Hans Hilfiker on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hans Hilfiker (15 September 1901 – 2 March 1993) was a
 Hilfiker joined the
Hilfiker joined the
 Hilfiker died in
Hilfiker died in
Hilfiker family website
(partial) * {{DEFAULTSORT:Hilfiker, Hans 1901 births 1993 deaths Swiss designers
Swiss
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
*Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
*Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss Internation ...
engineer and designer. In 1944, working for the Swiss Federal Railways
Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usuall ...
, he designed the Swiss railway clock
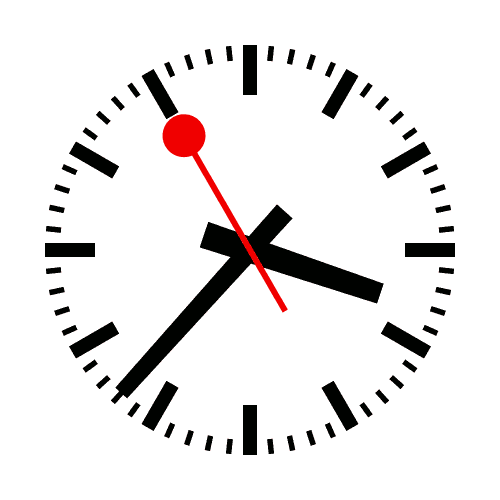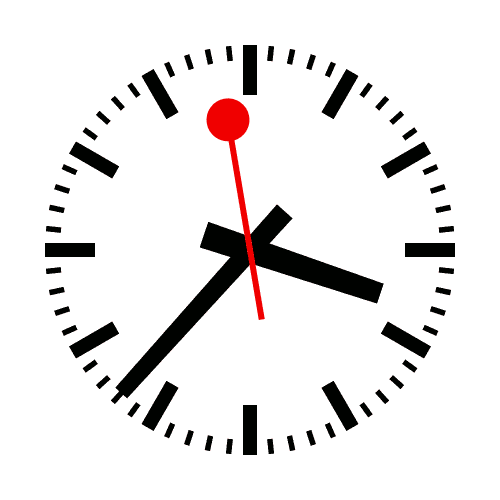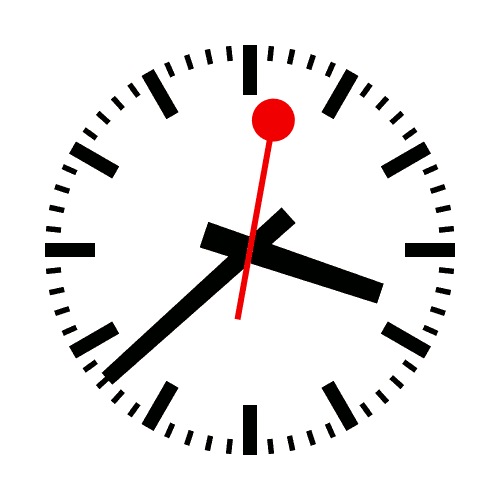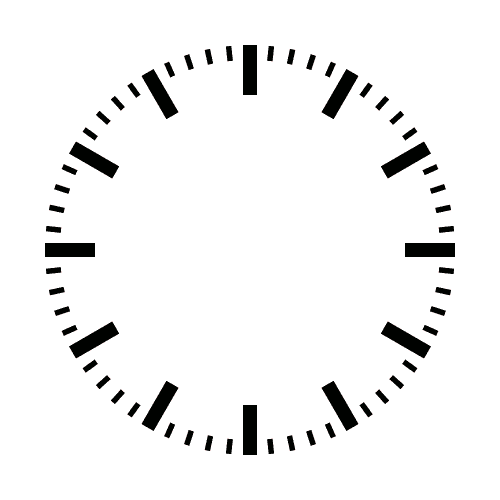
The Swiss railway clock was designed in 1944 by Hans Hilfiker, a Swiss engineer and Swiss Federal Railways (SBB) employee, together with , a clock manufacturer, for use by the SBB as a station clock. In 1953, Hilfiker added a red second hand ...
, which became an international icon. The SBB clock was not the only contribution by Hilfiker to modern living. He developed the concept of the fitted kitchen and was responsible for the standard Swiss dimensions for kitchen components (55/60/90 cm).
Early life
Hilfiker was born in Zurich, Switzerland on 15 September 1901. After attending primary and secondary school, Hilfiker completed an apprenticeship as a precision mechanic. He studied electrical and telecommunications engineering at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich and gained a diploma.Career
Siemens
Hilfiker began working for Albiswerk Zürich, aSiemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad.
The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', '' ...
production plant in 1925. He was transferred to Argentina in 1926 and became technical advisor to the telecommunications troops of the Argentine Army
The Argentine Army ( es, Ejército Argentino, EA) is the land force branch of the Armed Forces of the Argentine Republic and the senior military service of Argentina. Under the Argentine Constitution, the president of Argentina is the commander- ...
until 1928. His tasks included building workshops and mobile telephone exchanges, while also training telecommunications non-commissioned officers
A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is a military officer who has not pursued a commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority by promotion through the enlisted ranks. (Non-officers, which includes most or all enli ...
. As a senior engineer, he was involved in the construction of the Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
- Rosario
Rosario () is the largest city in the central provinces of Argentina, Argentine province of Santa Fe Province, Santa Fe. The city is located northwest of Buenos Aires, on the west bank of the Paraná River. Rosario is the third-most populous ci ...
telephone line through the Paraná River
The Paraná River ( es, Río Paraná, links=no , pt, Rio Paraná, gn, Ysyry Parana) is a river in south-central South America, running through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina for some ."Parana River". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Br ...
in 1929. He planned a submarine cable Submarine cable is any electrical cable that is laid on the seabed, although the term is often extended to encompass cables laid on the bottom of large freshwater bodies of water.
Examples include:
*Submarine communications cable
*Submarine power ...
running through the Río de la Plata
The Río de la Plata (, "river of silver"), also called the River Plate or La Plata River in English, is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River at Punta Gorda. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean and fo ...
to connect the Argentine and Uruguayan capitals in 1930. The same year, Hilfiker was transferred to Berlin and trained for the role of operating a Siemens subsidiary in Argentina. The plan however did not materialize and Hilfiker returned to Switzerland in 1931.
Swiss Federal Railways
 Hilfiker joined the
Hilfiker joined the Swiss Federal Railways
Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usuall ...
(SBB) as an engineer in construction department III in 1932. In his first year, he developed the first iteration of the later iconic Swiss railway clock
The Swiss railway clock was designed in 1944 by Hans Hilfiker, a Swiss engineer and Swiss Federal Railways (SBB) employee, together with , a clock manufacturer, for use by the SBB as a station clock. In 1953, Hilfiker added a red second hand ...
. The version which was first displayed at the Bahnhofplatz
The Bahnhofplatz (Train Station Plaza) is a plaza just outside the Old City of Bern, the medieval city center of Bern, Switzerland. It was built following the destruction of the '' Christoffelturm'' which had been part of the third city wal ...
(plaza) adjacent of Zürich Hauptbahnhof
Zürich Hauptbahnhof (often shortened to Zürich HB, or just HB; ''Zürich Main Station'' or ''Zürich Central Station'') is the largest railway station in Switzerland. Zürich is a major railway hub, with services to and from across Switzerland a ...
(Zürich Central Station) lacked the 'minute' and 'second' hands. Hilfiker would improve upon the design with the addition of a 'minute' hand in 1943. The following year, the SBB replaced all its clocks across the country in an effort to have a consistent clock face, which were all synchronized by a master clock linked to the telephone network. Hilfiker became deputy head of the construction department and head of the fixed electrical systems services. Among other things, he also designed a gantry crane to load heavy goods from the road onto the rail, the platform roof for Winterthur Grüze station, and a timetable projector for the Zurich station.
In 1955, Hilfiker launched the final iteration of the Swiss railway clock, which had been in development since 1952. A 'second' hand resembling a red signalling disk was added, which would pause slightly at the twelve o'clock mark, before jumping forward with the minute hand (''see illustration''). It became an international icon.
Therma AG
Between 1958 and 1968, Hilfike was a director of Therma AG located in Schwanden of thecanton of Glarus
The canton of Glarus (german: Kanton Glarus rm, Chantun Glaruna; french: Canton de Glaris; it, Canton Glarona) is a canton in east central Switzerland. The capital is Glarus.
The population speaks a variety of Alemannic German.
The majority of ...
. He developed a completely new kitchen range for Therma that consisted of modules that could be combined with one another. Until then, Therma had been producing standalone devices. With these system kitchens, he laid the foundation for the Swiss kitchen standard SINK (Swiss Industrial Commission for the Standardization of Kitchens), which deviated from the European one (width 55 instead of 60 cm). A prototype based on this standard was shown at the EXPO 1964 in Lausanne
, neighboring_municipalities= Bottens, Bretigny-sur-Morrens, Chavannes-près-Renens, Cheseaux-sur-Lausanne, Crissier, Cugy, Écublens, Épalinges, Évian-les-Bains (FR-74), Froideville, Jouxtens-Mézery, Le Mont-sur-Lausanne, Lugrin (FR-74), ...
. Hilfiker created an actual corporate design for Therma and restructured the manufacturing processes for the new fitted kitchens.
Death and legacy
 Hilfiker died in
Hilfiker died in Locarno
, neighboring_municipalities= Ascona, Avegno, Cadenazzo, Cugnasco, Gerra (Verzasca), Gambarogno, Gordola, Lavertezzo, Losone, Minusio, Muralto, Orselina, Tegna, Tenero-Contra
, twintowns =* Gagra, Georgia
* Karlovy Vary, Czech Republic
...
, Switzerland on 2 March 1993. The final iteration of his clock remains in use today and is a protected trademark of the SBB.
References
Works cited
* *External links
Hilfiker family website
(partial) * {{DEFAULTSORT:Hilfiker, Hans 1901 births 1993 deaths Swiss designers