Hanford Site on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Hanford Site is a decommissioned nuclear production complex operated by the United States federal government on the
The Hanford Site is a decommissioned nuclear production complex operated by the United States federal government on the
 The Hanford Site occupies roughly equivalent to half the total area of
The Hanford Site occupies roughly equivalent to half the total area of
National Register of Historic Places.)
/ref> In 1855

 The
The
 The construction workforce peaked at 45,096 on June 21, 1944. About thirteen percent were women, and non-whites made up 16.45 percent. African-Americans lived in segregated quarters, had their own
The construction workforce peaked at 45,096 on June 21, 1944. About thirteen percent were women, and non-whites made up 16.45 percent. African-Americans lived in segregated quarters, had their own
 Construction of the nuclear facilities proceeded rapidly. Before the end of the war in August 1945, the HEW built 554 buildings at Hanford, including three nuclear reactors (105B, 105D, and 105F) and three plutonium processing plants (221T, 221B, and 221U). The project required of roads, of railway, and four electrical substations. The HEW used of concrete and of structural steel.
Construction on B Reactor commenced in August 1943 and was completed on September 13, 1944. The reactor went Critical mass, critical in late September and, after overcoming neutron poisoning, produced its first plutonium on November 6, 1944. The reactors were Nuclear graphite, graphite moderated and water cooled. They consisted of a , graphite cylinder lying on its side, penetrated horizontally through its entire length by 2,004 aluminum tubes. containing of uranium slugs. They had no moving parts; the only sounds were those of the water pumps. Cooling water was pumped through the tubes at the rate of . This was enough water for a city of a million people.
Construction of the nuclear facilities proceeded rapidly. Before the end of the war in August 1945, the HEW built 554 buildings at Hanford, including three nuclear reactors (105B, 105D, and 105F) and three plutonium processing plants (221T, 221B, and 221U). The project required of roads, of railway, and four electrical substations. The HEW used of concrete and of structural steel.
Construction on B Reactor commenced in August 1943 and was completed on September 13, 1944. The reactor went Critical mass, critical in late September and, after overcoming neutron poisoning, produced its first plutonium on November 6, 1944. The reactors were Nuclear graphite, graphite moderated and water cooled. They consisted of a , graphite cylinder lying on its side, penetrated horizontally through its entire length by 2,004 aluminum tubes. containing of uranium slugs. They had no moving parts; the only sounds were those of the water pumps. Cooling water was pumped through the tubes at the rate of . This was enough water for a city of a million people.
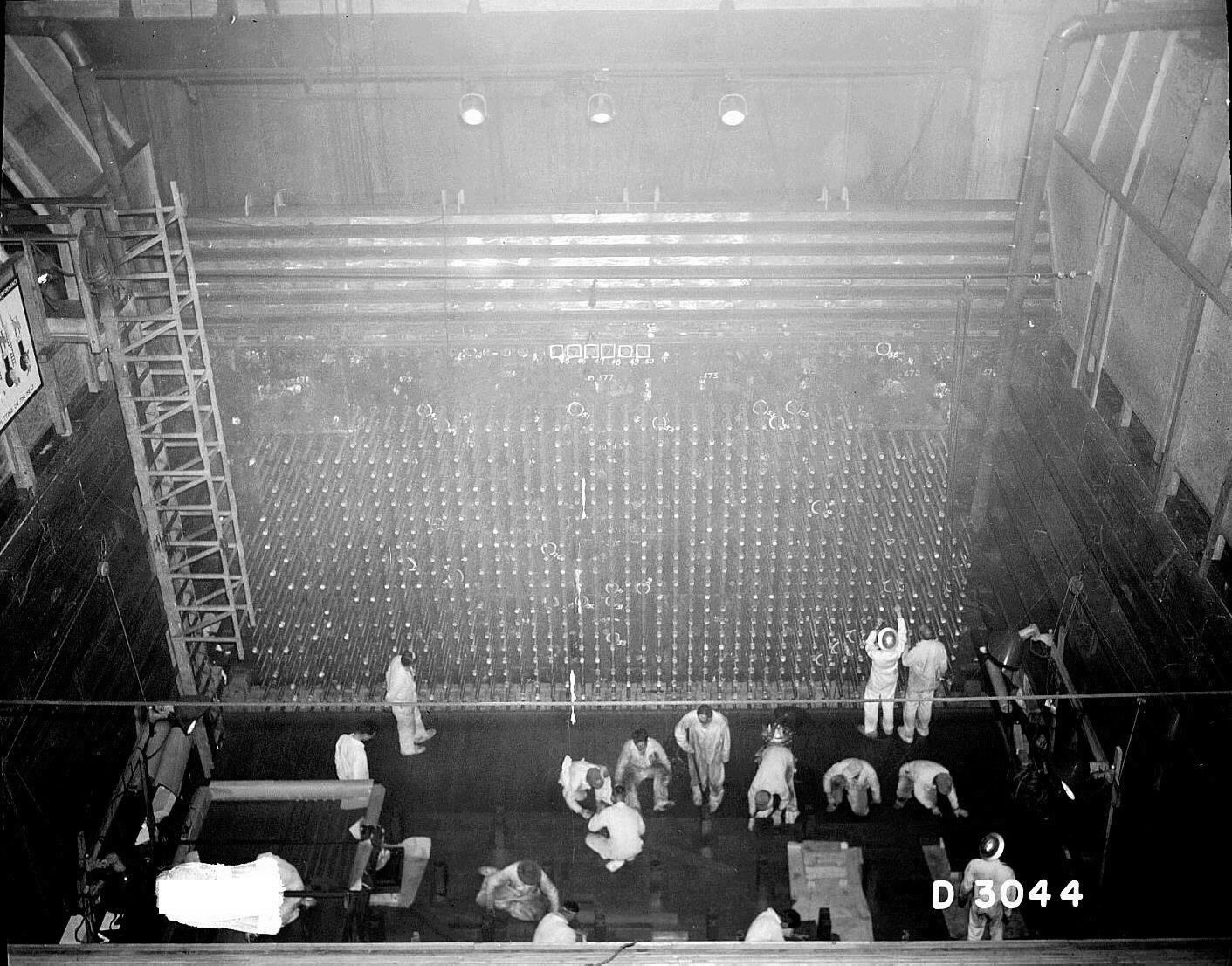 Irradiated fuel slugs were transported by rail to huge remotely operated chemical separation plants about away on a special railroad car operated by remote control. The separation buildings were massive windowless concrete structures, long, high and wide, with concrete walls thick. Inside the buildings were canyons and galleries where Bismuth-phosphate process, a series of chemical processing steps separated the small amount of plutonium from the remaining uranium and fission products.
Items were moved about with a long overhead crane. Once they began processing irradiated slugs, the machinery became so radioactive that it would be unsafe for humans ever to come in contact with it, so the engineers devised methods to allow for the replacement of components via remote control. Periscopes and closed-circuit television gave the operator a view of the process. They assembled the equipment by remote control as if the area was already radioactive. To receive the radioactive wastes from the chemical separations process, there were "tank farms" consisting of 64 single-shell underground waste tanks.
The first batch of plutonium was refined in the 221T plant from December 26, 1944, to February 2, 1945, and delivered to the Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos laboratory in New Mexico on February 5, 1945. Two identical reactors, DReactor and FReactor, came online on December 5, 1944, and February 15, 1945, respectively, and all three reactors were running at full power (250 megawatts) by March 8, 1945. By April kilogram-quantity shipments of plutonium were headed to Los Alamos. Road convoys replaced the trains in May, and in late July shipments began being dispatched by air from the airport at Hanford.
Irradiated fuel slugs were transported by rail to huge remotely operated chemical separation plants about away on a special railroad car operated by remote control. The separation buildings were massive windowless concrete structures, long, high and wide, with concrete walls thick. Inside the buildings were canyons and galleries where Bismuth-phosphate process, a series of chemical processing steps separated the small amount of plutonium from the remaining uranium and fission products.
Items were moved about with a long overhead crane. Once they began processing irradiated slugs, the machinery became so radioactive that it would be unsafe for humans ever to come in contact with it, so the engineers devised methods to allow for the replacement of components via remote control. Periscopes and closed-circuit television gave the operator a view of the process. They assembled the equipment by remote control as if the area was already radioactive. To receive the radioactive wastes from the chemical separations process, there were "tank farms" consisting of 64 single-shell underground waste tanks.
The first batch of plutonium was refined in the 221T plant from December 26, 1944, to February 2, 1945, and delivered to the Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos laboratory in New Mexico on February 5, 1945. Two identical reactors, DReactor and FReactor, came online on December 5, 1944, and February 15, 1945, respectively, and all three reactors were running at full power (250 megawatts) by March 8, 1945. By April kilogram-quantity shipments of plutonium were headed to Los Alamos. Road convoys replaced the trains in May, and in late July shipments began being dispatched by air from the airport at Hanford.
 Although the reactors could be shut down in two-and-a-half seconds, the decay of fission products meant that they would still generate heat due to the decay of fission products. It was therefore vital that the flow of water should not cease. If the power failed, the steam pumps would automatically cut in and continue to deliver water at full capacity for long enough to allow an orderly shutdown. This occurred on March 10, 1945, when a Japanese Fu-Go balloon bomb, balloon bomb struck a high-tension line between Grand Coulee and Bonneville. This caused an electrical surge in the lines to the reactors. A scram was automatically initiated and the safety devices shut the reactors down. The bomb failed to explode and the transmission line was not badly damaged. The Hanford Engineer Works was the only U.S. nuclear facility to come under enemy attack.
Hanford provided the plutonium for the bomb used in the 1945
Although the reactors could be shut down in two-and-a-half seconds, the decay of fission products meant that they would still generate heat due to the decay of fission products. It was therefore vital that the flow of water should not cease. If the power failed, the steam pumps would automatically cut in and continue to deliver water at full capacity for long enough to allow an orderly shutdown. This occurred on March 10, 1945, when a Japanese Fu-Go balloon bomb, balloon bomb struck a high-tension line between Grand Coulee and Bonneville. This caused an electrical surge in the lines to the reactors. A scram was automatically initiated and the safety devices shut the reactors down. The bomb failed to explode and the transmission line was not badly damaged. The Hanford Engineer Works was the only U.S. nuclear facility to come under enemy attack.
Hanford provided the plutonium for the bomb used in the 1945
 The other problem was that the bismuth phosphate process used to separate the plutonium left the uranium in an unrecoverable state. The Metallurgical Laboratory had researched a promising new redox separation process, using hexone as a solvent. The AEC was concerned about the supply of uranium, and the General Advisory Committee of the AEC recommended that construction of a redox plant be given top priority. Meanwhile, the waste-settling tanks filled up with sludge, and attempts to transport it to the waste storage (241) areas were unsuccessful. It was therefore decided to bypass the waste settling tanks and send sludge directly to the 200 area, and construction of a bypass commenced in August 1946. GE invited bids for the construction of a new waste storage tank farm. Efforts were made to make better use of the available uranium. Metal swarf, Turnings, cuttings and shavings from the slug manufacture process had been sent to the Ames Laboratory in Iowa for briquetting. The equipment there was shipped to the Hanford Engineer Works. The briquettes, along with uranium scrap metal, was sent to the Metal Hydrides Company for recasting into billets.
During 1947, tensions with the Soviet Union escalated as the
The other problem was that the bismuth phosphate process used to separate the plutonium left the uranium in an unrecoverable state. The Metallurgical Laboratory had researched a promising new redox separation process, using hexone as a solvent. The AEC was concerned about the supply of uranium, and the General Advisory Committee of the AEC recommended that construction of a redox plant be given top priority. Meanwhile, the waste-settling tanks filled up with sludge, and attempts to transport it to the waste storage (241) areas were unsuccessful. It was therefore decided to bypass the waste settling tanks and send sludge directly to the 200 area, and construction of a bypass commenced in August 1946. GE invited bids for the construction of a new waste storage tank farm. Efforts were made to make better use of the available uranium. Metal swarf, Turnings, cuttings and shavings from the slug manufacture process had been sent to the Ames Laboratory in Iowa for briquetting. The equipment there was shipped to the Hanford Engineer Works. The briquettes, along with uranium scrap metal, was sent to the Metal Hydrides Company for recasting into billets.
During 1947, tensions with the Soviet Union escalated as the  While this was being considered by the AEC, GE experimented with annealing, and found that if the reactors were run at and then slowly cooled, the graphite's crystalline structure could be restored. The reactors could be run at higher temperatures by increasing the power level. Some helium in the atmosphere surrounding the reactors was replaced with carbon dioxide, which conducted heat less efficiently. This allowed more heat to build up in the graphite. To reduce the incidence of cans jamming, their size was reduced from . More plutonium was produced by keeping the fuel elements in the reactor longer. Instead of pushing the entire tube out, half of it was, allowing elements to spend time in parts of the reactor where the neutron flux was less dense. The old reactors could now be run much longer. In December the AEC approved a scaled-back construction plan, with only one replacement reactor, at siteD (called DR), and one reactor at a new site (called H). The new reactors used the same designs as the wartime ones, although they had more pure graphite to allow them to be run at higher power levels, and smaller graphite blocks surrounding the process tubes to restrict expansion.
While this was being considered by the AEC, GE experimented with annealing, and found that if the reactors were run at and then slowly cooled, the graphite's crystalline structure could be restored. The reactors could be run at higher temperatures by increasing the power level. Some helium in the atmosphere surrounding the reactors was replaced with carbon dioxide, which conducted heat less efficiently. This allowed more heat to build up in the graphite. To reduce the incidence of cans jamming, their size was reduced from . More plutonium was produced by keeping the fuel elements in the reactor longer. Instead of pushing the entire tube out, half of it was, allowing elements to spend time in parts of the reactor where the neutron flux was less dense. The old reactors could now be run much longer. In December the AEC approved a scaled-back construction plan, with only one replacement reactor, at siteD (called DR), and one reactor at a new site (called H). The new reactors used the same designs as the wartime ones, although they had more pure graphite to allow them to be run at higher power levels, and smaller graphite blocks surrounding the process tubes to restrict expansion.
 The adult population of Richland had an average education of 12.5 years, and 40 percent of the men had attended college, compared with 22 percent in the state of Washington as a whole, and the median annual family income in 1959 was compared with . In 1950 26 percent of American families had an annual income of less than the poverty line of . In the nearby towns of Pasco and Kennewick, 24.4 and 25.2 percent respectively were below the poverty line; in Richland, it was just 4.9 percent. The percentage of high school graduates in Richland was 74.3 percent, compared with 53.5 in Pasco and 54.6 in Kennewick. Women constituted a quarter of the workforce, and the number of working wives was much higher than the national average. Although GE liked to present an image of a American middle class, middle-class community, most of the Hanford Site employees were working-class shift workers with high school education only.
There were few senior citizens in Richlandin 1947 the AEC still required retirees to give up their homesbut the birth rate in 1948 was 34 per 1,000, well above the national average of 20 per 1,000. This tapered off during the 1950s, but there remained a larger than usual number of school-age children. There were only seven black people in Richland in 1950; this increased to 189 by 1960, when they accounted for 1.3 percent of the population. Only two black people worked for the AEC at the Hanford Site in 1951, less than a dozen were employed by GE, and about 250 by the construction contractors. The use of eating and recreational facilities by black people was discouraged, but not prohibited. Black people were even less welcome in Kennewick; there were only four living there in 1950 and five in 1960. Kennewick was a sundown town where there was a curfew for black people. They congregated in Pasco, where 1,213 black people lived in a ghetto on the town's eastern fringe. They had no sewerage or running water in 1948, because the town's leaders felt that the black community should provide the to pay for it. Black residents also did not qualify for Federal Housing Administration (FHA) loans.
The adult population of Richland had an average education of 12.5 years, and 40 percent of the men had attended college, compared with 22 percent in the state of Washington as a whole, and the median annual family income in 1959 was compared with . In 1950 26 percent of American families had an annual income of less than the poverty line of . In the nearby towns of Pasco and Kennewick, 24.4 and 25.2 percent respectively were below the poverty line; in Richland, it was just 4.9 percent. The percentage of high school graduates in Richland was 74.3 percent, compared with 53.5 in Pasco and 54.6 in Kennewick. Women constituted a quarter of the workforce, and the number of working wives was much higher than the national average. Although GE liked to present an image of a American middle class, middle-class community, most of the Hanford Site employees were working-class shift workers with high school education only.
There were few senior citizens in Richlandin 1947 the AEC still required retirees to give up their homesbut the birth rate in 1948 was 34 per 1,000, well above the national average of 20 per 1,000. This tapered off during the 1950s, but there remained a larger than usual number of school-age children. There were only seven black people in Richland in 1950; this increased to 189 by 1960, when they accounted for 1.3 percent of the population. Only two black people worked for the AEC at the Hanford Site in 1951, less than a dozen were employed by GE, and about 250 by the construction contractors. The use of eating and recreational facilities by black people was discouraged, but not prohibited. Black people were even less welcome in Kennewick; there were only four living there in 1950 and five in 1960. Kennewick was a sundown town where there was a curfew for black people. They congregated in Pasco, where 1,213 black people lived in a ghetto on the town's eastern fringe. They had no sewerage or running water in 1948, because the town's leaders felt that the black community should provide the to pay for it. Black residents also did not qualify for Federal Housing Administration (FHA) loans.
 Soon after taking over from the Army, the AEC had contemplated the future of the communities of Richland, Oak Ridge and Los Alamos. The commissioners were eager to divest the AEC of the burden of their management. In 1947 AEC general manager Carroll L. Wilson commissioned Lyman S. Moore, the city manager of Portland, Maine, and an expert on municipal government, to produce a report on the management of the communities. He produced a road map to self-government. The first step was to overhaul the accounting system to produce comparable reports on housing, commercial operations, utilities and government. It would then be possible to move to changing market rates for rents, utilities and municipal services, and ultimately to establish self-government. There was scant enthusiasm for this in Richland, but the United States was engaged in an ideological conflict with the Soviet Union over the superiority of the American way. The AEC's September 1950 appropriation called upon it to take steps to impose democratic government and free enterprise on the AEC communities.
The first step was taken on October 1, 1953, when the AEC increased the rents in Richland by 25 percent to bring them into line with those in neighboring communities. In 1955 the town voted on disposal and incorporation; both measures were overwhelmingly defeated. Nonetheless, that year Congress passed Public Law 221, which provided for the transfer of government property in Richland to the townsfolk. Thousands of people attended protest rallies and sent angry letters and petitions to Congress. Congressional hearings were held, and prices set by the FHA were reduced. People who had been dispossessed by the acquisition process during the war petitioned to be allowed to buy their property back, but they were ignored. By July 1958 4,200 homes had been sold. After receiving assurances that the AEC would continue to subsidize schools and municipal services through the 1960s, the citizens of Richland voted for incorporation, and the town became self-governing on December 12, 1958. In 1960 Richland received an All-America City Award.
Soon after taking over from the Army, the AEC had contemplated the future of the communities of Richland, Oak Ridge and Los Alamos. The commissioners were eager to divest the AEC of the burden of their management. In 1947 AEC general manager Carroll L. Wilson commissioned Lyman S. Moore, the city manager of Portland, Maine, and an expert on municipal government, to produce a report on the management of the communities. He produced a road map to self-government. The first step was to overhaul the accounting system to produce comparable reports on housing, commercial operations, utilities and government. It would then be possible to move to changing market rates for rents, utilities and municipal services, and ultimately to establish self-government. There was scant enthusiasm for this in Richland, but the United States was engaged in an ideological conflict with the Soviet Union over the superiority of the American way. The AEC's September 1950 appropriation called upon it to take steps to impose democratic government and free enterprise on the AEC communities.
The first step was taken on October 1, 1953, when the AEC increased the rents in Richland by 25 percent to bring them into line with those in neighboring communities. In 1955 the town voted on disposal and incorporation; both measures were overwhelmingly defeated. Nonetheless, that year Congress passed Public Law 221, which provided for the transfer of government property in Richland to the townsfolk. Thousands of people attended protest rallies and sent angry letters and petitions to Congress. Congressional hearings were held, and prices set by the FHA were reduced. People who had been dispossessed by the acquisition process during the war petitioned to be allowed to buy their property back, but they were ignored. By July 1958 4,200 homes had been sold. After receiving assurances that the AEC would continue to subsidize schools and municipal services through the 1960s, the citizens of Richland voted for incorporation, and the town became self-governing on December 12, 1958. In 1960 Richland received an All-America City Award.
 The Soviet Union detonated its RDS-1, first atomic bomb on August 29, 1949. The explosion was detected by a U.S. Air Force weather reconnaissance aircraft four days later. In response, President Harry S. Truman authorized a crash program to develop the hydrogen bomb. Preliminary designs called for large amounts of tritium. This could be produced in a reactor using target slugs loaded with lithium deuteride and fuel rods containing enriched uranium. One or more reactors would have to be set aside for tritium production. HReactor was chosen, and started producing tritium in 1950. For the longer term, the AEC decided to construct new reactors, of a different design using enriched uranium and heavy water as a moderator, at a new site, which became the Savannah River Site. The outbreak of the Korean War in September 1951 prompted the AEC to authorize a sixth reactor at Hanford on January 23, 1951. Construction began in June. The new reactor was built in the Barea and called CReactor. The same basic graphite-moderated design was used, with improvements to give it a rated power of 750 MW. The new reactor became operational in November 1952.
On February 25, 1952, Truman authorized two more reactors at the Hanford Site. These were called K West and K East, and were sited at Coyote Rapids between the Band Dareas. They were known as "Jumbo" reactors for their much larger size. They still used the same graphite-moderator technology, but had improvements to allow them to operate at 1,800 MW. Each used of graphite, over a thousand tons more than the three wartime reactors, and had concrete shields instead of steel and masonite. They had more feed tubes and reduced spacing between them. Improvements in water-pump design allowed them to have eighteen pumps instead of the fifty in the wartime reactors, but were capable of pumping . As with the other reactors, the cooling water was collected in ponds, allowed to cool, and then tipped back into the river. An innovation was that heat from the cooling water was used to heat the work places. Each Jumbo reactor required about 300 operators to run it, compared with 400 for HReactor. This represented a saving of a million dollars a year (equivalent to $million in ). Although capable of being run at up to 4,400 MW, the AEC imposed an administrative limit of 4,000 MW on them. Since plutonium239 has a half-life of 24,100 years, AEC chairman Gordon Dean (lawyer), Gordon Dean calculated that sufficient plutonium would be produced by the mid-1960s. With this in mind, the reactors were designed with a life of twenty years.
The Soviet Union detonated its RDS-1, first atomic bomb on August 29, 1949. The explosion was detected by a U.S. Air Force weather reconnaissance aircraft four days later. In response, President Harry S. Truman authorized a crash program to develop the hydrogen bomb. Preliminary designs called for large amounts of tritium. This could be produced in a reactor using target slugs loaded with lithium deuteride and fuel rods containing enriched uranium. One or more reactors would have to be set aside for tritium production. HReactor was chosen, and started producing tritium in 1950. For the longer term, the AEC decided to construct new reactors, of a different design using enriched uranium and heavy water as a moderator, at a new site, which became the Savannah River Site. The outbreak of the Korean War in September 1951 prompted the AEC to authorize a sixth reactor at Hanford on January 23, 1951. Construction began in June. The new reactor was built in the Barea and called CReactor. The same basic graphite-moderated design was used, with improvements to give it a rated power of 750 MW. The new reactor became operational in November 1952.
On February 25, 1952, Truman authorized two more reactors at the Hanford Site. These were called K West and K East, and were sited at Coyote Rapids between the Band Dareas. They were known as "Jumbo" reactors for their much larger size. They still used the same graphite-moderator technology, but had improvements to allow them to operate at 1,800 MW. Each used of graphite, over a thousand tons more than the three wartime reactors, and had concrete shields instead of steel and masonite. They had more feed tubes and reduced spacing between them. Improvements in water-pump design allowed them to have eighteen pumps instead of the fifty in the wartime reactors, but were capable of pumping . As with the other reactors, the cooling water was collected in ponds, allowed to cool, and then tipped back into the river. An innovation was that heat from the cooling water was used to heat the work places. Each Jumbo reactor required about 300 operators to run it, compared with 400 for HReactor. This represented a saving of a million dollars a year (equivalent to $million in ). Although capable of being run at up to 4,400 MW, the AEC imposed an administrative limit of 4,000 MW on them. Since plutonium239 has a half-life of 24,100 years, AEC chairman Gordon Dean (lawyer), Gordon Dean calculated that sufficient plutonium would be produced by the mid-1960s. With this in mind, the reactors were designed with a life of twenty years.
 The U Plant was modified to use the REDOX process to recover uranium from the wastes left over from the bismuth phosphate process, but with a different solvent, tributyl phosphate. Because of the plant's layout, it could not use the tall columns and gravity flow that characterized the REDOX plant, so pulsed columns were used instead. The PUREX, plutonium uranium reduction extraction (PUREX) process was developed at GE's Knolls Atomic Power Laboratory, Knolls Laboratory. The PUREX Plant, known as APlant or Building 202A, commenced operation in 1955. Like the UPlant it used pulsed columns and tributyl phosphate as a solvent.
The plant was long, high and wide. The processing canyon contained eleven processing areas. It operated from 1956 to 1972, and again from 1983 to 1988, when it reprocessed spent fuel rods from the reactors, and processed approximately 66,400 metric tons of uranium fuel rods. The Band T Plants were shut down after it became operational in 1956, having processed 8,100 metric tons of fuel rods. During the 1940s, the Hanford Site dumped into the Columbia River each day. This rose to per day between 1951 and 1953, and peaked at per day in 1959.
The U Plant was modified to use the REDOX process to recover uranium from the wastes left over from the bismuth phosphate process, but with a different solvent, tributyl phosphate. Because of the plant's layout, it could not use the tall columns and gravity flow that characterized the REDOX plant, so pulsed columns were used instead. The PUREX, plutonium uranium reduction extraction (PUREX) process was developed at GE's Knolls Atomic Power Laboratory, Knolls Laboratory. The PUREX Plant, known as APlant or Building 202A, commenced operation in 1955. Like the UPlant it used pulsed columns and tributyl phosphate as a solvent.
The plant was long, high and wide. The processing canyon contained eleven processing areas. It operated from 1956 to 1972, and again from 1983 to 1988, when it reprocessed spent fuel rods from the reactors, and processed approximately 66,400 metric tons of uranium fuel rods. The Band T Plants were shut down after it became operational in 1956, having processed 8,100 metric tons of fuel rods. During the 1940s, the Hanford Site dumped into the Columbia River each day. This rose to per day between 1951 and 1953, and peaked at per day in 1959.
 N Reactor was destined to be the last of its kind, but also had many new features as a product of 1960s technology. Its zirconium alloy-clad fuel slugs were long and in diameter. It had automated fuel-loading and unloading systems, a boron-ball scram system, and a state-of-the-art control room. It was the first American graphite-moderated power reactor, and the first American dual-purpose reactor, although other countries had them. The dual-purpose concept involved trade-offs that made both purposes less efficient: power required a steam turbine, but high water temperatures risked slug failure. The solution was to build a pressurized water reactor, in which the water was pressurized to allow it to remain liquid above . The reactor exceeded its original $145million budget (equivalent to $million in ) and cost $205million budget (equivalent to $million in ).
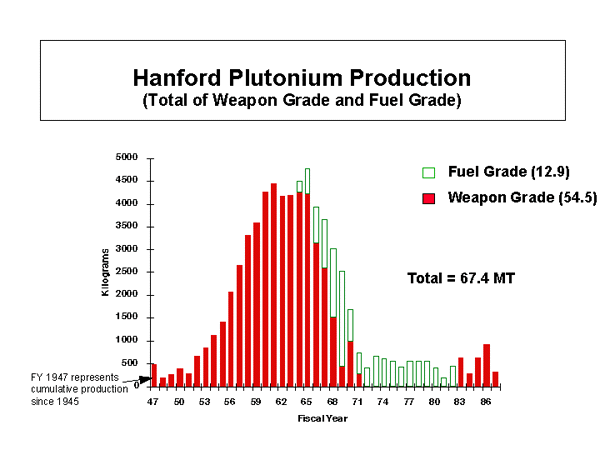
The Hanford Site was now home to nine nuclear reactors along the Columbia River, five reprocessing plants on the central plateau, and more than nine hundred support buildings and radiological laboratories around the site. Extensive modifications and upgrades were made to the original three World WarII reactors, and a total of 177 underground waste tanks were built. Hanford was at its peak production from 1956 to 1965. Over the forty years of operation the site produced about 67.4 metric tons of plutonium, of which 54.5 metric tons was weapons-grade plutonium, supplying the majority of the 60,000 weapons in the U.S. arsenal. In 1983 and 1984, 425 kilograms of weapons-grade plutonium was extracted from reactor-grade plutonium. Tritium, polonium210, thulium-170, iridium-192, and uranium-233 were also produced.
N Reactor was destined to be the last of its kind, but also had many new features as a product of 1960s technology. Its zirconium alloy-clad fuel slugs were long and in diameter. It had automated fuel-loading and unloading systems, a boron-ball scram system, and a state-of-the-art control room. It was the first American graphite-moderated power reactor, and the first American dual-purpose reactor, although other countries had them. The dual-purpose concept involved trade-offs that made both purposes less efficient: power required a steam turbine, but high water temperatures risked slug failure. The solution was to build a pressurized water reactor, in which the water was pressurized to allow it to remain liquid above . The reactor exceeded its original $145million budget (equivalent to $million in ) and cost $205million budget (equivalent to $million in ).
The Hanford Site was now home to nine nuclear reactors along the Columbia River, five reprocessing plants on the central plateau, and more than nine hundred support buildings and radiological laboratories around the site. Extensive modifications and upgrades were made to the original three World WarII reactors, and a total of 177 underground waste tanks were built. Hanford was at its peak production from 1956 to 1965. Over the forty years of operation the site produced about 67.4 metric tons of plutonium, of which 54.5 metric tons was weapons-grade plutonium, supplying the majority of the 60,000 weapons in the U.S. arsenal. In 1983 and 1984, 425 kilograms of weapons-grade plutonium was extracted from reactor-grade plutonium. Tritium, polonium210, thulium-170, iridium-192, and uranium-233 were also produced.
 By 1963 the AEC had estimated that it had sufficient plutonium for its needs for the foreseeable future, and planned to shut down the production reactors. To mitigate the economic impact, closures were carried out over a period of six years. The change of policy was not publicly announced; instead, each round of closures was accompanied by a statement that production needs could be met by the remaining facilities. The first round of closures was announced by President Lyndon B. Johnson, Johnson on January 8, 1964. DR, H and FReactors were shut down in 1964 and, 1965. In 1967 the AEC announced that another reactor would be shut down. This was DReactor, which was shut down on June 25, 1967. BReactor followed on February 12, 1968.
In January 1969 AEC chairman Glenn Seaborg, under pressure from the newly elected Nixon administration to cut costs, announced that the three reactors built in the 1950s, C, KE and KW, would be shut down in 1969 and 1970. The REDOX and PUREX facilities were placed on standby status in December 1967 and June 1972 respectively. Between 1967 and 1971, the number of workers employed at the Hanford Site plummeted from 8,500 to 5,500. The incremental closures did nothing to reduce the public outcry; if anything, the reverse was the case. The AEC was replaced by the Energy Research and Development Administration in 1974, and it in turn was succeeded by the DOE in 1977. The regulation and licensing of commercial reactors was devolved to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC).
The closures left only N Reactor, which continued to operate as a dual-purpose reactor, providing power to the civilian electrical grid via the WPPSS. By 1966 it was producing 35 percent of the United States' nuclear-generated electricity. Costs were lower than anticipated, allowing the WPPSS to retire $25million budget (equivalent to $million in ) of the $122million (equivalent to $million in ) it had raised in Bond (finance), bonds to finance the project. The Chernobyl disaster in the Soviet Union in April 1986 prompted multiple reviews of the safety of American reactors. Of all the reactors in the U.S., NReactor was the most similar to the ill-fated No.4 Reactor at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, in that it was graphite-moderated, although NReactor used pressurized water rather than boiling water as a coolant. Like all the Hanford Site's reactors, it had no containment vessel and would never have passed the NRC's reactor safety requirements had they been applied to it. There was a public outcry, and the Government Accountability Office recommended closure. NReactor was shut down in January 1987. The PUREX plant reopened in 1983 to reprocess N Reactor reactor-grade fuel into weapon-grade fuel. This ended in December 1988, and it returned to standby status in October 1990. The uranium trioxide plant closed in 1995, the PUREX plant closed for good in 1997, and the BPlant in 1998. The TPlant remained in use, handling the storage, packaging and decontamination of radioactive wastes. It became the longest operational nuclear facility in the world.
By 1963 the AEC had estimated that it had sufficient plutonium for its needs for the foreseeable future, and planned to shut down the production reactors. To mitigate the economic impact, closures were carried out over a period of six years. The change of policy was not publicly announced; instead, each round of closures was accompanied by a statement that production needs could be met by the remaining facilities. The first round of closures was announced by President Lyndon B. Johnson, Johnson on January 8, 1964. DR, H and FReactors were shut down in 1964 and, 1965. In 1967 the AEC announced that another reactor would be shut down. This was DReactor, which was shut down on June 25, 1967. BReactor followed on February 12, 1968.
In January 1969 AEC chairman Glenn Seaborg, under pressure from the newly elected Nixon administration to cut costs, announced that the three reactors built in the 1950s, C, KE and KW, would be shut down in 1969 and 1970. The REDOX and PUREX facilities were placed on standby status in December 1967 and June 1972 respectively. Between 1967 and 1971, the number of workers employed at the Hanford Site plummeted from 8,500 to 5,500. The incremental closures did nothing to reduce the public outcry; if anything, the reverse was the case. The AEC was replaced by the Energy Research and Development Administration in 1974, and it in turn was succeeded by the DOE in 1977. The regulation and licensing of commercial reactors was devolved to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC).
The closures left only N Reactor, which continued to operate as a dual-purpose reactor, providing power to the civilian electrical grid via the WPPSS. By 1966 it was producing 35 percent of the United States' nuclear-generated electricity. Costs were lower than anticipated, allowing the WPPSS to retire $25million budget (equivalent to $million in ) of the $122million (equivalent to $million in ) it had raised in Bond (finance), bonds to finance the project. The Chernobyl disaster in the Soviet Union in April 1986 prompted multiple reviews of the safety of American reactors. Of all the reactors in the U.S., NReactor was the most similar to the ill-fated No.4 Reactor at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, in that it was graphite-moderated, although NReactor used pressurized water rather than boiling water as a coolant. Like all the Hanford Site's reactors, it had no containment vessel and would never have passed the NRC's reactor safety requirements had they been applied to it. There was a public outcry, and the Government Accountability Office recommended closure. NReactor was shut down in January 1987. The PUREX plant reopened in 1983 to reprocess N Reactor reactor-grade fuel into weapon-grade fuel. This ended in December 1988, and it returned to standby status in October 1990. The uranium trioxide plant closed in 1995, the PUREX plant closed for good in 1997, and the BPlant in 1998. The TPlant remained in use, handling the storage, packaging and decontamination of radioactive wastes. It became the longest operational nuclear facility in the world.
 All but one of the Hanford production reactors were Nuclear entombment, entombed ("cocooned") to allow the radioactive materials to decay, and the surrounding structures removed and buried. This involved the removal of hundreds of tons of asbestos, concrete, steel and contaminated soil. The pumps and tunnels were dug up and razed, as were the auxiliary buildings. What was left were the core and shields. These were sealed up and a sloped steel roof added to draw off rainwater. Cocooning of CReactor commenced in 1996, and was completed in 1998. DReactor followed in 2002, FReactor followed in 2003, DRReactor in 2004. and HReactor in 2005. N Reactor was cocooned in 2012, and KE and KW in 2022.
The exception was B Reactor, which was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1992.NRHP site #92000245. (See also the commercial sit
All but one of the Hanford production reactors were Nuclear entombment, entombed ("cocooned") to allow the radioactive materials to decay, and the surrounding structures removed and buried. This involved the removal of hundreds of tons of asbestos, concrete, steel and contaminated soil. The pumps and tunnels were dug up and razed, as were the auxiliary buildings. What was left were the core and shields. These were sealed up and a sloped steel roof added to draw off rainwater. Cocooning of CReactor commenced in 1996, and was completed in 1998. DReactor followed in 2002, FReactor followed in 2003, DRReactor in 2004. and HReactor in 2005. N Reactor was cocooned in 2012, and KE and KW in 2022.
The exception was B Reactor, which was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1992.NRHP site #92000245. (See also the commercial sit
National Register of Historic Places
) Some historians advocated converting it into a museum. It was designated a National Historic Landmark by the National Park Service on August 19, 2008, and on November 10, 2015, it became part of the
 When GE announced that it was ending the contract to run the Hanford Site in 1963, the AEC decided to separate the contract among multiple operators. The contract to run the research laboratory at the Hanford Site was awarded to the Battelle Memorial Institute of Columbus, Ohio, on May 28, 1964, and the laboratory became the Pacific Northwest Laboratory when it took over management on January 4, 1965. In 1995 it achieved national laboratory status and became The
When GE announced that it was ending the contract to run the Hanford Site in 1963, the AEC decided to separate the contract among multiple operators. The contract to run the research laboratory at the Hanford Site was awarded to the Battelle Memorial Institute of Columbus, Ohio, on May 28, 1964, and the laboratory became the Pacific Northwest Laboratory when it took over management on January 4, 1965. In 1995 it achieved national laboratory status and became The  Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) Hanford Observatory is an interferometer searching for Gravitational wave#Interferometers, gravitational waves. The observatory at the Hanford Site was one of two, the other being in Livingston, Louisiana. The project was run as a cooperative venture by MIT and Caltech. The $211million price tag (equivalent to $million in ) generated debate about pork barreling and government funding of expensive Big Science projects, especially one as uncertain of success as LIGO. The Hanford Site was chosen from seventeen contenders for one of the two sites, mainly due to its relative isolation. In 2016 it was announced that gravitational waves had been detected. In 2018 the American Physical Society (APS) designated the two LIGO observatories as APS historic sites.
The
Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) Hanford Observatory is an interferometer searching for Gravitational wave#Interferometers, gravitational waves. The observatory at the Hanford Site was one of two, the other being in Livingston, Louisiana. The project was run as a cooperative venture by MIT and Caltech. The $211million price tag (equivalent to $million in ) generated debate about pork barreling and government funding of expensive Big Science projects, especially one as uncertain of success as LIGO. The Hanford Site was chosen from seventeen contenders for one of the two sites, mainly due to its relative isolation. In 2016 it was announced that gravitational waves had been detected. In 2018 the American Physical Society (APS) designated the two LIGO observatories as APS historic sites.
The  The Hanford Reach was preserved as the finest salmon breeding ground in the Pacific Northwest. The end of plutonium production at the Hanford Site meant that it no longer required the areas around the old production sites. On June 9, 2000, President Bill Clinton designated almost of the Hanford Site as a National monument (United States), national monument. The Hanford Reach National Monument is managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service under an agreement with the DOE. On June 28, 2000, a fire burned of the monument.
The Hanford Reach was preserved as the finest salmon breeding ground in the Pacific Northwest. The end of plutonium production at the Hanford Site meant that it no longer required the areas around the old production sites. On June 9, 2000, President Bill Clinton designated almost of the Hanford Site as a National monument (United States), national monument. The Hanford Reach National Monument is managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service under an agreement with the DOE. On June 28, 2000, a fire burned of the monument.
 The plutonium separation process resulted in the release of radioactive isotopes into the air, which were carried by the wind throughout southeastern Washington and into parts of Idaho, Montana, Oregon, and British Columbia. Downwinders were exposed to radionuclides, particularly iodine-131, with the heaviest releases from 1945 to 1951. These radionuclides entered the food chain via dairy cows grazing on contaminated fields; hazardous fallout was ingested by communities who consumed radioactive food and milk. Most of these airborne releases were a part of Hanford's routine operations, while a few of the larger releases occurred in isolated incidents. In 1949 an intentional release known as the "Green Run" released of iodine131 over two days. A U.S. government report released in 1992 estimated that of iodine131 had been released into the river and air from the Hanford Site between 1944 and 1947.
Beginning in the 1960s scientists with the United States Public Health Service, U.S. Public Health Service published reports about radioactivity released from Hanford, and there were protests from the health departments of Oregon and Washington. In response to an article in the ''Spokane Spokesman Review'' in September 1985, the DOE announced it would declassify environmental records and, in February 1986, released 19,000 pages of previously unavailable historical documents about Hanford's operations. The Washington State Department of Health collaborated with the citizen-led Hanford Health Information Network (HHIN) to publicize data about the health effects of Hanford's operations. HHIN reports concluded that residents who lived downwind from Hanford or who used the Columbia River downstream were exposed to elevated doses of radiation that placed them at increased risk for various cancers and other diseases, particularly forms of thyroid disease. A mass tort lawsuit brought by two thousand Hanford downwinders against the federal government spent many years in the court system. In 2005 two of six plaintiffs who went to trial were awarded $500,000 in damages. The DOE resolved the final cases in October 2015, paying out more than $60million in legal fees and $7million in damages.
Radioactive materials were known to be leaking from Hanford into the environment. The highest tritium concentration detected in riverbank springs during 2002 was at the Hanford townsite. An iodine-129 concentration of was found in a Hanford townsite spring. The WHO guidelines for radionuclides in drinking water limits levels of iodine129 at 1Bq/L, and tritium at 10,000Bq/L. A September 2005 Pacific Northwest National Laboraory report noted "Detected radionuclides include strontium90, technetium99, iodine129, uranium234, -235, and -238, and tritium. Other detected contaminants include arsenic, chromium, chloride, fluoride, nitrate, and sulfate ... concentrations of radionuclides including tritium, technetium99, and iodine129 in riverbank springs near the Hanford townsite have generally been increasing since 1994. This is an area where a major Groundwater#Pollution, groundwater plume from the 200 East Area intercepts the river. However, tritium concentration has declined since 1997."
The plutonium separation process resulted in the release of radioactive isotopes into the air, which were carried by the wind throughout southeastern Washington and into parts of Idaho, Montana, Oregon, and British Columbia. Downwinders were exposed to radionuclides, particularly iodine-131, with the heaviest releases from 1945 to 1951. These radionuclides entered the food chain via dairy cows grazing on contaminated fields; hazardous fallout was ingested by communities who consumed radioactive food and milk. Most of these airborne releases were a part of Hanford's routine operations, while a few of the larger releases occurred in isolated incidents. In 1949 an intentional release known as the "Green Run" released of iodine131 over two days. A U.S. government report released in 1992 estimated that of iodine131 had been released into the river and air from the Hanford Site between 1944 and 1947.
Beginning in the 1960s scientists with the United States Public Health Service, U.S. Public Health Service published reports about radioactivity released from Hanford, and there were protests from the health departments of Oregon and Washington. In response to an article in the ''Spokane Spokesman Review'' in September 1985, the DOE announced it would declassify environmental records and, in February 1986, released 19,000 pages of previously unavailable historical documents about Hanford's operations. The Washington State Department of Health collaborated with the citizen-led Hanford Health Information Network (HHIN) to publicize data about the health effects of Hanford's operations. HHIN reports concluded that residents who lived downwind from Hanford or who used the Columbia River downstream were exposed to elevated doses of radiation that placed them at increased risk for various cancers and other diseases, particularly forms of thyroid disease. A mass tort lawsuit brought by two thousand Hanford downwinders against the federal government spent many years in the court system. In 2005 two of six plaintiffs who went to trial were awarded $500,000 in damages. The DOE resolved the final cases in October 2015, paying out more than $60million in legal fees and $7million in damages.
Radioactive materials were known to be leaking from Hanford into the environment. The highest tritium concentration detected in riverbank springs during 2002 was at the Hanford townsite. An iodine-129 concentration of was found in a Hanford townsite spring. The WHO guidelines for radionuclides in drinking water limits levels of iodine129 at 1Bq/L, and tritium at 10,000Bq/L. A September 2005 Pacific Northwest National Laboraory report noted "Detected radionuclides include strontium90, technetium99, iodine129, uranium234, -235, and -238, and tritium. Other detected contaminants include arsenic, chromium, chloride, fluoride, nitrate, and sulfate ... concentrations of radionuclides including tritium, technetium99, and iodine129 in riverbank springs near the Hanford townsite have generally been increasing since 1994. This is an area where a major Groundwater#Pollution, groundwater plume from the 200 East Area intercepts the river. However, tritium concentration has declined since 1997."
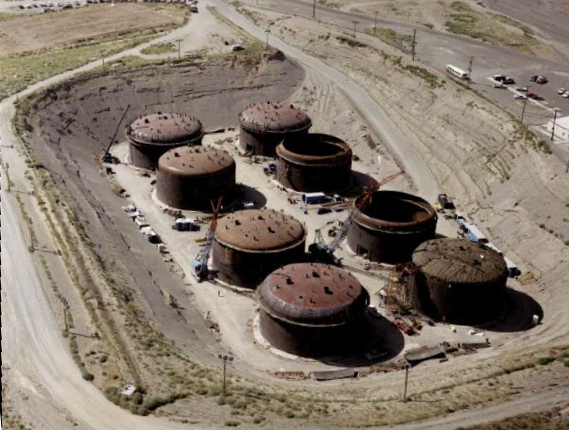 Of the 177 tanks at Hanford, 149 had a single shell. Historically single-shell tanks were used for storing radioactive liquid waste and designed to last twenty years. By 2005 some liquid waste was transferred from single-shell tanks to (safer) double-shell tanks. A substantial amount of residue remains in the older single-shell tanks with one containing an estimated of radioactive sludge, for example. It is believed that up to six of these "empty" tanks were leaking. Two tanks were reportedly leaking per year each, while the remaining four tanks were each leaking per year. In February 2013 Washington Governor Jay Inslee announced that a tank storing radioactive waste at the site had been leaking liquids on average of per year. He said that though the leak posed no immediate health risk to the public, it should not be an excuse for not doing anything. On February 22, 2013, he stated that six more tanks were leaking.
Of the 177 tanks at Hanford, 149 had a single shell. Historically single-shell tanks were used for storing radioactive liquid waste and designed to last twenty years. By 2005 some liquid waste was transferred from single-shell tanks to (safer) double-shell tanks. A substantial amount of residue remains in the older single-shell tanks with one containing an estimated of radioactive sludge, for example. It is believed that up to six of these "empty" tanks were leaking. Two tanks were reportedly leaking per year each, while the remaining four tanks were each leaking per year. In February 2013 Washington Governor Jay Inslee announced that a tank storing radioactive waste at the site had been leaking liquids on average of per year. He said that though the leak posed no immediate health risk to the public, it should not be an excuse for not doing anything. On February 22, 2013, he stated that six more tanks were leaking.
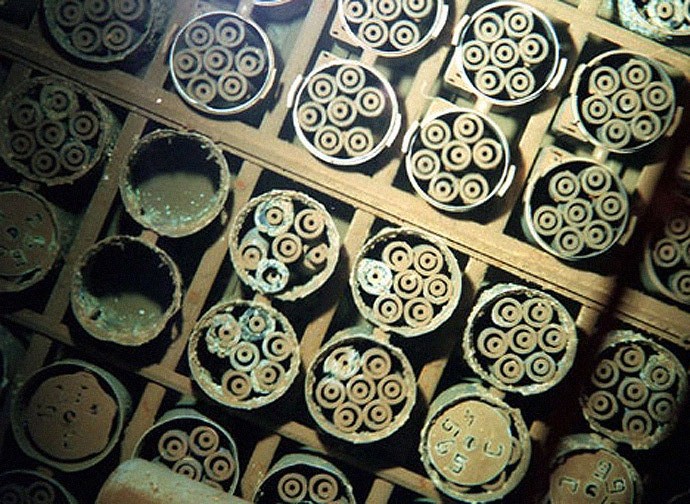 Decades of manufacturing left behind of high level waste, high-level radioactive waste stored within 177 storage tanks, an additional of solid radioactive waste, and areas of heavy technetium-99 and uranium-contaminated groundwater beneath three tank farms on the site as well as the potential for future groundwater contamination beneath currently contaminated soils. On June 25, 1988, the Hanford Site was divided into four areas and proposed for inclusion on the National Priorities List.
On May 15, 1989, the Washington Department of Ecology, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and the DOE entered into the Tri-Party Agreement, which provides a legal framework for environmental remediation at Hanford. By 2014 the agencies were engaged in the world's largest environmental cleanup, with many challenges to be resolved in the face of overlapping technical, political, regulatory, and cultural interests. The cleanup effort was focused on three outcomes: restoring the Columbia River corridor for other uses, converting the central plateau to long-term waste treatment and storage, and preparing for the future.
In 2011 DOE, the federal agency charged with overseeing the site, "interim stabilized" 149 single-shell tanks by pumping nearly all the liquid waste out into 28 newer double-shell tanks. Solids, known as salt cake and sludge, remained. The DOE later found water intruding into at least 14 single-shell tanks and that one of them had been leaking about per year into the ground since about 2010. In 2012 the DOE also discovered a leak from a double-shell tank caused by construction flaws and corrosion in the tank's bottom, and that twelve other double-shell tanks had similar construction flaws. Since then, the DOE began monitoring single-shell tanks monthly and double-shell tanks every three years. The DOE also changed the methods by which they monitored the tanks. In March 2014 the DOE announced further delays in the construction of the Waste Treatment Plant, which will affect the schedule for removing waste from the tanks. Intermittent discoveries of undocumented contamination have slowed the pace and raised the cost of cleanup.
Decades of manufacturing left behind of high level waste, high-level radioactive waste stored within 177 storage tanks, an additional of solid radioactive waste, and areas of heavy technetium-99 and uranium-contaminated groundwater beneath three tank farms on the site as well as the potential for future groundwater contamination beneath currently contaminated soils. On June 25, 1988, the Hanford Site was divided into four areas and proposed for inclusion on the National Priorities List.
On May 15, 1989, the Washington Department of Ecology, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and the DOE entered into the Tri-Party Agreement, which provides a legal framework for environmental remediation at Hanford. By 2014 the agencies were engaged in the world's largest environmental cleanup, with many challenges to be resolved in the face of overlapping technical, political, regulatory, and cultural interests. The cleanup effort was focused on three outcomes: restoring the Columbia River corridor for other uses, converting the central plateau to long-term waste treatment and storage, and preparing for the future.
In 2011 DOE, the federal agency charged with overseeing the site, "interim stabilized" 149 single-shell tanks by pumping nearly all the liquid waste out into 28 newer double-shell tanks. Solids, known as salt cake and sludge, remained. The DOE later found water intruding into at least 14 single-shell tanks and that one of them had been leaking about per year into the ground since about 2010. In 2012 the DOE also discovered a leak from a double-shell tank caused by construction flaws and corrosion in the tank's bottom, and that twelve other double-shell tanks had similar construction flaws. Since then, the DOE began monitoring single-shell tanks monthly and double-shell tanks every three years. The DOE also changed the methods by which they monitored the tanks. In March 2014 the DOE announced further delays in the construction of the Waste Treatment Plant, which will affect the schedule for removing waste from the tanks. Intermittent discoveries of undocumented contamination have slowed the pace and raised the cost of cleanup.
 The cleanup effort was managed by the DOE under the oversight of the two regulatory agencies. A citizen-led Hanford Advisory Board provides recommendations from community stakeholders, including local and state governments, regional environmental organizations, business interests, and Native American tribes. Citing the 2014 Hanford Lifecycle Scope Schedule and Cost report, the 2014 estimated cost of the remaining Hanford cleanup is $113.6billionmore than $3billion per year for the next six years, with a lower cost projection of approximately $2billion per year until 2046. About eleven thousand workers were on site to consolidate, clean up, and mitigate waste, contaminated buildings, and contaminated soil. Originally scheduled to be complete within thirty years, the cleanup was less than half finished by 2008. Of the four areas that were formally listed as Superfund sites on October 4, 1989, only one has been removed from the list following cleanup. While major releases of radioactive material ended with the reactor shutdown in the 1970s and many of the most dangerous wastes are contained, there were continued concerns about contaminated groundwater headed toward the Columbia River and about workers' health and safety.
The cleanup effort was managed by the DOE under the oversight of the two regulatory agencies. A citizen-led Hanford Advisory Board provides recommendations from community stakeholders, including local and state governments, regional environmental organizations, business interests, and Native American tribes. Citing the 2014 Hanford Lifecycle Scope Schedule and Cost report, the 2014 estimated cost of the remaining Hanford cleanup is $113.6billionmore than $3billion per year for the next six years, with a lower cost projection of approximately $2billion per year until 2046. About eleven thousand workers were on site to consolidate, clean up, and mitigate waste, contaminated buildings, and contaminated soil. Originally scheduled to be complete within thirty years, the cleanup was less than half finished by 2008. Of the four areas that were formally listed as Superfund sites on October 4, 1989, only one has been removed from the list following cleanup. While major releases of radioactive material ended with the reactor shutdown in the 1970s and many of the most dangerous wastes are contained, there were continued concerns about contaminated groundwater headed toward the Columbia River and about workers' health and safety.
 The most significant challenge is stabilizing the of high-level radioactive waste stored in the 177 underground tanks. By 1998 about a third of these tanks had leaked waste into the soil and groundwater. By 2008 most of the liquid waste had been transferred to more secure double-shelled tanks; however, of liquid waste, together with of salt cake and sludge, remains in the single-shelled tanks. DOE lacks information about the extent to which the 27 double-shell tanks may be susceptible to corrosion. Without determining the extent to which the factors that contributed to the leak in AY102 were similar to the other 27 double-shell tanks, DOE could not be sure how long its double-shell tanks can safely store waste. That waste was originally scheduled to be removed by 2018. By 2008 the revised deadline was 2040. By 2008 of radioactive waste was traveling through the groundwater toward the Columbia River. This waste was expected to reach the river in twelve to fifty years if cleanup does not proceed on schedule.
Under the Tri-Party Agreement, lower-level hazardous wastes are buried in huge lined pits that will be sealed and monitored with sophisticated instruments for many years. Disposal of plutonium and other high-level wastes is a more difficult problem that continues to be a subject of intense debate. As an example, plutonium239 has a half-life of 24,100 years, and a decay of ten half-lives is required before a sample is considered to cease its radioactivity. In 2000 the DOE awarded a $4.3billion contract to Bechtel, a San Francisco-based construction and engineering firm, to build a Radioactive waste#Vitrification, vitrification plant to combine the dangerous wastes with glass to render them stable. Construction began in 2002. The plant was originally scheduled to be operational by 2011, with vitrification completed by 2028. According to a 2012 study by the Government Accountability Office, there were a number of serious unresolved technical and managerial problems. In 2013 the estimated costs were $13.4billion with commencement of operations estimated to be in 2022 and about three decades of operation. A potential radioactive leak was reported in 2013; the cleanup was estimated to have cost $40billion, with $115billion more required. Another leak was reported in April 2021.
The most significant challenge is stabilizing the of high-level radioactive waste stored in the 177 underground tanks. By 1998 about a third of these tanks had leaked waste into the soil and groundwater. By 2008 most of the liquid waste had been transferred to more secure double-shelled tanks; however, of liquid waste, together with of salt cake and sludge, remains in the single-shelled tanks. DOE lacks information about the extent to which the 27 double-shell tanks may be susceptible to corrosion. Without determining the extent to which the factors that contributed to the leak in AY102 were similar to the other 27 double-shell tanks, DOE could not be sure how long its double-shell tanks can safely store waste. That waste was originally scheduled to be removed by 2018. By 2008 the revised deadline was 2040. By 2008 of radioactive waste was traveling through the groundwater toward the Columbia River. This waste was expected to reach the river in twelve to fifty years if cleanup does not proceed on schedule.
Under the Tri-Party Agreement, lower-level hazardous wastes are buried in huge lined pits that will be sealed and monitored with sophisticated instruments for many years. Disposal of plutonium and other high-level wastes is a more difficult problem that continues to be a subject of intense debate. As an example, plutonium239 has a half-life of 24,100 years, and a decay of ten half-lives is required before a sample is considered to cease its radioactivity. In 2000 the DOE awarded a $4.3billion contract to Bechtel, a San Francisco-based construction and engineering firm, to build a Radioactive waste#Vitrification, vitrification plant to combine the dangerous wastes with glass to render them stable. Construction began in 2002. The plant was originally scheduled to be operational by 2011, with vitrification completed by 2028. According to a 2012 study by the Government Accountability Office, there were a number of serious unresolved technical and managerial problems. In 2013 the estimated costs were $13.4billion with commencement of operations estimated to be in 2022 and about three decades of operation. A potential radioactive leak was reported in 2013; the cleanup was estimated to have cost $40billion, with $115billion more required. Another leak was reported in April 2021.
 In May 2007 state and federal officials began closed-door negotiations about the possibility of extending legal cleanup deadlines for waste vitrification in exchange for shifting the focus of the cleanup to urgent priorities, such as groundwater remediation. Those talks stalled in October 2007. In early 2008 a $600million cut to the Hanford cleanup budget was proposed. Washington state officials expressed concern about the budget cuts, as well as missed deadlines and recent safety lapses at the site, and threatened to file a lawsuit alleging that the DOE was in violation of environmental laws. They appeared to step back from that threat in April 2008 after another meeting of federal and state officials resulted in progress toward a tentative agreement. Some of the radioactive waste at Hanford was supposed to be stored in the planned Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository, but after that project was suspended, Washington State sued, joined by South Carolina. Their first suit was dismissed in July 2011. In a subsequent suit, federal authorities were ordered to either approve or reject plans for the Yucca Mountain storage site.
During excavations from 2004 to 2007, a sample of purified plutonium was uncovered inside a safe in a waste trench, and has been dated to about the 1940s, making it the second-oldest sample of purified plutonium known to exist. Analyses published in 2009 concluded that the sample originated at Oak Ridge, and was one of several sent to Hanford for optimization tests of the TPlant until Hanford could produce its own plutonium. Documents refer to such a sample, belonging to "Watt's group", which was disposed of in its safe when a radiation leak was suspected.
In May 2007 state and federal officials began closed-door negotiations about the possibility of extending legal cleanup deadlines for waste vitrification in exchange for shifting the focus of the cleanup to urgent priorities, such as groundwater remediation. Those talks stalled in October 2007. In early 2008 a $600million cut to the Hanford cleanup budget was proposed. Washington state officials expressed concern about the budget cuts, as well as missed deadlines and recent safety lapses at the site, and threatened to file a lawsuit alleging that the DOE was in violation of environmental laws. They appeared to step back from that threat in April 2008 after another meeting of federal and state officials resulted in progress toward a tentative agreement. Some of the radioactive waste at Hanford was supposed to be stored in the planned Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository, but after that project was suspended, Washington State sued, joined by South Carolina. Their first suit was dismissed in July 2011. In a subsequent suit, federal authorities were ordered to either approve or reject plans for the Yucca Mountain storage site.
During excavations from 2004 to 2007, a sample of purified plutonium was uncovered inside a safe in a waste trench, and has been dated to about the 1940s, making it the second-oldest sample of purified plutonium known to exist. Analyses published in 2009 concluded that the sample originated at Oak Ridge, and was one of several sent to Hanford for optimization tests of the TPlant until Hanford could produce its own plutonium. Documents refer to such a sample, belonging to "Watt's group", which was disposed of in its safe when a radiation leak was suspected.
Federal agency
that regulates Hanford cleanup
State agency
that regulates Hanford cleanup *Historic American Engineering Record documentation: ** ** ** ** ** ** ** {{portal bar, Energy, History of science, Nuclear technology, Pacific Northwest, World War II, United States Hanford Site, Geography of Benton County, Washington Columbia River Environmental disasters in the United States Geography of Washington (state) Historic American Engineering Record in Washington (state) History of Washington (state) History of the Manhattan Project Industrial buildings and structures in Washington (state) Nuclear history of the United States Nuclear weapons infrastructure of the United States Radioactive waste repositories in the United States Tri-Cities, Washington United States Department of Energy facilities Buildings and structures in Benton County, Washington Tourist attractions in Benton County, Washington Radioactively contaminated areas 1943 establishments in Washington (state) Military Superfund sites Superfund sites in Washington (state) Military research of the United States Gravitational-wave astronomy Atomic tourism Nuclear accidents and incidents in the United States Decommissioned nuclear power stations in the United States
 The Hanford Site is a decommissioned nuclear production complex operated by the United States federal government on the
The Hanford Site is a decommissioned nuclear production complex operated by the United States federal government on the Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, C ...
in Benton County in the U.S. state of Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
. The site has been known by many names, including SiteW and the Hanford Nuclear Reservation. Established in 1943 as part of the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
, the site was home to the Hanford Engineer Works
The Hanford Engineer Works was a nuclear production complex established by the United States federal government in 1943 as part of the Manhattan Project during World War II. The site, located at the Hanford Site on the Columbia River in Bento ...
and B Reactor, the first full-scale plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibi ...
production reactor in the world. Plutonium manufactured at the site was used in the first atomic bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
, which was tested in the Trinity nuclear test
Trinity was the code name of the first detonation of a nuclear weapon. It was conducted by the United States Army at 5:29 a.m. on July 16, 1945, as part of the Manhattan Project. The test was conducted in the Jornada del Muerto desert abo ...
, and in the Fat Man
"Fat Man" (also known as Mark III) is the codename for the type of nuclear bomb the United States detonated over the Japanese city of Nagasaki on 9 August 1945. It was the second of the only two nuclear weapons ever used in warfare, the fir ...
bomb that was used in the bombing of Nagasaki
The United States detonated two atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki on 6 and 9 August 1945, respectively. The two bombings killed between 129,000 and 226,000 people, most of whom were civilians, and remain the on ...
.
During the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, the project expanded to include nine nuclear reactors and five large plutonium processing complexes, which produced plutonium for most of the more than sixty thousand weapons built for the U.S. nuclear arsenal. Nuclear technology
Nuclear technology is technology that involves the nuclear reactions of atomic nuclei. Among the notable nuclear technologies are nuclear reactors, nuclear medicine and nuclear weapons. It is also used, among other things, in smoke detectors an ...
developed rapidly during this period, and Hanford scientists produced major technological achievements. Many early safety procedures and waste disposal practices were inadequate, resulting in the release of significant amounts of radioactive materials into the air and the Columbia River.
The weapons production reactors were decommissioned at the end of the Cold War, and the Hanford Site became the focus of the nation's largest environmental cleanup
Environmental remediation deals with the removal of pollution or contaminants from environmental media such as soil, groundwater, sediment, or surface water. Remedial action is generally subject to an array of regulatory requirements, and may also ...
. Besides the cleanup project, Hanford hosted a commercial nuclear power plant, the Columbia Generating Station
Columbia Generating Station is a nuclear commercial energy facility located on the Hanford Site, north of Richland, Washington. It is owned and operated by Energy Northwest, a Washington state, not-for-profit joint operating agency. Licensed by ...
, and various centers for scientific research and development, such as the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) is one of the United States Department of Energy national laboratories, managed by the Department of Energy's (DOE) Office of Science. The main campus of the laboratory is in Richland, Washington.
O ...
, the Fast Flux Test Facility
The Fast Flux Test Facility (FFTF) is a 400 MW thermal, liquid sodium cooled, nuclear test reactor owned by the U.S. Department of Energy.
It does not generate electricity. It is situated in the ''400 Area'' of the Hanford Site, which is located ...
and the LIGO Hanford Observatory. In 2015 it was designated as part of the Manhattan Project National Historical Park
Manhattan Project National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park commemorating the Manhattan Project that is run jointly by the National Park Service and Department of Energy. The park consists of three units: one in Oak Ri ...
.
Geography
 The Hanford Site occupies roughly equivalent to half the total area of
The Hanford Site occupies roughly equivalent to half the total area of Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
within Benton County, Washington
Benton County is a county in the south-central portion of the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2020 census, its population was 206,873. The county seat is Prosser, and its largest city is Kennewick. The Columbia River demarcates the coun ...
. This land is closed to the general public. It is a desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
environment receiving less than of annual precipitation, covered mostly by shrub-steppe vegetation. The Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, C ...
flows along the site for approximately , forming its northern and eastern boundary. The Columbia and Yakima River
The Yakima River is a tributary of the Columbia River in south central and eastern Washington state, named for the indigenous Yakama people. Lewis and Clark mention in their journals that the Chin-nâm pam (or the Lower Snake River Chamnapam Nat ...
s contain salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the ...
, sturgeon
Sturgeon is the common name for the 27 species of fish belonging to the family Acipenseridae. The earliest sturgeon fossils date to the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretace ...
, steelhead trout
Steelhead, or occasionally steelhead trout, is the common name of the anadromous form of the coastal rainbow trout or redband trout (O. m. gairdneri). Steelhead are native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific basin in Northeast Asia and N ...
and bass, and wildlife in the area includes skunk
Skunks are mammals in the family Mephitidae. They are known for their ability to spray a liquid with a strong, unpleasant scent from their anal glands. Different species of skunk vary in appearance from black-and-white to brown, cream or ginge ...
s, muskrat
The muskrat (''Ondatra zibethicus'') is a medium-sized semiaquatic rodent native to North America and an introduced species in parts of Europe, Asia, and South America. The muskrat is found in wetlands over a wide range of climates and habitat ...
s, coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans'') is a species of canis, canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the wolf, and slightly smaller than the closely related eastern wolf and red wolf. It fills much of the same ecologica ...
s, raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight of ...
s, deer, eagles, hawks and owls. The flora includes sagebrush
Sagebrush is the common name of several woody and herbaceous species of plants in the genus ''Artemisia''. The best known sagebrush is the shrub ''Artemisia tridentata''. Sagebrushes are native to the North American west.
Following is an alph ...
, bitterbrush
''Purshia'' (bitterbrush or cliff-rose) is a small genus of 5–8 species of flowering plants in the family Rosaceae which are native to western North America.
Description
''Purshia'' species form deciduous or evergreen shrubs, typically reach ...
, a variety of grasses, prickly pear and willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist s ...
.
The original site was and included buffer areas across the river in Grant
Grant or Grants may refer to:
Places
*Grant County (disambiguation)
Australia
* Grant, Queensland, a locality in the Barcaldine Region, Queensland, Australia
United Kingdom
*Castle Grant
United States
* Grant, Alabama
*Grant, Inyo County, C ...
and Franklin
Franklin may refer to:
People
* Franklin (given name)
* Franklin (surname)
* Franklin (class), a member of a historical English social class
Places Australia
* Franklin, Tasmania, a township
* Division of Franklin, federal electoral d ...
counties. Some of this land has been returned to private use and is now covered with orchards, vineyards, and irrigated fields. The site is bordered on the southeast by the TriCities
Twin cities are a special case of two neighboring cities or urban centres that grow into a single conurbation – or narrowly separated urban areas – over time. There are no formal criteria, but twin cities are generally comparable in stat ...
, a metropolitan area composed of Richland, Kennewick
Kennewick () is a city in Benton County in the U.S. state of Washington. It is located along the southwest bank of the Columbia River, just southeast of the confluence of the Columbia and Yakima rivers and across from the confluence of the C ...
, Pasco, and smaller communities, and home to nearly 300,000 residents. Hanford is a primary economic base for these cities. In 2000 large portions of the original site were turned over to the Hanford Reach National Monument
The Hanford Reach National Monument is a national monument in the U.S. state of Washington. It was created in 2000, mostly from the former security buffer surrounding the Hanford Nuclear Reservation. The area has been untouched by development or ...
. The remainder was divided by function into three main areas: the nuclear reactors were located along the river in an area designated as the 100Area; the chemical separations complexes were located inland in the Central Plateau, designated as the 200Area; and various support facilities were located in the southeast corner of the site, designated as the 300 Area.
Climate
Hanford is the site of Washington state's highest recorded temperature of , reached on June 29, 2021.Early history
The confluence of theYakima
Yakima ( or ) is a city in and the county seat of Yakima County, Washington, and the state's 11th-largest city by population. As of the 2020 census, the city had a total population of 96,968 and a metropolitan population of 256,728. The uninco ...
, Snake
Snakes are elongated, Limbless vertebrate, limbless, carnivore, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other Squamata, squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping Scale (zoology), scales. Ma ...
, and Columbia rivers has been a meeting place for native peoples for centuries. The archaeological record of Native American habitation of this area stretches back over ten thousand years. Tribes and nations including the Yakama
The Yakama are a Native American tribe with nearly 10,851 members, based primarily in eastern Washington state.
Yakama people today are enrolled in the federally recognized tribe, the Confederated Tribes and Bands of the Yakama Nation. Their ...
, Nez Perce
The Nez Percé (; autonym in Nez Perce language: , meaning "we, the people") are an Indigenous people of the Plateau who are presumed to have lived on the Columbia River Plateau in the Pacific Northwest region for at least 11,500 years.Ames, K ...
, and Umatilla used the area for hunting, fishing, and gathering plant foods. Archaeologist
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
s have identified numerous Native American sites, including "pit house villages, open campsites, fish farming sites, hunting/kill sites, game drive complexes, quarries, and spirit quest sites", and two archaeological sites were listed on the National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic v ...
in 1976.Hanford Island Archaeological Site (NRHP #76001870) and Hanford North Archaeological District (NRHP #76001871). (See also the commercial sitNational Register of Historic Places.)
/ref> In 1855
Isaac Stevens
Isaac Ingalls Stevens (March 25, 1818 – September 1, 1862) was an American military officer and politician who served as governor of the Territory of Washington from 1853 to 1857, and later as its delegate to the United States House of Represe ...
, the governor of the Territory of Washington
The Territory of Washington was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1853, until November 11, 1889, when the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Washington. It was created from the ...
, negotiated with the Native American tribes to establish a reservation system. Treaties were signed, but were often ignored, as the reservation system was not compatible with their traditional food-gathering or family groupings. In September 1858 a military expedition under Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of ...
George Wright George Wright may refer to:
Politics, law and government
* George Wright (MP) (died 1557), MP for Bedford and Wallingford
* George Wright (governor) (1779–1842), Canadian politician, lieutenant governor of Prince Edward Island
* George Wright ...
defeated the Native American tribes in the Battle of Spokane Plains to force compliance with the reservation system. Nonetheless, Native American use of the area continued into the 20th century. The Wanapum
The Wanapum tribe of Native Americans formerly lived along the Columbia River from above Priest Rapids down to the mouth of the Snake River in what is now the US state of Washington. About 60 Wanapum still live near the present day site of Pri ...
people were never forced onto a reservation, and they lived along the Columbia River in the Priest Rapids Valley until 1943.
After gold was discovered in British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
, prospectors explored the Columbia River basin in search of gold, but with little success. Walla Walla Walla Walla can refer to:
* Walla Walla people, a Native American tribe after which the county and city of Walla Walla, Washington, are named
* Place of many rocks in the Australian Aboriginal Wiradjuri language, the origin of the name of the town ...
, which had been established as a military post in 1858, became a center for mining supplies, and a general store was established at White Bluffs. A ranch was established in Yakima Valley by Ben Snipes in 1859, and the Northern Pacific Railroad
The Northern Pacific Railway was a transcontinental railroad that operated across the northern tier of the western United States, from Minnesota to the Pacific Northwest. It was approved by 38th United States Congress, Congress in 1864 and given ...
was extended into the area, beginning in 1879. Railroad engineers founded the towns of Kennewick and Pasco. Settlers moved into the region, initially along the Columbia River south of Priest Rapids. They established farms and orchards supported by small-scale irrigation projects, but most went bankrupt in the Panic of 1893
The Panic of 1893 was an economic depression in the United States that began in 1893 and ended in 1897. It deeply affected every sector of the economy, and produced political upheaval that led to the political realignment of 1896 and the pres ...
. The Reclamation Act of 1902
The Reclamation Act (also known as the Lowlands Reclamation Act or National Reclamation Act) of 1902 () is a United States federal law that funded irrigation projects for the arid lands of 20 states in the American West.
The act at first cover ...
provided for federal government participation in the financing of irrigation projects, and the population began expanding again, with small town centers at Hanford, White Bluffs and Richland established between 1905 and 1910. The Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
of the 1930s decreased the price of agricultural commodities and many farms were foreclosed or abandoned. The economy was supported by the construction of the Grand Coulee Dam
Grand Coulee Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington, built to produce hydroelectric power and provide irrigation water. Constructed between 1933 and 1942, Grand Coulee originally had two powerh ...
between 1933 and 1942, and the establishment of the Naval Air Station Pasco in 1942.
Manhattan Project
Contractor selection
DuringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the S-1 Section of the federal Office of Scientific Research and Development
The Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) was an agency of the United States federal government created to coordinate scientific research for military purposes during World War II. Arrangements were made for its creation during May 1 ...
(OSRD) sponsored a research project on plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibi ...
. Research was conducted by scientists at the University of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chicago is consistently ranked among the b ...
Metallurgical Laboratory. At the time, plutonium was a rare element that had only recently been synthesized in laboratories. It was theorized that plutonium was fissile
In nuclear engineering, fissile material is material capable of sustaining a nuclear fission chain reaction. By definition, fissile material can sustain a chain reaction with neutrons of thermal energy. The predominant neutron energy may be typ ...
and could be used in an atomic bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
. The United States government was concerned that Germany was developing a nuclear weapons program. The Metallurgical Laboratory physicists worked on designing nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from nu ...
s ("piles") that could irradiate uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
and transmute it into plutonium. Meanwhile, chemists investigated ways to separate plutonium from uranium.
In September 1942 Brigadier General
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed ...
Leslie R. Groves Jr.
Lieutenant general (United States), Lieutenant General Leslie Richard Groves Jr. (17 August 1896 – 13 July 1970) was a United States Army Corps of Engineers Officer (armed forces), officer who oversaw the construction of the Pentagon and di ...
became the director of the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
, as it came to be known. The project to build industrial-size plants for the manufacture of plutonium was codenamed the X10 project. Groves engaged DuPont
DuPont de Nemours, Inc., commonly shortened to DuPont, is an American multinational chemical company first formed in 1802 by French-American chemist and industrialist Éleuthère Irénée du Pont de Nemours. The company played a major role in ...
, a firm he had worked with in the past on the construction of explosives plants, to design, construct and operate the plutonium manufacturing complex. To avoid being labeled as merchants of death
Merchants of death was an epithet used in the U.S. in the 1930s to attack industries and banks that had supplied and funded World War I (then called the Great War).
Origin
The term originated in 1932 as the title of an article about an arms d ...
, as the company had been after World WarI, DuPont's executive committee insisted that it should receive no payment. For legal reasons, a Cost Plus Fixed Fee
A cost-plus contract, also termed a cost plus contract, is a contract such that a contractor is paid for all of its allowed expenses, ''plus'' additional payment to allow for a profit.Walter S. Carpenter Jr.
Walter Samuel Carpenter Jr. (January 8, 1888 – February 2, 1976) was an American corporate executive from Wilmington, Delaware, who oversaw the DuPont company's involvement in the Manhattan Project to produce an atomic bomb for use during Wo ...
, was given assurances that the government was assuming all responsibility for the hazards involved in the project.
Site selection
Carpenter expressed reservations about building the reactors at Oak Ridge, Tennessee; withKnoxville
Knoxville is a city in and the county seat of Knox County in the U.S. state of Tennessee. As of the 2020 United States census, Knoxville's population was 190,740, making it the largest city in the East Tennessee Grand Division and the state's ...
only away, a catastrophic accident might result in loss of life and severe health effects. Even a less deadly accident might disrupt vital war production, particularly of aluminum, and force the evacuation of the Manhattan Project's isotope separation
Isotope separation is the process of concentrating specific isotopes of a chemical element by removing other isotopes. The use of the nuclides produced is varied. The largest variety is used in research (e.g. in chemistry where atoms of "marker" n ...
plants. Spreading the facilities at Oak Ridge out more would require the purchase of more land and the expansion needed was still uncertain; for planning purposes, six reactors and four chemical separation plants were envisioned.
The ideal site was described by eight criteria:
#A clean and abundant water supply (at least )
#A large electric power supply (about 100,000 KW)
#A "hazardous manufacturing area" of at least
#Space for laboratory facilities at least from the nearest reactor or separations plant
#The employees' village no less than upwind of the plant
#No towns of more than a thousand people closer than from the hazardous rectangle
#No main highway, railway, or employee village closer than from the hazardous rectangle
#Ground that could bear heavy loads
The most important of these criteria was the availability of electric power. The needs of war industries had created power shortages in many parts of the country, and use of the Tennessee Valley Authority
The Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) is a federally owned electric utility corporation in the United States. TVA's service area covers all of Tennessee, portions of Alabama, Mississippi, and Kentucky, and small areas of Georgia, North Carolina ...
(TVA) was ruled out because the Clinton Engineer Works
The Clinton Engineer Works (CEW) was the production installation of the Manhattan Project that during World War II produced the enriched uranium used in the 1945 bombing of Hiroshima, as well as the first examples of reactor-produced pluton ...
was expected to use up all its surplus power. This led to consideration of alternative sites in the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
and Southwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
, where there was surplus electrical power. Between December 18 and 31, 1942, just twelve days after the Metallurgical Laboratory team led by Enrico Fermi
Enrico Fermi (; 29 September 1901 – 28 November 1954) was an Italian (later naturalized American) physicist and the creator of the world's first nuclear reactor, the Chicago Pile-1. He has been called the "architect of the nuclear age" and ...
started up Chicago Pile 1, the first nuclear reactor, a three-man party consisting of Colonel Franklin T. Matthias
Franklin Thompson Matthias (13 March 1908 – 3 December 1993) was an American civil engineer who directed the construction of the Hanford nuclear site, a key facility of the Manhattan Project during World War II.
A graduate of the University o ...
and DuPont engineers A. E. S. Hall and Gilbert P. Church inspected the most promising potential sites. Matthias reported to Groves that the Hanford Site was "far more favorable in virtually all respects than any other"; the survey party was particularly impressed by the fact that a high-voltage power line from Grand Coulee Dam to Bonneville Dam
Bonneville Lock and Dam consists of several run-of-the-river dam structures that together complete a span of the Columbia River between the U.S. states of Oregon and Washington at River Mile 146.1. The dam is located east of Portland, Oregon, ...
ran through the site, and there was an electrical substation
A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform any of several other important functions. Between the generating station and ...
on its edge. Groves visited the site on January 16, 1943, and approved the selection. The facility became known as the Hanford Engineer Works
The Hanford Engineer Works was a nuclear production complex established by the United States federal government in 1943 as part of the Manhattan Project during World War II. The site, located at the Hanford Site on the Columbia River in Bento ...
(HEW), and the site was codenamed SiteW.
Land acquisition

 The
The Secretary of War
The secretary of war was a member of the U.S. president's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War", had been appointed to serve the Congress of the ...
, Henry L. Stimson
Henry Lewis Stimson (September 21, 1867 – October 20, 1950) was an American statesman, lawyer, and Republican Party politician. Over his long career, he emerged as a leading figure in U.S. foreign policy by serving in both Republican and D ...
, authorized the acquisition of the land on February 8, 1943. A Manhattan District project office opened in Prosser, Washington
Prosser () is a city in and the county seat of Benton County, Washington, United States. Situated along the Yakima River, it had a population of 5,714 at the 2010 census.
History
Prosser was long home to Native Americans who lived and fished ...
, on February 22, and the Washington Title Insurance Company opened an office there to furnish title
A title is one or more words used before or after a person's name, in certain contexts. It may signify either generation, an official position, or a professional or academic qualification. In some languages, titles may be inserted between the f ...
certificates. Federal Judge Lewis B. Schwellenbach issued an order of possession under the Second War Powers Act the following day, and the first tract was acquired on March 10. Some 4,218 tracts totaling were to be acquired, making it one of the largest land acquisition projects in American history.
Most of the land (some 88 percent) was sagebrush, where eighteen to twenty thousand sheep grazed. About eleven percent was farmland, although not all was under cultivation. Farmers felt that they should be compensated for the value of the crops they had planted as well as for the land itself. Because construction plans had not yet been drawn up, and work on the site could not immediately commence, Groves decided to postpone the taking of the physical possession of properties under cultivation to allow farmers to harvest the crops they had already planted. This reduced the hardship on the farmers, and avoided the wasting of food at a time when the nation was facing food shortages and the federal government was urging citizens to plant victory garden
Victory gardens, also called war gardens or food gardens for defense, were vegetable, fruit, and herb gardens planted at private residences and public parks in the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia and Germany during World War I ...
s. The War Department War Department may refer to:
* War Department (United Kingdom)
* United States Department of War (1789–1947)
See also
* War Office, a former department of the British Government
* Ministry of defence
* Ministry of War
* Ministry of Defence
* D ...
arranged with Federal Prison Industries
Federal Prison Industries, Inc. (FPI), doing business as UNICOR (stylized as unicor) since 1977, is a wholly owned United States government corporation created in 1934 as a prison labor program for inmates within the Federal Bureau of Prisons, ...
for crops to be harvested by prisoners from the McNeil Island Penitentiary
The McNeil Island Corrections Center (MICC) was a prison in the northwest United States, operated by the Washington State Department of Corrections. It was on McNeil Island in Puget Sound in unincorporated Pierce County, near Steilacoom, Washin ...
.
The harvest in the spring and summer of 1943 was exceptionally good, and high crop prices due to the war greatly increased land prices. It also promoted exaggerated ideas about the value of the land, leading to litigation. Discontent over the acquisition was apparent in letters sent from Hanford Site residents to the War and Justice Department
A justice ministry, ministry of justice, or department of justice is a ministry or other government agency in charge of the administration of justice. The ministry or department is often headed by a minister of justice (minister for justice in a ...
s, and the Truman Committee began making inquiries. Stimson met with chairman of the committee, Senator Harry S. Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A leader of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 34th vice president from January to April 1945 under Franklin ...
, who agreed to remove the Hanford Site from the committee's investigations on the grounds of national security. Trial juries were sympathetic to the claims of the landowners and the payments awarded were well in excess of the government appraisals. When the Manhattan Project ended on December 31, 1946, there were still 237 tracts remaining to be settled.
About 1,500 residents of Hanford, White Bluffs, and nearby settlements were relocated, as well as the Wanapum people, Confederated Tribes and Bands of the Yakima Nation
The Yakama Indian Reservation (spelled Yakima until 1994) is a Native American reservation in Washington state of the federally recognized tribe known as the Confederated Tribes and Bands of the Yakama Nation. The tribe is made up of Klikitat ...
, the Confederated Tribes of the Umatilla Indian Reservation
The Umatilla Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation in the Pacific Northwest of the United States. It was created by The Treaty of June 9, 1855 between the United States and members of the Walla, Cayuse, and Umatilla tribes. It lies in nort ...
, and the Nez Perce Tribe. Native Americans were accustomed to fishing in the Columbia River near White Bluffs for two or three weeks in October. The fish they caught was dried and provided food for the winter. They rejected offers of an annual cash payment, and a deal was struck allowing the chief and his two assistants to issue passes to fish at the site. This authority was later revoked for security reasons. Matthias gave assurances that Native American graves would be treated with respect, but it would be fifteen years before the Wanapum people were allowed access to mark the cemeteries. In 1997 the elders were permitted to bring children and young adults onto the site once a year to learn about their sacred sites.
Construction workforce
DuPont advertised for workers in newspapers for an unspecified "war construction project" in southeastern Washington, offering an "attractive scale of wages" and living facilities. Normally for a development in such an isolated area, employees would be accommodated on site, but in this case for security and safety reasons it was desirable to locate them at least away. Even the construction workforce could not be housed on site, because some plant operations would have to be carried out during start-up testing. The Army and DuPont engineers decided to create two communities: a temporary constructions camp and a more substantial operating village. Construction was expedited by locating them on the sites of existing villages to take advantage of the buildings, roads and utility infrastructure already in place. They established the construction camp on the site of the village of Hanford, and the operating village on that of Richland. The construction workforce peaked at 45,096 on June 21, 1944. About thirteen percent were women, and non-whites made up 16.45 percent. African-Americans lived in segregated quarters, had their own
The construction workforce peaked at 45,096 on June 21, 1944. About thirteen percent were women, and non-whites made up 16.45 percent. African-Americans lived in segregated quarters, had their own mess
The mess (also called a mess deck aboard ships) is a designated area where military personnel socialize, eat and (in some cases) live. The term is also used to indicate the groups of military personnel who belong to separate messes, such as the o ...
es and recreation areas, and were paid less than white workers. Three types of accommodation were provided at Hanford: barracks, hutments and trailer parking. The first workers to arrive lived in tents while they erected the first barracks. Barracks construction commenced on April 6, 1943, and eventually 195 barracks were erected: 110 for white men, 21 for black men, 57 for white women and seven for black women. Hutments were prefabricated plywood
Plywood is a material manufactured from thin layers or "plies" of wood veneer that are glued together with adjacent layers having their wood grain rotated up to 90 degrees to one another. It is an engineered wood from the family of manufactured ...
and Celotex
Celotex Corporation is a defunct American manufacturer of insulation and construction materials. It was the subject of a number of high-profile lawsuits over products containing asbestos in the 1980s, eventually declaring Chapter 11 bankruptcy in ...
dwellings capable of accommodating ten to twenty workers each. Between them, the barracks and hutments held 39,050 workers. Many workers had their own trailers, taking their families with them from one wartime construction job to the next. Seven trailer camps were established, and at the peak of construction work 12,008 people were living in them.
DuPont put the contract for building the village of Richland out to tender, and the contract was awarded to the lowest bidder, G. Albin Pehrson, on March 16, 1943. Pehrson produced a series of standard house designs based on the Cape Cod
Cape Cod is a peninsula extending into the Atlantic Ocean from the southeastern corner of mainland Massachusetts, in the northeastern United States. Its historic, maritime character and ample beaches attract heavy tourism during the summer mont ...
and ranch-style house design fashions of the day. Pehrson accepted the need for speed and efficiency, but his vision of a model late-20th-century community differed from the austere concept of Groves. Pehrson ultimately had his way on most issues, because DuPont was his contractor, not the Army. The resulting compromise would handicap Richland for many years with inadequate sidewalks, stores and shops, no civic center, and roads that were too narrow. Unlike Oak Ridge and Los Alamos, New Mexico, Los Alamos, Richland was not surrounded by a high wire fence. Because it was open, Matthias asked DuPont to ensure that it was kept neat and tidy.
Construction
 Construction of the nuclear facilities proceeded rapidly. Before the end of the war in August 1945, the HEW built 554 buildings at Hanford, including three nuclear reactors (105B, 105D, and 105F) and three plutonium processing plants (221T, 221B, and 221U). The project required of roads, of railway, and four electrical substations. The HEW used of concrete and of structural steel.
Construction on B Reactor commenced in August 1943 and was completed on September 13, 1944. The reactor went Critical mass, critical in late September and, after overcoming neutron poisoning, produced its first plutonium on November 6, 1944. The reactors were Nuclear graphite, graphite moderated and water cooled. They consisted of a , graphite cylinder lying on its side, penetrated horizontally through its entire length by 2,004 aluminum tubes. containing of uranium slugs. They had no moving parts; the only sounds were those of the water pumps. Cooling water was pumped through the tubes at the rate of . This was enough water for a city of a million people.
Construction of the nuclear facilities proceeded rapidly. Before the end of the war in August 1945, the HEW built 554 buildings at Hanford, including three nuclear reactors (105B, 105D, and 105F) and three plutonium processing plants (221T, 221B, and 221U). The project required of roads, of railway, and four electrical substations. The HEW used of concrete and of structural steel.
Construction on B Reactor commenced in August 1943 and was completed on September 13, 1944. The reactor went Critical mass, critical in late September and, after overcoming neutron poisoning, produced its first plutonium on November 6, 1944. The reactors were Nuclear graphite, graphite moderated and water cooled. They consisted of a , graphite cylinder lying on its side, penetrated horizontally through its entire length by 2,004 aluminum tubes. containing of uranium slugs. They had no moving parts; the only sounds were those of the water pumps. Cooling water was pumped through the tubes at the rate of . This was enough water for a city of a million people.
Production process
Uranium arrived at the Hanford Engineer Works in the form of Billet (semi-finished product), billets. In the Metal Fabrication and Testing (500) Area they were extruded into rods and machined into cylindrical pieces, in diameter and long, known as "slugs". The initial charge of the three reactors required more than twenty thousand billets, and another two thousand were required each month. Uranium was highly reactive with water, so to protect them from corrosion by the cooling water they were canned in aluminum a molten bath of copper–tin alloy, and the cap was arc welding, arc welded on. A defective can could burst and jam in the reactor, stop the flow of cooling water, and force a complete shutdown of the reactor, so the canning process had to be exacting. Irradiated fuel slugs were transported by rail to huge remotely operated chemical separation plants about away on a special railroad car operated by remote control. The separation buildings were massive windowless concrete structures, long, high and wide, with concrete walls thick. Inside the buildings were canyons and galleries where Bismuth-phosphate process, a series of chemical processing steps separated the small amount of plutonium from the remaining uranium and fission products.
Items were moved about with a long overhead crane. Once they began processing irradiated slugs, the machinery became so radioactive that it would be unsafe for humans ever to come in contact with it, so the engineers devised methods to allow for the replacement of components via remote control. Periscopes and closed-circuit television gave the operator a view of the process. They assembled the equipment by remote control as if the area was already radioactive. To receive the radioactive wastes from the chemical separations process, there were "tank farms" consisting of 64 single-shell underground waste tanks.
The first batch of plutonium was refined in the 221T plant from December 26, 1944, to February 2, 1945, and delivered to the Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos laboratory in New Mexico on February 5, 1945. Two identical reactors, DReactor and FReactor, came online on December 5, 1944, and February 15, 1945, respectively, and all three reactors were running at full power (250 megawatts) by March 8, 1945. By April kilogram-quantity shipments of plutonium were headed to Los Alamos. Road convoys replaced the trains in May, and in late July shipments began being dispatched by air from the airport at Hanford.
Irradiated fuel slugs were transported by rail to huge remotely operated chemical separation plants about away on a special railroad car operated by remote control. The separation buildings were massive windowless concrete structures, long, high and wide, with concrete walls thick. Inside the buildings were canyons and galleries where Bismuth-phosphate process, a series of chemical processing steps separated the small amount of plutonium from the remaining uranium and fission products.
Items were moved about with a long overhead crane. Once they began processing irradiated slugs, the machinery became so radioactive that it would be unsafe for humans ever to come in contact with it, so the engineers devised methods to allow for the replacement of components via remote control. Periscopes and closed-circuit television gave the operator a view of the process. They assembled the equipment by remote control as if the area was already radioactive. To receive the radioactive wastes from the chemical separations process, there were "tank farms" consisting of 64 single-shell underground waste tanks.
The first batch of plutonium was refined in the 221T plant from December 26, 1944, to February 2, 1945, and delivered to the Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos laboratory in New Mexico on February 5, 1945. Two identical reactors, DReactor and FReactor, came online on December 5, 1944, and February 15, 1945, respectively, and all three reactors were running at full power (250 megawatts) by March 8, 1945. By April kilogram-quantity shipments of plutonium were headed to Los Alamos. Road convoys replaced the trains in May, and in late July shipments began being dispatched by air from the airport at Hanford.
Production activities
 Although the reactors could be shut down in two-and-a-half seconds, the decay of fission products meant that they would still generate heat due to the decay of fission products. It was therefore vital that the flow of water should not cease. If the power failed, the steam pumps would automatically cut in and continue to deliver water at full capacity for long enough to allow an orderly shutdown. This occurred on March 10, 1945, when a Japanese Fu-Go balloon bomb, balloon bomb struck a high-tension line between Grand Coulee and Bonneville. This caused an electrical surge in the lines to the reactors. A scram was automatically initiated and the safety devices shut the reactors down. The bomb failed to explode and the transmission line was not badly damaged. The Hanford Engineer Works was the only U.S. nuclear facility to come under enemy attack.
Hanford provided the plutonium for the bomb used in the 1945
Although the reactors could be shut down in two-and-a-half seconds, the decay of fission products meant that they would still generate heat due to the decay of fission products. It was therefore vital that the flow of water should not cease. If the power failed, the steam pumps would automatically cut in and continue to deliver water at full capacity for long enough to allow an orderly shutdown. This occurred on March 10, 1945, when a Japanese Fu-Go balloon bomb, balloon bomb struck a high-tension line between Grand Coulee and Bonneville. This caused an electrical surge in the lines to the reactors. A scram was automatically initiated and the safety devices shut the reactors down. The bomb failed to explode and the transmission line was not badly damaged. The Hanford Engineer Works was the only U.S. nuclear facility to come under enemy attack.
Hanford provided the plutonium for the bomb used in the 1945 Trinity nuclear test
Trinity was the code name of the first detonation of a nuclear weapon. It was conducted by the United States Army at 5:29 a.m. on July 16, 1945, as part of the Manhattan Project. The test was conducted in the Jornada del Muerto desert abo ...
. Throughout this period, the Manhattan Project maintained a top-secret classification. Fewer than one percent of Hanford's workers knew they were working on a nuclear weapons project. Groves noted in his memoirs that "We made certain that each member of the project thoroughly understood his part in the total effort; that, and nothing more." The existence and purpose of Hanford was publicly revealed through press releases on August 7 and 9, 1945, after the bombing of Hiroshima but before Hanford plutonium in a Fat Man
"Fat Man" (also known as Mark III) is the codename for the type of nuclear bomb the United States detonated over the Japanese city of Nagasaki on 9 August 1945. It was the second of the only two nuclear weapons ever used in warfare, the fir ...
bomb was used in the bombing of Nagasaki
The United States detonated two atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki on 6 and 9 August 1945, respectively. The two bombings killed between 129,000 and 226,000 people, most of whom were civilians, and remain the on ...
on August 9.
Matthias was succeeded as area engineer by Colonel Frederick J. Clarke in January 1946. DuPont would soon be gone too. Carpenter asked to be released from the contract. Groves informed Robert P. Patterson, who had succeeded Stimson as Secretary of War on September 21, 1945, Groves's choice of replacement was General Electric (GE), which took over operations at Hanford on September 1, 1946, and accepted a formal control on September 30. On December 31, 1946, the Manhattan Project ended and control of the Hanford Site passed to the United States Atomic Energy Commission, Atomic Energy Commission (AEC). The total cost of the Hanford Engineer Works up to that time was .
Cold War
Production problems
GE inherited serious problems. Running the reactors continuously at full power had resulted in the Wigner effect, swelling of the graphite due to the displacement of the atoms in its crystalline structure by collisions with neutrons. This had the potential to buckle the aluminum tubes used for the fuel and control rods and disable the reactors completely if a water pipe ruptured. The polonium-210 used in the Fat Man's neutron initiators had a half-life of only 138 days, so it was essential to keep a reactor running or the weapons would be rendered inoperative. The Army therefore shut down BReactor on March 19. In August 1946 Franklin was informed that irradiating the feed to produce over 200 grams of plutonium per metric ton of uranium was resulting in too much undesirable plutonium-240 in the product. The power level on Dand FReactors was reduced, which also extended their useful life. Some experiments were conducted with Annealing (materials science), annealing the graphite. It was found in laboratory testing of samples that heating to retired the graphite by 24 percent, to by 45 percent and to by 94 percent, but the consequences of heating the reactors so much had to be considered before this was attempted. The other problem was that the bismuth phosphate process used to separate the plutonium left the uranium in an unrecoverable state. The Metallurgical Laboratory had researched a promising new redox separation process, using hexone as a solvent. The AEC was concerned about the supply of uranium, and the General Advisory Committee of the AEC recommended that construction of a redox plant be given top priority. Meanwhile, the waste-settling tanks filled up with sludge, and attempts to transport it to the waste storage (241) areas were unsuccessful. It was therefore decided to bypass the waste settling tanks and send sludge directly to the 200 area, and construction of a bypass commenced in August 1946. GE invited bids for the construction of a new waste storage tank farm. Efforts were made to make better use of the available uranium. Metal swarf, Turnings, cuttings and shavings from the slug manufacture process had been sent to the Ames Laboratory in Iowa for briquetting. The equipment there was shipped to the Hanford Engineer Works. The briquettes, along with uranium scrap metal, was sent to the Metal Hydrides Company for recasting into billets.
During 1947, tensions with the Soviet Union escalated as the
The other problem was that the bismuth phosphate process used to separate the plutonium left the uranium in an unrecoverable state. The Metallurgical Laboratory had researched a promising new redox separation process, using hexone as a solvent. The AEC was concerned about the supply of uranium, and the General Advisory Committee of the AEC recommended that construction of a redox plant be given top priority. Meanwhile, the waste-settling tanks filled up with sludge, and attempts to transport it to the waste storage (241) areas were unsuccessful. It was therefore decided to bypass the waste settling tanks and send sludge directly to the 200 area, and construction of a bypass commenced in August 1946. GE invited bids for the construction of a new waste storage tank farm. Efforts were made to make better use of the available uranium. Metal swarf, Turnings, cuttings and shavings from the slug manufacture process had been sent to the Ames Laboratory in Iowa for briquetting. The equipment there was shipped to the Hanford Engineer Works. The briquettes, along with uranium scrap metal, was sent to the Metal Hydrides Company for recasting into billets.
During 1947, tensions with the Soviet Union escalated as the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
set in. Clarke was succeeded by Carleton Shugg on September 2. Within days of arrival he demanded overtime be used to speed up construction work then in progress. The size of the nuclear stockpile was limited by plutonium production. There was enough for thirteen bombs at the end of 1947. Walter J. Williams, the AEC's director of production, worked with GE engineers to produce plans for three replacement reactors (called BR, DR and FR). To save time and money, they would be built adjacent to the existing reactors, where they would be able to use their cooling water and separation facilities. Two more reactors would then be built on new sites.
 While this was being considered by the AEC, GE experimented with annealing, and found that if the reactors were run at and then slowly cooled, the graphite's crystalline structure could be restored. The reactors could be run at higher temperatures by increasing the power level. Some helium in the atmosphere surrounding the reactors was replaced with carbon dioxide, which conducted heat less efficiently. This allowed more heat to build up in the graphite. To reduce the incidence of cans jamming, their size was reduced from . More plutonium was produced by keeping the fuel elements in the reactor longer. Instead of pushing the entire tube out, half of it was, allowing elements to spend time in parts of the reactor where the neutron flux was less dense. The old reactors could now be run much longer. In December the AEC approved a scaled-back construction plan, with only one replacement reactor, at siteD (called DR), and one reactor at a new site (called H). The new reactors used the same designs as the wartime ones, although they had more pure graphite to allow them to be run at higher power levels, and smaller graphite blocks surrounding the process tubes to restrict expansion.
While this was being considered by the AEC, GE experimented with annealing, and found that if the reactors were run at and then slowly cooled, the graphite's crystalline structure could be restored. The reactors could be run at higher temperatures by increasing the power level. Some helium in the atmosphere surrounding the reactors was replaced with carbon dioxide, which conducted heat less efficiently. This allowed more heat to build up in the graphite. To reduce the incidence of cans jamming, their size was reduced from . More plutonium was produced by keeping the fuel elements in the reactor longer. Instead of pushing the entire tube out, half of it was, allowing elements to spend time in parts of the reactor where the neutron flux was less dense. The old reactors could now be run much longer. In December the AEC approved a scaled-back construction plan, with only one replacement reactor, at siteD (called DR), and one reactor at a new site (called H). The new reactors used the same designs as the wartime ones, although they had more pure graphite to allow them to be run at higher power levels, and smaller graphite blocks surrounding the process tubes to restrict expansion.
Growth of Richland
The population of Richland had already begun to increase again. In 1946 the Hanford Site had 4,479 operating employees and 141 construction workers. Two years later this had increased to 8,628 operating employees and 14,671 construction workers. Richland grew from 14,000 people in 1947 to 22,000 in 1950. To house the construction workers, a new construction camp was established called North Richland, which had a peak population of 13,000 in 1948. Many operating employees and construction workers also lived in Kennewick and Pasco. Shugg arranged for barracks to be brought by barge down the Columbia River from the old Naval Air Station Pasco. About 3,850 houses remained from the war; these were augmented by 800 houses and 64 apartments in 1947, and another 1,000 houses and apartments in 1948. Although the population stabilized, a housing shortage persisted into the 1950s. GE closed down the last of the dormitories in 1958. Richland had a newspaper, the ''Richland Villager'', and every resident received a free copy. Commercial concession holders were pressured to buy adverting space. The villagers paid low rents for their houses, and Village Services was available to help with unpacking, laying carpets or babysitting. The adult population of Richland had an average education of 12.5 years, and 40 percent of the men had attended college, compared with 22 percent in the state of Washington as a whole, and the median annual family income in 1959 was compared with . In 1950 26 percent of American families had an annual income of less than the poverty line of . In the nearby towns of Pasco and Kennewick, 24.4 and 25.2 percent respectively were below the poverty line; in Richland, it was just 4.9 percent. The percentage of high school graduates in Richland was 74.3 percent, compared with 53.5 in Pasco and 54.6 in Kennewick. Women constituted a quarter of the workforce, and the number of working wives was much higher than the national average. Although GE liked to present an image of a American middle class, middle-class community, most of the Hanford Site employees were working-class shift workers with high school education only.
There were few senior citizens in Richlandin 1947 the AEC still required retirees to give up their homesbut the birth rate in 1948 was 34 per 1,000, well above the national average of 20 per 1,000. This tapered off during the 1950s, but there remained a larger than usual number of school-age children. There were only seven black people in Richland in 1950; this increased to 189 by 1960, when they accounted for 1.3 percent of the population. Only two black people worked for the AEC at the Hanford Site in 1951, less than a dozen were employed by GE, and about 250 by the construction contractors. The use of eating and recreational facilities by black people was discouraged, but not prohibited. Black people were even less welcome in Kennewick; there were only four living there in 1950 and five in 1960. Kennewick was a sundown town where there was a curfew for black people. They congregated in Pasco, where 1,213 black people lived in a ghetto on the town's eastern fringe. They had no sewerage or running water in 1948, because the town's leaders felt that the black community should provide the to pay for it. Black residents also did not qualify for Federal Housing Administration (FHA) loans.
The adult population of Richland had an average education of 12.5 years, and 40 percent of the men had attended college, compared with 22 percent in the state of Washington as a whole, and the median annual family income in 1959 was compared with . In 1950 26 percent of American families had an annual income of less than the poverty line of . In the nearby towns of Pasco and Kennewick, 24.4 and 25.2 percent respectively were below the poverty line; in Richland, it was just 4.9 percent. The percentage of high school graduates in Richland was 74.3 percent, compared with 53.5 in Pasco and 54.6 in Kennewick. Women constituted a quarter of the workforce, and the number of working wives was much higher than the national average. Although GE liked to present an image of a American middle class, middle-class community, most of the Hanford Site employees were working-class shift workers with high school education only.
There were few senior citizens in Richlandin 1947 the AEC still required retirees to give up their homesbut the birth rate in 1948 was 34 per 1,000, well above the national average of 20 per 1,000. This tapered off during the 1950s, but there remained a larger than usual number of school-age children. There were only seven black people in Richland in 1950; this increased to 189 by 1960, when they accounted for 1.3 percent of the population. Only two black people worked for the AEC at the Hanford Site in 1951, less than a dozen were employed by GE, and about 250 by the construction contractors. The use of eating and recreational facilities by black people was discouraged, but not prohibited. Black people were even less welcome in Kennewick; there were only four living there in 1950 and five in 1960. Kennewick was a sundown town where there was a curfew for black people. They congregated in Pasco, where 1,213 black people lived in a ghetto on the town's eastern fringe. They had no sewerage or running water in 1948, because the town's leaders felt that the black community should provide the to pay for it. Black residents also did not qualify for Federal Housing Administration (FHA) loans.
 Soon after taking over from the Army, the AEC had contemplated the future of the communities of Richland, Oak Ridge and Los Alamos. The commissioners were eager to divest the AEC of the burden of their management. In 1947 AEC general manager Carroll L. Wilson commissioned Lyman S. Moore, the city manager of Portland, Maine, and an expert on municipal government, to produce a report on the management of the communities. He produced a road map to self-government. The first step was to overhaul the accounting system to produce comparable reports on housing, commercial operations, utilities and government. It would then be possible to move to changing market rates for rents, utilities and municipal services, and ultimately to establish self-government. There was scant enthusiasm for this in Richland, but the United States was engaged in an ideological conflict with the Soviet Union over the superiority of the American way. The AEC's September 1950 appropriation called upon it to take steps to impose democratic government and free enterprise on the AEC communities.
The first step was taken on October 1, 1953, when the AEC increased the rents in Richland by 25 percent to bring them into line with those in neighboring communities. In 1955 the town voted on disposal and incorporation; both measures were overwhelmingly defeated. Nonetheless, that year Congress passed Public Law 221, which provided for the transfer of government property in Richland to the townsfolk. Thousands of people attended protest rallies and sent angry letters and petitions to Congress. Congressional hearings were held, and prices set by the FHA were reduced. People who had been dispossessed by the acquisition process during the war petitioned to be allowed to buy their property back, but they were ignored. By July 1958 4,200 homes had been sold. After receiving assurances that the AEC would continue to subsidize schools and municipal services through the 1960s, the citizens of Richland voted for incorporation, and the town became self-governing on December 12, 1958. In 1960 Richland received an All-America City Award.
Soon after taking over from the Army, the AEC had contemplated the future of the communities of Richland, Oak Ridge and Los Alamos. The commissioners were eager to divest the AEC of the burden of their management. In 1947 AEC general manager Carroll L. Wilson commissioned Lyman S. Moore, the city manager of Portland, Maine, and an expert on municipal government, to produce a report on the management of the communities. He produced a road map to self-government. The first step was to overhaul the accounting system to produce comparable reports on housing, commercial operations, utilities and government. It would then be possible to move to changing market rates for rents, utilities and municipal services, and ultimately to establish self-government. There was scant enthusiasm for this in Richland, but the United States was engaged in an ideological conflict with the Soviet Union over the superiority of the American way. The AEC's September 1950 appropriation called upon it to take steps to impose democratic government and free enterprise on the AEC communities.
The first step was taken on October 1, 1953, when the AEC increased the rents in Richland by 25 percent to bring them into line with those in neighboring communities. In 1955 the town voted on disposal and incorporation; both measures were overwhelmingly defeated. Nonetheless, that year Congress passed Public Law 221, which provided for the transfer of government property in Richland to the townsfolk. Thousands of people attended protest rallies and sent angry letters and petitions to Congress. Congressional hearings were held, and prices set by the FHA were reduced. People who had been dispossessed by the acquisition process during the war petitioned to be allowed to buy their property back, but they were ignored. By July 1958 4,200 homes had been sold. After receiving assurances that the AEC would continue to subsidize schools and municipal services through the 1960s, the citizens of Richland voted for incorporation, and the town became self-governing on December 12, 1958. In 1960 Richland received an All-America City Award.
Wahluke Slope
Immediately outside the Hanford Site lay an area known as the Wahluke Slope. Most of this land was owned by large landholders who had purchased it cheaply during the Great Depression, hoping to reap large profits when the Columbia Basin Project (CBP) irrigated the land at public expense. In July 1948, the AEC designated of the Wahluke Slope as a "central zone" where farming was prohibited. Flanking it on both sides were "secondary control zones" where irrigation was prohibited, but was farmed by a small number of ranchers. In 1953, the AEC granted the CBP right of way access for roads, canals and power lines. Political pressure from landholders led to the AEC releasing in 1953, and another in 1958 for farming, habitation and irrigation. Most of the land was retained by the large landowners, who used it for agribusiness or sold it at a profit, but the Bureau of Land Management held lotteries to grant land to veterans who passed financial and political background security checks. Some went bankrupt, but those with persistence and capital in the form of government-backed loans, prospered. In 1965, the AEC announced its intention to release another to the United States Bureau of Reclamation, Bureau of Reclamation (BOR) for non-residential farming. However, studies revealed a potential for irrigation to cause landslides, and the BOR decided not to develop the land. In November 1971, the AEC issued permits to the United States Fish and Wildlife Service and the Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife to turn it into wildlife refuges. The western part became the Saddle Mountain Wildlife Refuge and the eastern part, the Wahluke Wildlife Recreation Area.Camp Hanford
During the war the Hanford Site was patroled by a Military Police Corps (United States), Military Police detachment which, as of June 1945, had forty soldiers. In April 1947 they were replaced by GE security guards, who were issued with M8 Greyhound armored cars. The Army was concerned that U.S. plutonium production was centered at one vulnerable site. In March 1950 the 5th Anti-aircraft Artillery Group arrived to provide air defenses, and established its headquarters in North Richland. The group consisted of four battalions, the 83rd, 501st, 518th, and 519th Anti-aircraft Artillery Battalions, each of which had four batteries of 120 mm Gun M1, 120 mm anti-aircraft guns. Each battery had four guns, which were deployed in sandbagged revetments on a site with wooden, prefabricated metal and containing barracks, latrines, mess halls, motor pools, radars and administrative facilities. The military base was designated "Camp Hanford" in 1951. The following year the guns were augmented by MIM-3 Nike Ajax, Nike Ajax missiles, which were deployed at three sites on Wahluke Slope and one on what is now the Fitzner-Eberhardt Arid Lands Ecology Reserve. Each site had two underground missile storage magazines, twenty missiles and eight missile launchers. The Nike Ajax missiles were later replaced with Nike Hercules missiles. The development of intercontinental ballistic missiles made the missiles obsolete, and Camp Hanford became an outpost of Fort Lewis (Washington), Fort Lewis on July 1, 1959. The missile batteries were disbanded in 1960, and Camp Hanford was closed on March 31, 1961.Early expansion
Cold War tensions escalated in April 1948 with the Berlin Airlift. Construction was under way on the new DRand HReactors, but the quickest way to increase production was to restart BReactor. This was authorized later that month. Shugg was recalled to Washington, DC, to serve as the AEC deputy general manager in August, and was succeeded by Frederick C. Schlemmer on September 16. In turn, he was succeeded by David F. Shaw on June 1, 1950. Shaw was succeeded by James E. Travis in June 1955, and he remained the site manager until June 1965. It was also possible to improve productivity. Zirconium was added to the cans to stabilize them under high exposures, and tests confirmed that they could withstand three times the exposure used in 1946 without rupture. In March 1950 GE was authorized to run the reactors at 305 MW instead of 250. This cut the use of raw materials by half, and yielded forty percent more plutonium per operating dollar. The Soviet Union detonated its RDS-1, first atomic bomb on August 29, 1949. The explosion was detected by a U.S. Air Force weather reconnaissance aircraft four days later. In response, President Harry S. Truman authorized a crash program to develop the hydrogen bomb. Preliminary designs called for large amounts of tritium. This could be produced in a reactor using target slugs loaded with lithium deuteride and fuel rods containing enriched uranium. One or more reactors would have to be set aside for tritium production. HReactor was chosen, and started producing tritium in 1950. For the longer term, the AEC decided to construct new reactors, of a different design using enriched uranium and heavy water as a moderator, at a new site, which became the Savannah River Site. The outbreak of the Korean War in September 1951 prompted the AEC to authorize a sixth reactor at Hanford on January 23, 1951. Construction began in June. The new reactor was built in the Barea and called CReactor. The same basic graphite-moderated design was used, with improvements to give it a rated power of 750 MW. The new reactor became operational in November 1952.
On February 25, 1952, Truman authorized two more reactors at the Hanford Site. These were called K West and K East, and were sited at Coyote Rapids between the Band Dareas. They were known as "Jumbo" reactors for their much larger size. They still used the same graphite-moderator technology, but had improvements to allow them to operate at 1,800 MW. Each used of graphite, over a thousand tons more than the three wartime reactors, and had concrete shields instead of steel and masonite. They had more feed tubes and reduced spacing between them. Improvements in water-pump design allowed them to have eighteen pumps instead of the fifty in the wartime reactors, but were capable of pumping . As with the other reactors, the cooling water was collected in ponds, allowed to cool, and then tipped back into the river. An innovation was that heat from the cooling water was used to heat the work places. Each Jumbo reactor required about 300 operators to run it, compared with 400 for HReactor. This represented a saving of a million dollars a year (equivalent to $million in ). Although capable of being run at up to 4,400 MW, the AEC imposed an administrative limit of 4,000 MW on them. Since plutonium239 has a half-life of 24,100 years, AEC chairman Gordon Dean (lawyer), Gordon Dean calculated that sufficient plutonium would be produced by the mid-1960s. With this in mind, the reactors were designed with a life of twenty years.
The Soviet Union detonated its RDS-1, first atomic bomb on August 29, 1949. The explosion was detected by a U.S. Air Force weather reconnaissance aircraft four days later. In response, President Harry S. Truman authorized a crash program to develop the hydrogen bomb. Preliminary designs called for large amounts of tritium. This could be produced in a reactor using target slugs loaded with lithium deuteride and fuel rods containing enriched uranium. One or more reactors would have to be set aside for tritium production. HReactor was chosen, and started producing tritium in 1950. For the longer term, the AEC decided to construct new reactors, of a different design using enriched uranium and heavy water as a moderator, at a new site, which became the Savannah River Site. The outbreak of the Korean War in September 1951 prompted the AEC to authorize a sixth reactor at Hanford on January 23, 1951. Construction began in June. The new reactor was built in the Barea and called CReactor. The same basic graphite-moderated design was used, with improvements to give it a rated power of 750 MW. The new reactor became operational in November 1952.
On February 25, 1952, Truman authorized two more reactors at the Hanford Site. These were called K West and K East, and were sited at Coyote Rapids between the Band Dareas. They were known as "Jumbo" reactors for their much larger size. They still used the same graphite-moderator technology, but had improvements to allow them to operate at 1,800 MW. Each used of graphite, over a thousand tons more than the three wartime reactors, and had concrete shields instead of steel and masonite. They had more feed tubes and reduced spacing between them. Improvements in water-pump design allowed them to have eighteen pumps instead of the fifty in the wartime reactors, but were capable of pumping . As with the other reactors, the cooling water was collected in ponds, allowed to cool, and then tipped back into the river. An innovation was that heat from the cooling water was used to heat the work places. Each Jumbo reactor required about 300 operators to run it, compared with 400 for HReactor. This represented a saving of a million dollars a year (equivalent to $million in ). Although capable of being run at up to 4,400 MW, the AEC imposed an administrative limit of 4,000 MW on them. Since plutonium239 has a half-life of 24,100 years, AEC chairman Gordon Dean (lawyer), Gordon Dean calculated that sufficient plutonium would be produced by the mid-1960s. With this in mind, the reactors were designed with a life of twenty years.
Separation facilities
In addition to the new reactors there were also new separation facilities. The AEC had long been dissatisfied with the wasteful bismuth phosphate separation process. GE conducted research into an alternative, reduction-oxidation (REDOX) process. This used methyl isobutyl ketone (hexone) as a solvent. It was developed at the Hanford Site in the 3706 Building and tested in the 321 Building. The AEC approved the REDOX process in May 1949, and work began on the new plant the following year. Construction ran behind schedule, and it did not commence operation until January 1952. Known as the 202-S Building or the SPlant, it was long and wide, and could process up to twelve metric tons of uranium per day, compared with the Band TPlants' 1.5 tons per day. It also had the advantage of consolidating the separation activities in one building. Unlike the bismuth phosphate process, it produced uranium as a byproduct. The low flash point of hexone meant that special precautions had to be taken against the possibility of an explosion. The hexone could not be reused as it was highly water-soluble and was unstable in nitric acid. Removing the uranium meant that the waste products were highly radioactive. The facility operated until 1967 and processed approximately 22,400 metric tons of uranium fuel rods. The U Plant was modified to use the REDOX process to recover uranium from the wastes left over from the bismuth phosphate process, but with a different solvent, tributyl phosphate. Because of the plant's layout, it could not use the tall columns and gravity flow that characterized the REDOX plant, so pulsed columns were used instead. The PUREX, plutonium uranium reduction extraction (PUREX) process was developed at GE's Knolls Atomic Power Laboratory, Knolls Laboratory. The PUREX Plant, known as APlant or Building 202A, commenced operation in 1955. Like the UPlant it used pulsed columns and tributyl phosphate as a solvent.
The plant was long, high and wide. The processing canyon contained eleven processing areas. It operated from 1956 to 1972, and again from 1983 to 1988, when it reprocessed spent fuel rods from the reactors, and processed approximately 66,400 metric tons of uranium fuel rods. The Band T Plants were shut down after it became operational in 1956, having processed 8,100 metric tons of fuel rods. During the 1940s, the Hanford Site dumped into the Columbia River each day. This rose to per day between 1951 and 1953, and peaked at per day in 1959.
The U Plant was modified to use the REDOX process to recover uranium from the wastes left over from the bismuth phosphate process, but with a different solvent, tributyl phosphate. Because of the plant's layout, it could not use the tall columns and gravity flow that characterized the REDOX plant, so pulsed columns were used instead. The PUREX, plutonium uranium reduction extraction (PUREX) process was developed at GE's Knolls Atomic Power Laboratory, Knolls Laboratory. The PUREX Plant, known as APlant or Building 202A, commenced operation in 1955. Like the UPlant it used pulsed columns and tributyl phosphate as a solvent.
The plant was long, high and wide. The processing canyon contained eleven processing areas. It operated from 1956 to 1972, and again from 1983 to 1988, when it reprocessed spent fuel rods from the reactors, and processed approximately 66,400 metric tons of uranium fuel rods. The Band T Plants were shut down after it became operational in 1956, having processed 8,100 metric tons of fuel rods. During the 1940s, the Hanford Site dumped into the Columbia River each day. This rose to per day between 1951 and 1953, and peaked at per day in 1959.N Reactor
The reactors had all been built for plutonium production, but with the Atomic Energy Act of 1954, the Eisenhower administration began shifting resources to nuclear power generation. By the late 1950s the reactors built during the war were approaching retirement age, and in 1957 GE commenced planning to build a new reactor that would be clean, safe and efficient, and able to generate electric power as well as produce plutonium. Construction commenced in 1959, but the electric power features were not authorized until 1962, so while it was producing plutonium in 1964, electric power did not follow until 1966. Experts debated whether nuclear power would be economically competitive with hydroelectric power, and Congress debated whether the government should be in the electricity generation business. On November 28, 1961, the AEC reached an agreement with the Washington Public Power Supply System (WPPSS) for the latter to purchase its electricity. N Reactor was destined to be the last of its kind, but also had many new features as a product of 1960s technology. Its zirconium alloy-clad fuel slugs were long and in diameter. It had automated fuel-loading and unloading systems, a boron-ball scram system, and a state-of-the-art control room. It was the first American graphite-moderated power reactor, and the first American dual-purpose reactor, although other countries had them. The dual-purpose concept involved trade-offs that made both purposes less efficient: power required a steam turbine, but high water temperatures risked slug failure. The solution was to build a pressurized water reactor, in which the water was pressurized to allow it to remain liquid above . The reactor exceeded its original $145million budget (equivalent to $million in ) and cost $205million budget (equivalent to $million in ).
The Hanford Site was now home to nine nuclear reactors along the Columbia River, five reprocessing plants on the central plateau, and more than nine hundred support buildings and radiological laboratories around the site. Extensive modifications and upgrades were made to the original three World WarII reactors, and a total of 177 underground waste tanks were built. Hanford was at its peak production from 1956 to 1965. Over the forty years of operation the site produced about 67.4 metric tons of plutonium, of which 54.5 metric tons was weapons-grade plutonium, supplying the majority of the 60,000 weapons in the U.S. arsenal. In 1983 and 1984, 425 kilograms of weapons-grade plutonium was extracted from reactor-grade plutonium. Tritium, polonium210, thulium-170, iridium-192, and uranium-233 were also produced.
N Reactor was destined to be the last of its kind, but also had many new features as a product of 1960s technology. Its zirconium alloy-clad fuel slugs were long and in diameter. It had automated fuel-loading and unloading systems, a boron-ball scram system, and a state-of-the-art control room. It was the first American graphite-moderated power reactor, and the first American dual-purpose reactor, although other countries had them. The dual-purpose concept involved trade-offs that made both purposes less efficient: power required a steam turbine, but high water temperatures risked slug failure. The solution was to build a pressurized water reactor, in which the water was pressurized to allow it to remain liquid above . The reactor exceeded its original $145million budget (equivalent to $million in ) and cost $205million budget (equivalent to $million in ).
The Hanford Site was now home to nine nuclear reactors along the Columbia River, five reprocessing plants on the central plateau, and more than nine hundred support buildings and radiological laboratories around the site. Extensive modifications and upgrades were made to the original three World WarII reactors, and a total of 177 underground waste tanks were built. Hanford was at its peak production from 1956 to 1965. Over the forty years of operation the site produced about 67.4 metric tons of plutonium, of which 54.5 metric tons was weapons-grade plutonium, supplying the majority of the 60,000 weapons in the U.S. arsenal. In 1983 and 1984, 425 kilograms of weapons-grade plutonium was extracted from reactor-grade plutonium. Tritium, polonium210, thulium-170, iridium-192, and uranium-233 were also produced.Decommissioning
 By 1963 the AEC had estimated that it had sufficient plutonium for its needs for the foreseeable future, and planned to shut down the production reactors. To mitigate the economic impact, closures were carried out over a period of six years. The change of policy was not publicly announced; instead, each round of closures was accompanied by a statement that production needs could be met by the remaining facilities. The first round of closures was announced by President Lyndon B. Johnson, Johnson on January 8, 1964. DR, H and FReactors were shut down in 1964 and, 1965. In 1967 the AEC announced that another reactor would be shut down. This was DReactor, which was shut down on June 25, 1967. BReactor followed on February 12, 1968.
In January 1969 AEC chairman Glenn Seaborg, under pressure from the newly elected Nixon administration to cut costs, announced that the three reactors built in the 1950s, C, KE and KW, would be shut down in 1969 and 1970. The REDOX and PUREX facilities were placed on standby status in December 1967 and June 1972 respectively. Between 1967 and 1971, the number of workers employed at the Hanford Site plummeted from 8,500 to 5,500. The incremental closures did nothing to reduce the public outcry; if anything, the reverse was the case. The AEC was replaced by the Energy Research and Development Administration in 1974, and it in turn was succeeded by the DOE in 1977. The regulation and licensing of commercial reactors was devolved to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC).
The closures left only N Reactor, which continued to operate as a dual-purpose reactor, providing power to the civilian electrical grid via the WPPSS. By 1966 it was producing 35 percent of the United States' nuclear-generated electricity. Costs were lower than anticipated, allowing the WPPSS to retire $25million budget (equivalent to $million in ) of the $122million (equivalent to $million in ) it had raised in Bond (finance), bonds to finance the project. The Chernobyl disaster in the Soviet Union in April 1986 prompted multiple reviews of the safety of American reactors. Of all the reactors in the U.S., NReactor was the most similar to the ill-fated No.4 Reactor at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, in that it was graphite-moderated, although NReactor used pressurized water rather than boiling water as a coolant. Like all the Hanford Site's reactors, it had no containment vessel and would never have passed the NRC's reactor safety requirements had they been applied to it. There was a public outcry, and the Government Accountability Office recommended closure. NReactor was shut down in January 1987. The PUREX plant reopened in 1983 to reprocess N Reactor reactor-grade fuel into weapon-grade fuel. This ended in December 1988, and it returned to standby status in October 1990. The uranium trioxide plant closed in 1995, the PUREX plant closed for good in 1997, and the BPlant in 1998. The TPlant remained in use, handling the storage, packaging and decontamination of radioactive wastes. It became the longest operational nuclear facility in the world.
By 1963 the AEC had estimated that it had sufficient plutonium for its needs for the foreseeable future, and planned to shut down the production reactors. To mitigate the economic impact, closures were carried out over a period of six years. The change of policy was not publicly announced; instead, each round of closures was accompanied by a statement that production needs could be met by the remaining facilities. The first round of closures was announced by President Lyndon B. Johnson, Johnson on January 8, 1964. DR, H and FReactors were shut down in 1964 and, 1965. In 1967 the AEC announced that another reactor would be shut down. This was DReactor, which was shut down on June 25, 1967. BReactor followed on February 12, 1968.
In January 1969 AEC chairman Glenn Seaborg, under pressure from the newly elected Nixon administration to cut costs, announced that the three reactors built in the 1950s, C, KE and KW, would be shut down in 1969 and 1970. The REDOX and PUREX facilities were placed on standby status in December 1967 and June 1972 respectively. Between 1967 and 1971, the number of workers employed at the Hanford Site plummeted from 8,500 to 5,500. The incremental closures did nothing to reduce the public outcry; if anything, the reverse was the case. The AEC was replaced by the Energy Research and Development Administration in 1974, and it in turn was succeeded by the DOE in 1977. The regulation and licensing of commercial reactors was devolved to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC).
The closures left only N Reactor, which continued to operate as a dual-purpose reactor, providing power to the civilian electrical grid via the WPPSS. By 1966 it was producing 35 percent of the United States' nuclear-generated electricity. Costs were lower than anticipated, allowing the WPPSS to retire $25million budget (equivalent to $million in ) of the $122million (equivalent to $million in ) it had raised in Bond (finance), bonds to finance the project. The Chernobyl disaster in the Soviet Union in April 1986 prompted multiple reviews of the safety of American reactors. Of all the reactors in the U.S., NReactor was the most similar to the ill-fated No.4 Reactor at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, in that it was graphite-moderated, although NReactor used pressurized water rather than boiling water as a coolant. Like all the Hanford Site's reactors, it had no containment vessel and would never have passed the NRC's reactor safety requirements had they been applied to it. There was a public outcry, and the Government Accountability Office recommended closure. NReactor was shut down in January 1987. The PUREX plant reopened in 1983 to reprocess N Reactor reactor-grade fuel into weapon-grade fuel. This ended in December 1988, and it returned to standby status in October 1990. The uranium trioxide plant closed in 1995, the PUREX plant closed for good in 1997, and the BPlant in 1998. The TPlant remained in use, handling the storage, packaging and decontamination of radioactive wastes. It became the longest operational nuclear facility in the world.
 All but one of the Hanford production reactors were Nuclear entombment, entombed ("cocooned") to allow the radioactive materials to decay, and the surrounding structures removed and buried. This involved the removal of hundreds of tons of asbestos, concrete, steel and contaminated soil. The pumps and tunnels were dug up and razed, as were the auxiliary buildings. What was left were the core and shields. These were sealed up and a sloped steel roof added to draw off rainwater. Cocooning of CReactor commenced in 1996, and was completed in 1998. DReactor followed in 2002, FReactor followed in 2003, DRReactor in 2004. and HReactor in 2005. N Reactor was cocooned in 2012, and KE and KW in 2022.
The exception was B Reactor, which was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1992.NRHP site #92000245. (See also the commercial sit
All but one of the Hanford production reactors were Nuclear entombment, entombed ("cocooned") to allow the radioactive materials to decay, and the surrounding structures removed and buried. This involved the removal of hundreds of tons of asbestos, concrete, steel and contaminated soil. The pumps and tunnels were dug up and razed, as were the auxiliary buildings. What was left were the core and shields. These were sealed up and a sloped steel roof added to draw off rainwater. Cocooning of CReactor commenced in 1996, and was completed in 1998. DReactor followed in 2002, FReactor followed in 2003, DRReactor in 2004. and HReactor in 2005. N Reactor was cocooned in 2012, and KE and KW in 2022.
The exception was B Reactor, which was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1992.NRHP site #92000245. (See also the commercial sitNational Register of Historic Places
) Some historians advocated converting it into a museum. It was designated a National Historic Landmark by the National Park Service on August 19, 2008, and on November 10, 2015, it became part of the
Manhattan Project National Historical Park
Manhattan Project National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park commemorating the Manhattan Project that is run jointly by the National Park Service and Department of Energy. The park consists of three units: one in Oak Ri ...
alongside other sites at Oak Ridge and Los Alamos. The United States Department of Energy (DOE) offers free guided tours of the site which can be reserved via the department's website, and are open to all ages. Between 2009 and 2018, approximately eighty thousand people visited the site, bringing an estimated annual tourist income of two million dollars to the surrounding area.
Later operations
Although uranium enrichment and plutonium breeding were slowly phased out, the nuclear legacy left an indelible mark on the Tri-Cities. Since World WarII, the area had developed from a small farming community to a booming "Atomic Frontier" to a powerhouse of the nuclear-industrial complex. Decades of federal investment created a community of highly skilled scientists and engineers. As a result of this concentration of specialized skills, the Hanford Site attempted to diversify its operations to include scientific research, test facilities, and commercial nuclear power production. When GE announced that it was ending the contract to run the Hanford Site in 1963, the AEC decided to separate the contract among multiple operators. The contract to run the research laboratory at the Hanford Site was awarded to the Battelle Memorial Institute of Columbus, Ohio, on May 28, 1964, and the laboratory became the Pacific Northwest Laboratory when it took over management on January 4, 1965. In 1995 it achieved national laboratory status and became The
When GE announced that it was ending the contract to run the Hanford Site in 1963, the AEC decided to separate the contract among multiple operators. The contract to run the research laboratory at the Hanford Site was awarded to the Battelle Memorial Institute of Columbus, Ohio, on May 28, 1964, and the laboratory became the Pacific Northwest Laboratory when it took over management on January 4, 1965. In 1995 it achieved national laboratory status and became The Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) is one of the United States Department of Energy national laboratories, managed by the Department of Energy's (DOE) Office of Science. The main campus of the laboratory is in Richland, Washington.
O ...
. Battelle's contract allowed it to perform research for both the government and private companies, and while its focus was on nuclear technology, safety and environmental issues, it was able to branch out into related areas. In 2022 the laboratory employed 5,314 staff and had an annual budget of $1.2billion.
The Fast Flux Test Facility
The Fast Flux Test Facility (FFTF) is a 400 MW thermal, liquid sodium cooled, nuclear test reactor owned by the U.S. Department of Energy.
It does not generate electricity. It is situated in the ''400 Area'' of the Hanford Site, which is located ...
(FFTF), was a national research facility that began operating in 1982. It was a 400 MW liquid-sodium-cooled fast-neutron reactor that could run on plutonium oxide, uranium oxide, or a mixture of the two. Although not a breeder reactor itself, it shared many same design features, and its purpose was to develop and test fuels, materials and components for the Clinch River Breeder Reactor project. The contract to construct and operate it was awarded to Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Westinghouse and 800 former Battelle employees who had been working on it were transferred. The Clinch River project was canceled by Congress in 1983, and the whole nuclear breeder program failed to eventuate. Nonetheless, the FFTF continued to operate until generating plutonium238 for nuclear power sources for NASA space missions and tritium for nuclear fusion research. It was shut down in 2009.
 Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) Hanford Observatory is an interferometer searching for Gravitational wave#Interferometers, gravitational waves. The observatory at the Hanford Site was one of two, the other being in Livingston, Louisiana. The project was run as a cooperative venture by MIT and Caltech. The $211million price tag (equivalent to $million in ) generated debate about pork barreling and government funding of expensive Big Science projects, especially one as uncertain of success as LIGO. The Hanford Site was chosen from seventeen contenders for one of the two sites, mainly due to its relative isolation. In 2016 it was announced that gravitational waves had been detected. In 2018 the American Physical Society (APS) designated the two LIGO observatories as APS historic sites.
The
Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) Hanford Observatory is an interferometer searching for Gravitational wave#Interferometers, gravitational waves. The observatory at the Hanford Site was one of two, the other being in Livingston, Louisiana. The project was run as a cooperative venture by MIT and Caltech. The $211million price tag (equivalent to $million in ) generated debate about pork barreling and government funding of expensive Big Science projects, especially one as uncertain of success as LIGO. The Hanford Site was chosen from seventeen contenders for one of the two sites, mainly due to its relative isolation. In 2016 it was announced that gravitational waves had been detected. In 2018 the American Physical Society (APS) designated the two LIGO observatories as APS historic sites.
The Columbia Generating Station
Columbia Generating Station is a nuclear commercial energy facility located on the Hanford Site, north of Richland, Washington. It is owned and operated by Energy Northwest, a Washington state, not-for-profit joint operating agency. Licensed by ...
is a 1,207 MW commercial nuclear power plant located on the Hanford Site north of Richland and operated by Energy Northwest, as the WPPSS has been known since 1998. Originally, five boiling water reactors were authorized in March 1973, but only one, WNP2, was completed. It began producing power in May 1984. The WNP-1 Reactor was budgeted to cost $660million in 1973 (equivalent to $million in ) and be completed by 1980. By 1986, the estimated cost had blown out to $3.8billion (equivalent to $billion in ) and the reactor was still unfinished. Meanwhile, the estimated total cost of the entire project had increased from $4.1billion in 1973 (equivalent to $billion in ) to $24billion in 1986 (equivalent to $billion in ). A net billing agreement that Senator Henry M. Jackson helped steer through Congress ensured that the bonds issue to finance their construction carried a AAA bond credit rating and therefore sold easily, but electricity tariffs had to be increased to repay the bond holders.
 The Hanford Reach was preserved as the finest salmon breeding ground in the Pacific Northwest. The end of plutonium production at the Hanford Site meant that it no longer required the areas around the old production sites. On June 9, 2000, President Bill Clinton designated almost of the Hanford Site as a National monument (United States), national monument. The Hanford Reach National Monument is managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service under an agreement with the DOE. On June 28, 2000, a fire burned of the monument.
The Hanford Reach was preserved as the finest salmon breeding ground in the Pacific Northwest. The end of plutonium production at the Hanford Site meant that it no longer required the areas around the old production sites. On June 9, 2000, President Bill Clinton designated almost of the Hanford Site as a National monument (United States), national monument. The Hanford Reach National Monument is managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service under an agreement with the DOE. On June 28, 2000, a fire burned of the monument.
Environmental concerns
Between 1944 and 1971, pump systems drew as much as of cooling water from the Columbia River to dissipate the heat produced by the reactors. Before its release into the river, the used water was held in large tanks known as retention basins for up to six hours. Longer-lived isotopes were not affected by this retention, and several becquerel, terabecquerels entered the river every day. The federal government kept knowledge about these radioactive releases secret. Another source of contaminated food came from Columbia River fish, an impact felt disproportionately by Native American communities who depended on the river for their customary diets. Radiation was later measured downstream as far west as the Washington and Oregon coasts. it was estimated that a person who had daily eaten of fish caught at Richland would have received an additional radiation dose of 1,300 millirems per year. Screens and fish ladders were used to protect wildlife. The plutonium separation process resulted in the release of radioactive isotopes into the air, which were carried by the wind throughout southeastern Washington and into parts of Idaho, Montana, Oregon, and British Columbia. Downwinders were exposed to radionuclides, particularly iodine-131, with the heaviest releases from 1945 to 1951. These radionuclides entered the food chain via dairy cows grazing on contaminated fields; hazardous fallout was ingested by communities who consumed radioactive food and milk. Most of these airborne releases were a part of Hanford's routine operations, while a few of the larger releases occurred in isolated incidents. In 1949 an intentional release known as the "Green Run" released of iodine131 over two days. A U.S. government report released in 1992 estimated that of iodine131 had been released into the river and air from the Hanford Site between 1944 and 1947.
Beginning in the 1960s scientists with the United States Public Health Service, U.S. Public Health Service published reports about radioactivity released from Hanford, and there were protests from the health departments of Oregon and Washington. In response to an article in the ''Spokane Spokesman Review'' in September 1985, the DOE announced it would declassify environmental records and, in February 1986, released 19,000 pages of previously unavailable historical documents about Hanford's operations. The Washington State Department of Health collaborated with the citizen-led Hanford Health Information Network (HHIN) to publicize data about the health effects of Hanford's operations. HHIN reports concluded that residents who lived downwind from Hanford or who used the Columbia River downstream were exposed to elevated doses of radiation that placed them at increased risk for various cancers and other diseases, particularly forms of thyroid disease. A mass tort lawsuit brought by two thousand Hanford downwinders against the federal government spent many years in the court system. In 2005 two of six plaintiffs who went to trial were awarded $500,000 in damages. The DOE resolved the final cases in October 2015, paying out more than $60million in legal fees and $7million in damages.
Radioactive materials were known to be leaking from Hanford into the environment. The highest tritium concentration detected in riverbank springs during 2002 was at the Hanford townsite. An iodine-129 concentration of was found in a Hanford townsite spring. The WHO guidelines for radionuclides in drinking water limits levels of iodine129 at 1Bq/L, and tritium at 10,000Bq/L. A September 2005 Pacific Northwest National Laboraory report noted "Detected radionuclides include strontium90, technetium99, iodine129, uranium234, -235, and -238, and tritium. Other detected contaminants include arsenic, chromium, chloride, fluoride, nitrate, and sulfate ... concentrations of radionuclides including tritium, technetium99, and iodine129 in riverbank springs near the Hanford townsite have generally been increasing since 1994. This is an area where a major Groundwater#Pollution, groundwater plume from the 200 East Area intercepts the river. However, tritium concentration has declined since 1997."
The plutonium separation process resulted in the release of radioactive isotopes into the air, which were carried by the wind throughout southeastern Washington and into parts of Idaho, Montana, Oregon, and British Columbia. Downwinders were exposed to radionuclides, particularly iodine-131, with the heaviest releases from 1945 to 1951. These radionuclides entered the food chain via dairy cows grazing on contaminated fields; hazardous fallout was ingested by communities who consumed radioactive food and milk. Most of these airborne releases were a part of Hanford's routine operations, while a few of the larger releases occurred in isolated incidents. In 1949 an intentional release known as the "Green Run" released of iodine131 over two days. A U.S. government report released in 1992 estimated that of iodine131 had been released into the river and air from the Hanford Site between 1944 and 1947.
Beginning in the 1960s scientists with the United States Public Health Service, U.S. Public Health Service published reports about radioactivity released from Hanford, and there were protests from the health departments of Oregon and Washington. In response to an article in the ''Spokane Spokesman Review'' in September 1985, the DOE announced it would declassify environmental records and, in February 1986, released 19,000 pages of previously unavailable historical documents about Hanford's operations. The Washington State Department of Health collaborated with the citizen-led Hanford Health Information Network (HHIN) to publicize data about the health effects of Hanford's operations. HHIN reports concluded that residents who lived downwind from Hanford or who used the Columbia River downstream were exposed to elevated doses of radiation that placed them at increased risk for various cancers and other diseases, particularly forms of thyroid disease. A mass tort lawsuit brought by two thousand Hanford downwinders against the federal government spent many years in the court system. In 2005 two of six plaintiffs who went to trial were awarded $500,000 in damages. The DOE resolved the final cases in October 2015, paying out more than $60million in legal fees and $7million in damages.
Radioactive materials were known to be leaking from Hanford into the environment. The highest tritium concentration detected in riverbank springs during 2002 was at the Hanford townsite. An iodine-129 concentration of was found in a Hanford townsite spring. The WHO guidelines for radionuclides in drinking water limits levels of iodine129 at 1Bq/L, and tritium at 10,000Bq/L. A September 2005 Pacific Northwest National Laboraory report noted "Detected radionuclides include strontium90, technetium99, iodine129, uranium234, -235, and -238, and tritium. Other detected contaminants include arsenic, chromium, chloride, fluoride, nitrate, and sulfate ... concentrations of radionuclides including tritium, technetium99, and iodine129 in riverbank springs near the Hanford townsite have generally been increasing since 1994. This is an area where a major Groundwater#Pollution, groundwater plume from the 200 East Area intercepts the river. However, tritium concentration has declined since 1997."
 Of the 177 tanks at Hanford, 149 had a single shell. Historically single-shell tanks were used for storing radioactive liquid waste and designed to last twenty years. By 2005 some liquid waste was transferred from single-shell tanks to (safer) double-shell tanks. A substantial amount of residue remains in the older single-shell tanks with one containing an estimated of radioactive sludge, for example. It is believed that up to six of these "empty" tanks were leaking. Two tanks were reportedly leaking per year each, while the remaining four tanks were each leaking per year. In February 2013 Washington Governor Jay Inslee announced that a tank storing radioactive waste at the site had been leaking liquids on average of per year. He said that though the leak posed no immediate health risk to the public, it should not be an excuse for not doing anything. On February 22, 2013, he stated that six more tanks were leaking.
Of the 177 tanks at Hanford, 149 had a single shell. Historically single-shell tanks were used for storing radioactive liquid waste and designed to last twenty years. By 2005 some liquid waste was transferred from single-shell tanks to (safer) double-shell tanks. A substantial amount of residue remains in the older single-shell tanks with one containing an estimated of radioactive sludge, for example. It is believed that up to six of these "empty" tanks were leaking. Two tanks were reportedly leaking per year each, while the remaining four tanks were each leaking per year. In February 2013 Washington Governor Jay Inslee announced that a tank storing radioactive waste at the site had been leaking liquids on average of per year. He said that though the leak posed no immediate health risk to the public, it should not be an excuse for not doing anything. On February 22, 2013, he stated that six more tanks were leaking.
Occupational health concerns
In 1976 Harold McCluskey, a Hanford technician, received the largest recorded dose of americium following a laboratory accident in the Plutonium Finishing Plant. Due to prompt medical intervention, he survived the incident and died eleven years later of natural causes. Since 1987, workers have reported exposure to harmful vapors after working around underground nuclear storage tanks, with no solution found. More than forty workers in 2014 alone reported smelling vapors and became ill with "nosebleeds, headaches, watery eyes, burning skin, contact dermatitis, increased heart rate, difficulty breathing, coughing, sore throats, expectorating, dizziness and nausea... Several of these workers have long-term disabilities." Doctors checked workers and cleared them to return to work. Monitors worn by tank workers have found no samples with chemicals close to the federal limit for occupational exposure. In August 2014 Occupational Safety and Health Administration, OSHA ordered the facility to rehire a contractor and pay $220,000 in back wages for firing the employee for whistleblowing on safety concerns at the site. On November 19, 2014, the attorney general of Washington, Bob Ferguson (politician), Bob Ferguson, said the state planned to sue the DOE and its contractor to protect workers from hazardous vapors at Hanford. A 2014 report by the DOE Savannah River National Laboratory initiated by 'Washington River Protection Solutions' found that DOE's methods to study vapor releases were inadequate, particularly, that they did not account for short but intense vapor releases. They recommended "proactively sampling the air inside tanks to determine its chemical makeup; accelerating new practices to prevent worker exposures; and modifying medical evaluations to reflect how workers are exposed to vapors".Cleanup under Superfund
Organization
 Decades of manufacturing left behind of high level waste, high-level radioactive waste stored within 177 storage tanks, an additional of solid radioactive waste, and areas of heavy technetium-99 and uranium-contaminated groundwater beneath three tank farms on the site as well as the potential for future groundwater contamination beneath currently contaminated soils. On June 25, 1988, the Hanford Site was divided into four areas and proposed for inclusion on the National Priorities List.
On May 15, 1989, the Washington Department of Ecology, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and the DOE entered into the Tri-Party Agreement, which provides a legal framework for environmental remediation at Hanford. By 2014 the agencies were engaged in the world's largest environmental cleanup, with many challenges to be resolved in the face of overlapping technical, political, regulatory, and cultural interests. The cleanup effort was focused on three outcomes: restoring the Columbia River corridor for other uses, converting the central plateau to long-term waste treatment and storage, and preparing for the future.
In 2011 DOE, the federal agency charged with overseeing the site, "interim stabilized" 149 single-shell tanks by pumping nearly all the liquid waste out into 28 newer double-shell tanks. Solids, known as salt cake and sludge, remained. The DOE later found water intruding into at least 14 single-shell tanks and that one of them had been leaking about per year into the ground since about 2010. In 2012 the DOE also discovered a leak from a double-shell tank caused by construction flaws and corrosion in the tank's bottom, and that twelve other double-shell tanks had similar construction flaws. Since then, the DOE began monitoring single-shell tanks monthly and double-shell tanks every three years. The DOE also changed the methods by which they monitored the tanks. In March 2014 the DOE announced further delays in the construction of the Waste Treatment Plant, which will affect the schedule for removing waste from the tanks. Intermittent discoveries of undocumented contamination have slowed the pace and raised the cost of cleanup.
Decades of manufacturing left behind of high level waste, high-level radioactive waste stored within 177 storage tanks, an additional of solid radioactive waste, and areas of heavy technetium-99 and uranium-contaminated groundwater beneath three tank farms on the site as well as the potential for future groundwater contamination beneath currently contaminated soils. On June 25, 1988, the Hanford Site was divided into four areas and proposed for inclusion on the National Priorities List.
On May 15, 1989, the Washington Department of Ecology, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and the DOE entered into the Tri-Party Agreement, which provides a legal framework for environmental remediation at Hanford. By 2014 the agencies were engaged in the world's largest environmental cleanup, with many challenges to be resolved in the face of overlapping technical, political, regulatory, and cultural interests. The cleanup effort was focused on three outcomes: restoring the Columbia River corridor for other uses, converting the central plateau to long-term waste treatment and storage, and preparing for the future.
In 2011 DOE, the federal agency charged with overseeing the site, "interim stabilized" 149 single-shell tanks by pumping nearly all the liquid waste out into 28 newer double-shell tanks. Solids, known as salt cake and sludge, remained. The DOE later found water intruding into at least 14 single-shell tanks and that one of them had been leaking about per year into the ground since about 2010. In 2012 the DOE also discovered a leak from a double-shell tank caused by construction flaws and corrosion in the tank's bottom, and that twelve other double-shell tanks had similar construction flaws. Since then, the DOE began monitoring single-shell tanks monthly and double-shell tanks every three years. The DOE also changed the methods by which they monitored the tanks. In March 2014 the DOE announced further delays in the construction of the Waste Treatment Plant, which will affect the schedule for removing waste from the tanks. Intermittent discoveries of undocumented contamination have slowed the pace and raised the cost of cleanup.
 The cleanup effort was managed by the DOE under the oversight of the two regulatory agencies. A citizen-led Hanford Advisory Board provides recommendations from community stakeholders, including local and state governments, regional environmental organizations, business interests, and Native American tribes. Citing the 2014 Hanford Lifecycle Scope Schedule and Cost report, the 2014 estimated cost of the remaining Hanford cleanup is $113.6billionmore than $3billion per year for the next six years, with a lower cost projection of approximately $2billion per year until 2046. About eleven thousand workers were on site to consolidate, clean up, and mitigate waste, contaminated buildings, and contaminated soil. Originally scheduled to be complete within thirty years, the cleanup was less than half finished by 2008. Of the four areas that were formally listed as Superfund sites on October 4, 1989, only one has been removed from the list following cleanup. While major releases of radioactive material ended with the reactor shutdown in the 1970s and many of the most dangerous wastes are contained, there were continued concerns about contaminated groundwater headed toward the Columbia River and about workers' health and safety.
The cleanup effort was managed by the DOE under the oversight of the two regulatory agencies. A citizen-led Hanford Advisory Board provides recommendations from community stakeholders, including local and state governments, regional environmental organizations, business interests, and Native American tribes. Citing the 2014 Hanford Lifecycle Scope Schedule and Cost report, the 2014 estimated cost of the remaining Hanford cleanup is $113.6billionmore than $3billion per year for the next six years, with a lower cost projection of approximately $2billion per year until 2046. About eleven thousand workers were on site to consolidate, clean up, and mitigate waste, contaminated buildings, and contaminated soil. Originally scheduled to be complete within thirty years, the cleanup was less than half finished by 2008. Of the four areas that were formally listed as Superfund sites on October 4, 1989, only one has been removed from the list following cleanup. While major releases of radioactive material ended with the reactor shutdown in the 1970s and many of the most dangerous wastes are contained, there were continued concerns about contaminated groundwater headed toward the Columbia River and about workers' health and safety.Cleanup activities
 The most significant challenge is stabilizing the of high-level radioactive waste stored in the 177 underground tanks. By 1998 about a third of these tanks had leaked waste into the soil and groundwater. By 2008 most of the liquid waste had been transferred to more secure double-shelled tanks; however, of liquid waste, together with of salt cake and sludge, remains in the single-shelled tanks. DOE lacks information about the extent to which the 27 double-shell tanks may be susceptible to corrosion. Without determining the extent to which the factors that contributed to the leak in AY102 were similar to the other 27 double-shell tanks, DOE could not be sure how long its double-shell tanks can safely store waste. That waste was originally scheduled to be removed by 2018. By 2008 the revised deadline was 2040. By 2008 of radioactive waste was traveling through the groundwater toward the Columbia River. This waste was expected to reach the river in twelve to fifty years if cleanup does not proceed on schedule.
Under the Tri-Party Agreement, lower-level hazardous wastes are buried in huge lined pits that will be sealed and monitored with sophisticated instruments for many years. Disposal of plutonium and other high-level wastes is a more difficult problem that continues to be a subject of intense debate. As an example, plutonium239 has a half-life of 24,100 years, and a decay of ten half-lives is required before a sample is considered to cease its radioactivity. In 2000 the DOE awarded a $4.3billion contract to Bechtel, a San Francisco-based construction and engineering firm, to build a Radioactive waste#Vitrification, vitrification plant to combine the dangerous wastes with glass to render them stable. Construction began in 2002. The plant was originally scheduled to be operational by 2011, with vitrification completed by 2028. According to a 2012 study by the Government Accountability Office, there were a number of serious unresolved technical and managerial problems. In 2013 the estimated costs were $13.4billion with commencement of operations estimated to be in 2022 and about three decades of operation. A potential radioactive leak was reported in 2013; the cleanup was estimated to have cost $40billion, with $115billion more required. Another leak was reported in April 2021.
The most significant challenge is stabilizing the of high-level radioactive waste stored in the 177 underground tanks. By 1998 about a third of these tanks had leaked waste into the soil and groundwater. By 2008 most of the liquid waste had been transferred to more secure double-shelled tanks; however, of liquid waste, together with of salt cake and sludge, remains in the single-shelled tanks. DOE lacks information about the extent to which the 27 double-shell tanks may be susceptible to corrosion. Without determining the extent to which the factors that contributed to the leak in AY102 were similar to the other 27 double-shell tanks, DOE could not be sure how long its double-shell tanks can safely store waste. That waste was originally scheduled to be removed by 2018. By 2008 the revised deadline was 2040. By 2008 of radioactive waste was traveling through the groundwater toward the Columbia River. This waste was expected to reach the river in twelve to fifty years if cleanup does not proceed on schedule.
Under the Tri-Party Agreement, lower-level hazardous wastes are buried in huge lined pits that will be sealed and monitored with sophisticated instruments for many years. Disposal of plutonium and other high-level wastes is a more difficult problem that continues to be a subject of intense debate. As an example, plutonium239 has a half-life of 24,100 years, and a decay of ten half-lives is required before a sample is considered to cease its radioactivity. In 2000 the DOE awarded a $4.3billion contract to Bechtel, a San Francisco-based construction and engineering firm, to build a Radioactive waste#Vitrification, vitrification plant to combine the dangerous wastes with glass to render them stable. Construction began in 2002. The plant was originally scheduled to be operational by 2011, with vitrification completed by 2028. According to a 2012 study by the Government Accountability Office, there were a number of serious unresolved technical and managerial problems. In 2013 the estimated costs were $13.4billion with commencement of operations estimated to be in 2022 and about three decades of operation. A potential radioactive leak was reported in 2013; the cleanup was estimated to have cost $40billion, with $115billion more required. Another leak was reported in April 2021.
 In May 2007 state and federal officials began closed-door negotiations about the possibility of extending legal cleanup deadlines for waste vitrification in exchange for shifting the focus of the cleanup to urgent priorities, such as groundwater remediation. Those talks stalled in October 2007. In early 2008 a $600million cut to the Hanford cleanup budget was proposed. Washington state officials expressed concern about the budget cuts, as well as missed deadlines and recent safety lapses at the site, and threatened to file a lawsuit alleging that the DOE was in violation of environmental laws. They appeared to step back from that threat in April 2008 after another meeting of federal and state officials resulted in progress toward a tentative agreement. Some of the radioactive waste at Hanford was supposed to be stored in the planned Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository, but after that project was suspended, Washington State sued, joined by South Carolina. Their first suit was dismissed in July 2011. In a subsequent suit, federal authorities were ordered to either approve or reject plans for the Yucca Mountain storage site.
During excavations from 2004 to 2007, a sample of purified plutonium was uncovered inside a safe in a waste trench, and has been dated to about the 1940s, making it the second-oldest sample of purified plutonium known to exist. Analyses published in 2009 concluded that the sample originated at Oak Ridge, and was one of several sent to Hanford for optimization tests of the TPlant until Hanford could produce its own plutonium. Documents refer to such a sample, belonging to "Watt's group", which was disposed of in its safe when a radiation leak was suspected.
In May 2007 state and federal officials began closed-door negotiations about the possibility of extending legal cleanup deadlines for waste vitrification in exchange for shifting the focus of the cleanup to urgent priorities, such as groundwater remediation. Those talks stalled in October 2007. In early 2008 a $600million cut to the Hanford cleanup budget was proposed. Washington state officials expressed concern about the budget cuts, as well as missed deadlines and recent safety lapses at the site, and threatened to file a lawsuit alleging that the DOE was in violation of environmental laws. They appeared to step back from that threat in April 2008 after another meeting of federal and state officials resulted in progress toward a tentative agreement. Some of the radioactive waste at Hanford was supposed to be stored in the planned Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository, but after that project was suspended, Washington State sued, joined by South Carolina. Their first suit was dismissed in July 2011. In a subsequent suit, federal authorities were ordered to either approve or reject plans for the Yucca Mountain storage site.
During excavations from 2004 to 2007, a sample of purified plutonium was uncovered inside a safe in a waste trench, and has been dated to about the 1940s, making it the second-oldest sample of purified plutonium known to exist. Analyses published in 2009 concluded that the sample originated at Oak Ridge, and was one of several sent to Hanford for optimization tests of the TPlant until Hanford could produce its own plutonium. Documents refer to such a sample, belonging to "Watt's group", which was disposed of in its safe when a radiation leak was suspected.
See also
*Lists of nuclear disasters and radioactive incidents *Timeline of nuclear weapons developmentNotes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * ** * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Explores the history of the Hanford nuclear reservation and the tri-cities of Richland, Pasco, and Kennewick, Washington * Recounts the role of the Hanford site in creation and continuation of nuclear weapons *External links
*Federal agency
that regulates Hanford cleanup
State agency
that regulates Hanford cleanup *Historic American Engineering Record documentation: ** ** ** ** ** ** ** {{portal bar, Energy, History of science, Nuclear technology, Pacific Northwest, World War II, United States Hanford Site, Geography of Benton County, Washington Columbia River Environmental disasters in the United States Geography of Washington (state) Historic American Engineering Record in Washington (state) History of Washington (state) History of the Manhattan Project Industrial buildings and structures in Washington (state) Nuclear history of the United States Nuclear weapons infrastructure of the United States Radioactive waste repositories in the United States Tri-Cities, Washington United States Department of Energy facilities Buildings and structures in Benton County, Washington Tourist attractions in Benton County, Washington Radioactively contaminated areas 1943 establishments in Washington (state) Military Superfund sites Superfund sites in Washington (state) Military research of the United States Gravitational-wave astronomy Atomic tourism Nuclear accidents and incidents in the United States Decommissioned nuclear power stations in the United States