Halecomorphi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Halecomorphi is a 




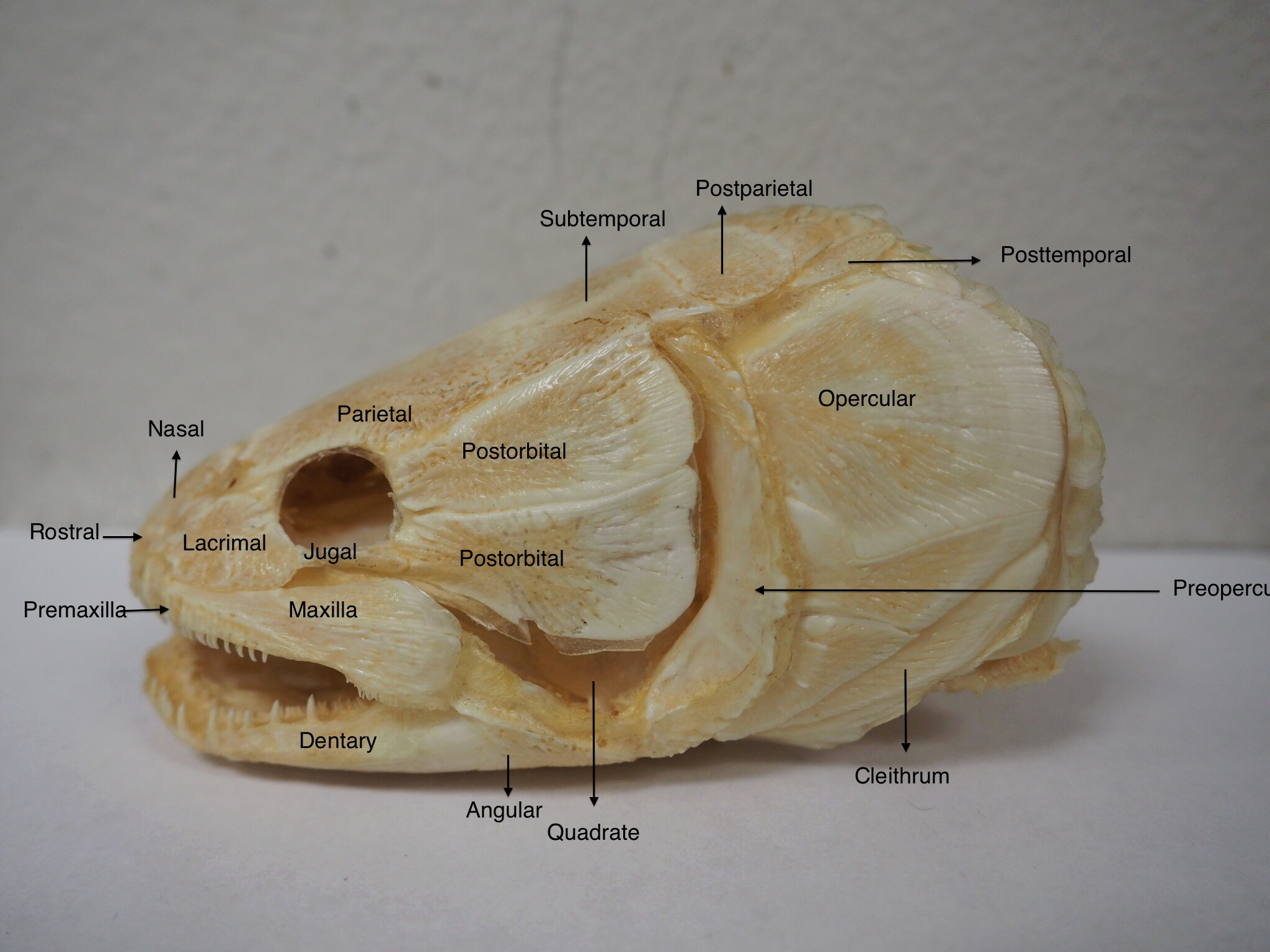 The Halecomorphi exhibit a combination of
The Halecomorphi exhibit a combination of
Interrelationships of Basal Neopterygians.
' S. 117-146 in: Melanie L. J. Stiassny, Lynne R. Parenti, G. David Johnson (Hrsg.): ''Interrelationships of Fishes.'' Academic Press, 1996, {{Taxonbar, from=Q4040348 Vertebrate unranked clades
taxon
In biology, a taxon ( back-formation from '' taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular n ...
of ray-finned
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fishes, is a class of bony fish. They comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species.
The ray-finned fishes are so called because their fins are webs of skin supported by bony or hor ...
bony fish
Osteichthyes (), popularly referred to as the bony fish, is a diverse superclass of fish that have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondrichthyes, which have skeletons primarily composed of cartila ...
in the clade Neopterygii
Neopterygii (from Greek νέος ''neos'' 'new' and πτέρυξ ''pteryx'' 'fin') is a subclass of ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii). Neopterygii includes the Holostei and the Teleostei, of which the latter comprise the vast majority of extant ...
. The sole living Halecomorph is the bowfin
The bowfin (''Amia calva'') is a bony fish, native to North America. Common names include mudfish, mud pike, dogfish, grindle, grinnel, swamp trout, and choupique. It is regarded as a relict, being the sole surviving species of the Halecomorp ...
(''Amia calva''), but the group contains many extinct species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of ...
in several families (including Amiidae, Caturidae
Caturidae is an extinct family of fishes belonging to the order Amiiformes (which contains the modern bowfin) which ranges from the Jurassic (possibly Triassic) to Cretaceous. Members of the family include ''Caturus
''Caturus'' (from el, ...
, Liodesmidae
''Liodesmus'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the early Toarcian stage of the Early Jurassic epoch.
See also
* Prehistoric fish
The evolution of fish began about 530 million years ago during the Cambrian ex ...
, Sinamiidae) in the order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...
Amiiformes
The Amiiformes order of fish has only one extant species, the bowfin (''Amia calva''). These Amiiformes are found in the freshwater systems of North America, in the United States and parts of southern Canada. They live in freshwater streams, riv ...
, as well as the extinct orders Ionoscopiformes, Panxianichthyiformes, and Parasemionotiformes
Parasemionotiformes is an extinct order of neopterygian ray-finned fish that existed globally during the Triassic period. It comprises the families Parasemionotidae and Promecosominidae. Many of the included genera are monotypic and most spec ...
. The fossil record of halecomorphs goes back at least to the Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a ...
epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided by ...
.


 The Halecomorphi exhibit a combination of
The Halecomorphi exhibit a combination of ancestral
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder or a forebear, is a parent or ( recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from w ...
features, such as most heavily mineralized scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number ...
, but also by more derived or "modern" features, particularly in the structure of the skull (e.g. position and shape of preopercles). Unique derived traits (synapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to hav ...
) of the Halecomorphi include:
*Unique jaw articulation in which the quadrate
Quadrate may refer to:
* Quadrate bone
* Quadrate (heraldry)
* Quadrate lobe of liver
* Quadrate tubercle
The quadrate tubercle is a small tubercle found upon the upper part of the femur. It serves as a point of insertion of the quadratus femori ...
and symplectic participate in the joint.
*Lengthened dorsal fins (in some species)
*Two biconcave vertebrae
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
per segment in the posterior body region (a condition known as diplospondyly)
*Fan like arrangement of small bones ( hypurals) in the tail.
Systematics and phylogeny
On the systematic position of the Halecomorphi, there are two competinghypotheses
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous obser ...
:
*The Halecostomi
Halecostomi is the name of a group of neopterygian fish uniting the halecomorphs (represented by the living bowfin and many extinct groups) and the teleosts, the largest group of extant ray-finned fish.
The Halecostomi hypothesis and the Ho ...
hypothesis proposes Halecomorphi as the sister group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
of Teleostei
Teleostei (; Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts ), is, by far, the largest infraclass in the class Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes, containing 96% of all extant species of fish. Tele ...
, the major group of living neopterygians, rendering the Holostei
Holostei is a group of ray-finned bony fish. It is divided into two major clades, the Halecomorphi, represented by a single living species, the bowfin ('' Amia calva''), as well as the Ginglymodi, the sole living representatives being the gars ...
paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be pa ...
.
*The Holostei hypothesis proposes Halecomorphi as the sister group of Ginglymodi
Ginglymodi is a clade of ray-finned fish containing modern-day gars (Lepisosteidae) and their extinct relatives, including the family Lepidotidae and the orders Semionotiformes and Kyphosichthyiformes, and various other extinct taxa. Gingly ...
, the group which includes gars (Lepisosteidae
Gars are members of the family Lepisosteidae, which are the only surviving members of the Ginglymodi, an ancient holosteian group of ray-finned fish, which first appeared during the Triassic, over 240 million years ago. Gars comprise seven l ...
) and their fossil relatives, rendering the Halecostomi paraphyletic.
The latter hypothesis is more widely accepted.
The following cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ...
summarizes the evolutionary relationships
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation te ...
of extinct (indicated with a dagger
A dagger is a fighting knife with a very sharp point and usually two sharp edges, typically designed or capable of being used as a thrusting or stabbing weapon.State v. Martin, 633 S.W.2d 80 (Mo. 1982): This is the dictionary or popular-use de ...
, †) and living orders
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
of Halecomorphi.
References
* Brian J. Gardiner, John G. Maisey, D. Tim J. Littlewood:Interrelationships of Basal Neopterygians.
' S. 117-146 in: Melanie L. J. Stiassny, Lynne R. Parenti, G. David Johnson (Hrsg.): ''Interrelationships of Fishes.'' Academic Press, 1996, {{Taxonbar, from=Q4040348 Vertebrate unranked clades