History of martial arts on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Although the earliest evidence of
Humanities dimension of physiotherapy, rehabilitation, nursing and public health
'. p. 21 Dating back to 3000 BC in
Academia Encounters the Chinese Martial arts
''China Review International'' 6 (2): 319–332. ISSN 1069-5834 Jiǎolì is also mentioned in the
A South Indian Martial Art and the Yoga and Ayurvedic Paradigms.
A Chronological History of the Martial Arts and Combative Sports.
''Electronic Journals of Martial Arts and Sciences''. The former included the bow and
''Traditional Iranian Martial Arts (Varzesh-e Pahlavani)''
pahlvani.com: Menlo Park. Accessed: 2007-02-08 to be traceable back to Arsacid Parthian times (132 BCE - 226 CE), and is still widely practiced today in the region. Following the development of
 European martial arts become tangible in Greek antiquity with
European martial arts become tangible in Greek antiquity with
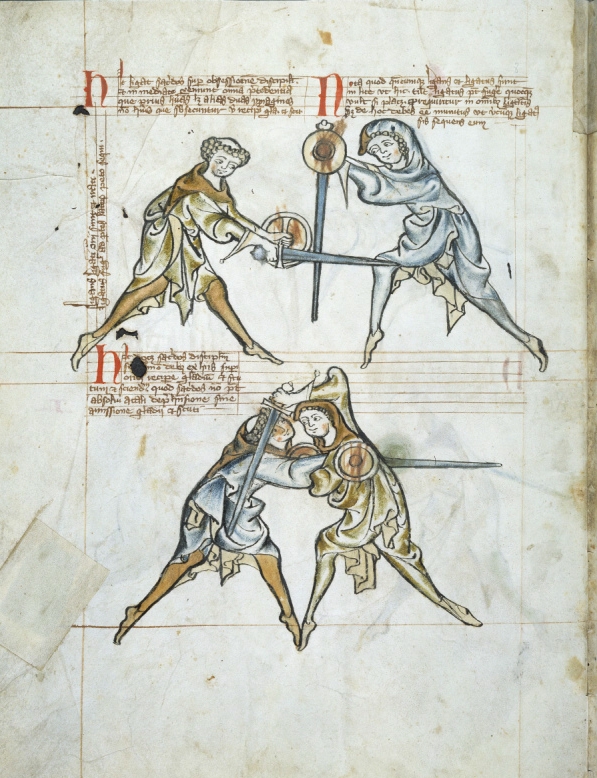 Pictorial sources of medieval combat include the Bayeux tapestry (11th century), the Morgan Bible (13th century).
The Icelandic sagas contain many realistic descriptions of Viking Age combat.
The earliest extant dedicated martial arts manual is the MS I.33 (c. 1300), detailing
Pictorial sources of medieval combat include the Bayeux tapestry (11th century), the Morgan Bible (13th century).
The Icelandic sagas contain many realistic descriptions of Viking Age combat.
The earliest extant dedicated martial arts manual is the MS I.33 (c. 1300), detailing
martial arts
Martial arts are codified systems and traditions of combat practiced for a number of reasons such as self-defense; military and law enforcement applications; combat sport, competition; physical, mental, and spiritual development; entertainment; a ...
goes back millennia, the true roots are difficult to reconstruct. Inherent patterns of human aggression
Aggression is overt or covert, often harmful, social interaction with the intention of inflicting damage or other harm upon another individual; although it can be channeled into creative and practical outlets for some. It may occur either reacti ...
which inspire practice of mock combat
Mock combat involves the execution of combative actions without intent to harm. Participants can engage in such sparring for ritual, training, recreational or performance reasons. The nature of mock combat can vary from realistic to symbolic.
M ...
(in particular wrestling
Wrestling is a series of combat sports involving grappling-type techniques such as clinch fighting, throws and takedowns, joint locks, pins and other grappling holds. Wrestling techniques have been incorporated into martial arts, combat ...
) and optimization of serious close combat
Close combat means a violent physical confrontation between two or more opponents at short range.''MCRP 3-02B: Close Combat'', Washington, D.C.: Department Of The Navy, Headquarters United States Marine Corps, 12 February 1999Matthews, Phil, CQB ...
as cultural universal
A cultural universal (also called an anthropological universal or human universal) is an element, pattern, trait, or institution that is common to all known human cultures worldwide. Taken together, the whole body of cultural universals is known ...
s are doubtlessly inherited from the pre-human stage and were made into an "art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
" from the earliest emergence of that concept. Indeed, many universals of martial art are fixed by the specifics of human physiology
The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.
It comprises a head ...
and not dependent on a specific tradition or era.
Specific martial traditions become identifiable in Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
, with disciplines such as shuai jiao
Shuai Jiao () is the term pertaining to the ancient jacket wrestling wushu style of Beijing, Tianjin and Baoding of Hebei Province in the North China Plain which was codified by Shan Pu Ying (善撲营 The Battalion of Excellency in Catching) o ...
, Greek wrestling
Greek wrestling ( grc-gre, πάλη, pálē), also known as Ancient Greek wrestling and Palé, was the most popular organized sport in Ancient Greece. A point was scored when one player touched the ground with his back, hip or shoulder, or conced ...
or those described in the Indian epics
Indian epic poetry is the epic poetry written in the Indian subcontinent, traditionally called ''Kavya'' (or ''Kāvya''; Sanskrit: काव्य, IAST: ''kāvyá''). The ''Ramayana'' and the ''Mahabharata'', which were originally composed in ...
or the Spring and Autumn Annals
The ''Spring and Autumn Annals'' () is an ancient Chinese chronicle that has been one of the core Chinese classics since ancient times. The ''Annals'' is the official chronicle of the State of Lu, and covers a 241-year period from 722 to 481 ...
of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
.
Early history
The earliest evidence for specifics of martial arts as practiced in the past comes from depictions of fights, both infigurative art
Figurative art, sometimes written as figurativism, describes artwork (particularly paintings and sculptures) that is clearly derived from real object sources and so is, by definition, representational. The term is often in contrast to abstract a ...
and in early literature, besides analysis of archaeological evidence, especially of weapon
A weapon, arm or armament is any implement or device that can be used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime, law enforcement, s ...
ry. The oldest work of art depicting scenes of battle, dating back 3400 BC, was the Ancient Egyptian paintings showing some form of struggle.Iwona Czerwinska Pawluk and Walery Zukow (2011). Humanities dimension of physiotherapy, rehabilitation, nursing and public health
'. p. 21 Dating back to 3000 BC in
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
(Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
), reliefs and the poems depicting struggle were found. In Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
, drawings and sketches from 2879 BCE describe certain ways of combat using sword, stick, bow, and spears.
The spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fasten ...
has been in use since the Lower Paleolithic
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears in ...
and retained its central importance well into the 2nd millennium AD. The bow appears in the Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coin ...
and is likewise only gradually replaced by the crossbow
A crossbow is a ranged weapon using an elastic launching device consisting of a bow-like assembly called a ''prod'', mounted horizontally on a main frame called a ''tiller'', which is hand-held in a similar fashion to the stock of a long fi ...
, and eventually firearm
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
s, in the Present Day. True bladed weapon
An edged weapon, or bladed weapon, is a melee weapon with a cutting edge. Bladed weapons include swords, daggers, knives, and bayonets. Edged weapons are used to cut, hack, or slash; some edged weapons (such as many kinds of swords) may also permit ...
s appear in the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
with the stone axe
A hand axe (or handaxe or Acheulean hand axe) is a prehistoric stone tool with two faces that is the longest-used tool in human history, yet there is no academic consensus on what they were used for. It is made from stone, usually flint or che ...
, and diversify in shape in the course of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
(khopesh
The ''khopesh'' ('; also vocalized khepesh) is an Egyptian sickle-shaped sword that evolved from battle axes.
Description
A typical ''khopesh'' is 50–60 cm (20–24 inches) in length, though smaller examples also exist. The inside c ...
/kopis
The term kopis ( grc, Κόπις) in Ancient Greece could describe a heavy knife with a forward-curving blade, primarily used as a tool for cutting meat, for ritual slaughter and animal sacrifice, or refer to a single edged cutting or "cut and ...
, sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
, dagger
A dagger is a fighting knife with a very sharp point and usually two sharp edges, typically designed or capable of being used as a thrusting or stabbing weapon.State v. Martin, 633 S.W.2d 80 (Mo. 1982): This is the dictionary or popular-use de ...
)
Some early examples are the depiction of wrestling
Wrestling is a series of combat sports involving grappling-type techniques such as clinch fighting, throws and takedowns, joint locks, pins and other grappling holds. Wrestling techniques have been incorporated into martial arts, combat ...
techniques in a tomb
A tomb ( grc-gre, τύμβος ''tumbos'') is a :wikt:repository, repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes. Placing a corpse into a tomb can be ...
of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt
The Middle Kingdom of Egypt (also known as The Period of Reunification) is the period in the history of ancient Egypt following a period of political division known as the First Intermediate Period. The Middle Kingdom lasted from approximatel ...
at Beni Hasan
Beni Hasan (also written as Bani Hasan, or also Beni-Hassan) ( ar, بني حسن) is an ancient Egyptian cemetery. It is located approximately to the south of modern-day Minya in the region known as Middle Egypt, the area between Asyut and Mem ...
(c. 2000 BC) and pictorial representations of fist fighting in the Minoan civilization
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age Aegean civilization on the island of Crete and other Aegean Islands, whose earliest beginnings were from 3500BC, with the complex urban civilization beginning around 2000BC, and then declining from 1450BC ...
dating to the 2nd millennium BCE.
In ancient China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, Yellow Emperor
The Yellow Emperor, also known as the Yellow Thearch or by his Chinese name Huangdi (), is a deity ('' shen'') in Chinese religion, one of the legendary Chinese sovereigns and culture heroes included among the mytho-historical Three Soverei ...
(2698 BC) is described as a famous general
A general officer is an Officer (armed forces), officer of highest military ranks, high rank in the army, armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers t ...
who, before becoming China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
’s leader, wrote lengthy treatises on medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
, astrology
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of Celestial o ...
and the martial arts
Martial arts are codified systems and traditions of combat practiced for a number of reasons such as self-defense; military and law enforcement applications; combat sport, competition; physical, mental, and spiritual development; entertainment; a ...
. Literary descriptions of combat began in the 2nd millennium BC, with mention of weaponry and combat in texts like the Gilgamesh epic or the Rig-Veda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one S ...
. Detailed description of Late Bronze Age to Early Iron Age hand-to-hand combat with spear, sword and shield are found in the ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odysse ...
'' (c. 8th century BC) and also the ''Mahabharatha
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the Kuruks ...
''.
Africa
AnEgypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
ian fresco, dated to 3400 BC, and depicting military training at Beni Hassan is the world's oldest known artistic representation of an organised fighting system. In gymnasiums similar to those of Greece, recruits would practice wrestling, callisthenics and duelling with single-stick. The attacking weapon apparently had a basket-guard protecting the hand, while the left forearm had a splint strapped on to serve as a shield. Soldiers fought with spears, large shields with an eye-hole, clubs, axes, poleaxes, flails, bows, slings, and swords of various forms.
Later, martial styles as varied as Gidigbo (a form of wrestling practiced by the Yoruba people
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute ...
of Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
), Donga (a form of stickfighting practiced by the Suri people of Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
), Musangwe (a form of bare-knuckle boxing practiced by the Venda people
The Venḓa (VhaVenḓa or Vhangona) are a Southern African Bantu people living mostly near the South African-Zimbabwean border.
The history of the Venda starts from the Kingdom of Mapungubwe (9th Century) where King Shiriyadenga was
the fi ...
of South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
), Tahtib (a form of stickfighting practiced by the Copt
Copts ( cop, ⲛⲓⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ ; ar, الْقِبْط ) are a Christians, Christian ethnoreligious group indigenous to North Africa who have primarily inhabited the area of modern Egypt and Sudan since Ancient history, antiqui ...
s of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
) and Engolo (a form of kicking, dodging and leg sweeping practiced by the tribes of the Cunene river
The Cunene (Portuguese spelling) or Kunene (common Namibian spelling) is a river in Southern Africa. It flows from the Angola highlands south to the border with Namibia. It then flows west along the border until it reaches the Atlantic Ocean. It ...
region of Angola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
), to name just a few, were developed by cultures all over Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
.
China
Antiquity (Zhou to Jin)
A hand-to-hand combat theory, including the integration of notions of "hard" and "soft" techniques, is expounded in the story of the ''Maiden of Yue'' in theSpring and Autumn Annals
The ''Spring and Autumn Annals'' () is an ancient Chinese chronicle that has been one of the core Chinese classics since ancient times. The ''Annals'' is the official chronicle of the State of Lu, and covers a 241-year period from 722 to 481 ...
of Wu and Yue (5th century BCE).
The '' Han History Bibliographies'' record that, by the Former Han
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
(206 BC – 9 AD), there was a distinction between no-holds-barred weaponless fighting, which it calls ''shǒubó'' (手搏), for which "how-to" manuals had already been written, and sportive wrestling, then known as juélì or jiǎolì (角力).
Wrestling is also documented in the Shǐ Jì, ''Records of the Grand Historian
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese hist ...
'', written by Sima Qian
Sima Qian (; ; ) was a Chinese historian of the early Han dynasty (206AD220). He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for his ''Records of the Grand Historian'', a general history of China covering more than two thousand years b ...
(c. 100 BCE).Henning, Stanley E. (Fall 1999)Academia Encounters the Chinese Martial arts
''China Review International'' 6 (2): 319–332. ISSN 1069-5834 Jiǎolì is also mentioned in the
Classic of Rites
The ''Book of Rites'', also known as the ''Liji'', is a collection of texts describing the social forms, administration, and ceremonial rites of the Zhou dynasty as they were understood in the Warring States and the early Han periods. The ''Book ...
(1st century BCE).Classic of Rites
The ''Book of Rites'', also known as the ''Liji'', is a collection of texts describing the social forms, administration, and ceremonial rites of the Zhou dynasty as they were understood in the Warring States and the early Han periods. The ''Book ...
. Chapter 6, Yuèlìng. Line 108.
In the 1st century, "Six Chapters of Hand Fighting", were included in the ''Han Shu'' (history of the Former Han Dynasty) written by Ban Gu
Ban Gu (AD32–92) was a Chinese historian, politician, and poet best known for his part in compiling the ''Book of Han'', the second of China's 24 dynastic histories. He also wrote a number of '' fu'', a major literary form, part prose ...
.
The Five Animals
In Chinese martial arts, there are fighting styles that are modeled after animals.
In Southern styles, especially those associated with Guangdong and Fujian provinces, there are five traditional animal styles known as Ng Ying Kung Fu (Chines ...
concept in Chinese martial arts is attributed to Hua Tuo
Hua Tuo ( 140–208), courtesy name Yuanhua, was a Chinese physician who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty. The historical texts '' Records of the Three Kingdoms'' and '' Book of the Later Han'' record Hua Tuo as the first person in Ch ...
, a 3rd-century physician.
Middle Ages
In theTang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
, descriptions of sword dance
Sword dances are recorded throughout world history. There are various traditions of solo and mock-battle (Pyrrhic) sword dances from Africa, Asia and Europe.
General types of sword dance include:
*solo dancers around swords – such as t ...
s were immortalized in poems by Li Bai
Li Bai (, 701–762), also pronounced as Li Bo, courtesy name Taibai (), was a Chinese poet, acclaimed from his own time to the present as a brilliant and romantic figure who took traditional poetic forms to new heights. He and his friend Du F ...
and Du Fu
Du Fu (; 712–770) was a Tang dynasty poet and politician. Along with his elder contemporary and friend Li Bai (Li Po), he is frequently called the greatest of the Chinese poets.Ebrey, 103. His greatest ambition was to serve his country as ...
. In the Song and Yuan dynasties, xiangpu (the earliest form of sumo
is a form of competitive full-contact wrestling where a ''rikishi'' (wrestler) attempts to force his opponent out of a circular ring (''dohyō'') or into touching the ground with any body part other than the soles of his feet (usually by thr ...
) contests were sponsored by the imperial courts.
In regard to the Shaolin fighting system, the oldest evidence of Shaolin participation in combat is a stele from 728 CE that attests to two occasions: a defense of the Shaolin Monastery
Shaolin Monastery (少林寺 ''Shàolínsì''), also known as Shaolin Temple, is a renowned monastic institution recognized as the birthplace of Chan Buddhism and the cradle of Shaolin Kung Fu. It is located at the foot of Wuru Peak of the So ...
from bandits around 610 CE, and their subsequent role in the defeat of Wang Shichong
Wang Shichong (; 567– August 621), courtesy name Xingman (行滿), was a Chinese military general, monarch, and politician during the Sui dynasty who deposed Sui's last emperor Yang Tong and briefly ruled as the emperor of a succeeding state ...
at the Battle of Hulao
The Battle of Hulao () or Battle of Sishui (汜水之戰, Wade–Giles: Ssŭ Shui), on 28 May 621 was the main and final battle of the Luoyang–Hulao campaign between the rival Tang, Zheng, and Xia regimes during the transition from Sui to Tan ...
in 621 CE. From the 8th to the 15th centuries, there are no extant documents that provide evidence of Shaolin participation in combat.
Late Ming
The modern concepts of wushu emerge by the late Ming to early Qing dynasties (16th to 17th centuries). Between the 16th and 17th centuries there are at least forty extant sources which provided evidence that, not only did monks of Shaolin practice martial arts, but martial practice had become such an integral element of Shaolin monastic life that the monks felt the need to justify it by creating newBuddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
lore.
References of martial practice in Shaolin appear in various literary genres of the late Ming: the epitaphs of Shaolin warrior monks, martial-arts manuals, military encyclopedias, historical writings, travelogues, fiction, and even poetry. However these sources do not point out to any specific style originated in Shaolin.
These sources, in contrast to those from the Tang period, refer to Shaolin methods of armed combat. This include the forte of Shaolin monks and for which they had become famous — the staff (gun); General Qi Jiguang
Qi Jiguang (, November 12, 1528 – January 17, 1588), courtesy name Yuanjing, art names Nantang and Mengzhu, posthumous name Wuyi, was a Chinese military general and writer of the Ming dynasty. He is best known for leading the defense on the ...
included these techniques in his book, Treatise of Effective Discipline.
India
Antiquity
ClassicalSanskrit epics
Indian epic poetry is the epic poetry written in the Indian subcontinent, traditionally called ''Kavya'' (or ''Kāvya''; Sanskrit: काव्य, IAST: ''kāvyá''). The ''Ramayana'' and the ''Mahabharata'', which were originally composed in ...
contain the earliest written accounts of combat in India. The term ''dwandwayuddha'' referred to a duel, such that it was a battle between only two warriors and not armies. The ''Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the Kuruk ...
'' describes a prolonged battle between Arjuna
Arjuna (Sanskrit: अर्जुन, ), also known as Partha and Dhananjaya, is a character in several ancient Hindu texts, and specifically one of the major characters of the Indian epic Mahabharata. In the epic, he is the third among Panda ...
and Karna
Karna (Sanskrit: कर्ण, IAST: ''Karṇa''), also known as Vasusena, Anga-raja, and Radheya, is one of the main protagonists of the Hindu epic '' Mahābhārata''. He is the son of the sun god Surya and princess Kunti (mother of the ...
using bows, swords, trees, and fists.Zarrilli, Phillip BA South Indian Martial Art and the Yoga and Ayurvedic Paradigms.
University of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an educational institution, institution of higher education, higher (or Tertiary education, tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. Universities ty ...
. Stories describing Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
report that he sometimes engaged in wrestling matches where he used knee strikes to the chest, punches to the head, hair pulling, and strangleholds. Another unarmed battle in the ''Mahabharata'' describes two fighters boxing
Boxing (also known as "Western boxing" or "pugilism") is a combat sport in which two people, usually wearing protective gloves and other protective equipment such as hand wraps and mouthguards, throw punches at each other for a predetermined ...
with clenched fists and fighting with kick
A kick is a physical Strike (attack), strike using the leg, in unison usually with an area of the knee or lower using the foot, heel, tibia (shin), ball of the foot, blade of the foot, toes or knee (the latter is also known as a knee (strike), ...
s, finger strikes, knee strike
A knee strike (commonly referred to simply as a knee) is a strike (attack), strike with the knee, either with the kneecap or the surrounding area. Kneeing is a disallowed practice in many combat sports, especially to the head of a downed opponent. ...
s and headbutt
A headbutt is a targeted strike with the head, typically (when intentional) involving the use of robust parts of the headbutter's cranium as the area of impact. The most effective headbutts strike the most sensitive areas of an opponent, such as ...
s. Krishna Maharaja, who single-handedly overcame an elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae an ...
according to the Mahabharata, is credited with developing the sixteen principles of armed combat.
Many of the popular sports mentioned in the Vedas
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the ...
and the epics have their origins in military training, such as boxing (musti-yuddha
Musti-Yuddha (Sanskrit: मुष्टि युद्ध) is a traditional combat sport originating from the Indian subcontinent. The term literally means "fist combat", from the Sanskrit words ''muṣṭi'' (fist) and ''yuddha'' (fight, battle, ...
), wrestling (''malladwandwa''), chariot-racing (''rathachalan''), horse-riding (''aswarohana'') and archery (''dhanurvidya''). Competitions were held not just as a contest of the players' prowess but also as a means of finding a bridegroom.
Ten fighting styles of northern India were said to have been created in different areas based on animals and gods, and designed for the particular geography of their origin. Tradition ascribes their convergence to the 6th-century in the Buddhist university of Takshashila
Taxila or Takshashila (; sa, तक्षशिला; pi, ; , ; , ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and ...
, located in today's Punjab region.
Middle Ages
Like other branches ofSanskrit literature
Sanskrit literature broadly comprises all literature in the Sanskrit language. This includes texts composed in the earliest attested descendant of the Proto-Indo-Aryan language known as Vedic Sanskrit, texts in Classical Sanskrit as well as s ...
, treatises on martial arts become more systematic in the course of the 1st millennium CE. The grappling art of vajra-mushti
Vajra-musti (Sanskrit:, "thunder fist" or "diamond fist") refers to a "fist-load, knuckleduster-like" weapon and also a form of Indian wrestling in which the weapon is employed. The weapon is sometimes called ''Indra-musti'' which means Indra's f ...
is mentioned in sources of the early centuries CE. Military accounts of the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gol ...
(c. 240–480) and the later ''Agni Purana'' identify over 130 different weapons, divided into thrown and unthrown classes and further into sub-classes. The ''Kama Sutra
The ''Kama Sutra'' (; sa, कामसूत्र, , ; ) is an ancient Indian Sanskrit text on sexuality, eroticism and emotional fulfillment in life. Attributed to Vātsyāyana, the ''Kama Sutra'' is neither exclusively nor predominantly ...
'' written by Vātsyāyana
Vātsyāyana was an ancient Indian philosopher, known for authoring the ''Kama Sutra''. He was a brahmin, and lived in India during the second or third century CE, probably in Pataliputra (modern day Patna in Bihar).
He is not to be confused w ...
suggested that women should regularly "practice with sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
, single-stick, quarterstaff
A quarterstaff (plural quarterstaffs or quarterstaves), also short staff or simply staff is a traditional European pole weapon, which was especially prominent in England during the Early Modern period.
The term is generally accepted to refer t ...
, and bow and arrow
An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty (and usually sharp and pointed) arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers c ...
."
The ''Sushruta Samhita
The ''Sushruta Samhita'' (सुश्रुतसंहिता, IAST: ''Suśrutasaṃhitā'', literally "Suśruta's Compendium") is an ancient Sanskrit text on medicine and surgery, and one of the most important such treatises on this subj ...
'' (c. 4th century) identifies 107 vital points on the human body of which 64 were classified as being lethal if properly struck with a fist or stick. Sushruta
Sushruta, or ''Suśruta'' (Sanskrit: सुश्रुत, IAST: , ) was an ancient Indian physician. The ''Sushruta Samhita'' (''Sushruta's Compendium''), a treatise ascribed to him, is one of the most important surviving ancient treatises on ...
's work formed the basis of the medical discipline ayurveda
Ayurveda () is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. The theory and practice of Ayurveda is pseudoscientific. Ayurveda is heavily practiced in India and Nepal, where around 80% of the population repo ...
which was taught alongside various martial arts. With numerous other scattered references to vital points in Vedic and epic sources, it is certain that Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
's early fighters knew and practised attacking or defending vital points.
Fighting arts were not exclusive to the kshatriya
Kshatriya ( hi, क्षत्रिय) (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority") is one of the four varna (social orders) of Hindu society, associated with warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the con ...
caste, though the warrior class used the systems more extensively. The 8th-century text ''Kuvalaymala'' by Udyotanasuri recorded such systems being taught at gurukula
A or ( sa, गुरुकुल, gurukul) is a type of education system in ancient India with ('students' or 'disciples') living near or with the guru, in the same house. The guru-shishya tradition is a sacred one in Hinduism and possibly ap ...
educational institutions, where Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests (purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru ...
students from throughout the subcontinent "were learning and practicing archery, fighting with sword and shield, with daggers, sticks, lances, and with fists, and in duels (niuddham)."
The earliest extant manual of Indian martial arts is contained as chapters 248 to 251 in the ''Agni Purana
The ''Agni Purana'', ( sa, अग्नि पुराण, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas of Hinduism. The text is variously classified as a Purana related to Shaivism, Vaishnavism, Shaktism and Smartism, but also co ...
'' (c. 8th – 11th centuries), giving an account of ''dhanurveda
''Dhanurveda'' (धनुर्वेद) () is a Sanskrit treatise on warfare and archery, traditionally regarded as an upaveda attached to ''Yajurveda'' (1100800 BCE) and attributed either to Bhrigu or Vishvamitra or Bharadwaja. It is one among t ...
'' in a total of 104 shloka
Shloka or śloka ( sa, श्लोक , from the root , Macdonell, Arthur A., ''A Sanskrit Grammar for Students'', Appendix II, p. 232 (Oxford University Press, 3rd edition, 1927). in a broader sense, according to Monier-Williams's dictionary, is ...
.
These verses describe how to improve a warrior's individual prowess and kill enemies using various different methods in warfare, whether a warrior went to war in chariots, elephants, horses, or on foot. Foot methods were subdivided into armed combat and unarmed combat.J. R. Svinth (2002)A Chronological History of the Martial Arts and Combative Sports.
''Electronic Journals of Martial Arts and Sciences''. The former included the bow and
arrow
An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty (and usually sharp and pointed) arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers c ...
, the sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
, spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fasten ...
, noose
A noose is a loop at the end of a rope in which the knot tightens under load and can be loosened without untying the knot.
The knot can be used to secure a rope to a post, pole, or animal but only where the end is in a position that the loop can ...
, armour
Armour (British English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or fr ...
, iron dart, club
Club may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Club'' (magazine)
* Club, a ''Yie Ar Kung-Fu'' character
* Clubs (suit), a suit of playing cards
* Club music
* "Club", by Kelsea Ballerini from the album ''kelsea''
Brands and enterprises
...
, battle axe
A battle axe (also battle-axe, battle ax, or battle-ax) is an axe specifically designed for combat. Battle axes were specialized versions of utility axes. Many were suitable for use in one hand, while others were larger and were deployed two-ha ...
, discus, and the trident
A trident is a three- pronged spear. It is used for spear fishing and historically as a polearm.
The trident is the weapon of Poseidon, or Neptune, the God of the Sea in classical mythology. The trident may occasionally be held by other marine ...
. The latter included wrestling
Wrestling is a series of combat sports involving grappling-type techniques such as clinch fighting, throws and takedowns, joint locks, pins and other grappling holds. Wrestling techniques have been incorporated into martial arts, combat ...
, knee strikes
A knee strike (commonly referred to simply as a knee) is a strike with the knee, either with the kneecap or the surrounding area. Kneeing is a disallowed practice in many combat sports, especially to the head of a downed opponent. Styles such as ...
, and punching
Punching is a forming process that uses a punch press to force a tool, called a ''punch'', through the workpiece to create a hole via shearing. Punching is applicable to a wide variety of materials that come in sheet form, including sheet meta ...
and kicking
A kick is a physical Strike (attack), strike using the leg, in unison usually with an area of the knee or lower using the foot, heel, tibia (shin), ball of the foot, blade of the foot, toes or knee (the latter is also known as a knee (strike), ...
methods.
Japan
The historical origin of Japanese martial arts can be found in the warrior traditions of thesamurai
were the hereditary military nobility and officer caste of medieval and early-modern Japan from the late 12th century until their abolition in 1876. They were the well-paid retainers of the '' daimyo'' (the great feudal landholders). They h ...
and the caste system that restricted the use of weapons by members of the non-warrior classes. Originally, samurai were expected to be proficient in many weapons, as well as unarmed combat, and attain the highest possible mastery of combat skills, for the purpose of glorifying either themselves or their liege. A large number of schools evolved to teach these skills with those existing before the Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored practical imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ...
classed as or old stream. Over time there was a trend away from the traditional purpose to a philosophy of coupling spiritual goals with the striving to perfect their martial skills.
The Japanese Book of Five Rings dates to 1664.
Korea
Taekkyon
Taekkyon, Taekgyeon, Taekkyeon, or Taekyun (Korean: 태껸/ 택견/ 托肩, ) is a traditional Korean martial art.
It is characterized by fluid, dynamic foot movement called "''pum balki''" or Stepping-on-Triangles. Taekkyon includes hands and ...
is the traditional martial art of Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
. Taekkyon came into existence sometime before the Silla
Silla or Shilla (57 BCE – 935 CE) ( , Old Korean: Syera, Old Japanese: Siraki2) was a Korean kingdom located on the southern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula. Silla, along with Baekje and Goguryeo, formed the Three Kingdoms of K ...
dynasty united the peninsula. It is believed Taekkyon was known as Subak at that time. Taekkyon focuses on up-right fighting: footwork, kicks, strikes, blocks, throws and rhythm.
Ssireum
''Ssireum'' (Hangul: ) or Korean wrestling is a folk wrestling style and traditional national sport of Korea that began in the fourth century.
In the modern form each contestant wears only a belt (satba) that wraps around the waist and the th ...
is the traditional wrestling art of Korea. Gakjeochong (각저총:角抵塚) murals show that wrestling in Korea dates back as early as the pre-Three Kingdom era. The Book of Later Han, a Chinese document that was written either before or early in the history of the Three Kingdoms also has records of Korean wrestling. Ssireum first gained widespread popularity during the Joseon dynasty (1392-1910).
Two Korean martial arts manuals Muyejebo
The ''Muyejebo'' (''Compendium of Several Martial Arts'') is the oldest extant Korean martial arts manual, written during the reign of King Seonjo (d. 1608).
The king died before the compendium was complete, and it was first published, with ...
and Muyedobotongji
Commissioned in 1790 by King Jeongjo (r. 1740–1810), the ''Muyedobotongji'' (or ''Muye Dobo Tong Ji''; translating to "Comprehensive Illustrated Manual of Martial Arts")
expanded on the eighteen weapons systems identified in the '' Muyeshinbo' ...
date from 1598 and 1790, respectively.
Sri Lanka
Angampora is an ancient Sri Lankan martial art that combines combat techniques, self-defense, sport, exercise, and meditation. According to apocryphal Sinhalese folklore, Angampora's history stretches to as far back as 3,000 years, with the Yaksha tribe (one of the four "hela" - the ancient tribes that inhabited the island) being identified as originators. With the advent of colonialism over the entirety of the island in 1815, Angampora fell into disuse and was very nearly lost as a part of the country's heritage. The British administration prohibited its practice due to the dangers posed by a civilian populace versed in a martial art, burning down any ''angan madu'' (practice huts devoted to the martial art) found: flouting of the law was punished by a gunshot to the knee, effectively crippling practitioners; Angampora nevertheless survived within a few families, allowing it to emerge into mainstream Sri Lankan culture post-independence.Persia (Iran)
The traditionalPersian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
style of grappling
Grappling, in hand-to-hand combat, describes sports that consist of gripping or seizing the opponent. Grappling is used at close range to gain a physical advantage over an opponent, either by imposing a position or causing injury. Grappling i ...
was known as koshti, with the physical exercise and schooled sport known as varzesh-e bastani
Pahlevani and zourkhaneh rituals is the name inscribed by UNESCO for varzesh-e pahlavāni ( fa, آیین پهلوانی و زورخانهای, "heroic sport") or varzesh-e bāstāni (; , "ancient sport"), a traditional system of athletics a ...
. It is saidNekoogar, Farzad (1996)''Traditional Iranian Martial Arts (Varzesh-e Pahlavani)''
pahlvani.com: Menlo Park. Accessed: 2007-02-08 to be traceable back to Arsacid Parthian times (132 BCE - 226 CE), and is still widely practiced today in the region. Following the development of
Sufi Islam
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, r ...
in the 8th century CE, varzesh-e pahlavani absorbed philosophical and spiritual components from that religion.
Pahlevani and zourkhaneh rituals is also an ancient martial art and the name inscribed by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
for varzesh-e pahlavāni ( fa, آیین پهلوانی و زورخانهای, "heroic sport") or varzesh-e bāstāni (; ''varzeš-e bāstānī'', "ancient sport"), a traditional system of athletics originally used to train warriors in Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
(Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
), and first appearing under this name and form in the Safavid era, with similarities to systems in adjacent lands under other names.
Turkic
Other historical grappling styles from the region include Turkic forms such askurash 'HISTORY OF KURASH''
Kurash is an ancient type of upright jacket grappling which originated in the territory of modern Uzbekistan. According to the latest scientific research the age of Kurash is at least three and a half thousand years. Kurash is ...
, köräş 'HISTORY OF KURASH''
Kurash is an ancient type of upright jacket grappling which originated in the territory of modern Uzbekistan. According to the latest scientific research the age of Kurash is at least three and a half thousand years. Kurash is ...
and yağlı güreş
Oil wrestling ( tr, Yağlı güreş), also called grease wrestling, is a traditional Turkish sport, where participants, called ''pehlivan'' (wrestlers) or ''baspehlivan'' (master wrestlers), wrestle while covered in oil. Competitions are held in ...
.
Arab
The north Arabian tradition of horsemanship quickly became an integral part of warfare throughout theArab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
and much of the West Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
. The Middle Ages saw the flourishing of the furusiyya
' (; also transliterated as ) is the historical Arabic term for equestrian martial exercise. ''Furūsiyya'' “Knighthood” is a martial tradition dating back to Pre-Islamic Arabia
Its main branches concerned horsemanship (including aspects ...
culture, combining the ancient Bedouin concept of honour (''muru'ah'') with the Islamic ideals of chivalry. A ' (meaning knight or horseman) would first hone his skills in wrestling and armed combat on the ground before learning to fight while mounted. Furusiyya literature from the 9th to 15th century deal with equestrianism, archery, military strategy, duelling and charging with the lance. Armed fighting included the use of the sword (''sayf''), spear, lance, javelin, dagger (''jambiya''), staff, axe (''tabar''), warhammer, and curved bow. There is also ''Tahtib'' (التحطيب) which was practiced in ancient Egypt and is still performed in celebrations.
Europe
Antiquity
 European martial arts become tangible in Greek antiquity with
European martial arts become tangible in Greek antiquity with pankration
Pankration (; el, παγκράτιον) was a sporting event introduced into the Greek Olympic Games in 648 BC, which was an empty-hand submission sport with few rules. The athletes used boxing and wrestling techniques but also others, such as ...
and other martially oriented disciplines of the ancient Olympic Games
The ancient Olympic Games (Ὀλυμπιακοὶ ἀγῶνες; la, Olympia, neuter plural: "the Olympics") were a series of athletic competitions among representatives of city-states and were one of the Panhellenic Games of Ancient Greece. ...
. Boxing became Olympic
Olympic or Olympics may refer to
Sports
Competitions
* Olympic Games, international multi-sport event held since 1896
** Summer Olympic Games
** Winter Olympic Games
* Ancient Olympic Games, ancient multi-sport event held in Olympia, Greece b ...
in Greece as early as 688 BCE. Detailed depictions of wrestling techniques are preserved in vase paintings of the Classical period. Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
's ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odysse ...
'' has a number of detailed descriptions of single combat
Single combat is a duel between two single warriors which takes place in the context of a battle between two armies.
Instances of single combat are known from Classical Antiquity and the Middle Ages. The champions were often combatants who repres ...
with spear, sword and shield.
Gladiatorial combat
A gladiator ( la, gladiator, "swordsman", from , "sword") was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gla ...
appears to have Etruscan roots, and is documented in Rome from the 260s BCE.
The papyrus fragment known as P.Oxy. III 466 Papyrus Oxyrhynchus III 466 (P. Oxy. III,466) is a fragmentary 2nd century Greek papyrus manuscript containing instructions for wrestling, including the description of various grips and holds, constituting the earliest historical European martial ...
dating from the 2nd century gives the earliest surviving description in writing of wrestling techniques.
In Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label=Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after ...
, a Mediterranean island, a fighting style which has been called ''istrumpa'' was practised in the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
, as demonstrated by the finding of a little bronze statue (known as "''Bronzetto dei lottatori''" or "bronze of the fighting men"), which shows two fighters struggling with each other on the ground.
Middle Ages
 Pictorial sources of medieval combat include the Bayeux tapestry (11th century), the Morgan Bible (13th century).
The Icelandic sagas contain many realistic descriptions of Viking Age combat.
The earliest extant dedicated martial arts manual is the MS I.33 (c. 1300), detailing
Pictorial sources of medieval combat include the Bayeux tapestry (11th century), the Morgan Bible (13th century).
The Icelandic sagas contain many realistic descriptions of Viking Age combat.
The earliest extant dedicated martial arts manual is the MS I.33 (c. 1300), detailing sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
and buckler combat, compiled in a Franconian monastery. The manuscript consists of 64 images with Latin commentary, interspersed with technical vocabulary in Middle High German, German. While there are earlier manuals of wrestling techniques, I.33 is the earliest known manual dedicated to teaching armed single combat.
Wrestling throughout the Middle Ages was practiced by all social strata. Jousting and the medieval tournament, tournament were popular martial arts practiced by nobility throughout the High and Late Middle Ages.
The Late Middle Ages see the appearance of elaborate fencing systems, such as the German school of fencing, German or Italian school of fencing, Italian schools. Fencing schools (''Fechtschulen'') for the new bourgeois class become popular, increasing the demand for professional instructors (fencing masters, ''Fechtmeister''). The martial arts techniques taught in this period is preserved in a number of 15th-century ''Fechtbücher''.
Renaissance to Early Modern period
The late medieval German school survives into the German Renaissance, and there are a number of printed 16th-century manuals (notably the one by Joachim Meyer, 1570). But by the 17th century, the German school declines in favour of the Italian Dardi school, reflecting the transition to rapier fencing in the upper classes. Wrestling comes to be seen as an ignoble pursuit proper for the lower classes and until its 19th-century revival as a modern sport becomes restricted to folk wrestling. In the Baroque period, fashion shifts from Italian to Spanish masters, and their elaborate systems of Destreza. In the mid-18th century, in keeping with the general Rococo fashion, French masters rise to international prominence, introducing the foil (fencing), foil, and much of the Fencing terms, terminology still current in modern sports fencing. There are also a number of Early Modern fencing masters of note in England, such as George Silver and Joseph Swetnam. Academic fencing takes its origin in the Middle Ages, and is subject to the changes of fencing fashion throughout the Early Modern period. It establishes itself as the separate style of Mensur fencing in the 18thModern history (1800 to present)
The Western interest in East Asian martial arts dates back to the late 19th century, due to the increase in trade between the West withChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
and Japan. European martial arts before that time was focused on the duelling sword among the upper classes on one hand, and various styles of folk wrestling among the lower classes on the other.
Savate appears in the early 19th century in France, as a mix between English boxing and French folk kicking techniques. At that time, in France, it existed in gyms called ''salles d'armes'' where savate, English boxing, fencing, canne de combat and sometimes even wrestling
Wrestling is a series of combat sports involving grappling-type techniques such as clinch fighting, throws and takedowns, joint locks, pins and other grappling holds. Wrestling techniques have been incorporated into martial arts, combat ...
was practiced.
Edward William Barton-Wright, a British railway engineer who had studied jujutsu while working in Japan between 1894 and 1897, was the first man known to have taught Asian martial arts in Europe. He also founded an eclectic martial arts style named Bartitsu which combined jujutsu, judo, wrestling, boxing, savate and stick fighting. Also during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, catch wrestling contests became immensely popular in Europe.
The development of Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu from the early 20th century is a good example of the worldwide cross-pollination and syncretism of martial arts traditions.
The later 1970s and 1980s witnessed an increased media interest in the martial arts, thanks in part to Asian and Hollywood martial arts movies and very popular television shows like "Kung Fu (TV series), Kung Fu", "Martial Law (TV series), Martial Law" and "The Green Hornet#Television, The Green Hornet" that incorporated martial arts moments or themes. Following Bruce Lee, both Jackie Chan and Jet Li are prominent movie figures who have been responsible for promoting Chinese martial arts in recent years.
Combined Olympic medal table
Martial arts have been a part of the modern Olympic games since 1896. The following table is correct up to and including the 2021 Summer Games.Reconstruction
The reconstruction of a martial art as practiced in a specific period is distinct from the practice of a traditional fighting system handed down by way of master-student transmission. The largest movement of martial arts reconstruction is the Historical European Martial Arts revival (HEMA), gaining momentum since the late 1990s. To a limited extent, there are also attempts to reconstruct other styles, such as Korean swordsmanship and Persian armed combat called ''razmafzar''. The Japanese term Koryū refers to "old schools" of martial arts which predate 1868; it does not imply that historical styles are actively reconstructed, just that the school's tradition goes back 150 years or more. A reconstructed martial art necessarily rests on historical records, either combat manuals or pictorial representations. Martial arts reconstruction specifically does not claim an unbroken tradition of some historical martial arts. On the contrary, the premise is that in an unbroken tradition, styles significantly evolve over time. It is not necessary for the tradition to have been interrupted in order to reconstruct an earlier style; a case in point is classical fencing which reconstructs the sport fencing of the 19th century before it evolved into current Olympic fencing, or historical German ''ringen'' which over time developed into contemporary styles of folk wrestling. Claims of ancient martial arts which survive unchanged by unbroken tradition (e.g. as suggested by Yehoshua Sofer), do not fall under reconstruction and are by their nature unverifiable, even to the person making the claim. Certain modern schools of Ninjutsu may fall under the category of martial arts reconstruction; the Bujinkan organization claims to base their teaching on a manuscript documenting a historical school, known as Togakure-ryū, dated to the 12th century. But as this manuscript is supposedly in the private possession of Masaaki Hatsumi, its authenticity, or indeed existence, cannot be verified by independent parties.See also
*Martial arts timeline *History of sport *History of archery *History of warfare *History of wrestling *History of physical training and fitnessReferences
Bibliography
*Michael B. Poliakoff, ''Combat Sports in the Ancient World: Competition, Violence, and Culture'' Sports and History Series, Yale University Press (1987). *Thomas A. Green, Joseph R. Svinth (eds.), ''Martial Arts of the World: An Encyclopedia of History and Innovation'', 2010, two volumes: vol. 1: 'Regions and Individual Arts', ; vol. 2: 'Themes', . {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Martial Arts Martial arts Historical martial arts, * History of sports by sport, Martial arts