Ground-controlled Intercept on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ground-controlled interception (GCI) is an 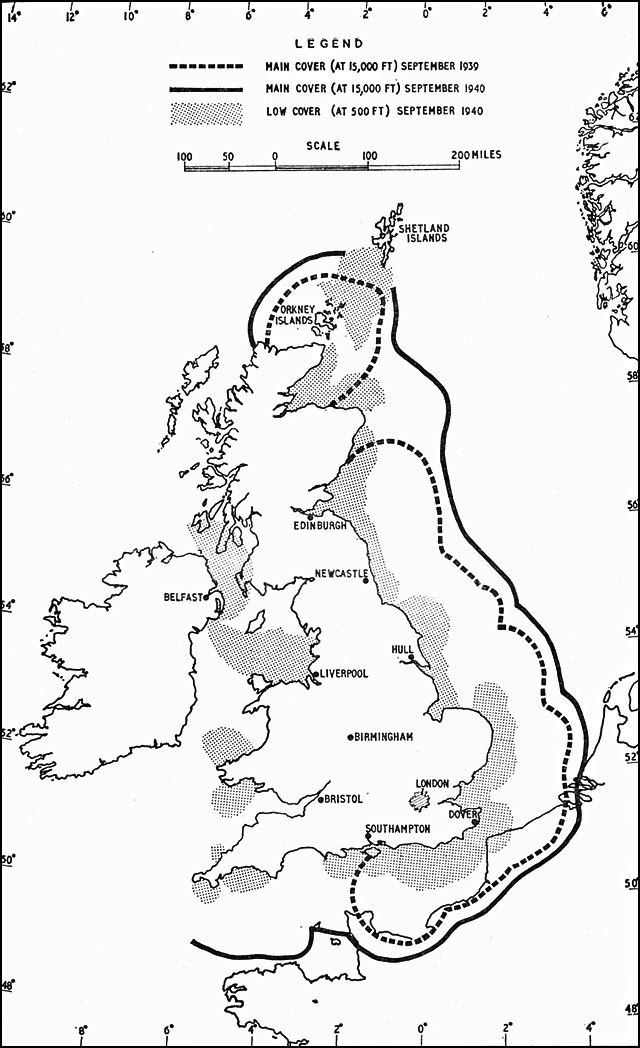
Radarpages.co.uk GCI page
GCI Online Radar Museum
Ground Controlled Interception Radars in Operation Neptune/Overlord
(pdf) {{DEFAULTSORT:Ground-Controlled Interception Ground-controlled Military radars
air defence
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based, ...
tactic whereby one or more radar station
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weat ...
s or other observational stations are linked to a command communications centre which guides interceptor aircraft
An interceptor aircraft, or simply interceptor, is a type of fighter aircraft designed specifically for the defensive interception role against an attacking enemy aircraft, particularly bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that are cap ...
to an airborne target. This tactic was pioneered during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
by the London Air Defence Area
The London Air Defence Area (LADA) was the name given to the organisation created to defend London from the increasing threat from German airships during World War I. Formed in September 1915, it was commanded initially by Admiral Sir Percy Scott ...
organization, which became the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and ...
's Dowding system
The Dowding system was the world's first wide-area ground-controlled interception network, controlling the airspace across the United Kingdom from northern Scotland to the southern coast of England. It used a widespread dedicated land-line telep ...
in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the first national-scale system. The ''Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
'' introduced similar systems during the war, but most other combatants did not suffer the same threat of air attack and did not develop complex systems like these until the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
era.
Today the term GCI refers to the style of battle direction, but during WWII it also referred to the radars themselves. Specifically, the term was used to describe a new generation of radars that spun on their vertical axis in order to provide a complete 360 degree view of the sky around the station. Previous systems, notably Chain Home
Chain Home, or CH for short, was the codename for the ring of coastal Early Warning radar stations built by the Royal Air Force (RAF) before and during the Second World War to detect and track aircraft. Initially known as RDF, and given the off ...
(CH), could only be directed along angles in front of the antennas, and were unable to direct traffic once it passed behind their shore-side locations. GCI radars began to replace CH starting in 1941/42, allowing a single station to control the entire battle from early detection to directing the fighters to intercept.
GCI systems grew in size and sophistication during the post-war era, in response to the overwhelming threat of nuclear attack. The US' SAGE
Sage or SAGE may refer to:
Plants
* ''Salvia officinalis'', common sage, a small evergreen subshrub used as a culinary herb
** Lamiaceae, a family of flowering plants commonly known as the mint or deadnettle or sage family
** ''Salvia'', a large ...
system was perhaps the most complex attempted, using building-filling computers linked to dozens of radars and other sensors to automate the entire task of identifying an enemy aircraft's track and directing interceptor aircraft
An interceptor aircraft, or simply interceptor, is a type of fighter aircraft designed specifically for the defensive interception role against an attacking enemy aircraft, particularly bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that are cap ...
or surface-to-air missile
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft syst ...
s against it. In some cases, SAGE sent commands directly to the aircraft's autopilot
An autopilot is a system used to control the path of an aircraft, marine craft or spacecraft without requiring constant manual control by a human operator. Autopilots do not replace human operators. Instead, the autopilot assists the operator' ...
s, bringing the aircraft within attack range entirely under computer control. The RAF counterpart, ROTOR
Rotor may refer to:
Science and technology
Engineering
*Rotor (electric), the non-stationary part of an alternator or electric motor, operating with a stationary element so called the stator
* Helicopter rotor, the rotary wing(s) of a rotorcraft ...
remained a mostly manual system.
Today, GCI is still important for most nations, although Airborne Early Warning and Control
Airborne or Airborn may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Films
* ''Airborne'' (1962 film), a 1962 American film directed by James Landis
* ''Airborne'' (1993 film), a comedy–drama film
* ''Airborne'' (1998 film), an action film sta ...
, with or without support from GCI, generally offers much greater range due to the much more distant radar horizon
The radar horizon is a critical area of performance for aircraft detection systems that is defined by the distance at which the radar beam rises enough above the Earth's surface to make detection of a target at low level impossible. It is associ ...
.

World War II
In the originalDowding system
The Dowding system was the world's first wide-area ground-controlled interception network, controlling the airspace across the United Kingdom from northern Scotland to the southern coast of England. It used a widespread dedicated land-line telep ...
of fighter control, information from the Chain Home
Chain Home, or CH for short, was the codename for the ring of coastal Early Warning radar stations built by the Royal Air Force (RAF) before and during the Second World War to detect and track aircraft. Initially known as RDF, and given the off ...
coastal radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
stations was relayed by phone to a number of operators on the ground floor of the "filter room" at Fighter Command's headquarters at RAF Bentley Priory
RAF Bentley Priory was a non-flying Royal Air Force station near Stanmore in the London Borough of Harrow. It was the headquarters of Fighter Command in the Battle of Britain and throughout the Second World War. During the war, two enemy bomb ...
. Here the information from the radar was combined with reports from the Royal Observer Corps
The Royal Observer Corps (ROC) was a civil defence organisation intended for the visual detection, identification, tracking and reporting of aircraft over Great Britain. It operated in the United Kingdom between 29 October 1925 and 31 December ...
and radio direction finding
Direction finding (DF), or radio direction finding (RDF), isin accordance with International Telecommunication Union (ITU)defined as radio location that uses the reception of radio waves to determine the direction in which a radio station ...
systems and merged to produce a single set of "tracks", identified by number. These tracks were then telephoned to the Group headquarters that would be responsible for dealing with that target. Group would assign fighter squadrons to the tracks, and phone the information to Section headquarters, who were in direct contact with the fighters. These fighter aircraft could then be "scrambled
Scrambled eggs is a dish made from eggs (usually chicken eggs) stirred, whipped or beaten together while being gently heated, typically with salt, butter, oil and sometimes other ingredients.
Preparation
Only eggs are necessary to make scrambled ...
" to intercept the aircraft.
Because the Chain Home radar stations faced out to sea, once airborne intruders had crossed the British coast they could no longer be tracked by radar; and accordingly the interception direction centres relied on visual and aural sightings of the Observer Corps for continually updated information on the location and heading of enemy aircraft formations. While this arrangement worked acceptably during the daylight raids of the Battle of Britain
The Battle of Britain, also known as the Air Battle for England (german: die Luftschlacht um England), was a military campaign of the Second World War, in which the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) of the Royal Navy defende ...
, subsequent bombing attacks of The Blitz
The Blitz was a German bombing campaign against the United Kingdom in 1940 and 1941, during the Second World War. The term was first used by the British press and originated from the term , the German word meaning 'lightning war'.
The Germa ...
demonstrated that such techniques were wholly inadequate for identifying and tracking aircraft at night.
Experiments in addressing this problem started with manually directed radars being used as a sort of radio-searchlight, but this proved too difficult to use in practice. Another attempt was made by using a height finding radar turned on its side in order to scan an arc in front of the station. This proved very workable, and was soon extended to covering a full 360 degrees by making minor changes to the support and bearing systems. Making a display system, the "Plan Position Indicator
A plan position indicator (PPI) is a type of radar display that represents the radar antenna in the center of the display, with the distance from it and height above ground drawn as concentric circles. As the radar antenna rotates, a radial tra ...
" (PPI), that displayed a 360 degree pattern proved surprisingly easy, and test systems were available by late 1940.
Starting in 1941 the RAF began deploying production models of the GCI radar, first with expedient solutions known as the AMES Type 8
Ames may refer to:
Places United States
* Ames, Arkansas, a place in Arkansas
* Ames, Colorado
* Ames, Illinois
* Ames, Indiana
* Ames, Iowa, the most populous city bearing this name
* Ames, Kansas
* Ames, Nebraska
* Ames, New York
* Ames, O ...
, and then permanent stations based on the much larger AMES Type 7
The AMES Type 7, also known as the Final GCI, was a ground-based radar system introduced during World War II by the Royal Air Force (RAF). The Type 7 was the first truly modern radar used by the Allies, providing a 360 degree view of the airspace a ...
. Unlike the earlier system where radar data was forwarded by telephone and plotted on a map, GCI radars combined all of these functions into a single station. The PPI was in the form of a 2D top-down display showing both the targets and the intercepting night fighter
A night fighter (also known as all-weather fighter or all-weather interceptor for a period of time after the Second World War) is a fighter aircraft adapted for use at night or in other times of bad visibility. Night fighters began to be used i ...
s. Interceptions could be arranged directly from the display, without any need to forward the information over telephone links or similar. This not only greatly eased the task of arranging the interception, but greatly reduced the required manpower as well.
As the system became operational the success of the RAF night fighter force began to shoot up. This was further aided by the introduction of the Bristol Beaufighter
The Bristol Type 156 Beaufighter (often called the Beau) is a British multi-role aircraft developed during the Second World War by the Bristol Aeroplane Company. It was originally conceived as a heavy fighter variant of the Bristol Beaufort ...
and its AI Mk. IV radar
Radar, Airborne Interception, Mark IV (AI Mk. IV), produced by USA as SCR-540, was the world's first operational air-to-air radar system. Early Mk. III units appeared in July 1940 on converted Bristol Blenheim light bombers, while the definit ...
which became available in numbers at the same time. These two systems proved to be a potent combination, and interception rates doubled every month from January 1941 until the ''Luftwaffe'' campaign ended in May.
The Germans were quite slow to follow in terms of PPI and did not order operational versions of their Jagdschloss radar
Jagdschloss, officially the FuG 404, was the designation of a German early warning and battle control radar developed just prior to the start of World War II. Although it was built in limited numbers, Jadgschloss is historically important as the ...
until late in 1943, with deliveries being relatively slow after that. Many were still under construction when the war ended in 1945.
Post WWII
More recently, in both theKorean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
and Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
wars, the North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu River, Y ...
ns and North Vietnam
North Vietnam, officially the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV; vi, Việt Nam Dân chủ Cộng hòa), was a socialist state supported by the Soviet Union (USSR) and the People's Republic of China (PRC) in Southeast Asia that existed f ...
ese had important GCI systems which helped them harass the opposing forces (although in both cases due to the superiority in the number of US planes the effect was eventually minimised ). GCI was important to the US and allied forces during these conflicts also, although not so much as for their opponents.
The most advanced GCI system deployed to date was the US's Semi Automatic Ground Environment
The Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) was a system of large computers and associated networking equipment that coordinated data from many radar sites and processed it to produce a single unified image of the airspace over a wide area. S ...
(SAGE) system. SAGE used massive computers to combine reports sent in via teleprinter
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint configurations. Initia ...
from the Pinetree Line
The Pinetree Line was a series of radar stations located across the northern United States and southern Canada at about the 50th parallel north, along with a number of other stations located on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic and Pacific coasts. ...
and other radar networks to produce a picture of all of the air traffic in a particular "sector"s area. The information was then displayed on terminals in the building, allowing operators to pick defensive assets (fighters and missiles) to be directed onto the target simply by selecting them on the terminal. Messages would then automatically be routed back out via teleprinter to the fighter airbases with interception instructions on them.
The system was later upgraded to relay directional information directly to the autopilot
An autopilot is a system used to control the path of an aircraft, marine craft or spacecraft without requiring constant manual control by a human operator. Autopilots do not replace human operators. Instead, the autopilot assists the operator' ...
s of the interceptor aircraft
An interceptor aircraft, or simply interceptor, is a type of fighter aircraft designed specifically for the defensive interception role against an attacking enemy aircraft, particularly bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that are cap ...
like the F-106 Delta Dart
The Convair F-106 Delta Dart was the primary all-weather interceptor aircraft of the United States Air Force from the 1960s through to the 1980s. Designed as the so-called "Ultimate Interceptor", it proved to be the last specialist interceptor i ...
. The pilot was tasked primarily with getting the aircraft into the air (and back), and then flying in a parking orbit until called for. When an interception mission started, the SAGE computers automatically flew the plane into range of the target, allowing the pilot to concentrate solely on operating the complex onboard radar.
The RAF's post-war system was originally ROTOR
Rotor may refer to:
Science and technology
Engineering
*Rotor (electric), the non-stationary part of an alternator or electric motor, operating with a stationary element so called the stator
* Helicopter rotor, the rotary wing(s) of a rotorcraft ...
, which was largely an expanded and rationalized version of their wartime system and remained entirely manual in operation. This was upset by the introduction of the AMES Type 80
The AMES Type 80, sometimes known by its development rainbow code Green Garlic, was a powerful early warning (EW) and ground-controlled interception (GCI) radar developed by the Telecommunications Research Establishment (TRE) and built by Decca f ...
radar, which was originally intended as a very long-range early warning system for ROTOR but demonstrated its ability to control interceptions as well. This led to the abandonment of the ROTOR network and its operation being handled at the Type 80 "Master Radar Stations". In the 1960s the Linesman/Mediator
Linesman/Mediator was a dual-purpose civil and military radar network in the United Kingdom between the 1960s and 1984. The military side (Linesman) was replaced by the Improved United Kingdom Air Defence Ground Environment (IUKADGE), while the ...
project looked to computerize the system in a fashion similar to SAGE, but was years late, significantly underpowered, and never operated properly. There was some thought given to sending directions to the English Electric Lightning
The English Electric Lightning is a British fighter aircraft that served as an interceptor during the 1960s, the 1970s and into the late 1980s. It was capable of a top speed of above Mach 2. The Lightning was designed, developed, and manufa ...
interceptors in a fashion similar to SAGE, but this was never implemented.
GCI is typically augmented with the presence of extremely large early warning radar
An early-warning radar is any radar system used primarily for the long-range detection of its targets, i.e., allowing defences to be alerted as ''early'' as possible before the intruder reaches its target, giving the air defences the maximum t ...
arrays, which could alert GCI to inbound hostile aircraft hours before they arrive, giving enough time to prepare and launch aircraft and set them up for an intercept either using their own radars or with the assistance of regular radar stations once the bogeys approach their coverage. An example of this type of system is Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
's Jindalee over-the-horizon radar Jindalee may refer to:
* Jindalee, New South Wales
* Jindalee, Queensland
* Jindalee, Western Australia
* Jindalee Operational Radar Network
See also
* ''Jindalee Lady
''Jindalee Lady'' is a 1992 Australian film about an Aboriginal Australia ...
. Such radars typically operate by bouncing their signal off layers in the atmosphere.
Airborne Early Warning and Control
In more recent years, GCI has been supplanted, or replaced outright, with the introduction ofAirborne Early Warning and Control
Airborne or Airborn may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Films
* ''Airborne'' (1962 film), a 1962 American film directed by James Landis
* ''Airborne'' (1993 film), a comedy–drama film
* ''Airborne'' (1998 film), an action film sta ...
(AEW&C, often called AWACS) aircraft. AEW&C tends to be superior in that, being airborne and being able to look down, it can see targets fairly far away at low level, as long as it can pick them out from the ground clutter. AEW&C aircraft are extremely expensive, however, and generally require aircraft to be dedicated to protecting them. A combination of both techniques is really ideal, but GCI is typically only available in the defence of one's homeland, rather than in expeditionary types of battles.
The strengths of GCI are that it can cover far more airspace than AEW&C without costing as much and areas that otherwise would be blind-spots for AEW&C can be covered by cleverly placed radar stations. AEW&C also relies on aircraft which may require defence and a few aircraft are more vulnerable than many ground-based radar stations. If a single AEW&C aircraft is shot down or otherwise taken out of the picture, there will be a serious gap in air defence until another can replace it, where in the case of GCI, many radar stations would have to be taken off the air before it became a serious problem. In both cases a strike on a command center could be very serious.
Either GCI or AEW&C can be used to give defending aircraft a major advantage during the actual interception by allowing them to sneak up on enemy aircraft without giving themselves away by using their own radar sets. Typically, to perform an interception by themselves beyond visual range, the aircraft would have to search the sky for intruders with their radars, the energy from which might be noticed by the intruder's radar warning receiver
Radar warning receiver (RWR) systems detect the radio emissions of radar systems. Their primary purpose is to issue a warning when a radar signal that might be a threat is detected, like a fighter aircraft's fire control radar. The warning can th ...
(RWR) electronics, thus alerting the intruders that they may be coming under attack. With GCI or AEW&C, the defending aircraft can be vectored to an interception course, perhaps sliding in on the intruder's tail position without being noticed, firing passive homing missiles and then turning away. Alternatively, they could turn their radars on at the final moment, so that they can get a radar lock and guide their missiles. This greatly increases the interceptor's chance of success and survival.
See also
*Signal Corps Radio
Signal Corps Radios were U.S. Army military communications components that comprised "sets". Under the Army Nomenclature System, the abbreviation SCR initially designated "Set, Complete Radio", but was later misinterpreted as "Signal Corps Radio."
...
* Sector clock
A Sector clock or colour change clock was a round colour-coded clock used at military airfields and observation posts in the United Kingdom to help track the movements of enemy aircraft and control friendly aircraft.
History
Originally known a ...
* ROTOR
Rotor may refer to:
Science and technology
Engineering
*Rotor (electric), the non-stationary part of an alternator or electric motor, operating with a stationary element so called the stator
* Helicopter rotor, the rotary wing(s) of a rotorcraft ...
* Linesman/Mediator
Linesman/Mediator was a dual-purpose civil and military radar network in the United Kingdom between the 1960s and 1984. The military side (Linesman) was replaced by the Improved United Kingdom Air Defence Ground Environment (IUKADGE), while the ...
* Boeing Ground-to-Air Pilotless Aircraft
Boeing's Ground-to-Air Pilotless Aircraft (GAPA) was a short-range anti-aircraft missile (SAM) developed in the late 1940s by the US Army Air Force, and then the US Air Force after 1948. It was given the reference number SAM-A-1, the first Surface- ...
* UCAV
An unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV), also known as a combat drone, colloquially shortened as drone or battlefield UAV, is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) that is used for intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance ...
* STRIL
wedishTactical (Fighting Command) and Air Defence Control System ( sv, Stridsledning och luftbevakning, STRIL, , Combat control and air surveillance) in forms of STRIL 50 (operational in the 1950s) and STRIL 60 (operational in the 196 ...
References
Radarpages.co.uk GCI page
GCI Online Radar Museum
External links
Ground Controlled Interception Radars in Operation Neptune/Overlord
(pdf) {{DEFAULTSORT:Ground-Controlled Interception Ground-controlled Military radars