Hadrosaurinae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed

 Further discoveries such as "''
Further discoveries such as "'' Twenty years later, in 1964, another very important work would be published, this time by John H. Ostrom. It challenged the idea that hadrosaurs were semi-aquatic animals, which had been held since the work of Leidy back in the 1850s. This new approach was backed using evidence of the environment and climate they lived in, co-existing flora and fauna, physical anatomy, and preserved stomach context from mummies. Based on evaluation of all this data, Ostrom found the idea that hadrosaurs were adapted for aquatic life incredibly lacking, and instead proposed they were capable terrestrial animals that browsed on plants such as
Twenty years later, in 1964, another very important work would be published, this time by John H. Ostrom. It challenged the idea that hadrosaurs were semi-aquatic animals, which had been held since the work of Leidy back in the 1850s. This new approach was backed using evidence of the environment and climate they lived in, co-existing flora and fauna, physical anatomy, and preserved stomach context from mummies. Based on evaluation of all this data, Ostrom found the idea that hadrosaurs were adapted for aquatic life incredibly lacking, and instead proposed they were capable terrestrial animals that browsed on plants such as
 Below is a cladogram from Prieto-Marquez ''et al.'' 2016. This cladogram is a recent modification of the original 2010 analysis, including more characters and taxa. The resulting cladistic tree of their analysis was resolved using Maximum-Parsimony. 61 hadrosauroid species were included, characterized for 273 morphological features: 189 for cranial features and 84 for postcranial features. When characters had multiple states that formed an evolutionary scheme, they were ordered to account for the evolution of one state into the next. The final tree was run through TNT version 1.0.
Below is a cladogram from Prieto-Marquez ''et al.'' 2016. This cladogram is a recent modification of the original 2010 analysis, including more characters and taxa. The resulting cladistic tree of their analysis was resolved using Maximum-Parsimony. 61 hadrosauroid species were included, characterized for 273 morphological features: 189 for cranial features and 84 for postcranial features. When characters had multiple states that formed an evolutionary scheme, they were ordered to account for the evolution of one state into the next. The final tree was run through TNT version 1.0.

 The following cladogram is from Ramírez-Velasco (2022), including most recently named taxa.
The following cladogram is from Ramírez-Velasco (2022), including most recently named taxa.
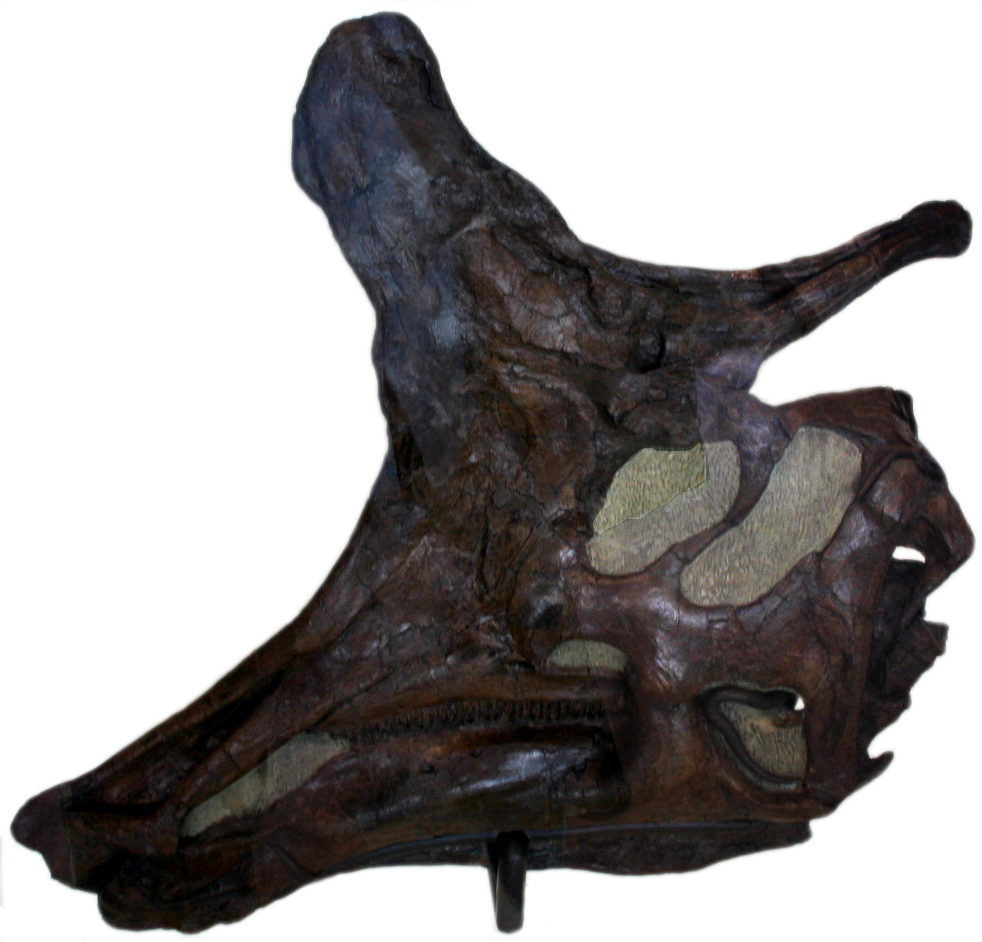
 The most recognizable aspect of hadrosaur anatomy is the flattened and laterally stretched rostral bones, which gives the distinct duck-bill look. Some members of the hadrosaurs also had massive crests on their heads, probably for display. In some genera, including ''Edmontosaurus'', the whole front of the skull was flat and broadened out to form a beak, which was ideal for clipping leaves and twigs from the
The most recognizable aspect of hadrosaur anatomy is the flattened and laterally stretched rostral bones, which gives the distinct duck-bill look. Some members of the hadrosaurs also had massive crests on their heads, probably for display. In some genera, including ''Edmontosaurus'', the whole front of the skull was flat and broadened out to form a beak, which was ideal for clipping leaves and twigs from the
 While studying the chewing methods of hadrosaurids in 2009, the paleontologists Vincent Williams, Paul Barrett, and
While studying the chewing methods of hadrosaurids in 2009, the paleontologists Vincent Williams, Paul Barrett, and  Mallon ''et al.'' (2013) examined herbivore coexistence on the island continent of
Mallon ''et al.'' (2013) examined herbivore coexistence on the island continent of
 As with previous studies, EQ values were investigated, although a wider number range was given to account for uncertainty in brain and body mass. The range for the adult ''Hypacrosaurus'' was 2.3 to 3.7; the lowest end of this range was still higher than modern reptiles and most non-
As with previous studies, EQ values were investigated, although a wider number range was given to account for uncertainty in brain and body mass. The range for the adult ''Hypacrosaurus'' was 2.3 to 3.7; the lowest end of this range was still higher than modern reptiles and most non-

UCMP Tree of Life
{{Taxonbar, from=Q271841 Santonian first appearances Maastrichtian extinctions Taxa named by Edward Drinker Cope Fossil taxa described in 1869 Prehistoric dinosaur families
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s, are members of the ornithischia
Ornithischia () is an extinct order of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek s ...
n family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (), that started out as small, bipedal running grazers and grew in size and numbers until they became one of the most successful groups of herbivores in the Cretaceous wo ...
family, which includes genera such as ''Edmontosaurus
''Edmontosaurus'' ( ) (meaning "lizard from Edmonton") is a genus of hadrosaurid (duck-billed) dinosaur. It contains two known species: ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' and ''Edmontosaurus annectens''. Fossils of ''E. regalis'' have been found in rocks ...
'' and ''Parasaurolophus
''Parasaurolophus'' (; meaning "near crested lizard" in reference to '' Saurolophus)'' is a genus of herbivorous hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaur that lived in what is now North America and possibly Asia during the Late Cretaceous Period, abou ...
'', was a common group of herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
s during the Late Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
Period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
. Hadrosaurids are descendants of the Upper Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
/Lower Cretaceous iguanodontia
Iguanodontia (the iguanodonts) is a clade of herbivorous dinosaurs that lived from the Middle Jurassic to Late Cretaceous. Some members include ''Camptosaurus'', ''Dryosaurus'', ''Iguanodon'', ''Tenontosaurus'', and the hadrosaurids or "duck-bi ...
n dinosaurs and had a similar body layout. Hadrosaurs were among the most dominant herbivores during the Late Cretaceous in Asia and North America, and during the close of the Cretaceous several lineages dispersed into Europe, Africa, South America and Antarctica.
Like other ornithischia
Ornithischia () is an extinct order of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek s ...
ns, hadrosaurids had a predentary
Ornithischia () is an extinct order of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek st ...
bone and a pubic bone which was positioned backwards in the pelvis. Unlike more primitive iguanodonts, the teeth of hadrosaurids are stacked into complex structures known as dental batteries
Dinosaur teeth have been studied since 1822 when Mary Ann Mantell (1795-1869) and her husband Dr Gideon Algernon Mantell (1790-1852) discovered an ''Iguanodon'' tooth in Sussex in England. Unlike mammal teeth, individual dinosaur teeth are gener ...
, which acted as effective grinding surfaces. Hadrosauridae is divided into two principal subfamilies: the lambeosaurines (Lambeosaurinae
Lambeosaurinae is a group of crested hadrosaurid dinosaurs.
Classification
Lambeosaurines have been traditionally split into the tribes or clades Parasaurolophini (''Parasaurolophus'', ''Charonosaurus'', others (?).) and Lambeosaurini (''Coryt ...
), which had hollow cranial crests or tubes; and the saurolophines (Saurolophinae
Saurolophinae is a subfamily of hadrosaurid dinosaurs. It has since the mid-20th century generally been called the Hadrosaurinae, a group of largely non-crested hadrosaurs related to the crested sub-family Lambeosaurinae. However, the name Hadro ...
), identified as hadrosaurines (Hadrosaurinae) in most pre-2010 works, which lacked hollow cranial crests (solid crests were present in some forms). Saurolophines tended to be bulkier than lambeosaurines. Lambeosaurines included the aralosaurins, tsintaosaurins, lambeosaurins and parasaurolophins, while saurolophines included the brachylophosaurins, kritosaurins, saurolophins and edmontosaurins.
Hadrosaurids were facultative bipeds
A facultative biped is an animal that is capable of walking or running on two legs (bipedal), as a response to exceptional circumstances (facultative), while normally walking or running on four limbs or more. In contrast, obligate bipedalism is w ...
, with the young of some species walking mostly on two legs and the adults walking mostly on four.
History of discovery

Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden
Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden (September 7, 1829 – December 22, 1887) was an American geologist noted for his pioneering surveying expeditions of the Rocky Mountains in the late 19th century. He was also a physician who served with the Union Ar ...
, during expeditions near the Judith River
The Judith River is a tributary of the Missouri River, approximately 124 mi (200 km) long, running through central Montana in the United States. It rises in the Little Belt Mountains and flows northeast past Utica and Hobson. It is ...
in 1854 through 1856, discovered the very first dinosaur fossils recognized from North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
. These specimens were obtained by Joseph Leidy
Joseph Mellick Leidy (September 9, 1823 – April 30, 1891) was an American paleontologist, parasitologist and anatomist.
Leidy was professor of anatomy at the University of Pennsylvania, later was a professor of natural history at Swarthmore ...
, who described and named them in 1856; two of the several species named were ''Trachodon mirabilis
''Trachodon'' (meaning "rough tooth") is a dubious genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur based on teeth from the Campanian-age Upper Cretaceous Judith River Formation of Montana, U.S.Leidy, J. (1856). "Notice of remains of extinct reptiles and fishes, ...
'' of the Judith River Formation
The Judith River Formation is a fossil-bearing geologic formation in Montana, and is part of the Judith River Group. It dates to the Late Cretaceous, between 79 and 75.3 million years ago, corresponding to the "Judithian" land vertebrate age. It ...
and ''Thespesius occidentalis
''Thespesius'' (meaning "wondrous one") is a dubious genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur from the late Maastrichtian-age Upper Cretaceous Lance Formation of South Dakota.
History
In 1855 geologist Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden sent a number of fossils ...
'' of the " Great Lignite Formation". The former was based on a collection of teeth whilst the later on two and a . Although most of the ''Trachodon'' teeth turned out to belong to ceratopsids, the holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several ...
and remains of ''T. occidentalis'' would come to be recognized as the first recognized hadrosaur specimens. Around the same time in Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, on the other side of the continent, geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, althou ...
William Parker Foulke
William Parker Foulke (1816–1865) discovered the first full dinosaur skeleton in North America (''Hadrosaurus foulkii'', which means "Foulke's big lizard") in Haddonfield, New Jersey in 1858.
Born in Philadelphia, and a descendant of Welsh ...
was informed of numerous large bones accidentally uncovered by farmer John E. Hopkins some twenty years earlier. Foulke obtained permission to investigate the now scattered fossils in 1858, and these specimens as well were given to Leidy. They were described in the same year as '' Hadrosaurus foulkii'', giving a slightly better picture of the form of a hadrosaur. Leidy provided additional description in a 1865 paper.Lull, Richard Swann; and Wright, Nelda E. (1942). ''Hadrosaurian Dinosaurs of North America'' Among his 1858 work Leidy briefly suggested that the animal was likely amphibious in nature; this school of thought about hadrosaurs would come to be dominant for over a century to come.
 Further discoveries such as "''
Further discoveries such as "''Hadrosaurus minor
''Hadrosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaurs that lived in North America during the Late Cretaceous Period in what is now the Woodbury Formation about 80 million to 78 million years ago. The holotype specimen was found in f ...
''" and "''Ornithotarsus immanis
''Hadrosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaurs that lived in North America during the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), Period in what is now the Woodbury Formation about 80 million to 78 million years ago. The holotype speci ...
''" would come from the East, and Edward Drinker Cope
Edward Drinker Cope (July 28, 1840 – April 12, 1897) was an American zoologist, paleontologist, comparative anatomist, herpetologist, and ichthyologist. Born to a wealthy Quaker family, Cope distinguished himself as a child prodigy interested ...
led an expedition to the Judith River Formation where ''Trachodon'' was found. Upon the fragments discovered he named seven new species in two genera, as well as assigning material to ''Hadrosaurus''. Cope had studied the jaws of hadrosaurs and come to the conclusion that the teeth were fragile and could have been dislodged incredibly easily. As such, he supposed the animals must have fed largely on soft water plants; he presented this idea to the Philadelphia Academy in 1883, and this idea would come to be very influential on future study. Research would continue in the Judith River area for years to come, but the formation never yielded much more than fragmentary remains, and Cope's species as well as ''Trachodon'' itself would be in time be seen as of doubtful validity. The Eastern states, too, would never yield particularly informative specimens. Instead, other sites in the American West would come to provide many very complete specimens that would form the backbone of hadrosaur research. One such specimen was the very complete AMNH 5060
The ''Edmontosaurus'' mummy AMNH 5060 is an exceptionally well-preserved fossil of a dinosaur in the collection of the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH). Discovered in 1908 in the United States near Lusk, Wyoming, it was the first dino ...
( belonging to ''Edmontosaurus annectens''), recovered in 1908 by the fossil collector Charles Hazelius Sternberg
Charles Hazelius Sternberg (June 15, 1850 – July 20, 1943) was an American fossil collector and paleontologist. He was active in both fields from 1876 to 1928, and collected fossils for Edward Drinker Cope and Othniel C. Marsh, and for the ...
and his three sons in Converse County, Wyoming
Converse County is a county located in the U.S. state of Wyoming. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 13,751. Its county seat is Douglas.
History
Converse County was created in 1888 by the legislature of the Wyoming Territ ...
. It was described by Henry Osborn in 1912, who dubbed it the "Dinosaur mummy". This specimen's skin was almost completely preserved in the form of impressions. The skin around its hands, thought to represent webbing, was seen as further bolstering the idea that hadrosaurs were very aquatic animals.
Cope had planned to write a monograph
A monograph is a specialist work of writing (in contrast to reference works) or exhibition on a single subject or an aspect of a subject, often by a single author or artist, and usually on a scholarly subject.
In library cataloging, ''monograph ...
about the group Ornithopoda
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (), that started out as small, bipedal running grazers and grew in size and numbers until they became one of the most successful groups of herbivores in the Cretaceous world ...
, but never made much progress towards it before his death. This unrealized endeavor would come to be the inspiration for Richard Swann Lull
Richard Swann Lull (November 6, 1867 – April 22, 1957) was an American paleontologist and Sterling Professor at Yale University who is largely remembered now for championing a non-Darwinian view of evolution, whereby mutation(s) could unl ...
and Nelda Wright to work on a similar project decades later. Eventually they realized the whole of Ornithopoda was too broad of a scope, until eventually it was narrowed down to specifically North American hadrosaurs. Their monograph, ''Hadrosaurian Dinosaurs of North America'', was published in 1942, and looked back at the whole of understanding about the family. It was designed as a definitive work, covering all aspects of their biology and evolution, and as part of it every known species was re-evaluated and many of them redescribed. They agreed with prior authors on the semi-aquatic nature of hadrosaurs, but re-evaluated Cope's idea of weak jaws and found quite the opposite. The teeth were rooted in strong batteries and would be continuously replaced to prevent them getting worn down. Such a system seemed incredibly overbuilt for the job of eating soft Mesozoic plants, and this fact confused the authors. Though they stil proposed a diet of water plants, they considered it likely this would be supplemented by occasional forrays into browsing on land plants.
 Twenty years later, in 1964, another very important work would be published, this time by John H. Ostrom. It challenged the idea that hadrosaurs were semi-aquatic animals, which had been held since the work of Leidy back in the 1850s. This new approach was backed using evidence of the environment and climate they lived in, co-existing flora and fauna, physical anatomy, and preserved stomach context from mummies. Based on evaluation of all this data, Ostrom found the idea that hadrosaurs were adapted for aquatic life incredibly lacking, and instead proposed they were capable terrestrial animals that browsed on plants such as
Twenty years later, in 1964, another very important work would be published, this time by John H. Ostrom. It challenged the idea that hadrosaurs were semi-aquatic animals, which had been held since the work of Leidy back in the 1850s. This new approach was backed using evidence of the environment and climate they lived in, co-existing flora and fauna, physical anatomy, and preserved stomach context from mummies. Based on evaluation of all this data, Ostrom found the idea that hadrosaurs were adapted for aquatic life incredibly lacking, and instead proposed they were capable terrestrial animals that browsed on plants such as conifers
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All extan ...
. He remained uncertain, however, as to the purpose of the paddle-like hand Osborn had described, as well as their long and somewhat paddle-like tails. Thus he agreed with the idea that hadrosaurs would have taken refuge from predators in water. Numerous important studies would follow this; Ostrom's student Peter Dodson published a paper about lambeosaur
Lambeosaurinae is a group of crested hadrosaurid dinosaurs.
Classification
Lambeosaurines have been traditionally split into the tribes or clades Parasaurolophini (''Parasaurolophus'', ''Charonosaurus'', others (?).) and Lambeosaurini (''Cor ...
skull anatomy that made enormous changes to hadrosaur taxonomy in 1975, and Michael K. Brett-Surman conducted a full revision of the group as part of his Graduate studies through the 1970s and 1980s. John R. Horner
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second E ...
would also begin to leave his impact on the field, including with the naming of ''Maiasaura
''Maiasaura'' (from the Greek ''μαῖα'', meaning "good mother" and ''σαύρα'', the feminine form of ''saurus'', meaning "reptile") is a large herbivorous saurolophine hadrosaurid ("duck-billed") dinosaur genus that lived in the area curre ...
'' in 1979.
Hadrosaur research experienced a surge in the decade of the 2000s, similar to the research of other dinosaurs. In response to this, the Royal Ontario Museum
The Royal Ontario Museum (ROM) is a museum of art, world culture and natural history in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is one of the largest museums in North America and the largest in Canada. It attracts more than one million visitors every year ...
and the Royal Tyrrell Museum
The Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology (RTMP, and often referred to as the Royal Tyrrell Museum) is a palaeontology museum and research facility in Drumheller, Alberta, Canada. The museum was named in honour of Joseph Burr Tyrrell, and is situ ...
collaborated to arrange the International Hadrosaur Symposium, a professional meeting about ongoing hadrosaur research that was held at the latter institution on September 22 and 23 in 2011. Over fifty presentations were made at the event, thirty-six of which were later incorporated into a book, titled ''Hadrosaurs
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which incl ...
'', published in 2015. The volume was brought together primarily by palaeontologists David A. Eberth and David C. Evans, and featured an afterword from John R. Horner
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second E ...
, all of whom also contributed to one or more of the studies published therein. The first chapter of the volume was a study by David B. Weishampel about the rate of ornithopod research over history, and the interest in different aspects of it over that history, using the 2004 volume ''The Dinosauria
''The Dinosauria'' is an extensive book on dinosaurs, compiled by David B. Weishampel, Peter Dodson, and Halszka Osmólska. It has been published in 2 editions, with the first edition published in 1990, consisting of material from 23 scientists.B ...
'' as the source of data on the amount of works published in each decade. Various periods of high and low activity were found, but the twenty-first century was found to overwhelmingly be the most prolific time, with over two-hundred papers published. The advent of the internet was cited as a likely catalyst for this boom. Hadrosaur research experienced high levels of diversity within the decade, with previously uncommon subjects such as growth, phylogeny, and biogeography experiencing more attention, though the functional morphology of hadrosaurids was found to have declined in study since the Dinosaur Renaissance.
Classification
The family Hadrosauridae was first used by Edward Drinker Cope in 1869, then containing only ''Hadrosaurus
''Hadrosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaurs that lived in North America during the Late Cretaceous Period in what is now the Woodbury Formation about 80 million to 78 million years ago. The holotype specimen was found in f ...
''. Since its creation, a major division has been recognized in the group between the hollow-crested subfamily Lambeosaurinae
Lambeosaurinae is a group of crested hadrosaurid dinosaurs.
Classification
Lambeosaurines have been traditionally split into the tribes or clades Parasaurolophini (''Parasaurolophus'', ''Charonosaurus'', others (?).) and Lambeosaurini (''Coryt ...
and the subfamily Saurolophinae
Saurolophinae is a subfamily of hadrosaurid dinosaurs. It has since the mid-20th century generally been called the Hadrosaurinae, a group of largely non-crested hadrosaurs related to the crested sub-family Lambeosaurinae. However, the name Hadro ...
, historically known as Hadrosaurinae. Both of these have been robustly supported in all recent literature. Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
analysis has increased the resolution of hadrosaurid relationships considerably, leading to the widespread usage of tribes (a taxonomic unit below subfamily) to describe the finer relationships within each group of hadrosaurids. .
Lambeosaurines have also been traditionally split into Parasaurolophini
Parasaurolophini is a tribe of derived corythosaurian lambeosaurine hadrosaurids that are native to Asia, and North America. It is defined as everything closer to ''Parasaurolophus walkeri'' than to '' Lambeosaurus lambei''. It currently contain ...
and Lambeosaurini
Lambeosaurini, previously known as Corythosaurini, is one of four tribes of hadrosaurid ornithopods from the family Lambeosaurinae. It is defined as all lambeosaurines closer to '' Lambeosaurus lambei'' than to ''Parasaurolophus walkeri, Tsintaos ...
. These terms entered the formal literature in Evans and Reisz's 2007 redescription of ''Lambeosaurus
''Lambeosaurus'' ( , meaning " Lambe's lizard") is a genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur that lived about 75 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous period (Campanian stage) of North America. This bipedal/quadrupedal, herbivorous dinosaur is k ...
magnicristatus''. Lambeosaurini is defined as all taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ...
more closely related ''Lambeosaurus lambei'' than to ''Parasaurolophus walkeri'', and Parasaurolophini as all those taxa closer to ''P. walkeri'' than to ''L. lambei''. In recent years Tsintaosaurini
Tsintaosaurini is a tribe of basal lambeosaurine hadrosaurs native to Eurasia. It is thought to contains the genera ''Tsintaosaurus'' (from China), '' Pararhabdodon'' (from Spain) and '' Koutalisaurus'' (also from Spain), though some studies hav ...
and Aralosaurini have also emerged.
The use of the term Hadrosaurinae was questioned in a comprehensive study of hadrosaurid relationships by Albert Prieto-Márquez in 2010. Prieto-Márquez noted that, though the name Hadrosaurinae had been used for the clade of mostly crestless hadrosaurids by nearly all previous studies, its type species, ''Hadrosaurus
''Hadrosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaurs that lived in North America during the Late Cretaceous Period in what is now the Woodbury Formation about 80 million to 78 million years ago. The holotype specimen was found in f ...
foulkii'', has almost always been excluded from the clade that bears its name, in violation of the rules for naming animals set out by the ICZN
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is a widely accepted convention in zoology that rules the formal scientific naming of organisms treated as animals. It is also informally known as the ICZN Code, for its publisher, the I ...
. Prieto-Márquez defined Hadrosaurinae as just the lineage containing ''H. foulkii'', and used the name Saurolophinae instead for the traditional grouping.
Phylogeny
Hadrosauridae was first defined as aclade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
, by Forster, in a 1997 abstract, as simply "Lambeosaurinae plus Hadrosaurinae and their most recent common ancestor". In 1998, Paul Sereno
Paul Callistus Sereno (born October 11, 1957) is a professor of paleontology at the University of Chicago and a National Geographic "explorer-in-residence" who has discovered several new dinosaur species on several continents, including at sites ...
defined the clade Hadrosauridae as the most inclusive possible group containing ''Saurolophus
''Saurolophus'' (; meaning "lizard crest") is a genus of large hadrosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of Asia and North America, that lived in what is now the Horseshoe Canyon and Nemegt formations about 70 million to 68 million ...
'' (a well-known saurolophine) and ''Parasaurolophus
''Parasaurolophus'' (; meaning "near crested lizard" in reference to '' Saurolophus)'' is a genus of herbivorous hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaur that lived in what is now North America and possibly Asia during the Late Cretaceous Period, abou ...
'' (a well-known lambeosaurine), later emending the definition to include ''Hadrosaurus
''Hadrosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaurs that lived in North America during the Late Cretaceous Period in what is now the Woodbury Formation about 80 million to 78 million years ago. The holotype specimen was found in f ...
'', the type genus of the family, which ICZN
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is a widely accepted convention in zoology that rules the formal scientific naming of organisms treated as animals. It is also informally known as the ICZN Code, for its publisher, the I ...
rules state must be included, despite its status as a ''nomen dubium''. According to Horner ''et al.'' (2004), Sereno's definition would place a few other well-known hadrosaurs (such as ''Telmatosaurus
''Telmatosaurus'' (meaning "marsh lizard") is a genus of basal hadrosauromorph dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Romania. It was a relatively small hadrosaur, measuring approximately in length and in body mass, which has been explained as a ...
'' and ''Bactrosaurus
''Bactrosaurus'' (; meaning "Club lizard," "baktron" = club + ''sauros'' = lizard) is a genus of herbivorous hadrosauroid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, about 96-85 million years ago. The position ''Bactrosaurus'' occupi ...
'') outside the family, which led them to define the family to include ''Telmatosaurus'' by default. Prieto-Marquez reviewed the phylogeny of Hadrosauridae in 2010, including many taxa potentially within the family.
 Below is a cladogram from Prieto-Marquez ''et al.'' 2016. This cladogram is a recent modification of the original 2010 analysis, including more characters and taxa. The resulting cladistic tree of their analysis was resolved using Maximum-Parsimony. 61 hadrosauroid species were included, characterized for 273 morphological features: 189 for cranial features and 84 for postcranial features. When characters had multiple states that formed an evolutionary scheme, they were ordered to account for the evolution of one state into the next. The final tree was run through TNT version 1.0.
Below is a cladogram from Prieto-Marquez ''et al.'' 2016. This cladogram is a recent modification of the original 2010 analysis, including more characters and taxa. The resulting cladistic tree of their analysis was resolved using Maximum-Parsimony. 61 hadrosauroid species were included, characterized for 273 morphological features: 189 for cranial features and 84 for postcranial features. When characters had multiple states that formed an evolutionary scheme, they were ordered to account for the evolution of one state into the next. The final tree was run through TNT version 1.0.

 The following cladogram is from Ramírez-Velasco (2022), including most recently named taxa.
The following cladogram is from Ramírez-Velasco (2022), including most recently named taxa.
Anatomy
 The most recognizable aspect of hadrosaur anatomy is the flattened and laterally stretched rostral bones, which gives the distinct duck-bill look. Some members of the hadrosaurs also had massive crests on their heads, probably for display. In some genera, including ''Edmontosaurus'', the whole front of the skull was flat and broadened out to form a beak, which was ideal for clipping leaves and twigs from the
The most recognizable aspect of hadrosaur anatomy is the flattened and laterally stretched rostral bones, which gives the distinct duck-bill look. Some members of the hadrosaurs also had massive crests on their heads, probably for display. In some genera, including ''Edmontosaurus'', the whole front of the skull was flat and broadened out to form a beak, which was ideal for clipping leaves and twigs from the forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
s of Asia, Europe and North America. However, the back of the mouth contained thousands of teeth suitable for grinding food before it was swallowed. This has been hypothesized to have been a crucial factor in the success of this group in the Cretaceous compared to the sauropod
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their bo ...
s.
Skin impressions of multiple hadrosaurs have been found. From these impressions, the hadrosaurs were determined to be scaled, and not feathered like some dinosaurs of other groups.
Hadrosaurs, much like sauropods
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their b ...
, are noted for having their manus united in a fleshy, often nail-less pad.
The two major divisions of hadrosaurids are differentiated by their cranial ornamentation. While members of the Lambeosaurinae
Lambeosaurinae is a group of crested hadrosaurid dinosaurs.
Classification
Lambeosaurines have been traditionally split into the tribes or clades Parasaurolophini (''Parasaurolophus'', ''Charonosaurus'', others (?).) and Lambeosaurini (''Coryt ...
subfamily have hollow crests that differ depending on species, members of the Saurolophinae
Saurolophinae is a subfamily of hadrosaurid dinosaurs. It has since the mid-20th century generally been called the Hadrosaurinae, a group of largely non-crested hadrosaurs related to the crested sub-family Lambeosaurinae. However, the name Hadro ...
( Hadrosaurinae) subfamily have solid crests or none at all. Lambeosaurine crests had air chambers that may have produced a distinct sound and meant that their crests could have been used for both an audio and visual display.
Paleobiology
Diet
 While studying the chewing methods of hadrosaurids in 2009, the paleontologists Vincent Williams, Paul Barrett, and
While studying the chewing methods of hadrosaurids in 2009, the paleontologists Vincent Williams, Paul Barrett, and Mark Purnell
Mark Andrew Purnell is a British palaeontologist, Professor of Palaeobiology at the University of Leicester.
Purnell is an expert in conodont biostratigraphy (principally Carboniferous) and conodont palaeobiology, focussing especially on atte ...
found that hadrosaurs likely grazed on horsetails and vegetation close to the ground, rather than browsing higher-growing leaves and twigs. This conclusion was based on the evenness of scratches on hadrosaur teeth, which suggested the hadrosaur used the same series of jaw motions over and over again. As a result, the study determined that the hadrosaur diet was probably made of leaves and lacked the bulkier items, such as twigs or stems, that might have required a different chewing method and created different wear patterns. However, Purnell said these conclusions were less secure than the more conclusive evidence regarding the motion of teeth while chewing.
The hypothesis that hadrosaurs were likely grazers rather than browsers appears to contradict previous findings from preserved stomach contents found in the fossilized guts in previous hadrosaur studies. The most recent such finding before the publication of the Purnell study was conducted in 2008, when a team led by University of Colorado at Boulder
The University of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder, CU, or Colorado) is a public research university in Boulder, Colorado. Founded in 1876, five months before Colorado became a state, it is the flagship university of the University of Colorado sys ...
graduate student Justin S. Tweet found a homogeneous accumulation of millimeter-scale leaf fragments in the gut region of a well-preserved partially grown ''Brachylophosaurus
''Brachylophosaurus'' ( or ; meaning "short-crested lizard", Greek ''brachys'' = short + ''lophos'' = crest + ''sauros'' = lizard, referring to its small crest) was a mid-sized member of the hadrosaurid family of dinosaurs. It is known from sev ...
''. As a result of that finding, Tweet concluded in September 2008 that the animal was likely a browser, not a grazer. In response to such findings, Purnell said that preserved stomach contents are questionable because they do not necessarily represent the usual diet of the animal. The issue remains a subject of debate.This information comes from the aforementioned Alan Boyle source from June 29, 2009. However, this specific information is not included in the body of the article, but rather a response by Boyle to comments in the article. Since the comments were written by Boyle himself, and since they cite information he received specifically from Purnell, they are as legitimate a source of information as the article itself.
 Mallon ''et al.'' (2013) examined herbivore coexistence on the island continent of
Mallon ''et al.'' (2013) examined herbivore coexistence on the island continent of Laramidia
Laramidia was an island continent that existed during the Late Cretaceous period (99.6–66 Ma), when the Western Interior Seaway split the continent of North America in two. In the Mesozoic era, Laramidia was an island land mass separated from A ...
, during the Late Cretaceous. It was concluded that hadrosaurids could reach low-growing trees and shrubs that were out of the reach of ceratopsids, ankylosaurs, and other small herbivores. Hadrosaurids were capable of feeding up to 2 m when standing quadrupedally, and up to 5 m bipedally.
Coprolite
A coprolite (also known as a coprolith) is fossilized feces. Coprolites are classified as trace fossils as opposed to body fossils, as they give evidence for the animal's behaviour (in this case, diet) rather than morphology. The name is de ...
s (fossilized droppings) of some Late Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
hadrosaurs show that the animals sometimes deliberately ate rotting wood. Wood itself is not nutritious, but decomposing wood would have contained fungi, decomposed wood material and detritus
In biology, detritus () is dead particulate organic material, as distinguished from dissolved organic material. Detritus typically includes the bodies or fragments of bodies of dead organisms, and fecal material. Detritus typically hosts commun ...
-eating invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
s, all of which would have been nutritious. Examination of hadrosaur coprolites from the Grand Staircase-Escalante indicates that shellfish such as crustaceans were also an important component of the hadrosaur diet.
Neurology

Hadrosaurs
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which incl ...
have been noted as having the most complex brains among ornithopods, and indeed among ornithischian
Ornithischia () is an extinct order of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek st ...
dinosaurs as a whole. The brains of hadrosaurid dinosaurs have been studied as far back at the late 19th century, when Othniel Charles Marsh
Othniel Charles Marsh (October 29, 1831 – March 18, 1899) was an American professor of Paleontology in Yale College and President of the National Academy of Sciences. He was one of the preeminent scientists in the field of paleontology. Among h ...
made an endocast
An endocast is the internal cast of a hollow object, often referring to the cranial vault in the study of brain development in humans and other organisms. Endocasts can be artificially made for examining the properties of a hollow, inaccessible sp ...
of a specimen then referred to ''Claosaurus annectens
''Edmontosaurus annectens'' (meaning "connected lizard from Edmonton") is a species of flat-headed and duck-billed (hadrosaurid) dinosaur from the very end of the Cretaceous Period, in what is now North America. Remains of ''E. annectens'' have b ...
''; only basic remarks were possible but it was noted that the organ was proportionally small. John Ostram
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second ...
would give a more informed analysis and review in 1961, pulling on data from ''Edmontosaurus regalis
''Edmontosaurus regalis'' is a species of comb-crested hadrosaurid (duck-billed) dinosaur. Fossils of ''E. regalis'' have been found in rocks of western North America that date from the late Campanian stage of the Cretaceous Period 73 million y ...
'', ''E. annectens'', and ''Gryposaurus notabilis'' (then considered a synonym of ''Kritosaurus
''Kritosaurus'' is an incompletely known genus of hadrosaurid (duck-billed) dinosaur. It lived about 74.5-66 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous of North America. The name means "separated lizard" (referring to the arrangement of the cheek ...
''). Though still obviously small, Ostram recognized that the brains may be more significantly developed than expected, but supported the view that dinosaur brains would've only filled some of the endocranial cavity, limiting possibility of analysis. In 1977 James Hopson
James Allen Hopson (born 1935) is an American paleontologist and professor (now retired) at the University of Chicago. His work has focused on the evolution of the synapsids (a group of amniotes that includes the mammals), and has been focused ...
introduce the use of estimated encephalization quotient
Encephalization quotient (EQ), encephalization level (EL), or just encephalization is a relative brain size measure that is defined as the ratio between observed to predicted brain mass for an animal of a given size, based on nonlinear regressi ...
s to the topic of dinosaur intelligence, finding ''Edmontosaurus'' to have an EQ of 1.5, above that of other ornithischians including earlier relatives like ''Camptosaurus
''Camptosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of plant-eating, beaked ornithischian dinosaurs of the Late Jurassic period of western North America and possibly also Europe. The name means 'flexible lizard' ( Greek (') meaning 'bent' and (') meaning 'li ...
'' and ''Iguanodon
''Iguanodon'' ( ; meaning 'iguana-tooth'), named in 1825, is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur. While many species have been classified in the genus ''Iguanodon'', dating from the late Jurassic Period to the early Cretaceous Period of Asia, Eu ...
'' and similar to that of carnosaurian
Carnosauria is an extinct large group of predatory dinosaurs that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. Starting from the 1990s, scientists have discovered some very large carnosaurs in the carcharodontosaurid family, such as ' ...
theropods and modern crocodilians
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period (Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living re ...
but below that of coelurosaurian theropods. Reasonings suggested for their comparably high intelligence were the need for acute senses in the lack of defensive weapons, and more complex intraspecific
Biological specificity is the tendency of a characteristic such as a behavior or a biochemical variation to occur in a particular species.
Biochemist Linus Pauling stated that "Biological specificity is the set of characteristics of living organ ...
behaviours as indicated by their acoustic and visual display structures.
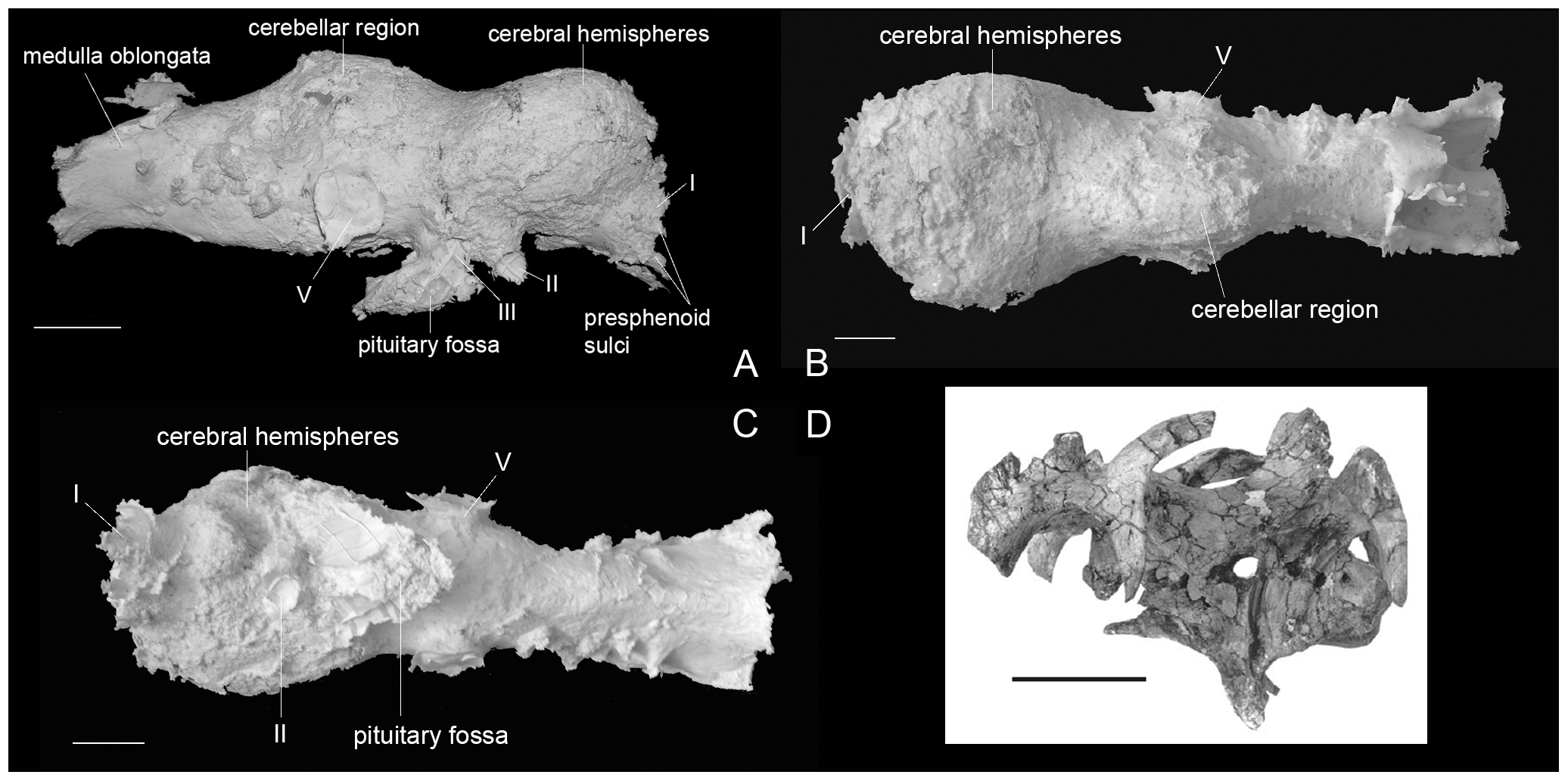
The advent of CT scanning for use in palaeontology has allowed for more widespread application of this without the need for specimen destruction. Modern research using these methods has focused largely on hadrosaurs. In a 2009 study by palaeontologist David C. Evans and colleagues, the brains of lambeosaurine
Lambeosaurinae is a group of crested hadrosaurid dinosaurs.
Classification
Lambeosaurines have been traditionally split into the tribes or clades Parasaurolophini ('' Parasaurolophus'', ''Charonosaurus'', others (?).) and Lambeosaurini (''Cor ...
hadrosaur genera ''Hypacrosaurus
''Hypacrosaurus'' (meaning "near the highest lizard" reek υπο-, ''hypo-'' = less + ακρος, ''akros'', high because it was almost but not quite as large as ''Tyrannosaurus'') was a genus of duckbill dinosaur similar in appearance to ''Co ...
'' (adult specimen ROM
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* ...
702), ''Corythosaurus
''Corythosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of hadrosaurid "duck-billed" dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Period (geology), Period, about 77–75.7 million years ago. It lived in what is now North America. Its name means "helmet lizard", derived fr ...
'' (juvenile specimen ROM 759 and subadult specimen CMN 34825), and ''Lambeosaurus
''Lambeosaurus'' ( , meaning " Lambe's lizard") is a genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur that lived about 75 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous period (Campanian stage) of North America. This bipedal/quadrupedal, herbivorous dinosaur is k ...
'' (juvenile specimen ROM 758) were scanned and compared to each other (on a phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
and ontogenetic
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the st ...
level), related taxa, and previous predictions, the first such large-scale look into the neurology of the subfamily. Contra the early works, Evans' studies indicate that only some regions of the hadrosaur brain (the dorsal portion and much of the hindbrain) were loosely correlated to the brain wall, like modern reptiles, with the ventral and lateral regions correlating fairly closely. Also unlike modern reptiles, the brains of the juveniles did not seem to correlate any closer to the brain wall than those of adults. It was cautioned, however, that very young individuals were not included in the study.
 As with previous studies, EQ values were investigated, although a wider number range was given to account for uncertainty in brain and body mass. The range for the adult ''Hypacrosaurus'' was 2.3 to 3.7; the lowest end of this range was still higher than modern reptiles and most non-
As with previous studies, EQ values were investigated, although a wider number range was given to account for uncertainty in brain and body mass. The range for the adult ''Hypacrosaurus'' was 2.3 to 3.7; the lowest end of this range was still higher than modern reptiles and most non-maniraptoran
Maniraptora is a clade of coelurosaurian dinosaurs which includes the birds and the non-avian dinosaurs that were more closely related to them than to ''Ornithomimus velox''. It contains the major subgroups Avialae, Deinonychosauria, Oviraptoros ...
dinosaurs (nearly all having EQs below two), but fell well short of maniraptorans themselves, which had quotients higher than four. The size of the cerebral hemispheres
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres ...
was, for the first time, remarked upon. It was found to taking up around 43% of endocranial volume (not considering olfactory bulbs
The olfactory bulb (Latin: ''bulbus olfactorius'') is a neural structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, the sense of smell. It sends olfactory information to be further processed in the amygdala, the orbitofrontal cortex (O ...
) in ROM 702. This is comparable to their size in saurolophine
Saurolophinae is a subfamily (biology), subfamily of hadrosaurid dinosaurs. It has since the mid-20th century generally been called the Hadrosaurinae, a group of largely non-crested hadrosaurs related to the crested sub-family Lambeosaurinae. How ...
hadrosaurs, but far larger than in any ornithischians outside of Hadrosauriformes, and all large saurischian
Saurischia ( , meaning "reptile-hipped" from the Greek ' () meaning 'lizard' and ' () meaning 'hip joint') is one of the two basic divisions of dinosaurs (the other being Ornithischia), classified by their hip structure. Saurischia and Ornithis ...
dinosaurs; maniraptors ''Conchoraptor
''Conchoraptor'' (meaning "conch plunderer") is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous epoch, about 70 million years ago. It is known from the Barun Goyot and Nemegt formations of Mongolia.
Discovery
Wh ...
'' and ''Archaeopteryx
''Archaeopteryx'' (; ), sometimes referred to by its German name, "" ( ''Primeval Bird''), is a genus of bird-like dinosaurs. The name derives from the ancient Greek (''archaīos''), meaning "ancient", and (''ptéryx''), meaning "feather" ...
'', an early bird, had very similar proportions. This lends further support to the idea of complex behaviours and relatively high intelligence, for non-avian dinosaurs, in hadrosaurids.
''Amurosaurus
''Amurosaurus'' (; "Amur lizard") is a genus of lambeosaurine hadrosaurid dinosaur found in the latest Cretaceous period (66 million years ago)Godefroit, P., Lauters, P., Van Itterbeeck, J., Bolotsky, Y. and Bolotsky, I.Y. (2011). "Recent advanc ...
'', a close relative of the taxa from the 2009 study, was the subject of a 2013 paper once again looking into a cranial endocast. A nearly identical EQ range of 2.3 to 3.8 was found, and it was again noted this was higher than that of living reptiles, sauropod
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their bo ...
s and other ornithischians, but different EQ estimates for theropods were cited, placing the hadrosaur numbers significantly below even more basal theropods like ''Ceratosaurus
''Ceratosaurus'' (from Greek κέρας/κέρατος, ' meaning "horn" and σαῦρος ' meaning "lizard") was a carnivorous theropod dinosaur in the Late Jurassic period ( Kimmeridgian to Tithonian). The genus was first described in 1 ...
'' (with an EQ range of 3.31 to 5.07) and ''Allosaurus
''Allosaurus'' () is a genus of large carnosaurian theropod dinosaur that lived 155 to 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic epoch ( Kimmeridgian to late Tithonian). The name "''Allosaurus''" means "different lizard" alludin ...
'' (with a range of 2.4 to 5.24, compared to only 1.6 in the 2009 study); more bird-like coelurosaurians theropods such as ''Troodon'' had stated EQs higher than seven. Additionally, the relative cerebral volume was only 30% in ''Amurosaurus'', significantly lower than in ''Hypacrosaurus'', closer to that of theropods like ''Tyrannosaurus'' (with 33%), though still distinctly larger than previously estimated numbers for more primitive iguanodonts like ''Lurdusaurus'' and ''Iguanodon'' (both at 19%). This demonstrated a previously unrecognized level of variation in neuro-anatomy within Hadrosauridae.
Reproduction

Neonate
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to ...
sized hadrosaur fossils have been documented in the scientific literature
: ''For a broader class of literature, see Academic publishing.''
Scientific literature comprises scholarly publications that report original empirical and theoretical work in the natural and social sciences. Within an academic field, scient ...
.Tanke, D.H. and Brett-Surman, M.K. 2001. Evidence of Hatchling and Nestling-Size Hadrosaurs (Reptilia:Ornithischia) from Dinosaur Provincial Park (Dinosaur Park Formation: Campanian), Alberta, Canada. pp. 206-218. In: Mesozoic Vertebrate Life—New Research Inspired by the Paleontology of Philip J. Currie. Edited by D.H. Tanke and K. Carpenter. Indiana University Press: Bloomington. xviii + 577 pp. Tiny hadrosaur footprints have been discovered in the Blackhawk Formation of Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
.
In a 2001 review of hadrosaur eggshell
An eggshell is the outer covering of a hard-shelled egg and of some forms of eggs with soft outer coats.
Diversity
Worm eggs
Nematode eggs present a two layered structure: an external vitellin layer made of chitin that confers mechanical ...
and hatchling material from Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
's Dinosaur Park Formation
The Dinosaur Park Formation is the uppermost member of the Belly River Group (also known as the Judith River Group), a major geologic unit in southern Alberta. It was deposited during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, between about 76. ...
, Darren Tanke
Darren H. Tanke (born 1960) is a Canadian fossil preparation technician of the Dinosaur Research Program at the Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology in Drumheller, Alberta. Born in Calgary, Tanke became interested in natural history at an early ...
and M. K. Brett-Surman concluded that hadrosaurs nested in both the ancient upland and lowlands of the formation's depositional environment. The upland nesting grounds may have been preferred by the less common hadrosaurs, like ''Brachylophosaurus
''Brachylophosaurus'' ( or ; meaning "short-crested lizard", Greek ''brachys'' = short + ''lophos'' = crest + ''sauros'' = lizard, referring to its small crest) was a mid-sized member of the hadrosaurid family of dinosaurs. It is known from sev ...
'' and ''Parasaurolophus
''Parasaurolophus'' (; meaning "near crested lizard" in reference to '' Saurolophus)'' is a genus of herbivorous hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaur that lived in what is now North America and possibly Asia during the Late Cretaceous Period, abou ...
''. However, the authors were unable to determine what specific factors shaped nesting ground choice in the formation's hadrosaurs. They suggested that behavior, diet, soil condition, and competition between dinosaur species all potentially influenced where hadrosaurs nested.
Sub-centimeter fragments of pebbly-textured hadrosaur eggshell have been reported from the Dinosaur Park Formation. This eggshell is similar to the hadrosaur eggshell of Devil's Coulee in southern Alberta as well as that of the Two Medicine
Two Medicine is the collective name of a region located in the southeastern section of Glacier National Park, in the U.S. state of Montana. It has a campground alongside Two Medicine Lake. From the period starting in the late 1890s until the com ...
and Judith River Formations
The Judith River Formation is a fossil-bearing geologic formation in Montana, and is part of the Judith River Group. It dates to the Late Cretaceous, between 79 and 75.3 million years ago, corresponding to the "Judithian" land vertebrate age. It ...
in Montana, United States. While present, dinosaur eggshell is very rare in the Dinosaur Park Formation and is only found in two different microfossil sites. These sites are distinguished by large numbers of pisidiid
''Pisidium'' is a genus of very small or minute freshwater clams known as pill clams or pea clams, aquatic bivalve molluscs in the family Sphaeriidae, the pea clams and fingernail clams.
In some bivalve classification systems, the family Spha ...
clams
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve molluscs. The word is often applied only to those that are edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the seafloor or riverbeds. Clams have two ...
and other less common shelled invertebrates, like unionid
The Unionidae are a family of freshwater mussels, the largest in the order Unionida, the bivalve molluscs sometimes known as river mussels, or simply as unionids.
The range of distribution for this family is world-wide. It is at its most diverse ...
clams and snails. This association is not a coincidence, as the invertebrate shells would have slowly dissolved and released enough basic calcium carbonate to protect the eggshells from naturally occurring acids that otherwise would have dissolved them and prevented fossilization.
In contrast with eggshell fossils, the remains of very young hadrosaurs are somewhat common. Tanke has observed that an experienced collector could discover multiple juvenile hadrosaur specimens in a single day. The most common remains of young hadrosaurs in the Dinosaur Park Formation are dentaries
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
, bones from limbs and feet, as well as vertebral centra
Centra is a convenience shop chain that operates throughout Ireland. The chain operates as a symbol group owned by Musgrave Group, the food wholesaler, meaning the stores are all owned by individual franchisees.
The chain has three different ...
. The material showed little or none of the abrasion that would have resulted from transport, meaning the fossils were buried near their point of origin. Bonebeds 23, 28, 47, and 50 are productive sources of young hadrosaur remains in the formation, especially bonebed 50. The bones of juvenile hadrosaurs and fossil eggshell fragments are not known to have been preserved in association with each other, despite both being present in the formation.
Growth and development
The limbs of the juvenile hadrosaurs are anatomically and proportionally similar to those of adult animals. However, the joints often show "predepositional erosion or concave articular surfaces", which was probably due to the cartilaginous cap covering the ends of the bones. The pelvis of a young hadrosaur was similar to that of an older individual. Evidence suggests that young hadrosaurs would have walked on only their two hind legs, while adults would have walked on all four. As the animal aged, the front limbs became more robust in order to take on weight, while the back legs became less robust as they transitioned to walking on all four legs. Furthermore, the animals’ front limbs were shorter than their back limbs.Daily activity patterns
Comparisons between the scleral rings of several hadrosaur genera (''Corythosaurus
''Corythosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of hadrosaurid "duck-billed" dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Period (geology), Period, about 77–75.7 million years ago. It lived in what is now North America. Its name means "helmet lizard", derived fr ...
'', ''Prosaurolophus
''Prosaurolophus'' (; meaning "before ''Saurolophus''", in comparison to the later dinosaur with a similar head crest) is a genus of hadrosaurid (or duck-billed) dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of North America. It is known from the remains of ...
'', and ''Saurolophus
''Saurolophus'' (; meaning "lizard crest") is a genus of large hadrosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of Asia and North America, that lived in what is now the Horseshoe Canyon and Nemegt formations about 70 million to 68 million ...
'') and modern birds and reptiles suggest that they may have been cathemeral
Cathemerality, sometimes called metaturnality, is an organismal activity pattern of irregular intervals during the day or night in which food is acquired, socializing with other organisms occurs, and any other activities necessary for livelihood ar ...
, active throughout the day at short intervals.
Pathology
Spondyloarthropathy
Spondyloarthropathy or spondyloarthrosis refers to any joint disease of the vertebral column. As such, it is a class or category of diseases rather than a single, specific entity. It differs from spondylopathy, which is a disease of the vertebra ...
has been documented in the spine of a 78-million year old hadrosaurid. Other examples of pathologies in hadrosaurs include healed wounds from predators, such as those found in ''Edmontosaurus annectens'', and tumors such as hemangiomas, desmoplastic fibroma, metastatic cancer, and osteoblastomas, found in genera such as ''Brachylophosaurus'' and ''Edmontosaurus''. ot printed until 2000/ref> Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a family of orthopedic diseases of the joint that occur in children, adolescents and rapidly growing animals, particularly pigs, horses, dogs, and broiler chickens. They are characterized by interruption of the blood supply of a ...
is also commonly found in hadrosaurs.
References
External links
*Timeline of hadrosaur research
A timeline is a display of a list of events in chronological order. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it, and usually contemporaneous events.
Timelines can use any suitable scale represent ...
UCMP Tree of Life
{{Taxonbar, from=Q271841 Santonian first appearances Maastrichtian extinctions Taxa named by Edward Drinker Cope Fossil taxa described in 1869 Prehistoric dinosaur families