|
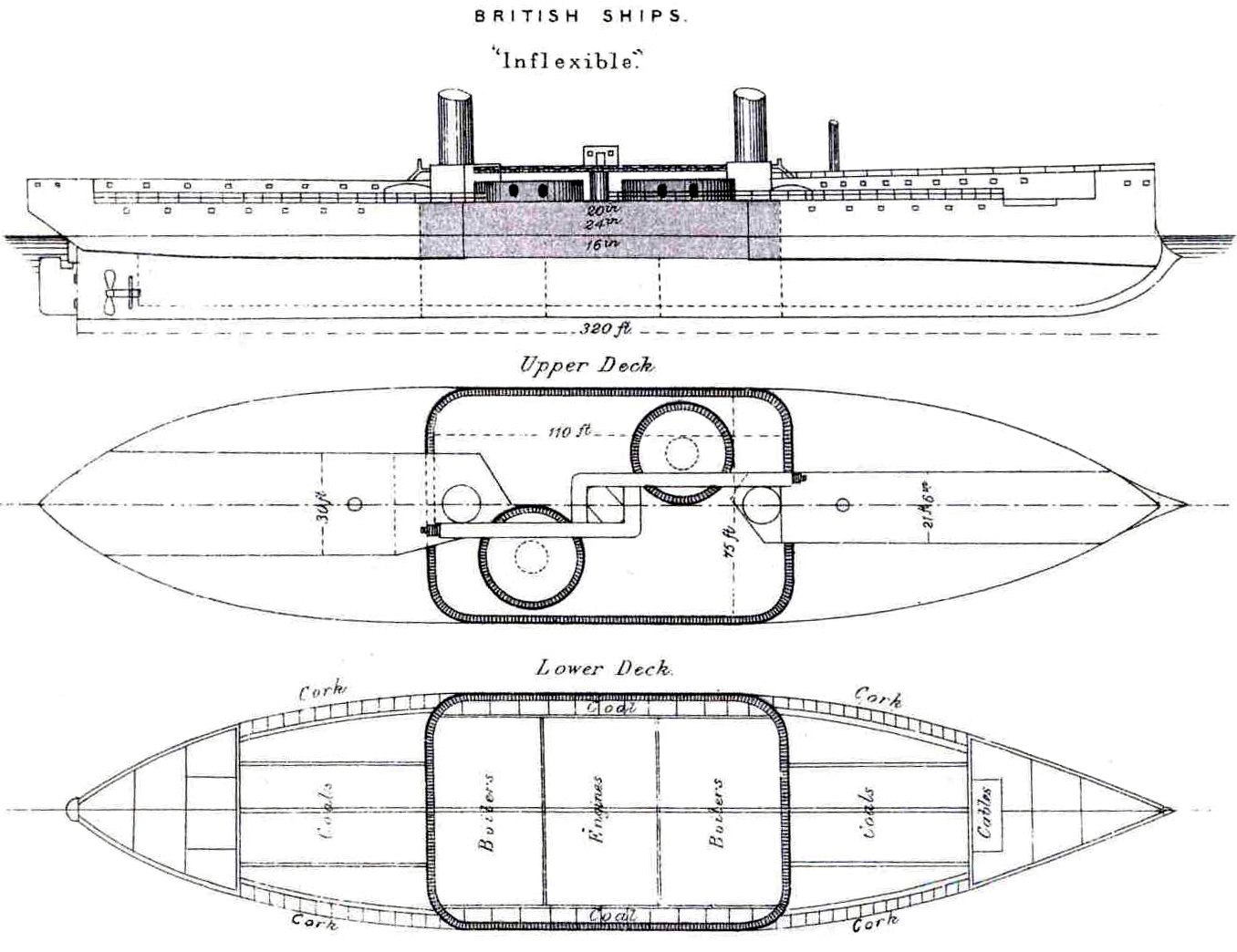
Armoured Citadel
In a warship an armored citadel is an armored box enclosing the machinery and magazine spaces formed by the armored deck, the waterline belt, and the transverse bulkheads. In many post-World War I warships, armor was concentrated in a very strong citadel, with the rest of the ship virtually unprotected, which was found to be the most effective defence; this is referred to as all or nothing armor. In a non-military ship a citadel is a secure space equipped with means of communication and emergency supplies, used typically in case of piracy Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v .... Citations Bibliography * {{cite book, last1=Raven, first1=Alan, last2=Roberts, first2=John, title=British Cruisers of World War Two, year=1980, publisher=Naval Institute Press, locatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magazine (artillery)
Magazine is the name for an item or place within which ammunition or other explosive material is stored. It is taken originally from the Arabic word "makhāzin" (مخازن), meaning 'storehouses', via Italian and Middle French. The term is also used for a place where large quantities of ammunition are stored for later distribution, or an ammunition dump. This usage is less common. Field magazines In the early history of tube artillery drawn by horses (and later by mechanized vehicles), ammunition was carried in separate unarmored wagons or vehicles. These soft-skinned vehicles were extremely vulnerable to enemy fire and to explosions caused by a weapons malfunction. Therefore, as part of setting up an artillery battery, a designated place would be used to shelter the ready ammunition. In the case of batteries of towed artillery the temporary magazine would be placed, if possible, in a pit, or natural declivity, or surrounded by sandbags or earthworks. Circumstances mig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deck (ship)
A deck is a permanent covering over a Compartment (ship), compartment or a hull (watercraft), hull of a ship. On a boat or ship, the primary or upper deck is the horizontal structure that forms the "roof" of the hull, strengthening it and serving as the primary working surface. Vessels often have more than one level both within the hull and in the superstructure above the primary deck, similar to the floors of a multi-storey building, that are also referred to as decks, as are certain compartments and decks built over specific areas of the superstructure. Decks for some purposes have specific names. Structure The main purpose of the upper or primary deck is structural, and only secondarily to provide weather-tightness and support people and equipment. The deck serves as the lid to the complex box girder which can be identified as the hull. It resists Tension (physics), tension, Compression (physics), compression, and racking forces. The deck's scantling is usually the same as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belt Armor
Belt armor is a layer of heavy metal armor plated onto or within the outer hulls of warships, typically on battleships, battlecruisers and cruisers, and aircraft carriers. The belt armor is designed to prevent projectiles from penetrating to the heart of a warship. When struck by an artillery shell or underwater torpedo, the belt armor either absorbs the impact and explosion with its sheer thickness and strength, or else uses sloping to redirect the projectile and its blast downwards. Typically, the main armor belt covers the warship from its main deck down to some distance below the waterline. If, instead of forming the outer hull, the armor belt is built inside the hull, it is installed at a sloped angle for improved protection, as described above. The torpedo bulkhead Frequently, the main belt's armor plates were supplemented with a torpedo bulkhead spaced several meters behind the main belt, designed to maintain the ship's watertight integrity even if the main be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulkhead (partition)
A bulkhead is an upright wall within the hull of a ship or within the fuselage of an airplane. Other kinds of partition elements within a ship are decks and deckheads. Etymology The word ''bulki'' meant "cargo" in Old Norse. During the 15th century sailors and builders in Europe realized that walls within a vessel would prevent cargo from shifting during passage. In shipbuilding, any vertical panel was called a head. So walls installed abeam (side-to-side) in a vessel's hull were called "bulkheads". Now, the term bulkhead applies to every vertical panel aboard a ship, except for the hull itself. History Bulkhead partitions are considered to have been a feature of Chinese junks, a type of ship. Song Dynasty author Zhu Yu (fl. 12th century) wrote in his book of 1119 that the hulls of Chinese ships had a bulkhead build. The 5th-century book ''Garden of Strange Things'' by Liu Jingshu mentioned that a ship could allow water to enter the bottom without sinking. Archaeolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific Ocean, Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in Genocides in history (World War I through World War II), genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the Spanish flu, 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising French Third Republic, France, Russia, and British Empire, Britain) and the Triple A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All Or Nothing (armor)
All or nothing is a method of naval warship armor, best known for its employment on dreadnought battleships. The concept involves heavily armoring the areas most important to a ship while the rest of the ship receives no armor. The "all or nothing" concept avoided light or moderate thicknesses of armor: armor was used in the greatest practicable thickness or not at all, thereby providing "either total or negligible protection". Compared to previous armoring systems, "all or nothing" ships had thicker armor covering a smaller proportion of the hull. The ironclad battleship launched in 1876 had featured a heavily armored central citadel, with relatively unarmored ends; however, by the era of , battleships were armored over the length of the ship with varying zones of heavy, moderate or light armor. The U.S. Navy adopted what was formally called "all or nothing" armor in the Standard-type battleships, starting with the laid down in 1912. The Imperial Japanese Navy soon imple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piracy In The 21st Century
Piracy in the 21st century (commonly known as modern piracy) has taken place in a number of waters around the world, including the Gulf of Guinea, Strait of Malacca, Sulu and Celebes Seas, Indian Ocean, and Falcon Lake. Waters Caribbean Due to the crisis in Bolivarian Venezuela, issues of piracy returned to the Caribbean in the 2010s, with the increase of pirates being compared to piracy off the coast of Somalia due to the similar socioeconomic origins. In 2016, former fishermen became pirates, appearing in the state of Sucre, with attacks happening daily and multiple killings occurring. By 2018 as Venezuelans became more desperate, fears arose that Venezuelan pirates would spread throughout Caribbean waters. Falcon Lake Piracy on Falcon Lake involves crime at the border between the United States and Mexico on Falcon Lake. The lake is a reservoir constructed in 1954 and is a known drug smuggling route.. A turf war between rival drug cartels for control of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Compartments
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, and 13% wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(cropped).jpg)

