heel (shoe) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The heel is the prominence at the posterior end of the foot. It is based on the projection of one bone, the calcaneus or heel bone, behind the articulation of the bones of the lower leg.
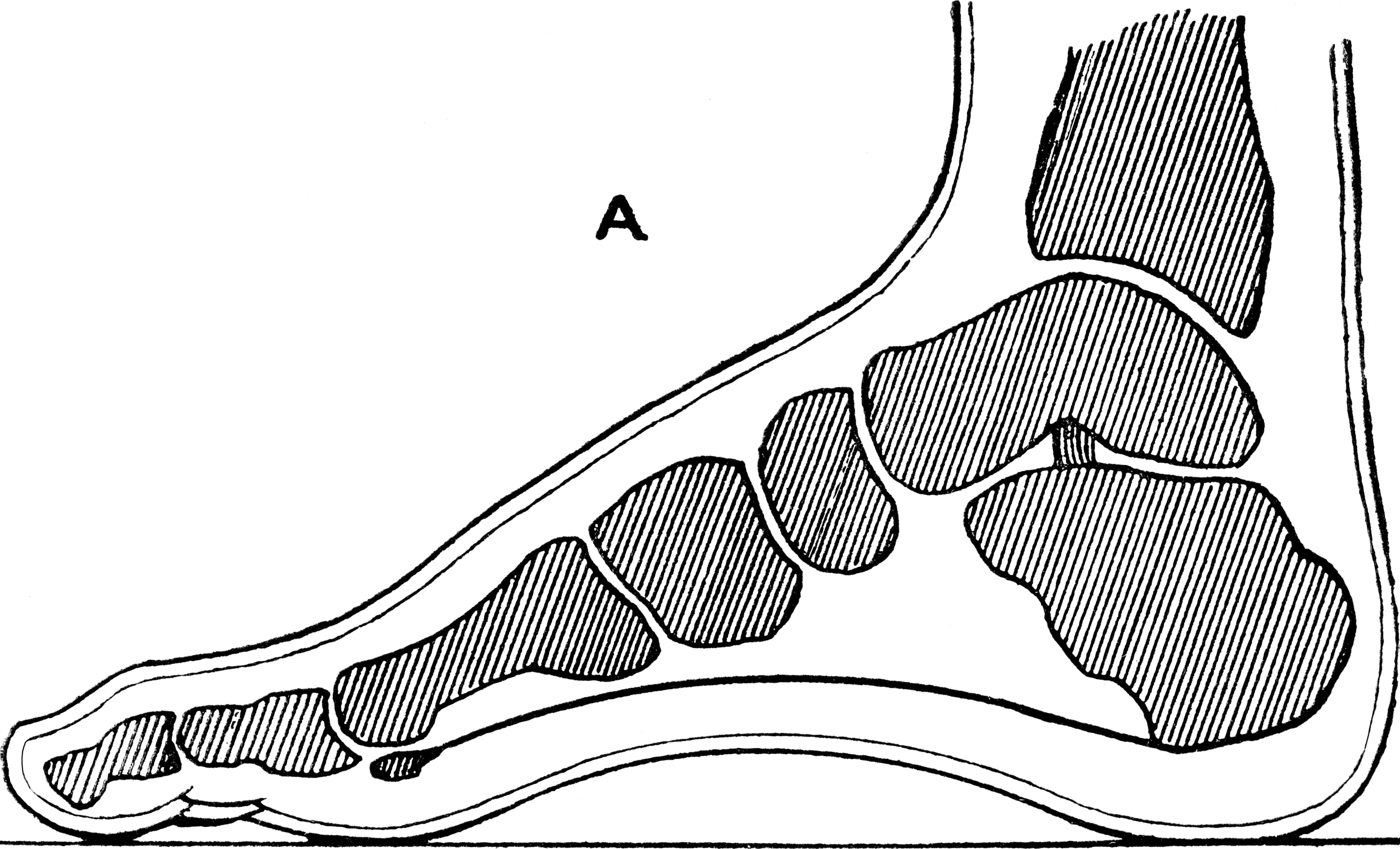
 To distribute the compressive forces exerted on the heel during gait, and especially the stance phase when the heel contacts the ground, the sole of the foot is covered by a layer of subcutaneous connective tissue up to 2 cm thick (under the heel). This tissue has a system of pressure chambers that both acts as a shock absorber and stabilises the sole. Each of these chambers contains fibrofatty tissue covered by a layer of tough connective tissue made of collagen fibers. These septa ("walls") are firmly attached both to the plantar aponeurosis above and the sole's
To distribute the compressive forces exerted on the heel during gait, and especially the stance phase when the heel contacts the ground, the sole of the foot is covered by a layer of subcutaneous connective tissue up to 2 cm thick (under the heel). This tissue has a system of pressure chambers that both acts as a shock absorber and stabilises the sole. Each of these chambers contains fibrofatty tissue covered by a layer of tough connective tissue made of collagen fibers. These septa ("walls") are firmly attached both to the plantar aponeurosis above and the sole's
Structure

skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have diffe ...
below. The sole of the foot is one of the most highly vascularized regions of the body surface, and the dense system of blood vessels further stabilize the septa.
The Achilles tendon is the muscle tendon of the triceps surae, a "three-headed" group of muscles—the soleus and the two heads of the gastrocnemius. The main function of the triceps surae is plantar flexion, i.e. to stretch the foot downward. It is accompanied by a "fourth head", the slight plantaris muscle, the long slender tendon of which is also attached to the heel bone but not visible.
Function
The compressive forces applied to the foot are distributed along five rays, three medial (side of big toe) and two lateral (side of little toe). The lateral rays stretch over the cuboid bone to the heel bone and the medial rays over the three cuneiform bones and the navicular bone to the ankle bone. Because the ankle bone is placed over the heel bone, these rays are adjacent near the toes but overriding near the heel, and together they form the arches of the foot that are optimized to distributed compressive forces across an uneven terrain. In this context the heel thus forms the posterior point of support that together with the balls of the large and little toes bear the brunt of the loads.Cracked heels
Cracked heels is a common health problem and it may causeinfection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable d ...
s. It is caused by dryness of the foot skin, and accumulation of dead skin. Over time it may cause pain and irritations. Various moisturising creams and foot files are available to cure and prevent it.
Other animals
In the long-footed mammals, both the hoofed species ( unguligrade) and the clawed forms which walk on the toes ( digitigrade), the heel is well above the ground at the apex of the angular joint known as the hock. In plantigrade species it rests on the ground. In birds, the heel is the backward-pointing joint which is often mistaken as the "knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the human leg, leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest join ...
" (the actual knee of birds is hidden under the plumage).
See also
* Achilles' heel a metaphor for weakness *Heel of Italy
it, Pugliese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographic ...
, the SE (after its position in the 'boot')
* Ball of the foot
The ball of the foot is the padded portion of the sole between the toes and the arch, underneath the heads of the metatarsal bones.
In comparative foot morphology, the ball is most analogous to the metacarpal (forepaw) or metatarsal (hindpaw) ...
* Calcaneal spur heel-bone
* Callus Hard skin which may cause painful cracks in the heel and sole of the foot
* Plantar fasciitis "policeman's heel" disorder
* High-heeled footwear
High-heeled shoes, also known as high heels, are a type of shoe with an angled sole. The heel in such shoes is raised above the ball of the foot. High heels cause the legs to appear longer, make the wearer appear taller, and accentuate th ...
fashion
* Squatting position
Notes
References
* {{Authority control Foot