Harold Eugene Edgerton on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Harold Eugene "Doc" Edgerton (April 6, 1903 – January 4, 1990), also known as Papa Flash, was an American scientist and researcher, a professor of
 In 1925 Edgerton received a bachelor's degree in
In 1925 Edgerton received a bachelor's degree in

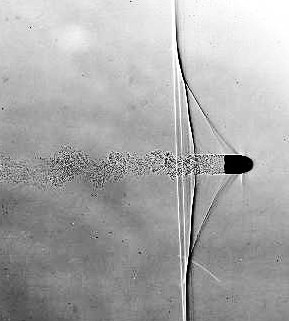 In 1937 Edgerton began a lifelong association with photographer Gjon Mili, who used stroboscopic equipment, in particular, multiple studio electronic flash units, to produce photographs, many of which appeared in ''Life'' magazine. When taking multiflash photographs this strobe light equipment could flash up to 120 times a second. Edgerton was a pioneer in using short duration electronic flash in photographing fast events photography, subsequently using the technique to capture images of balloons at different stages of their bursting, a bullet during its impact with an apple, or using multiflash to track the motion of a devil stick, for example.
He was awarded a bronze medal by the
In 1937 Edgerton began a lifelong association with photographer Gjon Mili, who used stroboscopic equipment, in particular, multiple studio electronic flash units, to produce photographs, many of which appeared in ''Life'' magazine. When taking multiflash photographs this strobe light equipment could flash up to 120 times a second. Edgerton was a pioneer in using short duration electronic flash in photographing fast events photography, subsequently using the technique to capture images of balloons at different stages of their bursting, a bullet during its impact with an apple, or using multiflash to track the motion of a devil stick, for example.
He was awarded a bronze medal by the
The Edgerton Digital Collections
website by the MIT Museum with thousands of photographs and scanned notebooks.
The Edgerton Center at MIT
– Early photographs from Edgerton's laboratory, including water from the tap, MIT Collections
Biographical timeline
*
The Edgerton Explorit Center in Aurora, NEThe SPIE Harold E. Edgerton Award
* * ttp://www.nasonline.org/publications/biographical-memoirs/memoir-pdfs/edgerton-harold.pdf National Academy of Sciences Biographical Memoir {{DEFAULTSORT:Edgerton, Doc 1903 births 1990 deaths Pioneers of photography People from Aurora, Nebraska People from Fremont, Nebraska University of Nebraska–Lincoln alumni MIT School of Engineering faculty MIT School of Engineering alumni National Medal of Science laureates National Medal of Technology recipients Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences Burials at Mount Auburn Cemetery Howard N. Potts Medal recipients 20th-century American engineers 20th-century American photographers Engineers from Nebraska Photographers from Nebraska Members of the American Philosophical Society Acacia members
electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a Private university, private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of moder ...
. He is largely credited with transforming the stroboscope
A stroboscope, also known as a strobe, is an instrument used to make a cyclically moving object appear to be slow-moving, or stationary. It consists of either a rotating disk with slots or holes or a lamp such as a flashtube which produces br ...
from an obscure laboratory instrument into a common device. He also was deeply involved with the development of sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances ( ranging), communicate with or detect objects o ...
and deep-sea photography, and his equipment was used in collaboration with Jacques Cousteau
Jacques-Yves Cousteau, (, also , ; 11 June 191025 June 1997) was a French naval officer, oceanographer, filmmaker and author. He co-invented the first successful open-circuit self-contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA), called the ...
in searches for shipwrecks and even the Loch Ness Monster
The Loch Ness Monster (), known affectionately as Nessie, is a mythical creature in Scottish folklore that is said to inhabit Loch Ness in the Scottish Highlands. It is often described as large, long-necked, and with one or more humps protrud ...
.
Biography
Early years
Edgerton was born in Fremont, Nebraska, on April 6, 1903, the son of Mary Nettie Coe and Frank Eugene Edgerton, a descendant of Samuel Edgerton, the son of Richard Edgerton, one of the founders ofNorwich, Connecticut
Norwich ( ) is a city in New London County, Connecticut, United States. The Yantic River, Yantic, Shetucket River, Shetucket, and Quinebaug Rivers flow into the city and form its harbor, from which the Thames River (Connecticut), Thames River f ...
, and Alice Ripley, a great-granddaughter of Governor William Bradford (1590–1657) of the Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes spelled Plimouth) was the first permanent English colony in New England from 1620 and the third permanent English colony in America, after Newfoundland and the Jamestown Colony. It was settled by the passengers on t ...
and a passenger on the Mayflower
''Mayflower'' was an English sailing ship that transported a group of English families, known today as the Pilgrims, from England to the New World in 1620. After 10 weeks at sea, ''Mayflower'', with 102 passengers and a crew of about 30, reac ...
. His father was a lawyer, journalist, author and orator and served as the assistant attorney general of Nebraska from 1911 to 1915. Edgerton grew up in Aurora, Nebraska. He also spent some of his childhood years in Washington, DC, and Lincoln, Nebraska
Lincoln is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of Nebraska. The city covers and had a population of 291,082 as of the 2020 census. It is the state's List of cities in Nebraska, second-most populous city a ...
.
Education
 In 1925 Edgerton received a bachelor's degree in
In 1925 Edgerton received a bachelor's degree in electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Uni ...
where he became a member of Acacia fraternity
Acacia Fraternity is a social fraternity founded in 1904 at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, Michigan. The fraternity has 24 active chapters and 3 associate chapters throughout Canada and the United States. The fraternity was ...
. He earned an SM in electrical engineering from MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of modern technology and sc ...
in 1927. Edgerton used stroboscopes to study synchronous motor
A synchronous electric motor is an AC electric motor in which, at steady state,
the rotation of the shaft is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current; the rotation period is exactly equal to an integer number of AC cycles. Sync ...
s for his ScD thesis in electrical engineering at MIT, awarded in 1931. He credited Charles Stark Draper with inspiring him to photograph everyday objects using electronic flash; the first was a stream of water from a faucet.
In 1936 Edgerton visited hummingbird expert May Rogers Webster. He was able to illustrate with her help that it was possible to take photographs of the birds beating their wings 60 times a second using an exposure of one hundred thousandth of a second. A picture of her with the birds flying around her appeared in National Geographic
''National Geographic'' (formerly ''The National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as ''Nat Geo'') is an American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. The magazine was founded in 1888 as a scholarly journal, nine ...
.
Career

 In 1937 Edgerton began a lifelong association with photographer Gjon Mili, who used stroboscopic equipment, in particular, multiple studio electronic flash units, to produce photographs, many of which appeared in ''Life'' magazine. When taking multiflash photographs this strobe light equipment could flash up to 120 times a second. Edgerton was a pioneer in using short duration electronic flash in photographing fast events photography, subsequently using the technique to capture images of balloons at different stages of their bursting, a bullet during its impact with an apple, or using multiflash to track the motion of a devil stick, for example.
He was awarded a bronze medal by the
In 1937 Edgerton began a lifelong association with photographer Gjon Mili, who used stroboscopic equipment, in particular, multiple studio electronic flash units, to produce photographs, many of which appeared in ''Life'' magazine. When taking multiflash photographs this strobe light equipment could flash up to 120 times a second. Edgerton was a pioneer in using short duration electronic flash in photographing fast events photography, subsequently using the technique to capture images of balloons at different stages of their bursting, a bullet during its impact with an apple, or using multiflash to track the motion of a devil stick, for example.
He was awarded a bronze medal by the Royal Photographic Society
The Royal Photographic Society of Great Britain, commonly known as the Royal Photographic Society (RPS), is the world's oldest photographic society having been in continuous existence since 1853. It was founded in London, England, in 1853 as th ...
in 1934, the Howard N. Potts Medal from the Franklin Institute
The Franklin Institute is a science museum and a center of science education and research in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It is named after the American scientist and wikt:statesman, statesman Benjamin Franklin. It houses the Benjamin Franklin ...
in 1941, the Golden Plate Award of the American Academy of Achievement
The American Academy of Achievement, colloquially known as the Academy of Achievement, is a nonprofit educational organization that recognizes some of the highest-achieving people in diverse fields and gives them the opportunity to meet one ano ...
in 1966, the David Richardson Medal by the Optical Society of America
Optica, founded as the Optical Society of America (later the Optical Society), is a professional society of individuals and companies with an interest in optics and photonics. It publishes journals, organizes conferences and exhibitions, and ca ...
in 1968, the Albert A. Michelson Medal from the same Franklin Institute in 1969, and the National Medal of Science
The National Medal of Science is an honor bestowed by the President of the United States to individuals in science and engineering who have made important contributions to the advancement of knowledge in the fields of behavioral science, behavior ...
in 1973.
Edgerton partnered with Kenneth J. Germeshausen to do consulting for industrial clients. Later Herbert Grier joined them. The company name "Edgerton, Germeshausen, and Grier" was changed to EG&G in 1947. EG&G became a prime contractor for the Atomic Energy Commission and had a major role in photographing and recording nuclear tests for the US through the fifties and sixties. For this role Edgerton and Charles Wykoff and others at EG&G developed and manufactured the Rapatronic camera.
His work was instrumental in the development of side-scan sonar technology, used to scan the sea floor for wrecks. Edgerton worked with undersea explorer Jacques Cousteau
Jacques-Yves Cousteau, (, also , ; 11 June 191025 June 1997) was a French naval officer, oceanographer, filmmaker and author. He co-invented the first successful open-circuit self-contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA), called the ...
, by first providing him with custom-designed underwater photographic equipment featuring electronic flash, and then by developing sonar techniques used to discover the '' Britannic''. Edgerton participated in the discovery of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
battleship USS ''Monitor''. While working with Cousteau, he acquired the nickname "Papa Flash". In 1988 Doc Edgerton worked with Paul Kronfield in Greece on a sonar search for the lost city of Helike
Helike (; , pronounced , modern ) was an ancient Greek polis or city-state that was submerged by a tsunami in the winter of 373 BC.
It was located in the Regional units of Greece, regional unit of Achaea, northern Peloponnesos, two kilometres ( ...
, believed to be the basis for the legend of Atlantis
Atlantis () is a fictional island mentioned in Plato's works '' Timaeus'' and ''Critias'' as part of an allegory on the hubris of nations. In the story, Atlantis is described as a naval empire that ruled all Western parts of the known world ...
.
Edgerton co-founded EG&G, Inc., which manufactured advanced electronic equipment including side-scan sonars and sub-bottom profiling equipment. EG&G also invented and manufactured the Krytron
The krytron is a cold-cathode gas-filled tube intended for use as a very high-speed switch, somewhat similar to the thyratron. It consists of a sealed glass tube with four electrodes. A small triggering pulse on the control grid, grid electrode s ...
, the detonation trigger for the hydrogen bomb
A thermonuclear weapon, fusion weapon or hydrogen bomb (H-bomb) is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation nuclear bombs, a more compact size, a lo ...
, and an EG&G division supervised many of America's nuclear tests.
In addition to having the scientific and engineering acumen to perfect strobe light
A strobe light or stroboscopic lamp, commonly called a strobe, is a device used to produce regular flashes of light. It is one of a number of devices that can be used as a stroboscope. The word originated from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning ...
ing commercially, Edgerton is equally recognized for his visual aesthetic: many of the striking images he created in illuminating phenomena that occurred too fast for the naked eye now adorn art museums worldwide. In 1940, his high speed stroboscopic short film '' Quicker'n a Wink'' won an Oscar
Oscar, OSCAR, or The Oscar may refer to:
People and fictional and mythical characters
* Oscar (given name), including lists of people and fictional characters named Oscar, Óscar or Oskar
* Oscar (footballer, born 1954), Brazilian footballer ...
.
Edgerton was appointed a professor of electrical engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1934. At MIT Edgerton created a technology lab nicknamed Strobe Alley, considered by author Pagan Kennedy as a forerunner of the Hackerspace
A hackerspace (also referred to as a hacklab, hackspace, or makerspace) is a community-operated, often "not for profit" (501(c)(3) in the United States), workspace where people with common interests, such as computers, machining, technology, sci ...
. This lab and its encouragement of tinkering and invention influenced the careers of MIT students such as Martin Klein, who contributed to the development of side scan sonar.
In 1956, Edgerton was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (The Academy) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, and other ...
. He became a member of the United States National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, NGO, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the ...
in 1964 and a member of the American Philosophical Society
The American Philosophical Society (APS) is an American scholarly organization and learned society founded in 1743 in Philadelphia that promotes knowledge in the humanities and natural sciences through research, professional meetings, publicat ...
in 1972. He was especially loved by MIT students for his willingness to teach and his kindness: "The trick to education", he said, "is to teach people in such a way that they don't realize they're learning until it's too late". His last undergraduate class, taught during fall semester 1977, was a freshman seminar titled "Bird and Insect Photography". One of the graduate student dormitories at MIT carries his name.
In 1962, Edgerton appeared on '' I've Got a Secret'', where he demonstrated strobe flash photography by shooting a bullet into a playing card and photographing the result.
Edgerton's work was featured in an October 1987 ''National Geographic Magazine
''National Geographic'' (formerly ''The National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as ''Nat Geo'') is an American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. The magazine was founded in 1888 as a scholarly journal, nine ...
'' article entitled "Doc Edgerton: the man who made time stand still".
Family
After graduating from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Edgerton married Esther May Garrett in 1928. She was born in Aurora, Nebraska, on September 8, 1903, and died on March 9, 2002, inCharleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the List of municipalities in South Carolina, most populous city in the U.S. state of South Carolina. The city lies just south of the geographical midpoint of South Carolina's coastline on Charleston Harbor, an inlet of the Atla ...
. She received a bachelor's degree in mathematics, music and education from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln. A skilled pianist and singer, she attended the New England Conservatory of Music
The New England Conservatory of Music (NEC) is a Private college, private music school in Boston, Massachusetts. The conservatory is located on Huntington Avenue along Avenue of the Arts (Boston), the Avenue of the Arts near Boston Symphony Ha ...
and taught in public schools in Aurora, Nebraska and Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
. During their marriage they had three children: Mary Louise (April 21, 1931), William Eugene (8/9/1933), Robert Frank (5/10/1935). His sister, Mary Ellen Edgerton, was the wife of L. Welch Pogue (1899–2003) a pioneering aviation attorney and Chairman of the old Civil Aeronautics Board
The Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB) was an agency of the federal government of the United States, formed in 1940 from a split of the Civil Aeronautics Authority and abolished in 1985, that regulated aviation services (including scheduled passe ...
. The technology writer, journalist, and commentator David Pogue
David Welch Pogue (born March 9, 1963) is an American technology and science writer and TV presenter, and correspondent for ''CBS News Sunday Morning''.
He has hosted 18 ''Nova'' specials on PBS, including '' Nova ScienceNow'', the ''Making Stu ...
is his great nephew.
Death
Edgerton remained active throughout his later years, and was seen on the MIT campus many times after his official retirement. He died suddenly on January 4, 1990, at the MIT Faculty Club at the age of 86, and is buried inMount Auburn Cemetery
Mount Auburn Cemetery, located in Cambridge and Watertown, Massachusetts, is the first rural or garden cemetery in the United States. It is the burial site of many prominent Boston Brahmins, and is a National Historic Landmark.
Dedicated in ...
, Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 Unit ...
, Massachusetts.
Legacy
On July 3, 1990, in an effort to memorialize Edgerton's accomplishments, several community members in Aurora, Nebraska, decided to construct a "Hands-On" science center. It was designated as a "teaching museum", that would preserve Doc's work and artifacts, as well as feature the "Explorit Zone" where people of all ages could participate in hands-on exhibits and interact with live science demonstrations. After five years of private and community-wide fund-raising, as well as individual investments by Doc's surviving family members, the Edgerton Explorit Center was officially dedicated on September 9, 1995, in Aurora. At MIT, the Edgerton Center, founded in 1992, is a hands-on laboratory resource for undergraduate and graduate students, and also conducts educational outreach programs for high school students and teachers.Works
*''Flash! Seeing the Unseen by Ultra High-Speed Photography'' (1939, with James R. Killian Jr.). Boston: Hale, Cushman & Flint. *''Electronic Flash, Strobe'' (1970). New York: McGraw-Hill. *''Moments of Vision'' (1979, with Mr. Killian). Cambridge, Massachusetts: MIT. *''Sonar Images'' (1986, with Mr. Killian). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall. *''Stopping Time'', a collection of his photographs, (1987). New York: H.N. Abrams.Photographs
Some of Edgerton's noted photographs are : *''Hummingbirds
Hummingbirds are birds native to the Americas and comprise the Family (biology), biological family Trochilidae. With approximately 366 species and 113 genus, genera, they occur from Alaska to Tierra del Fuego, but most species are found in Cen ...
'' (1936)
*''Football Kick'' (1938)
* '' Gussie Moran's Tennis Swing'' (1949)
*''Diver'' (1955)
*'' Milk Drop Coronet'' (1957)
*''Cranberry Juice into Milk'' (1960)
*''Moscow Circus'' (1963)
*''Bullet Through Banana'' (1964)
*''.30 Bullet Piercing an Apple'' (1964)
*''Cutting the Card Quickly'' (1964)
*''Pigeon Release'' (1965)
*''Bullet Through Candle Flame'' (1973) (with Kim Vandiver)
Exhibitions
*''Flashes of Inspiration: The Work of Harold Edgerton,'' Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 2009. *''Seeing the Unseen: The High Speed Photography of Dr. Harold Edgerton,''Ikon Gallery
The Ikon Gallery () is an England, English art gallery, gallery of contemporary art, located in Brindleyplace, Birmingham. It is housed in the Listed building, Grade II listed, neo-Gothic former Oozells Street Board School, designed by John Henr ...
, Birmingham, January 1976; then toured to The Photographers' Gallery, London; Hatton Gallery, Newcastle University; Midland Group
The Midland Group is an international trading and investment holding company. Registered in Guernsey under the name Midland Resources Holding Ltd, the group owns a number of subsidiaries across the agriculture, manufacturing, real estate, shippin ...
Gallery, Nottingham; Modern Art Oxford
Modern Art Oxford is an art gallery established in 1965 in Oxford, England. From 1965 to 2002, it was called The Museum of Modern Art, Oxford.
The gallery presents exhibitions of modern and contemporary art. It has a national and international ...
; and Arnolfini, Bristol
Arnolfini is an international arts centre and gallery in Bristol, England. It has a programme of contemporary art exhibitions, artist's performance, music and dance events, poetry and book readings, talks, lectures and cinema. There is also ...
. Curated by John Myers and Geoffrey Holt.
*''Seeing the Unseen: Photographs and films by Harold E. Edgerton,'' The Pallasades Shopping Centre, Birmingham. A repeat organised by Ikon Gallery of the previous exhibition.
Collections
Edgerton's work is held in the following public collection: *Museum of Modern Art
The Museum of Modern Art (MoMA) is an art museum located in Midtown Manhattan, New York City, on 53rd Street (Manhattan), 53rd Street between Fifth Avenue, Fifth and Sixth Avenues. MoMA's collection spans the late 19th century to the present, a ...
, New York City: 29 prints (as of July 2018)
* International Photography Hall of Fame, St. Louis, MO
* Winnipeg Art Gallery , Qaumajuq - Winnipeg, MB: 60 prints
See also
*Air-gap flash
An air-gap flash is a photographic light source capable of producing sub-microsecond light flashes, allowing for (ultra) high-speed photography. This is achieved by a high-voltage (20 kV typically) electric discharge between two electrodes ...
References
Further reading
* Bruce, Roger R. (editor); Collins, Douglas, et al., ''Seeing the unseen : Dr. Harold E. Edgerton and the wonders of Strobe Alley'', Rochester, N.Y. : Pub. Trust of George Eastman House; Cambridge, Massachusetts : Distributed by MIT Press, 1994. *PBS ''Nova'' series: "Edgerton and His Incredible Seeing Machines". NOVA explores the fascinating world of Dr. Harold Edgerton, electronics wizard and inventor extraordinaire, whose invention of the electronic strobe, a "magic lamp," has enabled the human eye to see the unseen." Original broadcast date: 01/15/85External links
The Edgerton Digital Collections
website by the MIT Museum with thousands of photographs and scanned notebooks.
The Edgerton Center at MIT
– Early photographs from Edgerton's laboratory, including water from the tap, MIT Collections
Biographical timeline
*
The Edgerton Explorit Center in Aurora, NE
* * ttp://www.nasonline.org/publications/biographical-memoirs/memoir-pdfs/edgerton-harold.pdf National Academy of Sciences Biographical Memoir {{DEFAULTSORT:Edgerton, Doc 1903 births 1990 deaths Pioneers of photography People from Aurora, Nebraska People from Fremont, Nebraska University of Nebraska–Lincoln alumni MIT School of Engineering faculty MIT School of Engineering alumni National Medal of Science laureates National Medal of Technology recipients Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences Burials at Mount Auburn Cemetery Howard N. Potts Medal recipients 20th-century American engineers 20th-century American photographers Engineers from Nebraska Photographers from Nebraska Members of the American Philosophical Society Acacia members