|
Seker
Seker (; also spelled Sokar, and in Greek, Sokaris or Socharis) is a falcon god of the Memphite necropolis in the Ancient Egyptian religion. Name Although the meaning of his name remains uncertain, the Egyptians in the Pyramid Texts linked his name to the anguished cry of Osiris to Isis 'Sy-k-ri' ('hurry to me'),The Routledge Dictionary of Egyptian Gods and Goddesses, George Hart or possibly ''skr,'' meaning "cleaning the mouth". In the underworld, Seker is strongly linked with two other gods, Ptah the Creator god and chief god of Memphis, and Osiris the god of the dead. In later periods, this connection was expressed as the triple god Ptah-Seker-Osiris. The Faiyumic Coptic form ⲥⲓⲭⲟⲗ is possibly preserved in a personal name ⲥⲉⲛⲥⲓⲭⲟⲗ "daughter of Sokar". Appearance Seker was usually depicted as a mummified hawk and sometimes as a mound from which the head of a hawk appears. Here he is called 'he who is on his sand'. Sometimes he is shown on his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wsjr'', cop, ⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲉ , ; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎𐤓, romanized: ʾsr) is the god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He was classically depicted as a green-skinned deity with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive atef crown, and holding a symbolic crook and flail. He was one of the first to be associated with the mummy wrap. When his brother, Set cut him up into pieces after killing him, Osiris' wife Isis found all the pieces and wrapped his body up, enabling him to return to life. Osiris was widely worshipped until the decline of ancient Egyptian religion during the rise of Christianity in the Roman Empire. Osiris was at times considered the eldest son of the earth god Geb and the sky goddess Nut, as well as being brother and husband of Isis, and brother of Set, Nephthys, and Horus the Elder, with Horus the Younger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amduat
The Amduat ( egy, jmj dwꜣt, literally "That Which Is In the Afterworld", also translated as "Text of the Hidden Chamber Which is in the Underworld" and "Book of What is in the Underworld"; ar, كتاب الآخرة, Kitab al-Akhira) is an important ancient Egyptian funerary text of the New Kingdom of Egypt. Like many funerary texts, it was found written on the inside of the pharaoh's tomb for reference. Unlike other funerary texts, however, it was reserved only for pharaohs (until the Twenty-first Dynasty almost exclusively) or very favored nobility.Hornung (1999), p.27 It tells the story of Ra, the Egyptian sun god who travels through the underworld, from the time when the sun sets in the west and rises again in the east. It is said that the dead Pharaoh is taking this same journey, ultimately to become one with Ra and live forever. The underworld is divided into twelve hours of the night, each representing different allies and enemies for the Pharaoh/sun god to encounter. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underworld. The concept of an underworld is found in almost every civilization and "may be as old as humanity itself". Common features of underworld myths are accounts of living people making journeys to the underworld, often for some heroic purpose. Other myths reinforce traditions that entrance of souls to the underworld requires a proper observation of ceremony, such as the ancient Greek story of the recently dead Patroclus haunting Achilles until his body could be properly buried for this purpose. Persons having social status were dressed and equipped in order to better navigate the underworld. A number of mythologies incorporate the concept of the soul of the deceased making its own journey to the underworld, with the dead needing to be taken a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptah
Ptah ( egy, ptḥ, reconstructed ; grc, Φθά; cop, ⲡⲧⲁϩ; Phoenician: 𐤐𐤕𐤇, romanized: ptḥ) is an ancient Egyptian deity, a creator god and patron deity of craftsmen and architects. In the triad of Memphis, he is the husband of Sekhmet and the father of Nefertem. He was also regarded as the father of the sage Imhotep. Origin and symbolism Ptah is an Egyptian creator god who conceived the world and brought it into being through the creative power of speech. A hymn to Ptah dating to the Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt says Ptah "crafted the world in the design of his heart," and the Shabaka Stone, from the Twenty-Fifth Dynasty, says Ptah "gave life to all the gods and their '' ka''s as well, through this heart and this tongue." He bears many epithets that describe his role in ancient Egyptian religion and its importance in society at the time: * ''Ptah the begetter of the first beginning'' * ''Ptah lord of truth'' * ''Ptah lord of eternity'' * ''Ptah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underworld. The concept of an underworld is found in almost every civilization and "may be as old as humanity itself". Common features of underworld myths are accounts of living people making journeys to the underworld, often for some heroic purpose. Other myths reinforce traditions that entrance of souls to the underworld requires a proper observation of ceremony, such as the ancient Greek story of the recently dead Patroclus haunting Achilles until his body could be properly buried for this purpose. Persons having social status were dressed and equipped in order to better navigate the underworld. A number of mythologies incorporate the concept of the soul of the deceased making its own journey to the underworld, with the dead needing to be taken a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
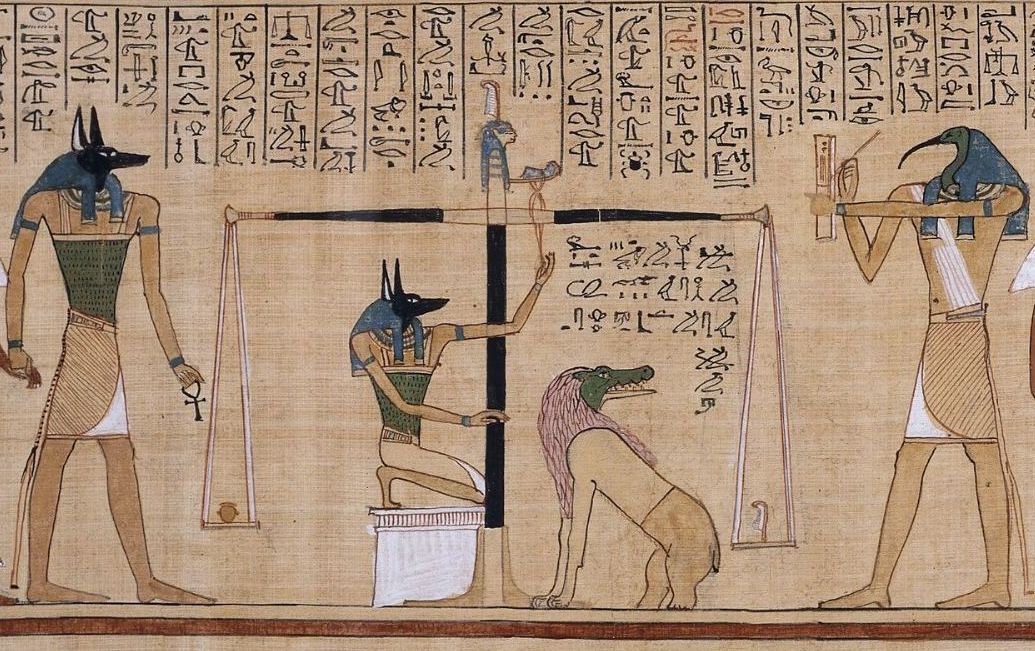
Book Of The Dead
The ''Book of the Dead'' ( egy, 𓂋𓏤𓈒𓈒𓈒𓏌𓏤𓉐𓂋𓏏𓂻𓅓𓉔𓂋𓅱𓇳𓏤, ''rw n(y)w prt m hrw(w)'') is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom (around 1550 BCE) to around 50 BCE. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated ''rw nw prt m hrw'', is translated as ''Book of Coming Forth by Day'' or ''Book of Emerging Forth into the Light''. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the ''Duat'', or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name ''Todtenbuch'' (modern spelling ''Totenbuch''), translated to English as Book of the Dead. The ''Book of the Dead'', which was placed in the coffin or burial chamber of the deceased, was part of a trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. The metal is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanis, Egypt
Tanis ( grc, Τάνις or Τανέως ) or San al-Hagar ( ar, صان الحجر, Ṣān al-Ḥaǧar; egy, ḏꜥn.t ; ; cop, ϫⲁⲛⲓ or or ) is the Greek name for ancient Egyptian ''ḏꜥn.t'', an important archaeological site in the north-eastern Nile Delta of Egypt, and the location of a city of the same name. It is located on the Tanitic branch of the Nile, which has long since silted up. The first study of Tanis dates to 1798 during Napoléon Bonaparte's expedition to Egypt. Engineer Pierre Jacotin drew up a map of the site in the ''Description de l'Égypte''. It was first excavated in 1825 by Jean-Jacques Rifaud, who discovered the two pink granite sphinxes now in the Musée du Louvre, and then by François Auguste Ferdinand Mariette between 1860 and 1864, and subsequently by William Matthew Flinders Petrie from 1883 to 1886. The work was taken over by Pierre Montet from 1929 to 1956, who discovered the royal necropolis dating to the Third Intermediate Period in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheshonq II
Heqakheperre Shoshenq II or Shoshenq IIa was a pharaoh of the Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt. He was the only ruler of this dynasty whose tomb was not plundered by tomb robbers. His final resting place was discovered within an antechamber of Psusennes I's tomb at Tanis by Pierre Montet in 1939. Montet removed the coffin lid of Shoshenq II on March 20, 1939, in the presence of king Farouk of Egypt himself. It proved to contain many jewel-encrusted bracelets and pectorals, along with a beautiful hawkheaded silver coffin and a gold funerary mask. The facemask had been placed upon the head of the king. Montet later discovered the intact tombs of two Twenty-first Dynasty kings (Psusennes I and Amenemope) a year later in February and April 1940 respectively. Shoshenq II's prenomen, Heqakheperre Setepenre, means "The manifestation of Ra rules, the chosen one of Ra." Shoshenq II's enigmatic identity There is a small possibility that Shoshenq II was the son of Shoshenq I. Two bracelets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memphis, Egypt
, alternate_name = , image = , alt = , caption = Ruins of the pillared hall of Ramesses IIat Mit Rahina , map_type = Egypt#Africa , map_alt = , map_size = , relief = , coordinates = , location = Mit Rahina, Giza Governorate, Egypt , region = Lower Egypt , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = Unknown, was already in existence during Iry-Hor's reignP. Tallet, D. Laisnay: ''Iry-Hor et Narmer au Sud-Sinaï (Ouadi 'Ameyra), un complément à la chronologie des expéditios minière égyptiene'', in: BIFAO 112 (2012), 381–395available online/ref> , material = , built = Earlier than 31st century BC , abandoned = 7th century AD , epochs = Early Dynastic Period to Early Middle Ages , cultures = , dependency_of = , occupants = , event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opet Festival
The Opet Festival (the Beautiful Festival of Opet/Opeth/''heb nefer en Ipet'') was an annual Ancient Egyptian Festival celebrated in Thebes (Luxor), especially in the New Kingdom and later periods, during the second month of the season of Akhet, the flooding of the Nile. The festival was celebrated to promote the Fertility of Amun-Re and the Pharaoh, who was also believed to be the spiritual offspring of Amun-Re; the Son/Daughter of Amun-Re. John Coleman Darnell argues that “Opet began on II Akhet 15 under Thutmose III and lasted 11 days (Sethe 1907: 824, line 10); by the beginning of the reign of Ramesses III, the festival stretched over 24 days.” The Festival included a ritual procession of the Barque (a ceremonial boat that was used to transport statues of gods and deities) of the cult statue of “Amun-Re, supreme god, his wife, Mut, and his son, Khons.” This procession carried the statue for 2 km from Karnak Temple to “Luxor Temple, destination of the Opet Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Ten Commandments (1956 Film)
''The Ten Commandments'' is a 1956 American epic religious drama film produced, directed, and narrated by Cecil B. DeMille, shot in VistaVision (color by Technicolor), and released by Paramount Pictures. Based on the 1949 novel ''Prince of Egypt'' by Dorothy Clarke Wilson, the 1859 novel ''Pillar of Fire'' by J. H. Ingraham, the 1937 novel ''On Eagle's Wings'' by A. E. Southon, and the Book of Exodus, ''The Ten Commandments'' dramatizes the biblical story of the life of Moses, an adopted Egyptian prince who becomes the deliverer of his real brethren, the enslaved Hebrews, and thereafter leads the Exodus to Mount Sinai, where he receives, from God, the Ten Commandments. The film stars Charlton Heston in the lead role, Yul Brynner as Rameses, Anne Baxter as Nefretiri, Edward G. Robinson as Dathan, Yvonne De Carlo as Sephora, Debra Paget as Lilia, and John Derek as Joshua; and features Sir Cedric Hardwicke as Seti I, Nina Foch as Bithiah, Martha Scott as Yochabel, Judith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |