|
Lambeosaurini
Lambeosaurini, previously known as Corythosaurini, is one of four tribes of hadrosaurid ornithopods from the family Lambeosaurinae. It is defined as all lambeosaurines closer to ''Lambeosaurus lambei'' than to ''Parasaurolophus walkeri, Tsintaosaurus spinorhinus, or Aralosaurus tuberiferus'', which define the other three tribes. Members of this tribe possess a distinctive protruding cranial crest. Lambeosaurins walked the earth for a period of around 12 million years in the Late Cretaceous, though they were confined to regions of modern-day North America and Asia. History of classification The term Corythosaurini was first used by Brett-Surman in 1989, who characterized the taxon via reference to the premaxilary expansion into a hollow helmet-like cranial crest, as well as higher neural spines. The clade was formally defined via phylogenetic analysis by Evans and Reisz in 2007, and this was confirmed by multiple other analyses. In 2011, Sullivan ''et al.'' observed that by the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambeosaurinae
Lambeosaurinae is a group of crested hadrosaurid dinosaurs. Classification Lambeosaurines have been traditionally split into the tribes or clades Parasaurolophini (''Parasaurolophus'', ''Charonosaurus'', others (?).) and Lambeosaurini (''Corythosaurus'', ''Hypacrosaurus'', ''Lambeosaurus'', others.). Corythosaurini (synonym of Lambeosaurini, see below) and Parasaurolophini as terms entered the formal literature in Evans and Reisz's 2007 redescription of ''Lambeosaurus magnicristatus''. Corythosaurini was defined as all taxa more closely related to ''Corythosaurus casuarius'' than to ''Parasaurolophus walkeri'', and Parasaurolophini as all those taxa closer to ''P. walkeri'' than to ''C. casuarius''. In this study, ''Charonosaurus'' and ''Parasaurolophus'' are parasaurolophins, and ''Corythosaurus'', ''Hypacrosaurus'', ''Lambeosaurus'', ''Nipponosaurus'', and ''Olorotitan'' are corythosaurins. However, later researchers pointed out that due to the rules of priority set forth b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amurosaurus
''Amurosaurus'' (; "Amur lizard") is a genus of lambeosaurine hadrosaurid dinosaur found in the latest Cretaceous period (66 million years ago)Godefroit, P., Lauters, P., Van Itterbeeck, J., Bolotsky, Y. and Bolotsky, I.Y. (2011). "Recent advances on study of hadrosaurid dinosaurs in Heilongjiang (Amur) River area between China and Russia." ''Global Geology'', 2011(3). of eastern Asia. Fossil bones of adults are rare, but an adult would most likely have been at least long. According to Gregory S. Paul, it was about long and weighed about . Discovery and naming Russian paleontologists Yuri Bolotsky and Sergei Kurzanov first described and named this dinosaur in 1991. The generic name is derived from the Amur River and the Greek word ''sauros'' ("lizard"). The Amur (called Heilongjiang or "Black Dragon River" in Chinese) forms the border of Russia and China, and is near where this dinosaur's remains were found. There is one known species (''A. riabinini''), named in honor of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrosauridae
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which includes genera such as ''Edmontosaurus'' and ''Parasaurolophus'', was a common group of herbivores during the Late Cretaceous Period. Hadrosaurids are descendants of the Upper Jurassic/Lower Cretaceous iguanodontian dinosaurs and had a similar body layout. Hadrosaurs were among the most dominant herbivores during the Late Cretaceous in Asia and North America, and during the close of the Cretaceous several lineages dispersed into Europe, Africa, South America and Antarctica. Like other ornithischians, hadrosaurids had a predentary bone and a pubic bone which was positioned backwards in the pelvis. Unlike more primitive iguanodonts, the teeth of hadrosaurids are stacked into complex structures known as dental batteries, which acted as effective g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canardia
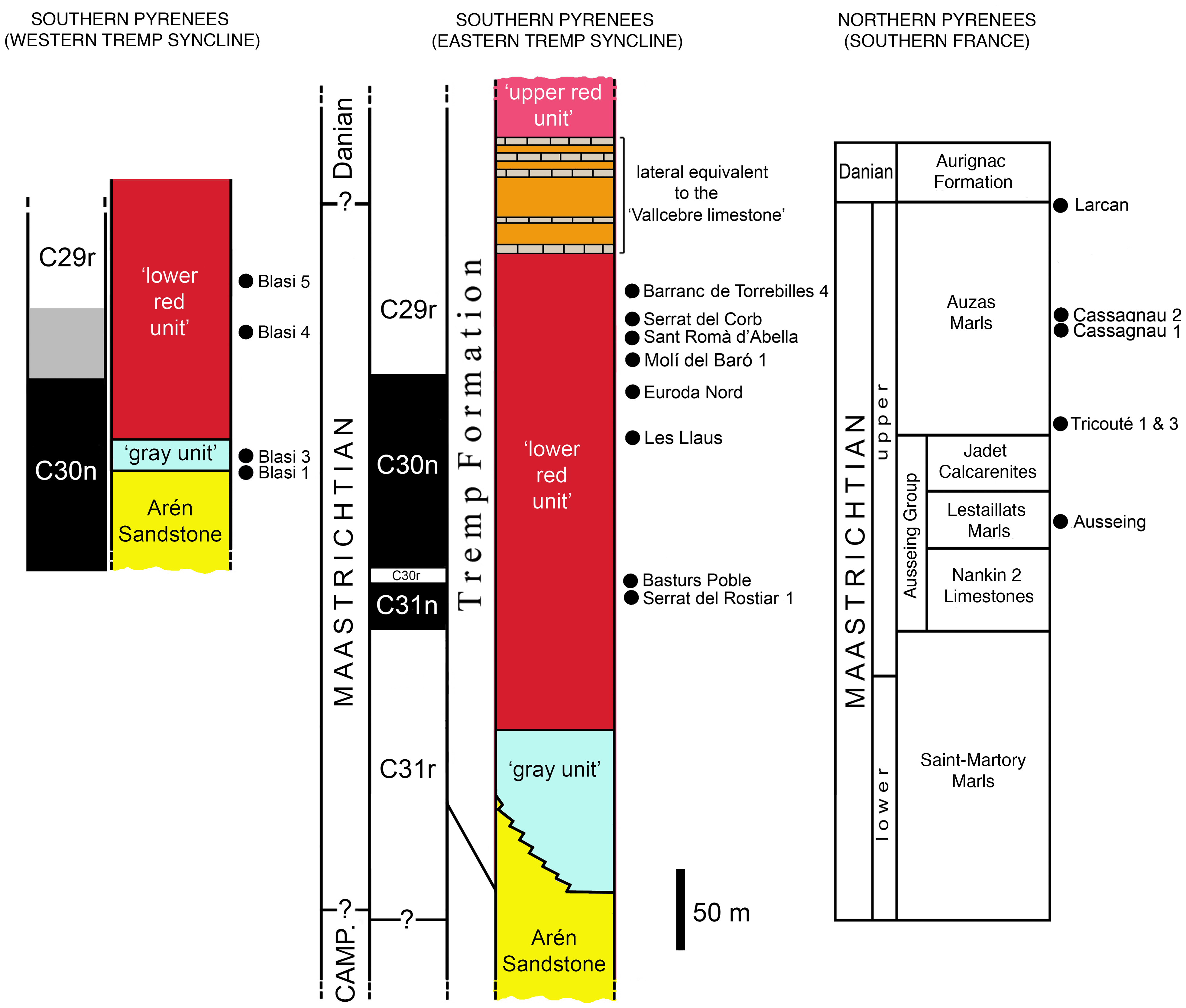
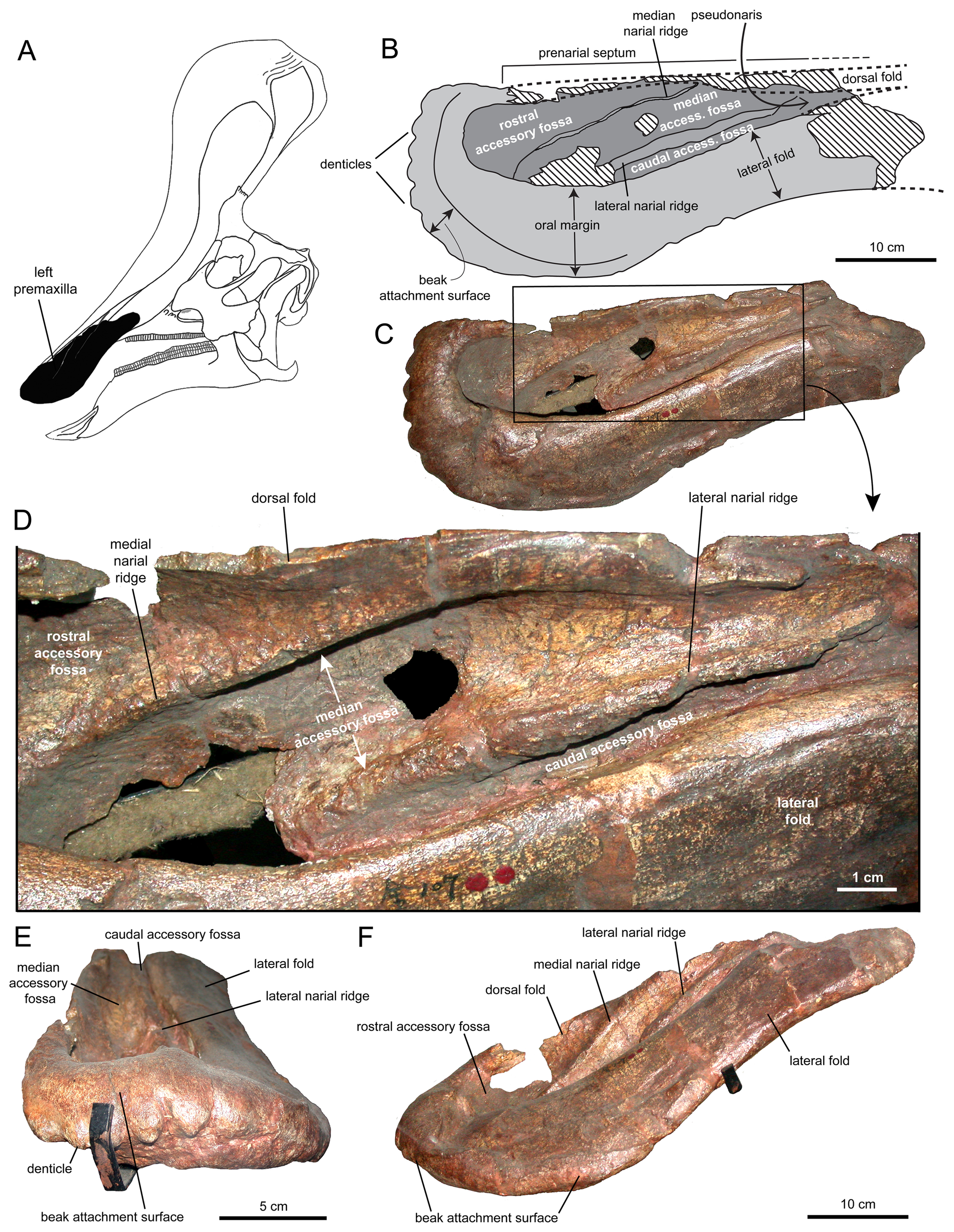
''Canardia'' is an extinct genus of lambeosaurine dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous Marnes d'Auzas Formation (late Maastrichtian stage) of Haute-Garonne department, in Occitanie region, southwestern France. The type species ''Canardia garonnensis'' was first described and named by Albert Prieto-Márquez, Fabio M. Dalla Vecchia, Rodrigo Gaete and Àngel Galobart in 2013. It is only known from juvenile specimens. The name of the genus comes from “canard”, the French word for “duck”, an allusion to the fact that this animal belongs to the hadrosaurids which are also known as duck-billed dinosaurs. The specific epithet ''garonnensis'' refers to the Haute-Garonne department where this dinosaur has been found. Although universally recognized as a lambeosaurine, its precise position within them is debated. Some authors consider it as a close relative of the genus ''Aralosaurus'' from Central Asia with which it would form the tribe Aralosaurini, while others include it in a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambeosaurus
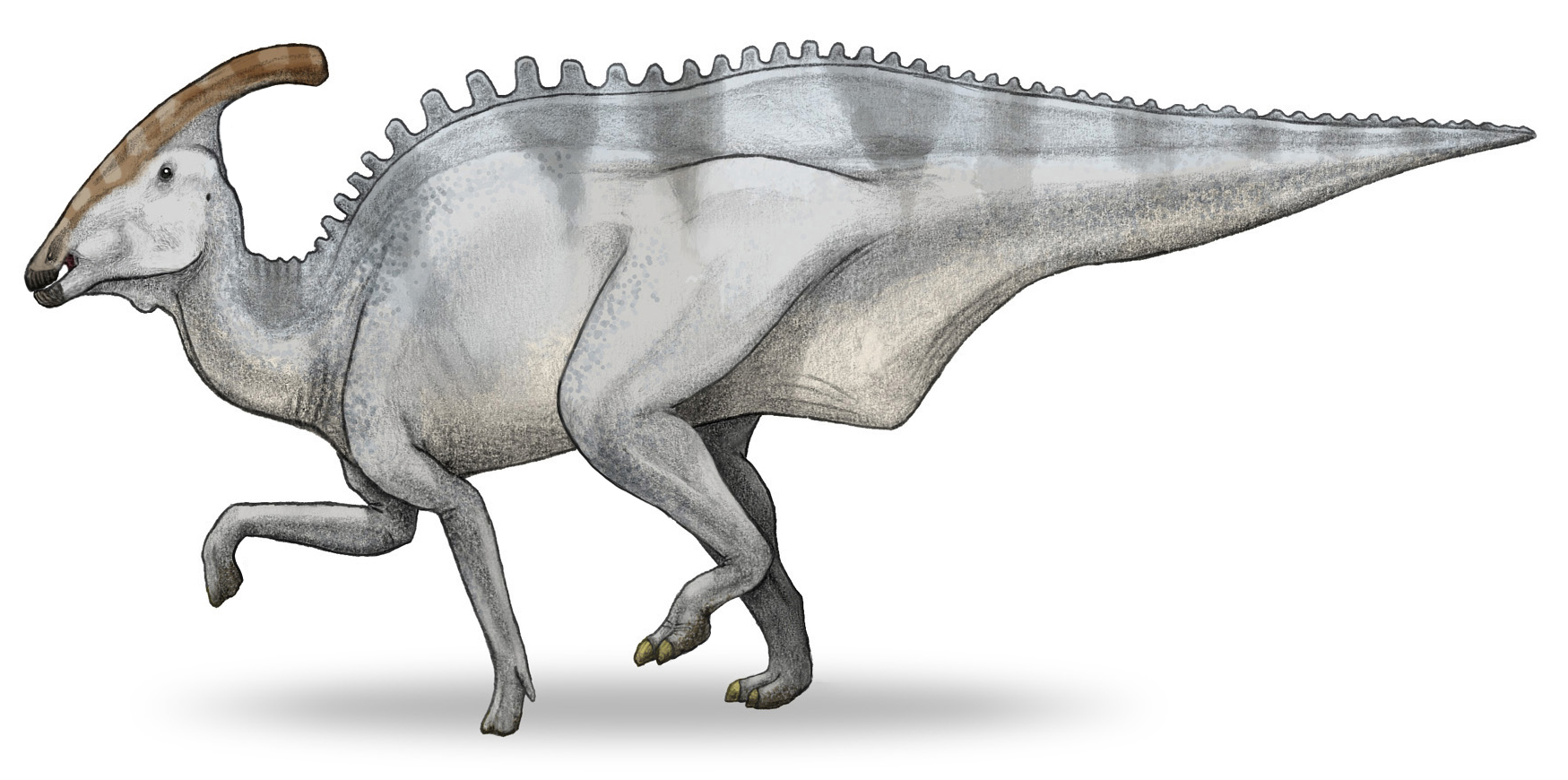
''Lambeosaurus'' ( , meaning " Lambe's lizard") is a genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur that lived about 75 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous period (Campanian stage) of North America. This bipedal/quadrupedal, herbivorous dinosaur is known for its distinctive hollow cranial crest, which in the best-known species resembled a mitten. Several possible species have been named, from Canada, the United States, and Mexico, but only the two Canadian species are currently recognized as valid. Material relevant to the genus was first named by Lawrence Lambe in 1902. Over twenty years later, the modern name was coined in 1923 by William Parks, in honour of Lambe, based on better preserved specimens. The genus has a complicated taxonomic history, in part because small-bodied crested hadrosaurids now recognized as juveniles were once thought to belong to their own genera and species. Currently, the various skulls assigned to the type species ''L. lambei'' are interpreted as showi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corythosaurus
''Corythosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of hadrosaurid "duck-billed" dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Period (geology), Period, about 77–75.7 million years ago. It lived in what is now North America. Its name means "helmet lizard", derived from Ancient Greek, Greek κόρυς. It was named and described in 1914 by Barnum Brown. ''Corythosaurus'' is now thought to be a Lambeosaurinae, lambeosaurine, related to ''Nipponosaurus'', ''Velafrons'', ''Hypacrosaurus'', and ''Olorotitan''. ''Corythosaurus'' has an estimated length of , and has a skull, including the crest, that is tall. ''Corythosaurus'' is known from many complete specimens, including the nearly complete holotype found by Brown in 1911. The holotype skeleton is only missing the last section of the tail, and part of the forelimbs, but was preserved with impressions of polygonal scales. ''Corythosaurus'' is known from many skulls with tall crests. The crests resemble the crests of the cassowary and a Corinthian helmet. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypacrosaurus
''Hypacrosaurus'' (meaning "near the highest lizard" reek υπο-, ''hypo-'' = less + ακρος, ''akros'', high because it was almost but not quite as large as ''Tyrannosaurus'') was a genus of duckbill dinosaur similar in appearance to ''Corythosaurus''. Like ''Corythosaurus'', it had a tall, hollow rounded crest, although not as large and straight. It is known from the remains of two species that spanned 75 to 67 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous of Alberta, Canada, and Montana, United States, and is the latest hollow-crested duckbill known from good remains in North America. It was an obscure genus until the discovery in the 1990s of nests, eggs, and hatchlings belonging to ''H. stebingeri''. Discovery and history The type remains of ''Hypacrosaurus'' were collected in 1910 by Barnum Brown for the American Museum of Natural History. The remains, a partial postcranial skeleton consisting of several vertebrae and a partial pelvis (AMNH 5204), came from along the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pararhabdodon
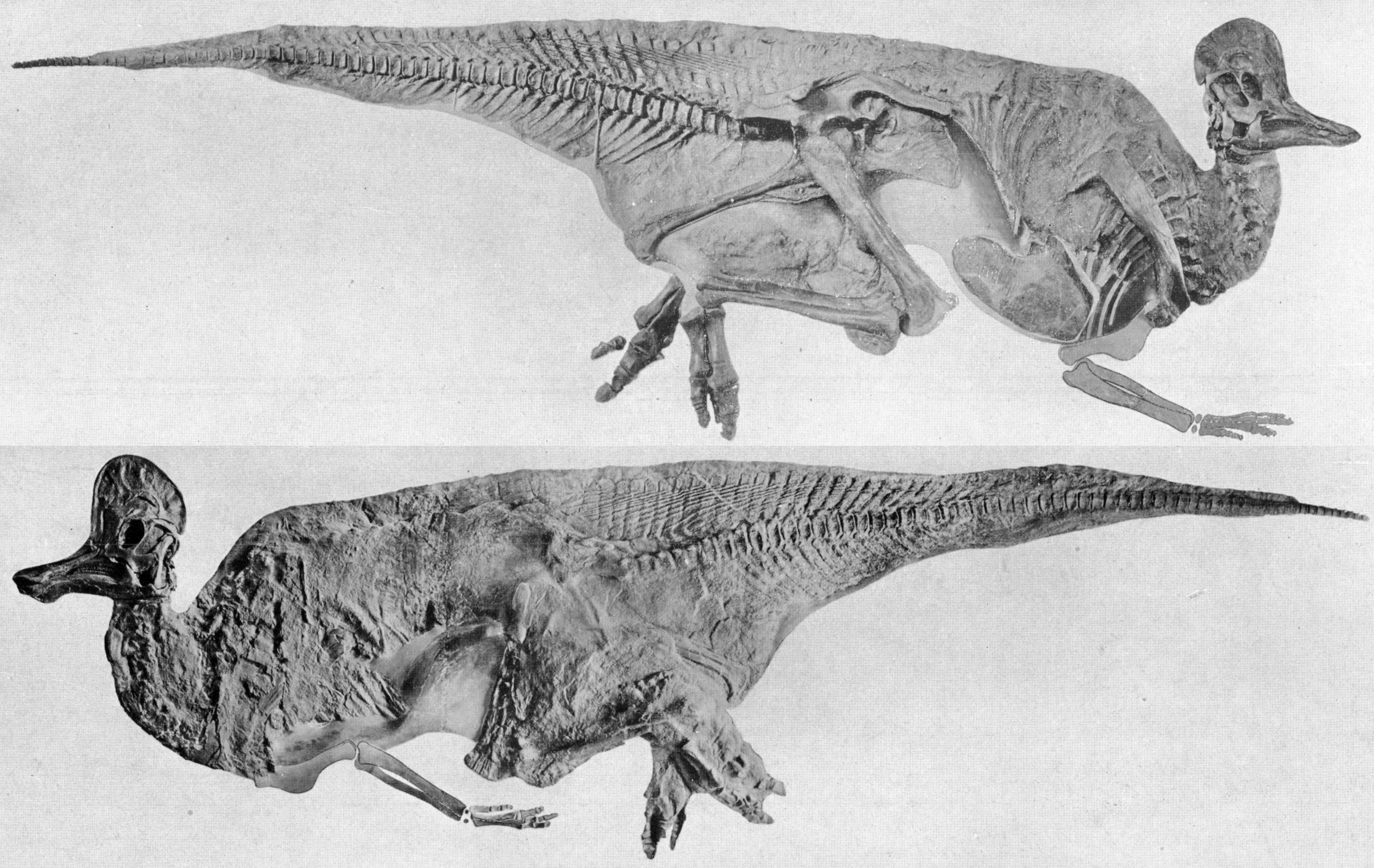
''Pararhabdodon'' (meaning "near fluted tooth" in reference to ''Rhabdodon'') is a genus of tsintaosaurin hadrosaurid dinosaur, from the Maastrichtian-age Upper Cretaceous Tremp Group of Spain. The first remains were discovered from the Sant Romà d’Abella fossil locality and assigned to the genus ''Rhabdodon'', and later named as the distinct species ''Pararhabdodon isonensis'' in 1993. Known material includes assorted postcranial remains, mostly vertebrae, as well as from the skull. Specimens from other sites, including remains from France, a maxilla previously considered the distinct taxon ''Koutalisaurus kohlerorum'', an additional maxilla from another locality, the material assigned to the genera ''Blasisaurus'' and ''Arenysaurus'', and the extensive Basturs Poble bonebed have been considered at different times to belong to the species, but all of these assignments have more recently been questioned. It was one of the last non-avian dinosaurs known from the fossil record th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aralosaurus
''Aralosaurus'' was a genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what is now Kazakhstan. It is known only by a posterior half of a skull (devoid of its mandible) and some post-cranial bones found in the Bostobe Formation in rocks dated from the Upper Santonian-Lower Campanian boundary, at about 83.6 Ma (millions of years). Only one species is known, ''Aralosaurus tuberiferus'', described by Anatoly Konstantinovich Rozhdestvensky in 1968. The genus name means Aral Sea lizard, because it was found to the northeast of the Aral Sea. The specific epithet ''tuberiferus'' means bearing a tuber because the posterior part of the nasal bone rises sharply in front of the orbits like an outgrowth. ''Aralosaurus'' was originally reconstituted with a nasal arch similar to that of North American ''Kritosaurus'' (a comparison based on a specimen now placed in the genus ''Gryposaurus''). For many years, ''Aralosaurus'' was thus placed in the clade of the Hadrosaurinae. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aralosaurini
Aralosaurini is a proposed tribe of hadrosaurid dinosaurs belonging to the subfamily Lambeosaurinae. The members of this group lived in Asia and Europe during the end of the Late Cretaceous about 83.6 to 66.0 million years ago. The clade may not be monophyletic, with ''Canardia'' and ''Aralosaurus'' potentially instead being unrelated primitive members of the subfamily. Description The Aralosaurini are distinguished by their maxilla whose anterior part is elevated dorsally. More precisely, the rostrodorsal region of the bone widens to form a prominent subrectangular flange, which rises vertically above the rostroventral process. ''Aralosaurus'' was previously reconstituted with a nasal boss similar to that of ''Gryposaurus'' and classified as a member of Hadrosaurinae. A new study of the incomplete skull of the animal showed that the fragmentary nasal was in fact a portion of a hollow structure that communicated with the respiratory system. Which is a typical lambeosaurine featur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsintaosaurus
''Tsintaosaurus'' (; meaning "Qingdao lizard", after the old transliteration "Tsingtao") is a genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur from China. It was about long and weighed . The type species is ''Tsintaosaurus spinorhinus'', first described by Chinese paleontologist C. C. Young in 1958. A hadrosaur, ''Tsintaosaurus'' had a characteristic 'duck bill' snout and a battery of powerful teeth which it used to chew vegetation. It usually walked on all fours, but could rear up on its hind legs to scout for predators and flee when it spotted one. Like other hadrosaurs, ''Tsintaosaurus'' probably lived in herds. Discovery and naming In 1950, at Hsikou, near Chingkangkou, in Laiyang, Shandong, in the eastern part of China, various remains of large hadrosaurids were uncovered. In 1958 these were described by Chinese paleontologist Yang Zhongjian ("C.C. Young") as the type species ''Tsintaosaurus spinorhinus''. The generic name is derived from the city of Qingdao, earlier often transliterat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charonosaurus
''Charonosaurus'' ( ; meaning " Charon's lizard") is a genus of dinosaur whose fossils were discovered by Godefroit, Zan & Jin in 2000 on the south bank of the Amur River, dividing China from Russia. It is monotypic, consisting of the species ''C. jiayinensis''. Description ''Charonosaurus'' is a very large lambeosaurine hadrosaur, estimated around in length and in body mass.Holtz, Thomas R. Jr. (2012) ''Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-Date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages,'Winter 2011 Appendix./ref> It is known from a partial skull (Holotype: CUST J-V1251-57 (Changchun University of Sciences and Technology, Changchun, Jilin Province, China) found in the Late Maastrichtian Yuliangze Formation, west of Jiayin village, Heilongjiang Province, northeastern China. Adult and juvenile hadrosaur remains discovered in the same area and formation likely represent the same taxon and supply information on most of the postcranial skeleton; the femur length was up to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |