Hermeric on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Hermeric (died 441) was the king of the Suevi from at least 419 and possibly as early as 406 until his abdication in 438.
Hermeric (died 441) was the king of the Suevi from at least 419 and possibly as early as 406 until his abdication in 438.
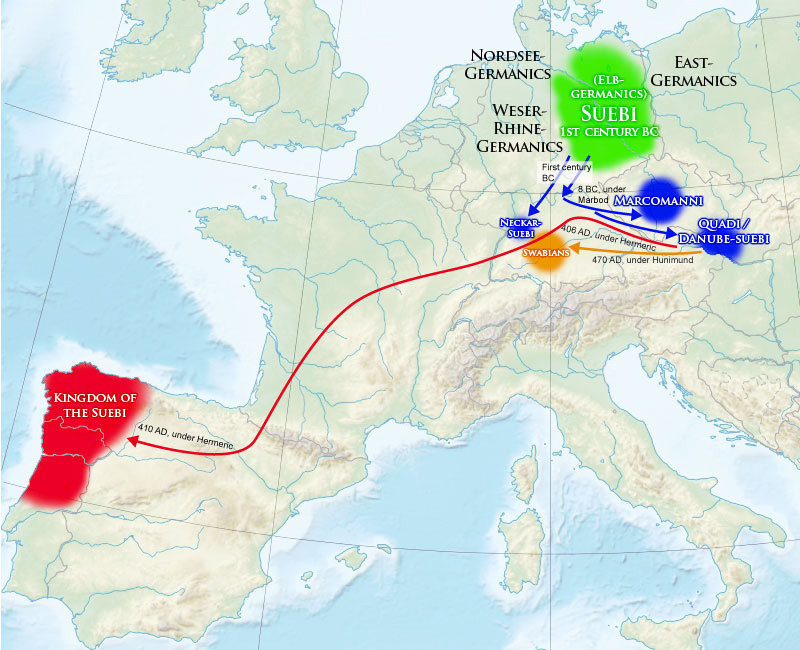 Nothing is known for sure about Hermeric before 419, the year in which he is first mentioned; namely, he became king of the Suebi (or Suevi) in the city of
Nothing is known for sure about Hermeric before 419, the year in which he is first mentioned; namely, he became king of the Suebi (or Suevi) in the city of
"The Career of the 'Comes Hispaniarum' Asterius."
''Phoenix'', Vol. 54, No. 1/2. (Spring–Summer, 2000), pp. 123–141. {{Galician monarchs 5th-century Suebian kings 441 deaths Germanic warriors Year of birth unknown
 Hermeric (died 441) was the king of the Suevi from at least 419 and possibly as early as 406 until his abdication in 438.
Hermeric (died 441) was the king of the Suevi from at least 419 and possibly as early as 406 until his abdication in 438.
Biography
Before 419
 Nothing is known for sure about Hermeric before 419, the year in which he is first mentioned; namely, he became king of the Suebi (or Suevi) in the city of
Nothing is known for sure about Hermeric before 419, the year in which he is first mentioned; namely, he became king of the Suebi (or Suevi) in the city of Braga
Braga ( , ; cel-x-proto, Bracara) is a city and a municipality, capital of the northwestern Portuguese district of Braga and of the historical and cultural Minho Province. Braga Municipality has a resident population of 193,333 inhabitants (in ...
(Bracara Augusta) according to bishop Hydatius
Hydatius, also spelled Idacius (c. 400 – c. 469) was a late Western Roman writer and clergyman. The bishop of Aquae Flaviae in the Roman province of Gallaecia (almost certainly the modern Chaves, Portugal, in the modern district of Vila Real), ...
(who wrote his chronicle around the year 470). Although bishop Isidore of Seville
Isidore of Seville ( la, Isidorus Hispalensis; c. 560 – 4 April 636) was a Spanish scholar, theologian, and archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded, in the words of 19th-century historian Montalembert, as "the last scholar of ...
, writing his ''Historia de regibus Gothorum, Vandalorum et Suevorum
The ''Historia de regibus Gothorum, Vandalorum et Suevorum'' ("History of the Kings of the Goths, Vandals and Suevi") is a Latin history of the Goths from 265 to 624, written by Isidore of Seville. It is a condensed account and, due to its diver ...
'' two centuries after the fact, claims that Hermeric was already king of the Suebi from 406, Isidore based himself on primarily on Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian presbyter, priest, Confessor of the Faith, confessor, th ...
, Hydatius
Hydatius, also spelled Idacius (c. 400 – c. 469) was a late Western Roman writer and clergyman. The bishop of Aquae Flaviae in the Roman province of Gallaecia (almost certainly the modern Chaves, Portugal, in the modern district of Vila Real), ...
, Prosper of Aquitaine
Prosper of Aquitaine ( la, Prosper Aquitanus; – AD), a Christian writer and disciple of Augustine of Hippo, was the first continuator of Jerome's Universal Chronicle.
Life
Prosper was a native of Aquitaine, and may have been educated at ...
and Orosius
Paulus Orosius (; born 375/385 – 420 AD), less often Paul Orosius in English, was a Roman priest, historian and theologian, and a student of Augustine of Hippo. It is possible that he was born in '' Bracara Augusta'' (now Braga, Portugal), t ...
, none of whom mentions Hermeric prior to 419.
Hermeric was a pagan
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. ...
and an enemy of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
throughout his life. He is given a reign of thirty-two years in most manuscripts of Isidore of Seville's '' Historia Suevorum'', but one manuscript does list his reign as fourteen years.Thompson, 129 and 306n32.
According to Thompson (1982)'s interpretation of Isidore, Hermeric led the Suevi across the Rhine along with the Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal Kingdom, Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The ...
and Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Al ...
in December 406. They crossed Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
and the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to C ...
and settled in Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hispania ...
. Kulikowski (2000 & 2015) argued that the Suebi probably stayed in northern Gaul throughout 407 to 409, and moved to Galicia between 409 and 411. While Theodore Mommsen
Christian Matthias Theodor Mommsen (; 30 November 1817 – 1 November 1903) was a German classical scholar, historian, jurist, journalist, politician and archaeologist. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest classicists of the 19th centur ...
believed the Suevi were ''foederati
''Foederati'' (, singular: ''foederatus'' ) were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as ''foedus'', with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the ''socii'', but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign stat ...
'' and Ernst Stein seconded the notion by believing they had made an agreement with the Roman usurper
Roman usurpers were individuals or groups of individuals who obtained or tried to obtain power by force and without legitimate legal authority. Usurpation was endemic during the Roman imperial era, especially from the crisis of the third century ...
Magnus Maximus
Magnus Maximus (; cy, Macsen Wledig ; died 8 August 388) was Roman emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 383 to 388. He usurped the throne from emperor Gratian in 383 through negotiation with emperor Theodosius I.
He was made emperor in B ...
whereby they received the western half of Iberia, there is no primary evidence for any alliance between the Suevi and Rome.Thompson, 153–154. In 411 (according to Ludwig Schmidt) or 417 (according to Felix Dahn
Felix Dahn (9 February 1834 – 3 January 1912) was a German law professor, German nationalist author, poet and historian.
Biography
Ludwig Julius Sophus Felix Dahn was born in Hamburg as the oldest son of Friedrich (1811–1889) and Constanze ...
), Hermeric made a treaty with the Roman emperor Honorius, but in fact the only event of note in 411 was the division of Iberia ''sorte'' (by lot) between the barbarian peoples. The east of the province of Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia (Spain), Galicia, Norte, Portugal, northern Portugal, Asturias and León (province), Leon and the lat ...
with its capital of Braga
Braga ( , ; cel-x-proto, Bracara) is a city and a municipality, capital of the northwestern Portuguese district of Braga and of the historical and cultural Minho Province. Braga Municipality has a resident population of 193,333 inhabitants (in ...
(Bracara Augusta) fell to the Suevi, while the west of the province went to the populous Hasdingi The Hasdingi were one of the Vandal peoples of the Roman era. The Vandals were Germanic peoples, who are believed to have spoken an East Germanic language, and were first reported during the first centuries of the Roman empire in the area which is ...
. Between 416 and 418, the Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
under Wallia
Wallia or Walha ( Spanish: ''Walia'', Portuguese ''Vália''), ( 385 – 418) was king of the Visigoths from 415 to 418, earning a reputation as a great warrior and prudent ruler. He was elected to the throne after Athaulf and then Sigeric were ...
made war on Hermeric on behalf of Rome.
After 419
In 419, after a personal dispute between Hermeric and the Vandal kingGunderic
Gunderic ( la, Gundericus; 379–428), King of Hasding Vandals (407-418), then King of Vandals and Alans (418–428), led the Hasding Vandals, a Germanic tribe originally residing near the Oder River, to take part in the barbarian invasions of ...
, the Vandals attacked the Suevi and trapped Hermeric in the Nervasian (Erbasian) Mountains before the Roman general Asterius intervened and the Vandals retreated.Thompson, 165. Thereafter, until the Vandals left Iberia for Africa in 429, Hermeric remained peaceful, but in 430 he began to raid Gallaecia.
In 431 a Gallaecian named Hydatius
Hydatius, also spelled Idacius (c. 400 – c. 469) was a late Western Roman writer and clergyman. The bishop of Aquae Flaviae in the Roman province of Gallaecia (almost certainly the modern Chaves, Portugal, in the modern district of Vila Real), ...
went to Flavius Aëtius
Aetius (also spelled Aëtius; ; 390 – 454) was a Roman general and statesman of the closing period of the Western Roman Empire. He was a military commander and the most influential man in the Empire for two decades (433454). He managed pol ...
to plead for help against the Suevi, but Aëtius delayed until 432 the sending of the comes
''Comes'' ( ), plural ''comites'' ( ), was a Roman title or office, and the origin Latin form of the medieval and modern title "count".
Before becoming a word for various types of title or office, the word originally meant "companion", either i ...
Censorius
Censorius (died 448) was a count (''comes'') of the Western Roman Empire from 432 until his death. He is mentioned in the ''Chronicle'' of Hydatius under the years 432 and 440.
In 432, 437, and 440 he was sent into Hispania as an ambassador to th ...
. According to Hydatius' ''Chronicle'' of contemporary events, the Gallaecian ''plebs'' in the better-fortified strongpoints defeated Hermeric and his men, inflicting heavy casualties and taking many prisoners, which forced the Sueves to release the Gallaecian families they had taken captive (430).Thompson, 178.
In 435, "on episcopal intervention", possibly Hydatius', Hermeric made peace with the Gallaecians.Thompson, 179 and 301n94. In that same year, Hermeric negotiated through the Catholic bishop Symphosius
Symphosius (sometimes, in older scholarship and less properly, Symposius) was the author of the ''Aenigmata'', an influential collection of 100 Latin riddles, probably from the late antique period. They have been transmitted along with their soluti ...
directly with the Western Roman Emperor. In 437, Censorius made a second expedition accompanied by Fretimund.
After seven years of illness, Hermeric was forced to retire from the kingship in 438 and pass it on to his son Rechila
Rechila (died 448) was the Suevic king of Galicia from 438 until his death. There are few primary sources for his life, but Hydatius was a contemporary Christian (non- Arian) chronicler in Galicia.
When his father, Hermeric, turned ill in 438, h ...
. The story, recorded in Isidore, that Hermeric sent Rechila to Baetica
Hispania Baetica, often abbreviated Baetica, was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula). Baetica was bordered to the west by Lusitania, and to the northeast by Hispania Tarraconensis. Baetica remained one of the basi ...
to defeat Andevotus, ''Romanae militiae dux'', is false, as there is no contemporary evidence that Hermeric retained any authority after his abdication.Thompson, 120. There appears to have been no principle of elective monarchy among the Suevi and the successes of their raids may have accounted for the contentment of their people. Hermeric's royal line lasted until 456.
In 429, there appeared briefly a Suevic military leader named Heremigarius Heremigarius (also Hermigarius or Hermegarius) ( fl. 427–428) was a Suevic military leader operating in Lusitania in the early fifth century. He may have been a joint monarch with Hermeric or his successor, but no primary source directly attest ...
operating in Lusitania
Lusitania (; ) was an ancient Iberian Roman province located where modern Portugal (south of the Douro river) and
a portion of western Spain (the present Extremadura and the province of Salamanca) lie. It was named after the Lusitani or Lusita ...
who may have been a joint monarch with Hermeric, but there is no primary source to prove it.Thompson, 166.
Misspelling issues
Hermeric has been sometimes misspelled as or confused withHermeneric
Hermeneric was a Suevic King of Galicia according to a now lost document described by the priest Antonio de Yepes. According to Yepes, the king reigned around 485, which falls within a century-long period (469–c.560) of obscurity during whi ...
in written documents. This is a quite significant issue among scholars and in academia.
See also
*Cindazunda Cindazunda was the daughter of Hermeric, king of the Suebi in the territory that would become Spain's Galiza and both the Norte Region, Portugal, Norte Region and the Centro Region of Portugal. She married Attaces, king of the Alans, in the early 5t ...
Notes
Sources
*Thompson, E. A.
Edward Arthur Thompson (22 May 1914 – 1 January 1994) was an Irish-born British Marxist historian of classics and medieval studies. He was professor and director of the classics department at the University of Nottingham from 1948 to 197 ...
''Romans and Barbarians: The Decline of the Western Empire''. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1982. .
*Kulikowski, Michael"The Career of the 'Comes Hispaniarum' Asterius."
''Phoenix'', Vol. 54, No. 1/2. (Spring–Summer, 2000), pp. 123–141. {{Galician monarchs 5th-century Suebian kings 441 deaths Germanic warriors Year of birth unknown