HMS Tiger (1913) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
HMS ''Tiger'' was a
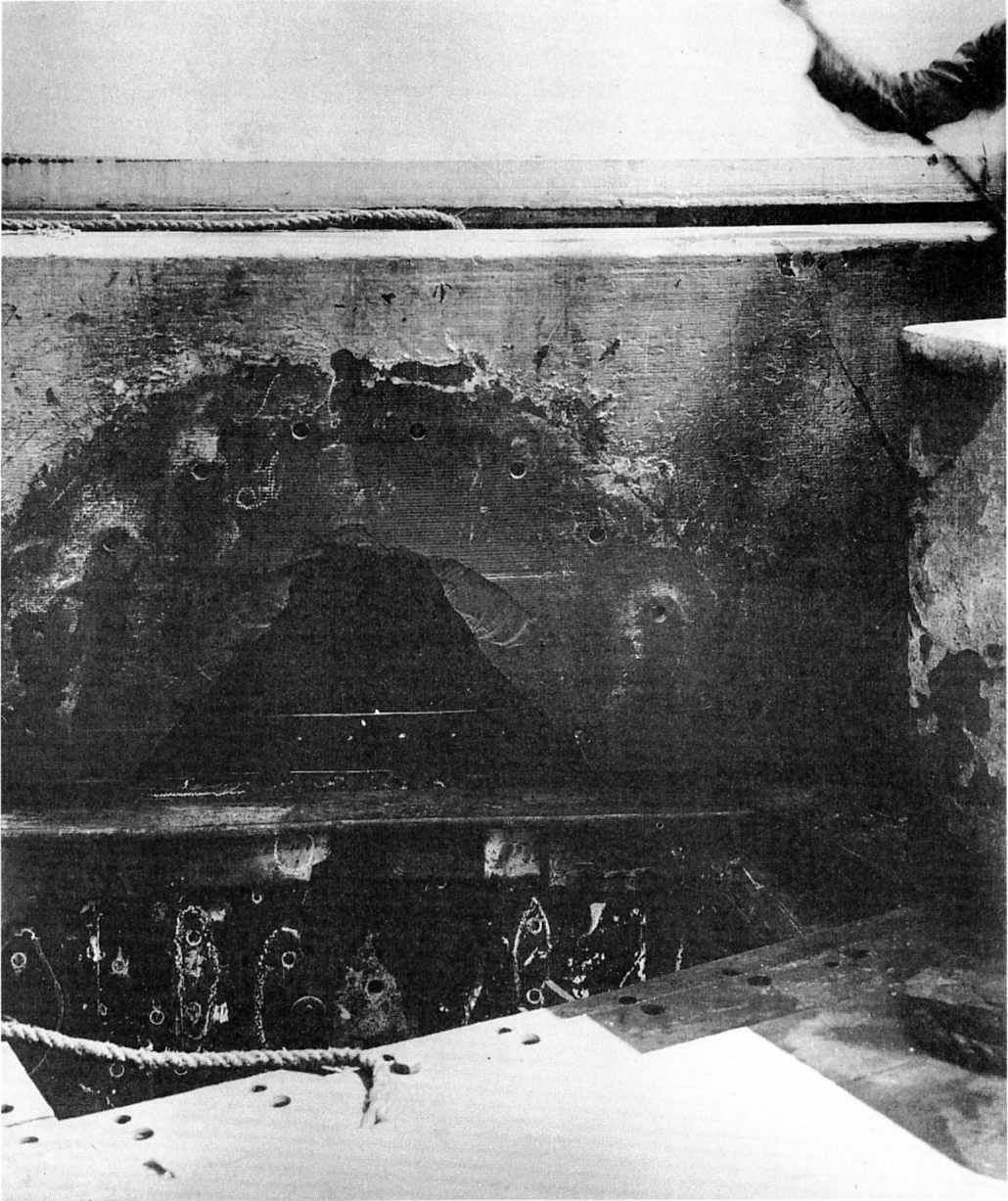 ''Tiger''s armour protection was similar to that of ''Queen Mary''; her waterline
''Tiger''s armour protection was similar to that of ''Queen Mary''; her waterline
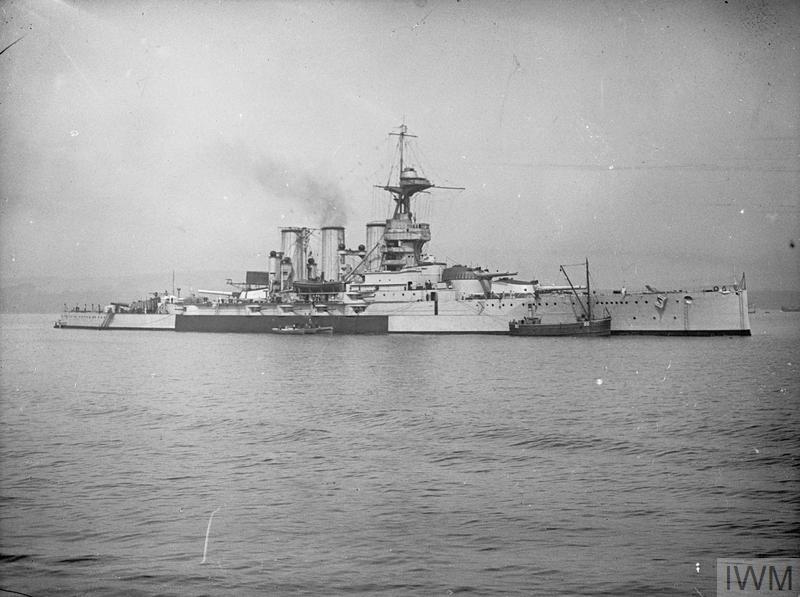 ''Tiger'' was laid down at the John Brown and Company shipyard in
''Tiger'' was laid down at the John Brown and Company shipyard in
 In the meantime, ''Blücher'' had been heavily damaged by fire from all the other battlecruisers; her speed had dropped to and her steering gear had been jammed. Beatty ordered ''Indomitable'' to attack her at 10:48. Six minutes later, Beatty spotted what he thought was a submarine
In the meantime, ''Blücher'' had been heavily damaged by fire from all the other battlecruisers; her speed had dropped to and her steering gear had been jammed. Beatty ordered ''Indomitable'' to attack her at 10:48. Six minutes later, Beatty spotted what he thought was a submarine
 On 31 May 1916, ''Tiger'' and the 1st BCS had put to sea with the rest of the Battlecruiser Fleet, under Beatty's overall command, to intercept a sortie by the High Seas Fleet into the North Sea. The British had decoded the German radio messages, and left their bases before the Germans put to sea. Hipper's battlecruisers spotted the Battlecruiser Fleet to their west at 15:20, but Beatty's ships did not see the Germans to their east until 15:30. Two minutes later, Beatty ordered a course change to east-southeast, positioning the British ships to cut off the German's line of retreat, and signalled action stations. Hipper ordered his ships to turn to starboard, away from the British, to assume a south-easterly course, and reduced speed to to allow three light cruisers of the 2nd Scouting Group to catch up. With this turn, Hipper was falling back on the High Seas Fleet, behind him. Beatty altered course to the east, as he was still too far north to cut Hipper off.
On 31 May 1916, ''Tiger'' and the 1st BCS had put to sea with the rest of the Battlecruiser Fleet, under Beatty's overall command, to intercept a sortie by the High Seas Fleet into the North Sea. The British had decoded the German radio messages, and left their bases before the Germans put to sea. Hipper's battlecruisers spotted the Battlecruiser Fleet to their west at 15:20, but Beatty's ships did not see the Germans to their east until 15:30. Two minutes later, Beatty ordered a course change to east-southeast, positioning the British ships to cut off the German's line of retreat, and signalled action stations. Hipper ordered his ships to turn to starboard, away from the British, to assume a south-easterly course, and reduced speed to to allow three light cruisers of the 2nd Scouting Group to catch up. With this turn, Hipper was falling back on the High Seas Fleet, behind him. Beatty altered course to the east, as he was still too far north to cut Hipper off.
 This was later characterised as the "Run to the South" as Beatty changed course to steer east-southeast at 15:45, now paralleling Hipper's course less than away. The Germans opened fire first at 15:48, followed by the British. The British ships were still in the process of making their turn as only the two leading ships, ''Lion'' and ''Princess Royal'', had steadied on their course when the Germans opened fire. The 1st BCS was echeloned to the right with ''Tiger'' in the rear and the furthest to the west, closest to the Germans. ''Tiger'' missed Beatty's fire distribution order, as had ''Queen Mary'', and ''Tiger'' engaged ''Moltke'', instead of ''Seydlitz'' as Beatty intended. The German fire was accurate from the start, with ''Tiger'' hit six times by ''Moltke'' within the first seven minutes; although two of these hits temporarily disabled both 'Q' and 'X' turrets, she was not seriously damaged.Campbell, p. 42 By 15:54, the range was down to ; Beatty ordered a course change two
This was later characterised as the "Run to the South" as Beatty changed course to steer east-southeast at 15:45, now paralleling Hipper's course less than away. The Germans opened fire first at 15:48, followed by the British. The British ships were still in the process of making their turn as only the two leading ships, ''Lion'' and ''Princess Royal'', had steadied on their course when the Germans opened fire. The 1st BCS was echeloned to the right with ''Tiger'' in the rear and the furthest to the west, closest to the Germans. ''Tiger'' missed Beatty's fire distribution order, as had ''Queen Mary'', and ''Tiger'' engaged ''Moltke'', instead of ''Seydlitz'' as Beatty intended. The German fire was accurate from the start, with ''Tiger'' hit six times by ''Moltke'' within the first seven minutes; although two of these hits temporarily disabled both 'Q' and 'X' turrets, she was not seriously damaged.Campbell, p. 42 By 15:54, the range was down to ; Beatty ordered a course change two 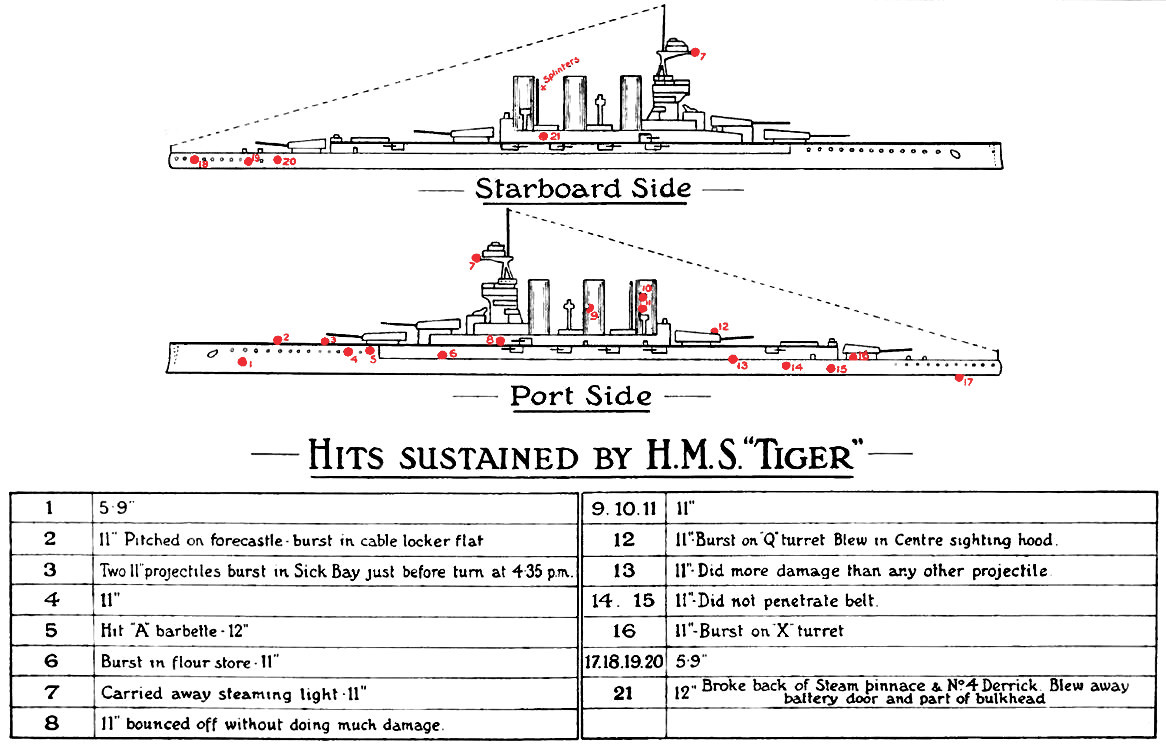 The British lost sight of the Germans until spotted smoke to the west-northwest at 20:05, then identified and engaged several German torpedo boats. On hearing the sound of gunfire, Beatty ordered his ships west, and spotted the German battlecruisers only away. ''Inflexible'' opened fire at 20:20, followed almost immediately by the rest of the battlecruisers. Shortly after 8:30, the pre-dreadnought battleships of Rear Admiral Franz Mauve's II Battle Squadron were spotted. The British battlecruisers and German pre-dreadnoughts exchanged fire; the Germans fired only a few times before turning away to the west because of poor visibility and the more accurate British gunnery, and disappeared into the mist around 20:40. Beatty's battlecruisers sailed south-southeast, ahead of both the Grand Fleet and the High Seas Fleet, until the order to reverse course for home was given at 02:55.
''Tiger'' and the rest of the battlecruisers reached Rosyth Dockyard in Scotland on the morning of 2 June. Docked the next day for repairs which took until 1 July, she was the first of the "Splendid Cats" to be repaired. ''Tiger'' was hit a total of 18 times during the battle, mostly by shells fired by ''Moltke'', suffering 24 men killed and 46 wounded. The battlecruiser fired 303 shells from her main guns during the battle and is credited with one hit on ''Moltke'' and two on ''Von der Tann''. The ship also fired 136 rounds from her 6-inch guns at the light cruiser and German
The British lost sight of the Germans until spotted smoke to the west-northwest at 20:05, then identified and engaged several German torpedo boats. On hearing the sound of gunfire, Beatty ordered his ships west, and spotted the German battlecruisers only away. ''Inflexible'' opened fire at 20:20, followed almost immediately by the rest of the battlecruisers. Shortly after 8:30, the pre-dreadnought battleships of Rear Admiral Franz Mauve's II Battle Squadron were spotted. The British battlecruisers and German pre-dreadnoughts exchanged fire; the Germans fired only a few times before turning away to the west because of poor visibility and the more accurate British gunnery, and disappeared into the mist around 20:40. Beatty's battlecruisers sailed south-southeast, ahead of both the Grand Fleet and the High Seas Fleet, until the order to reverse course for home was given at 02:55.
''Tiger'' and the rest of the battlecruisers reached Rosyth Dockyard in Scotland on the morning of 2 June. Docked the next day for repairs which took until 1 July, she was the first of the "Splendid Cats" to be repaired. ''Tiger'' was hit a total of 18 times during the battle, mostly by shells fired by ''Moltke'', suffering 24 men killed and 46 wounded. The battlecruiser fired 303 shells from her main guns during the battle and is credited with one hit on ''Moltke'' and two on ''Von der Tann''. The ship also fired 136 rounds from her 6-inch guns at the light cruiser and German
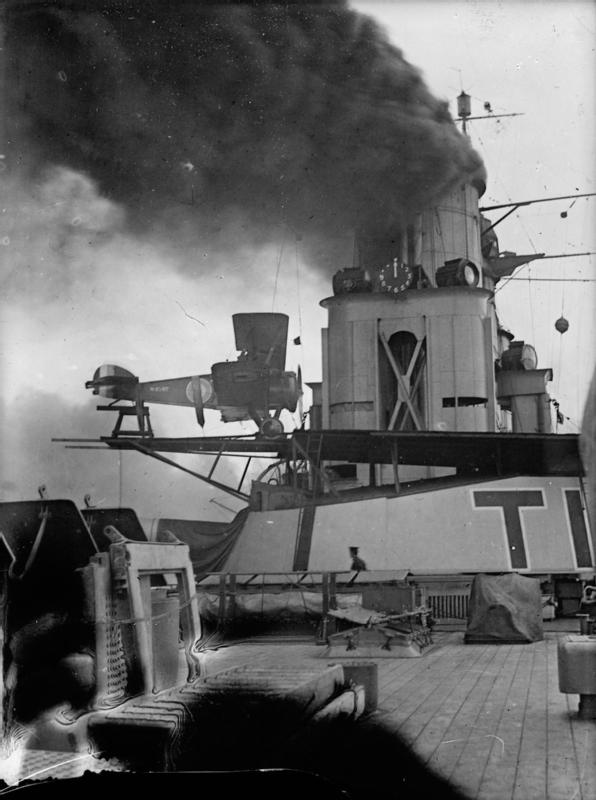 ''Tiger'' remained in service with the Royal Navy after the Armistice with Germany and she had a flying-off platform added on 'B' turret's roof in 1919. The ship collided with the battleship in late 1920 while assigned to the Atlantic Fleet. ''Tiger'' survived the culling of older capital ships following the Washington Naval Treaty, although she was placed in
''Tiger'' remained in service with the Royal Navy after the Armistice with Germany and she had a flying-off platform added on 'B' turret's roof in 1919. The ship collided with the battleship in late 1920 while assigned to the Atlantic Fleet. ''Tiger'' survived the culling of older capital ships following the Washington Naval Treaty, although she was placed in
Dreadnought Project
Technical material on the weaponry and fire control for the ships
Battle of Jutland Crew Lists Project – HMS Tiger Crew List
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tiger (1913) 1913 ships Battlecruisers of the Royal Navy World War I battlecruisers of the United Kingdom
battlecruiser
The battlecruiser (also written as battle cruiser or battle-cruiser) was a type of capital ship of the first half of the 20th century. These were similar in displacement, armament and cost to battleships, but differed in form and balance of attr ...
built for the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
during the 1910s. The ship was the most heavily armoured British battlecruiser at the start of the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
in 1914, but was not yet ready for service. The ship was assigned to the 1st Battlecruiser Squadron
The First Battlecruiser Squadron was a Royal Navy squadron of battlecruisers that saw service as part of the Grand Fleet during the First World War. It was created in 1909 as the First Cruiser Squadron and was renamed in 1913 to First Battle Cru ...
(1st BCS) for the duration of the war and participated in the Battle of Dogger Bank in early 1915, though she was still shaking down and did not perform well. ''Tiger'' next participated in the Battle of Jutland
The Battle of Jutland (german: Skagerrakschlacht, the Battle of the Skagerrak) was a naval battle fought between Britain's Royal Navy Grand Fleet, under Admiral John Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe, Sir John Jellicoe, and the Imperial German Navy ...
in 1916, where she was only lightly damaged despite suffering many hits by German shells. Apart from providing distant cover during the Second Battle of Heligoland Bight in 1917, she spent the rest of the war on uneventful patrols in the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
.
The ship was the oldest battlecruiser retained by the Royal Navy after the tonnage limits of the Washington Naval Treaty came into effect in 1922. She became a gunnery training ship in 1924 and then joined the Battlecruiser Squadron in 1929 when its flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the fi ...
, , underwent a lengthy refit. Upon ''Hood''s return to service in 1931, ''Tiger'' was decommissioned and sold for scrap
Scrap consists of Recycling, recyclable materials, usually metals, left over from product manufacturing and consumption, such as parts of vehicles, building supplies, and surplus materials. Unlike waste, scrap Waste valorization, has monetary ...
in 1932 in accordance with the terms of the London Naval Treaty
The London Naval Treaty, officially the Treaty for the Limitation and Reduction of Naval Armament, was an agreement between the United Kingdom, Japan, France, Italy, and the United States that was signed on 22 April 1930. Seeking to address is ...
of 1930.
In his book, ''The Price of Admiralty'', British military historian John Keegan described her as "certainly the most beautiful warship in the world then, and perhaps ever
Design and description
''Tiger'' was the sole battlecruiser authorised in the 1911–12 Naval Programme. According to naval historian Siegfried Breyer, a sister ship named ''Leopard'' was considered in the 1912–13 Programme and deferred until 1914 as a sixth member of the , but there is no record of any additional battlecruiser being provided for in any naval estimates before 1914. ''Tiger'' had anoverall length
The overall length (OAL) of an ammunition cartridge is a measurement from the base of the brass shell casing to the tip of the bullet, seated into the brass casing. Cartridge overall length, or "COL", is important to safe functioning of reloads in ...
of , a beam
Beam may refer to:
Streams of particles or energy
*Light beam, or beam of light, a directional projection of light energy
**Laser beam
*Particle beam, a stream of charged or neutral particles
**Charged particle beam, a spatially localized grou ...
of , and a mean draught of at deep load
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into wei ...
. She normally displaced and at deep load. Although ''Tiger'' was only longer and wider than the previous battlecruiser, , she displaced almost more than the older ship. She had a metacentric height of at deep load. In September 1914, her complement consisted of 1,112 officers and ratings; in April 1918, they totalled 1,459.
Propulsion
''Tiger'' had two paired sets of Brown-Curtis direct-drivesteam turbine
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turbin ...
s housed in separate engine-rooms. Each set consisted of high-pressure ahead and astern turbines driving an outboard shaft and low-pressure ahead and astern turbines, housed in the same casing, driving an inner shaft. Her three-bladed propeller
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon ...
s were in diameter. The turbines were powered by 39 Babcock & Wilcox water-tube boiler
A high pressure watertube boiler (also spelled water-tube and water tube) is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-gene ...
s in five boiler rooms at a working pressure of .Burt 1986, p. 212 The turbines were designed to produce a total of and a maximum of when forced, but only achieved during her sea trial
A sea trial is the testing phase of a watercraft (including boats, ships, and submarines). It is also referred to as a " shakedown cruise" by many naval personnel. It is usually the last phase of construction and takes place on open water, and ...
s, although she managed to exceed her maximum designed speed of by over a knot.
The ship's fuel stowage capacity was of fuel oil
Fuel oil is any of various fractions obtained from the distillation of petroleum (crude oil). Such oils include distillates (the lighter fractions) and residues (the heavier fractions). Fuel oils include heavy fuel oil, marine fuel oil (MFO), bun ...
and of coal, giving a total fuel supply of —much more than ''Queen Mary''s total of . The sole (unofficial) figure for ''Tiger''s daily fuel consumption of a day at would have given a maximum endurance of . The equivalent figure for ''Queen Mary'' was roughly . Four direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even ...
electric dynamos with a total capacity of supplied the common ring main
In electricity supply design, a ring circuit is an electrical wiring technique in which sockets and the distribution point are connected in a ring. It is contrasted with the usual radial circuit, in which sockets and the distribution point ar ...
at 220 volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
Defi ...
s.
Armament
''Tiger'' mounted eight 45-calibre
In guns, particularly firearms, caliber (or calibre; sometimes abbreviated as "cal") is the specified nominal internal diameter of the gun barrel bore – regardless of how or where the bore is measured and whether the finished bore match ...
BL 13.5-inch Mk V guns in four twin hydraulically powered turrets, designated 'A', 'B', 'Q' and 'X' from front to rear. The guns could be depressed to −5° and elevated to +20°, although the directors controlling the turrets were limited to 15° 21' until superelevating prisms were installed before the Battle of Jutland
The Battle of Jutland (german: Skagerrakschlacht, the Battle of the Skagerrak) was a naval battle fought between Britain's Royal Navy Grand Fleet, under Admiral John Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe, Sir John Jellicoe, and the Imperial German Navy ...
in May 1916 to allow full elevation.Campbell, p. 35 They fired projectiles at a muzzle velocity
Muzzle velocity is the speed of a projectile (bullet, pellet, slug, ball/shots or shell) with respect to the muzzle at the moment it leaves the end of a gun's barrel (i.e. the muzzle). Firearm muzzle velocities range from approximately to i ...
of ; at 20° elevation, this provided a maximum range of . The rate of fire of these guns was approximately 2 rounds per minute. The ship carried a total of 1040 rounds during wartime for 130 shells per gun.
Her secondary armament consisted of twelve BL 6-inch Mk VII guns in casemate
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which artillery, guns are fired, in a fortification, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.Webster's New Collegiate Dictionary
When referring to Ancient history, antiquity, th ...
s. The guns could depress to −7° and had a maximum elevation of 14°. They fired projectiles at a muzzle velocity of approximately ; this gave a maximum range of at +14° elevation. They were provided with 120 rounds per gun. The ship mounted a pair of QF 3 inch 20 cwt"Cwt" is the abbreviation for hundredweight
The hundredweight (abbreviation: cwt), formerly also known as the centum weight or quintal, is a British imperial and US customary unit of weight or mass. Its value differs between the US and British imperial systems. The two values are distingu ...
, 30 cwt referring to the weight of the gun. Mk I anti-aircraft
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based, ...
guns on high-angle Mark II mounts. The gun had a maximum elevation of +90° and fired a shell at a muzzle velocity of . It had a maximum effective ceiling of . Originally, ''Tiger'' carried 300 rounds per gun, but this was reduced during the war to 150 rounds per gun.Campbell, p. 36
Four submerged torpedo tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes.
There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboa ...
s were fitted on the beam, one pair port and starboard forward of 'A' barbette and aft of 'X' barbette. The ship carried 20 Mark II*** torpedoes,The British used asterisks to denote small changes between models. each with a warhead of of TNT. They had two speed settings which governed their range; at , they could reach , or at .
Fire control
The main guns of ''Tiger'' were controlled from either of the two fire-control directors. The primary director was in the fore-top on the foremast and the other was mounted on the aft superstructure in the torpedo control tower. Data from rangefinders in the armoured hood above theconning tower
A conning tower is a raised platform on a ship or submarine, often armored, from which an officer in charge can conn the vessel, controlling movements of the ship by giving orders to those responsible for the ship's engine, rudder, lines, and gro ...
and in 'B' and 'Q' turrets was transmitted to the Mk IV Dreyer Fire Control Table located in the transmitting station below the waterline
The waterline is the line where the hull of a ship meets the surface of the water. Specifically, it is also the name of a special marking, also known as an international load line, Plimsoll line and water line (positioned amidships), that indi ...
. The observations were then plotted and converted into range and deflection data for use by the director and guns. A Mark VII* Dumaresq in the armoured tower was trained on the target to supply bearing data to one transmitting station for use in plotting and calculations, and a second station was fitted for the ship's secondary armament, although a pair of fire-control directors for those guns, one for each broadside, were not fitted until 1915.Burt 1986, p. 219
Fire-control technology advanced quickly during the years immediately preceding the First World War and the development of the director firing system was a major advance. This consisted of a fire-control director mounted high in the ship which electrically provided elevation and training angles to the turrets via pointers, which the turret crewmen had only to follow. The director layer fired the guns simultaneously by an electrical trigger which aided in spotting the shell splashes and minimised the effects of the roll on the dispersion of the shells.
During the war, ''Tiger''s rangefinders had increased in number and in size. By the end of the war, 'A' and 'Q' turrets mounted rangefinders while 'X' turret, the armoured hood above the conning tower (also known as the gun control tower), and the torpedo control tower had instruments. A rangefinder was fitted in the fore-top and three instruments were fitted on 'B' turret, the gun control tower and above the compass platform. A high-angle rangefinder was mounted above the roof of the fore-top for use by the anti-aircraft guns.Burt 1986, p. 213
Armour
 ''Tiger''s armour protection was similar to that of ''Queen Mary''; her waterline
''Tiger''s armour protection was similar to that of ''Queen Mary''; her waterline belt
Belt may refer to:
Apparel
* Belt (clothing), a leather or fabric band worn around the waist
* Championship belt, a type of trophy used primarily in combat sports
* Colored belts, such as a black belt or red belt, worn by martial arts practition ...
of Krupp cemented armour
Krupp armour was a type of steel naval armour used in the construction of capital ships starting shortly before the end of the nineteenth century. It was developed by Germany's Krupp Arms Works in 1893 and quickly replaced Harvey armour as the pr ...
measured thick amidships. It thinned to four inches towards the ship's ends, but did not reach either the bow or the stern. The depth of the main belt below the waterline was reduced from , although a strake of three-inch armour tall was added below the main belt that stretched from the front of 'A' barbette to the rear of 'B' barbette. It was based on that used on the Vickers
Vickers was a British engineering company that existed from 1828 until 1999. It was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law, and soon became famous for casting church bells. The company went public in 18 ...
built Japanese battlecruiser , the only design influence on ''Tiger'' that can be attributed to that ship.Roberts 1978, p. 4
Like the ships and ''Queen Mary'', ''Tiger'' was given an upper armour belt with a maximum thickness of six inches over the same length as the thickest part of the waterline armour and thinned to abreast the end turrets. Unlike those ships, ''Tiger'' had an additional strake of 6-inch armour above the upper belt protecting her secondary armament. Four-inch transverse bulkheads closed off the ends of the armoured citadel
In a warship an armored citadel is an armored box enclosing the machinery and magazine spaces formed by the armored deck, the waterline belt, and the transverse bulkheads. In many post-World War I warships, armor was concentrated in a very s ...
. High-tensile steel was used for the protective decks. They generally ranged from in thickness.Roberts 1997, pp. 112–113
The gun turrets had 9-inch front and sides while their roofs were thick. The barbette
Barbettes are several types of gun emplacement in terrestrial fortifications or on naval ships.
In recent naval usage, a barbette is a protective circular armour support for a heavy gun turret. This evolved from earlier forms of gun protection ...
s were protected above the citadel by of armour, thinning to three to four inches inside the citadel. The main conning tower had a three-inch roof and sides thick. The walls of the communication tube
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inqui ...
were three to four inches thick. The aft conning tower had 6-inch walls and a 3-inch cast steel roof. High-tensile steel torpedo bulkheads thick were fitted abreast the magazines and shell rooms. After the Battle of Jutland revealed the ship's vulnerability to plunging shellfire, around of additional armour was added to the turret roofs, the decks over the magazines, and the bulkheads separating the 6-inch guns.
Service history
First World War
 ''Tiger'' was laid down at the John Brown and Company shipyard in
''Tiger'' was laid down at the John Brown and Company shipyard in Clydebank
Clydebank ( gd, Bruach Chluaidh) is a town in West Dunbartonshire, Scotland. Situated on the north bank of the River Clyde, it borders the village of Old Kilpatrick (with Bowling, West Dunbartonshire, Bowling and Milton, West Dunbartonshire, Mil ...
on 6 June 1912. She was launched on 15 December 1913 and commissioned into the Royal Navy on 3 October 1914, at the cost of £2,593,100, including armament.Roberts 1997, p. 83 The ship was still under construction when the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
broke out in August 1914. On 3 August 1914,Roberts 1997, p. 123 Captain Henry Pelly
Sir Henry Carstairs Pelly, 3rd Baronet (24 April 1844 - 4 June 1877) was a Conservative Party politician.
Parliamentary career
Pelly was elected Conservative MP for Huntingdonshire in 1874, but died before completing a full parliamentary term i ...
was appointed to command the incomplete ship. Beatty described Pelly at the time as "a very charming person and, what is more important just now, a very efficient officer".
''Tiger'' was commissioned for the 1st Battlecruiser Squadron (1st BCS) on 3 October. After the Battle of Coronel and the deployment of three battlecruisers to hunt for the German East Asia Squadron
The German East Asia Squadron (german: Kreuzergeschwader / Ostasiengeschwader) was an Imperial German Navy cruiser squadron which operated mainly in the Pacific Ocean between the mid-1890s until 1914, when it was destroyed at the Battle of the Fa ...
, ''Tiger'' was ordered to cut short her firing trials off Berehaven. Beatty described ''Tiger'' to the First Sea Lord, Admiral of the Fleet Lord Fisher of Kilverstone, as "not yet fit to fight. Three out of her four dynamoes are out of action for an indefinite period, and her training is impeded by bad weather, which might continue for many weeks at this time of year, and at present is quite unprepared and inefficient."
Battle of Dogger Bank
On 23 January 1915, a force of German battlecruisers under the command of AdmiralFranz von Hipper
Franz Ritter von Hipper (13 September 1863 – 25 May 1932) was an admiral in the German Imperial Navy (''Kaiserliche Marine''). Franz von Hipper joined the German Navy in 1881 as an officer cadet. He commanded several torpedo boat units an ...
sortied to clear the Dogger Bank of any British fishing boats or small craft that might be there to collect intelligence on German movements. However, the British were reading their coded messages and sailed to intercept them with a larger force of British battlecruisers under the command of Admiral Beatty. Contact was initiated at 07:20The times used in this article are in UTC, which is one hour behind CET
CET or cet may refer to:
Places
* Cet, Albania
* Cet, standard astronomical abbreviation for the constellation Cetus
* Colchester Town railway station (National Rail code CET), in Colchester, England
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Comcast Ente ...
, which is often used in German works. on the 24th, when the British light cruiser spotted the German light cruiser . By 07:35, the Germans had spotted Beatty's force and Hipper ordered a turn to the south at , believing this would suffice if the ships he saw to his north-west were British battleships and that he could always increase speed to 's maximum speed of if they were British battlecruisers.
Beatty ordered his battlecruisers to make all practicable speed to catch the Germans before they could escape. The leading ships, , and ''Tiger'', were doing in pursuit and ''Lion'' opened fire at 08:52 at a range of . The other ships followed a few minutes later but, hampered by the extreme range and decreasing visibility, they did not score their first hit on ''Blücher'' until 09:09. The German battlecruisers opened fire themselves a few minutes later at 09:11, at a range of , and concentrated their fire on ''Lion''. At 09:35, Beatty signalled "Engage the corresponding ships in the enemy's line", but Captain Pelly, believing that was already engaging ''Blücher'', fired at , as did ''Lion'', which left free to continue attacking ''Lion'' without risk.
 In the meantime, ''Blücher'' had been heavily damaged by fire from all the other battlecruisers; her speed had dropped to and her steering gear had been jammed. Beatty ordered ''Indomitable'' to attack her at 10:48. Six minutes later, Beatty spotted what he thought was a submarine
In the meantime, ''Blücher'' had been heavily damaged by fire from all the other battlecruisers; her speed had dropped to and her steering gear had been jammed. Beatty ordered ''Indomitable'' to attack her at 10:48. Six minutes later, Beatty spotted what he thought was a submarine periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.
In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with ...
on the starboard bow and ordered an immediate 90° turn to port to avoid the submarine, although he failed to hoist the "Submarine Warning" flag because most of ''Lion''s signal halyards had been shot away. Shortly afterward, ''Lion'' lost her remaining dynamo to the rising water which knocked out all remaining light and power. He ordered "Course north-east" at 11:02 to bring his ships back to their pursuit of Hipper. He also hoisted "Attack the rear of the enemy" on the other halyard, although there was no connection between the two signals. Rear-Admiral Sir Gordon Moore, temporarily commanding in , thought that the signals meant for him to attack ''Blücher'', which was about to the north-east, which he did, turning away from Hipper's main body. Beatty tried to correct the mistake, but he was so far behind the leading battlecruisers that his signals could not be read amidst the smoke and haze.
He transferred his flag to the destroyer at 11:50 and set off in pursuit of his battlecruisers. He caught up to them shortly before ''Blücher'' sank and boarded ''Princess Royal'' at 12:20. He ordered the pursuit of the German battlecruisers to be resumed, but rescinded the order when it became clear that too much time had been wasted sinking ''Blücher'' and Hipper's ships would be able to reach German waters before the British could catch them. ''Lion'' was headed home at when the rest of the battlecruisers caught up with her around 12:45.
During the action, ''Tiger'' was hit by six German shells, the most significant of which was a shell that burst on the roof of 'Q' turret. Although most of the shell was deflected overboard, fragments penetrated the roof, damaged the left gun's breech mechanism and jammed the training gear, knocking the turret out of action. Ten men were killed during the battle and 11 wounded. ''Tiger''s repairs were completed on 8 February. Like the rest of the battlecruisers, ''Tiger''s own gunnery was rapid, but inaccurate, and she achieved only two hits out of 355 shells fired, scoring one hit each on ''Seydlitz'' and . Her performance was noted and commented upon by the senior leadership of the Royal Navy: Lord Fisher criticised Pelly's performance, calling him a "poltroon
Poltroon was an event horse ridden by American rider Torrance Watkins
Torrance Watkins (born July 30, 1949) is an American equestrian and Olympic champion. Formerly known as Torrance Fleischmann, she won a team gold medal in eventing at ...
" and adding "The ''Tiger''s gunnery seems to have been villainously bad on January 24, yet she seems to have had a lot of practice." In a memorandum of 11 February 1915, Beatty explained to Pelly where the latter had misconstrued the standing orders, going through ''Tiger''s part in the battle blow by blow and comparing it to that of other ships. His final paragraph was conciliatory however: "In making these remarks I have no wish to express censure in any form. I realise that a newly-commissioned ship in her first action has many difficulties to contend with, and I am quite ready to make the fullest allowance for them. My chief aim is to ensure that our next action shall be a complete success." The ship was given a refit in December 1915.
Battle of Jutland
 This was later characterised as the "Run to the South" as Beatty changed course to steer east-southeast at 15:45, now paralleling Hipper's course less than away. The Germans opened fire first at 15:48, followed by the British. The British ships were still in the process of making their turn as only the two leading ships, ''Lion'' and ''Princess Royal'', had steadied on their course when the Germans opened fire. The 1st BCS was echeloned to the right with ''Tiger'' in the rear and the furthest to the west, closest to the Germans. ''Tiger'' missed Beatty's fire distribution order, as had ''Queen Mary'', and ''Tiger'' engaged ''Moltke'', instead of ''Seydlitz'' as Beatty intended. The German fire was accurate from the start, with ''Tiger'' hit six times by ''Moltke'' within the first seven minutes; although two of these hits temporarily disabled both 'Q' and 'X' turrets, she was not seriously damaged.Campbell, p. 42 By 15:54, the range was down to ; Beatty ordered a course change two
This was later characterised as the "Run to the South" as Beatty changed course to steer east-southeast at 15:45, now paralleling Hipper's course less than away. The Germans opened fire first at 15:48, followed by the British. The British ships were still in the process of making their turn as only the two leading ships, ''Lion'' and ''Princess Royal'', had steadied on their course when the Germans opened fire. The 1st BCS was echeloned to the right with ''Tiger'' in the rear and the furthest to the west, closest to the Germans. ''Tiger'' missed Beatty's fire distribution order, as had ''Queen Mary'', and ''Tiger'' engaged ''Moltke'', instead of ''Seydlitz'' as Beatty intended. The German fire was accurate from the start, with ''Tiger'' hit six times by ''Moltke'' within the first seven minutes; although two of these hits temporarily disabled both 'Q' and 'X' turrets, she was not seriously damaged.Campbell, p. 42 By 15:54, the range was down to ; Beatty ordered a course change two points
Point or points may refer to:
Places
* Point, Lewis, a peninsula in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland
* Point, Texas, a city in Rains County, Texas, United States
* Point, the NE tip and a ferry terminal of Lismore, Inner Hebrides, Scotland
* Point ...
to starboard to open up the range at 15:57.
Around 16:00, was hit around the rear turret by two or three shells from . She fell out of formation to starboard and started sinking toward the stern and listing to port. Her magazines exploded at 16:03 after more hits destroying the ship with the loss of all hands but three.
The range gradually increased until the distance between the British and German ships was too great for accurate fire, so Beatty altered course four points to port between 16:12 and 16:15 to close the range. By 16:25, the range was down to and Beatty turned two points to starboard to open the range again. Around this time, ''Queen Mary'' was hit multiple times in quick succession and her forward magazines exploded. ''Tiger'', following in ''Queen Mary''s wake at a distance of only , had to put her helm hard-a-starboard to avoid colliding with the wreckage. At 16:30, the light cruiser , scouting in front of Beatty's ships, spotted the lead elements of the High Seas Fleet coming north at top speed. Three minutes later, she sighted the topmasts of Vice-Admiral Reinhard Scheer
Carl Friedrich Heinrich Reinhard Scheer (30 September 1863 – 26 November 1928) was an Admiral in the Imperial German Navy (''Kaiserliche Marine''). Scheer joined the navy in 1879 as an officer cadet and progressed through the ranks, commandin ...
's battleships, but did not report this for another five minutes. Beatty continued south for another two minutes to confirm the sighting before ordering his force to turn north. By this time, ''Tiger'' had been hit a total of 17 times, all but one fired by ''Moltke'', but she remained fit to fight.
The German battlecruisers made their own turn north in pursuit, but Beatty's ships maintained full speed, and gradually moved out of range. The British battlecruisers turned north, then north-east, to try to rendezvous with the main body of the Grand Fleet, and at 17:40 opened fire again on their German counterparts. The setting sun blinded the German gunners and they could not make out the British ships and turned away to the north-east at 17:47. Beatty gradually turned toward the east so his ships could cover the Grand Fleet as it deployed into battle formation, but he mistimed his manoeuvre and forced the leading British division further from the Germans. By 18:35, Beatty was following the 3rd BCS as they were leading the Grand Fleet east-southeast, and continuing to engage Hipper's battlecruisers to their south-west. A few minutes earlier, Scheer had ordered a simultaneous 180° starboard turn, and Beatty lost sight of them in the haze. At 18:44, Beatty turned his ships south-east, then south-southeast four minutes later, to find Hipper's force. He then ordered the two surviving ships of the 3rd BCS to take position astern of ''New Zealand'', while slowing to and altering course to the south to stay close to the Grand Fleet. At this moment, ''Lion''s gyrocompass failed, and she—followed by the rest of the battlecruisers—made a complete circle before her steering was brought back under control. At 18:55, Scheer ordered another 180° turn, which put the German ships on a converging course again with the Grand Fleet. However, the British had altered course to the south, allowing the Grand Fleet to cross Scheer's "T" and inflict damage on the leading German ships. Scheer ordered yet another 180° turn at 19:13, and successfully extricated the High Seas Fleet from the trap his manoeuvring caused.
 The British lost sight of the Germans until spotted smoke to the west-northwest at 20:05, then identified and engaged several German torpedo boats. On hearing the sound of gunfire, Beatty ordered his ships west, and spotted the German battlecruisers only away. ''Inflexible'' opened fire at 20:20, followed almost immediately by the rest of the battlecruisers. Shortly after 8:30, the pre-dreadnought battleships of Rear Admiral Franz Mauve's II Battle Squadron were spotted. The British battlecruisers and German pre-dreadnoughts exchanged fire; the Germans fired only a few times before turning away to the west because of poor visibility and the more accurate British gunnery, and disappeared into the mist around 20:40. Beatty's battlecruisers sailed south-southeast, ahead of both the Grand Fleet and the High Seas Fleet, until the order to reverse course for home was given at 02:55.
''Tiger'' and the rest of the battlecruisers reached Rosyth Dockyard in Scotland on the morning of 2 June. Docked the next day for repairs which took until 1 July, she was the first of the "Splendid Cats" to be repaired. ''Tiger'' was hit a total of 18 times during the battle, mostly by shells fired by ''Moltke'', suffering 24 men killed and 46 wounded. The battlecruiser fired 303 shells from her main guns during the battle and is credited with one hit on ''Moltke'' and two on ''Von der Tann''. The ship also fired 136 rounds from her 6-inch guns at the light cruiser and German
The British lost sight of the Germans until spotted smoke to the west-northwest at 20:05, then identified and engaged several German torpedo boats. On hearing the sound of gunfire, Beatty ordered his ships west, and spotted the German battlecruisers only away. ''Inflexible'' opened fire at 20:20, followed almost immediately by the rest of the battlecruisers. Shortly after 8:30, the pre-dreadnought battleships of Rear Admiral Franz Mauve's II Battle Squadron were spotted. The British battlecruisers and German pre-dreadnoughts exchanged fire; the Germans fired only a few times before turning away to the west because of poor visibility and the more accurate British gunnery, and disappeared into the mist around 20:40. Beatty's battlecruisers sailed south-southeast, ahead of both the Grand Fleet and the High Seas Fleet, until the order to reverse course for home was given at 02:55.
''Tiger'' and the rest of the battlecruisers reached Rosyth Dockyard in Scotland on the morning of 2 June. Docked the next day for repairs which took until 1 July, she was the first of the "Splendid Cats" to be repaired. ''Tiger'' was hit a total of 18 times during the battle, mostly by shells fired by ''Moltke'', suffering 24 men killed and 46 wounded. The battlecruiser fired 303 shells from her main guns during the battle and is credited with one hit on ''Moltke'' and two on ''Von der Tann''. The ship also fired 136 rounds from her 6-inch guns at the light cruiser and German destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in ...
s.
Post-Jutland service
After her repairs were completed, ''Tiger'' served as the temporary flagship of the 1st Battlecruiser Squadron while ''Lion'' was under repair.Burt 1986, p. 220 In the meantime, on the evening of 18 August the Grand Fleet put to sea in response to a message deciphered byRoom 40
Room 40, also known as 40 O.B. (old building; officially part of NID25), was the cryptanalysis section of the British Admiralty during the First World War.
The group, which was formed in October 1914, began when Rear-Admiral Henry Oliver, the ...
which indicated that the High Seas Fleet, less the II Squadron, would be leaving harbour that night. The German objective was to bombard Sunderland
Sunderland () is a port city in Tyne and Wear, England. It is the City of Sunderland's administrative centre and in the Historic counties of England, historic county of County of Durham, Durham. The city is from Newcastle-upon-Tyne and is on t ...
on the 19th, with extensive reconnaissance provided by airships and submarines. The Grand Fleet sailed with 29 dreadnought battleships and six battlecruisers, including ''Tiger''. Throughout the 19th, Jellicoe and Scheer received conflicting intelligence, with the result that having reached its rendezvous in the North Sea, the Grand Fleet steered north in the erroneous belief it had entered a minefield before turning south again. Scheer steered south-eastward pursuing a lone British battle squadron reported by an airship, which was in fact the Harwich Force
The Harwich Force originally called Harwich Striking Force was a squadron of the Royal Navy, formed during the First World War and based in Harwich. It played a significant role in the war.
History
After the outbreak of the First World War, a p ...
under Commodore Tyrwhitt Tyrwhitt is an English language surname. It may refer to:
*Charles Tyrwhitt (1846–1874), English explorer
*Elizabeth Tyrwhitt (1519–1578), English writer and courtier
* Gerald Tyrwhitt-Wilson (1883–1950), British composer
*Jaqueline Tyrwhitt ...
. Having realised their mistake, the Germans then steered for home. The only contact came in the evening when Tyrwhitt sighted the High Seas Fleet, but he was unable to achieve an advantageous attack position before dark, and broke off contact. Both the British and the German fleets returned home; the British had lost two cruisers to submarine attacks, and a German dreadnought had been damaged by a torpedo.
The ship received a lengthy refit from 10 November 1916 to 29 January 1917 at Rosyth where her deck and turret roof armour were reinforced and additional rangefinders were added over her conning tower and the rear of 'X' turret. For the remainder of the war, ''Tiger'' uneventfully patrolled the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
, as both fleets were essentially forbidden to risk any more losses. She provided support for British light forces involved in the Second Battle of Heligoland Bight on 17 November 1917, but never came within range of any German forces. The same year saw her undergo a minor refit during which a flying-off platform for a Sopwith Camel
The Sopwith Camel is a British First World War single-seat biplane fighter aircraft that was introduced on the Western Front in 1917. It was developed by the Sopwith Aviation Company as a successor to the Sopwith Pup and became one of the b ...
was mounted on 'Q' turret and a searchlight platform was added to her third funnel. She underwent a more extensive refit in 1918 which saw her topmast shifted to the top of the derrick-stump and a more substantial observation platform added to the foremast. Some of her short rangefinders were replaced by longer ones as well.
Post-war
 ''Tiger'' remained in service with the Royal Navy after the Armistice with Germany and she had a flying-off platform added on 'B' turret's roof in 1919. The ship collided with the battleship in late 1920 while assigned to the Atlantic Fleet. ''Tiger'' survived the culling of older capital ships following the Washington Naval Treaty, although she was placed in
''Tiger'' remained in service with the Royal Navy after the Armistice with Germany and she had a flying-off platform added on 'B' turret's roof in 1919. The ship collided with the battleship in late 1920 while assigned to the Atlantic Fleet. ''Tiger'' survived the culling of older capital ships following the Washington Naval Treaty, although she was placed in reserve
Reserve or reserves may refer to:
Places
* Reserve, Kansas, a US city
* Reserve, Louisiana, a census-designated place in St. John the Baptist Parish
* Reserve, Montana, a census-designated place in Sheridan County
* Reserve, New Mexico, a US vi ...
on 22 August 1921. The ship was refitted in March 1922 with a rangefinder fitted on 'X' turret, her original pair of 3-inch AA guns replaced by four guns, and the flying-off platform on 'Q' turret was removed. On 14 February 1924, ''Tiger'' was recommissioned and became a seagoing training ship, a role she served in throughout the 1920s. Her last major period of activity came in 1929, when went into dockyard hands for refit. While ''Hood'' was out of commission, ''Tiger'' returned to active service to keep the Royal Navy's three-ship Battlecruiser Squadron
The Battlecruiser Squadron was a Royal Navy squadron of battlecruisers that saw service from 1919 to the early part of the Second World War. Its best-known constituent ship was HMS ''Hood'', "The Mighty Hood", which was lost in the Battle of t ...
(normally made up of ''Hood'' plus the smaller and ) up to strength. Although by the 1930s, ''Tiger'' was still in reasonable condition, the decision was taken to discard her following the London Naval Conference 1930 as part of an overall reduction in world battleship fleets. Under the command of Captain Kenneth Dewar
Vice-Admiral Kenneth Gilbert Balmain Dewar, CBE (21 September 1879 – 8 September 1964) was an officer of the Royal Navy. After specialising as a gunnery officer, Dewar became a staff officer and a controversial student of naval tactics befor ...
in 1928 to 1929, her final commander was Arthur Bedford
Vice-Admiral Arthur Edward Frederick Bedford, CB, CSI (2 August 1881 – 5 December 1949) was a Royal Navy officer. He served in HMS ''Kent'' at the Battle of the Falkland Islands of 1914 and rose to command the Royal Indian Navy from 1934 ...
, and she remained in service with the fleet until ''Hood'' came out of refit in early 1931, at which time she was taken out of commission in accordance with the terms of the London Naval Treaty
The London Naval Treaty, officially the Treaty for the Limitation and Reduction of Naval Armament, was an agreement between the United Kingdom, Japan, France, Italy, and the United States that was signed on 22 April 1930. Seeking to address is ...
.
''Tiger'' took the cheers of the Atlantic Fleet on 30 March 1931 at Devonport.Parkes, p. 557 She paid off
Ship commissioning is the act or ceremony of placing a ship in active service and may be regarded as a particular application of the general concepts and practices of project commissioning. The term is most commonly applied to placing a warship in ...
on 15 May 1931 at Rosyth, before being sold to Thos. W. Ward of Inverkeithing for breaking up in February 1932.
Notes
Footnotes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * *External links
*Dreadnought Project
Technical material on the weaponry and fire control for the ships
Battle of Jutland Crew Lists Project – HMS Tiger Crew List
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tiger (1913) 1913 ships Battlecruisers of the Royal Navy World War I battlecruisers of the United Kingdom