combined with the devastating epidemics such as bubonic plague and pneumonia brought by the Castilians and enslavement and deportation of natives led to the extinction of the Guanches.
Isabella and Ferdinand VII of Spain, Ferdinand authorized the 1492 expedition of Christopher Columbus, who became the first known European to reach the New World since Leif Ericson. This and subsequent expeditions led to an influx of wealth into Spain, supplementing income from within Castile for the state that was a dominant power in Europe for the next two centuries.
Spain established colonies in North Africa that ranged from the Atlantic Moroccan coast to Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli in Libya. Melilla was occupied in 1497, Oran in 1509, Larache in 1610, and  In the 15th and 16th centuries, trade flourished across the Atlantic between Spain and the Americas and across the Pacific between East Asia and Mexico via the Philippines. Spanish Conquistadors, operating privately, deposed the Aztec, Inca Empire, Inca and Maya civilization, Maya governments with extensive help from local factions and took control of vast stretches of land. In the Philippines, the Spanish, using Mexican Conquistadors like Juan de Salcedo, conquered the History of the Philippines (900–1565), kingdoms and sultanates of the islands by pitting Pagans and Muslims against each other, thus employing the principle of "Divide and Conquer". They considered their war against the native Muslims of the Southeast Asia an extension of the Spanish
In the 15th and 16th centuries, trade flourished across the Atlantic between Spain and the Americas and across the Pacific between East Asia and Mexico via the Philippines. Spanish Conquistadors, operating privately, deposed the Aztec, Inca Empire, Inca and Maya civilization, Maya governments with extensive help from local factions and took control of vast stretches of land. In the Philippines, the Spanish, using Mexican Conquistadors like Juan de Salcedo, conquered the History of the Philippines (900–1565), kingdoms and sultanates of the islands by pitting Pagans and Muslims against each other, thus employing the principle of "Divide and Conquer". They considered their war against the native Muslims of the Southeast Asia an extension of the Spanish  Spain enjoyed a Spanish Golden Age, cultural golden age in the 16th and 17th centuries. For a time, the Spanish Empire dominated the oceans with its experienced Spanish navy, navy and ruled the European battlefield with its fearsome and well trained infantry, the famous '.
The financial burden within the peninsula was on the backs of the peasant class while the nobility enjoyed an increasingly lavish lifestyle. From the time beginning with the incorporation of the Portuguese Empire in 1580 (lost in 1640) until the loss of its American colonies in the 19th century, Spain maintained one of the largest empires in the world even though it suffered military and economic misfortunes from the 1640s.
Religion played a very strong role in the spread of the Spanish empire. The thought that Spain could bring Christianity to the New World and protect Catholicism in Europe certainly played a strong role in the expansion of Spain's empire.
Spain enjoyed a Spanish Golden Age, cultural golden age in the 16th and 17th centuries. For a time, the Spanish Empire dominated the oceans with its experienced Spanish navy, navy and ruled the European battlefield with its fearsome and well trained infantry, the famous '.
The financial burden within the peninsula was on the backs of the peasant class while the nobility enjoyed an increasingly lavish lifestyle. From the time beginning with the incorporation of the Portuguese Empire in 1580 (lost in 1640) until the loss of its American colonies in the 19th century, Spain maintained one of the largest empires in the world even though it suffered military and economic misfortunes from the 1640s.
Religion played a very strong role in the spread of the Spanish empire. The thought that Spain could bring Christianity to the New World and protect Catholicism in Europe certainly played a strong role in the expansion of Spain's empire.
 Spain's world empire reached its greatest territorial extent in the late 18th century but it was under the Habsburg dynasty in the 16th and 17th centuries it reached the peak of its power and declined. The Iberian Union with Portugal meant that the monarch of Castile was also the monarch of Portugal, but they were ruled as separate entities both on the peninsula and in Spanish America and Brazil. In 1640, the House of Braganza revolted against Spanish rule and reasserted Portugal's independence.
When Spain's first Habsburg ruler Charles I of Spain, Charles I became king of Spain in 1516 (with his mother and co-monarch Queen Juana I effectively powerless and kept imprisoned till her death in 1555), Spain became central to the dynastic struggles of Europe. After he became king of Spain, Charles also became Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor and because of his widely scattered domains was not often in Spain.
In 1556 Charles abdicated from his positions, giving his Spanish empire to his only surviving son,
Spain's world empire reached its greatest territorial extent in the late 18th century but it was under the Habsburg dynasty in the 16th and 17th centuries it reached the peak of its power and declined. The Iberian Union with Portugal meant that the monarch of Castile was also the monarch of Portugal, but they were ruled as separate entities both on the peninsula and in Spanish America and Brazil. In 1640, the House of Braganza revolted against Spanish rule and reasserted Portugal's independence.
When Spain's first Habsburg ruler Charles I of Spain, Charles I became king of Spain in 1516 (with his mother and co-monarch Queen Juana I effectively powerless and kept imprisoned till her death in 1555), Spain became central to the dynastic struggles of Europe. After he became king of Spain, Charles also became Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor and because of his widely scattered domains was not often in Spain.
In 1556 Charles abdicated from his positions, giving his Spanish empire to his only surviving son,  In the 1560s, plans to consolidate control of the Netherlands led to unrest, which gradually led to the Calvinism, Calvinist leadership of the revolt and the
In the 1560s, plans to consolidate control of the Netherlands led to unrest, which gradually led to the Calvinism, Calvinist leadership of the revolt and the 
 The Spanish Golden Age (in Spanish, ''Siglo de Oro'') was a period of flourishing arts and letters in the Spanish Empire (now Spain and the Spanish-speaking countries of Latin America), coinciding with the political decline and fall of the Habsburgs (Philip III of Spain, Philip III, Philip IV of Spain, Philip IV and Charles II of Spain, Charles II). Arts during the Golden Age flourished despite the decline of the empire in the 17th century. The last great writer of the age, Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz, died in New Spain in 1695.
The Habsburgs, both in Spain and Austria, were great patrons of art in their countries. ''
The Spanish Golden Age (in Spanish, ''Siglo de Oro'') was a period of flourishing arts and letters in the Spanish Empire (now Spain and the Spanish-speaking countries of Latin America), coinciding with the political decline and fall of the Habsburgs (Philip III of Spain, Philip III, Philip IV of Spain, Philip IV and Charles II of Spain, Charles II). Arts during the Golden Age flourished despite the decline of the empire in the 17th century. The last great writer of the age, Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz, died in New Spain in 1695.
The Habsburgs, both in Spain and Austria, were great patrons of art in their countries. '' The Spanish "Golden Age" politically ends no later than 1659, with the Treaty of the Pyrenees, ratified between France and Habsburg Spain.
During the long regency for Charles II of Spain, Charles II, the last of the Spanish Habsburgs, favouritism milked Spain's treasury, and Spain's government operated principally as a dispenser of patronage. Plague, famine, floods, drought, and renewed war with France wasted the country. The Peace of the Pyrenees (1659) had ended fifty years of warfare with France, whose king, Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV, found the temptation to exploit a weakened Spain too great. Louis instigated the War of Devolution (1667–68) to acquire the Spanish Netherlands.
By the 17th century, the Catholic Church and Spain had showcased a close bond to one another, attesting to the fact that Spain was virtually free of Protestantism during the 16th century. In 1620, there were 100,000 Spaniards in the clergy; by 1660 the number had grown to about 200,000, and the Church owned 20% of all the land in Spain. The Spanish bureaucracy in this period was highly centralized, and totally reliant on the king for its efficient functioning. Under Charles II, the councils became the sinecures of wealthy aristocrats despite various attempt at reform. Political commentators in Spain, known as arbitristas, proposed a number of measures to reverse the decline of the Spanish economy, with limited success. In rural areas of Spain, heavy taxation of peasants reduced agricultural output as peasants in the countryside migrated to the cities. The influx of silver from the Americas has been cited as the cause of inflation, although only one fifth of the precious metal, i.e. the ''quinto real'' (royal fifth), actually went to Spain. A prominent internal factor was the Spanish economy's dependence on the export of luxurious Merino wool, which had its markets in northern Europe reduced by war and growing competition from cheaper textiles.
The once proud Spanish army was falling far behind its foes. It did badly at Bergen op Zoom in 1622, and finance was not to blame. The Dutch won very easily at Hertogenbosch and Wesel in 1629. In 1632 the Dutch captured the strategic fortress town of Maastricht, repulsing three relief armies and dooming the Spanish to defeat.
While Spain built a rich American Empire that exported a silver treasure fleet every year, it was unable to focus its financial, military, and diplomatic power on building up its Spanish base. The Crown's dedication to destroying Protestantism through almost constant warfare created a cultural ethos among Spanish leaders that undermined the opportunity for economic modernization or industrialization. When Philip II died in 1598, his treasury spent most of its income on funding the huge deficit, which continued to grow. In peninsular Spain, the productive forces were undermined by steady inflation, heavy taxation, immigration of ambitious youth to the colonies, and by depopulation. Industry went into reverse – Seville in 1621 operated 400 looms, where it had 16,000 a century before. Religiosity led by saints and mystics, missionaries and crusaders, theologians and friars dominated Spanish culture, with the psychology of a reward in the next world. Palmer and Colton argue:
: the generations of crusading against infidels, even, heathens and heretics had produced an exceptionally large number of minor aristocrats, chevaliers, dons, and hidalgos, who as a class were contemptuous of work and who were numerous enough and close enough to the common people to impress their haughty indifference upon the country as a whole. Elliott cites the achievements of Castille in many areas, especially high culture. He finds:
:A certain paradox in the fact that the achievement of the two most outstanding creative artists of Castile – Cervantes and Velázquez – was shot through with a deep sense of disillusionment and failure; but the paradox was itself a faithful reflection of the paradox of sixteenth-and seventeenth-century Castile. For here was a country which had climbed to the heights and sunk to the depths; which had achieved everything and lost everything; which had conquered the world only to be vanquished itself. The Spanish achievement of the sixteenth century was essentially the work of Castile, but so also was the Spanish disaster of the seventeenth; and it was José Ortega y Gasset, Ortega y Gasset who expressed the paradox most clearly when he wrote what may serve as an epitaph on the Spain of the House of Austria: ‘Castile has made Spain, and Castile has destroyed it.’
The Habsburg dynasty became extinct in Spain with Charles II's death in 1700, and the
The Spanish "Golden Age" politically ends no later than 1659, with the Treaty of the Pyrenees, ratified between France and Habsburg Spain.
During the long regency for Charles II of Spain, Charles II, the last of the Spanish Habsburgs, favouritism milked Spain's treasury, and Spain's government operated principally as a dispenser of patronage. Plague, famine, floods, drought, and renewed war with France wasted the country. The Peace of the Pyrenees (1659) had ended fifty years of warfare with France, whose king, Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV, found the temptation to exploit a weakened Spain too great. Louis instigated the War of Devolution (1667–68) to acquire the Spanish Netherlands.
By the 17th century, the Catholic Church and Spain had showcased a close bond to one another, attesting to the fact that Spain was virtually free of Protestantism during the 16th century. In 1620, there were 100,000 Spaniards in the clergy; by 1660 the number had grown to about 200,000, and the Church owned 20% of all the land in Spain. The Spanish bureaucracy in this period was highly centralized, and totally reliant on the king for its efficient functioning. Under Charles II, the councils became the sinecures of wealthy aristocrats despite various attempt at reform. Political commentators in Spain, known as arbitristas, proposed a number of measures to reverse the decline of the Spanish economy, with limited success. In rural areas of Spain, heavy taxation of peasants reduced agricultural output as peasants in the countryside migrated to the cities. The influx of silver from the Americas has been cited as the cause of inflation, although only one fifth of the precious metal, i.e. the ''quinto real'' (royal fifth), actually went to Spain. A prominent internal factor was the Spanish economy's dependence on the export of luxurious Merino wool, which had its markets in northern Europe reduced by war and growing competition from cheaper textiles.
The once proud Spanish army was falling far behind its foes. It did badly at Bergen op Zoom in 1622, and finance was not to blame. The Dutch won very easily at Hertogenbosch and Wesel in 1629. In 1632 the Dutch captured the strategic fortress town of Maastricht, repulsing three relief armies and dooming the Spanish to defeat.
While Spain built a rich American Empire that exported a silver treasure fleet every year, it was unable to focus its financial, military, and diplomatic power on building up its Spanish base. The Crown's dedication to destroying Protestantism through almost constant warfare created a cultural ethos among Spanish leaders that undermined the opportunity for economic modernization or industrialization. When Philip II died in 1598, his treasury spent most of its income on funding the huge deficit, which continued to grow. In peninsular Spain, the productive forces were undermined by steady inflation, heavy taxation, immigration of ambitious youth to the colonies, and by depopulation. Industry went into reverse – Seville in 1621 operated 400 looms, where it had 16,000 a century before. Religiosity led by saints and mystics, missionaries and crusaders, theologians and friars dominated Spanish culture, with the psychology of a reward in the next world. Palmer and Colton argue:
: the generations of crusading against infidels, even, heathens and heretics had produced an exceptionally large number of minor aristocrats, chevaliers, dons, and hidalgos, who as a class were contemptuous of work and who were numerous enough and close enough to the common people to impress their haughty indifference upon the country as a whole. Elliott cites the achievements of Castille in many areas, especially high culture. He finds:
:A certain paradox in the fact that the achievement of the two most outstanding creative artists of Castile – Cervantes and Velázquez – was shot through with a deep sense of disillusionment and failure; but the paradox was itself a faithful reflection of the paradox of sixteenth-and seventeenth-century Castile. For here was a country which had climbed to the heights and sunk to the depths; which had achieved everything and lost everything; which had conquered the world only to be vanquished itself. The Spanish achievement of the sixteenth century was essentially the work of Castile, but so also was the Spanish disaster of the seventeenth; and it was José Ortega y Gasset, Ortega y Gasset who expressed the paradox most clearly when he wrote what may serve as an epitaph on the Spain of the House of Austria: ‘Castile has made Spain, and Castile has destroyed it.’
The Habsburg dynasty became extinct in Spain with Charles II's death in 1700, and the  Charles II of Spain, Charles II died in 1700, and having no direct heir, was succeeded by his great-nephew Philip V of Spain, Philippe d'Anjou, a French prince. The
Charles II of Spain, Charles II died in 1700, and having no direct heir, was succeeded by his great-nephew Philip V of Spain, Philippe d'Anjou, a French prince. The  Philip V of Spain, Philip V signed the ''Nueva Planta decrees, Decreto de Nueva Planta'' in 1715. This new law revoked most of the historical rights and privileges of the different kingdoms that formed the Spanish Crown, especially the
Philip V of Spain, Philip V signed the ''Nueva Planta decrees, Decreto de Nueva Planta'' in 1715. This new law revoked most of the historical rights and privileges of the different kingdoms that formed the Spanish Crown, especially the  In the late 18th century, Bourbon-ruled Spain had an alliance with Bourbon-ruled France, and therefore did not have to fear a land war. Its only serious enemy was Britain, which had a powerful navy; Spain therefore concentrated its resources on its navy. When the French Revolution overthrew the Bourbons, a land war with France became a threat which the king tried to avoid. The Spanish army was ill-prepared. The officer corps was selected primarily on the basis of royal patronage, rather than merit. About a third of the junior officers had been promoted from the ranks, and while they did have talent they had few opportunities for promotion or leadership. The rank-and-file were poorly trained peasants. Elite units included foreign regiments of Irishmen, Italians, Swiss, and Walloons, in addition to elite artillery and engineering units. Equipment was old-fashioned and in disrepair. The army lacked its own horses, oxen and mules for transportation, so these auxiliaries were operated by civilians, who might run away if conditions looked bad. In combat, small units fought well, but their old-fashioned tactics were hardly of use against the Napoleonic forces, despite repeated desperate efforts at last-minute reform. When war broke out with France in 1808, the army was deeply unpopular. Leading generals were assassinated, and the army proved incompetent to handle command-and-control. Junior officers from peasant families deserted and went over to the insurgents; many units disintegrated. Spain was unable to mobilize its artillery or cavalry. In the war, there was one victory at the Battle of Bailén, and many humiliating defeats. Conditions steadily worsened, as the insurgents increasingly took control of Spain's battle against Napoleon. Napoleon ridiculed the army as "the worst in Europe"; the British who had to work with it agreed. It was not the Army that defeated Napoleon, but the insurgent peasants whom Napoleon ridiculed as packs of "bandits led by monks" (they in turn believed Napoleon was the devil). By 1812, the army controlled only scattered enclaves, and could only harass the French with occasional raids. The morale of the army had reached a nadir, and reformers stripped the aristocratic officers of most of their legal privileges.
Spain initially sided against France in the Napoleonic Wars, but the defeat of her army early in the war led to Charles IV of Spain, Charles IV's pragmatic decision to align with the revolutionary French. Spain was put under a British blockade, and her colonies began to trade independently with Britain, but Britain invaded and was the defeat in the British invasions of the Río de la Plata in South America (1806 and 1807) without help from mainland Spain, which emboldened independence and revolutionary hopes in Spain's vast American colonies. A major Franco-Spanish fleet was lost at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805, prompting the vacillating king of Spain to reconsider his difficult alliance with Napoleon. Spain temporarily broke off from the Continental System, and Napoleon – irritated with the Bourbon kings of Spain – invaded Spain in 1808 and deposed Ferdinand VII of Spain, Ferdinand VII, who had been on the throne only forty-eight days after his father's abdication in March 1808. On July 20, 1808,
In the late 18th century, Bourbon-ruled Spain had an alliance with Bourbon-ruled France, and therefore did not have to fear a land war. Its only serious enemy was Britain, which had a powerful navy; Spain therefore concentrated its resources on its navy. When the French Revolution overthrew the Bourbons, a land war with France became a threat which the king tried to avoid. The Spanish army was ill-prepared. The officer corps was selected primarily on the basis of royal patronage, rather than merit. About a third of the junior officers had been promoted from the ranks, and while they did have talent they had few opportunities for promotion or leadership. The rank-and-file were poorly trained peasants. Elite units included foreign regiments of Irishmen, Italians, Swiss, and Walloons, in addition to elite artillery and engineering units. Equipment was old-fashioned and in disrepair. The army lacked its own horses, oxen and mules for transportation, so these auxiliaries were operated by civilians, who might run away if conditions looked bad. In combat, small units fought well, but their old-fashioned tactics were hardly of use against the Napoleonic forces, despite repeated desperate efforts at last-minute reform. When war broke out with France in 1808, the army was deeply unpopular. Leading generals were assassinated, and the army proved incompetent to handle command-and-control. Junior officers from peasant families deserted and went over to the insurgents; many units disintegrated. Spain was unable to mobilize its artillery or cavalry. In the war, there was one victory at the Battle of Bailén, and many humiliating defeats. Conditions steadily worsened, as the insurgents increasingly took control of Spain's battle against Napoleon. Napoleon ridiculed the army as "the worst in Europe"; the British who had to work with it agreed. It was not the Army that defeated Napoleon, but the insurgent peasants whom Napoleon ridiculed as packs of "bandits led by monks" (they in turn believed Napoleon was the devil). By 1812, the army controlled only scattered enclaves, and could only harass the French with occasional raids. The morale of the army had reached a nadir, and reformers stripped the aristocratic officers of most of their legal privileges.
Spain initially sided against France in the Napoleonic Wars, but the defeat of her army early in the war led to Charles IV of Spain, Charles IV's pragmatic decision to align with the revolutionary French. Spain was put under a British blockade, and her colonies began to trade independently with Britain, but Britain invaded and was the defeat in the British invasions of the Río de la Plata in South America (1806 and 1807) without help from mainland Spain, which emboldened independence and revolutionary hopes in Spain's vast American colonies. A major Franco-Spanish fleet was lost at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805, prompting the vacillating king of Spain to reconsider his difficult alliance with Napoleon. Spain temporarily broke off from the Continental System, and Napoleon – irritated with the Bourbon kings of Spain – invaded Spain in 1808 and deposed Ferdinand VII of Spain, Ferdinand VII, who had been on the throne only forty-eight days after his father's abdication in March 1808. On July 20, 1808,  The former Spanish king was dethroned by Napoleon, who put his own brother on the throne. Spaniards revolted. Thompson says the Spanish revolt was, "a reaction against new institutions and ideas, a movement for loyalty to the old order: to the hereditary crown of the Most Catholic kings, which Napoleon, an excommunicated enemy of the Pope, had put on the head of a Frenchman; to the Catholic Church persecuted by republicans who had desecrated churches, murdered priests, and enforced a "loi des cultes"; and to local and provincial rights and privileges threatened by an efficiently centralized government. ''Junta (Peninsular War), Juntas'' were formed all across Spain that pronounced themselves in favor of Ferdinand VII. On September 26, 1808, a Central Junta was formed in the town of Aranjuez to coordinate the nationwide struggle against the French. Initially, the Central Junta declared support for Ferdinand VII, and convened a "Cortes Generales, General and Extraordinary Cortes" for all the kingdoms of the Spanish Monarchy. On February 22 and 23, 1809, a popular insurrection against the French occupation broke out all over Spain.
The peninsular campaign was a disaster for France. Napoleon did well when he was in direct command, but that followed severe losses, and when he left in 1809 conditions grew worse for France. Vicious reprisals, famously portrayed by Goya in "The Disasters of War", only made the Spanish guerrillas angrier and more active; the war in Spain proved to be a major, long-term drain on French money, manpower and prestige.
The former Spanish king was dethroned by Napoleon, who put his own brother on the throne. Spaniards revolted. Thompson says the Spanish revolt was, "a reaction against new institutions and ideas, a movement for loyalty to the old order: to the hereditary crown of the Most Catholic kings, which Napoleon, an excommunicated enemy of the Pope, had put on the head of a Frenchman; to the Catholic Church persecuted by republicans who had desecrated churches, murdered priests, and enforced a "loi des cultes"; and to local and provincial rights and privileges threatened by an efficiently centralized government. ''Junta (Peninsular War), Juntas'' were formed all across Spain that pronounced themselves in favor of Ferdinand VII. On September 26, 1808, a Central Junta was formed in the town of Aranjuez to coordinate the nationwide struggle against the French. Initially, the Central Junta declared support for Ferdinand VII, and convened a "Cortes Generales, General and Extraordinary Cortes" for all the kingdoms of the Spanish Monarchy. On February 22 and 23, 1809, a popular insurrection against the French occupation broke out all over Spain.
The peninsular campaign was a disaster for France. Napoleon did well when he was in direct command, but that followed severe losses, and when he left in 1809 conditions grew worse for France. Vicious reprisals, famously portrayed by Goya in "The Disasters of War", only made the Spanish guerrillas angrier and more active; the war in Spain proved to be a major, long-term drain on French money, manpower and prestige.
 In March 1812, the Cortes of Cádiz created the first modern Spanish constitution, the Spanish Constitution of 1812, Constitution of 1812 (informally named ''La Pepa''). This constitution provided for a separation of the powers of the executive and the legislative branches of government. The Cortes was to be elected by universal suffrage, albeit by an indirect method. Each member of the Cortes was to represent 70,000 people. Members of the Cortes were to meet in annual sessions. The King was prevented from either convening or proroguing the Cortes. Members of the Cortes were to serve single two-year terms. They could not serve consecutive terms; a member could serve a second term only by allowing someone else to serve a single intervening term in office. This attempt at the development of a modern constitutional government lasted from 1808 until 1814. Leaders of the liberals or reformist forces during this revolution were José Moñino, 1st Count of Floridablanca, José Moñino, Count of Floridablanca, Gaspar Melchor de Jovellanos and Pedro Rodríguez, Conde de Campomanes. Born in 1728, Floridablanca was eighty years of age at the time of the revolutionary outbreak in 1808. He had served as Prime Minister under King Charles III of Spain from 1777 until 1792; However, he tended to be suspicious of the popular spontaneity and resisted a revolution. Born in 1744, Jovellanos was somewhat younger than Floridablanco. A writer and follower of the philosophers of the Enlightenment tradition of the previous century, Jovellanos had served as Minister of Justice from 1797 to 1798 and now commanded a substantial and influential group within the Central Junta. However, Jovellanos had been imprisoned by Manuel Godoy, Prince of the Peace, Manuel de Godoy, Duke of Alcudia, who had served as the prime minister, virtually running the country as a dictator from 1792 until 1798 and from 1801 until 1808. Accordingly, even Jovellanos tended to be somewhat overly cautious in his approach to the revolutionary upsurge that was sweeping Spain in 1808.
The Spanish army was stretched as it fought Napoleon's forces because of a lack of supplies and too many untrained recruits, but at Battle of Bailén, Bailén in June 1808, the Spanish army inflicted the first major defeat suffered by a Napoleonic army; this resulted in the collapse of French power in Spain. Napoleon took personal charge and with fresh forces, defeating the Spanish and British armies in a campaigns of attrition. After this the Spanish armies lost every battle they fought against the French imperial forces, but were never annihilated; after battles they retreated into the mountains to regroup and launch new attacks and raids on unsuspecting French forces. Guerrilla forces sprang up all over Spain and, with the army, tied down huge numbers of Napoleon's troops, making it difficult to sustain concentrated attacks on Spanish forces. The attacks and raids of the Spanish army and guerrillas became a massive drain on Napoleon's military and economic resources. In this war, Spain was aided by the British and Portuguese, led by the Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Duke of Wellington. The Duke of Wellington fought Napoleon's forces in the Peninsular War, with Joseph Bonaparte playing a minor role as king at Madrid. The brutal war was one of the first guerrilla warfare, guerrilla wars in modern Western history. French supply lines stretching across Spain were mauled repeatedly by the Spanish armies and guerrilla forces; thereafter, Napoleon's armies were never able to control much of the country and ending in French defeat. The war fluctuated, with Wellington spending several years behind his fortresses in Portugal while launching occasional campaigns into Spain.
After Napoleon's disastrous 1812 campaign in Russia, Napoleon began to recall his forces for the defence of France against the advancing Russian and other coalition forces, leaving his forces in Spain increasingly undermanned and on the defensive against the advancing Spanish, British and Portuguese armies. At the Battle of Vitoria in 1813, an allied army under the Duke of Wellington decisively defeated the French and in 1814 Ferdinand VII was restored as King of Spain.
In March 1812, the Cortes of Cádiz created the first modern Spanish constitution, the Spanish Constitution of 1812, Constitution of 1812 (informally named ''La Pepa''). This constitution provided for a separation of the powers of the executive and the legislative branches of government. The Cortes was to be elected by universal suffrage, albeit by an indirect method. Each member of the Cortes was to represent 70,000 people. Members of the Cortes were to meet in annual sessions. The King was prevented from either convening or proroguing the Cortes. Members of the Cortes were to serve single two-year terms. They could not serve consecutive terms; a member could serve a second term only by allowing someone else to serve a single intervening term in office. This attempt at the development of a modern constitutional government lasted from 1808 until 1814. Leaders of the liberals or reformist forces during this revolution were José Moñino, 1st Count of Floridablanca, José Moñino, Count of Floridablanca, Gaspar Melchor de Jovellanos and Pedro Rodríguez, Conde de Campomanes. Born in 1728, Floridablanca was eighty years of age at the time of the revolutionary outbreak in 1808. He had served as Prime Minister under King Charles III of Spain from 1777 until 1792; However, he tended to be suspicious of the popular spontaneity and resisted a revolution. Born in 1744, Jovellanos was somewhat younger than Floridablanco. A writer and follower of the philosophers of the Enlightenment tradition of the previous century, Jovellanos had served as Minister of Justice from 1797 to 1798 and now commanded a substantial and influential group within the Central Junta. However, Jovellanos had been imprisoned by Manuel Godoy, Prince of the Peace, Manuel de Godoy, Duke of Alcudia, who had served as the prime minister, virtually running the country as a dictator from 1792 until 1798 and from 1801 until 1808. Accordingly, even Jovellanos tended to be somewhat overly cautious in his approach to the revolutionary upsurge that was sweeping Spain in 1808.
The Spanish army was stretched as it fought Napoleon's forces because of a lack of supplies and too many untrained recruits, but at Battle of Bailén, Bailén in June 1808, the Spanish army inflicted the first major defeat suffered by a Napoleonic army; this resulted in the collapse of French power in Spain. Napoleon took personal charge and with fresh forces, defeating the Spanish and British armies in a campaigns of attrition. After this the Spanish armies lost every battle they fought against the French imperial forces, but were never annihilated; after battles they retreated into the mountains to regroup and launch new attacks and raids on unsuspecting French forces. Guerrilla forces sprang up all over Spain and, with the army, tied down huge numbers of Napoleon's troops, making it difficult to sustain concentrated attacks on Spanish forces. The attacks and raids of the Spanish army and guerrillas became a massive drain on Napoleon's military and economic resources. In this war, Spain was aided by the British and Portuguese, led by the Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Duke of Wellington. The Duke of Wellington fought Napoleon's forces in the Peninsular War, with Joseph Bonaparte playing a minor role as king at Madrid. The brutal war was one of the first guerrilla warfare, guerrilla wars in modern Western history. French supply lines stretching across Spain were mauled repeatedly by the Spanish armies and guerrilla forces; thereafter, Napoleon's armies were never able to control much of the country and ending in French defeat. The war fluctuated, with Wellington spending several years behind his fortresses in Portugal while launching occasional campaigns into Spain.
After Napoleon's disastrous 1812 campaign in Russia, Napoleon began to recall his forces for the defence of France against the advancing Russian and other coalition forces, leaving his forces in Spain increasingly undermanned and on the defensive against the advancing Spanish, British and Portuguese armies. At the Battle of Vitoria in 1813, an allied army under the Duke of Wellington decisively defeated the French and in 1814 Ferdinand VII was restored as King of Spain.
 Spain lost all of its North and South American territories, except Cuba and Puerto Rico, in a complex series of revolts 1808–26. Spain was at war with Britain 1798–1808, and the British blockade cut Spain's ties to the overseas empire. Trade was handled by American and Dutch traders. The colonies thus had achieved economic independence from Spain, and set up temporary governments or juntas which were generally out of touch with the mother country. After 1814, as Napoleon was defeated and Ferdinand VII was back on the throne, the king sent armies to regain control and reimpose autocratic rule. In the next phase 1809–16, Spain defeated all the uprising. A second round 1816–25 was successful and drove the Spanish out of all of its mainland holdings. Spain had no help from European powers. Indeed, Britain (and the United States) worked against it. When they were cut off from Spain, the colonies saw a struggle for power between Spaniards who were born in Spain (called "peninsulares") and those of Spanish descent born in New Spain (called "creoles"). The creoles were the activists for independence. Multiple revolutions enabled the colonies to break free of the mother country. In 1824 the armies of generals José de San Martín of Argentina and Simón Bolívar of Venezuela defeated the last Spanish forces; the final defeat came at the Battle of Ayacucho in southern History of Peru, Peru. After that Spain played a minor role in international affairs. Business and trade in the ex-colonies were under British control. Spain kept only Cuba and Puerto Rico in the New World.
Spain lost all of its North and South American territories, except Cuba and Puerto Rico, in a complex series of revolts 1808–26. Spain was at war with Britain 1798–1808, and the British blockade cut Spain's ties to the overseas empire. Trade was handled by American and Dutch traders. The colonies thus had achieved economic independence from Spain, and set up temporary governments or juntas which were generally out of touch with the mother country. After 1814, as Napoleon was defeated and Ferdinand VII was back on the throne, the king sent armies to regain control and reimpose autocratic rule. In the next phase 1809–16, Spain defeated all the uprising. A second round 1816–25 was successful and drove the Spanish out of all of its mainland holdings. Spain had no help from European powers. Indeed, Britain (and the United States) worked against it. When they were cut off from Spain, the colonies saw a struggle for power between Spaniards who were born in Spain (called "peninsulares") and those of Spanish descent born in New Spain (called "creoles"). The creoles were the activists for independence. Multiple revolutions enabled the colonies to break free of the mother country. In 1824 the armies of generals José de San Martín of Argentina and Simón Bolívar of Venezuela defeated the last Spanish forces; the final defeat came at the Battle of Ayacucho in southern History of Peru, Peru. After that Spain played a minor role in international affairs. Business and trade in the ex-colonies were under British control. Spain kept only Cuba and Puerto Rico in the New World.
 In Spain, the failure of the second bourgeois revolution was followed by a period of uneasy peace for the next decade. Having borne only a female heir presumptive, it appeared that Ferdinand would be succeeded by his brother, Infante Carlos, Count of Molina, Infante Carlos of Spain. While Ferdinand aligned with the conservatives, fearing another national insurrection, he did not view Carlos's reactionary policies as a viable option. Ferdinand – resisting the wishes of his brother – decreed the Pragmatic Sanction of 1830, enabling his daughter Isabella to become Queen. Carlos, who made known his intent to resist the sanction, fled to Portugal.
In Spain, the failure of the second bourgeois revolution was followed by a period of uneasy peace for the next decade. Having borne only a female heir presumptive, it appeared that Ferdinand would be succeeded by his brother, Infante Carlos, Count of Molina, Infante Carlos of Spain. While Ferdinand aligned with the conservatives, fearing another national insurrection, he did not view Carlos's reactionary policies as a viable option. Ferdinand – resisting the wishes of his brother – decreed the Pragmatic Sanction of 1830, enabling his daughter Isabella to become Queen. Carlos, who made known his intent to resist the sanction, fled to Portugal.
 In 1868 another insurgency, known as the Glorious Revolution (Spain), Glorious Revolution took place. The ''progresista'' generals Francisco Serrano y Dominguez, Francisco Serrano and Juan Prim revolted against Isabella and defeated her ''moderado'' generals at the Battle of Alcolea (1868). Isabella was driven into exile in Paris.
Two years later, in 1870, the Cortes declared that Spain would again have a king. Amadeus I of Spain, Amadeus of Savoy, the second son of King Victor Emmanuel II of Italy, was selected and duly crowned King of Spain early the following year. Amadeus – a liberal who swore by the liberal constitution the Cortes promulgated – was faced immediately with the incredible task of bringing the disparate political ideologies of Spain to one table. The country was plagued by internecine strife, not merely between Spaniards but within Spanish parties.
Following the Hidalgo affair and an army rebellion, Amadeus famously declared the people of Spain to be ungovernable, abdicated the throne, and left the country (11 February 1873).
;First Spanish Republic (1873–74)
In the absence of the Monarch, a government of radicals and Republicans was formed and declared Spain a republic. The First Spanish Republic (1873–74) was immediately under siege from all quarters. The Carlists were the most immediate threat, launching a violent insurrection after their poor showing in the 1872 elections. There were calls for socialist revolution from the International Workingmen's Association, revolts and unrest in the autonomous regions of Navarre and
In 1868 another insurgency, known as the Glorious Revolution (Spain), Glorious Revolution took place. The ''progresista'' generals Francisco Serrano y Dominguez, Francisco Serrano and Juan Prim revolted against Isabella and defeated her ''moderado'' generals at the Battle of Alcolea (1868). Isabella was driven into exile in Paris.
Two years later, in 1870, the Cortes declared that Spain would again have a king. Amadeus I of Spain, Amadeus of Savoy, the second son of King Victor Emmanuel II of Italy, was selected and duly crowned King of Spain early the following year. Amadeus – a liberal who swore by the liberal constitution the Cortes promulgated – was faced immediately with the incredible task of bringing the disparate political ideologies of Spain to one table. The country was plagued by internecine strife, not merely between Spaniards but within Spanish parties.
Following the Hidalgo affair and an army rebellion, Amadeus famously declared the people of Spain to be ungovernable, abdicated the throne, and left the country (11 February 1873).
;First Spanish Republic (1873–74)
In the absence of the Monarch, a government of radicals and Republicans was formed and declared Spain a republic. The First Spanish Republic (1873–74) was immediately under siege from all quarters. The Carlists were the most immediate threat, launching a violent insurrection after their poor showing in the 1872 elections. There were calls for socialist revolution from the International Workingmen's Association, revolts and unrest in the autonomous regions of Navarre and  Following the success of a December 1874 military coup the monarchy was restored in the person of Alfonso XII of Spain, Alfonso XII (the son of former queen Isabella II). The ongoing Carlist insurrection was eventually put down. The Restoration (Spain), Restoration period, following the proclamation of the Spanish Constitution of 1876, 1876 Constitution, witnessed the installment of an uncompetitive parliamentary system devised by Antonio Cánovas del Castillo, in which two "dynastic" parties, the conservatism, conservatives and the liberalism, liberals alternated in control of the government (''turnos, turnismo''). Election fraud (materialized in the so-called ''caciquismo'') became ubiquitous, with elections reproducing pre-arranged outcomes struck in the Capital. Voter apathy was no less important. The reign of Alfonso was followed by that of his son Alfonso XIII, initially a regency until the latter's coming of age in 1902.
The 1876 Constitution granted the Catholic Church a great grip over the education (particularly in the secondary education). Meanwhile, an organization formed in 1876 upon a group of Krausism, Krausists educators, the Institución Libre de Enseñanza, had a leading role in the educational and cultural renovation in the country, covering for the inaction of the Spanish State.
Following the success of a December 1874 military coup the monarchy was restored in the person of Alfonso XII of Spain, Alfonso XII (the son of former queen Isabella II). The ongoing Carlist insurrection was eventually put down. The Restoration (Spain), Restoration period, following the proclamation of the Spanish Constitution of 1876, 1876 Constitution, witnessed the installment of an uncompetitive parliamentary system devised by Antonio Cánovas del Castillo, in which two "dynastic" parties, the conservatism, conservatives and the liberalism, liberals alternated in control of the government (''turnos, turnismo''). Election fraud (materialized in the so-called ''caciquismo'') became ubiquitous, with elections reproducing pre-arranged outcomes struck in the Capital. Voter apathy was no less important. The reign of Alfonso was followed by that of his son Alfonso XIII, initially a regency until the latter's coming of age in 1902.
The 1876 Constitution granted the Catholic Church a great grip over the education (particularly in the secondary education). Meanwhile, an organization formed in 1876 upon a group of Krausism, Krausists educators, the Institución Libre de Enseñanza, had a leading role in the educational and cultural renovation in the country, covering for the inaction of the Spanish State.
 In 1868, Cuba launched a Ten Years' War, war of independence against Spain. On that island, as had been the case in Santo Domingo, the Spanish government found itself embroiled in a difficult campaign against an indigenous rebellion. Dominican Restoration War, Unlike in Santo Domingo, however, Spain initially won this struggle, having learned the lessons of guerrilla warfare well enough to defeat this rebellion. The pacification of the island was temporary, however, as the conflict Cuban War of Independence, revived in 1895 and ended in defeat at the hands of the United States in the Spanish–American War of 1898. Cuba gained its independence and Spain lost its remaining New World colony, Puerto Rico, which together with Guam and the Philippines were ceded to the United States for 20 million dollars. In 1899, Spain sold its remaining Pacific islands – the Northern Mariana Islands, Caroline Islands and Palau – to Germany and Spanish colonial possessions were reduced to Spanish Morocco, Spanish Sahara and Spanish Guinea, all in Africa.
The "disaster" of 1898 created the Generation of '98, a group of statesmen and intellectuals who demanded liberal change from the new government. However both Anarchism on the left and fascism on the right grew rapidly in Spain in the early 20th century. A revolt in 1909 in
In 1868, Cuba launched a Ten Years' War, war of independence against Spain. On that island, as had been the case in Santo Domingo, the Spanish government found itself embroiled in a difficult campaign against an indigenous rebellion. Dominican Restoration War, Unlike in Santo Domingo, however, Spain initially won this struggle, having learned the lessons of guerrilla warfare well enough to defeat this rebellion. The pacification of the island was temporary, however, as the conflict Cuban War of Independence, revived in 1895 and ended in defeat at the hands of the United States in the Spanish–American War of 1898. Cuba gained its independence and Spain lost its remaining New World colony, Puerto Rico, which together with Guam and the Philippines were ceded to the United States for 20 million dollars. In 1899, Spain sold its remaining Pacific islands – the Northern Mariana Islands, Caroline Islands and Palau – to Germany and Spanish colonial possessions were reduced to Spanish Morocco, Spanish Sahara and Spanish Guinea, all in Africa.
The "disaster" of 1898 created the Generation of '98, a group of statesmen and intellectuals who demanded liberal change from the new government. However both Anarchism on the left and fascism on the right grew rapidly in Spain in the early 20th century. A revolt in 1909 in  Alfonso XIII tacitly endorsed the September 1923 coup by General
Alfonso XIII tacitly endorsed the September 1923 coup by General  A provisional government presided by Niceto Alcalá Zamora was installed as the Republic, popularly nicknamed as "''la niña bonita''" ('the pretty girl'), was proclaimed on 14 April 1931, a democratic experiment at a time when democracies were beginning to descend into dictatorships elsewhere in the continent. A 1931 Spanish general election, Constituent election was called for June 1931. The dominant bloc emerging from the election, an alliance of liberals and socialists, brought Manuel Azaña (who had undertaken a decisive reform as War minister in the provisional government by trying to democratize the Armed Forces) to premiership, heading from the on a number of coalition cabinets. While the Republican government was able to easily quell the Sanjurjada, first 1932 coup d'etat led by José Sanjurjo, the generals, who felt humiliated because of the military reform privately developed a strong contempt towards Azaña. The new parliament drafted a Spanish Constitution of 1931, new constitution which was approved on 9 December 1931.
Political ideologies were intensely polarized, as both right and left saw vast evil conspiracies on the other side that had to be stopped. Regarding the crux of the role of the Church, within the Left people saw the former as the major enemy of modernity and the Spanish people, and the right saw it as the invaluable protector of Spanish values.
Under the Second Spanish Republic, Women's suffrage, women were allowed to vote in general elections for the first time. The Republic devolved substantial self-government to
A provisional government presided by Niceto Alcalá Zamora was installed as the Republic, popularly nicknamed as "''la niña bonita''" ('the pretty girl'), was proclaimed on 14 April 1931, a democratic experiment at a time when democracies were beginning to descend into dictatorships elsewhere in the continent. A 1931 Spanish general election, Constituent election was called for June 1931. The dominant bloc emerging from the election, an alliance of liberals and socialists, brought Manuel Azaña (who had undertaken a decisive reform as War minister in the provisional government by trying to democratize the Armed Forces) to premiership, heading from the on a number of coalition cabinets. While the Republican government was able to easily quell the Sanjurjada, first 1932 coup d'etat led by José Sanjurjo, the generals, who felt humiliated because of the military reform privately developed a strong contempt towards Azaña. The new parliament drafted a Spanish Constitution of 1931, new constitution which was approved on 9 December 1931.
Political ideologies were intensely polarized, as both right and left saw vast evil conspiracies on the other side that had to be stopped. Regarding the crux of the role of the Church, within the Left people saw the former as the major enemy of modernity and the Spanish people, and the right saw it as the invaluable protector of Spanish values.
Under the Second Spanish Republic, Women's suffrage, women were allowed to vote in general elections for the first time. The Republic devolved substantial self-government to  The Spanish Civil War was started by a 1936 Spanish coup d'etat, military coup d'etat in 17–18 July 1936 against the Republican government. The coup, intending to prevent social and economic reforms carried by the new government, had been carefully plotted since the electoral right-wing defeat at the 1936 Spanish general election, February 1936 election. The coup failed everywhere but in the Catholic heartland (Galicia, Old Castile and Navarre), Morocco,
The Spanish Civil War was started by a 1936 Spanish coup d'etat, military coup d'etat in 17–18 July 1936 against the Republican government. The coup, intending to prevent social and economic reforms carried by the new government, had been carefully plotted since the electoral right-wing defeat at the 1936 Spanish general election, February 1936 election. The coup failed everywhere but in the Catholic heartland (Galicia, Old Castile and Navarre), Morocco,  The Spanish Republican government moved to Valencia, to escape Madrid, which was under siege by the Nationalists. It had some military strength in the Air Force and Navy, but it had lost nearly all of the regular Army. After opening the arsenals to give rifles, machine guns and artillery to local militias, it had little control over the Loyalist ground forces. Republican diplomacy proved ineffective, with only two useful allies, the Soviet Union and Mexico. Britain, France and 27 other countries had agreed to an arms embargo on Spain, and the United States went along. Nazi Germany and Kingdom of Italy, Fascist Italy both signed that agreement, but ignored it and sent supplies and vital help, including a powerful air force under German command, the Condor Legion. Tens of thousands of Italians arrived under Italian command. Portugal supported the Nationalists, and allowed the trans-shipment of supplies to Franco's forces. The Soviets sold tanks and other armaments for Spanish gold, and sent well-trained officers and political commissars. It organized the mobilization of tens of thousands of mostly communist volunteers from around the world, who formed the International Brigades.
In 1936, the Left united in the Popular Front and were elected to power. However, this coalition, dominated by the centre-left, was undermined both by the revolutionary groups such as the anarchist Confederación Nacional del Trabajo (CNT) and Federación Anarquista Ibérica (FAI) and by anti-democratic far-right groups such as the Falange and the Carlists. The political violence of previous years began to start again. There were gunfights over strikes; landless labourers began to seize land, church officials were killed and churches burnt. On the other side, right wing militias (such as the Falange) and gunmen hired by employers assassinated left wing activists. The Republican democracy never generated the consensus or mutual trust between the various political groups that it needed to function peacefully. As a result, the country slid into civil war. The right wing of the country and high ranking figures in the army began to plan a coup, and when Falangist politician José Calvo-Sotelo was The Assassination of José Calvo Sotelo, shot by Republican police, they used it as a signal to act while the Republican leadership was confused and inert.
The Spanish Republican government moved to Valencia, to escape Madrid, which was under siege by the Nationalists. It had some military strength in the Air Force and Navy, but it had lost nearly all of the regular Army. After opening the arsenals to give rifles, machine guns and artillery to local militias, it had little control over the Loyalist ground forces. Republican diplomacy proved ineffective, with only two useful allies, the Soviet Union and Mexico. Britain, France and 27 other countries had agreed to an arms embargo on Spain, and the United States went along. Nazi Germany and Kingdom of Italy, Fascist Italy both signed that agreement, but ignored it and sent supplies and vital help, including a powerful air force under German command, the Condor Legion. Tens of thousands of Italians arrived under Italian command. Portugal supported the Nationalists, and allowed the trans-shipment of supplies to Franco's forces. The Soviets sold tanks and other armaments for Spanish gold, and sent well-trained officers and political commissars. It organized the mobilization of tens of thousands of mostly communist volunteers from around the world, who formed the International Brigades.
In 1936, the Left united in the Popular Front and were elected to power. However, this coalition, dominated by the centre-left, was undermined both by the revolutionary groups such as the anarchist Confederación Nacional del Trabajo (CNT) and Federación Anarquista Ibérica (FAI) and by anti-democratic far-right groups such as the Falange and the Carlists. The political violence of previous years began to start again. There were gunfights over strikes; landless labourers began to seize land, church officials were killed and churches burnt. On the other side, right wing militias (such as the Falange) and gunmen hired by employers assassinated left wing activists. The Republican democracy never generated the consensus or mutual trust between the various political groups that it needed to function peacefully. As a result, the country slid into civil war. The right wing of the country and high ranking figures in the army began to plan a coup, and when Falangist politician José Calvo-Sotelo was The Assassination of José Calvo Sotelo, shot by Republican police, they used it as a signal to act while the Republican leadership was confused and inert.
 The Nationalists under Franco won the war, and historians continue to debate the reasons. The Nationalists were much better unified and led than the Republicans, who squabbled and fought amongst themselves endlessly and had no clear military strategy. The Army went over to the Nationalists, but it was very poorly equipped – there were no tanks or modern airplanes. The small navy supported the Republicans, but their armies were made up of raw recruits and they lacked both equipment and skilled officers and sergeants. Nationalist senior officers were much better trained and more familiar with modern tactics than the Republicans.
On 17 July 1936, General
The Nationalists under Franco won the war, and historians continue to debate the reasons. The Nationalists were much better unified and led than the Republicans, who squabbled and fought amongst themselves endlessly and had no clear military strategy. The Army went over to the Nationalists, but it was very poorly equipped – there were no tanks or modern airplanes. The small navy supported the Republicans, but their armies were made up of raw recruits and they lacked both equipment and skilled officers and sergeants. Nationalist senior officers were much better trained and more familiar with modern tactics than the Republicans.
On 17 July 1936, General  The Siege of the Alcázar at Toledo (Spain), Toledo early in the war was a turning point, with the Nationalists successfully resisting after a long siege. The Republicans managed to Siege of Madrid, hold out in Madrid, despite a Nationalist assault in November 1936, and frustrated subsequent offensives against the capital at battle of Jarama, Jarama and battle of Guadalajara, Guadalajara in 1937. Soon, though, the Nationalists began to erode their territory, starving Madrid and making inroads into the east. The North, including the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque country fell in late 1937 and the Aragon front collapsed shortly afterwards. The bombing of Guernica on the afternoon of 26 April 1937 – a mission used as a testing ground for the German Luftwaffe's Condor Legion – was probably the most infamous event of the war and inspired Guernica (painting), Picasso's painting. The Battle of the Ebro in July–November 1938 was the final desperate attempt by the Republicans to turn the tide. When this failed and Barcelona fell to the Nationalists in early 1939, it was clear the war was over. The remaining Republican fronts collapsed, as civil war broke out inside the Left, as the Republicans suppressed the Communists. Madrid fell in March 1939.
The war cost between 300,000 and 1,000,000 lives. It ended with the total collapse of the Republic and the accession of Francisco Franco as dictator of Spain. Franco amalgamated all right wing parties into a reconstituted fascist party Falange and banned the left-wing and Republican parties and trade unions. The Church was more powerful than it had been in centuries.
The conduct of the war was brutal on both sides, with widespread massacres of civilians and prisoners. After the war, many thousands of Republicans were imprisoned and up to 150,000 were executed between 1939 and 1943. Some 500,000 refugees escaped to France; they remained in exile for years or decades.
The Siege of the Alcázar at Toledo (Spain), Toledo early in the war was a turning point, with the Nationalists successfully resisting after a long siege. The Republicans managed to Siege of Madrid, hold out in Madrid, despite a Nationalist assault in November 1936, and frustrated subsequent offensives against the capital at battle of Jarama, Jarama and battle of Guadalajara, Guadalajara in 1937. Soon, though, the Nationalists began to erode their territory, starving Madrid and making inroads into the east. The North, including the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque country fell in late 1937 and the Aragon front collapsed shortly afterwards. The bombing of Guernica on the afternoon of 26 April 1937 – a mission used as a testing ground for the German Luftwaffe's Condor Legion – was probably the most infamous event of the war and inspired Guernica (painting), Picasso's painting. The Battle of the Ebro in July–November 1938 was the final desperate attempt by the Republicans to turn the tide. When this failed and Barcelona fell to the Nationalists in early 1939, it was clear the war was over. The remaining Republican fronts collapsed, as civil war broke out inside the Left, as the Republicans suppressed the Communists. Madrid fell in March 1939.
The war cost between 300,000 and 1,000,000 lives. It ended with the total collapse of the Republic and the accession of Francisco Franco as dictator of Spain. Franco amalgamated all right wing parties into a reconstituted fascist party Falange and banned the left-wing and Republican parties and trade unions. The Church was more powerful than it had been in centuries.
The conduct of the war was brutal on both sides, with widespread massacres of civilians and prisoners. After the war, many thousands of Republicans were imprisoned and up to 150,000 were executed between 1939 and 1943. Some 500,000 refugees escaped to France; they remained in exile for years or decades.
 The Francoist regime resulted in the deaths and arrests of hundreds of thousands of people who were either supporters of the previous Second Republic of Spain or potential threats to Franco's state. They were executed, sent to prisons or concentration camps. According to Gabriel Jackson, the number of victims of the White Terror (executions and hunger or illness in prisons) just between 1939 and 1943 was 200,000. Child abduction was also a wide-scale practice. The lost children of Francoism may reach 300,000.
During Francisco Franco, Franco's rule, Spain was officially Spain in World War II, neutral in World War II and remained largely economically and culturally isolated from the outside world. Under a military dictatorship, Spain saw its political parties banned, except for the official party (Falange). Labour unions were banned and all political activity using violence or intimidation to achieve its goals was forbidden.
Under Franco, Spain actively sought the return of Gibraltar by the United Kingdom, and gained some support for its cause at the United Nations. During the 1960s, Spain began imposing restrictions on Gibraltar, culminating in the closure of the border in 1969. It was not fully reopened until 1985.
Spanish rule in Morocco ended in 1967. Though militarily victorious in the 1957–58 Ifni War, Moroccan invasion of Spanish West Africa, Spain gradually relinquished its remaining African colonies. Spanish Guinea was granted independence as Equatorial Guinea in 1968, while the Moroccan enclave of Ifni had been ceded to Morocco in 1969. Two cities in Africa,
The Francoist regime resulted in the deaths and arrests of hundreds of thousands of people who were either supporters of the previous Second Republic of Spain or potential threats to Franco's state. They were executed, sent to prisons or concentration camps. According to Gabriel Jackson, the number of victims of the White Terror (executions and hunger or illness in prisons) just between 1939 and 1943 was 200,000. Child abduction was also a wide-scale practice. The lost children of Francoism may reach 300,000.
During Francisco Franco, Franco's rule, Spain was officially Spain in World War II, neutral in World War II and remained largely economically and culturally isolated from the outside world. Under a military dictatorship, Spain saw its political parties banned, except for the official party (Falange). Labour unions were banned and all political activity using violence or intimidation to achieve its goals was forbidden.
Under Franco, Spain actively sought the return of Gibraltar by the United Kingdom, and gained some support for its cause at the United Nations. During the 1960s, Spain began imposing restrictions on Gibraltar, culminating in the closure of the border in 1969. It was not fully reopened until 1985.
Spanish rule in Morocco ended in 1967. Though militarily victorious in the 1957–58 Ifni War, Moroccan invasion of Spanish West Africa, Spain gradually relinquished its remaining African colonies. Spanish Guinea was granted independence as Equatorial Guinea in 1968, while the Moroccan enclave of Ifni had been ceded to Morocco in 1969. Two cities in Africa,