Hannibal (The A-Team) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hannibal (; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋, ''Ḥannibaʿl''; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of
 Hannibal was a common Semitic Phoenician-Carthaginian personal name. It is recorded in Carthaginian sources as ( xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋). It is a combination of the common Phoenician masculine given name
Hannibal was a common Semitic Phoenician-Carthaginian personal name. It is recorded in Carthaginian sources as ( xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋). It is a combination of the common Phoenician masculine given name
 Hannibal was one of the sons of
Hannibal was one of the sons of
 This journey was originally planned by Hannibal's brother-in-law Hasdrubal the Fair, who became a Carthaginian general in the Iberian Peninsula in 229 BC. He maintained this post for eight years until 221 BC. Soon the Romans became aware of an alliance between Carthage and the
This journey was originally planned by Hannibal's brother-in-law Hasdrubal the Fair, who became a Carthaginian general in the Iberian Peninsula in 229 BC. He maintained this post for eight years until 221 BC. Soon the Romans became aware of an alliance between Carthage and the
 Hannibal's perilous march brought him into the Roman territory and frustrated the attempts of the enemy to fight out the main issue on foreign ground. His sudden appearance among the
Hannibal's perilous march brought him into the Roman territory and frustrated the attempts of the enemy to fight out the main issue on foreign ground. His sudden appearance among the
 The only alternative route to central Italy lay at the mouth of the
The only alternative route to central Italy lay at the mouth of the
 In the spring of 216 BC, Hannibal took the initiative and seized the large supply depot at Cannae in the Apulian plain. By capturing Cannae, Hannibal had placed himself between the Romans and their crucial sources of supply. Once the Roman Senate resumed their consular elections in 216 BC, they appointed Gaius Terentius Varro and Lucius Aemilius Paullus (consul 219 BC), Lucius Aemilius Paullus as Roman consul, consuls. In the meantime, the Romans hoped to gain success through sheer strength and weight of numbers, and they raised a new army of unprecedented size, estimated by some to be as large as 100,000 men, but more likely around 50,000–80,000.Cottrell, Leonard, ''Enemy of Rome'', Evans Bros, 1965,
The Romans and allied legions resolved to confront Hannibal and marched southward to Apulia. They eventually found him on the left bank of the Aufidus River, and encamped away. On this occasion, the two armies were combined into one, the consuls having to alternate their command on a daily basis. According to Livy, Varro was a man of reckless and hubristic nature and it was his turn to command on the day of battle. (This account is possibly biased against Varro as its main source, Polybius, was a client of Paullus's aristocratic family whereas Varro was less distinguished. Some historians have suggested the sheer size of the army may have required both generals to command a wing each. This theory is supported by the fact that, after Varro survived the battle he was pardoned by the Senate, which would be peculiar if he were the sole commander at fault.)
Hannibal capitalized on the eagerness of the Romans and drew them into a trap by using an Pincer movement, envelopment tactic. This eliminated the Roman numerical advantage by shrinking the combat area. Hannibal drew up his least reliable infantry in the centre in a semicircle curving towards the Romans. Placing them forward of the wings allowed them room to fall back, luring the Romans after them, while the cavalry on the flanks dealt with their Roman counterparts. Hannibal's wings were composed of the Gallic and Numidian cavalry. The Roman legions forced their way through Hannibal's weak centre, but the Libyan mercenaries on the wings, swung around by the movement, menaced their flanks.
The onslaught of Hannibal's cavalry was irresistible. Hannibal's chief cavalry commander, Maharbal, led the mobile Numidian cavalry on the right; they shattered the Roman cavalry opposing them. Hannibal's Iberian and Gallic heavy cavalry on the left, led by Hanno, defeated the Roman heavy cavalry, and then both the Carthaginian heavy cavalry and the Numidians attacked the legions from behind. As a result, the Roman army was hemmed in with no means of escape.
Due to these brilliant tactics, Hannibal managed to surround and destroy all but a small remnant of his enemy, despite his own inferior numbers. Depending upon the source, it is estimated that 50,000–70,000 Romans were killed or captured. Among the dead were Roman consul Lucius Aemilius Paullus (consul 219 BC), Lucius Aemilius Paullus, two consuls for the preceding year, two quaestors, 29 of the 48 military tribunes, and an additional eighty senators (at a time when the Roman Senate was composed of no more than 300 men, this constituted 25%–30% of the governing body). This makes the battle one of the most catastrophic defeats in the history of ancient Rome, and one of the bloodiest battles in all of human history (in terms of the number of lives lost in a single day).
After Cannae, the Romans were very hesitant to confront Hannibal in pitched battle, preferring instead to weaken him by attrition, relying on their advantages of interior lines, supply, and manpower. As a result, Hannibal fought no more major battles in Italy for the rest of the war. It is believed that his refusal to bring the war to Rome itself was due to a lack of commitment from Carthage of men, money, and material — principally siege equipment. Whatever the reason, the choice prompted Maharbal to say, "Hannibal, you know how to gain a victory, but not how to use one."
As a result of this victory, many parts of Italy joined Hannibal's cause. As Polybius notes, "How much more serious was the defeat of Cannae, than those that preceded it can be seen by the behaviour of Rome's allies; before that fateful day, their loyalty remained unshaken, now it began to waver for the simple reason that they despaired of Roman Power." During that same year, the Greek cities in Sicily were induced to revolt against Roman political control, while Macedonian King Philip V of Macedon, Philip V Macedonian–Carthaginian Treaty, pledged his support to Hannibal—thus initiating the First Macedonian War against Rome. Hannibal also secured an alliance with newly appointed tyrant Hieronymus of Syracuse. It is often argued that, if Hannibal had received proper material reinforcements from Carthage, he might have succeeded with a direct attack upon Rome. Instead, he had to content himself with subduing the fortresses that still held out against him, and the only other notable event of 216 BC was the defection of certain Italian territories, including Capua, the second largest city of Italy, which Hannibal made his new base. However, only a few of the Italian city-states that he had expected to gain as allies defected to him.
In the spring of 216 BC, Hannibal took the initiative and seized the large supply depot at Cannae in the Apulian plain. By capturing Cannae, Hannibal had placed himself between the Romans and their crucial sources of supply. Once the Roman Senate resumed their consular elections in 216 BC, they appointed Gaius Terentius Varro and Lucius Aemilius Paullus (consul 219 BC), Lucius Aemilius Paullus as Roman consul, consuls. In the meantime, the Romans hoped to gain success through sheer strength and weight of numbers, and they raised a new army of unprecedented size, estimated by some to be as large as 100,000 men, but more likely around 50,000–80,000.Cottrell, Leonard, ''Enemy of Rome'', Evans Bros, 1965,
The Romans and allied legions resolved to confront Hannibal and marched southward to Apulia. They eventually found him on the left bank of the Aufidus River, and encamped away. On this occasion, the two armies were combined into one, the consuls having to alternate their command on a daily basis. According to Livy, Varro was a man of reckless and hubristic nature and it was his turn to command on the day of battle. (This account is possibly biased against Varro as its main source, Polybius, was a client of Paullus's aristocratic family whereas Varro was less distinguished. Some historians have suggested the sheer size of the army may have required both generals to command a wing each. This theory is supported by the fact that, after Varro survived the battle he was pardoned by the Senate, which would be peculiar if he were the sole commander at fault.)
Hannibal capitalized on the eagerness of the Romans and drew them into a trap by using an Pincer movement, envelopment tactic. This eliminated the Roman numerical advantage by shrinking the combat area. Hannibal drew up his least reliable infantry in the centre in a semicircle curving towards the Romans. Placing them forward of the wings allowed them room to fall back, luring the Romans after them, while the cavalry on the flanks dealt with their Roman counterparts. Hannibal's wings were composed of the Gallic and Numidian cavalry. The Roman legions forced their way through Hannibal's weak centre, but the Libyan mercenaries on the wings, swung around by the movement, menaced their flanks.
The onslaught of Hannibal's cavalry was irresistible. Hannibal's chief cavalry commander, Maharbal, led the mobile Numidian cavalry on the right; they shattered the Roman cavalry opposing them. Hannibal's Iberian and Gallic heavy cavalry on the left, led by Hanno, defeated the Roman heavy cavalry, and then both the Carthaginian heavy cavalry and the Numidians attacked the legions from behind. As a result, the Roman army was hemmed in with no means of escape.
Due to these brilliant tactics, Hannibal managed to surround and destroy all but a small remnant of his enemy, despite his own inferior numbers. Depending upon the source, it is estimated that 50,000–70,000 Romans were killed or captured. Among the dead were Roman consul Lucius Aemilius Paullus (consul 219 BC), Lucius Aemilius Paullus, two consuls for the preceding year, two quaestors, 29 of the 48 military tribunes, and an additional eighty senators (at a time when the Roman Senate was composed of no more than 300 men, this constituted 25%–30% of the governing body). This makes the battle one of the most catastrophic defeats in the history of ancient Rome, and one of the bloodiest battles in all of human history (in terms of the number of lives lost in a single day).
After Cannae, the Romans were very hesitant to confront Hannibal in pitched battle, preferring instead to weaken him by attrition, relying on their advantages of interior lines, supply, and manpower. As a result, Hannibal fought no more major battles in Italy for the rest of the war. It is believed that his refusal to bring the war to Rome itself was due to a lack of commitment from Carthage of men, money, and material — principally siege equipment. Whatever the reason, the choice prompted Maharbal to say, "Hannibal, you know how to gain a victory, but not how to use one."
As a result of this victory, many parts of Italy joined Hannibal's cause. As Polybius notes, "How much more serious was the defeat of Cannae, than those that preceded it can be seen by the behaviour of Rome's allies; before that fateful day, their loyalty remained unshaken, now it began to waver for the simple reason that they despaired of Roman Power." During that same year, the Greek cities in Sicily were induced to revolt against Roman political control, while Macedonian King Philip V of Macedon, Philip V Macedonian–Carthaginian Treaty, pledged his support to Hannibal—thus initiating the First Macedonian War against Rome. Hannibal also secured an alliance with newly appointed tyrant Hieronymus of Syracuse. It is often argued that, if Hannibal had received proper material reinforcements from Carthage, he might have succeeded with a direct attack upon Rome. Instead, he had to content himself with subduing the fortresses that still held out against him, and the only other notable event of 216 BC was the defection of certain Italian territories, including Capua, the second largest city of Italy, which Hannibal made his new base. However, only a few of the Italian city-states that he had expected to gain as allies defected to him.
 In March 212 BC, Hannibal Battle of Tarentum (212 BC), captured Taranto, Tarentum in a surprise attack but he failed to obtain control of its harbour. The tide was slowly turning against him, and in favour of Rome.
The Roman consuls mounted a Battle of Capua, siege of Capua in 212 BC. Hannibal attacked them, forcing their withdrawal from Campania. He moved to Lucania and destroyed a 16,000-man Roman army at the Battle of the Silarus, with 15,000 Romans killed. Another opportunity presented itself soon after, a Roman army of 18,000 men being destroyed by Hannibal at the Battle of Herdonia (212 BC), first battle of Herdonia with 16,000 Romans dead, freeing Apulia from the Romans for the year. The Roman consuls mounted another Battle of Capua (211 BC), siege of Capua in 211 BC, conquering the city. Hannibal attempted to lift the siege with an assault on the Roman siege lines but failed. He marched on Rome to force the recall of the Roman armies. He drew off 15,000 Roman soldiers, but the siege continued and Capua fell. In 212 BC, Marcellus Siege of Syracuse (213–212 BC), conquered Syracuse and the Romans destroyed the Carthaginian army in Sicily in 211–210 BC. In 210 BC, the Romans entered into an alliance with the Aetolian League to counter Philip V of Macedon. Philip, who attempted to exploit Rome's preoccupation in Italy to conquer Illyria, now found himself under attack from several sides at once and was quickly subdued by Rome and her Greek allies.
In 210 BC, Hannibal again proved his superiority in tactics by inflicting a severe defeat at the Battle of Herdonia (210 BC), Battle of Herdonia (modern Ordona) in Apulia upon a proconsular army and, in 208 BC, destroyed a Roman force engaged in the siege of Locri at the Battle of Petelia. But with the loss of Tarentum in 209 BC and the gradual reconquest by the Romans of
In March 212 BC, Hannibal Battle of Tarentum (212 BC), captured Taranto, Tarentum in a surprise attack but he failed to obtain control of its harbour. The tide was slowly turning against him, and in favour of Rome.
The Roman consuls mounted a Battle of Capua, siege of Capua in 212 BC. Hannibal attacked them, forcing their withdrawal from Campania. He moved to Lucania and destroyed a 16,000-man Roman army at the Battle of the Silarus, with 15,000 Romans killed. Another opportunity presented itself soon after, a Roman army of 18,000 men being destroyed by Hannibal at the Battle of Herdonia (212 BC), first battle of Herdonia with 16,000 Romans dead, freeing Apulia from the Romans for the year. The Roman consuls mounted another Battle of Capua (211 BC), siege of Capua in 211 BC, conquering the city. Hannibal attempted to lift the siege with an assault on the Roman siege lines but failed. He marched on Rome to force the recall of the Roman armies. He drew off 15,000 Roman soldiers, but the siege continued and Capua fell. In 212 BC, Marcellus Siege of Syracuse (213–212 BC), conquered Syracuse and the Romans destroyed the Carthaginian army in Sicily in 211–210 BC. In 210 BC, the Romans entered into an alliance with the Aetolian League to counter Philip V of Macedon. Philip, who attempted to exploit Rome's preoccupation in Italy to conquer Illyria, now found himself under attack from several sides at once and was quickly subdued by Rome and her Greek allies.
In 210 BC, Hannibal again proved his superiority in tactics by inflicting a severe defeat at the Battle of Herdonia (210 BC), Battle of Herdonia (modern Ordona) in Apulia upon a proconsular army and, in 208 BC, destroyed a Roman force engaged in the siege of Locri at the Battle of Petelia. But with the loss of Tarentum in 209 BC and the gradual reconquest by the Romans of
 In 203 BC, Hannibal was recalled from Italy by the war party in Carthage. After leaving a record of his expedition engraved in Punic language, Punic and Greek language, Greek upon bronze tablets in the Temple of Juno Lacinia (Crotone), Temple of Juno Lacinia at Crotone, Crotona, he sailed back to Africa. His arrival immediately restored the predominance of the war party, which placed him in command of a combined force of African conscription, levies and his mercenaries from Italy. In 202 BC, Hannibal met Scipio in a fruitless peace conference. Despite mutual admiration, negotiations floundered due to Roman allegations of "Punic Faith," referring to the breach of protocols that ended the First Punic War by the Carthaginian attack on Saguntum, and a Carthaginian attack on a stranded Roman fleet. Scipio and Carthage had worked out a peace plan, which was approved by Rome. The terms of the treaty were quite modest, but the war had been long for the Romans. Carthage could keep its African territory but would lose its overseas empire. Masinissa ( Numidia) was to be independent. Also, Carthage was to reduce its fleet and pay a war indemnity. But Carthage then made a terrible blunder. Its long-suffering citizens had captured a stranded Roman fleet in the Gulf of Tunis and stripped it of supplies, an action that aggravated the faltering negotiations. Fortified by both Hannibal and the supplies, the Carthaginians rebuffed the treaty and Roman protests. The decisive battle of Zama soon followed; the defeat removed Hannibal's air of invincibility.
In 203 BC, Hannibal was recalled from Italy by the war party in Carthage. After leaving a record of his expedition engraved in Punic language, Punic and Greek language, Greek upon bronze tablets in the Temple of Juno Lacinia (Crotone), Temple of Juno Lacinia at Crotone, Crotona, he sailed back to Africa. His arrival immediately restored the predominance of the war party, which placed him in command of a combined force of African conscription, levies and his mercenaries from Italy. In 202 BC, Hannibal met Scipio in a fruitless peace conference. Despite mutual admiration, negotiations floundered due to Roman allegations of "Punic Faith," referring to the breach of protocols that ended the First Punic War by the Carthaginian attack on Saguntum, and a Carthaginian attack on a stranded Roman fleet. Scipio and Carthage had worked out a peace plan, which was approved by Rome. The terms of the treaty were quite modest, but the war had been long for the Romans. Carthage could keep its African territory but would lose its overseas empire. Masinissa ( Numidia) was to be independent. Also, Carthage was to reduce its fleet and pay a war indemnity. But Carthage then made a terrible blunder. Its long-suffering citizens had captured a stranded Roman fleet in the Gulf of Tunis and stripped it of supplies, an action that aggravated the faltering negotiations. Fortified by both Hannibal and the supplies, the Carthaginians rebuffed the treaty and Roman protests. The decisive battle of Zama soon followed; the defeat removed Hannibal's air of invincibility.
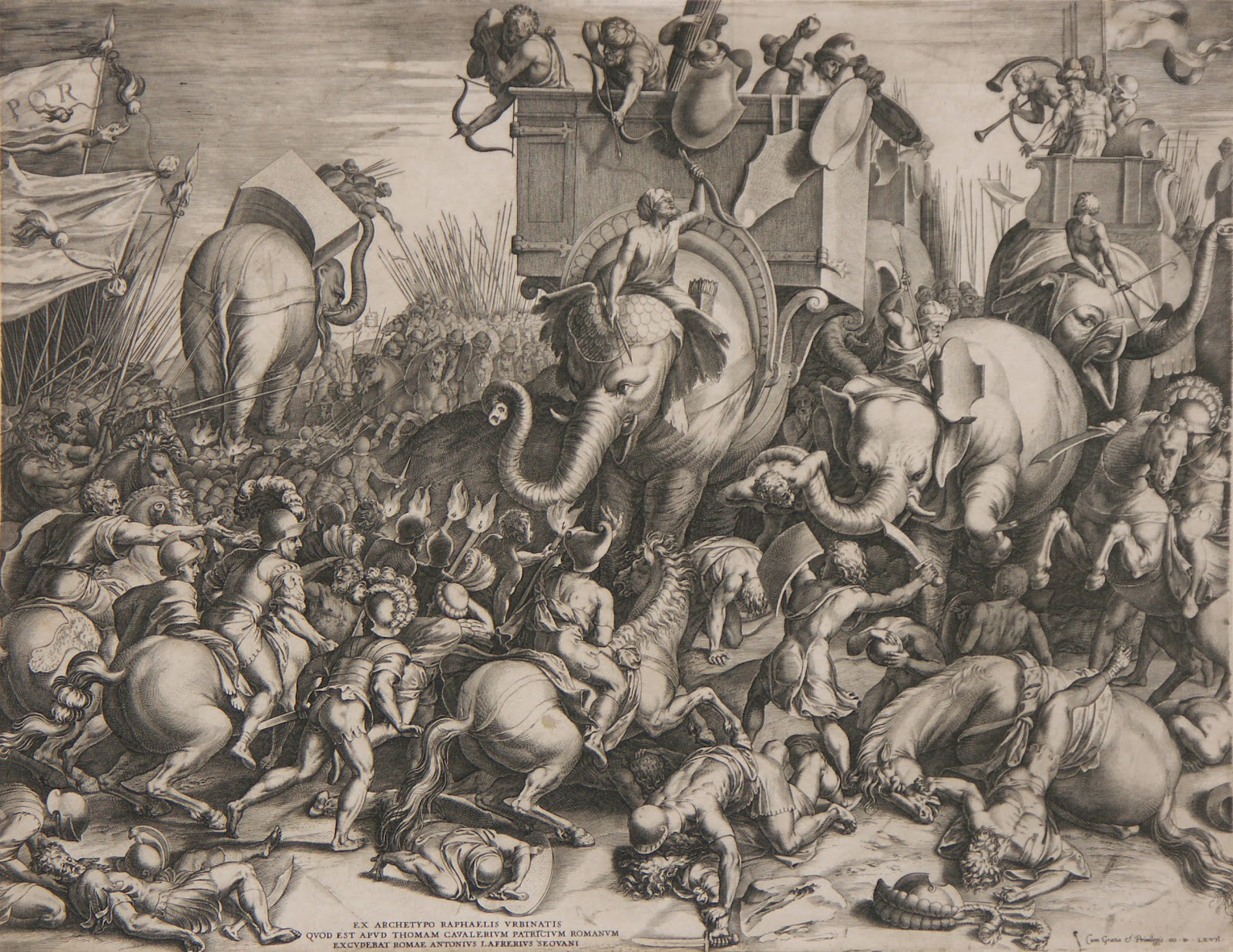 The Roman cavalry won an early victory by swiftly routing the Carthaginian horse and because standard Roman tactics for limiting the effectiveness of the Carthaginian war elephants were successful, including playing trumpets to frighten the elephants into running into the Carthaginian lines. Some historians say that the elephants routed the Carthaginian cavalry and not the Romans, whilst others suggest that it was actually a tactical retreat planned by Hannibal. Whatever the truth, the battle remained closely fought. At one point, it seemed that Hannibal was on the verge of victory, but Scipio was able to rally his men, and his cavalry, having routed the Carthaginian cavalry, attacked Hannibal's rear. This two-pronged attack caused the Carthaginian formation to collapse.
With their foremost general defeated, the Carthaginians had no choice but to surrender. Carthage lost approximately 20,000 troops with an additional 15,000 wounded. In contrast, the Romans suffered only 2,500 casualties. The last major battle of the Second Punic War resulted in a loss of respect for Hannibal by his fellow Carthaginians. The conditions of defeat were such that Carthage could no longer battle for Mediterranean supremacy.
The Roman cavalry won an early victory by swiftly routing the Carthaginian horse and because standard Roman tactics for limiting the effectiveness of the Carthaginian war elephants were successful, including playing trumpets to frighten the elephants into running into the Carthaginian lines. Some historians say that the elephants routed the Carthaginian cavalry and not the Romans, whilst others suggest that it was actually a tactical retreat planned by Hannibal. Whatever the truth, the battle remained closely fought. At one point, it seemed that Hannibal was on the verge of victory, but Scipio was able to rally his men, and his cavalry, having routed the Carthaginian cavalry, attacked Hannibal's rear. This two-pronged attack caused the Carthaginian formation to collapse.
With their foremost general defeated, the Carthaginians had no choice but to surrender. Carthage lost approximately 20,000 troops with an additional 15,000 wounded. In contrast, the Romans suffered only 2,500 casualties. The last major battle of the Second Punic War resulted in a loss of respect for Hannibal by his fellow Carthaginians. The conditions of defeat were such that Carthage could no longer battle for Mediterranean supremacy.
 Hannibal was still only 46 at the conclusion of the Second Punic War in 201 BC and soon showed that he could be a statesman as well as a soldier. Following the conclusion of a peace that left Carthage saddled with an indemnity of ten thousand Attic talent, talents, he was elected shophet, suffete (chief magistrate) of the Carthaginian state.Gavin de Beer, De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). ''Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy'' p.291. After an audit confirmed Carthage had the resources to pay the indemnity without increasing taxation, Hannibal initiated a reorganization of state finances aimed at eliminating corruption and recovering embezzled funds., by Livy
The principal beneficiaries of these financial peculations had been the oligarchs of the Hundred and Four. In order to reduce the power of the oligarchs, Hannibal passed a law stipulating the Hundred and Four be chosen by direct election rather than co-option. He also used citizen support to change the term of office in the Hundred and Four from life to a year, with none permitted to "hold office for two consecutive years."
Hannibal was still only 46 at the conclusion of the Second Punic War in 201 BC and soon showed that he could be a statesman as well as a soldier. Following the conclusion of a peace that left Carthage saddled with an indemnity of ten thousand Attic talent, talents, he was elected shophet, suffete (chief magistrate) of the Carthaginian state.Gavin de Beer, De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). ''Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy'' p.291. After an audit confirmed Carthage had the resources to pay the indemnity without increasing taxation, Hannibal initiated a reorganization of state finances aimed at eliminating corruption and recovering embezzled funds., by Livy
The principal beneficiaries of these financial peculations had been the oligarchs of the Hundred and Four. In order to reduce the power of the oligarchs, Hannibal passed a law stipulating the Hundred and Four be chosen by direct election rather than co-option. He also used citizen support to change the term of office in the Hundred and Four from life to a year, with none permitted to "hold office for two consecutive years."
 In July 190 BC, Hannibal ordered his fleet to set sail from Seleucia Pieria along the southern Asia Minor coast in order to reinforce the rest of the Seleucid navy at Ephesus. The following month Hannibal's fleet clashed with the Rhodes, Rhodian navy in the Battle of Side. The faster Rhodian ships managed to heavily damage half of Hannibal's warships through the manoeuvre, forcing him to retreat. Hannibal had preserved most of his fleet; however, he was in no position to unite with Polyxenidas' fleet at Ephesus since his ships required lengthy repairs. The ensuing Battle of Myonessus resulted in a Roman-Rhodian victory, which cemented Roman control over the Aegean Sea, enabling them to launch an invasion of Seleucid Asia Minor. The two armies faced off in the
In July 190 BC, Hannibal ordered his fleet to set sail from Seleucia Pieria along the southern Asia Minor coast in order to reinforce the rest of the Seleucid navy at Ephesus. The following month Hannibal's fleet clashed with the Rhodes, Rhodian navy in the Battle of Side. The faster Rhodian ships managed to heavily damage half of Hannibal's warships through the manoeuvre, forcing him to retreat. Hannibal had preserved most of his fleet; however, he was in no position to unite with Polyxenidas' fleet at Ephesus since his ships required lengthy repairs. The ensuing Battle of Myonessus resulted in a Roman-Rhodian victory, which cemented Roman control over the Aegean Sea, enabling them to launch an invasion of Seleucid Asia Minor. The two armies faced off in the
 Hannibal is generally regarded as one of the best military strategists and tacticians of all time, the double envelopment at Cannae an enduring legacy of tactical brilliance. According to
Hannibal is generally regarded as one of the best military strategists and tacticians of all time, the double envelopment at Cannae an enduring legacy of tactical brilliance. According to  Count Alfred von Schlieffen developed his "Schlieffen Plan" (1905/1906) from his military studies, including the envelopment technique that Hannibal employed in the Battle of Cannae. George S. Patton believed himself a reincarnation of Hannibal—as well as of many other people, including a Roman legionary and a Napoleonic soldier. Norman Schwarzkopf Jr., the commander of the Coalition of the Gulf War of 1990–1991, claimed, "The technology of war may change, the sophistication of weapons certainly changes. But those same principles of war that applied to the days of Hannibal apply today."
According to the military historian Theodore Ayrault Dodge,
Count Alfred von Schlieffen developed his "Schlieffen Plan" (1905/1906) from his military studies, including the envelopment technique that Hannibal employed in the Battle of Cannae. George S. Patton believed himself a reincarnation of Hannibal—as well as of many other people, including a Roman legionary and a Napoleonic soldier. Norman Schwarzkopf Jr., the commander of the Coalition of the Gulf War of 1990–1991, claimed, "The technology of war may change, the sophistication of weapons certainly changes. But those same principles of war that applied to the days of Hannibal apply today."
According to the military historian Theodore Ayrault Dodge,
 The teenaged Sigmund Freud regarded Hannibal as a "hero"; the founder of psychoanalysis portrays an idealized image of the Carthaginian general in his analysis of his "dreams of Rome" in ''The Interpretation of Dreams''. Freud then associates this phenomenon with the adage "All roads lead to Rome". He writes in ''The Interpretation of Dreams'': "Hannibal and Rome symbolized for the adolescent that I was the opposition between the tenacity of Judaism and the organizing spirit of the Catholic Church".
A fictional opera called ''Hannibal'' appears at the beginning of the musical The Phantom of the Opera (1986 musical), ''Phantom Of The Opera''.
Kocaeli Province, Kocaeli in Turkey has a cenotaph built in Hannibal's memory. Even though the location of Hannibal's tomb could not be determined precisely in the studies carried out due to Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, Atatürk's great interest, a monumental cenotaph was built in the south of present-day Gebze as an expression of Atatürk's will and Atatürk's respect for Hannibal.
Since 2011, Hannibal has appeared as one of the main characters, with Scipio Africanus, of the ''Ad Astra'' manga in which Mihachi Kagano traces the course of the Second Punic War. The two generals appear as allies in the ''Drifters (manga), Drifters'' manga, having been teleported to another dimension to wage war together.
Tunisia national football team, Tunisia's home and away kit for the 2022 FIFA World Cup was inspired by the Ksour Essef cuirass, a piece of body armor believed to be worn by Carthaginian soldiers under the command of general Hannibal.
The teenaged Sigmund Freud regarded Hannibal as a "hero"; the founder of psychoanalysis portrays an idealized image of the Carthaginian general in his analysis of his "dreams of Rome" in ''The Interpretation of Dreams''. Freud then associates this phenomenon with the adage "All roads lead to Rome". He writes in ''The Interpretation of Dreams'': "Hannibal and Rome symbolized for the adolescent that I was the opposition between the tenacity of Judaism and the organizing spirit of the Catholic Church".
A fictional opera called ''Hannibal'' appears at the beginning of the musical The Phantom of the Opera (1986 musical), ''Phantom Of The Opera''.
Kocaeli Province, Kocaeli in Turkey has a cenotaph built in Hannibal's memory. Even though the location of Hannibal's tomb could not be determined precisely in the studies carried out due to Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, Atatürk's great interest, a monumental cenotaph was built in the south of present-day Gebze as an expression of Atatürk's will and Atatürk's respect for Hannibal.
Since 2011, Hannibal has appeared as one of the main characters, with Scipio Africanus, of the ''Ad Astra'' manga in which Mihachi Kagano traces the course of the Second Punic War. The two generals appear as allies in the ''Drifters (manga), Drifters'' manga, having been teleported to another dimension to wage war together.
Tunisia national football team, Tunisia's home and away kit for the 2022 FIFA World Cup was inspired by the Ksour Essef cuirass, a piece of body armor believed to be worn by Carthaginian soldiers under the command of general Hannibal.
online review
* * * * *
- translated by J.C. Rolfe
''Hannibal''
by Jacob Abbott
Hannibal's life by Cornelius Nepos, Latin transcription and translation to German
The History of Hannibal
{{Authority control Hannibal, 3rd-century BC Punic people 2nd-century BC Punic people 247 BC births 180s BC deaths Ancient people who committed suicide Carthaginian commanders of the Second Punic War Carthaginian generals Marching Military personnel who committed suicide Politicians who committed suicide Suicides by poison Suicides in Turkey
Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the cla ...
in their battle against the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
during the Second Punic War. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest military commanders in history.
Hannibal's father, Hamilcar Barca
Hamilcar Barca or Barcas ( xpu, 𐤇𐤌𐤋𐤒𐤓𐤕𐤟𐤁𐤓𐤒, ''Ḥomilqart Baraq''; –228BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman, leader of the Barcid family, and father of Hannibal, Hasdrubal and Mago. He was also father- ...
, was a leading Carthaginian general during the First Punic War. His younger brothers were Mago and Hasdrubal Hasdrubal ( grc-gre, Ἀσδρούβας, ''Hasdroúbas'') is the Latinized form of the Carthaginian name ʿAzrubaʿal ( xpu, 𐤏𐤆𐤓𐤁𐤏𐤋 , , "Help of Baal").
It may refer to:
* Hasdrubal I of Carthage was the Magonid king of Ancien ...
; his brother-in-law was Hasdrubal the Fair
Hasdrubal the Fair ( xpu, 𐤏𐤆𐤓𐤁𐤏𐤋 , ''ʿAzrobaʿl''; –221BC) was a Carthaginian military leader and politician, governor in Iberia after Hamilcar Barca's death, and founder of Cartagena.
Family
Livy's ''History of Rome'' rec ...
, who commanded other Carthaginian armies. Hannibal lived during a period of great tension in the Mediterranean Basin, triggered by the emergence of the Roman Republic as a great power with its defeat of Carthage in the First Punic War. Revanchism
Revanchism (french: revanchisme, from ''revanche'', "revenge") is the political manifestation of the will to reverse territorial losses incurred by a country, often following a war or social movement. As a term, revanchism originated in 1870s Fr ...
prevailed in Carthage, symbolized by the pledge that Hannibal made to his father to "never be a friend of Rome".
In 218 BC, Hannibal attacked Saguntum (modern Sagunto
Sagunto ( ca-valencia, Sagunt) is a municipality of Spain, located in the province of Valencia, Valencian Community. It belongs to the modern fertile ''comarca'' of Camp de Morvedre. It is located c. 30 km north of the city of Valencia, cl ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
), an ally of Rome, in Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hisp ...
, sparking the Second Punic War. Hannibal invaded Italy by crossing the Alps with North African
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in t ...
war elephant
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elepha ...
s. In his first few years in Italy, he won a succession of victories at the Battle of the Trebia, Lake Trasimene, and Cannae, inflicting heavy losses on the Romans. Hannibal was distinguished for his ability to determine both his and his opponent's respective strengths and weaknesses, and to plan battles accordingly. His well-planned strategies allowed him to conquer and ally with several Italian cities that were previously allied to Rome. Hannibal occupied most of southern Italy for 15 years. The Romans, led by Fabius Maximus
Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus, surnamed Cunctator ( 280 – 203 BC), was a Roman statesman and general of the third century BC. He was consul five times (233, 228, 215, 214, and 209 BC) and was appointed dictator in 221 and 217 BC. He was ...
, avoided heavy confrontation with him, instead waging a war of attrition
Attrition may refer to
*Attrition warfare, the military strategy of wearing down the enemy by continual losses in personnel and material
**War of Attrition, fought between Egypt and Israel from 1968 to 1970
**War of attrition (game), a model of agg ...
. Carthaginian defeats in Hispania prevented Hannibal from being reinforced, and he was unable to win a decisive victory. A counter-invasion of North Africa, led by Roman General Scipio Africanus, forced him to return to Carthage. Hannibal was eventually defeated at the Battle of Zama
The Battle of Zama was fought in 202 BC near Zama, now in Tunisia, and marked the end of the Second Punic War. A Roman army led by Publius Cornelius Scipio, with crucial support from Numidian leader Masinissa, defeated the Carthaginian ...
, ending the war in a Roman victory.
After the war, Hannibal successfully ran for the office of sufet. He enacted political and financial reforms to enable the payment of the war indemnity imposed by Rome; however, those reforms were unpopular with members of the Carthaginian aristocracy and in Rome, and he fled into voluntary exile. During this time, he lived at the Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
court, where he acted as military advisor to Antiochus III the Great
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the res ...
in his war against Rome. Antiochus met defeat at the Battle of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of Pe ...
and was forced to accept Rome's terms, and Hannibal fled again, making a stop in the Kingdom of Armenia. His flight ended in the court of Bithynia. He was betrayed to the Romans and died by suicide with poison.
Hannibal is considered one of the greatest military tacticians and generals of antiquity, alongside Philip of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king (''basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the a ...
, Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
, Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
, Scipio Africanus and Pyrrhus. According to Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
, Scipio asked Hannibal "who the greatest general was", to which Hannibal replied "either Alexander or Pyrrhus, then himself".Plutarch, ''Life of Titus Flamininus'' 21.3–4. Plutarch adds that "when asked what his choices would be if he had beaten Scipio, he replied that he would be the best of them all". However, Plutarch gives another version in his ''Life of Pyrrhus'', 8.2: "Pyrrhus, Scipio, then myself".
Name
 Hannibal was a common Semitic Phoenician-Carthaginian personal name. It is recorded in Carthaginian sources as ( xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋). It is a combination of the common Phoenician masculine given name
Hannibal was a common Semitic Phoenician-Carthaginian personal name. It is recorded in Carthaginian sources as ( xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋). It is a combination of the common Phoenician masculine given name Hanno
Hanno may refer to:
People
* Hanno (given name)
:* Hanunu (8th century BC), Philistine king previously rendered by scholars as "Hanno"
*Hanno ( xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤀 , '; , ''Hannōn''), common Carthaginian name
:* Hanno the Navigator, Carthagi ...
with the Northwest Semitic
Northwest Semitic is a division of the Semitic languages comprising the indigenous languages of the Levant. It emerged from Proto-Semitic in the Early Bronze Age. It is first attested in proper names identified as Amorite in the Middle Bronze A ...
Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
ite deity Baal
Baal (), or Baal,; phn, , baʿl; hbo, , baʿal, ). ( ''baʿal'') was a title and honorific meaning "owner", "lord" in the Northwest Semitic languages spoken in the Levant during antiquity. From its use among people, it came to be applied t ...
(lit, "lord") a major god of the Carthaginians ancestral homeland of Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
in Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
. Its precise vocalization remains a matter of debate. Suggested readings include ''Ḥannobaʿal'',Brown, John Pairman. 2000. Israel and Hellas: Sacred institutions with Roman counterparts. P.126–128 ''Ḥannibaʿl'', or ''Ḥannibaʿal'', meaning "Baʿal/The lord is gracious", "Baʿal Has Been Gracious",Baier, Thomas. 2004. Studien zu Plautus' Poenulus. P.174 or "The Grace of Baʿal".Benz, Franz L. 1982. Personal Names in the Phoenician and Punic Inscriptions. P.313-314 It is equivalent to the fellow Semitic Hebrew name Haniel
Haniel ( he, חַנִּיאֵל, ''Ḥannīʾēl'', "God is my grace"; cop, ⲁⲛⲁⲛⲓⲏⲗ ''Ananiēl''; ar, عنيائيل, '), also known as Hananel, Anael, Hanael or Aniel, is an angel in Jewish lore and angelology, and is often i ...
. Greek historians
Hellenic historiography (or Greek historiography) involves efforts made by Greeks to track and record historical events. By the 5th century BC, it became an integral part of ancient Greek literature and held a prestigious place in later Roman histo ...
rendered the name as ''Anníbas'' ().
The Phoenicians and Carthaginians, like many West Asian Semitic peoples, did not use hereditary surnames, but were typically distinguished from others bearing the same name using patronymic
A patronymic, or patronym, is a component of a personal name based on the given name of one's father, grandfather (avonymic), or an earlier male ancestor.
Patronymics are still in use, including mandatory use, in many countries worldwide, alt ...
s or epithets. Although he is by far the most famous Hannibal, when further clarification is necessary he is usually referred to as "Hannibal, son of Hamilcar", or "Hannibal the Barcid", the latter term applying to the family of his father, Hamilcar Barca
Hamilcar Barca or Barcas ( xpu, 𐤇𐤌𐤋𐤒𐤓𐤕𐤟𐤁𐤓𐤒, ''Ḥomilqart Baraq''; –228BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman, leader of the Barcid family, and father of Hannibal, Hasdrubal and Mago. He was also father- ...
. '' Barca'' ( xpu, 𐤁𐤓𐤒, ) is a Semitic cognomen
A ''cognomen'' (; plural ''cognomina''; from ''con-'' "together with" and ''(g)nomen'' "name") was the third name of a citizen of ancient Rome, under Roman naming conventions. Initially, it was a nickname, but lost that purpose when it became here ...
meaning "lightning" or "thunderbolt", a surname acquired by Hamilcar on account of the swiftness and ferocity of his attacks. Barca is cognate with similar names for lightning found among the Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
, Assyrians, Babylonians
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. 1 ...
, Arameans, Amorites
The Amorites (; sux, 𒈥𒌅, MAR.TU; Akkadian: 𒀀𒈬𒊒𒌝 or 𒋾𒀉𒉡𒌝/𒊎 ; he, אֱמוֹרִי, 'Ĕmōrī; grc, Ἀμορραῖοι) were an ancient Northwest Semitic-speaking people from the Levant who also occupied lar ...
, Moabites, Edomites
Edom (; Edomite: ; he, אֱדוֹם , lit.: "red"; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Egyptian: ) was an ancient kingdom in Transjordan, located between Moab to the northeast, the Arabah to the west, and the Arabian Desert to the south and east.N ...
and other fellow Asiatic Semitic peoples. Although they did not inherit the surname from their father, Hamilcar's progeny are collectively known as the Barcids
The Barcid ( phn, 𐤁𐤓𐤒, baraq) family was a notable family in the ancient city of Carthage; many of its members were fierce enemies of the Roman Republic. "Barcid" is an adjectival form coined by historians (''cf.'' " Ramesside" and "Abb ...
. Modern historians occasionally refer to Hannibal's brothers as Hasdrubal Barca
Hasdrubal Barca (245– 22June 207BC), a latinization of ʿAzrubaʿal ( xpu, 𐤏𐤆𐤓𐤁𐤏𐤋 ) son of Hamilcar Barca, was a Carthaginian general in the Second Punic War. He was the brother of Hannibal and Mago Barca.
Youth and Iberi ...
and Mago Barca
Mago Barca ( xpu, 𐤌𐤂𐤍 𐤁𐤓𐤒, ; 243–203BC) was a Barcid Carthaginian who played an important role in the Second Punic War, leading forces of Carthage against the Roman Republic in Iberia and northern and central Italy. Ma ...
to distinguish them from the multitudes of other Carthaginians named Hasdrubal and Mago, but this practice is ahistorical and is rarely applied to Hannibal.
Background and early career
 Hannibal was one of the sons of
Hannibal was one of the sons of Hamilcar Barca
Hamilcar Barca or Barcas ( xpu, 𐤇𐤌𐤋𐤒𐤓𐤕𐤟𐤁𐤓𐤒, ''Ḥomilqart Baraq''; –228BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman, leader of the Barcid family, and father of Hannibal, Hasdrubal and Mago. He was also father- ...
, a Carthaginian leader, and an unknown mother. He was born in what is present-day northern Tunisia, one of many Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
regions colonised by the Canaanites from their homelands in Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
, a region corresponding with the Mediterranean coasts of modern Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
and Syria. He had several sisters whose names are unknown, and two brothers, Hasdrubal Hasdrubal ( grc-gre, Ἀσδρούβας, ''Hasdroúbas'') is the Latinized form of the Carthaginian name ʿAzrubaʿal ( xpu, 𐤏𐤆𐤓𐤁𐤏𐤋 , , "Help of Baal").
It may refer to:
* Hasdrubal I of Carthage was the Magonid king of Ancien ...
and Mago. His brothers-in-law were Hasdrubal the Fair
Hasdrubal the Fair ( xpu, 𐤏𐤆𐤓𐤁𐤏𐤋 , ''ʿAzrobaʿl''; –221BC) was a Carthaginian military leader and politician, governor in Iberia after Hamilcar Barca's death, and founder of Cartagena.
Family
Livy's ''History of Rome'' rec ...
and the Numidian
Numidia (Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisi ...
king Naravas
Naravas ( Old Libyan: ''Nrbs(h)''; , ) was a Numidian chief in the Mercenary War of the Carthaginian state. Naravas is the Greek form of Narbal or Naarbaal.
Alliance with Hamilcar Barca
During the Punic Wars, Naravas had joined the army of Spe ...
. He was still a child when his sisters married, and his brothers-in-law were close associates during his father's struggles in the Mercenary War
The Mercenary War, also known as the Truceless War, was a mutiny by troops that were employed by Carthage at the end of the First Punic War (264241 BC), supported by uprisings of African settlements revolting against Carthaginian contro ...
and the Punic conquest of the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
.
After Carthage's defeat in the First Punic War, Hamilcar set out to improve his family's and Carthage's fortunes. With that in mind and supported by Gades, Hamilcar began the subjugation of the tribes of the Iberian Peninsula (Modern Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
). Carthage at the time was in such a poor state that it lacked a navy able to transport his army; instead, Hamilcar had to march his forces across Numidia towards the Pillars of Hercules
The Pillars of Hercules ( la, Columnae Herculis, grc, Ἡράκλειαι Στῆλαι, , ar, أعمدة هرقل, Aʿmidat Hiraql, es, Columnas de Hércules) was the phrase that was applied in Antiquity to the promontories that flank t ...
and then cross the Strait of Gibraltar.
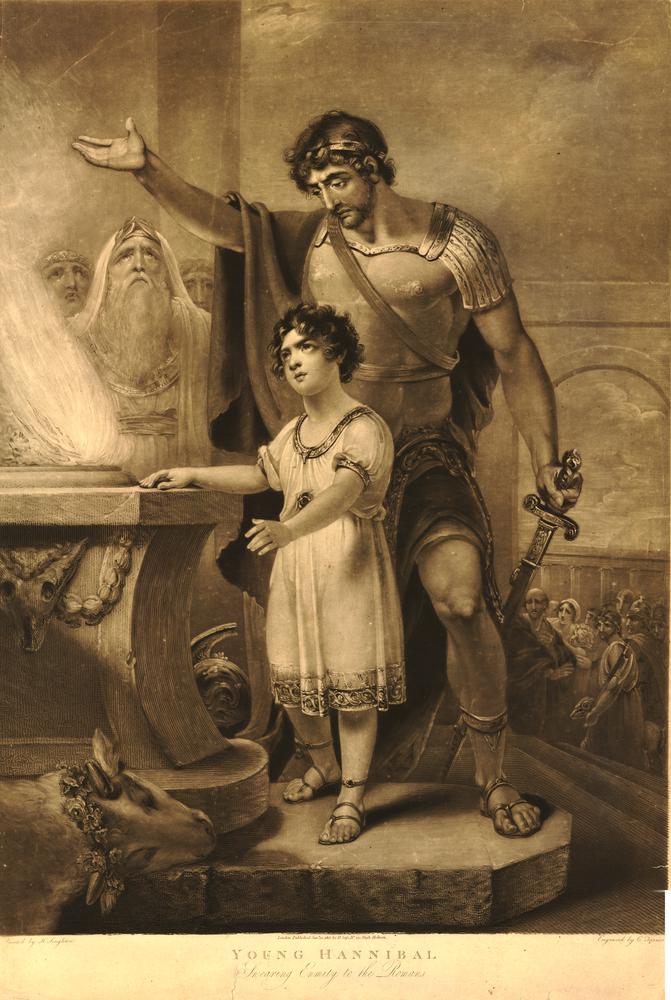
According to Polybius, Hannibal much later said that when he came upon his father and begged to go with him, Hamilcar agreed and demanded that he swear that as long as he lived he would never be a friend of Rome. There is even an account of him at a very young age (9 years old) begging his father to take him to an overseas war. In the story, Hannibal's father took him up and brought him to a sacrificial chamber. Hamilcar held Hannibal over the fire roaring in the chamber and made him swear that he would never be a friend of Rome. Other sources report that Hannibal told his father, "I swear so soon as age will permit...I will use fire and steel to arrest the destiny of Rome." According to the tradition, Hannibal's oath took place in the town of Peñíscola
Peníscola () or Peñíscola (), anglicised as Peniscola, is a municipality in the Province of Castellón, Valencian Community, Spain. The town is located on the Costa del Azahar, north of the Serra d'Irta along the Mediterranean coast. It is a p ...
, today part of the Valencian Community
The Valencian Community ( ca-valencia, Comunitat Valenciana, es, Comunidad Valenciana) is an autonomous community of Spain. It is the fourth most populous Spanish autonomous community after Andalusia, Catalonia and the Community of Madrid wi ...
, Spain.
Hannibal's father went about the conquest of Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hisp ...
. When his father drowned in battle, Hannibal's brother-in-law Hasdrubal the Fair
Hasdrubal the Fair ( xpu, 𐤏𐤆𐤓𐤁𐤏𐤋 , ''ʿAzrobaʿl''; –221BC) was a Carthaginian military leader and politician, governor in Iberia after Hamilcar Barca's death, and founder of Cartagena.
Family
Livy's ''History of Rome'' rec ...
succeeded to his command of the army with Hannibal (then 18 years old) serving as an officer under him. Hasdrubal pursued a policy of consolidation of Carthage's Iberian interests, even signing a treaty with Rome whereby Carthage would not expand north of the Ebro
, name_etymology =
, image = Zaragoza shel.JPG
, image_size =
, image_caption = The Ebro River in Zaragoza
, map = SpainEbroBasin.png
, map_size =
, map_caption = The Ebro ...
so long as Rome did not expand south of it. Hasdrubal also endeavoured to consolidate Carthaginian power through diplomatic relationships with the native tribes of Iberia and native Berbers of the North African coasts., by Livy
Upon the assassination of Hasdrubal in 221 BC, Hannibal (now 26 years old) was proclaimed commander-in-chief by the army and confirmed in his appointment by the Carthaginian government. The Roman scholar Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
gives a depiction of the young Carthaginian: "No sooner had he arrived...the old soldiers fancied they saw Hamilcar in his youth given back to them; the same bright look; the same fire in his eye, the same trick of countenance and features. Never was one and the same spirit more skilful to meet opposition, to obey, or to command
Livy also records that Hannibal married a woman of Castulo
Castulo (Latin: ''Castulo''; Iberian: ''Kastilo'') was an Iberian town and bishopric (now Latin titular see located in the Andalusian province of Jaén, in south-central Spain, near modern Linares.
History
Evidence of human presence sin ...
, a powerful Spanish city closely allied with Carthage. The Roman epic poet
An epic poem, or simply an epic, is a lengthy narrative poem typically about the extraordinary deeds of extraordinary characters who, in dealings with gods or other superhuman forces, gave shape to the mortal universe for their descendants.
...
Silius Italicus names her as Imilce. Silius suggests a Greek origin for Imilce, but Gilbert Charles-Picard
Gilbert Picard, called Gilbert Charles-Picard, (15 October 1913 – 21 December 1998) was a 20th-century French historian and archaeologist, a specialist of North Africa during Antiquity.
The son of Hellenist Charles Picard (1883–1965), h ...
argued for a Punic heritage based on an etymology from the Semitic root m-l-k ('chief, the 'king'). Silius also suggests the existence of a son, who is otherwise not attested by Livy, Polybius, or Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἀππιανὸς Ἀλεξανδρεύς ''Appianòs Alexandreús''; la, Appianus Alexandrinus; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who flourished during the reigns of Emperors of Rome Trajan, Ha ...
. The son may have been named Haspar or Aspar, although this is disputed.
After he assumed command, Hannibal spent two years consolidating his holdings and completing the conquest of Hispania, south of the Ebro. In his first campaign, Hannibal attacked and stormed the Olcades The Olcades were an ancient stock-raising pre- Roman people from Hispania, who lived to the west of the Turboletae in the southeastern fringe of the Iberian system mountains.
Origins
Related to both the Celtiberians and Carpetani, the Olcades ...
' strongest centre, Alithia, which promptly led to their surrender, and brought Punic power close to the River Tagus
The Tagus ( ; es, Tajo ; pt, Tejo ; see below) is the longest river in the Iberian Peninsula. The river rises in the Montes Universales near Teruel, in mid-eastern Spain, flows , generally west with two main south-westward sections, to e ...
. His following campaign in 220 BC was against the Vaccaei
The Vaccaei or Vaccei were a pre-Roman Celtic people of Spain, who inhabited the sedimentary plains of the central Duero valley, in the Meseta Central of northern Hispania (specifically in Castile and León). Their capital was ''Intercatia'' in P ...
to the west, where he stormed the Vaccaen strongholds of Helmantice and Arbucala. On his return home, laden with many spoils, a coalition of Spanish tribes, led by the Carpetani
The Carpetani (Greek: ''Karpetanoi'') were one of the Celtic pre- Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula (the Roman Hispania, modern Spain and Portugal), akin to the Celtiberians, dwelling in the central part of the '' meseta'' - the high centr ...
, attacked, and Hannibal won his first major battlefield success and showed off his tactical skills at the battle of the River Tagus. However, Rome, fearing the growing strength of Hannibal in Iberia, made an alliance with the city of Saguntum
Sagunto ( ca-valencia, Sagunt) is a municipality of Spain, located in the province of Valencia, Valencian Community. It belongs to the modern fertile ''comarca'' of Camp de Morvedre. It is located c. 30 km north of the city of Valencia, cl ...
, which lay a considerable distance south of the River Ebro, and claimed the city as its protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its int ...
. Hannibal not only perceived this as a breach of the treaty signed with Hasdrubal, but as he was already planning an attack on Rome, this was his way to start the war. So he laid siege to the city, which fell after eight months.
Hannibal sent the booty from Saguntum to Carthage, a shrewd move which gained him much support from the government; Livy records that only Hanno II the Great
Hanno II the Great ( xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤀, ) was a wealthy Carthaginian aristocrat in the 3rd century BC.
Hanno's wealth was based on the land he owned in Africa and the Iberian Peninsula, and during the First Punic War he led the ...
spoke against him. In Rome, the Senate reacted to this apparent violation of the treaty by dispatching a delegation to Carthage to demand whether Hannibal had destroyed Saguntum in accordance with orders from Carthage. The Carthaginian Senate responded with legal arguments observing the lack of ratification by either government for the treaty alleged to have been violated. The delegation's leader, Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus
Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus, surnamed Cunctator ( 280 – 203 BC), was a Roman statesman and general of the third century BC. He was consul five times (233, 228, 215, 214, and 209 BC) and was appointed dictator in 221 and 217 BC. He was ...
, demanded Carthage choose between war and peace, to which his audience replied that Rome could choose. Fabius chose war.
Second Punic War in Italy (218–204 BC)
Overland journey to Italy
 This journey was originally planned by Hannibal's brother-in-law Hasdrubal the Fair, who became a Carthaginian general in the Iberian Peninsula in 229 BC. He maintained this post for eight years until 221 BC. Soon the Romans became aware of an alliance between Carthage and the
This journey was originally planned by Hannibal's brother-in-law Hasdrubal the Fair, who became a Carthaginian general in the Iberian Peninsula in 229 BC. He maintained this post for eight years until 221 BC. Soon the Romans became aware of an alliance between Carthage and the Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
of the Po Valley in Northern Italy. The Celts were amassing forces to invade farther south in Italy, presumably with Carthaginian backing. Therefore, the Romans pre-emptively invaded the Po region in 225 BC. By 220 BC, the Romans had annexed the area as Cisalpine Gaul. Hasdrubal was assassinated around the same time (221 BC), bringing Hannibal to the fore. It seems that the Romans lulled themselves into a false sense of security, having dealt with the threat of a Gallo-Carthaginian invasion, and perhaps knowing that the original Carthaginian commander had been killed.
Hannibal departed Cartagena, Spain (New Carthage) in late spring of 218 BC. He fought his way through the northern tribes to the foothills of the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
, subduing the tribes through clever mountain tactics and stubborn fighting. He left a detachment of 20,000 troops to garrison the newly conquered region. At the Pyrenees, he released 11,000 Iberian troops who showed reluctance to leave their homeland. Hannibal reportedly entered Gaul with 40,000 foot soldiers and 12,000 horsemen.
Hannibal recognized that he still needed to cross the Pyrenees, the Alps, and many significant rivers. Additionally, he would have to contend with opposition from the Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
s, whose territory he passed through. Starting in the spring of 218 BC, he crossed the Pyrenees and reached the Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; wae, Rotten ; frp, Rôno ; oc, Ròse ) is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Ar ...
by conciliating the Gaulish chiefs along his passage before the Romans could take any measures to bar his advance, arriving at the Rhône in September. Hannibal's army numbered 38,000 infantry, 8,000 cavalry, and 38 elephants, almost none of which would survive the harsh conditions of the Alps.
Hannibal outmanoeuvred the natives who had tried to prevent his crossing, then evaded a Roman force marching from the Mediterranean coast by turning inland up the valley of the Rhône. His exact route over the Alps has been the source of scholarly dispute ever since (Polybius, the surviving ancient account closest in time to Hannibal's campaign, reports that the route was already debated). The most influential modern theories favour either a march up the valley of the Drôme
Drôme (; Occitan: ''Droma''; Arpitan: ''Drôma'') is the southernmost department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of Southeastern France. Named after the river Drôme, it had a population of 516,762 as of 2019.
and a crossing of the main range to the south of the modern highway over the Col de Montgenèvre
The Col de Montgenèvre (; elevation 1860 m.) is a high mountain pass in the Cottian Alps, in France 2 kilometres away from Italy.
Description
The pass takes its name from the village Montgenèvre (Hautes-Alpes), which lies in the vicinity ...
or a march farther north up the valleys of the Isère and Arc crossing the main range near the present Col de Mont Cenis or the Little St Bernard Pass
The Little St Bernard Pass (French: ''Col du Petit Saint-Bernard'', Italian: ''Colle del Piccolo San Bernardo'') is a mountain pass in the Alps on the France–Italy border. Its saddle is at 2188 metres above sea level. It is located between S ...
. Recent numismatic evidence suggests that Hannibal's army may have passed within sight of the Matterhorn
The (, ; it, Cervino, ; french: Cervin, ; rm, Matterhorn) is a mountain of the Alps, straddling the main watershed and border between Switzerland and Italy. It is a large, near-symmetric pyramidal peak in the extended Monte Rosa area of the ...
. Stanford geoarchaeologist Patrick Hunt argues that Hannibal took the Col de Clapier mountain pass, claiming the Clapier most accurately met ancient depictions of the route: wide view of Italy, pockets of year-round snow, and a large campground. Other scholars have doubts, proposing that Hannibal took the easier route across Petit Mount Cenis. Hunt responds to this by proposing that Hannibal's Celtic guides purposefully misguided the Carthaginian general.
Most recently, W. C. Mahaney has argued Col de la Traversette closest fits the records of ancient authors. Biostratigraphic archaeological data has reinforced the case for Col de la Traversette; analysis of peat bogs near watercourses on both sides of the pass's summit showed that the ground was heavily disturbed "by thousands, perhaps tens of thousands, of animals and humans" and that the soil bore traces of unique levels of ''Clostridia
The Clostridia are a highly polyphyletic class of Bacillota, including ''Clostridium'' and other similar genera. They are distinguished from the Bacilli by lacking aerobic respiration. They are obligate anaerobes and oxygen is toxic to them. S ...
'' bacteria associated with the digestive tract of horses and mules. Radiocarbon dating secured dates of 2168 BP or c. 218 BC, the year of Hannibal's march. Mahaney ''et al''. have concluded that this and other evidence strongly supports the Col de la Traversette as being the "Hannibalic Route" as had been argued by Gavin de Beer
Sir Gavin Rylands de Beer (1 November 1899 – 21 June 1972) was a British evolutionary embryologist, known for his work on heterochrony as recorded in his 1930 book ''Embryos and Ancestors''. He was director of the Natural History Museum, Lond ...
in 1954. De Beer was one of only three interpreters—the others being John Lazenby and Jakob Seibert – to have visited all the Alpine high passes and presented a view on which was most plausible. Both De Beer and Siebert had selected the Col de la Traversette as the one most closely matching the ancient descriptions. Polybius wrote that Hannibal had crossed the highest of the Alpine passes: Col de la Traversette, between the upper Guil valley and the upper Po river is the highest pass. It is moreover the most southerly, as Varro
Marcus Terentius Varro (; 116–27 BC) was a Roman polymath and a prolific author. He is regarded as ancient Rome's greatest scholar, and was described by Petrarch as "the third great light of Rome" (after Vergil and Cicero). He is sometimes calle ...
in his ''De re rustica'' relates, agreeing that Hannibal's Pass was the highest in Western Alps and the most southerly. Mahaney ''et al''. argue that factors used by De Beer to support Col de la Traversette including "gauging ancient place names against modern, close scrutiny of times of flood in major rivers and distant viewing of the Po plains" taken together with "massive radiocarbon and microbiological and parasitical evidence" from the alluvial sediments either side of the pass furnish "supporting evidence, proof if you will" that Hannibal's invasion went that way. If Hannibal had ascended the Col de la Traversette, the Po Valley would indeed have been visible from the pass's summit, vindicating Polybius's account.
By Livy's account, the crossing was accomplished in the face of huge difficulties. These Hannibal surmounted with ingenuity, such as when he used vinegar and fire to break through a rockfall. According to Polybius, he arrived in Italy accompanied by 20,000 foot soldiers, 4,000 horsemen, and only a few elephants. The fired rockfall event is mentioned only by Livy; Polybius is mute on the subject and there is no evidence of carbonized rock at the only two-tier rockfall in the Western Alps, located below the Col de la Traversette (Mahaney, 2008). If Polybius is correct in his figure for the number of troops that he commanded after the crossing of the Rhône, this would suggest that he had lost almost half of his force. Historians such as Serge Lancel have questioned the reliability of the figures for the number of troops that he had when he left Hispania. From the start, he seems to have calculated that he would have to operate without aid from Hispania.
Hannibal's vision of military affairs was derived partly from the teaching of his Greek tutors and partly from experience gained alongside his father, and it stretched over most of the Hellenistic World of his time. Indeed, the breadth of his vision gave rise to his grand strategy of conquering Rome by opening a northern front and subduing allied city-states on the peninsula, rather than by attacking Rome directly. Historical events that led to the defeat of Carthage during the First Punic War when his father commanded the Carthaginian Army also led Hannibal to plan the invasion of Italy by land across the Alps.
The task involved the mobilization of between 60,000 and 100,000 troops and the training of a war-elephant corps, all of which had to be provisioned along the way. The alpine invasion of Italy was a military operation that would shake the Mediterranean World of 218 BC with repercussions for more than two decades.
Battle of Trebia
 Hannibal's perilous march brought him into the Roman territory and frustrated the attempts of the enemy to fight out the main issue on foreign ground. His sudden appearance among the
Hannibal's perilous march brought him into the Roman territory and frustrated the attempts of the enemy to fight out the main issue on foreign ground. His sudden appearance among the Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
s of the Po Valley, moreover, enabled him to detach those tribes from their new allegiance to the Romans before the Romans could take steps to check the rebellion. Publius Cornelius Scipio was the consul who commanded the Roman force sent to intercept Hannibal (he was also the father of Scipio Africanus). He had not expected Hannibal to make an attempt to cross the Alps, since the Romans were prepared to fight the war in the Iberian Peninsula. With a small detachment still positioned in Gaul, Scipio made an attempt to intercept Hannibal. He succeeded, through prompt decision and speedy movement, in transporting his army to Italy by sea in time to meet Hannibal. Hannibal's forces moved through the Po Valley and were engaged in the Battle of Ticinus
The battle of Ticinus was fought between the Carthaginian forces of Hannibal and a Roman army under Publius Cornelius Scipio in late November 218 BC as part of the Second Punic War. It took place in the flat country on the right bank of the ...
. Here, Hannibal forced the Romans to evacuate the plain of Lombardy, by virtue of his superior cavalry. Dodge, Theodore. ''Hannibal''. Cambridge Massachusetts: Da Capo Press, 1891 The victory was minor, but it encouraged the Gauls and Ligurians to join the Carthaginian cause. Their troops bolstered his army back to around 40,000 men. Scipio was severely injured, his life only saved by the bravery of his son who rode back onto the field to rescue his fallen father. Scipio retreated across the Trebia to camp at Placentia with his army mostly intact.
The other Roman consul
A consul held the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC), and ancient Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum'' (an ascending sequence of public offices to which politic ...
ar army was rushed to the Po Valley. Even before news of the defeat at Ticinus had reached Rome, the Senate had ordered Consul Tiberius Sempronius Longus to bring his army back from Sicily to meet Scipio and face Hannibal. Hannibal, by skilful manoeuvres, was in position to head him off, for he lay on the direct road between Placentia and Arminum, by which Sempronius would have to march to reinforce Scipio. He then captured Clastidium, from which he drew large amounts of supplies for his men. But this gain was not without loss, as Sempronius avoided Hannibal's watchfulness, slipped around his flank, and joined his colleague in his camp near the Trebia River near Placentia. There Hannibal had an opportunity to show his masterful military skill at the Trebia in December of the same year, after wearing down the superior Roman infantry, when he cut it to pieces with a surprise attack and ambush from the flanks.
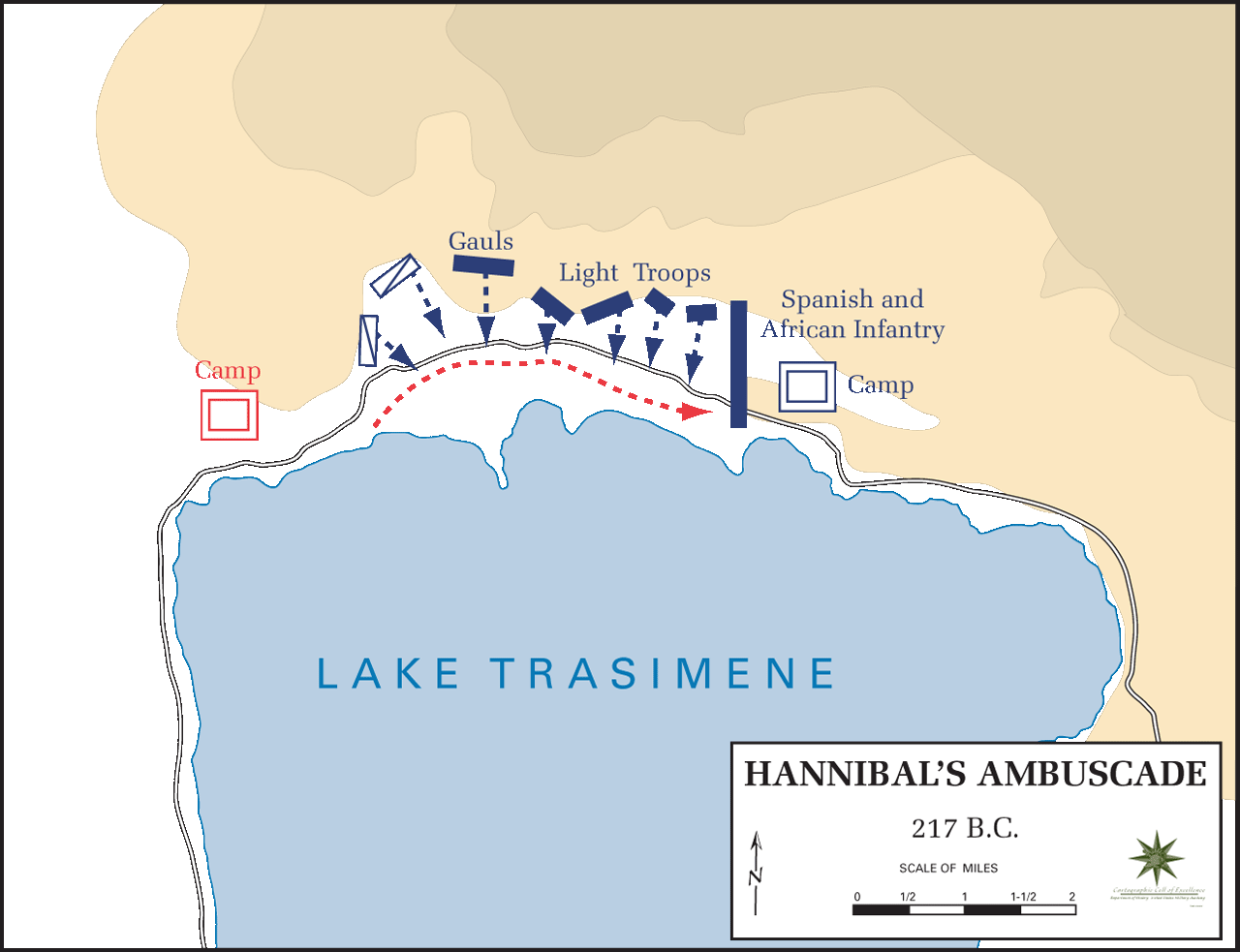
Battle of Lake Trasimene
Hannibal quartered his troops for the winter with the Gauls, whose support for him had abated. Fearing the possibility of an assassination attempt by his Gallic allies, Hannibal had a number of wigs made, dyed to suit the appearance of persons differing widely in age, and kept constantly changing them, so that any would-be assassins wouldn't recognize him. In the spring of 217 BC, Hannibal decided to find a more reliable base of operations farther south. Gnaeus Servilius and Gaius Flaminius (the new consuls of Rome) were expecting Hannibal to advance on Rome, and they took their armies to block the eastern and western routes that Hannibal could use. The only alternative route to central Italy lay at the mouth of the
The only alternative route to central Italy lay at the mouth of the Arno
The Arno is a river in the Tuscany region of Italy. It is the most important river of central Italy after the Tiber.
Source and route
The river originates on Monte Falterona in the Casentino area of the Apennines, and initially takes a ...
. This area was practically one huge marsh, and happened to be overflowing more than usual during this particular season. Hannibal knew that this route was full of difficulties, but it remained the surest and certainly the quickest way to central Italy. Polybius claims that Hannibal's men marched for four days and three nights "through a land that was under water", suffering terribly from fatigue and enforced want of sleep. He crossed without opposition over both the Apennines (during which he lost his right eye because of conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is inflammation of the outermost layer of the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelid. It makes the eye appear pink or reddish. Pain, burning, scratchiness, or itchiness may occur. The ...
) and the seemingly impassable Arno, but he lost a large part of his force in the marshy lowlands of the Arno.
He arrived in Etruria in the spring of 217 BC and decided to lure the main Roman army under Flaminius into a pitched battle by devastating the region that Flaminius had been sent to protect. As Polybius recounts, "he annibalcalculated that, if he passed the camp and made a descent into the district beyond, Flaminius (partly for fear of popular reproach and partly of personal irritation) would be unable to endure watching passively the devastation of the country but would spontaneously follow him... and give him opportunities for attack." At the same time, Hannibal tried to break the allegiance of Rome's allies by proving that Flaminius was powerless to protect them. Despite this, Flaminius remained passively encamped at Arretium. Hannibal marched boldly around Flaminius' left flank, unable to draw him into battle by mere devastation, and effectively cut him off from Rome (thus executing the first recorded turning movement In military tactics, a turning movement is a form of maneuver in which the attacking force seeks to avoid the enemy's principal defensive positions by seizing objectives behind the enemy's current positions, thereby causing the enemy force to move o ...
in military history). He then advanced through the uplands of Etruria, provoking Flaminius into a hasty pursuit and catching him in a defile on the shore of Lake Trasimenus. There Hannibal destroyed Flaminius' army in the waters or on the adjoining slopes, killing Flaminius as well (see Battle of Lake Trasimene
The Battle of Lake Trasimene was fought when a Carthaginian force under Hannibal ambushed a Roman army commanded by Gaius Flaminius on 21 June 217 BC, during the Second Punic War. It took place on the north shore of Lake Trasimene, to th ...
). This was the most costly ambush that the Romans ever sustained until the Battle of Carrhae
The Battle of Carrhae () was fought in 53 BC between the Roman Republic and the Parthian Empire near the ancient town of Carrhae (present-day Harran, Turkey). An invading force of seven legions of Roman heavy infantry under Marcus Liciniu ...
against the Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conque ...
.
Hannibal had now disposed of the only field force that could check his advance upon Rome, but he realized that, without siege engine
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while oth ...
s, he could not hope to take the capital. He opted to exploit his victory by entering into central and southern Italy and encouraging a general revolt against the sovereign power.
The Romans appointed Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus
Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus, surnamed Cunctator ( 280 – 203 BC), was a Roman statesman and general of the third century BC. He was consul five times (233, 228, 215, 214, and 209 BC) and was appointed dictator in 221 and 217 BC. He was ...
as their dictator. Departing from Roman military traditions, Fabius adopted the strategy named after him, avoiding open battle while placing several Roman armies in Hannibal's vicinity in order to watch and limit his movements.
Hannibal ravaged Apulia but was unable to bring Fabius to battle, so he decided to march through Samnium
Samnium ( it, Sannio) is a Latin exonym for a region of Southern Italy anciently inhabited by the Samnites. Their own endonyms were ''Safinim'' for the country (attested in one inscription and one coin legend) and ''Safineis'' for the The ...
to Campania
(man), it, Campana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demog ...
, one of the richest and most fertile provinces of Italy, hoping that the devastation would draw Fabius into battle. Fabius closely followed Hannibal's path of destruction, yet still refused to let himself be drawn out of the defensive. This strategy was unpopular with many Romans, who believed that it was a form of cowardice.
Hannibal decided that it would be unwise to winter in the already devastated lowlands of Campania, but Fabius had trapped him there by ensuring that all the exit passes were blocked. This situation led to the night Battle of Ager Falernus
The Battle of Ager Falernus was a skirmish during the Second Punic War between the armies of Rome and Carthage. After winning the Battle of Lake Trasimene in Italy in 217 BC, the army commanded by Hannibal marched south and reached Campania. The ...
. Hannibal had his men tie burning torches to the horns of a herd of cattle and drive them up the heights nearby. Some of the Romans, seeing a moving column of lights, were tricked into believing it was the Carthaginian army marching to escape along the heights. As they moved off in pursuit of this decoy, Hannibal managed to move his army in complete silence through the dark lowlands and up to an unguarded pass. Fabius himself was within striking distance but in this case his caution worked against him, as rightly sensing a trick he stayed put. Thus, Hannibal managed to stealthily escape with his entire army intact.
What Hannibal achieved in extricating his army was, as Adrian Goldsworthy
Adrian Keith Goldsworthy (; born 1969) is a British historian and novelist who specialises in ancient Roman history.
Education
Adrian Goldsworthy attended Westbourne School, Penarth. He then read Ancient and Modern History at St John's Colleg ...
puts it, "a classic of ancient generalship, finding its way into nearly every historical narrative of the war and being used by later military manuals". This was a severe blow to Fabius' prestige and soon after this his period of dictatorial power ended. For the winter, Hannibal found comfortable quarters in the Apulian plain.
Battle of Cannae
 In the spring of 216 BC, Hannibal took the initiative and seized the large supply depot at Cannae in the Apulian plain. By capturing Cannae, Hannibal had placed himself between the Romans and their crucial sources of supply. Once the Roman Senate resumed their consular elections in 216 BC, they appointed Gaius Terentius Varro and Lucius Aemilius Paullus (consul 219 BC), Lucius Aemilius Paullus as Roman consul, consuls. In the meantime, the Romans hoped to gain success through sheer strength and weight of numbers, and they raised a new army of unprecedented size, estimated by some to be as large as 100,000 men, but more likely around 50,000–80,000.Cottrell, Leonard, ''Enemy of Rome'', Evans Bros, 1965,
The Romans and allied legions resolved to confront Hannibal and marched southward to Apulia. They eventually found him on the left bank of the Aufidus River, and encamped away. On this occasion, the two armies were combined into one, the consuls having to alternate their command on a daily basis. According to Livy, Varro was a man of reckless and hubristic nature and it was his turn to command on the day of battle. (This account is possibly biased against Varro as its main source, Polybius, was a client of Paullus's aristocratic family whereas Varro was less distinguished. Some historians have suggested the sheer size of the army may have required both generals to command a wing each. This theory is supported by the fact that, after Varro survived the battle he was pardoned by the Senate, which would be peculiar if he were the sole commander at fault.)
Hannibal capitalized on the eagerness of the Romans and drew them into a trap by using an Pincer movement, envelopment tactic. This eliminated the Roman numerical advantage by shrinking the combat area. Hannibal drew up his least reliable infantry in the centre in a semicircle curving towards the Romans. Placing them forward of the wings allowed them room to fall back, luring the Romans after them, while the cavalry on the flanks dealt with their Roman counterparts. Hannibal's wings were composed of the Gallic and Numidian cavalry. The Roman legions forced their way through Hannibal's weak centre, but the Libyan mercenaries on the wings, swung around by the movement, menaced their flanks.
The onslaught of Hannibal's cavalry was irresistible. Hannibal's chief cavalry commander, Maharbal, led the mobile Numidian cavalry on the right; they shattered the Roman cavalry opposing them. Hannibal's Iberian and Gallic heavy cavalry on the left, led by Hanno, defeated the Roman heavy cavalry, and then both the Carthaginian heavy cavalry and the Numidians attacked the legions from behind. As a result, the Roman army was hemmed in with no means of escape.
Due to these brilliant tactics, Hannibal managed to surround and destroy all but a small remnant of his enemy, despite his own inferior numbers. Depending upon the source, it is estimated that 50,000–70,000 Romans were killed or captured. Among the dead were Roman consul Lucius Aemilius Paullus (consul 219 BC), Lucius Aemilius Paullus, two consuls for the preceding year, two quaestors, 29 of the 48 military tribunes, and an additional eighty senators (at a time when the Roman Senate was composed of no more than 300 men, this constituted 25%–30% of the governing body). This makes the battle one of the most catastrophic defeats in the history of ancient Rome, and one of the bloodiest battles in all of human history (in terms of the number of lives lost in a single day).
After Cannae, the Romans were very hesitant to confront Hannibal in pitched battle, preferring instead to weaken him by attrition, relying on their advantages of interior lines, supply, and manpower. As a result, Hannibal fought no more major battles in Italy for the rest of the war. It is believed that his refusal to bring the war to Rome itself was due to a lack of commitment from Carthage of men, money, and material — principally siege equipment. Whatever the reason, the choice prompted Maharbal to say, "Hannibal, you know how to gain a victory, but not how to use one."
As a result of this victory, many parts of Italy joined Hannibal's cause. As Polybius notes, "How much more serious was the defeat of Cannae, than those that preceded it can be seen by the behaviour of Rome's allies; before that fateful day, their loyalty remained unshaken, now it began to waver for the simple reason that they despaired of Roman Power." During that same year, the Greek cities in Sicily were induced to revolt against Roman political control, while Macedonian King Philip V of Macedon, Philip V Macedonian–Carthaginian Treaty, pledged his support to Hannibal—thus initiating the First Macedonian War against Rome. Hannibal also secured an alliance with newly appointed tyrant Hieronymus of Syracuse. It is often argued that, if Hannibal had received proper material reinforcements from Carthage, he might have succeeded with a direct attack upon Rome. Instead, he had to content himself with subduing the fortresses that still held out against him, and the only other notable event of 216 BC was the defection of certain Italian territories, including Capua, the second largest city of Italy, which Hannibal made his new base. However, only a few of the Italian city-states that he had expected to gain as allies defected to him.
In the spring of 216 BC, Hannibal took the initiative and seized the large supply depot at Cannae in the Apulian plain. By capturing Cannae, Hannibal had placed himself between the Romans and their crucial sources of supply. Once the Roman Senate resumed their consular elections in 216 BC, they appointed Gaius Terentius Varro and Lucius Aemilius Paullus (consul 219 BC), Lucius Aemilius Paullus as Roman consul, consuls. In the meantime, the Romans hoped to gain success through sheer strength and weight of numbers, and they raised a new army of unprecedented size, estimated by some to be as large as 100,000 men, but more likely around 50,000–80,000.Cottrell, Leonard, ''Enemy of Rome'', Evans Bros, 1965,
The Romans and allied legions resolved to confront Hannibal and marched southward to Apulia. They eventually found him on the left bank of the Aufidus River, and encamped away. On this occasion, the two armies were combined into one, the consuls having to alternate their command on a daily basis. According to Livy, Varro was a man of reckless and hubristic nature and it was his turn to command on the day of battle. (This account is possibly biased against Varro as its main source, Polybius, was a client of Paullus's aristocratic family whereas Varro was less distinguished. Some historians have suggested the sheer size of the army may have required both generals to command a wing each. This theory is supported by the fact that, after Varro survived the battle he was pardoned by the Senate, which would be peculiar if he were the sole commander at fault.)
Hannibal capitalized on the eagerness of the Romans and drew them into a trap by using an Pincer movement, envelopment tactic. This eliminated the Roman numerical advantage by shrinking the combat area. Hannibal drew up his least reliable infantry in the centre in a semicircle curving towards the Romans. Placing them forward of the wings allowed them room to fall back, luring the Romans after them, while the cavalry on the flanks dealt with their Roman counterparts. Hannibal's wings were composed of the Gallic and Numidian cavalry. The Roman legions forced their way through Hannibal's weak centre, but the Libyan mercenaries on the wings, swung around by the movement, menaced their flanks.
The onslaught of Hannibal's cavalry was irresistible. Hannibal's chief cavalry commander, Maharbal, led the mobile Numidian cavalry on the right; they shattered the Roman cavalry opposing them. Hannibal's Iberian and Gallic heavy cavalry on the left, led by Hanno, defeated the Roman heavy cavalry, and then both the Carthaginian heavy cavalry and the Numidians attacked the legions from behind. As a result, the Roman army was hemmed in with no means of escape.
Due to these brilliant tactics, Hannibal managed to surround and destroy all but a small remnant of his enemy, despite his own inferior numbers. Depending upon the source, it is estimated that 50,000–70,000 Romans were killed or captured. Among the dead were Roman consul Lucius Aemilius Paullus (consul 219 BC), Lucius Aemilius Paullus, two consuls for the preceding year, two quaestors, 29 of the 48 military tribunes, and an additional eighty senators (at a time when the Roman Senate was composed of no more than 300 men, this constituted 25%–30% of the governing body). This makes the battle one of the most catastrophic defeats in the history of ancient Rome, and one of the bloodiest battles in all of human history (in terms of the number of lives lost in a single day).
After Cannae, the Romans were very hesitant to confront Hannibal in pitched battle, preferring instead to weaken him by attrition, relying on their advantages of interior lines, supply, and manpower. As a result, Hannibal fought no more major battles in Italy for the rest of the war. It is believed that his refusal to bring the war to Rome itself was due to a lack of commitment from Carthage of men, money, and material — principally siege equipment. Whatever the reason, the choice prompted Maharbal to say, "Hannibal, you know how to gain a victory, but not how to use one."
As a result of this victory, many parts of Italy joined Hannibal's cause. As Polybius notes, "How much more serious was the defeat of Cannae, than those that preceded it can be seen by the behaviour of Rome's allies; before that fateful day, their loyalty remained unshaken, now it began to waver for the simple reason that they despaired of Roman Power." During that same year, the Greek cities in Sicily were induced to revolt against Roman political control, while Macedonian King Philip V of Macedon, Philip V Macedonian–Carthaginian Treaty, pledged his support to Hannibal—thus initiating the First Macedonian War against Rome. Hannibal also secured an alliance with newly appointed tyrant Hieronymus of Syracuse. It is often argued that, if Hannibal had received proper material reinforcements from Carthage, he might have succeeded with a direct attack upon Rome. Instead, he had to content himself with subduing the fortresses that still held out against him, and the only other notable event of 216 BC was the defection of certain Italian territories, including Capua, the second largest city of Italy, which Hannibal made his new base. However, only a few of the Italian city-states that he had expected to gain as allies defected to him.
Stalemate
The war in Italy settled into a strategic stalemate. The Romans used the Attrition warfare, attritional strategy that Fabius had taught them, which, they finally realized, was the only feasible means of defeating Hannibal. Indeed, Fabius received the name "Cunctator" ("the Delayer") because of his policy of not meeting Hannibal in open battle but through attrition. The Romans deprived Hannibal of a large-scale battle and instead assaulted his weakening army with multiple smaller armies in an attempt to both weary him and create unrest in his troops. For the next few years, Hannibal was forced to sustain a scorched earth policy and obtain local provisions for protracted and ineffectual operations throughout southern Italy. His immediate objectives were reduced to minor operations centred mainly around the cities ofCampania
(man), it, Campana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demog ...
.
The forces detached to his lieutenants were generally unable to hold their own, and neither his home government nor his new ally Philip V of Macedon helped to make up his losses. His position in southern Italy, therefore, became increasingly difficult and his chance of ultimately conquering Rome grew ever more remote. Hannibal still won a number of notable victories: completely destroying two Roman armies in 212 BC, and killing two consuls (including the famed Marcus Claudius Marcellus) in a battle in 208 BC. However, Hannibal slowly began losing ground—inadequately supported by his Italian allies, abandoned by his government (either because of jealousy or simply because Carthage was overstretched), and unable to match Rome's resources. He was never able to bring about another grand decisive victory that could produce a lasting strategic change.
Carthaginian political will was embodied in the ruling oligarchy. There was a Carthaginian Senate, but the real power was with the inner "Council of 30 Nobles" and the board of judges from ruling families known as the "Hundred and Four". These two bodies came from the wealthy, commercial families of Carthage. Two political factions operated in Carthage: the war party, also known as the "Barcids" (Hannibal's family name), and the peace party led by Hanno the Great#Hanno II the Great, Hanno II the Great. Hanno had been instrumental in denying Hannibal's requested reinforcements following the battle at Cannae.
Hannibal started the war without the full backing of Carthaginian oligarchy. His attack of Saguntum had presented the oligarchy with a choice of war with Rome or loss of prestige in Iberia. The oligarchy, not Hannibal, controlled the strategic resources of Carthage. Hannibal constantly sought reinforcements from either Iberia or North Africa. Hannibal's troops who were lost in combat were replaced with less well-trained and motivated mercenaries from Italy or Gaul. The commercial interests of the Carthaginian oligarchy dictated the reinforcement and supply of Iberia rather than Hannibal throughout the campaign.
Hannibal's retreat in Italy
 In March 212 BC, Hannibal Battle of Tarentum (212 BC), captured Taranto, Tarentum in a surprise attack but he failed to obtain control of its harbour. The tide was slowly turning against him, and in favour of Rome.
The Roman consuls mounted a Battle of Capua, siege of Capua in 212 BC. Hannibal attacked them, forcing their withdrawal from Campania. He moved to Lucania and destroyed a 16,000-man Roman army at the Battle of the Silarus, with 15,000 Romans killed. Another opportunity presented itself soon after, a Roman army of 18,000 men being destroyed by Hannibal at the Battle of Herdonia (212 BC), first battle of Herdonia with 16,000 Romans dead, freeing Apulia from the Romans for the year. The Roman consuls mounted another Battle of Capua (211 BC), siege of Capua in 211 BC, conquering the city. Hannibal attempted to lift the siege with an assault on the Roman siege lines but failed. He marched on Rome to force the recall of the Roman armies. He drew off 15,000 Roman soldiers, but the siege continued and Capua fell. In 212 BC, Marcellus Siege of Syracuse (213–212 BC), conquered Syracuse and the Romans destroyed the Carthaginian army in Sicily in 211–210 BC. In 210 BC, the Romans entered into an alliance with the Aetolian League to counter Philip V of Macedon. Philip, who attempted to exploit Rome's preoccupation in Italy to conquer Illyria, now found himself under attack from several sides at once and was quickly subdued by Rome and her Greek allies.
In 210 BC, Hannibal again proved his superiority in tactics by inflicting a severe defeat at the Battle of Herdonia (210 BC), Battle of Herdonia (modern Ordona) in Apulia upon a proconsular army and, in 208 BC, destroyed a Roman force engaged in the siege of Locri at the Battle of Petelia. But with the loss of Tarentum in 209 BC and the gradual reconquest by the Romans of
In March 212 BC, Hannibal Battle of Tarentum (212 BC), captured Taranto, Tarentum in a surprise attack but he failed to obtain control of its harbour. The tide was slowly turning against him, and in favour of Rome.
The Roman consuls mounted a Battle of Capua, siege of Capua in 212 BC. Hannibal attacked them, forcing their withdrawal from Campania. He moved to Lucania and destroyed a 16,000-man Roman army at the Battle of the Silarus, with 15,000 Romans killed. Another opportunity presented itself soon after, a Roman army of 18,000 men being destroyed by Hannibal at the Battle of Herdonia (212 BC), first battle of Herdonia with 16,000 Romans dead, freeing Apulia from the Romans for the year. The Roman consuls mounted another Battle of Capua (211 BC), siege of Capua in 211 BC, conquering the city. Hannibal attempted to lift the siege with an assault on the Roman siege lines but failed. He marched on Rome to force the recall of the Roman armies. He drew off 15,000 Roman soldiers, but the siege continued and Capua fell. In 212 BC, Marcellus Siege of Syracuse (213–212 BC), conquered Syracuse and the Romans destroyed the Carthaginian army in Sicily in 211–210 BC. In 210 BC, the Romans entered into an alliance with the Aetolian League to counter Philip V of Macedon. Philip, who attempted to exploit Rome's preoccupation in Italy to conquer Illyria, now found himself under attack from several sides at once and was quickly subdued by Rome and her Greek allies.
In 210 BC, Hannibal again proved his superiority in tactics by inflicting a severe defeat at the Battle of Herdonia (210 BC), Battle of Herdonia (modern Ordona) in Apulia upon a proconsular army and, in 208 BC, destroyed a Roman force engaged in the siege of Locri at the Battle of Petelia. But with the loss of Tarentum in 209 BC and the gradual reconquest by the Romans of Samnium
Samnium ( it, Sannio) is a Latin exonym for a region of Southern Italy anciently inhabited by the Samnites. Their own endonyms were ''Safinim'' for the country (attested in one inscription and one coin legend) and ''Safineis'' for the The ...
and Lucania, his hold on south Italy was almost lost. In 207 BC, he succeeded in making his way again into Apulia, where he waited to concert measures for a combined march upon Rome with his brother Hasdrubal Hasdrubal ( grc-gre, Ἀσδρούβας, ''Hasdroúbas'') is the Latinized form of the Carthaginian name ʿAzrubaʿal ( xpu, 𐤏𐤆𐤓𐤁𐤏𐤋 , , "Help of Baal").
It may refer to:
* Hasdrubal I of Carthage was the Magonid king of Ancien ...
. On hearing, however, of his brother's defeat and death at the battle of the Metaurus, he retired to Calabria, where he maintained himself for the ensuing years. His brother's head had been cut off, carried across Italy, and tossed over the palisade of Hannibal's camp as a cold message of the iron-clad will of the Roman Republic. The combination of these events marked the end to Hannibal's success in Italy. With the failure of his brother Mago in Liguria (205–203 BC) and of his own negotiations with Phillip V, the last hope of recovering his ascendancy in Italy was lost. In 203 BC, after nearly fifteen years of fighting in Italy and with the military fortunes of Carthage rapidly declining, Hannibal was recalled to Carthage to direct the defence of his native country against a Roman invasion under Scipio Africanus.
Conclusion of the Second Punic War (203–201 BC)
Return to Carthage
 In 203 BC, Hannibal was recalled from Italy by the war party in Carthage. After leaving a record of his expedition engraved in Punic language, Punic and Greek language, Greek upon bronze tablets in the Temple of Juno Lacinia (Crotone), Temple of Juno Lacinia at Crotone, Crotona, he sailed back to Africa. His arrival immediately restored the predominance of the war party, which placed him in command of a combined force of African conscription, levies and his mercenaries from Italy. In 202 BC, Hannibal met Scipio in a fruitless peace conference. Despite mutual admiration, negotiations floundered due to Roman allegations of "Punic Faith," referring to the breach of protocols that ended the First Punic War by the Carthaginian attack on Saguntum, and a Carthaginian attack on a stranded Roman fleet. Scipio and Carthage had worked out a peace plan, which was approved by Rome. The terms of the treaty were quite modest, but the war had been long for the Romans. Carthage could keep its African territory but would lose its overseas empire. Masinissa ( Numidia) was to be independent. Also, Carthage was to reduce its fleet and pay a war indemnity. But Carthage then made a terrible blunder. Its long-suffering citizens had captured a stranded Roman fleet in the Gulf of Tunis and stripped it of supplies, an action that aggravated the faltering negotiations. Fortified by both Hannibal and the supplies, the Carthaginians rebuffed the treaty and Roman protests. The decisive battle of Zama soon followed; the defeat removed Hannibal's air of invincibility.
In 203 BC, Hannibal was recalled from Italy by the war party in Carthage. After leaving a record of his expedition engraved in Punic language, Punic and Greek language, Greek upon bronze tablets in the Temple of Juno Lacinia (Crotone), Temple of Juno Lacinia at Crotone, Crotona, he sailed back to Africa. His arrival immediately restored the predominance of the war party, which placed him in command of a combined force of African conscription, levies and his mercenaries from Italy. In 202 BC, Hannibal met Scipio in a fruitless peace conference. Despite mutual admiration, negotiations floundered due to Roman allegations of "Punic Faith," referring to the breach of protocols that ended the First Punic War by the Carthaginian attack on Saguntum, and a Carthaginian attack on a stranded Roman fleet. Scipio and Carthage had worked out a peace plan, which was approved by Rome. The terms of the treaty were quite modest, but the war had been long for the Romans. Carthage could keep its African territory but would lose its overseas empire. Masinissa ( Numidia) was to be independent. Also, Carthage was to reduce its fleet and pay a war indemnity. But Carthage then made a terrible blunder. Its long-suffering citizens had captured a stranded Roman fleet in the Gulf of Tunis and stripped it of supplies, an action that aggravated the faltering negotiations. Fortified by both Hannibal and the supplies, the Carthaginians rebuffed the treaty and Roman protests. The decisive battle of Zama soon followed; the defeat removed Hannibal's air of invincibility.
Battle of Zama (202 BC)
Unlike most battles of the Second Punic War, at Zama the Romans were superior in cavalry and the Carthaginians had the edge in infantry. This Roman cavalry superiority was due to the betrayal of Masinissa, who had earlier assisted Carthage in Iberia but changed sides in 206 BC with the promise of land, and due to his personal conflicts with Syphax, a Carthaginian ally. Although the ageing Hannibal was suffering from mental exhaustion and deteriorating health after years of campaigning in Italy, the Carthaginians still had the advantage in numbers and were boosted by the presence of 80 war elephants. The Roman cavalry won an early victory by swiftly routing the Carthaginian horse and because standard Roman tactics for limiting the effectiveness of the Carthaginian war elephants were successful, including playing trumpets to frighten the elephants into running into the Carthaginian lines. Some historians say that the elephants routed the Carthaginian cavalry and not the Romans, whilst others suggest that it was actually a tactical retreat planned by Hannibal. Whatever the truth, the battle remained closely fought. At one point, it seemed that Hannibal was on the verge of victory, but Scipio was able to rally his men, and his cavalry, having routed the Carthaginian cavalry, attacked Hannibal's rear. This two-pronged attack caused the Carthaginian formation to collapse.
With their foremost general defeated, the Carthaginians had no choice but to surrender. Carthage lost approximately 20,000 troops with an additional 15,000 wounded. In contrast, the Romans suffered only 2,500 casualties. The last major battle of the Second Punic War resulted in a loss of respect for Hannibal by his fellow Carthaginians. The conditions of defeat were such that Carthage could no longer battle for Mediterranean supremacy.
The Roman cavalry won an early victory by swiftly routing the Carthaginian horse and because standard Roman tactics for limiting the effectiveness of the Carthaginian war elephants were successful, including playing trumpets to frighten the elephants into running into the Carthaginian lines. Some historians say that the elephants routed the Carthaginian cavalry and not the Romans, whilst others suggest that it was actually a tactical retreat planned by Hannibal. Whatever the truth, the battle remained closely fought. At one point, it seemed that Hannibal was on the verge of victory, but Scipio was able to rally his men, and his cavalry, having routed the Carthaginian cavalry, attacked Hannibal's rear. This two-pronged attack caused the Carthaginian formation to collapse.
With their foremost general defeated, the Carthaginians had no choice but to surrender. Carthage lost approximately 20,000 troops with an additional 15,000 wounded. In contrast, the Romans suffered only 2,500 casualties. The last major battle of the Second Punic War resulted in a loss of respect for Hannibal by his fellow Carthaginians. The conditions of defeat were such that Carthage could no longer battle for Mediterranean supremacy.
Later career
Peacetime Carthage (200–196 BC)
 Hannibal was still only 46 at the conclusion of the Second Punic War in 201 BC and soon showed that he could be a statesman as well as a soldier. Following the conclusion of a peace that left Carthage saddled with an indemnity of ten thousand Attic talent, talents, he was elected shophet, suffete (chief magistrate) of the Carthaginian state.Gavin de Beer, De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). ''Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy'' p.291. After an audit confirmed Carthage had the resources to pay the indemnity without increasing taxation, Hannibal initiated a reorganization of state finances aimed at eliminating corruption and recovering embezzled funds., by Livy
The principal beneficiaries of these financial peculations had been the oligarchs of the Hundred and Four. In order to reduce the power of the oligarchs, Hannibal passed a law stipulating the Hundred and Four be chosen by direct election rather than co-option. He also used citizen support to change the term of office in the Hundred and Four from life to a year, with none permitted to "hold office for two consecutive years."
Hannibal was still only 46 at the conclusion of the Second Punic War in 201 BC and soon showed that he could be a statesman as well as a soldier. Following the conclusion of a peace that left Carthage saddled with an indemnity of ten thousand Attic talent, talents, he was elected shophet, suffete (chief magistrate) of the Carthaginian state.Gavin de Beer, De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). ''Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy'' p.291. After an audit confirmed Carthage had the resources to pay the indemnity without increasing taxation, Hannibal initiated a reorganization of state finances aimed at eliminating corruption and recovering embezzled funds., by Livy
The principal beneficiaries of these financial peculations had been the oligarchs of the Hundred and Four. In order to reduce the power of the oligarchs, Hannibal passed a law stipulating the Hundred and Four be chosen by direct election rather than co-option. He also used citizen support to change the term of office in the Hundred and Four from life to a year, with none permitted to "hold office for two consecutive years."
Exile (after 195 BC)
Seven years after the victory of Zama, the Romans, alarmed by Carthage's renewed prosperity and suspicious that Hannibal had been in contact with Antiochus III the Great, Antiochus III of the Seleucid Empire, sent a delegation to Carthage alleging that Hannibal was helping an enemy of Rome.Gavin de Beer, De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). ''Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy'' p.296. Aware that he had many enemies, not least of which due to his financial reforms eliminating opportunities for oligarchical graft, Hannibal fled into voluntary exile before the Romans could demand that Carthage surrender him into their custody. He journeyed first to Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre, the mother city of Carthage, and then to Antioch, before he finally reached Ephesus, where he was honourably received by Antiochus. Livy states that the Seleucid king consulted Hannibal on the strategic concerns of making war on Rome. According to Cicero, while at the court of Antiochus, Hannibal attended a lecture by Phormio, a philosopher, that ranged through many topics. When Phormio finished a discourse on the duties of a general, Hannibal was asked his opinion. He replied, "I have seen during my life many old fools; but this one beats them all." Another story, according to Aulus Gellius, is that after Antiochus III showed off the gigantic and elaborately equipped army he had created to invade Greece to Hannibal, he asked him if they would be enough for the Roman Republic, to which Hannibal replied, "I think all this will be enough, yes, quite enough, for the Romans, even though they are most avaricious." In the summer of 193 BC, tensions flared up between the Seleucids and Rome. Antiochus gave tacit support to Hannibal's plans of launching an anti-Roman coup d'état in Carthage, yet it was not carried out. The Carthaginian general also advised equipping a fleet and landing a body of troops in the south of Italy, offering to take command himself. In 190 BC, after having suffered a series of defeats in the Roman–Seleucid War, Antiochus gave Hannibal his first significant military command after spending five years in the Seleucid court. Hannibal was tasked with building a fleet in Cilicia from scratch. Although Phoenician territories like Tyre and Sidon possessed the necessary combination of raw materials, technical expertise, and experienced personnel, it took much longer than expected for it to be completed, most likely due to wartime shortages. In July 190 BC, Hannibal ordered his fleet to set sail from Seleucia Pieria along the southern Asia Minor coast in order to reinforce the rest of the Seleucid navy at Ephesus. The following month Hannibal's fleet clashed with the Rhodes, Rhodian navy in the Battle of Side. The faster Rhodian ships managed to heavily damage half of Hannibal's warships through the manoeuvre, forcing him to retreat. Hannibal had preserved most of his fleet; however, he was in no position to unite with Polyxenidas' fleet at Ephesus since his ships required lengthy repairs. The ensuing Battle of Myonessus resulted in a Roman-Rhodian victory, which cemented Roman control over the Aegean Sea, enabling them to launch an invasion of Seleucid Asia Minor. The two armies faced off in the
In July 190 BC, Hannibal ordered his fleet to set sail from Seleucia Pieria along the southern Asia Minor coast in order to reinforce the rest of the Seleucid navy at Ephesus. The following month Hannibal's fleet clashed with the Rhodes, Rhodian navy in the Battle of Side. The faster Rhodian ships managed to heavily damage half of Hannibal's warships through the manoeuvre, forcing him to retreat. Hannibal had preserved most of his fleet; however, he was in no position to unite with Polyxenidas' fleet at Ephesus since his ships required lengthy repairs. The ensuing Battle of Myonessus resulted in a Roman-Rhodian victory, which cemented Roman control over the Aegean Sea, enabling them to launch an invasion of Seleucid Asia Minor. The two armies faced off in the Battle of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of Pe ...
, north-east of Magnesia ad Sipylum. The battle resulted in a decisive Roman-Pergamene victory. The truce was signed at Sardes in January 189 BC, whereupon Antiochus agreed to abandon his claims on all lands west of the Taurus Mountains, paid a heavy war indemnity and promised to hand over Hannibal and other notable enemies of Rome from among his allies.
According to Strabo and Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
, Hannibal also received hospitality at the Armenian royal court of Artaxias I. The authors add an apocryphal story of how Hannibal planned and supervised the building of the new royal capital Artaxata. Suspicious that Antiochus was prepared to surrender him to the Romans, Hannibal fled to Crete, but he soon went back to Anatolia and sought refuge with Prusias I of Bithynia, who was engaged in warfare with Rome's ally, Eumenes II, King Eumenes II of Pergamon. Hannibal went on to serve Prusias in this war. During one of the naval victories he gained over Eumenes, Hannibal had large pots filled with venomous snakes thrown onto Eumenes' ships. Hannibal also went on to defeat Eumenes in two other battles on land.Cornelius Nepos, ''Hannibal'' 12.
Death (183–181 BC)
At this stage, the Romans intervened and threatened Bithynia into giving up Hannibal. Prusias I of Bithynia, Prusias agreed, but the general was determined not to fall into his enemy's hands. The precise year and cause of Hannibal's death are unknown. Pausanias wrote that Hannibal's death occurred after his finger was wounded by his drawn sword while mounting his horse, resulting in a fever and then his death three days later. Cornelius Nepos andLivy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
, however, tell a different story, namely that the ex-consul Titus Quinctius Flamininus, on discovering that Hannibal was in Bithynia, went there in an embassy to demand his surrender from King Prusias I of Bithynia, Prusias. Hannibal, discovering that the castle where he was living was surrounded by Roman soldiers and he could not escape, took poison. Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἀππιανὸς Ἀλεξανδρεύς ''Appianòs Alexandreús''; la, Appianus Alexandrinus; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who flourished during the reigns of Emperors of Rome Trajan, Ha ...
writes that it was Prusias who poisoned Hannibal.
Pliny the Elder and Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
, in his life of Flamininus, record that Hannibal's tomb was at Libyssa on the coast of the Sea of Marmara. According to some, Libyssa was sited at Gebze (between Bursa and Üskudar), but W. M. Leake, identifying Gebze with ancient Dakibyza, placed it further west. Before dying, Hannibal is said to have left behind a letter declaring, "Let us relieve the Romans from the anxiety they have so long experienced, since they think it tries their patience too much to wait for an old man's death".
Appian wrote of a prophecy about Hannibal's death, which stated that "Libyssan earth shall cover Hannibal's remains." This, he wrote, made Hannibal believe that he would die in Libya, but instead, it was at the Bithynian Libyssa that he would die.
In his ''Annales'', Titus Pomponius Atticus reports that Hannibal's death occurred in 183 BC,Cornelius Nepos, ''Hannibal'' 13.1 and Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
implies the same. Polybius, who wrote nearest the event, gives 182 BC. Sulpicius Blitho records the death under 181 BC.
Legacy
Ancient world
Hannibal caused great distress to many in Roman society. He became such a figure of terror that, whenever disaster struck, the Roman senators would exclaim "''List of Latin phrases: H#Hannibal ad portas, Hannibal ad portas''" ("Hannibal is at the gates!") to express their fear or anxiety. This famous Latin phrase became a common expression that is often still used when a client arrives through the door or when one is faced with calamity. His legacy would be recorded by his Greek tutor, Sosylus of Lacedaemon. The works of Roman writers such asLivy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
(64 or 59 BC – AD 12 or 17), Frontinus ( AD 40–103), and Juvenal (1st–2nd century AD) show a grudging admiration for Hannibal. The Romans even built statues of the Carthaginian in the streets of Rome to advertise their defeat of such a worthy adversary. It is plausible to suggest that Hannibal engendered the greatest fear Rome had towards an enemy. Nevertheless, the Romans grimly refused to admit the possibility of defeat and rejected all overtures for peace; they even refused to accept the ransom of prisoners after Cannae.
During the war there are no reports of revolutions among the Roman citizens, no factions within the Senate desiring peace, no pro-Carthaginian Roman turncoats, no coups. Indeed, throughout the war Roman aristocrats ferociously competed with each other for positions of command to fight against Rome's most dangerous enemy. Hannibal's military genius was not enough to really disturb the Roman political process and the collective political and military capacity of the Roman people. As Lazenby states,
It says volumes, too, for their political maturity and respect for constitutional forms that the complicated machinery of government continued to function even amidst disaster—there are few states in the ancient world in which a general who had lost a battle like Cannae would have dared to remain, let alone would have continued to be treated respectfully as head of state.According to the historian Livy, the Romans feared Hannibal's military genius, and during Hannibal's march against Rome in 211 BC
a messenger who had travelled from Fregellae for a day and a night without stopping created great alarm in Rome, and the excitement was increased by people running about the City with wildly exaggerated accounts of the news he had brought. The wailing cry of the Women in ancient Rome, matrons was heard everywhere, not only in private houses but even in the temples. Here they knelt and swept the temple-floors with their dishevelled hair and lifted up their hands to heaven in piteous entreaty to the gods that they would deliver the City of Rome out of the hands of the enemy and preserve its mothers and children from injury and outrage.In the Senate the news was "received with varying feelings as men's temperaments differed," so it was decided to keep Capua under siege, but to send 15,000 infantry and 1,000 cavalry as reinforcements to Rome. According to Livy, the land occupied by Hannibal's army outside Rome in 211 BC was sold by a Roman while it was occupied. This may not be true, but as Lazenby states, "could well be, exemplifying as it does not only the supreme confidence felt by the Romans in ultimate victory, but also the way in which something like normal life continued." After Cannae the Romans showed a considerable steadfastness in adversity. An undeniable proof of Rome's confidence is demonstrated by the fact that after the Cannae disaster she was left virtually defenseless, but the Senate still chose not to withdraw a single garrison from an overseas province to strengthen the city. In fact, they were reinforced and the campaigns there maintained until victory was secured; beginning first in Sicily under the direction of Claudius Marcellus, and later in
Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hisp ...
under Scipio Africanus. Although the long-term consequences of Hannibal's war are debatable, this war was undeniably Rome's "finest hour".
Most of the sources available to historians about Hannibal are from Romans. They considered him the greatest enemy Rome had ever faced. Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
gives us the idea that Hannibal was extremely cruel. Even Cicero, when he talked of Rome and its two great enemies, spoke of the "honourable" Pyrrhus and the "cruel" Hannibal. Yet a different picture sometimes emerges. When Hannibal's successes had brought about the death of two Roman consul
A consul held the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC), and ancient Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum'' (an ascending sequence of public offices to which politic ...
s, he vainly searched for the body of Gaius Flaminius (consul 223 BC), Gaius Flaminius on the shores of Lake Trasimeno, Lake Trasimene, held ceremonial rituals in recognition of Lucius Aemilius Paullus (General), Lucius Aemilius Paullus, and sent Marcus Claudius Marcellus, Marcellus' ashes back to his family in Rome. Any bias attributed to Polybius, however, is more troublesome. Ronald J. Mellor, Ronald Mellor considered the Greek scholar a loyal partisan of Scipio Aemilianus, while H. Ormerod does not view him as an "altogether unprejudiced witness" when it came to his pet peeves, the Aetolians, the Carthaginians, and the Cretans. Nonetheless, Polybius did recognize that the reputation for cruelty the Romans attached to Hannibal might in reality have been due to mistaking him for one of his officers, Hannibal Monomachus.
Military history
 Hannibal is generally regarded as one of the best military strategists and tacticians of all time, the double envelopment at Cannae an enduring legacy of tactical brilliance. According to
Hannibal is generally regarded as one of the best military strategists and tacticians of all time, the double envelopment at Cannae an enduring legacy of tactical brilliance. According to Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἀππιανὸς Ἀλεξανδρεύς ''Appianòs Alexandreús''; la, Appianus Alexandrinus; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who flourished during the reigns of Emperors of Rome Trajan, Ha ...
, several years after the Second Punic War, Hannibal served as a political advisor in the Seleucid Kingdom and Scipio Africanus, Scipio arrived there on a diplomatic mission from Rome.
Military academies all over the world continue to study Hannibal's exploits, especially his victory at Cannae.
Maximilian Otto Bismarck Caspari, in his article in the Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition (1910–1911), praises Hannibal in these words:
Even the Roman chroniclers acknowledged Hannibal's supreme military leadership, writing that "he never required others to do what he could not and would not do himself". According to Polybius 23, 13, p. 423:
In modern Tunisia
Due to his origin and connection with the territory belongs to modern-day Tunisia, he is widely revered as a national hero in the Arab nation. Hannibal's profile appears on the Tunisian dinar, Tunisian five-dinar bill issued on 8 November 1993, as well as on another new bill put into circulation on 20 March 2013. His name also appears in that of a private television channel, Hannibal TV. A street in Carthage (municipality), Carthage, located near the Punic ports, bears his name; as does as a station on the Tunis-Goulette-Marsa, TGM railway line: "Carthage Hannibal". Plans envisage a mausoleum and a high colossus (disambiguation), colossus of Hannibal on the Byrsa, the highest point of Carthage overlooking Tunis.Other
 The teenaged Sigmund Freud regarded Hannibal as a "hero"; the founder of psychoanalysis portrays an idealized image of the Carthaginian general in his analysis of his "dreams of Rome" in ''The Interpretation of Dreams''. Freud then associates this phenomenon with the adage "All roads lead to Rome". He writes in ''The Interpretation of Dreams'': "Hannibal and Rome symbolized for the adolescent that I was the opposition between the tenacity of Judaism and the organizing spirit of the Catholic Church".
A fictional opera called ''Hannibal'' appears at the beginning of the musical The Phantom of the Opera (1986 musical), ''Phantom Of The Opera''.
Kocaeli Province, Kocaeli in Turkey has a cenotaph built in Hannibal's memory. Even though the location of Hannibal's tomb could not be determined precisely in the studies carried out due to Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, Atatürk's great interest, a monumental cenotaph was built in the south of present-day Gebze as an expression of Atatürk's will and Atatürk's respect for Hannibal.
Since 2011, Hannibal has appeared as one of the main characters, with Scipio Africanus, of the ''Ad Astra'' manga in which Mihachi Kagano traces the course of the Second Punic War. The two generals appear as allies in the ''Drifters (manga), Drifters'' manga, having been teleported to another dimension to wage war together.
Tunisia national football team, Tunisia's home and away kit for the 2022 FIFA World Cup was inspired by the Ksour Essef cuirass, a piece of body armor believed to be worn by Carthaginian soldiers under the command of general Hannibal.
The teenaged Sigmund Freud regarded Hannibal as a "hero"; the founder of psychoanalysis portrays an idealized image of the Carthaginian general in his analysis of his "dreams of Rome" in ''The Interpretation of Dreams''. Freud then associates this phenomenon with the adage "All roads lead to Rome". He writes in ''The Interpretation of Dreams'': "Hannibal and Rome symbolized for the adolescent that I was the opposition between the tenacity of Judaism and the organizing spirit of the Catholic Church".
A fictional opera called ''Hannibal'' appears at the beginning of the musical The Phantom of the Opera (1986 musical), ''Phantom Of The Opera''.
Kocaeli Province, Kocaeli in Turkey has a cenotaph built in Hannibal's memory. Even though the location of Hannibal's tomb could not be determined precisely in the studies carried out due to Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, Atatürk's great interest, a monumental cenotaph was built in the south of present-day Gebze as an expression of Atatürk's will and Atatürk's respect for Hannibal.
Since 2011, Hannibal has appeared as one of the main characters, with Scipio Africanus, of the ''Ad Astra'' manga in which Mihachi Kagano traces the course of the Second Punic War. The two generals appear as allies in the ''Drifters (manga), Drifters'' manga, having been teleported to another dimension to wage war together.
Tunisia national football team, Tunisia's home and away kit for the 2022 FIFA World Cup was inspired by the Ksour Essef cuirass, a piece of body armor believed to be worn by Carthaginian soldiers under the command of general Hannibal.
Timeline
See also
* Hannibal (given name), Other Hannibals in Carthaginian history * Military of Carthage * Alaric I * Arminius * Attila * Bato the Daesitiate * Boiorix * Brennus (leader of the Senones) * Mithridates VI of Pontus * Odoacer * Gaiseric * Septimius Severus, who refurbished Hannibal's tomb * Spartacus * Theodoric the GreatReferences
Citations
Sources
* *Further reading
* * * ; UK edition: London, Macmillan, 1981. * * * * * * * * * . * * * * * * *online review
* * * * *
External links
- translated by J.C. Rolfe
''Hannibal''
by Jacob Abbott
Hannibal's life by Cornelius Nepos, Latin transcription and translation to German
The History of Hannibal
{{Authority control Hannibal, 3rd-century BC Punic people 2nd-century BC Punic people 247 BC births 180s BC deaths Ancient people who committed suicide Carthaginian commanders of the Second Punic War Carthaginian generals Marching Military personnel who committed suicide Politicians who committed suicide Suicides by poison Suicides in Turkey