Head-up display on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
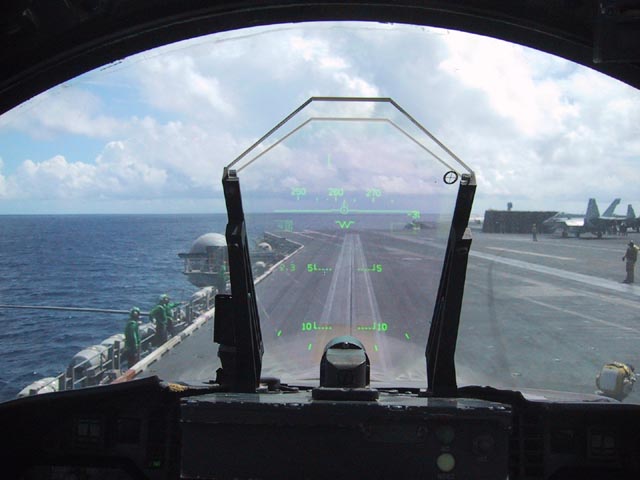 A head-up display, or heads-up display, also known as a HUD (), is any transparent display that presents data without requiring users to look away from their usual viewpoints. The origin of the name stems from a pilot being able to view information with the head positioned "up" and looking forward, instead of angled down looking at lower instruments. A HUD also has the advantage that the pilot's eyes do not need to refocus to view the outside after looking at the optically nearer instruments.
Although they were initially developed for military aviation, HUDs are now used in commercial aircraft, automobiles, and other (mostly professional) applications.
Head-up displays were a precursor technology to
A head-up display, or heads-up display, also known as a HUD (), is any transparent display that presents data without requiring users to look away from their usual viewpoints. The origin of the name stems from a pilot being able to view information with the head positioned "up" and looking forward, instead of angled down looking at lower instruments. A HUD also has the advantage that the pilot's eyes do not need to refocus to view the outside after looking at the optically nearer instruments.
Although they were initially developed for military aviation, HUDs are now used in commercial aircraft, automobiles, and other (mostly professional) applications.
Head-up displays were a precursor technology to
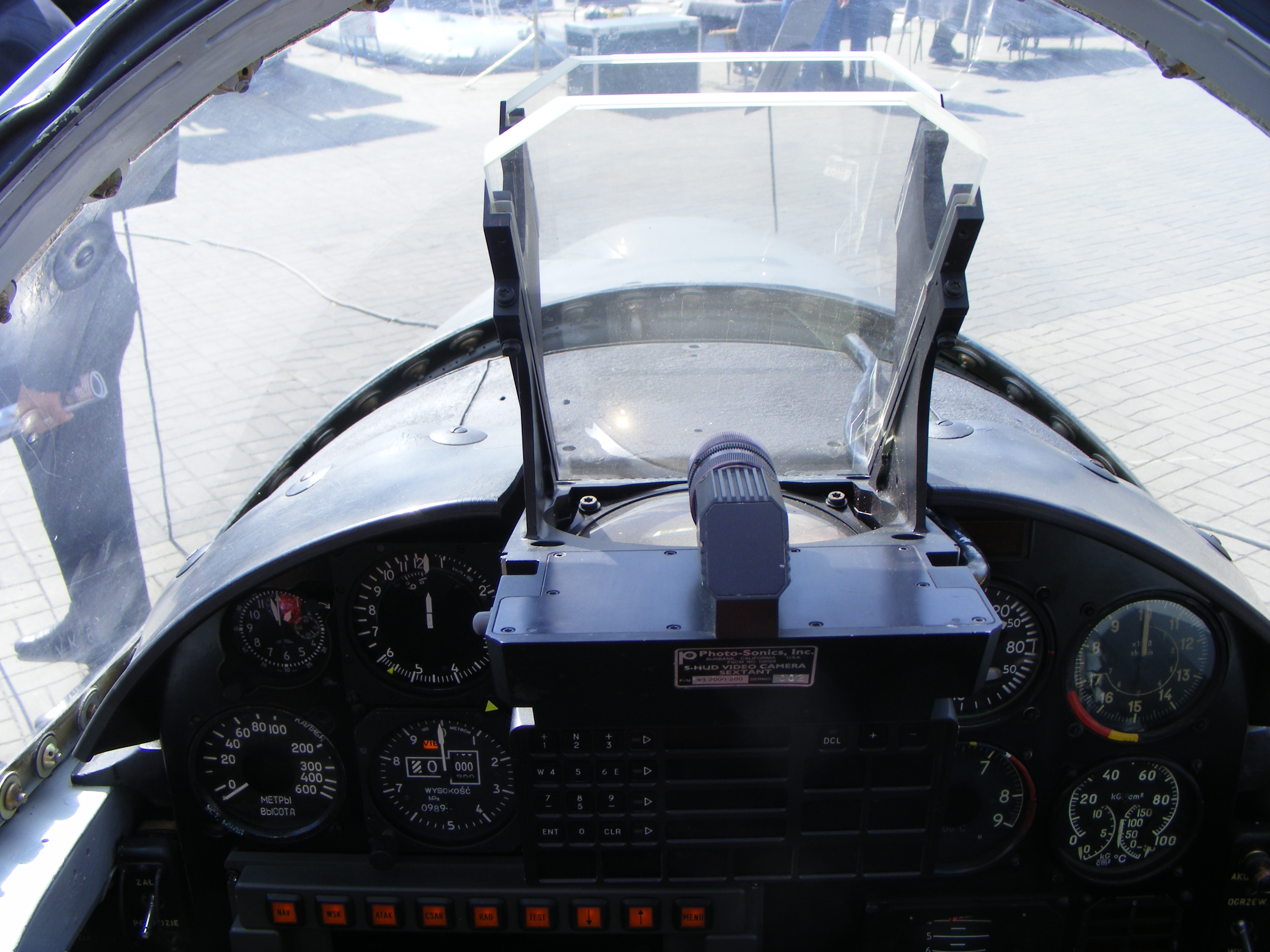 A typical HUD contains three primary components: a ''projector unit'', a ''combiner'', and a ''video generation computer''.
The projection unit in a typical HUD is an optical collimator setup: a
A typical HUD contains three primary components: a ''projector unit'', a ''combiner'', and a ''video generation computer''.
The projection unit in a typical HUD is an optical collimator setup: a
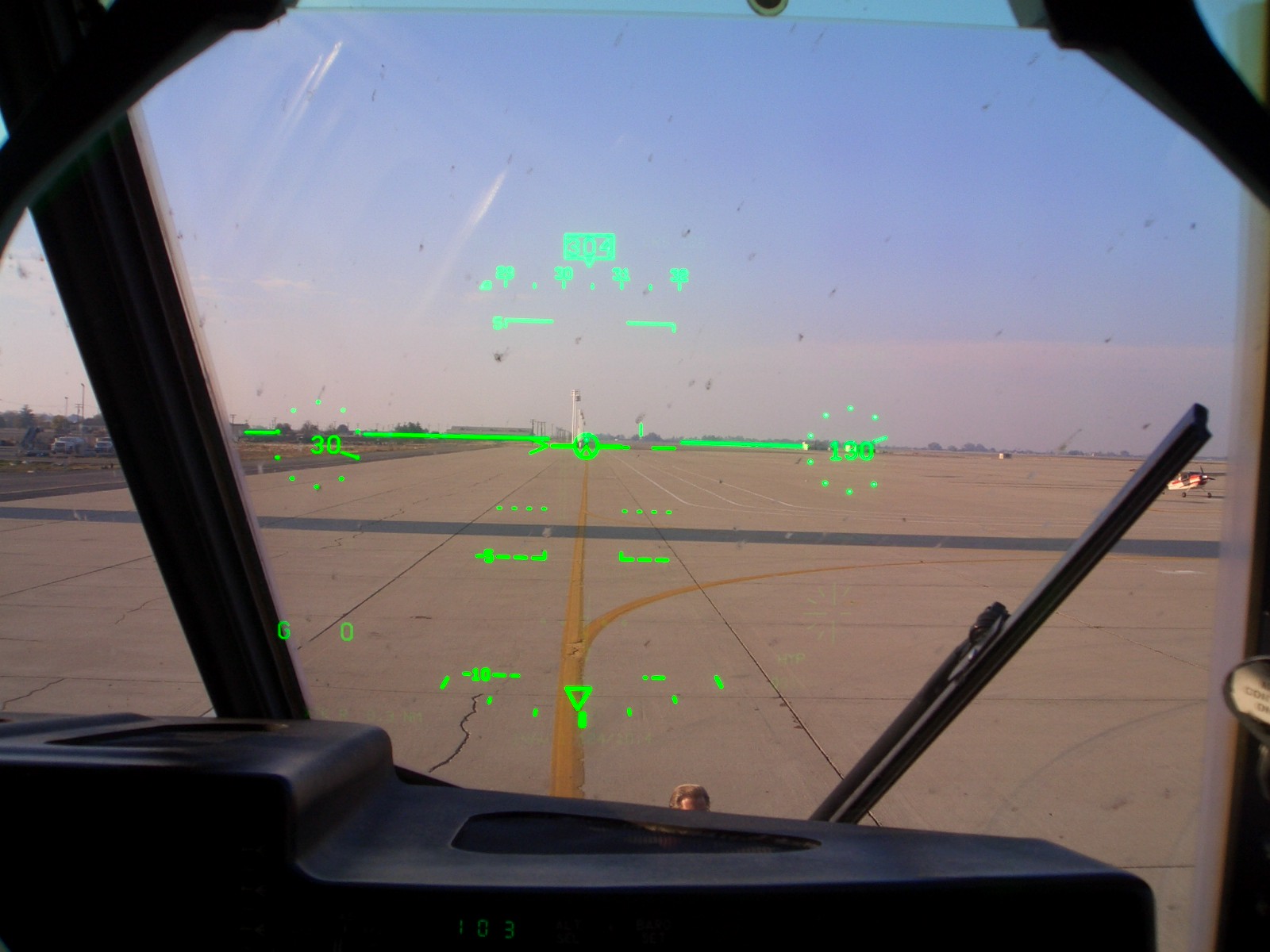
 HUDs evolved from the reflector sight, a pre-World War II
HUDs evolved from the reflector sight, a pre-World War II
 There are several factors that interplay in the design of a HUD:
* Field of View – also "FOV", indicates the angle(s), vertically as well as horizontally, subtended at the pilot's eye, at which the combiner displays symbology in relation to the outside view. A narrow FOV means that the view (of a runway, for example) through the combiner might include little additional information beyond the perimeters of the runway environment; whereas a wide FOV would allow a 'broader' view. For aviation applications, the major benefit of a wide FOV is that an aircraft approaching the runway in a crosswind might still have the runway in view through the combiner, even though the aircraft is pointed well away from the runway threshold; whereas with a narrow FOV the runway would be 'off the edge' of the combiner, out of the HUD's view. Because human eyes are separated, each eye receives a different image. The HUD image is viewable by one or both eyes, depending on technical and budget limitations in the design process. Modern expectations are that both eyes view the same image, in other words a "binocular Field of View (FOV)".
* Collimation – The projected image is collimated which makes the light rays parallel. Because the light rays are parallel the lens of the human eye focuses on infinity to get a clear image. Collimated images on the HUD combiner are perceived as existing at or near optical
There are several factors that interplay in the design of a HUD:
* Field of View – also "FOV", indicates the angle(s), vertically as well as horizontally, subtended at the pilot's eye, at which the combiner displays symbology in relation to the outside view. A narrow FOV means that the view (of a runway, for example) through the combiner might include little additional information beyond the perimeters of the runway environment; whereas a wide FOV would allow a 'broader' view. For aviation applications, the major benefit of a wide FOV is that an aircraft approaching the runway in a crosswind might still have the runway in view through the combiner, even though the aircraft is pointed well away from the runway threshold; whereas with a narrow FOV the runway would be 'off the edge' of the combiner, out of the HUD's view. Because human eyes are separated, each eye receives a different image. The HUD image is viewable by one or both eyes, depending on technical and budget limitations in the design process. Modern expectations are that both eyes view the same image, in other words a "binocular Field of View (FOV)".
* Collimation – The projected image is collimated which makes the light rays parallel. Because the light rays are parallel the lens of the human eye focuses on infinity to get a clear image. Collimated images on the HUD combiner are perceived as existing at or near optical
 In addition to the generic information described above, military applications include weapons system and sensor data such as:
* ''target designation (TD)'' indicator — places a cue over an air or ground target (which is typically derived from
In addition to the generic information described above, military applications include weapons system and sensor data such as:
* ''target designation (TD)'' indicator — places a cue over an air or ground target (which is typically derived from
 The use of head-up displays allows commercial aircraft substantial flexibility in their operations. Systems have been approved which allow reduced-visibility takeoffs, and landings, as well as full manual Category III A landings and roll-outs. Initially expensive and physically large, these systems were only installed on larger aircraft able to support them. Unfortunately these tended to be the same aircraft that as standard supported autoland (with the exception of certain turbo-propp types that had HUD as an option) making the head-up display unnecessary for Cat III landings - this delayed the adoption of HUD in commercial aircraft. At the same time, studies have shown that the use of a HUD during landings decreases the lateral deviation from centerline in all landing conditions, although the touchdown point along the centerline is not changed.
For
The use of head-up displays allows commercial aircraft substantial flexibility in their operations. Systems have been approved which allow reduced-visibility takeoffs, and landings, as well as full manual Category III A landings and roll-outs. Initially expensive and physically large, these systems were only installed on larger aircraft able to support them. Unfortunately these tended to be the same aircraft that as standard supported autoland (with the exception of certain turbo-propp types that had HUD as an option) making the head-up display unnecessary for Cat III landings - this delayed the adoption of HUD in commercial aircraft. At the same time, studies have shown that the use of a HUD during landings decreases the lateral deviation from centerline in all landing conditions, although the touchdown point along the centerline is not changed.
For
 In more advanced systems, such as the US
In more advanced systems, such as the US
www.regulations.gov a real-world visual image can be overlaid onto the combiner. Typically an
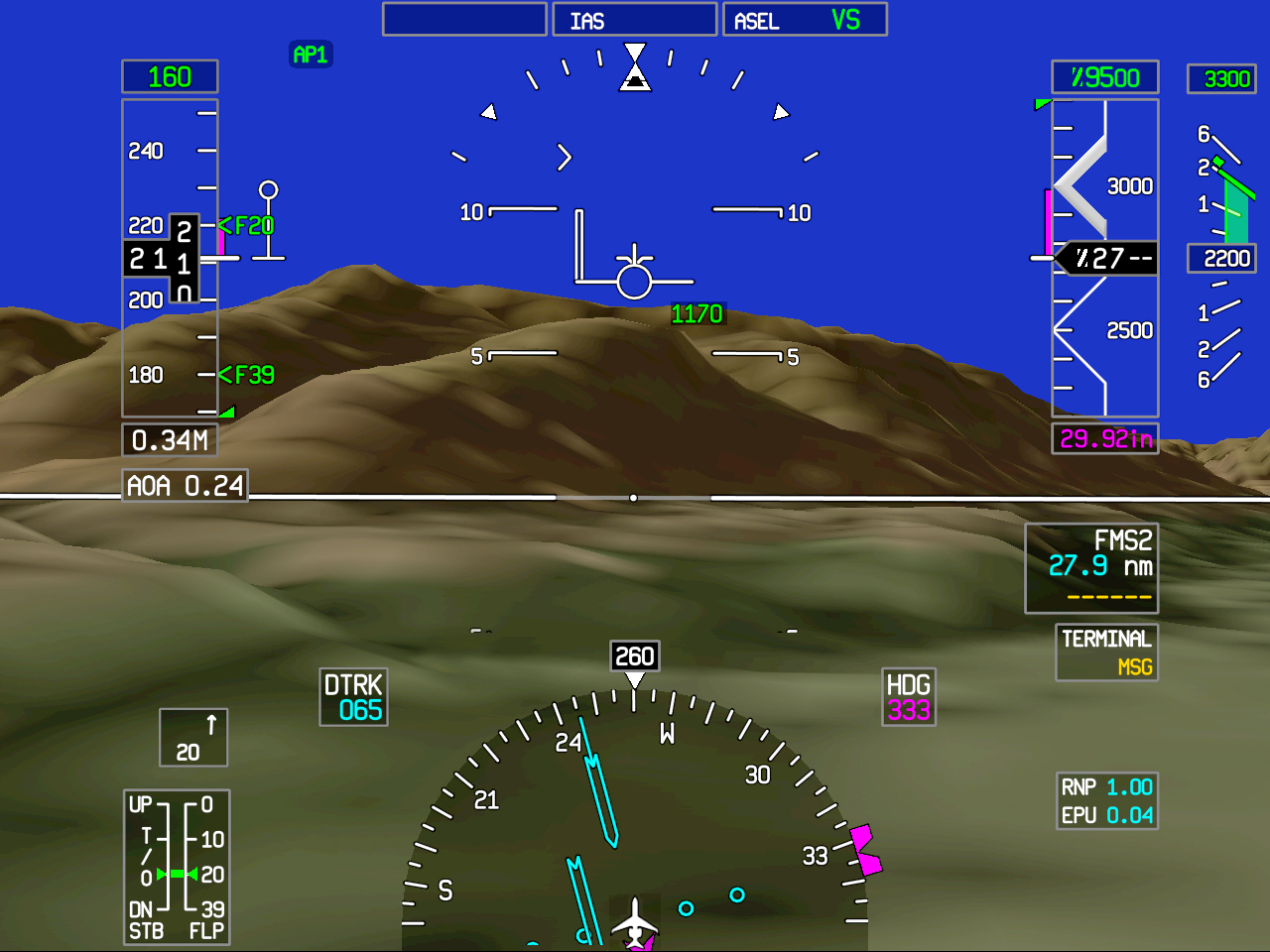 HUD systems are also being designed to display a synthetic vision system (SVS) graphic image, which uses high precision navigation, attitude, altitude and terrain databases to create realistic and intuitive views of the outside world.
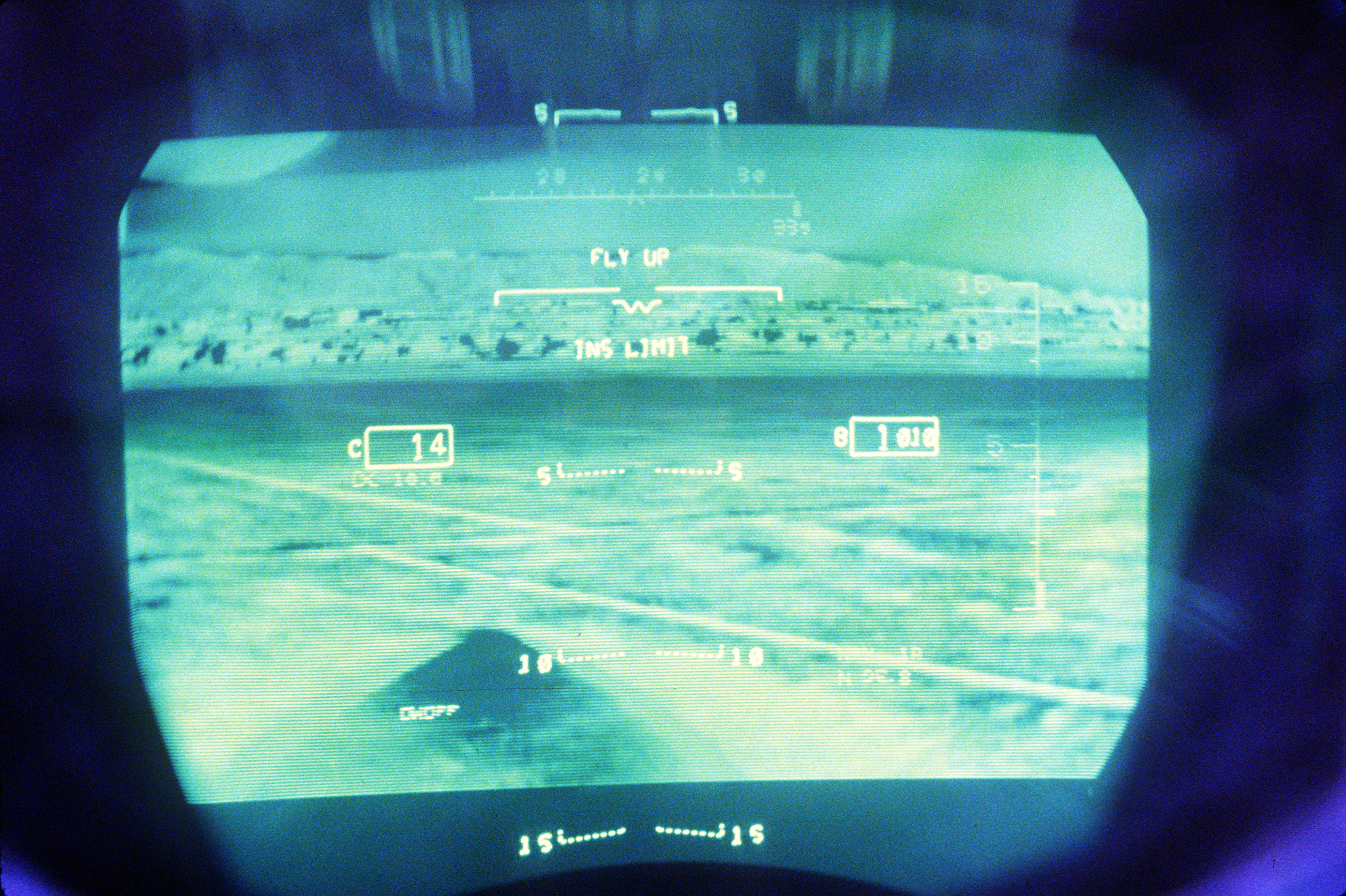
In the 1st SVS head down image shown on the right, immediately visible indicators include the airspeed tape on the left, altitude tape on the right, and turn/bank/slip/skid displays at the top center. The boresight symbol (-v-) is in the center and directly below that is the flight path vector (FPV) symbol (the circle with short wings and a vertical stabilizer). The horizon line is visible running across the display with a break at the center, and directly to the left are numbers at ±10 degrees with a short line at ±5 degrees (the +5 degree line is easier to see) which, along with the horizon line, show the pitch of the aircraft. Unlike this color depiction of SVS on a head down primary flight display, the SVS displayed on a HUD is monochrome – that is, typically, in shades of green.
The image indicates a wings level aircraft (i.e. the flight path vector symbol is flat relative to the horizon line and there is zero roll on the turn/bank indicator). Airspeed is 140 knots, altitude is 9,450 feet, heading is 343 degrees (the number below the turn/bank indicator). Close inspection of the image shows a small purple circle which is displaced from the flight path vector slightly to the lower right. This is the guidance cue coming from the Flight Guidance System. When stabilized on the approach, this purple symbol should be centered ''within'' the FPV.
The terrain is entirely computer generated from a high resolution terrain database.
In some systems, the SVS will calculate the aircraft's current flight path, or possible flight path (based on an aircraft performance model, the aircraft's current energy, and surrounding terrain) and then turn any obstructions red to alert the flight crew. Such a system might have helped prevent the crash of American Airlines Flight 965 into a mountain in December 1995.
On the left side of the display is an SVS-unique symbol, with the appearance of a purple, diminishing sideways ladder, and which continues on the right of the display. The two lines define a "tunnel in the sky". This symbol defines the desired trajectory of the aircraft in three dimensions. For example, if the pilot had selected an airport to the left, then this symbol would curve off to the left and down. If the pilot keeps the flight path vector alongside the trajectory symbol, the craft will fly the optimum path. This path would be based on information stored in the Flight Management System's database and would show the FAA-approved approach for that airport.
The tunnel in the sky can also greatly assist the pilot when more precise four-dimensional flying is required, such as the decreased vertical or horizontal clearance requirements of Required Navigation Performance (RNP). Under such conditions the pilot is given a graphical depiction of where the aircraft should be and where it should be going rather than the pilot having to mentally integrate altitude, airspeed, heading, energy and longitude and latitude to correctly fly the aircraft.
HUD systems are also being designed to display a synthetic vision system (SVS) graphic image, which uses high precision navigation, attitude, altitude and terrain databases to create realistic and intuitive views of the outside world.
In the 1st SVS head down image shown on the right, immediately visible indicators include the airspeed tape on the left, altitude tape on the right, and turn/bank/slip/skid displays at the top center. The boresight symbol (-v-) is in the center and directly below that is the flight path vector (FPV) symbol (the circle with short wings and a vertical stabilizer). The horizon line is visible running across the display with a break at the center, and directly to the left are numbers at ±10 degrees with a short line at ±5 degrees (the +5 degree line is easier to see) which, along with the horizon line, show the pitch of the aircraft. Unlike this color depiction of SVS on a head down primary flight display, the SVS displayed on a HUD is monochrome – that is, typically, in shades of green.
The image indicates a wings level aircraft (i.e. the flight path vector symbol is flat relative to the horizon line and there is zero roll on the turn/bank indicator). Airspeed is 140 knots, altitude is 9,450 feet, heading is 343 degrees (the number below the turn/bank indicator). Close inspection of the image shows a small purple circle which is displaced from the flight path vector slightly to the lower right. This is the guidance cue coming from the Flight Guidance System. When stabilized on the approach, this purple symbol should be centered ''within'' the FPV.
The terrain is entirely computer generated from a high resolution terrain database.
In some systems, the SVS will calculate the aircraft's current flight path, or possible flight path (based on an aircraft performance model, the aircraft's current energy, and surrounding terrain) and then turn any obstructions red to alert the flight crew. Such a system might have helped prevent the crash of American Airlines Flight 965 into a mountain in December 1995.
On the left side of the display is an SVS-unique symbol, with the appearance of a purple, diminishing sideways ladder, and which continues on the right of the display. The two lines define a "tunnel in the sky". This symbol defines the desired trajectory of the aircraft in three dimensions. For example, if the pilot had selected an airport to the left, then this symbol would curve off to the left and down. If the pilot keeps the flight path vector alongside the trajectory symbol, the craft will fly the optimum path. This path would be based on information stored in the Flight Management System's database and would show the FAA-approved approach for that airport.
The tunnel in the sky can also greatly assist the pilot when more precise four-dimensional flying is required, such as the decreased vertical or horizontal clearance requirements of Required Navigation Performance (RNP). Under such conditions the pilot is given a graphical depiction of where the aircraft should be and where it should be going rather than the pilot having to mentally integrate altitude, airspeed, heading, energy and longitude and latitude to correctly fly the aircraft.
Peter Felstead, Tel Aviv - IHS Jane's Defence Weekly, 27 March 2017
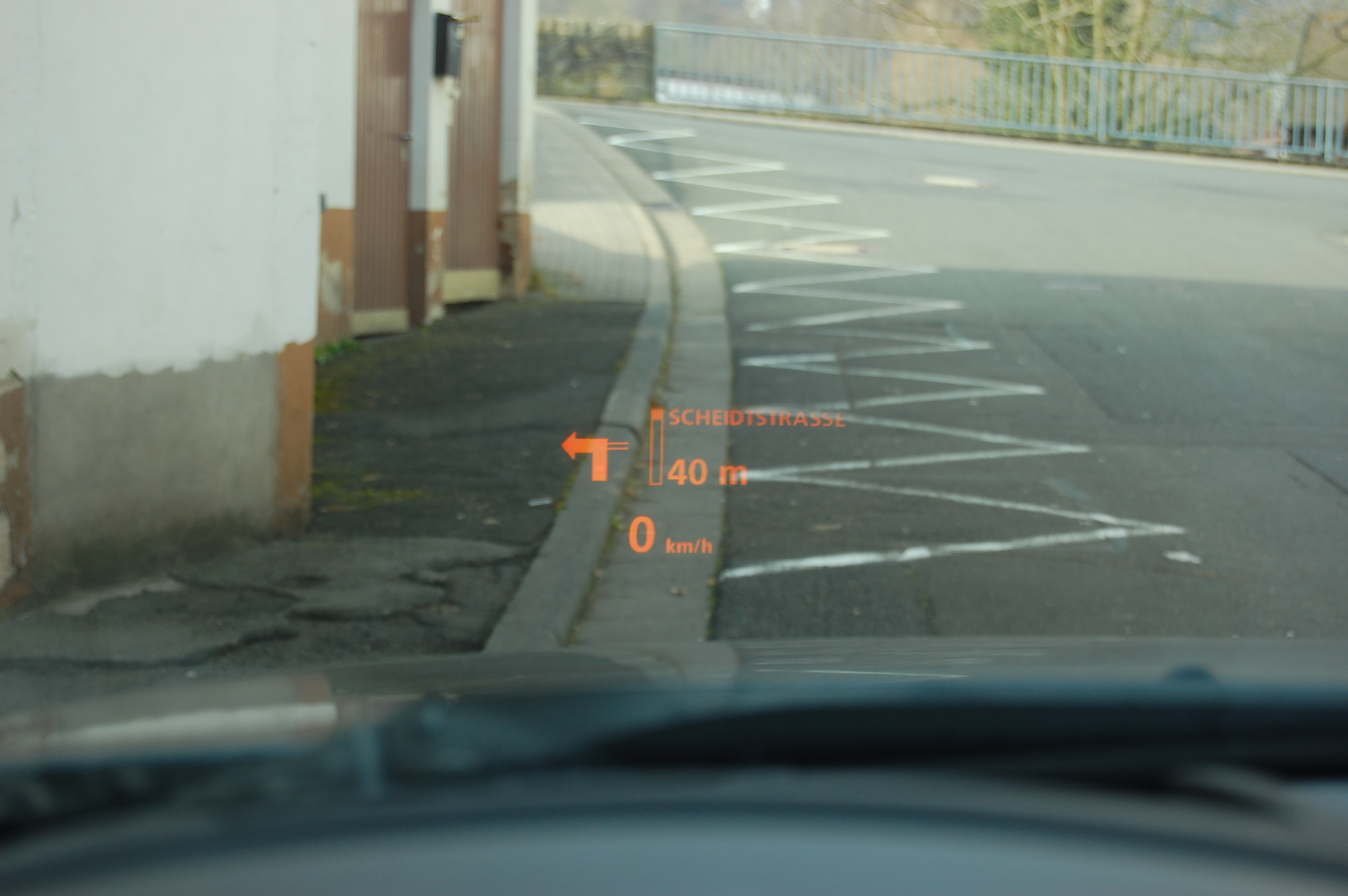
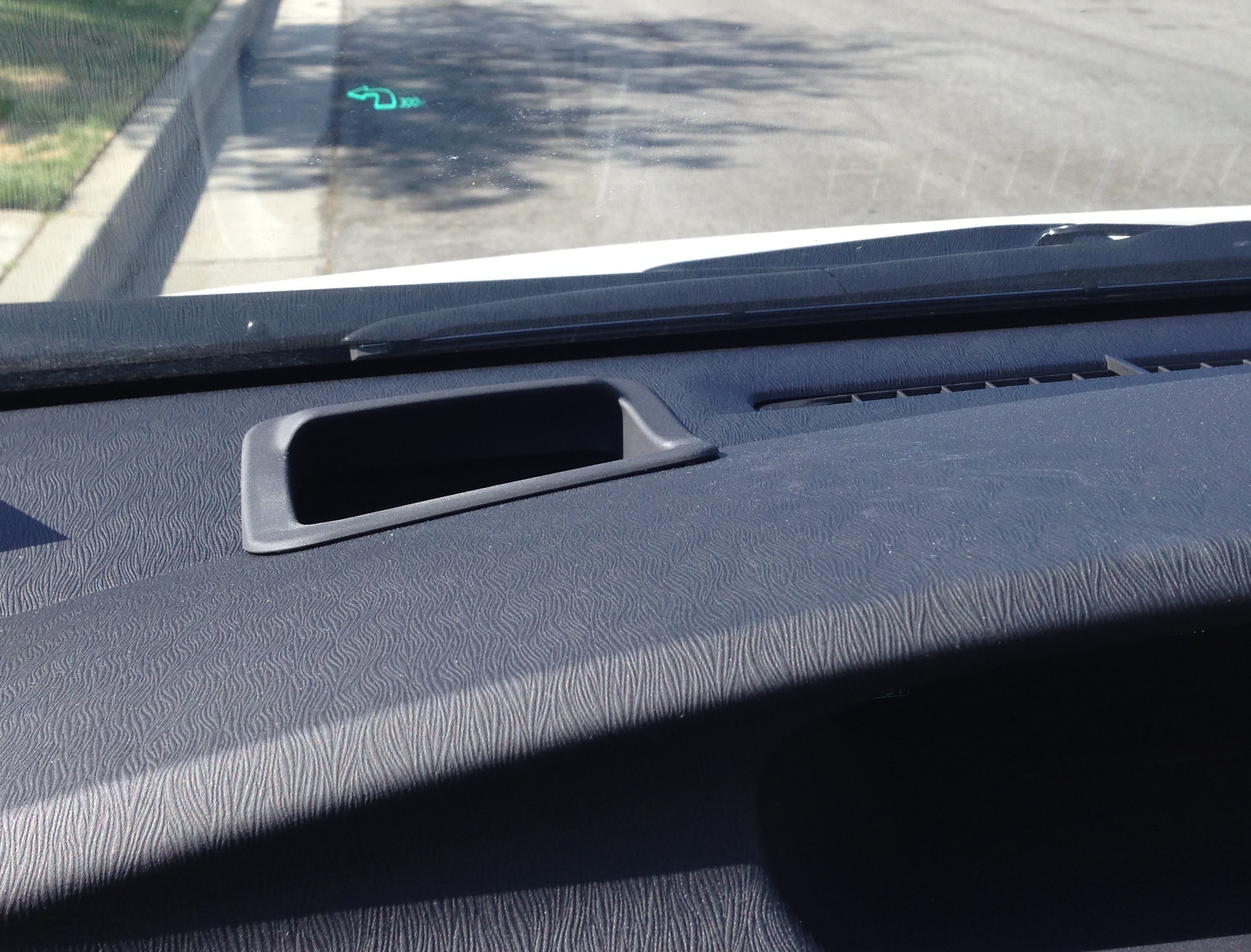
 These displays are becoming increasingly available in production cars, and usually offer
These displays are becoming increasingly available in production cars, and usually offer
Augmented reality glasses perform real-time language translation
''gizmag'', 29 July 2012.
Rochester Archives Article—'Buccaneer HUD PDU'
BBC Article—'Pacman comes to life virtually'
'Clinical evaluation of the 'head-up' display of anesthesia data'
'Elliott Brothers to BAE SYSTEMS' – a short history of Elliott Brothers
– a 1964 ''
Jaguar Unveils 'Virtual Widescreen' Technology to Assist Drivers – Latin Post
{{emerging technologies, displays=yes Vehicle technology Avionics Aircraft instruments Automotive technologies Optical devices Multimodal interaction Mixed reality British inventions Emerging technologies
 A head-up display, or heads-up display, also known as a HUD (), is any transparent display that presents data without requiring users to look away from their usual viewpoints. The origin of the name stems from a pilot being able to view information with the head positioned "up" and looking forward, instead of angled down looking at lower instruments. A HUD also has the advantage that the pilot's eyes do not need to refocus to view the outside after looking at the optically nearer instruments.
Although they were initially developed for military aviation, HUDs are now used in commercial aircraft, automobiles, and other (mostly professional) applications.
Head-up displays were a precursor technology to
A head-up display, or heads-up display, also known as a HUD (), is any transparent display that presents data without requiring users to look away from their usual viewpoints. The origin of the name stems from a pilot being able to view information with the head positioned "up" and looking forward, instead of angled down looking at lower instruments. A HUD also has the advantage that the pilot's eyes do not need to refocus to view the outside after looking at the optically nearer instruments.
Although they were initially developed for military aviation, HUDs are now used in commercial aircraft, automobiles, and other (mostly professional) applications.
Head-up displays were a precursor technology to augmented reality
Augmented reality (AR) is an interactive experience that combines the real world and computer-generated content. The content can span multiple sensory Modality (human–computer interaction), modalities, including visual, Hearing, auditory, hap ...
(AR), incorporating a subset of the features needed for the full AR experience, but lacking the necessary registration and tracking between the virtual content and the user's real-world environment.
Overview
 A typical HUD contains three primary components: a ''projector unit'', a ''combiner'', and a ''video generation computer''.
The projection unit in a typical HUD is an optical collimator setup: a
A typical HUD contains three primary components: a ''projector unit'', a ''combiner'', and a ''video generation computer''.
The projection unit in a typical HUD is an optical collimator setup: a convex lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), ...
or concave mirror with a cathode-ray tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms ( oscilloscope), pi ...
, light emitting diode display, or liquid crystal display
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but ...
at its focus. This setup (a design that has been around since the invention of the reflector sight in 1900) produces an image where the light is collimated, i.e. the focal point is perceived to be at infinity.
The combiner is typically an angled flat piece of glass (a beam splitter) located directly in front of the viewer, that redirects the projected image from projector in such a way as to see the field of view and the projected infinity image at the same time. Combiners may have special coatings that reflect the monochromatic
A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or palette is composed of one color (or values of one color). Images using only shades of grey are called grayscale (typically digital) or black-and-white (typically analog). In physics, monochro ...
light projected onto it from the projector unit while allowing all other wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tr ...
s of light to pass through. In some optical layouts combiners may also have a curved surface to refocus the image from the projector.
The computer provides the interface between the HUD (i.e. the projection unit) and the systems/data to be displayed and generates the imagery and symbology to be displayed by the projection unit .
Types
Other than fixed mounted HUD, there are alsohead-mounted display
A head-mounted display (HMD) is a display device, worn on the head or as part of a helmet (see Helmet-mounted display for aviation applications), that has a small display optic in front of one ( monocular HMD) or each eye (binocular HMD). An ...
s (HMDs). These include helmet-mounted displays (both abbreviated HMD), forms of HUD that feature a display element that moves with the orientation of the user's head.
Many modern fighters (such as the F/A-18, F-16
The General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon is a single-engine multirole fighter aircraft originally developed by General Dynamics for the United States Air Force (USAF). Designed as an air superiority day fighter, it evolved into a successful ...
, and Eurofighter) use both a HUD and HMD concurrently. The F-35 Lightning II was designed without a HUD, relying solely on the HMD, making it the first modern military fighter not to have a fixed HUD.
Generations
HUDs are split into four generations reflecting the technology used to generate the images. * First Generation—Use aCRT
CRT or Crt may refer to:
Science, technology, and mathematics Medicine and biology
* Calreticulin, a protein
*Capillary refill time, for blood to refill capillaries
*Cardiac resynchronization therapy and CRT defibrillator (CRT-D)
* Catheter-re ...
to generate an image on a phosphor screen, having the disadvantage of the phosphor screen coating degrading over time. The majority of HUDs in operation today are of this type.
* Second Generation—Use a solid state light source, for example LED, which is modulated by an LCD screen to display an image. These systems do not fade or require the high voltages of first generation systems. These systems are on commercial aircraft.
* Third Generation—Use optical waveguide
An optical waveguide is a physical structure that guides electromagnetic waves in the optical spectrum. Common types of optical waveguides include optical fiber waveguides, transparent dielectric waveguides made of plastic and glass, liquid light ...
s to produce images directly in the combiner rather than use a projection system.
* Fourth Generation—Use a scanning laser to display images and even video imagery on a clear transparent medium.
Newer micro-display imaging technologies are being introduced, including liquid crystal display
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but ...
(LCD), liquid crystal on silicon (LCoS), digital micro-mirrors (DMD), and organic light-emitting diode (OLED).
History

 HUDs evolved from the reflector sight, a pre-World War II
HUDs evolved from the reflector sight, a pre-World War II parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby object ...
-free optical sight technology for military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distin ...
fighter aircraft. The gyro gunsight added a reticle that moved based on the speed and turn rate to solve for the amount of lead
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate ...
needed to hit a target while maneuvering.
During the early 1940s, the Telecommunications Research Establishment (TRE), in charge of UK radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
development, found that Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
(RAF) night fighter
A night fighter (also known as all-weather fighter or all-weather interceptor for a period of time after the Second World War) is a fighter aircraft adapted for use at night or in other times of bad visibility. Night fighters began to be used ...
pilots were having a hard time reacting to the verbal instruction of the radar operator as they approached their targets. They experimented with the addition of a second radar display for the pilot, but found they had trouble looking up from the lit screen into the dark sky in order to find the target. In October 1942 they had successfully combined the image from the radar tube with a projection from their standard GGS Mk. II gyro gunsight on a flat area of the windscreen, and later in the gunsight itself. A key upgrade was the move from the original AI Mk. IV radar
Radar, Airborne Interception, Mark IV (AI Mk. IV), produced by USA as SCR-540, was the world's first operational Airborne Interception radar, air-to-air radar system. Early Mk. III units appeared in July 1940 on converted Bristol Blenheim ligh ...
to the microwave-frequency AI Mk. VIII radar found on the de Havilland Mosquito
The de Havilland DH.98 Mosquito is a British twin-engined, shoulder-winged, multirole combat aircraft, introduced during the World War II, Second World War. Unusual in that its frame was constructed mostly of wood, it was nicknamed the "Wooden ...
night fighter
A night fighter (also known as all-weather fighter or all-weather interceptor for a period of time after the Second World War) is a fighter aircraft adapted for use at night or in other times of bad visibility. Night fighters began to be used ...
. This set produced an artificial horizon
The attitude indicator (AI), formerly known as the gyro horizon or artificial horizon, is a flight instrument that informs the pilot of the aircraft orientation relative to Earth's horizon, and gives an immediate indication of the smallest or ...
that further eased head-up flying.
In 1955 the US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
's Office of Naval Research and Development did some research with a mockup HUD concept unit along with a sidestick controller in an attempt to ease the pilot's burden flying modern jet aircraft and make the instrumentation less complicated during flight. While their research was never incorporated in any aircraft of that time, the crude HUD mockup they built had all the features of today's modern HUD units.
HUD technology was next advanced by the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
in the Buccaneer, the prototype of which first flew on 1958. The aircraft was designed to fly at very low altitudes at very high speeds and drop bombs in engagements lasting seconds. As such, there was no time for the pilot to look up from the instruments to a bombsight. This led to the concept of a "Strike Sight" that would combine altitude, airspeed and the gun/bombsight into a single gunsight-like display. There was fierce competition between supporters of the new HUD design and supporters of the old electro-mechanical gunsight, with the HUD being described as a radical, even foolhardy option.
The Air Arm branch of the UK Ministry of Defence sponsored the development of a Strike Sight. The Royal Aircraft Establishment
The Royal Aircraft Establishment (RAE) was a British research establishment, known by several different names during its history, that eventually came under the aegis of the UK Ministry of Defence (MoD), before finally losing its identity in me ...
(RAE) designed the equipment and the earliest usage of the term "head-up-display" can be traced to this time. Production units were built by Rank Cintel, and the system was first integrated in 1958. The Cintel HUD business was taken over by Elliott Flight Automation and the Buccaneer HUD was manufactured and further developed, continuing up to a Mark III version with a total of 375 systems made; it was given a 'fit and forget' title by the Royal Navy and it was still in service nearly 25 years later. BAE Systems, as the successor to Elliotts via GEC-Marconi Avionics, thus has a claim to the world's first head-up display in operational service. A similar version that replaced the bombing modes with missile-attack modes was part of the AIRPASS
AIRPASS was a British airborne interception radar and fire-control radar system developed by Ferranti. It was the world's first airborne monopulse radar system and fed data to the world's first head-up display. The name is an acronym for "Ai ...
HUD fitted to the English Electric Lightning from 1959.
In the United Kingdom, it was soon noted that pilots flying with the new gunsights were becoming better at piloting their aircraft. At this point, the HUD expanded its purpose beyond weapon aiming to general piloting. In the 1960s, French test-pilot Gilbert Klopfstein created the first modern HUD and a standardized system of HUD symbols so that pilots would only have to learn one system and could more easily transition between aircraft. The modern HUD used in instrument flight rules
In aviation, instrument flight rules (IFR) is one of two sets of regulations governing all aspects of civil aviation aircraft operations; the other is visual flight rules (VFR).
The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration's (FAA) ''Instrument F ...
approaches to landing was developed in 1975.Spitzer, Cary R., ed. "Digital Avionics Handbook". Head-Up Displays. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 2001 Klopfstein pioneered HUD technology in military fighter jets and helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attribut ...
s, aiming to centralize critical flight data within the pilot's field of vision. This approach sought to increase the pilot's scan efficiency and reduce "task saturation" and information overload.
Use of HUDs then expanded beyond military aircraft. In the 1970s, the HUD was introduced to commercial aviation, and in 1988, the Oldsmobile Cutlass Supreme
The Oldsmobile Cutlass Supreme is a mid-size car produced by Oldsmobile between 1966 and 1997. It was positioned as a premium offering at the top of the Cutlass range. It began as a trim package, developed its own roofline, and rose during the m ...
became the first production car with a head-up display.
Until a few years ago, the Embraer 190, Saab 2000, Boeing 727, and Boeing 737
The Boeing 737 is a narrow-body aircraft produced by Boeing at its Renton Factory in Washington.
Developed to supplement the Boeing 727 on short and thin routes, the twinjet retains the 707 fuselage width and six abreast seating with two ...
Classic (737-300/400/500) and Next Generation
Next Generation or Next-Generation may refer to:
Publications and literature
* ''Next Generation'' (magazine), video game magazine that was made by the now defunct Imagine Media publishing company
* Next Generation poets (2004), list of young ...
aircraft (737-600/700/800/900 series) were the only commercial passenger aircraft available with HUDs. However, the technology is becoming more common with aircraft such as the Canadair RJ
The Bombardier CRJ or CRJ Series (for Canadair Regional Jet) is a family of regional jets introduced in 1991 by Bombardier Aerospace. The CRJ was formerly manufactured by Bombardier Aerospace with the manufacturing of the first CRJ generation, t ...
, Airbus A318
Airbus SE (; ; ; ) is a European multinational aerospace corporation. Airbus designs, manufactures and sells civil and military aerospace products worldwide and manufactures aircraft throughout the world. The company has three divisions: '' ...
and several business jets featuring the displays. HUDs have become standard equipment on the Boeing 787. Furthermore, the Airbus A320, A330, A340 and A380 families are currently undergoing the certification process for a HUD. HUDs were also added to the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ...
orbiter.
Design factors
 There are several factors that interplay in the design of a HUD:
* Field of View – also "FOV", indicates the angle(s), vertically as well as horizontally, subtended at the pilot's eye, at which the combiner displays symbology in relation to the outside view. A narrow FOV means that the view (of a runway, for example) through the combiner might include little additional information beyond the perimeters of the runway environment; whereas a wide FOV would allow a 'broader' view. For aviation applications, the major benefit of a wide FOV is that an aircraft approaching the runway in a crosswind might still have the runway in view through the combiner, even though the aircraft is pointed well away from the runway threshold; whereas with a narrow FOV the runway would be 'off the edge' of the combiner, out of the HUD's view. Because human eyes are separated, each eye receives a different image. The HUD image is viewable by one or both eyes, depending on technical and budget limitations in the design process. Modern expectations are that both eyes view the same image, in other words a "binocular Field of View (FOV)".
* Collimation – The projected image is collimated which makes the light rays parallel. Because the light rays are parallel the lens of the human eye focuses on infinity to get a clear image. Collimated images on the HUD combiner are perceived as existing at or near optical
There are several factors that interplay in the design of a HUD:
* Field of View – also "FOV", indicates the angle(s), vertically as well as horizontally, subtended at the pilot's eye, at which the combiner displays symbology in relation to the outside view. A narrow FOV means that the view (of a runway, for example) through the combiner might include little additional information beyond the perimeters of the runway environment; whereas a wide FOV would allow a 'broader' view. For aviation applications, the major benefit of a wide FOV is that an aircraft approaching the runway in a crosswind might still have the runway in view through the combiner, even though the aircraft is pointed well away from the runway threshold; whereas with a narrow FOV the runway would be 'off the edge' of the combiner, out of the HUD's view. Because human eyes are separated, each eye receives a different image. The HUD image is viewable by one or both eyes, depending on technical and budget limitations in the design process. Modern expectations are that both eyes view the same image, in other words a "binocular Field of View (FOV)".
* Collimation – The projected image is collimated which makes the light rays parallel. Because the light rays are parallel the lens of the human eye focuses on infinity to get a clear image. Collimated images on the HUD combiner are perceived as existing at or near optical infinity
Infinity is that which is boundless, endless, or larger than any natural number. It is often denoted by the infinity symbol .
Since the time of the ancient Greeks, the philosophical nature of infinity was the subject of many discussions am ...
. This means that the pilot's eyes do not need to refocus to view the outside world and the HUD display – the image appears to be "out there", overlaying the outside world. This feature is critical for effective HUDs: not having to refocus between HUD-displayed symbolic information and the outside world onto which that information is overlaid is one of the main advantages of collimated HUDs. It gives HUDs special consideration in safety-critical and time-critical manoeuvres, when the few seconds a pilot needs in order to re-focus inside the cockpit, and then back outside, are very critical: for example, in the final stages of landing. Collimation is therefore a primary distinguishing feature of high-performance HUDs and differentiates them from consumer-quality systems that, for example, simply reflect uncollimated information off a car's windshield (causing drivers to refocus and shift attention from the road ahead).
* Eyebox – The optical collimator produces a cylinder of parallel light so the display can only be viewed while the viewer's eyes are somewhere within that cylinder, a three-dimensional area called the ''head motion box'' or ''eyebox''. Modern HUD eyeboxes are usually about 5 lateral by 3 vertical by 6 longitudinal inches (13x8x15 cm). This allows the viewer some freedom of head movement but movement too far up/down or left/right will cause the display to vanish off the edge of the collimator and movement too far back will cause it to crop off around the edge ( vignette). The pilot is able to view the entire display as long as one of the eyes is inside the eyebox.
* Luminance/contrast – Displays have adjustments in luminance and contrast to account for ambient lighting, which can vary widely (e.g. from the glare of bright clouds to moonless night approaches to minimally lit fields).
* Boresight – Aircraft HUD components are very accurately aligned with the aircraft's three axes – a process called '' boresighting'' – so that displayed data conforms to reality typically with an accuracy of ±7.0 milliradian
A milliradian ( SI-symbol mrad, sometimes also abbreviated mil) is an SI derived unit for angular measurement which is defined as a thousandth of a radian (0.001 radian). Milliradians are used in adjustment of firearm sights by adjusti ...
s (±24 minutes of arc
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
), and may vary across the HUD's FOV. In this case the word "conform" means, "when an object is projected on the combiner and the actual object is visible, they will be aligned". This allows the display to show the pilot exactly where the artificial horizon is, as well as the aircraft's projected path with great accuracy. When Enhanced Vision is used, for example, the display of runway lights is aligned with the actual runway lights when the real lights become visible. Boresighting is done during the aircraft's building process and can also be performed in the field on many aircraft.
* Scaling – The displayed image (flight path, pitch and yaw scaling, etc.), is scaled to present to the pilot a picture that overlays the outside world in an exact 1:1 relationship. For example, objects (such as a runway threshold) that are 3 degrees below the horizon as viewed from the cockpit must appear at the −3 degree index on the HUD display.
* Compatibility – HUD components are designed to be compatible with other avionics, displays, etc.
Aircraft
On aircraft avionics systems, HUDs typically operate from dual independent redundant computer systems. They receive input directly from the sensors (pitot-static
A pitot-static system is a system of pressure-sensitive instruments that is most often used in aviation to determine an aircraft's airspeed, Mach number, altitude, and altitude trend. A pitot-static system generally consists of a pitot tube, a s ...
, gyroscopic, navigation, etc.) aboard the aircraft and perform their own computations rather than receiving previously computed data from the flight computers. On other aircraft (the Boeing 787, for example) the HUD guidance computation for Low Visibility Take-off (LVTO) and low visibility approach comes from the same flight guidance computer that drives the autopilot. Computers are integrated with the aircraft's systems and allow connectivity onto several different data buses such as the ARINC 429, ARINC 629, and MIL-STD-1553.
Displayed data
Typical aircraft HUDs displayairspeed
In aviation, airspeed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the air. Among the common conventions for qualifying airspeed are:
* Indicated airspeed ("IAS"), what is read on an airspeed gauge connected to a Pitot-static system;
* Calib ...
, altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
, a horizon line, heading, turn/bank and slip/skid indicators. These instruments are the minimum required by 14 CFR Part 91.
Other symbols
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different co ...
and data are also available in some HUDs:
* ''boresight'' or ''waterline'' symbol — is fixed on the display and shows where the nose of the aircraft is actually pointing.
* ''flight path vector (FPV)'' or ''velocity vector'' symbol — shows where the aircraft is actually going, as opposed to merely where it is pointed as with the boresight. For example, if the aircraft is pitched up but descending as may occur in high angle of attack flight or in flight through descending air, then the FPV symbol will be below the horizon even though the boresight symbol is above the horizon. During approach and landing, a pilot can fly the approach by keeping the FPV symbol at the desired descent angle and touchdown point on the runway.
* ''acceleration indicator'' or ''energy cue'' — typically to the left of the FPV symbol, it is above it if the aircraft is accelerating, and below the FPV symbol if decelerating.
* '' angle of attack indicator'' — shows the wing's angle relative to the airflow, often displayed as ''"α"''.
* navigation data and symbols — for approaches and landings, the flight guidance systems can provide visual cues based on navigation aids such as an Instrument Landing System
In aviation, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a precision radio navigation system that provides short-range guidance to aircraft to allow them to approach a runway at night or in bad weather. In its original form, it allows an aircraft to ...
or augmented Global Positioning System such as the Wide Area Augmentation System. Typically this is a circle which fits inside the flight path vector symbol. Pilots can fly along the correct flight path by "flying to" the guidance cue.
Since being introduced on HUDs, both the FPV and acceleration symbols are becoming standard on head-down displays (HDD). The actual form of the FPV symbol on an HDD is not standardized but is usually a simple aircraft drawing, such as a circle with two short angled lines, (180 ± 30 degrees) and "wings" on the ends of the descending line. Keeping the FPV on the horizon allows the pilot to fly level turns in various angles of bank.
Military aircraft specific applications
 In addition to the generic information described above, military applications include weapons system and sensor data such as:
* ''target designation (TD)'' indicator — places a cue over an air or ground target (which is typically derived from
In addition to the generic information described above, military applications include weapons system and sensor data such as:
* ''target designation (TD)'' indicator — places a cue over an air or ground target (which is typically derived from radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
or inertial navigation system
An inertial navigation system (INS) is a navigation device that uses motion sensors ( accelerometers), rotation sensors (gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning the position, the orientation, and the velocity (d ...
data).
* ''Vc'' — closing velocity with target.
* ''Range'' — to target, waypoint, etc.
* ''weapon seeker'' or sensor line of sight — shows where a seeker or sensor is pointing.
* ''weapon status'' — includes type and number of weapons selected, available, arming, etc.
VTOL/STOL approaches and landings
During the 1980s, the military tested the use of HUDs in vertical take off and landing (VTOL) and short take off and landing (STOL) aircraft. A HUD format was developed atNASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedi ...
Ames Research Center to provide pilots of V/STOL aircraft with complete flight guidance and control information for Category III C terminal-area flight operations. This includes a large variety of flight operations, from STOL flights on land-based runways to VTOL operations on aircraft carriers. The principal features of this display format are the integration of the flightpath and pursuit guidance information into a narrow field of view, easily assimilated by the pilot with a single glance, and the superposition of vertical and horizontal situation information. The display is a derivative of a successful design developed for conventional transport aircraft.
Civil aircraft specific applications
 The use of head-up displays allows commercial aircraft substantial flexibility in their operations. Systems have been approved which allow reduced-visibility takeoffs, and landings, as well as full manual Category III A landings and roll-outs. Initially expensive and physically large, these systems were only installed on larger aircraft able to support them. Unfortunately these tended to be the same aircraft that as standard supported autoland (with the exception of certain turbo-propp types that had HUD as an option) making the head-up display unnecessary for Cat III landings - this delayed the adoption of HUD in commercial aircraft. At the same time, studies have shown that the use of a HUD during landings decreases the lateral deviation from centerline in all landing conditions, although the touchdown point along the centerline is not changed.
For
The use of head-up displays allows commercial aircraft substantial flexibility in their operations. Systems have been approved which allow reduced-visibility takeoffs, and landings, as well as full manual Category III A landings and roll-outs. Initially expensive and physically large, these systems were only installed on larger aircraft able to support them. Unfortunately these tended to be the same aircraft that as standard supported autoland (with the exception of certain turbo-propp types that had HUD as an option) making the head-up display unnecessary for Cat III landings - this delayed the adoption of HUD in commercial aircraft. At the same time, studies have shown that the use of a HUD during landings decreases the lateral deviation from centerline in all landing conditions, although the touchdown point along the centerline is not changed.
For general aviation
General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations with the exception of commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as specialized aviation service ...
, MyGoFlight expects to receive a STC STC may refer to:
Education
* Saint Theresa's College (disambiguation), any of several institutions
* St. Thomas' College, Matale, Sri Lanka
* S. Thomas' College, Mount Lavinia, Sri Lanka
* Scott Theological College, Kenya
* Sha Tin College, H ...
and to retail its SkyDisplay HUD for $25,000 without installation for a single piston-engine as the Cirrus SR22s and more for Cessna Caravans or Pilatus PC-12
The Pilatus PC-12 is a pressurized, single-engined, turboprop aircraft, manufactured by Pilatus Aircraft of Stans, Switzerland, since 1991. It was designed as a high-performance utility aircraft that incorporates a large aft cargo door in add ...
s single-engine turboprops: 5 to 10% of a traditional HUD cost albeit it is non-conformal
Conformal may refer to:
* Conformal (software), in ASIC Software
* Conformal coating in electronics
* Conformal cooling channel, in injection or blow moulding
* Conformal field theory in physics, such as:
** Boundary conformal field theory ...
, not matching exactly the outside terrain.
Flight data from a tablet computer
A tablet computer, commonly shortened to tablet, is a mobile device, typically with a mobile operating system and touchscreen display processing circuitry, and a rechargeable battery in a single, thin and flat package. Tablets, being comput ...
can be projected on the $1,800 Epic Optix Eagle 1 HUD.
Enhanced flight vision systems
 In more advanced systems, such as the US
In more advanced systems, such as the US Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the largest transportation agency of the U.S. government and regulates all aspects of civil aviation in the country as well as over surrounding international waters. Its powers include air traffic m ...
(FAA)-labeled 'Enhanced Flight Vision System',U.S. DOT/FAA – Final Rule: Enhanced Flight Vision Systemswww.regulations.gov a real-world visual image can be overlaid onto the combiner. Typically an
infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from aroun ...
camera (either single or multi-band) is installed in the nose of the aircraft to display a conformed image to the pilot. 'EVS Enhanced Vision System' is an industry accepted term which the FAA decided not to use because "the FAA believes tcould be confused with the system definition and operational concept found in 91.175(l) and (m)" In one EVS installation, the camera is actually installed at the top of the vertical stabilizer rather than "as close as practical to the pilots eye position". When used with a HUD however, the camera must be mounted as close as possible to the pilots eye point as the image is expected to "overlay" the real world as the pilot looks through the combiner.
"Registration," or the accurate overlay of the EVS image with the real world image, is one feature closely examined by authorities prior to approval of a HUD based EVS. This is because of the importance of the HUD matching the real world.
While the EVS display can greatly help, the FAA has only relaxed operating regulations so an aircraft with EVS can perform a CATEGORY I approach to CATEGORY II minimums. In all other cases the flight crew must comply with all "unaided" visual restrictions. (For example, if the runway visibility is restricted because of fog, even though EVS may provide a clear visual image it is not appropriate (or legal) to maneuver the aircraft using only the EVS below 100 feet above ground level.)
Synthetic vision systems
Tanks
In mid-2017, the Israel Defense Forces will begin trials ofElbit
Elbit Systems Ltd. is an Israel-based international defense electronics company engaged in a wide range of programs throughout the world. The company, which includes Elbit Systems and its subsidiaries, operates in the areas of aerospace, land ...
's Iron Vision, the world's first helmet-mounted head-up display for tanks. Israel's Elbit, which developed the helmet-mounted display system for the F-35
The Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II is an American family of single-seat, single-engine, all-weather stealth multirole combat aircraft that is intended to perform both air superiority and strike missions. It is also able to provide ele ...
, plans Iron Vision to use a number of externally mounted cameras to project the 360° view of a tank's surroundings onto the helmet-mounted visors of its crew members. This allows the crew members to stay inside the tank, without having to open the hatches to see outside.IDF to trial Elbit's IronVision in Merkava MBTPeter Felstead, Tel Aviv - IHS Jane's Defence Weekly, 27 March 2017
Automobiles
speedometer
A speedometer or speed meter is a gauge that measures and displays the instantaneous speed of a vehicle. Now universally fitted to motor vehicles, they started to be available as options in the early 20th century, and as standard equipment ...
, tachometer, and navigation system displays. Night vision information is also displayed via HUD on certain automobiles. In contrast to most HUDs found in aircraft, automotive head-up displays are not parallax-free. The display may not be visible to a driver wearing sunglasses with polarised lenses.
Add-on HUD systems also exist, projecting the display onto a glass combiner mounted above or below the windshield, or using the windshield itself as the combiner.
In 2012, Pioneer Corporation introduced a HUD navigation system that replaces the driver-side sun visor and visually overlays animations of conditions ahead, a form of augmented reality (AR). Developed by Pioneer Corporation, AR-HUD became the first aftermarket automotive Head-Up Display to use a direct-to-eye laser beam scanning method, also known as virtual retinal display (VRD). AR-HUD's core technology involves a miniature laser beam scanning display developed by MicroVision, Inc.
MicroVision, Inc. is an American company that develops laser scanning technology for projection, 3D sensing, and image capture. MicroVision's display technology uses a micro-electrical mechanical systems (MEMS) scanning mirror with red, green, blu ...
Motorcycle helmet HUDs are also commercially available.
Uniti electric city car will replace the dashboard with a large HUD to display information directly on the windscreen
The windshield (North American English) or windscreen (Commonwealth English) of an aircraft, car, bus, motorbike, truck, train, boat or streetcar is the front window, which provides visibility while protecting occupants from the elements. ...
. The purpose is to increase safety as the driver will not have to move his eyes out from the road to look at the speed or the GPS screen.
In recent years, it has been argued that conventional HUDs will be replaced by holographic AR technologies, such as the ones developed by WayRay that use holographic optical elements (HOE). The HOE allows for a wider field of view while reducing the size of the device and making the solution customizable for any car model. Mercedes Benz introduced an Augmented Reality based Head Up Display while Faurecia invested in an eye gaze and finger controlled head up display.
Developmental / experimental uses
HUDs have been proposed or are being experimentally developed for a number of other applications. In the military, a HUD can be used to overlay tactical information such as the output of a laserrangefinder
A rangefinder (also rangefinding telemeter, depending on the context) is a device used to measure distances to remote objects. Originally optical devices used in surveying, they soon found applications in other fields, such as photography an ...
or squadmate locations to infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and m ...
men. A prototype HUD has also been developed that displays information on the inside of a swimmer's goggles or of a scuba diver's mask. HUD systems that project information directly onto the wearer's retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
with a low-powered laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The firs ...
( virtual retinal display) are also in experimentation.
Head-up displays can perform real-time language translation.Borghino, DariAugmented reality glasses perform real-time language translation
''gizmag'', 29 July 2012.
See also
*Acronyms and abbreviations in avionics
Below are abbreviations used in aviation, avionics, aerospace and aeronautics.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
N numbers (turbines)
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
V speeds
W
X
Y
Z
See also
* List of ...
* Augmented reality
Augmented reality (AR) is an interactive experience that combines the real world and computer-generated content. The content can span multiple sensory Modality (human–computer interaction), modalities, including visual, Hearing, auditory, hap ...
* Eyes-on-the-Road-Benefit
* EyeTap
* HUD (video gaming)
* Optical head-mounted display
* Smartglasses
* Virtual retinal display
* VR positional tracking
* Wearable computer
References
External links
Rochester Archives Article—'Buccaneer HUD PDU'
BBC Article—'Pacman comes to life virtually'
'Clinical evaluation of the 'head-up' display of anesthesia data'
'Elliott Brothers to BAE SYSTEMS' – a short history of Elliott Brothers
– a 1964 ''
Flight International
''Flight International'' is a monthly magazine focused on aerospace. Published in the United Kingdom and founded in 1909 as "A Journal devoted to the Interests, Practice, and Progress of Aerial Locomotion and Transport", it is the world's olde ...
'' article on flying using an early Specto head-up display
Jaguar Unveils 'Virtual Widescreen' Technology to Assist Drivers – Latin Post
{{emerging technologies, displays=yes Vehicle technology Avionics Aircraft instruments Automotive technologies Optical devices Multimodal interaction Mixed reality British inventions Emerging technologies