|
AI Mk. VIII Radar
Radar, Airborne Interception, Mark VIII, or AI Mk. VIII for short, was the first operational microwave-frequency Airborne Interception radar, air-to-air radar. It was used by Royal Air Force night fighters from late 1941 until the end of World War II. The basic concept, using a moving parabolic antenna to search for targets and track them accurately, remained in use by most airborne radars well into the 1980s. Low-level development began in 1939 but was greatly sped after the introduction of the cavity magnetron in early 1940. This operated at 9.1 cm wavelength (3 GHz), much shorter than the 1.5 m wavelength of the earlier AI Mk. IV radar, AI Mk. IV. Shorter wavelengths allowed it to use smaller and much more directional antennas. Mk. IV was blinded by the reflections off the ground from its wide broadcast pattern, which made it impossible to see targets flying at low altitudes. Mk. VIII could avoid this by keeping the antenna pointed upward, allowing it to see any a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
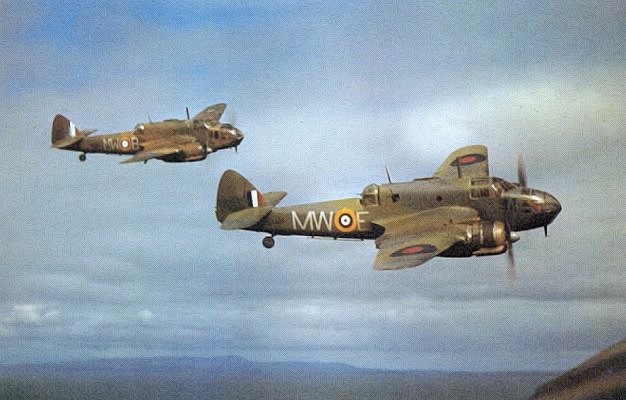
Bristol Beaufighter
The Bristol Type 156 Beaufighter (often called the Beau) is a British multi-role aircraft developed during the Second World War by the Bristol Aeroplane Company. It was originally conceived as a heavy fighter variant of the Bristol Beaufort torpedo bomber. The Beaufighter proved to be an effective night fighter, which came into service with the Royal Air Force (RAF) during the Battle of Britain, its large size allowing it to carry heavy armament and early airborne interception radar without major performance penalties. The Beaufighter was used in many roles; receiving the nicknames ''Rockbeau'' for its use as a rocket-armed ground attack aircraft and ''Torbeau'' as a torpedo bomber against Axis shipping, in which it replaced the Beaufort. In later operations, it served mainly as a maritime strike/ground attack aircraft, RAF Coastal Command having operated the largest number of Beaufighters amongst all other commands at one point. The Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) also m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Ministry Experimental Station
AMES, short Air Ministry Experimental Station, was the name given to the British Air Ministry's radar development team at Bawdsey Manor (afterwards RAF Bawdsey) in the immediate pre-World War II era. The team was forced to move on three occasions, changing names as part of these moves, so the AMES name applies only to the period between 1936 and 1939. Although used as a name by the team itself only briefly, the AMES acronym became the basis for naming Royal Air Force radar systems through the war. The same numbering sequence was used after the war as well, but often dropped the AMES from the name. A good example is the Type 80, which was officially AMES Type 80, but often appears without that marque. Many post-war systems were also assigned a rainbow code and are better known by that name. The AMES numbering scheme was often ''ad hoc'', with some entries simply being other sets operating together. For instance, the Type 21 was simply a Type 13 and Type 14 in a single vehicle conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Coastal Command
RAF Coastal Command was a formation within the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was founded in 1936, when the RAF was restructured into Fighter, Bomber and Coastal Commands and played an important role during the Second World War. Maritime Aviation had been neglected in the inter-war period, due to disagreements between the Royal Navy (RN) and RAF over the ownership, roles and investment in maritime air power. The Admiralty's main concern until 1937 was the return of the Fleet Air Arm to the Royal Navy while the RAF prioritised the development of a bombing force to provide a deterrent. Coastal Command was referred to as the "Cinderella Service" by A V Alexander, the First Lord of the Admiralty in November 1940. Soon after RAF Coastal Area was elevated to Coastal Command, its headquarters moved from Lee-on-Solent to Northwood in northwest London. During the Second World War, Coastal Command's most important contribution was the protection of Allied convoys from attacks by the Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkhas, and 28,330 volunteer reserve personnel. The modern British Army traces back to 1707, with antecedents in the English Army and Scots Army that were created during the Restoration in 1660. The term ''British Army'' was adopted in 1707 after the Acts of Union between England and Scotland. Members of the British Army swear allegiance to the monarch as their commander-in-chief, but the Bill of Rights of 1689 and Claim of Right Act 1689 require parliamentary consent for the Crown to maintain a peacetime standing army. Therefore, Parliament approves the army by passing an Armed Forces Act at least once every five years. The army is administered by the Ministry of Defence and commanded by the Chief of the General Staff. The Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
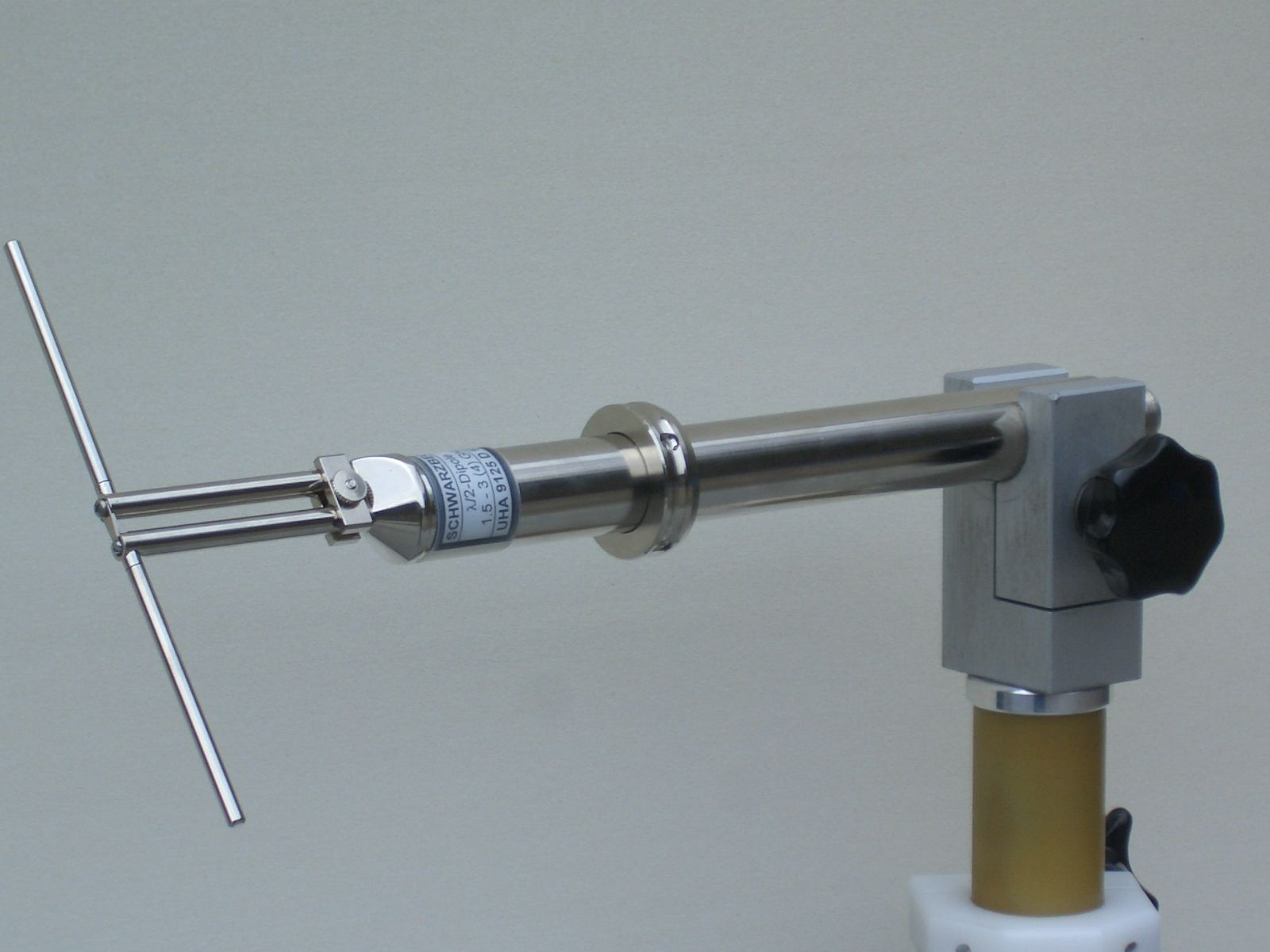
Half-wave Dipole
In radio and telecommunications a dipole antenna or doublet is the simplest and most widely used class of antenna. The dipole is any one of a class of antennas producing a radiation pattern approximating that of an elementary electric dipole with a radiating structure supporting a line current so energized that the current has only one node at each end. A dipole antenna commonly consists of two identical conductive elements such as metal wires or rods. The driving current from the transmitter is applied, or for receiving antennas the output signal to the receiver is taken, between the two halves of the antenna. Each side of the feedline to the transmitter or receiver is connected to one of the conductors. This contrasts with a monopole antenna, which consists of a single rod or conductor with one side of the feedline connected to it, and the other side connected to some type of ground. A common example of a dipole is the "rabbit ears" television antenna found on broadcast televi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna Gain
In electromagnetics, an antenna's gain is a key performance parameter which combines the antenna's directivity and radiation efficiency. The term ''power gain'' has been deprecated by IEEE. In a transmitting antenna, the gain describes how well the antenna converts input power into radio waves headed in a specified direction. In a receiving antenna, the gain describes how well the antenna converts radio waves arriving from a specified direction into electrical power. When no direction is specified, gain is understood to refer to the peak value of the gain, the gain in the direction of the antenna's main lobe. A plot of the gain as a function of direction is called the antenna pattern or radiation pattern. It is not to be confused with directivity, which does ''not'' take an antenna's radiation efficiency into account. Gain or 'absolute gain' is defined as "The ratio of the radiation intensity in a given direction to the radiation intensity that would be produced if the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward George Bowen
Edward George "Taffy" Bowen, CBE, FRS (14 January 1911 – 12 August 1991) was a Welsh physicist who made a major contribution to the development of radar. He was also an early radio astronomer, playing a key role in the establishment of radioastronomy in Australia and the United States. Early years Edward George Bowen was born at Cockett in Swansea, south Wales, to George Bowen and Ellen Ann (née Owen). George Bowen was a steelworker in a Swansea tinplate works. From an early age Bowen developed a strong interest in radio and cricket. He entered Swansea University and read physics and related subjects. He graduated with a First-Class Honours degree in 1930, and continued with postgraduate research on X-rays and the structure of alloys, earning an MSc in 1931. He completed his doctorate under Professor E.V. Appleton at King's College London. As part of his research, Bowen spent a large part of 1933 and 1934 working with a cathode-ray direction finder at the Radio Research S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Watson-Watt
Sir Robert Alexander Watson Watt (13 April 1892 – 5 December 1973) was a Scottish pioneer of radio direction finding and radar technology. Watt began his career in radio physics with a job at the Met Office, where he began looking for accurate ways to track thunderstorms using the radio signals given off by lightning. This led to the 1920s development of a system later known as high-frequency direction finding (HFDF or "huff-duff"). Although well publicized at the time, the system's enormous military potential was not developed until the late 1930s. Huff-duff allowed operators to determine the location of an enemy radio in seconds and it became a major part of the network of systems that helped defeat the threat of German U-boats during World War II. It is estimated that huff-duff was used in about a quarter of all attacks on U-boats. In 1935 Watt was asked to comment on reports of a German death ray based on radio. Watt and his assistant Arnold Frederic Wilkins quickly dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
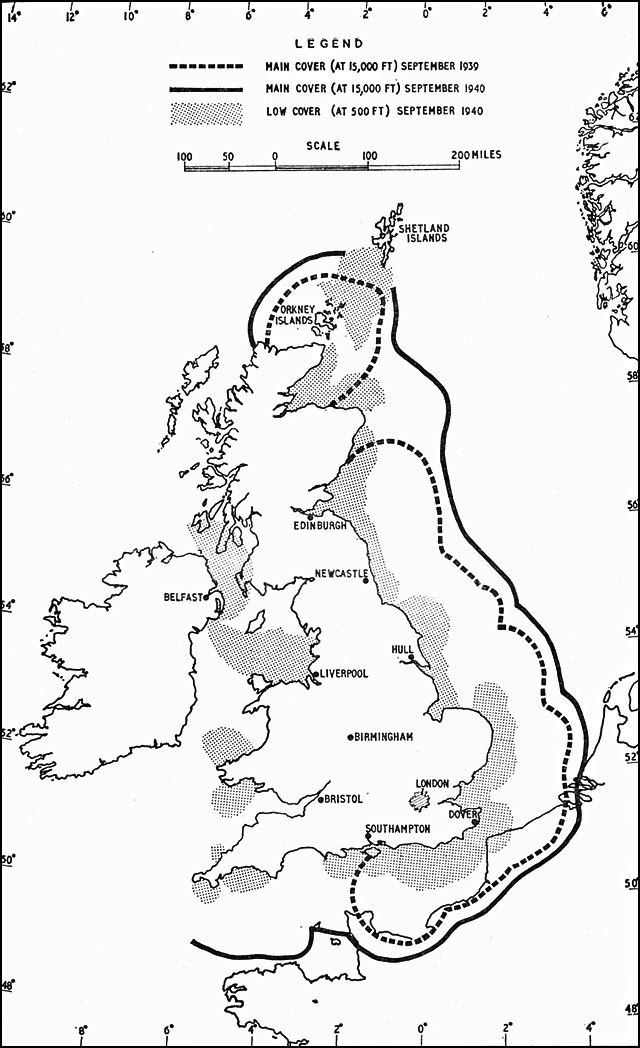
Dowding System
The Dowding system was the world's first wide-area ground-controlled interception network, controlling the airspace across the United Kingdom from northern Scotland to the southern coast of England. It used a widespread dedicated land-line telephone network to rapidly collect information from Chain Home (CH) radar stations and the Royal Observer Corps (ROC) in order to build a single image of the entire UK airspace and then direct defensive interceptor aircraft and anti-aircraft artillery against enemy targets. The system was built by the Royal Air Force just before the start of World War II, and proved decisive in the Battle of Britain. The Dowding system was developed after tests demonstrated problems relaying information to the fighters before it was out of date. Air Chief Marshal Hugh Dowding, commander of RAF Fighter Command, solved the problem through the use of hierarchical reporting chains. Information was sent to Fighter Command Headquarters (FCHQ) central ''filter room' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground-controlled Intercept
Ground-controlled interception (GCI) is an air defence tactic whereby one or more radar stations or other observational stations are linked to a command communications centre which guides interceptor aircraft to an airborne target. This tactic was pioneered during World War I by the London Air Defence Area organization, which became the Royal Air Force's Dowding system in World War II, the first national-scale system. The ''Luftwaffe'' introduced similar systems during the war, but most other combatants did not suffer the same threat of air attack and did not develop complex systems like these until the Cold War era. Today the term GCI refers to the style of battle direction, but during WWII it also referred to the radars themselves. Specifically, the term was used to describe a new generation of radars that spun on their vertical axis in order to provide a complete 360 degree view of the sky around the station. Previous systems, notably Chain Home (CH), could only be directed along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Tizard
Sir Henry Thomas Tizard (23 August 1885 – 9 October 1959) was an English chemist, inventor and Rector of Imperial College, who developed the modern "octane rating" used to classify petrol, helped develop radar in World War II, and led the first serious studies of UFOs. Life Tizard was born in Gillingham, Kent in 1885, the only son of Thomas Henry Tizard (1839–1924), naval officer and hydrographer, and his wife, Mary Elizabeth Churchward. His ambition to join the navy was thwarted by poor eyesight, and he instead studied at Westminster School and Magdalen College, Oxford, where he concentrated on mathematics and chemistry, doing work on indicators and the motions of ions in gases. Tizard graduated in 1908 and at his tutor's suggestion he spent time in Berlin, where he met and formed a close friendship with Frederick Alexander Lindemann, later an influential scientific advisor of Winston Churchill. In 1909, he became a researcher in the Davy–Faraday Laboratory of the Roy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |