Hathor temple on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Dendera Temple complex ( Ancient Egyptian: ''Iunet'' or ''Tantere''; the 19th-century English spelling in most sources, including Belzoni, was Tentyra; also spelled Denderah) is located about south-east of
Dendera Temple complex ( Ancient Egyptian: ''Iunet'' or ''Tantere''; the 19th-century English spelling in most sources, including Belzoni, was Tentyra; also spelled Denderah) is located about south-east of
 The whole complex covers some 40,000 square meters and is surrounded by a hefty
The whole complex covers some 40,000 square meters and is surrounded by a hefty

 The dominant building in the complex is the Temple of
The dominant building in the complex is the Temple of
 The sculptured Dendera zodiac (or Denderah zodiac) is a widely known relief found in a late Greco-Roman temple, containing images of
The sculptured Dendera zodiac (or Denderah zodiac) is a widely known relief found in a late Greco-Roman temple, containing images of
 The Hathor Temple has stone reliefs that depict
The Hathor Temple has stone reliefs that depict
 The Roman
The Roman
File:Dendera Römisches Mammisi 14.JPG, Side with reliefs
File:Roman Emperor Trajan at Dendera, Egypt.jpg, Roman Emperor
File:Dendera Temple.jpg, Satellite buildings of the Dendera Temple complex
File:SFEC EGYPT DENDERA 2006-006.JPG, Entrance to the Dendera Temple complex
File:Denderah portail.JPG, Entrance gate to the temple, with
Egyptian Stars under Paris Skies
'". pr.caltech.edu. * R. A. Parker, "
Ancient Egyptian Astronomy
'". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, Vol. 276, No. 1257, The Place of Astronomy in the Ancient World (May 2, 1974), pp. 51–65 * Marshall Clagett, "
Ancient Egyptian Science: A Source Book
'". Diane, 1989. * William Henry and Davenport Adams "
Egypt Past and Present: Described and Illustrated
'". T. Nelson and Sons, 1885. 380 pages. Page 218 - 226
Catchpenny Mysteries. * Frank Dörnenburg
Electric lights in Egypt?
2004. (ed. An analysis of how the Egyptians didn't have electricity). * Mariette, Auguste, ''Dendérah'', Bookshop A. Franck, Paris, 1875. * Fischer, H.G., ''Dendera in the third millennium B.C. down to the theban domination of upper Egypt'', J.J. Augustin publisher, New York, 1968.
Dendera Temple complex
satellite-sightseer.com.
(French)
High-resolution Images of Dendera Temple Ceiling
{{Authority control Archaeological sites in Egypt Egyptian temples Former religious buildings and structures in Egypt 1st-century BC religious buildings and structures Hellenistic architecture 23rd-century BC establishments Buildings and structures completed in the 23rd century BC
Dendera
Dendera ( ar, دَنْدَرة ''Dandarah''; grc, Τεντυρις or Τεντυρα; Bohairic cop, ⲛⲓⲧⲉⲛⲧⲱⲣⲓ, translit=Nitentōri; Sahidic cop, ⲛⲓⲧⲛⲧⲱⲣⲉ, translit=Nitntōre), also spelled ''Denderah'', ancient ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
. It is one of the best-preserved temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
complexes in Egypt. The area was used as the sixth nome of Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ar, صعيد مصر ', shortened to , , locally: ; ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the lands on both sides of the Nile that extend upriver from Lower Egypt in the north to Nubia in the south.
In ancient ...
, south of Abydos.
Description
mudbrick
A mudbrick or mud-brick is an air-dried brick, made of a mixture of loam, mud, sand and water mixed with a binding material such as rice husks or straw. Mudbricks are known from 9000 BCE, though since 4000 BCE, bricks have also bee ...
enclosed wall. Dendera was inhabited in prehistory, a useful oasis on the banks of the Nile. It seems that pharaoh Pepi I
Pepi I Meryre (also Pepy I) was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh, third king of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt, who ruled for over 40 years at the turn of the 24th and 23rd centuries BC, toward the end of the Old Kingdom period. He was the son of ...
(ca. 2250 BC) built on this site and evidence exists of a temple in the Eighteenth Dynasty (ca 1500 BC). The earliest extant building in the compound today is the mammisi A mammisi (mamisi) is an ancient Egyptian small chapel attached to a larger Egyptian temple, temple (usually in front of the Pylon (architecture), pylonsRachet, Guy (1994). ''Dizionario della civiltà egizia''. Rome: Gremese Editore. . p. 186.), bui ...
raised by Nectanebo II
Nectanebo II (Egyptian: ; grc-gre, Νεκτανεβώς ) was the last native ruler of Ancient Egypt, as well as the third and last pharaoh from the Thirtieth Dynasty of Egypt. He reigned from 358 to 340 BC.
Under Nectanebo II, Egypt prospered ...
– last of the native pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the an ...
s (360–343 BC). The features in the complex include:
* Hathor temple (the main temple)
* Temple of the birth of Isis
* Sacred Lake
* Sanatorium
* Mammisi of Nectanebo II
* Christian Basilica
* Roman Mammisi
* a Barque shrine
* Gateways of Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavi ...
and Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
* the Roman Kiosk
Nearby is the Dendera necropolis, a series of mastaba
A mastaba (, or ), also mastabah, mastabat or pr- djt (meaning "house of stability", " house of eternity" or "eternal house" in Ancient Egyptian), is a type of ancient Egyptian tomb in the form of a flat-roofed, rectangular structure with inwar ...
tomb
A tomb ( grc-gre, τύμβος ''tumbos'') is a :wikt:repository, repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes. Placing a corpse into a tomb can be ...
s. The necropolis
A necropolis (plural necropolises, necropoles, necropoleis, necropoli) is a large, designed cemetery with elaborate tomb monuments. The name stems from the Ancient Greek ''nekropolis'', literally meaning "city of the dead".
The term usually im ...
dates from the Early Dynastic Period of the Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth ...
to the First Intermediate Period of Egypt
The First Intermediate Period, described as a 'dark period' in ancient Egyptian history, spanned approximately 125 years, c. 2181–2055 BC, after the end of the Old Kingdom. It comprises the Seventh (although this is mostly considered spuriou ...
. The necropolis runs the eastern edge of the western hill and over the northern plain.
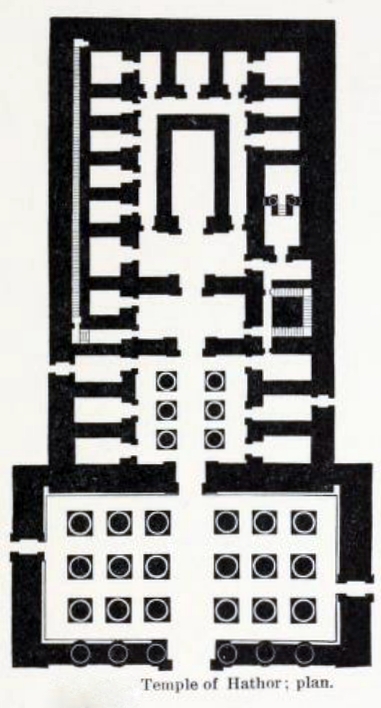
Hathor temple


 The dominant building in the complex is the Temple of
The dominant building in the complex is the Temple of Hathor
Hathor ( egy, ḥwt-ḥr, lit=House of Horus, grc, Ἁθώρ , cop, ϩⲁⲑⲱⲣ, Meroitic: ) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion who played a wide variety of roles. As a sky deity, she was the mother or consort of the sky ...
. The temple has been modified on the same site starting as far back as the Middle Kingdom, and continuing right up until the time of the Roman emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
. The existing structure began construction in the late Ptolemaic period at the time of Ptolemy Auletes
Ptolemy XII Neos Dionysus Philopator Philadelphus ( grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος Νέος Διόνυσος Φιλοπάτωρ Φιλάδελφος, Ptolemaios Neos Dionysos Philopatōr Philadelphos; – 51 BC) was a pharaoh of the Ptolemaic ...
in July 54 BCE. and the hypostyle hall was built in the Roman period
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
under Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
.
In Egypt, Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
was quite active in constructing buildings and decorating them. He appears, together with Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavi ...
, in offering scenes on the propylon of the Temple of Hathor. His cartouche
In Egyptian hieroglyphs, a cartouche is an oval with a line at one end tangent to it, indicating that the text enclosed is a royal name. The first examples of the cartouche are associated with pharaohs at the end of the Third Dynasty, but the fea ...
also appears in the column shafts of the Temple of Khnum
Khnum or also romanised Khnemu (; egy, 𓎸𓅱𓀭 ẖnmw, grc-koi, Χνοῦβις) was one of the earliest-known Egyptian deities, originally the god of the source of the Nile. Since the annual flooding of the Nile brought with it silt an ...
at Esna
Esna ( ar, إسنا , egy, jwny.t or ; cop, or ''Snē'' from ''tꜣ-snt''; grc-koi, Λατόπολις ''Latópolis'' or (''Pólis Látōn'') or (''Lattōn''); Latin: ''Lato''), is a city of Egypt. It is located on the west bank of ...
."Trajan was, in fact, quite active in Egypt. Separate scenes of Domitian and Trajan making offerings to the gods appear on reliefs on the propylon of the Temple of Hathor at Dendera. There are cartouches of Domitian and Trajan on the column shafts of the Temple of Knum at Esna, and on the exterior a frieze text mentions Domitian, Trajan, and Hadrian"
Layout elements of the temple are:
* Large Hypostyle Hall
In architecture, a hypostyle () hall has a roof which is supported by columns.
Etymology
The term ''hypostyle'' comes from the ancient Greek ὑπόστυλος ''hypóstȳlos'' meaning "under columns" (where ὑπό ''hypó'' means below or un ...
* Small Hypostyle Hall
* Laboratory
* Storage magazine
* Offering entry
* Treasury
A treasury is either
*A government department related to finance and taxation, a finance ministry.
*A place or location where treasure, such as currency or precious items are kept. These can be state or royal property, church treasure or in p ...
* Exit to well
* Access to stairwell
* Offering hall
* Hall of the Ennead
The Ennead or Great Ennead was a group of nine deities in Egyptian mythology worshipped at Heliopolis: the sun god Atum; his children Shu and Tefnut; their children Geb and Nut; and their children Osiris, Isis, Set, and Nephthys. The Ennead ...
* Great Seat and main sanctuary
* Shrine of the Nome of Dendera
* Shrine of Isis
Isis (; ''Ēse''; ; Meroitic: ''Wos'' 'a''or ''Wusa''; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎, romanized: ʾs) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingd ...
* Shrine of Sokar
* Shrine of Harsomtus
Horus or Heru, Hor, Har in Ancient Egyptian, is one of the most significant ancient Egyptian deities who served many functions, most notably as god of kingship and the sky. He was worshipped from at least the late prehistoric Egypt until the P ...
* Shrine of Hathor's Sistrum
A sistrum (plural: sistra or Latin sistra; from the Greek ''seistron'' of the same meaning; literally "that which is being shaken", from ''seiein'', "to shake") is a musical instrument of the percussion family, chiefly associated with ancient ...
* Shrine of gods of Lower Egypt
Lower Egypt ( ar, مصر السفلى '; ) is the northernmost region of Egypt, which consists of the fertile Nile Delta between Upper Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea, from El Aiyat, south of modern-day Cairo, and Dahshur. Historically, ...
* Shrine of Hathor
Hathor ( egy, ḥwt-ḥr, lit=House of Horus, grc, Ἁθώρ , cop, ϩⲁⲑⲱⲣ, Meroitic: ) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion who played a wide variety of roles. As a sky deity, she was the mother or consort of the sky ...
* Shrine of the throne of Rê
* Shrine of Rê
Ra (; egy, wikt:rꜥ, rꜥ; also transliterated ; cuneiform: ''ri-a'' or ''ri-ia''; Phoenician language, Phoenician: 𐤓𐤏,Corpus Inscriptionum Semiticarum, CIS I 3778 romanized: rʿ) or Re (; cop, ⲣⲏ, translit=Rē) was the ancient ...
* Shrine of Menat
In ancient Egyptian religion, a menat ( egy, mnj.t, ar, منات) was a type of artefact closely associated with the goddess Hathor.
Operation
The menat was held in the hand by its counterpoise and used as a rattle by Hathor's priestesses. It ...
collar
* Shrine of Ihy
Ihy is a god in ancient Egyptian mythology who represents the ecstasy of playing the sistrum. His name means "''sistrum player''". This is in allusion to his relationship with the goddess Hathor who was often said to be his mother. Ihy's symbols a ...
* The Pure Place
* Court of the First Feast
* Passage
* Staircase to roof
Depictions of Cleopatra VI
Cleopatra VI Tryphaena ( el, Κλεοπάτρα Τρύφαινα) or Cleopatra Tryphaena II (died c. 57 BC) was a queen of Ptolemaic Egypt who ruled alongside Berenice IV, who was either her sister or daughter. Although called ''Cleopatra VI Tryp ...
which appear on temple walls are good examples of Ptolemaic Egyptian art. On the rear of the temple exterior is a carving of Cleopatra VII Philopator (the popularly well known Cleopatra
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a ...
) and her son, Ptolemy XV Philopator Philometor Caesar (Caesarion
Ptolemy XV Caesar). (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος ; 23 June 47 BC – August 30 BC), nicknamed Caesarion (, "Little Caesar"), was the last pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt, reigning with his mother Cleopatra from 2 September 44 BC until her de ...
), who was fathered by Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
.
Dendera zodiac
 The sculptured Dendera zodiac (or Denderah zodiac) is a widely known relief found in a late Greco-Roman temple, containing images of
The sculptured Dendera zodiac (or Denderah zodiac) is a widely known relief found in a late Greco-Roman temple, containing images of Taurus
Taurus is Latin for 'bull' and may refer to:
* Taurus (astrology), the astrological sign
* Taurus (constellation), one of the constellations of the zodiac
* Taurus (mythology), one of two Greek mythological characters named Taurus
* '' Bos tauru ...
(the bull
A bull is an intact (i.e., not castrated) adult male of the species ''Bos taurus'' (cattle). More muscular and aggressive than the females of the same species (i.e., cows), bulls have long been an important symbol in many religions,
includin ...
) and the Libra
Libra generally refers to:
* Libra (constellation), a constellation
* Libra (astrology), an astrological sign based on the star constellation
Libra may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Libra'' (novel), a 1988 novel by Don DeLillo
Musi ...
(the balance
Balance or balancing may refer to:
Common meanings
* Balance (ability) in biomechanics
* Balance (accounting)
* Balance or weighing scale
* Balance as in equality or equilibrium
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Balance'' (1983 film), a Bulgaria ...
). A sketch was made of it during the Napoleonic campaign in Egypt
The French campaign in Egypt and Syria (1798–1801) was Napoleon Bonaparte's campaign in the Ottoman territories of Egypt and Syria, proclaimed to defend French trade interests, to establish scientific enterprise in the region. It was the pr ...
. In 1820 it was removed from the temple ceiling by French colonizers and replaced with a fake. There is controversy as to whether they were granted permission by Egypt's ruler, Muhammad Ali Pasha, to do so, or whether they stole it. The real one is now in the Louvre. Champollion's guess that it was Ptolemaic proved to be correct, and Egyptologists now date it to the first century BC.
Crypts
The subterranean Hathor temple tombs total twelve chambers. Some reliefs are dated to as late as the reign ofPtolemy XII Auletes
Ptolemy XII Neos Dionysus Philopator Philadelphus ( grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος Νέος Διόνυσος Φιλοπάτωρ Φιλάδελφος, Ptolemaios Neos Dionysos Philopatōr Philadelphos; – 51 BC) was a pharaoh of the Ptolemaic ...
. The crypt
A crypt (from Latin ''crypta'' "vault") is a stone chamber beneath the floor of a church or other building. It typically contains coffins, sarcophagi, or religious relics.
Originally, crypts were typically found below the main apse of a chur ...
s reportedly were used for storing vessels and divine iconography. An opening in the "Flame Room" floor leads to a narrow chamber with representations on the walls of the objects which were kept in them. In the second chamber, a relief depicts Pepi I offering a statuette of the god Ihy
Ihy is a god in ancient Egyptian mythology who represents the ecstasy of playing the sistrum. His name means "''sistrum player''". This is in allusion to his relationship with the goddess Hathor who was often said to be his mother. Ihy's symbols a ...
to four images of Hathor. In the crypt, reached from the "throne room", Ptolemy XII has jewelry and offerings for the gods.
The Dendera light
 The Hathor Temple has stone reliefs that depict
The Hathor Temple has stone reliefs that depict Harsomtus
Horus or Heru, Hor, Har in Ancient Egyptian, is one of the most significant ancient Egyptian deities who served many functions, most notably as god of kingship and the sky. He was worshipped from at least the late prehistoric Egypt until the P ...
, in the form of a snake, emerging from a lotus flower
''Nelumbo nucifera'', also known as sacred lotus, Laxmi lotus, Indian lotus, or simply lotus, is one of two extant species of aquatic plant in the family Nelumbonaceae. It is sometimes colloquially called a water lily, though this more often ref ...
. In six reliefs he is shown within an oval container called ''hn'', which might represent the womb of Nut
Nut often refers to:
* Nut (fruit), fruit composed of a hard shell and a seed, or a collective noun for dry and edible fruits or seeds
* Nut (hardware), fastener used with a bolt
Nut or Nuts may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Co ...
. These superficially resemble a lamp or light.
Restoration work
The Supreme Council of Antiquities began the project of restoration and maintenance of the temple in 2005, stopped in 2011, and then resumed in 2017, after the completion of the necessary scientific and archaeological studies along with careful experimental studies using the best methods and modern techniques. As of March 2021, the second phase of the restoration has been completed, which includes cleaning of the Great Pillars Hall and restoring the original colors and clarity of painted scenes on walls and ceilings. More activity continues at the temple, including a cooperative effort started in 2019 with the French Archaeological delegation, to turn the temple courtyard into an open museum.https://egymonuments.gov.eg/en/news/the-ministry-of-tourism-and-antiquities-completes-the-second-phase-of-the-restoration-and-developing-project-at-the-dendera-temple-in-qenaRoman mammisi
 The Roman
The Roman mammisi A mammisi (mamisi) is an ancient Egyptian small chapel attached to a larger Egyptian temple, temple (usually in front of the Pylon (architecture), pylonsRachet, Guy (1994). ''Dizionario della civiltà egizia''. Rome: Gremese Editore. . p. 186.), bui ...
is a subsidiary building dating to the reigns of Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
and Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good ...
. Numerous reliefs of Trajan making offerings to Egyptian deities can be seen.
Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
at Dendera, Egypt
File:Trajan_offers_to_Hathor_%26_Ra-Harakhte%2C_Dendera.jpg, Roman Emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
offers to Hathor and Ra-Harakhte, Dendera.
File:Emperor Trajan, Dendera.jpg, Emperor Trajan as a Pharaoh making an offering to the Gods, in Dendera.
Tourism
The Dendera complex has long been one of the most tourist-accessible ancient Egyptian places of worship. It used to be possible to visit virtually every part of the complex, from the crypts to the roof. However, the highest part of the roof of Hathor temple has been closed since 2003. The second stage of the roof was closed in November 2004, after a tourist got too close to the edge and fell to her death on the bedrock below.Gallery
bas-relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the ...
and sphinx
A sphinx ( , grc, σφίγξ , Boeotian: , plural sphinxes or sphinges) is a mythical creature with the head of a human, the body of a lion, and the wings of a falcon.
In Greek tradition, the sphinx has the head of a woman, the haunches of ...
File:Denderah3 Cleopatra Cesarion.jpg, Reliefs of Cleopatra VII and her son by Julius Caesar, Caesarion at the Dendera Temple
File:Temple of Hathor, Columns 2, Dendera, Egypt.jpg, Columns of the Hypostyle Hall
File:Temple of Hathor, Ceiling, Dendera, Egypt.jpg, Ceiling of the temple before restoration (photographed 2007)
File:Ceiling of Temple of Hathor.JPG, Restored ceiling of the Temple of Hathor (photographed 2011)
File:Temple of Hathor, Dark interior, Dendera, Egypt.jpg, Crypt
File:Dendara97HathorKiosk.jpg, Kiosk of Hathor on the temple roof
File:Roof of the Hathor Temple at Dendera (IV).jpg, Close-up of a column on the Kiosk
File:Denderah intérieur mammisi c.jpg, Digitally manipulated photograph of an interior wall in the Mammisi A mammisi (mamisi) is an ancient Egyptian small chapel attached to a larger Egyptian temple, temple (usually in front of the Pylon (architecture), pylonsRachet, Guy (1994). ''Dizionario della civiltà egizia''. Rome: Gremese Editore. . p. 186.), bui ...
, highlighting the bas-relief
See also
* Esna temple (inEsna
Esna ( ar, إسنا , egy, jwny.t or ; cop, or ''Snē'' from ''tꜣ-snt''; grc-koi, Λατόπολις ''Latópolis'' or (''Pólis Látōn'') or (''Lattōn''); Latin: ''Lato''), is a city of Egypt. It is located on the west bank of ...
)
* List of Ancient Egyptian sites
This is a list of ancient Egyptian sites, throughout all of Egypt and Nubia. Sites are listed by their classical name whenever possible, if not by their modern name, and lastly with their ancient name if no other is available.
Nomes
A nome ...
* Tomb of Meni
* Tomb of Nyibunesu
References
Further reading
* Jed Z. Buchwald, "Egyptian Stars under Paris Skies
'". pr.caltech.edu. * R. A. Parker, "
Ancient Egyptian Astronomy
'". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, Vol. 276, No. 1257, The Place of Astronomy in the Ancient World (May 2, 1974), pp. 51–65 * Marshall Clagett, "
Ancient Egyptian Science: A Source Book
'". Diane, 1989. * William Henry and Davenport Adams "
Egypt Past and Present: Described and Illustrated
'". T. Nelson and Sons, 1885. 380 pages. Page 218 - 226
Catchpenny Mysteries. * Frank Dörnenburg
Electric lights in Egypt?
2004. (ed. An analysis of how the Egyptians didn't have electricity). * Mariette, Auguste, ''Dendérah'', Bookshop A. Franck, Paris, 1875. * Fischer, H.G., ''Dendera in the third millennium B.C. down to the theban domination of upper Egypt'', J.J. Augustin publisher, New York, 1968.
External links
Dendera Temple complex
satellite-sightseer.com.
(French)
High-resolution Images of Dendera Temple Ceiling
{{Authority control Archaeological sites in Egypt Egyptian temples Former religious buildings and structures in Egypt 1st-century BC religious buildings and structures Hellenistic architecture 23rd-century BC establishments Buildings and structures completed in the 23rd century BC