HMNB Devonport on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
His Majesty's Naval Base, Devonport (HMNB Devonport) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the
 In 1588, the ships of the English Navy set sail for the
In 1588, the ships of the English Navy set sail for the
 The dockyard began in what is now known as the South Yard area of Devonport. It was here that Dummer built his groundbreaking stone dry dock (completely rebuilt in the 1840s). The numbers employed at the yard increased from 736 in 1711 to 2,464 in 1730.
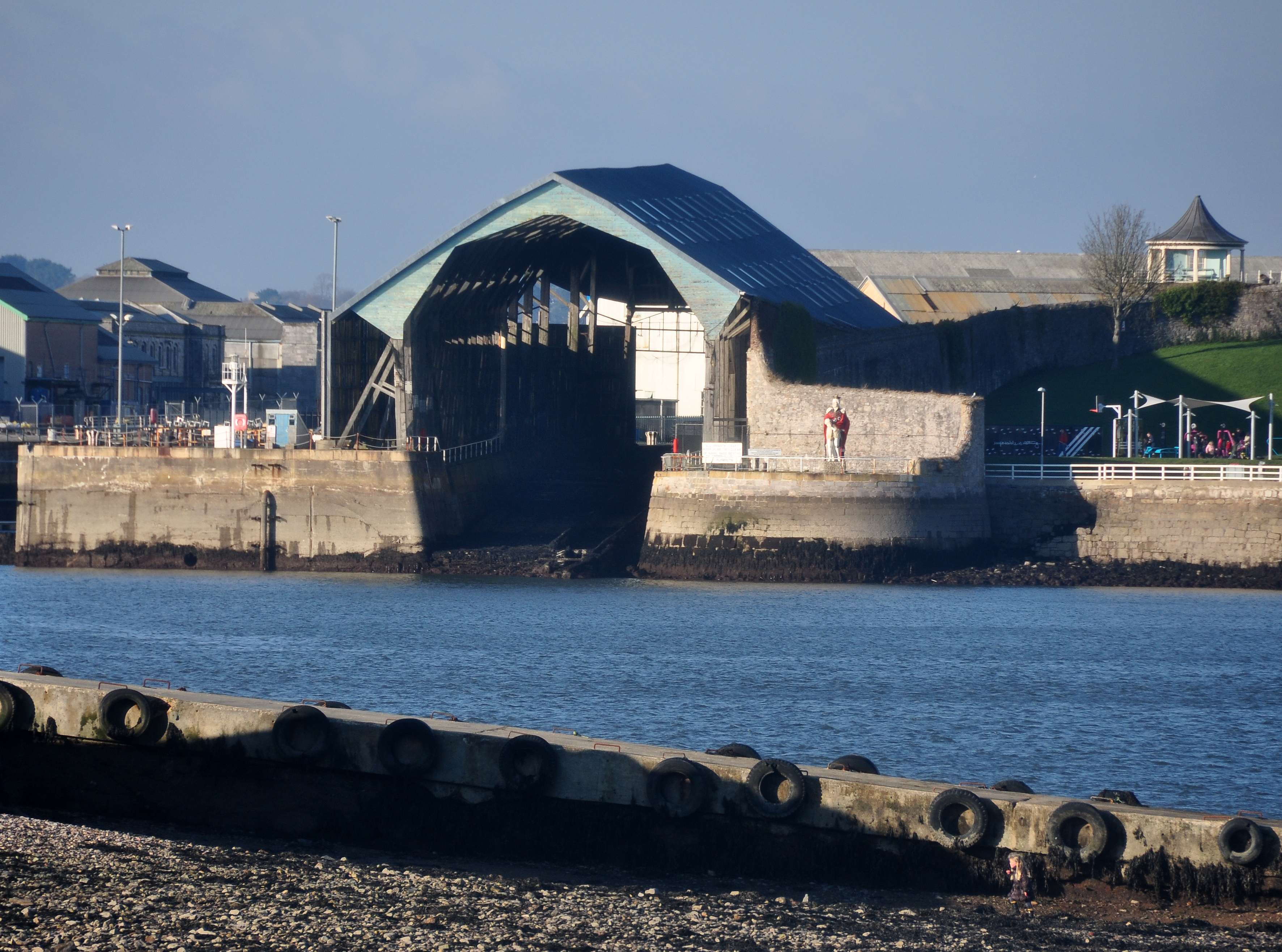
In the 1760s a period of expansion began, leading to a configuration which (despite subsequent rebuildings) can still be seen today : five slipways, four dry docks and a wet basin (slipways were used for shipbuilding, but the main business of the eighteenth-century yard was the repair, maintenance and equipping of the fleet, for which the dry docks and basin were used). One slipway (1774) survives unaltered from this period (Slip No.1): a rare survival. It is covered with a timber superstructure of 1814, a similarly rare and early survival of its type; indeed, only three such timber slip covers have survived in Britain, two of them at Devonport (the second of these, of similar vintage, stands over the former No.5 Slip; it was later converted to house the Scrieve Board, for full-size drafting of ship designs). The two additional docks were added, north of the double-dock, in 1762 and 1789 (both subsequently rebuilt).
The dockyard began in what is now known as the South Yard area of Devonport. It was here that Dummer built his groundbreaking stone dry dock (completely rebuilt in the 1840s). The numbers employed at the yard increased from 736 in 1711 to 2,464 in 1730.
In the 1760s a period of expansion began, leading to a configuration which (despite subsequent rebuildings) can still be seen today : five slipways, four dry docks and a wet basin (slipways were used for shipbuilding, but the main business of the eighteenth-century yard was the repair, maintenance and equipping of the fleet, for which the dry docks and basin were used). One slipway (1774) survives unaltered from this period (Slip No.1): a rare survival. It is covered with a timber superstructure of 1814, a similarly rare and early survival of its type; indeed, only three such timber slip covers have survived in Britain, two of them at Devonport (the second of these, of similar vintage, stands over the former No.5 Slip; it was later converted to house the Scrieve Board, for full-size drafting of ship designs). The two additional docks were added, north of the double-dock, in 1762 and 1789 (both subsequently rebuilt).
 Before the expansion could begin, a rocky hillside to the south had to be cut away; the rubble was used to reclaim the mudflats ready for building. To open up the site, the old ropehouse was demolished and a new rope-making complex built alongside the east perimeter wall of the expanded site (where it still survives in part, albeit rebuilt following a fire in 1812). Where the old ropehouse had stood a short canal known as the Camber was laid out, terminating in a
Before the expansion could begin, a rocky hillside to the south had to be cut away; the rubble was used to reclaim the mudflats ready for building. To open up the site, the old ropehouse was demolished and a new rope-making complex built alongside the east perimeter wall of the expanded site (where it still survives in part, albeit rebuilt following a fire in 1812). Where the old ropehouse had stood a short canal known as the Camber was laid out, terminating in a  The dockyard suffered severe damage in a large-scale fire on 25 September 1840, it started in the North Dock on and were completely gutted, threatened , and spread to nearby buildings and equipment. Estimates for the damage were put at £150,000 in the values of the day, and would have totalled £500,000 had the fire not been contained by demolishing several surrounding buildings.
Despite significant damage during the blitz, the South Yard still contains four scheduled monuments and over thirty listed buildings and structures (though some of these have been allowed to fall into a derelict state in recent years: the 18th-century South Sawmills and South
The dockyard suffered severe damage in a large-scale fire on 25 September 1840, it started in the North Dock on and were completely gutted, threatened , and spread to nearby buildings and equipment. Estimates for the damage were put at £150,000 in the values of the day, and would have totalled £500,000 had the fire not been contained by demolishing several surrounding buildings.
Despite significant damage during the blitz, the South Yard still contains four scheduled monuments and over thirty listed buildings and structures (though some of these have been allowed to fall into a derelict state in recent years: the 18th-century South Sawmills and South
 Provision of ships' armaments was not the responsibility of the Navy but of the independent Board of Ordnance, which already had a wharf and storage facility in the Mount Wise area of Plymouth. This, however, began to prove insufficient and in 1719 the board established a new gun wharf on land leased from one Sir Nicholas Morice, immediately to the north of the established Dockyard. The Morice Yard was a self-contained establishment with its own complex of workshops, workers, officers, offices and storehouses. Gunpowder was stored on site, which began to be a cause for concern among local residents (as was the older store in the Royal Citadel within the city of Plymouth). In time new gunpowder magazines were built further north, first at Keyham (1770s), but later (having to make way for further dockyard expansion) relocating to Bull Point (1850).
In contrast to South Yard, which fared badly in the Blitz, most of the original buildings survive at Morice Yard, enclosed behind their contemporary boundary wall; over a dozen of these are listed. On higher ground behind the wharf itself is a contemporary terrace of houses for officers (1720), built from stone rubble excavated during the yard's construction.
Morice Ordnance Yard remained independent from the dockyard until 1941, at which point it was integrated into the larger complex.
Provision of ships' armaments was not the responsibility of the Navy but of the independent Board of Ordnance, which already had a wharf and storage facility in the Mount Wise area of Plymouth. This, however, began to prove insufficient and in 1719 the board established a new gun wharf on land leased from one Sir Nicholas Morice, immediately to the north of the established Dockyard. The Morice Yard was a self-contained establishment with its own complex of workshops, workers, officers, offices and storehouses. Gunpowder was stored on site, which began to be a cause for concern among local residents (as was the older store in the Royal Citadel within the city of Plymouth). In time new gunpowder magazines were built further north, first at Keyham (1770s), but later (having to make way for further dockyard expansion) relocating to Bull Point (1850).
In contrast to South Yard, which fared badly in the Blitz, most of the original buildings survive at Morice Yard, enclosed behind their contemporary boundary wall; over a dozen of these are listed. On higher ground behind the wharf itself is a contemporary terrace of houses for officers (1720), built from stone rubble excavated during the yard's construction.
Morice Ordnance Yard remained independent from the dockyard until 1941, at which point it was integrated into the larger complex.
 In 1758, the Plymouth and Portsmouth Fortifications Act provided the means to construct a permanent landward defence for the dockyard complex. The Devonport Lines were a bastion fortification which consisted of an earthen rampart with a wide ditch and a
In 1758, the Plymouth and Portsmouth Fortifications Act provided the means to construct a permanent landward defence for the dockyard complex. The Devonport Lines were a bastion fortification which consisted of an earthen rampart with a wide ditch and a
 In the mid-nineteenth century, all royal dockyards faced the challenge of responding to the advent first of steam power and then metal hulls. Those unable to expand were closed; the rest underwent a transformation through growth and mechanisation. In 1860 the main dockyards' policing was also transferred to the new dockyard divisions of the Metropolitan Police, in Devonport's case No. 3 Division, which remained in that role until 1934.
In the mid-nineteenth century, all royal dockyards faced the challenge of responding to the advent first of steam power and then metal hulls. Those unable to expand were closed; the rest underwent a transformation through growth and mechanisation. In 1860 the main dockyards' policing was also transferred to the new dockyard divisions of the Metropolitan Police, in Devonport's case No. 3 Division, which remained in that role until 1934.
 At Devonport, in 1864, a separate, purpose-built steam yard was opened on a self-contained site at Keyham, just to the north of Morice Yard (and a tunnel was built linking the new yard with the old). A pair of basins (8–9 acres each) were constructed: No. 2 Basin gave access to three large dry-docks, while No. 3 Basin was the frontispiece to a huge integrated manufacturing complex. This became known as the Quadrangle: it housed foundries, forges, pattern shops, boilermakers and all manner of specialized workshops. Two stationary steam engines drove line shafts and heavy machinery, and the multiple flues were drawn by a pair of prominent chimneys. The building still stands, and is
At Devonport, in 1864, a separate, purpose-built steam yard was opened on a self-contained site at Keyham, just to the north of Morice Yard (and a tunnel was built linking the new yard with the old). A pair of basins (8–9 acres each) were constructed: No. 2 Basin gave access to three large dry-docks, while No. 3 Basin was the frontispiece to a huge integrated manufacturing complex. This became known as the Quadrangle: it housed foundries, forges, pattern shops, boilermakers and all manner of specialized workshops. Two stationary steam engines drove line shafts and heavy machinery, and the multiple flues were drawn by a pair of prominent chimneys. The building still stands, and is  In 1880 a Royal Naval Engineering College was established at Keyham, housed in a new building just outside the dockyard wall alongside the Quadrangle where students (who joined at 15 years of age) gained hands-on experience of the latest naval engineering techniques. The Engineering College moved to nearby Manadon in 1958; the
In 1880 a Royal Naval Engineering College was established at Keyham, housed in a new building just outside the dockyard wall alongside the Quadrangle where students (who joined at 15 years of age) gained hands-on experience of the latest naval engineering techniques. The Engineering College moved to nearby Manadon in 1958; the  In 1895 the decision was taken to expand the Keyham Steam Yard to accommodate the increasing size of modern warships. By 1907 Keyham, now renamed the North Yard, had more than doubled in size with the addition of No. 4 and No. 5 Basins (of 10 and 35 acres respectively), linked by a very large lock-cum-dock, 730 ft in length, alongside three more dry-docks of a similar size, able to "accommodate ships larger than any war-vessel yet constructed". In the 1970s the northern end of No. 5 Basin was converted to serve as a new Fleet Maintenance Base, to be built alongside a Submarine Refit Complex for nuclear submarines; an 80-ton cantilever crane, one of the largest in western Europe, was installed to lift nuclear cores from submarines in newly built adjacent dry docks.
Further north still, Weston Mill Lake (at one time Devonport's coaling yard) was converted in the 1980s to provide frigate berths for the Type 22 fleet. It is now where the Navy's amphibious warfare ships are based. In 2013 a new
In 1895 the decision was taken to expand the Keyham Steam Yard to accommodate the increasing size of modern warships. By 1907 Keyham, now renamed the North Yard, had more than doubled in size with the addition of No. 4 and No. 5 Basins (of 10 and 35 acres respectively), linked by a very large lock-cum-dock, 730 ft in length, alongside three more dry-docks of a similar size, able to "accommodate ships larger than any war-vessel yet constructed". In the 1970s the northern end of No. 5 Basin was converted to serve as a new Fleet Maintenance Base, to be built alongside a Submarine Refit Complex for nuclear submarines; an 80-ton cantilever crane, one of the largest in western Europe, was installed to lift nuclear cores from submarines in newly built adjacent dry docks.
Further north still, Weston Mill Lake (at one time Devonport's coaling yard) was converted in the 1980s to provide frigate berths for the Type 22 fleet. It is now where the Navy's amphibious warfare ships are based. In 2013 a new

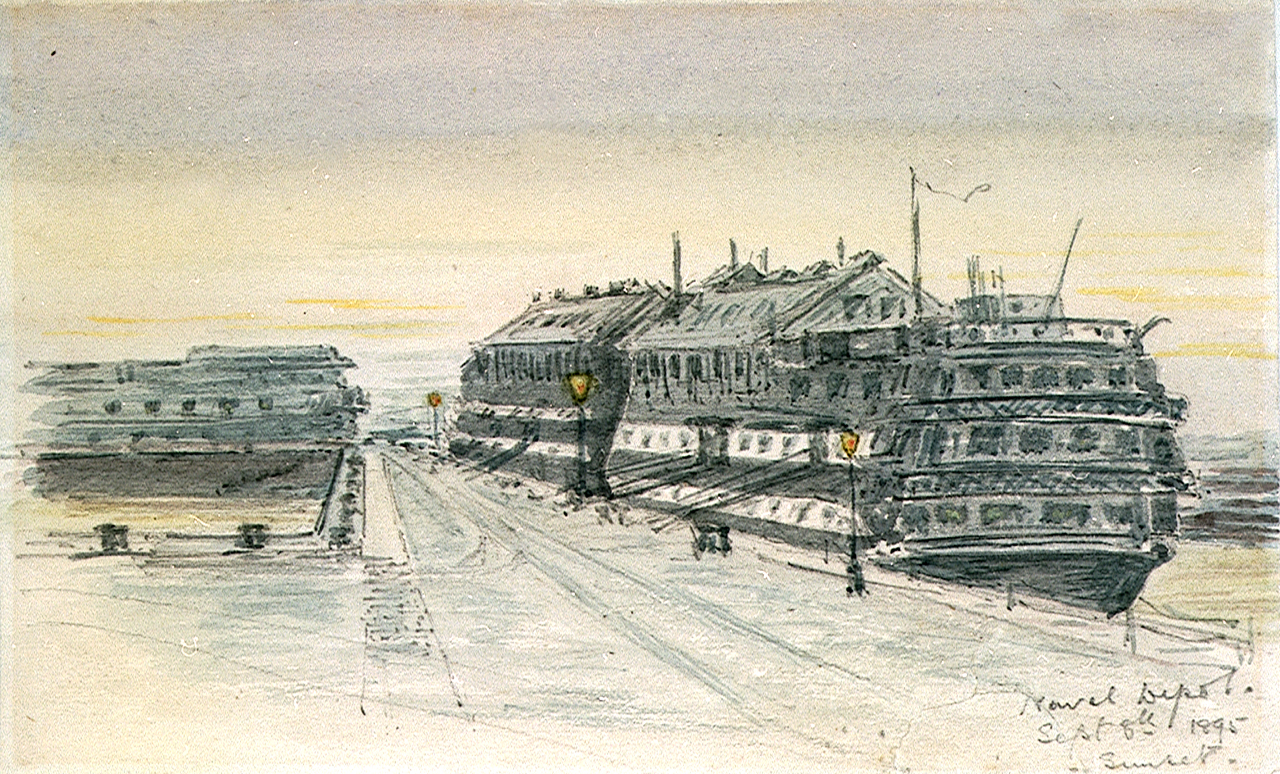 Until the late nineteenth century, sailors whose ships were being repaired or refitted, or who were awaiting allocation to a vessel, were accommodated in floating
Until the late nineteenth century, sailors whose ships were being repaired or refitted, or who were awaiting allocation to a vessel, were accommodated in floating  The prominent clock tower was built in 1896, containing a clock and bell by Gillett & Johnston; it initially functioned as a semaphore tower. 1898 saw the barracks expand to accommodate a further 1,000 men. The wardroom block dates from this period. More buildings were added in the early years of the twentieth century, including St Nicholas's Church. This part of the site contains some fourteen listed buildings and structures.
The prominent clock tower was built in 1896, containing a clock and bell by Gillett & Johnston; it initially functioned as a semaphore tower. 1898 saw the barracks expand to accommodate a further 1,000 men. The wardroom block dates from this period. More buildings were added in the early years of the twentieth century, including St Nicholas's Church. This part of the site contains some fourteen listed buildings and structures.
 * HMS ''Albion'' landing platform dock;
* HMS ''Bulwark'' landing platform dock (Regeneration refit until 2023).
* HMS ''Albion'' landing platform dock;
* HMS ''Bulwark'' landing platform dock (Regeneration refit until 2023).
 * (planned to transfer to HMNB Portsmouth)
*
*
*
*
*
* (Currently in LIFEX refit)
* (Currently in LIFEX refit)
In changes to base porting arrangements announced in November 2017, HM Ships ''Argyll'', ''Monmouth'' and ''Montrose'' were to join the Portsmouth Flotilla (however, ''Monmouth'' retired in 2021 and ''Montrose'' is scheduled to decommission in 2023 with her return from the Persian Gulf); HM Ships , ''Richmond'', and ''St Albans'' are moving in the opposite direction, to Devonport. ''Richmond'' becomes a Devonport ship on completion of her refit. ''St Albans'' moved to Devonport in July 2019 in preparation for her major refit.
* (planned to transfer to HMNB Portsmouth)
*
*
*
*
*
* (Currently in LIFEX refit)
* (Currently in LIFEX refit)
In changes to base porting arrangements announced in November 2017, HM Ships ''Argyll'', ''Monmouth'' and ''Montrose'' were to join the Portsmouth Flotilla (however, ''Monmouth'' retired in 2021 and ''Montrose'' is scheduled to decommission in 2023 with her return from the Persian Gulf); HM Ships , ''Richmond'', and ''St Albans'' are moving in the opposite direction, to Devonport. ''Richmond'' becomes a Devonport ship on completion of her refit. ''St Albans'' moved to Devonport in July 2019 in preparation for her major refit.
 * (completed refit and returned to sea for post-refit trials December 2022)
* (completed refit and returned to sea for post-refit trials December 2022)
 *
*
*
*
*
*
 Several sections of the historic South Yard are no longer used by the Ministry of Defence, though it is still currently a closed site and subject to security restrictions.
The deep-water access it offers has made the site desirable for manufacturers of ' superyachts' and in 2012 Princess Yachts acquired the freehold to at the southern end, with a view to building a construction facility. The company asserts that this development will "continue the boat building tradition within the dockyard" and "add drama to the site with yachts being moved around the quayside, launched on No. 3 Slip, tested in No. 2 Slip and moored alongside the quay wall". The site includes within it several listed buildings and scheduled ancient monuments, most notably the
Several sections of the historic South Yard are no longer used by the Ministry of Defence, though it is still currently a closed site and subject to security restrictions.
The deep-water access it offers has made the site desirable for manufacturers of ' superyachts' and in 2012 Princess Yachts acquired the freehold to at the southern end, with a view to building a construction facility. The company asserts that this development will "continue the boat building tradition within the dockyard" and "add drama to the site with yachts being moved around the quayside, launched on No. 3 Slip, tested in No. 2 Slip and moored alongside the quay wall". The site includes within it several listed buildings and scheduled ancient monuments, most notably the
 The Devonport Naval Heritage Centre is a maritime museum in Devonport's Historic South Yard. Run by volunteers, it is only accessible for pre-booked tours, or on Naval Base open days. Plymouth Naval Base Museum opened in 1969 following an appeal from the office of the Admiral-superintendent for items of memorabilia and was housed in the Dockyard Fire Station. Since then, the museum has expanded and now occupies, in addition, the 18th-century Pay Office and Porter's Lodge. The Scrieve Board (Project Managed by PDM) currently serves as a museum store. Discussions were underway in 2014 around removing the museum from the Dockyard and displaying some of its collections within an expanded
The Devonport Naval Heritage Centre is a maritime museum in Devonport's Historic South Yard. Run by volunteers, it is only accessible for pre-booked tours, or on Naval Base open days. Plymouth Naval Base Museum opened in 1969 following an appeal from the office of the Admiral-superintendent for items of memorabilia and was housed in the Dockyard Fire Station. Since then, the museum has expanded and now occupies, in addition, the 18th-century Pay Office and Porter's Lodge. The Scrieve Board (Project Managed by PDM) currently serves as a museum store. Discussions were underway in 2014 around removing the museum from the Dockyard and displaying some of its collections within an expanded
 The Naval base at Devonport is still nicknamed "Guzz" (or, sometimes, "Guz") by sailors and marines. One suggestion is that this originates from the word ''guzzle'' (to eat or drink greedily), which is likely to refer to the eating of
The Naval base at Devonport is still nicknamed "Guzz" (or, sometimes, "Guz") by sailors and marines. One suggestion is that this originates from the word ''guzzle'' (to eat or drink greedily), which is likely to refer to the eating of
Devonport Naval Heritage CentreQueen's Harbour Master Plymouth
{{DEFAULTSORT:Devonport Buildings and structures in Plymouth, Devon Royal Navy bases in England Royal Navy dockyards in England Tourist attractions in Plymouth, Devon Economy of Devon Trident (UK nuclear programme) Royal Navy submarine bases Industrial archaeological sites in Devon 1691 establishments in England
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
(the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Portsmouth
His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is lo ...
) and is the sole nuclear repair and refuelling facility for the Royal Navy. The largest naval base in Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
, HMNB Devonport is located in Devonport, in the west of the city of Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymouth ...
, England.
The base began as Royal Navy Dockyard in the late 17th century, but shipbuilding ceased at Devonport in the early 1970s, although ship maintenance work has continued. The now privatised maintenance facilities are operated by Babcock International Group
Babcock International Group plc is a British aerospace, defence and nuclear engineering services company based in London, England. It specialises in managing complex assets and infrastructure. Although the company has civil contracts, its main b ...
, who took over the previous owner Devonport Management Limited (DML) in 2007. DML had been running the Dockyard since privatisation in 1987.
From 1934 until the early 21st century the naval barracks on the site was named HMS ''Drake'' (it had previously been known as HMS ''Vivid'' after the base ship of the same name). The name HMS ''Drake'' and its command structure
A command hierarchy is a group of people who carry out orders based on others' authority within the group. It can be viewed as part of a power structure, in which it is usually seen as the most vulnerable and also the most powerful part.
Mili ...
has been extended to cover the entire base. The barracks buildings are now named the Fleet Accommodation Centre. In the early 1970s the newly styled 'Fleet Maintenance Base' was itself commissioned as HMS ''Defiance''; it remained so until 1994, when it was amalgamated into HMS ''Drake''.
HM Naval Base Devonport is the home port of the Devonport Flotilla which includes the s. In 2009 the Ministry of Defence
{{unsourced, date=February 2021
A ministry of defence or defense (see spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is an often-used name for the part of a government responsible for matters of defence, found in states ...
announced the conclusion of a long-running review of the long-term role of three naval bases. Devonport would no longer be used as a base for attack submarines after these moved to Faslane by 2017, and the Type 45 destroyers are based at Portsmouth. However, Devonport retains a long-term role as the dedicated home of the amphibious fleet, survey vessels and half the frigate fleet.
History
 In 1588, the ships of the English Navy set sail for the
In 1588, the ships of the English Navy set sail for the Spanish Armada
The Spanish Armada (a.k.a. the Enterprise of England, es, Grande y Felicísima Armada, links=no, lit=Great and Most Fortunate Navy) was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by the Duke of Medina Sidonia, an aris ...
through the mouth of the River Plym, thereby establishing the military presence in Plymouth. Sir Francis Drake is now an enduring legacy in Devonport, as the naval base has been named HMS ''Drake''.
Origins
In 1689 Prince William of Orange becameWilliam III William III or William the Third may refer to:
Kings
* William III of Sicily (c. 1186–c. 1198)
* William III of England and Ireland or William III of Orange or William II of Scotland (1650–1702)
* William III of the Netherlands and Luxembourg ...
and almost immediately he required the building of a new Royal Dockyard west of Portsmouth. Edmund Dummer, Surveyor of the Navy, travelled the West Country searching for an area where a dockyard could be built; he sent in two estimates for sites, one in Plymouth, Cattewater and one further along the coast, on the Hamoaze, a section of the River Tamar, in the parish of Stoke Damerel. Having dismissed the Plymouth site as inadequate, he settled on the Hamoaze area which soon became known as Plymouth Dock
Devonport ( ), formerly named Plymouth Dock or just Dock, is a district of Plymouth in the English county of Devon, although it was, at one time, the more important settlement. It became a county borough in 1889. Devonport was originally one ...
, later renamed Devonport. On 30 December 1690, a contract was let for a dockyard to be built: the start of Plymouth (later Devonport) Royal Dockyard. Having selected the location, Dummer was given responsibility for designing and building the new yard.
At the heart of his new dockyard, Dummer placed a stone-lined basin, giving access to what proved to be the first successful stepped stone dry dock in Europe. Previously the Navy Board had relied upon timber as the major building material for dry docks, which resulted in high maintenance costs and was also a fire risk. The docks Dummer designed were stronger with more secure foundations and stepped sides that made it easier for men to work beneath the hull of a docked vessel. These innovations also allowed rapid erection of staging and greater workforce mobility. He discarded the earlier three-sectioned hinged gate, which was labour-intensive in operation, and replaced it with the simpler and more mobile two-sectioned gate. A further, double-dock (i.e. long enough to accommodate two ships of the line, end to end) was added, just north of the basin, in the 1720s.
Dummer wished to ensure that naval dockyards were efficient working units that maximised available space, as evidenced by the simplicity of his design layout at Plymouth Dock. He introduced a centralised storage area (the quadrangular Great Storehouse) alongside the basin, and a logical positioning of other buildings around the yard. The southern boundary of his yard was formed by a 'double' rope-house (combining the previously separate tasks of spinning and laying within a single building); the upper floor was used for the repair of sails and a separate rigging house stood nearby. The smithery
A metalsmith or simply smith is a craftsperson fashioning useful items (for example, tools, kitchenware, tableware, jewelry, armor and weapons) out of various metals. Smithing is one of the oldest metalworking occupations. Shaping metal w ...
with its fire and forge was positioned to the north, safely separate from the other buildings. On high ground overlooking the rest of the yard he built a grand terrace of thirteen three-storey houses for the senior dockyard officers (the first known example in the country of a palace-front terrace); the commissioner was accommodated in the centre, and at each end of the terrace was a two-storey block of offices (one for the commissioner, the other for the Clerk of the Cheque). A chapel was built in 1700, alongside the Porter's Lodge at the main gate (it was destroyed by a fire in 1799).
Most of these buildings and structures were rebuilt over ensuing years, including Dummer's original basin and dry dock (today known as No. 1 Basin and No. 1 Dock). The terrace survived into the 20th century, but was largely destroyed in the Blitz along with several others of Devonport's historic buildings. Just one end section of the terrace survives; dating from 1692 to 1696, it is the earliest surviving building in any royal dockyard.
Development
From its original 17th-century site, the dockyard expanded in stages (first to the south and then progressively northwards) over the next centuries. The town that grew around the dockyard was called Plymouth Dock up to 1823, when the townspeople petitioned for it to be renamed Devonport. The dockyard followed suit twenty years later, becoming Devonport Royal Dockyard. In just under three centuries, over 300 vessels were built at Devonport, the last being HMS ''Scylla'' in 1971.South Yard
 The dockyard began in what is now known as the South Yard area of Devonport. It was here that Dummer built his groundbreaking stone dry dock (completely rebuilt in the 1840s). The numbers employed at the yard increased from 736 in 1711 to 2,464 in 1730.
In the 1760s a period of expansion began, leading to a configuration which (despite subsequent rebuildings) can still be seen today : five slipways, four dry docks and a wet basin (slipways were used for shipbuilding, but the main business of the eighteenth-century yard was the repair, maintenance and equipping of the fleet, for which the dry docks and basin were used). One slipway (1774) survives unaltered from this period (Slip No.1): a rare survival. It is covered with a timber superstructure of 1814, a similarly rare and early survival of its type; indeed, only three such timber slip covers have survived in Britain, two of them at Devonport (the second of these, of similar vintage, stands over the former No.5 Slip; it was later converted to house the Scrieve Board, for full-size drafting of ship designs). The two additional docks were added, north of the double-dock, in 1762 and 1789 (both subsequently rebuilt).
The dockyard began in what is now known as the South Yard area of Devonport. It was here that Dummer built his groundbreaking stone dry dock (completely rebuilt in the 1840s). The numbers employed at the yard increased from 736 in 1711 to 2,464 in 1730.
In the 1760s a period of expansion began, leading to a configuration which (despite subsequent rebuildings) can still be seen today : five slipways, four dry docks and a wet basin (slipways were used for shipbuilding, but the main business of the eighteenth-century yard was the repair, maintenance and equipping of the fleet, for which the dry docks and basin were used). One slipway (1774) survives unaltered from this period (Slip No.1): a rare survival. It is covered with a timber superstructure of 1814, a similarly rare and early survival of its type; indeed, only three such timber slip covers have survived in Britain, two of them at Devonport (the second of these, of similar vintage, stands over the former No.5 Slip; it was later converted to house the Scrieve Board, for full-size drafting of ship designs). The two additional docks were added, north of the double-dock, in 1762 and 1789 (both subsequently rebuilt).
 Before the expansion could begin, a rocky hillside to the south had to be cut away; the rubble was used to reclaim the mudflats ready for building. To open up the site, the old ropehouse was demolished and a new rope-making complex built alongside the east perimeter wall of the expanded site (where it still survives in part, albeit rebuilt following a fire in 1812). Where the old ropehouse had stood a short canal known as the Camber was laid out, terminating in a
Before the expansion could begin, a rocky hillside to the south had to be cut away; the rubble was used to reclaim the mudflats ready for building. To open up the site, the old ropehouse was demolished and a new rope-making complex built alongside the east perimeter wall of the expanded site (where it still survives in part, albeit rebuilt following a fire in 1812). Where the old ropehouse had stood a short canal known as the Camber was laid out, terminating in a boat
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size, shape, cargo or passenger capacity, or its ability to carry boats.
Small boats are typically found on i ...
basin with a boathouse. On the New Ground to the south a new smithery was constructed, in 1776, containing 48 forges; though subsequently rebuilt it too still stands, the earliest surviving smithery in any royal dockyard. Initially used for the manufacture of anchors and smaller metal items, it would later be expanded to fashion the iron braces with which wooden hulls and decks began to be strengthened; as such, it provided a hint of the huge change in manufacturing technology that would sweep the dockyards in the nineteenth century as sail began to make way for steam, and wood for iron and steel.
The most imposing building of this period was a double-quadrangular storehouse of 1761 (probably designed by Thomas Slade); replacing the Dummer's storehouse, it also incorporated a new rigging house and sail loft. It remained in use until it was destroyed in the Plymouth Blitz
The Plymouth Blitz was a series of bombing raids carried out by the Nazi German ''Luftwaffe'' on the English city of Plymouth in the Second World War. The bombings launched on numerous British cities were known as the Blitz.
The royal doc ...
; the same fate befell several other buildings of the 18th and early 19th century, including the long and prominent pedimented workshop with its central clocktower, built to accommodate a range of woodworkers and craftsmen, the adjacent pedimented dockyard offices and Edward Holl
Edward Holl was an architect to the Navy Board, then later Surveyor of Buildings (Royal Navy), Surveyor of Buildings to the Board of Admiralty of the Royal Navy.
His father is presumed to be Edward Holl, a stonemason from Beccles in Suffolk, who ...
's replacement Dockyard Church of 1814.
 The dockyard suffered severe damage in a large-scale fire on 25 September 1840, it started in the North Dock on and were completely gutted, threatened , and spread to nearby buildings and equipment. Estimates for the damage were put at £150,000 in the values of the day, and would have totalled £500,000 had the fire not been contained by demolishing several surrounding buildings.
Despite significant damage during the blitz, the South Yard still contains four scheduled monuments and over thirty listed buildings and structures (though some of these have been allowed to fall into a derelict state in recent years: the 18th-century South Sawmills and South
The dockyard suffered severe damage in a large-scale fire on 25 September 1840, it started in the North Dock on and were completely gutted, threatened , and spread to nearby buildings and equipment. Estimates for the damage were put at £150,000 in the values of the day, and would have totalled £500,000 had the fire not been contained by demolishing several surrounding buildings.
Despite significant damage during the blitz, the South Yard still contains four scheduled monuments and over thirty listed buildings and structures (though some of these have been allowed to fall into a derelict state in recent years: the 18th-century South Sawmills and South Smithery
A metalsmith or simply smith is a craftsperson fashioning useful items (for example, tools, kitchenware, tableware, jewelry, armor and weapons) out of various metals. Smithing is one of the oldest metalworking occupations. Shaping metal w ...
are both on the Heritage at Risk Register). In the space between the new slips and the new ropehouse, south of the boat pond, was a sizeable mast pond, flanked by mast-houses.
Morice Yard (New Gun Wharf)
 Provision of ships' armaments was not the responsibility of the Navy but of the independent Board of Ordnance, which already had a wharf and storage facility in the Mount Wise area of Plymouth. This, however, began to prove insufficient and in 1719 the board established a new gun wharf on land leased from one Sir Nicholas Morice, immediately to the north of the established Dockyard. The Morice Yard was a self-contained establishment with its own complex of workshops, workers, officers, offices and storehouses. Gunpowder was stored on site, which began to be a cause for concern among local residents (as was the older store in the Royal Citadel within the city of Plymouth). In time new gunpowder magazines were built further north, first at Keyham (1770s), but later (having to make way for further dockyard expansion) relocating to Bull Point (1850).
In contrast to South Yard, which fared badly in the Blitz, most of the original buildings survive at Morice Yard, enclosed behind their contemporary boundary wall; over a dozen of these are listed. On higher ground behind the wharf itself is a contemporary terrace of houses for officers (1720), built from stone rubble excavated during the yard's construction.
Morice Ordnance Yard remained independent from the dockyard until 1941, at which point it was integrated into the larger complex.
Provision of ships' armaments was not the responsibility of the Navy but of the independent Board of Ordnance, which already had a wharf and storage facility in the Mount Wise area of Plymouth. This, however, began to prove insufficient and in 1719 the board established a new gun wharf on land leased from one Sir Nicholas Morice, immediately to the north of the established Dockyard. The Morice Yard was a self-contained establishment with its own complex of workshops, workers, officers, offices and storehouses. Gunpowder was stored on site, which began to be a cause for concern among local residents (as was the older store in the Royal Citadel within the city of Plymouth). In time new gunpowder magazines were built further north, first at Keyham (1770s), but later (having to make way for further dockyard expansion) relocating to Bull Point (1850).
In contrast to South Yard, which fared badly in the Blitz, most of the original buildings survive at Morice Yard, enclosed behind their contemporary boundary wall; over a dozen of these are listed. On higher ground behind the wharf itself is a contemporary terrace of houses for officers (1720), built from stone rubble excavated during the yard's construction.
Morice Ordnance Yard remained independent from the dockyard until 1941, at which point it was integrated into the larger complex.
The Devonport Lines
 In 1758, the Plymouth and Portsmouth Fortifications Act provided the means to construct a permanent landward defence for the dockyard complex. The Devonport Lines were a bastion fortification which consisted of an earthen rampart with a wide ditch and a
In 1758, the Plymouth and Portsmouth Fortifications Act provided the means to construct a permanent landward defence for the dockyard complex. The Devonport Lines were a bastion fortification which consisted of an earthen rampart with a wide ditch and a glacis
A glacis (; ) in military engineering is an artificial slope as part of a medieval castle or in bastion fort, early modern fortresses. They may be constructed of earth as a temporary structure or of stone in more permanent structure. More genera ...
. The lines ran from Morice Yard on the River Tamar, enclosing the whole dockyard and town, finally meeting the river again at Stonehouse Pool, a total distance of 2,000 yards (1,800 metres). There were four bastions, Marlborough Bastion to the north, Granby Bastion to the north-east, Stoke Bastion to the east and George Bastion to the south east. There were originally two gates in the lines, the Stoke Barrier at the end of Fore Street and the Stonehouse Barrier. A third gate called New Passage was created in the 1780s, giving access to the Torpoint Ferry. After 1860, the fortifications were superseded by the Palmerston Forts around Plymouth and the land occupied by the lines was either sold or utilised by the dockyard.
Keyham (the North Yard)
 At Devonport, in 1864, a separate, purpose-built steam yard was opened on a self-contained site at Keyham, just to the north of Morice Yard (and a tunnel was built linking the new yard with the old). A pair of basins (8–9 acres each) were constructed: No. 2 Basin gave access to three large dry-docks, while No. 3 Basin was the frontispiece to a huge integrated manufacturing complex. This became known as the Quadrangle: it housed foundries, forges, pattern shops, boilermakers and all manner of specialized workshops. Two stationary steam engines drove line shafts and heavy machinery, and the multiple flues were drawn by a pair of prominent chimneys. The building still stands, and is
At Devonport, in 1864, a separate, purpose-built steam yard was opened on a self-contained site at Keyham, just to the north of Morice Yard (and a tunnel was built linking the new yard with the old). A pair of basins (8–9 acres each) were constructed: No. 2 Basin gave access to three large dry-docks, while No. 3 Basin was the frontispiece to a huge integrated manufacturing complex. This became known as the Quadrangle: it housed foundries, forges, pattern shops, boilermakers and all manner of specialized workshops. Two stationary steam engines drove line shafts and heavy machinery, and the multiple flues were drawn by a pair of prominent chimneys. The building still stands, and is Grade I listed
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
; architectural detailing was by Sir Charles Barry
Sir Charles Barry (23 May 1795 – 12 May 1860) was a British architect, best known for his role in the rebuilding of the Palace of Westminster (also known as the Houses of Parliament) in London during the mid-19th century, but also responsi ...
. English Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, medieval castles, Roman forts and country houses.
The charity states that i ...
calls it 'one of the most remarkable engineering buildings in the country'. The three dry docks were rebuilt, expanded and covered over in the 1970s to serve as the Frigate Refit Centre.
 In 1880 a Royal Naval Engineering College was established at Keyham, housed in a new building just outside the dockyard wall alongside the Quadrangle where students (who joined at 15 years of age) gained hands-on experience of the latest naval engineering techniques. The Engineering College moved to nearby Manadon in 1958; the
In 1880 a Royal Naval Engineering College was established at Keyham, housed in a new building just outside the dockyard wall alongside the Quadrangle where students (who joined at 15 years of age) gained hands-on experience of the latest naval engineering techniques. The Engineering College moved to nearby Manadon in 1958; the Jacobethan
The Jacobethan or Jacobean Revival architectural style is the mixed national Renaissance revival style that was made popular in England from the late 1820s, which derived most of its inspiration and its repertory from the English Renaissance (15 ...
-style building then went on to house the Dockyard Technical College for a time, but was demolished in 1985.
 In 1895 the decision was taken to expand the Keyham Steam Yard to accommodate the increasing size of modern warships. By 1907 Keyham, now renamed the North Yard, had more than doubled in size with the addition of No. 4 and No. 5 Basins (of 10 and 35 acres respectively), linked by a very large lock-cum-dock, 730 ft in length, alongside three more dry-docks of a similar size, able to "accommodate ships larger than any war-vessel yet constructed". In the 1970s the northern end of No. 5 Basin was converted to serve as a new Fleet Maintenance Base, to be built alongside a Submarine Refit Complex for nuclear submarines; an 80-ton cantilever crane, one of the largest in western Europe, was installed to lift nuclear cores from submarines in newly built adjacent dry docks.
Further north still, Weston Mill Lake (at one time Devonport's coaling yard) was converted in the 1980s to provide frigate berths for the Type 22 fleet. It is now where the Navy's amphibious warfare ships are based. In 2013 a new
In 1895 the decision was taken to expand the Keyham Steam Yard to accommodate the increasing size of modern warships. By 1907 Keyham, now renamed the North Yard, had more than doubled in size with the addition of No. 4 and No. 5 Basins (of 10 and 35 acres respectively), linked by a very large lock-cum-dock, 730 ft in length, alongside three more dry-docks of a similar size, able to "accommodate ships larger than any war-vessel yet constructed". In the 1970s the northern end of No. 5 Basin was converted to serve as a new Fleet Maintenance Base, to be built alongside a Submarine Refit Complex for nuclear submarines; an 80-ton cantilever crane, one of the largest in western Europe, was installed to lift nuclear cores from submarines in newly built adjacent dry docks.
Further north still, Weston Mill Lake (at one time Devonport's coaling yard) was converted in the 1980s to provide frigate berths for the Type 22 fleet. It is now where the Navy's amphibious warfare ships are based. In 2013 a new Royal Marines
The Corps of Royal Marines (RM), also known as the Royal Marines Commandos, are the UK's special operations capable commando force, amphibious light infantry and also one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy. The Corps of Royal Marine ...
base, RM Tamar, was opened alongside; as well as serving as headquarters for 1 Assault Group Royal Marines
47 Commando (Raiding Group) Royal Marines, formerly 1 Assault Group Royal Marines (2001-2019), provides the Royal Marines expertise and training in small boat operations, both amphibious and riverine. In addition, it trains and parents the Assau ...
, it can accommodate marines, alongside their ships, prior to deployment.
In 2011 the MOD sold the freehold of the North Yard to the Dockyard operator, Babcock; the site includes six listed buildings and structures, among them the Grade I listed Quadrangle.
The naval barracks (HMS ''Drake'')

 Until the late nineteenth century, sailors whose ships were being repaired or refitted, or who were awaiting allocation to a vessel, were accommodated in floating
Until the late nineteenth century, sailors whose ships were being repaired or refitted, or who were awaiting allocation to a vessel, were accommodated in floating hulks
The Hulk is a superhero appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. Created by writer Stan Lee and artist Jack Kirby, the character first appeared in the debut issue of '' The Incredible Hulk'' (May 1962). In his comic book ...
. Construction of an onshore barracks, just north-east of the North Yard, was completed in 1889 with accommodation for 2,500; sailors and officers moved in during June of that year. In 1894 a contingent of sixty Royal Navy homing pigeons was accommodated on the site.
 The prominent clock tower was built in 1896, containing a clock and bell by Gillett & Johnston; it initially functioned as a semaphore tower. 1898 saw the barracks expand to accommodate a further 1,000 men. The wardroom block dates from this period. More buildings were added in the early years of the twentieth century, including St Nicholas's Church. This part of the site contains some fourteen listed buildings and structures.
The prominent clock tower was built in 1896, containing a clock and bell by Gillett & Johnston; it initially functioned as a semaphore tower. 1898 saw the barracks expand to accommodate a further 1,000 men. The wardroom block dates from this period. More buildings were added in the early years of the twentieth century, including St Nicholas's Church. This part of the site contains some fourteen listed buildings and structures.
Today
The Royal Navy Dockyard consists of fourteen dry docks (docks numbered 1 to 15, but there is no 13 Dock), four miles (6 km) of waterfront, twenty-five tidal berths, five basins and an area of . The dockyard employs 2,500 service personnel and civilians, supports circa 400 local firms and contributes approximately 10% to the income of Plymouth. It is the base for HMS ''Triumph'', one of two remaining nuclear-powered hunter-killer submarines. Since 2002, it has been the main refitting base for all Royal Navy nuclear submarines Work was completed by Carillion in 2002 to build a refitting dock to support the Trident missile nuclear ballistic missile submarines. Devonport serves as headquarters for the Flag Officer Sea Training, which is responsible for the training of all the ships of the Navy and Royal Fleet Auxiliary, along with many from foreign naval services. The nuclear submarine refit base was put into special measures in 2013 by the Office for Nuclear Regulation (ONR) and it could be 2020 before enhanced monitoring ceases. Safety concerns on ageing facilities, stretched resources and increasing demand are blamed for the measures.Devonport Flotilla
Ships based at the port are known as the Devonport Flotilla. This includes the Navy's assault ships and . It also serves as home port to most of the hydrographic surveying fleet of the Royal Navy and eight Type 23 frigates as of 2021. In 2018 the Defence Secretary announced that the proposed new Type 26 frigates would all be based at Devonport.Amphibious assault ships
 * HMS ''Albion'' landing platform dock;
* HMS ''Bulwark'' landing platform dock (Regeneration refit until 2023).
* HMS ''Albion'' landing platform dock;
* HMS ''Bulwark'' landing platform dock (Regeneration refit until 2023).
Type 23 frigates
''Trafalgar''-class submarines
 * (completed refit and returned to sea for post-refit trials December 2022)
* (completed refit and returned to sea for post-refit trials December 2022)
Surveying squadron
 *
*
*
*
*
*
Antarctic patrol ship
*Other units based at Devonport
* Flag Officer Sea Training * Hydrographic, Meteorological & Oceanographic Training Group * HQ Amphibious Task Group * RNR * RM Tamar/47 Commando (Raiding Group) Royal Marines
47 Commando (Raiding Group) Royal Marines, formerly 1 Assault Group Royal Marines (2001-2019), provides the Royal Marines expertise and training in small boat operations, both amphibious and riverine. In addition, it trains and parents the Assaul ...
** 10 Landing Craft Training Squadron
** 4 Assault Squadron
** 6 Assault Squadron
** 9 Assault Squadron
** 539 Assault Squadron
* Hasler NSRC (Naval Service Recovery Centre) & Hasler Company Royal Marines
* Southern Diving Group RN
* Defence Estates South West
* Ministry of Defence Police
South Yard redevelopment

 Several sections of the historic South Yard are no longer used by the Ministry of Defence, though it is still currently a closed site and subject to security restrictions.
The deep-water access it offers has made the site desirable for manufacturers of ' superyachts' and in 2012 Princess Yachts acquired the freehold to at the southern end, with a view to building a construction facility. The company asserts that this development will "continue the boat building tradition within the dockyard" and "add drama to the site with yachts being moved around the quayside, launched on No. 3 Slip, tested in No. 2 Slip and moored alongside the quay wall". The site includes within it several listed buildings and scheduled ancient monuments, most notably the
Several sections of the historic South Yard are no longer used by the Ministry of Defence, though it is still currently a closed site and subject to security restrictions.
The deep-water access it offers has made the site desirable for manufacturers of ' superyachts' and in 2012 Princess Yachts acquired the freehold to at the southern end, with a view to building a construction facility. The company asserts that this development will "continue the boat building tradition within the dockyard" and "add drama to the site with yachts being moved around the quayside, launched on No. 3 Slip, tested in No. 2 Slip and moored alongside the quay wall". The site includes within it several listed buildings and scheduled ancient monuments, most notably the Grade I listed
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
East Ropery, together with several other 18th-century buildings and structures associated with rope-making in the Yard, the covered slip (No. 1 Slip) and the 'King's Hill Gazebo', built to commemorate a visit by King George III.
In 2014 it was announced, as part of a 'City Deal' regeneration agreement, that the South Yard would be 'unlocked' with a view to it becoming a 'marine industries hub'. As of 2016 the northern section of the South Yard (including the 18th-century dry docks, Nos. 2, 3 & 4) was being redeveloped in phases, with a marketing strategy focused on 'the development of marine industries and the high growth area of marine science and technology'; it has been renamed Oceansgate.
Areas to the south and east (with the exception of the area now occupied by Princess Yachts) are being retained by the MOD, with No. 4 Slip having been recently refurbished for use with landing craft
Landing craft are small and medium seagoing watercraft, such as boats and barges, used to convey a landing force (infantry and vehicles) from the sea to the shore during an amphibious assault. The term excludes landing ships, which are larger. Pr ...
.
Museum
 The Devonport Naval Heritage Centre is a maritime museum in Devonport's Historic South Yard. Run by volunteers, it is only accessible for pre-booked tours, or on Naval Base open days. Plymouth Naval Base Museum opened in 1969 following an appeal from the office of the Admiral-superintendent for items of memorabilia and was housed in the Dockyard Fire Station. Since then, the museum has expanded and now occupies, in addition, the 18th-century Pay Office and Porter's Lodge. The Scrieve Board (Project Managed by PDM) currently serves as a museum store. Discussions were underway in 2014 around removing the museum from the Dockyard and displaying some of its collections within an expanded
The Devonport Naval Heritage Centre is a maritime museum in Devonport's Historic South Yard. Run by volunteers, it is only accessible for pre-booked tours, or on Naval Base open days. Plymouth Naval Base Museum opened in 1969 following an appeal from the office of the Admiral-superintendent for items of memorabilia and was housed in the Dockyard Fire Station. Since then, the museum has expanded and now occupies, in addition, the 18th-century Pay Office and Porter's Lodge. The Scrieve Board (Project Managed by PDM) currently serves as a museum store. Discussions were underway in 2014 around removing the museum from the Dockyard and displaying some of its collections within an expanded Plymouth City Museum and Art Gallery
The Box is a museum, gallery and archive in Plymouth, Devon, England, opened in 2020 housing a collection of about 2 million items. The core of the building was previously Plymouth City Museum and Art Gallery which closed in 2016. The building wa ...
.
The nuclear-powered submarine , used in the Falklands War, is preserved in North Yard as a museum ship
A museum ship, also called a memorial ship, is a ship that has been preserved and converted into a museum open to the public for educational or memorial purposes. Some are also used for training and recruitment purposes, mostly for the small numb ...
, managed by the Heritage Centre.
Nuclear submarine decommissioning
Thirteen out of service nuclear submarines were stored at Devonport in 2018. * * (preserved in North Yard as a museum ship) * * * * * * * * * * * In 2018, the UK Parliament's Public Accounts Committee criticised the slow rate of decommissioning of these submarines, with theMinistry of Defence
{{unsourced, date=February 2021
A ministry of defence or defense (see spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is an often-used name for the part of a government responsible for matters of defence, found in states ...
admitting that it had put off decommissioning due to the cost. The National Audit Office in 2019 stated that the costs of laid up storage of all nuclear submarines had reached £500 million, and they represent a liability of £7.5 billion.
Nickname
 The Naval base at Devonport is still nicknamed "Guzz" (or, sometimes, "Guz") by sailors and marines. One suggestion is that this originates from the word ''guzzle'' (to eat or drink greedily), which is likely to refer to the eating of
The Naval base at Devonport is still nicknamed "Guzz" (or, sometimes, "Guz") by sailors and marines. One suggestion is that this originates from the word ''guzzle'' (to eat or drink greedily), which is likely to refer to the eating of cream tea
A cream tea (also known as a Devon cream tea, Devonshire tea, or Cornish cream tea) is an afternoon tea consisting of tea, scones, clotted cream (or, less authentically, whipped cream), jam, and sometimes butter. Cream teas are sold in te ...
s, a West Country
The West Country (occasionally Westcountry) is a loosely defined area of South West England, usually taken to include all, some, or parts of the counties of Cornwall, Devon, Dorset, Somerset, Bristol, and, less commonly, Wiltshire, Glouce ...
delicacy and, therefore, one with strong connections to the area around Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymouth ...
. Another explanation advanced is that "GUZZ" was the radio call sign for the nearby Admiralty wireless station (which was GZX) at Devil's Point, though this is disputed and has recently been disproved by reference to actual wireless telegraphy callsigns in existence over the past century.
Another explanation is that the name came from the Hindi
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of North India, northern, Central India, centr ...
word for a yard (36 inches), " guz", (also spelled "guzz", at the time) which entered the Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a com ...
, and Royal Navy usage, in the late 19th century, as sailors used to regularly abbreviate "The Dockyard" to simply "The Yard", leading to the slang use of the Hindi word for the unit of measurement of the same name. The Plymouth Herald newspaper attempted to summarise the differing theories, but no firm conclusion was reached. Charles Causley referred to Guz in one of his poems, "Song of the Dying Gunner A.A.1", published in 1951.
A "tiddy oggy" is naval slang for a Cornish Pasty and which was once the nickname for a sailor born and bred in Devonport. The traditional shout of " Oggy Oggy Oggy" was used to cheer on the Devonport team in the Navy's field gun competition.
Nuclear waste leaks
Devonport has been the site of a number of leaks of nuclear waste associated with the nuclear submarines based there. * November 2002: "Ten litres of radioactive coolant leaked from ''" * October 2005: "Previous reported radioactive spills at the dockyard include one in October 2005, when it was confirmed 10 litres of water leaked out as the main reactor circuit of HMS ''Victorious'' was being cleaned to reduce radiation." * November 2008: "The Royal Navy has confirmed up to 280 litres of water, likely to have been contaminated with tritium, poured from a burst hose as it was being pumped from the submarine in the early hours of Friday." * March 2009: "On 25 March radioactive water escaped from HMS ''Turbulent'' while the reactor's discharge system was being flushed at the Devonport naval dockyard"Administration
Commissioners of the Navy
Up until 1832 the Plymouth Royal Dockyard, was administered by a Commissioner of the Navy on behalf of the Navy Board in London included:Resident Commissioners Plymouth
* CaptainHenry Greenhill
Henry Greenhill (21 June 1646 – 24 May 1708) was a British mariner, Governor of the Gold Coast, commissioner of the navy and Member of Parliament.
Early life
Greenhill was a son of John Greenhill, registrar of the diocese of Salisbury, and Pe ...
(appointed 25 December 1691)
* Captain George St Lo
George St Lo (sometimes written as St Loe; 19 April 1655 – 20 September 1718) was a British naval officer and politician.
An officer of the Royal Navy who saw service during the Nine Years' War, and the War of the Spanish Succession. His car ...
(appointed 26 March 1695)
* Captain William Wright (appointed 1 May 1703)
* Captain Henry Greenhill
Henry Greenhill (21 June 1646 – 24 May 1708) was a British mariner, Governor of the Gold Coast, commissioner of the navy and Member of Parliament.
Early life
Greenhill was a son of John Greenhill, registrar of the diocese of Salisbury, and Pe ...
(appointed February 1704)
* Captain William Wright (appointed 1 July 1708)
* Captain Richard Edwards (appointed 19 June 1711)
* Captain Sir William Jumper (appointed 12 November 1714)
* Captain Thomas Swanton (appointed 30 March 1715)
* Captain Francis Dove (appointed 23 July 1716)
* Captain Sir Nicholas Trevanion (appointed 22 April 1726)
* Captain Matthew Morris (appointed 9 December 1737)
* Captain Philip Vanbrugh (appointed 8 January 1738)
* Captain Sir Frederick Rogers (appointed 3 October 1753)
* Mr Edward Le Cras (appointed December 1782)
* Captain Sir John Laforey (appointed 6 May 1784)
* Captain Robert Fanshawe (appointed 13 November 1789)
* Captain William Shield (appointed 12 December 1815 – 1822)
Resident Commissioners Devonport
* Captain William Shield, 1823–1828 * Captain Charles B H Ross, appointed 13 March 1829. By An Order in Council dated 27 June 1832 the role of the commissioner was replaced by an admiral-superintendent.Admiral Superintendents of the yard
In 1832 the Navy Board was abolished, everything except the gun wharves were brought under the direct control of the Admiralty. A serving Royal Navy officer, usually of rear-admiral rank, was appointed as admiral-superintendent of the dockyard; however, the post was sometimes held by a commodore-superintendent or even a vice-admiral. They were responsible for all the civilian support services operated by the dockyard departments. Included: * Rear-Admiral Sir Samuel Pym (appointed 16 December 1841) * Rear-Admiral Sir John Louis (appointed 16 December 1846) * Commodore Lord John Hay (appointed 9 February 1850) * Commodore Michael Seymour (appointed 8 September 1851) * Rear-Admiral Hon. Montagu Stopford (appointed 21 March 1854) * Rear-Admiral Henry Eden (appointed 4 August 1854) * Rear-Admiral Michael Seymour (appointed 12 December 1854) * Rear-Admiral Sir James Hanway Plumridge (appointed 19 February 1855) * Rear-Admiral Sir Thomas Sabine Pasley (appointed 4 December 1857) * Rear-AdmiralThomas Matthew Charles Symonds
Admiral of the Fleet Sir Thomas Matthew Charles Symonds, GCB (31 October 1811 – 14 November 1894) was a Royal Navy officer. He was commanding officer of which participated in the bombardment of Sevastopol during the Crimean War.
Symonds b ...
(appointed 1 December 1862)
* Vice-Admiral Hon. James Robert Drummond (appointed 24 April 1866)
* Rear-Admiral William Houston Stewart (appointed 5 June 1870)
* Vice-Admiral Sir William King-Hall (appointed 20 November 1871)
* Rear-Admiral William Charles Chamberlain (appointed 5 August 1875)
* Rear-Admiral George Ommanney Willes
Admiral Sir George Ommanney Willes (19 June 1823 – 18 February 1901) was a Royal Navy officer who went on to be Commander-in-Chief, Portsmouth.
Early life
Born at Hythe, Hampshire in 1823, Willes was the son of Captain George Willes, RN, by ...
(appointed 1 May 1876)
* Rear-Admiral Charles Webley Hope (appointed 1 February 1879)
* Rear-Admiral Charles Thomas Curme
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was "f ...
(appointed 20 February 1880)
* Rear-Admiral John Crawford Wilson (appointed 23 February 1885)
* Vice-Admiral Henry Duncan Grant
Henry may refer to:
People
*Henry (given name)
*Henry (surname)
* Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry
Royalty
* Portuguese royalty
** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal
** Henry, Count of Portugal, ...
(appointed 10 July 1885)
* Vice-Admiral Sir Walter James Hunt-Grubbe (appointed 1 August 1888)
* Rear-Admiral Sir Robert Henry More Molyneux (appointed 4 August 1891)
* Rear-Admiral Edmund John Church
Edmund is a masculine given name or surname in the English language. The name is derived from the Old English elements ''ēad'', meaning "prosperity" or "riches", and ''mund'', meaning "protector".
Persons named Edmund include:
People Kings and ...
(appointed 7 August 1894)
* Rear-Admiral Henry John Carr (appointed 3 November 1896)
* Vice-Admiral Sir Thomas Sturges Jackson (appointed 7 July 1899)
* Rear-Admiral William Hanam Henderson
William is a masculine given name of Norman French origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conqu ...
(appointed 11 July 1902 – made Vice-Admiral while in post, 1904)
* Vice-Admiral Charles James Barlow
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was ...
(appointed 31 March 1906)
* Vice-Admiral Charles Henry Cross
Admiral Charles Henry Cross (18 May 1852 – 1 January 1915) was a Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the f ...
(appointed 31 March 1908)
* Vice-Admiral Robert Henry Simpson Stokes
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honou ...
(appointed 4 October 1910)
* Rear-Admiral Godfrey Harry Brydges Mundy Godfrey may refer to:
People
* Godfrey (name), a given name and surname
* Godfrey (comedian), American comedian, actor
Places In the United States
* Godfrey, Georgia, an unincorporated community
* Godfrey, Illinois, a village
* Godfrey, Kansas ...
(appointed 11 December 1913)
* Rear-Admiral Sir Arthur Henniker-Hughan (appointed 18 December 1916)
* Rear-Admiral Edwin Veale Underhill (appointed 1 September 1919)
* Rear-Admiral Hugh Lindsay Patrick Heard (appointed 20 September 1922)
* Vice-Admiral Louis Charles Stirling Woollcombe Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
Derived or associated terms
* Lew ...
(appointed 1 November 1926)
* Vice-Admiral Oliver Backhouse
Admiral Oliver Backhouse, CB (5 June 1875 – 25 March 1943) was a Royal Navy officer.
Backhouse was the son of the banker Sir Jonathan Backhouse, 1st Baronet, and the younger brother of Sir Edmund Backhouse, 2nd Baronet
Sir Edmund Trelawny ...
(appointed 1 March 1927 and re-appointed 10 October 1929)
* Vice-Admiral Harold Owen Reinold
Harold may refer to:
People
* Harold (given name), including a list of persons and fictional characters with the name
* Harold (surname), surname in the English language
* András Arató, known in meme culture as "Hide the Pain Harold"
Arts a ...
(appointed 2 March 1931)
* Vice-Admiral Arthur Lionel Snagge
Vice-Admiral Arthur Lionel Snagge, CB (4 May 1878 - 1955) was a Royal Navy officer who was Admiral-Superintendent of Devonport Dockyard.
Naval career
Snagge entered the Royal Navy as an acting sub-lieutenant on 15 August 1898, and was confirme ...
(appointed 1935)
* Vice-Admiral Arthur Ninian Dowding
Arthur is a common male given name of Brythonic origin. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero King Arthur. The etymology is disputed. It may derive from the Celtic ''Artos'' meaning “Bear”. Another theory, more wi ...
(appointed 27 September 1938)
* Vice-Admiral Randolph Stewart Gresham Nicholson (appointed 18 December 1945)
* Admiral Philip King Enright (appointed 6 February 1950)
* Vice-Admiral Leslie Newton Brownfield
Leslie may refer to:
* Leslie (name), a name and list of people with the given name or surname, including fictional characters
Families
* Clan Leslie, a Scottish clan with the motto "grip fast"
* Leslie (Russian nobility), a Russian noble family ...
(appointed 31 March 1954)
* Vice-Admiral Lancelot Arthur Babington Peile
Lancelot du Lac (French for Lancelot of the Lake), also written as Launcelot and other variants (such as early German ''Lanzelet'', early French ''Lanselos'', early Welsh ''Lanslod Lak'', Italian ''Lancillotto'', Spanish ''Lanzarote del Lago' ...
(appointed November 1957)
* Vice-Admiral George David Archibald Gregory (appointed 29 September 1960)
* Rear-Admiral A J Cawthra (appointed 2 April 1964)
* Rear-Admiral Denis Bryan Harvey "Dick" Wildish (appointed 26 October 1966 until May 1970)
On 30 December 1970, Vice-Admiral J R McKaig was appointed as Port Admiral, His Majesty's Naval Base, Devonport, and Flag Officer, Plymouth. On 5 September 1971, all Flag Officers of the Royal Navy holding positions of Admiral Superintendents at Royal Dockyards were restyled as Port Admirals.
Port Admiral Devonport and Flag Officer Plymouth
Post holders included: * Vice-Admiral Sir Rae McKaig (December 1970 – March 1973) * Vice-Admiral Sir Arthur Power (March 1973 – February 1975) * Vice-Admiral Sir Gordon Tait (February 1975 – January 1977) * Vice-Admiral Sir John Forbes (January 1977 – January 1979) * Vice-Admiral Sir Peter Berger (January 1979 – February 1981) * Vice-Admiral Sir Simon Cassels (February 1981 – September 1982) * Vice-Admiral Sir David Brown (September 1982 – 1985) * Vice-Admiral Sir Robert Gerken (September 1985 – March 1987) * Vice-Admiral Sir John Webster (March 1987 – April 1990) * Vice-Admiral Sir Alan Grose (April 1990 – September 1992) * Vice-Admiral Sir Roy Newman (September 1992 – 1996)Associated establishments nearby
Several establishments were set up in the vicinity of Devonport and Plymouth in direct relationship either to the Royal Dockyard or to Plymouth's use as a base for the Fleet, including: * Royal Citadel, Plymouth (1665), built to defend the harbour and anchorage, currently the base of29 Commando Regiment
29 Commando Regiment, Royal Artillery is the Commando-trained unit of the British Army's Royal Artillery, based in Plymouth. The regiment is under the operational control of 3 Commando Brigade, to which it provides artillery support and gunnery ...
, Royal Artillery.
* Dockyard defences, including Devonport Lines (1758) and the later Palmerston Forts, Plymouth
* Royal Naval Hospital, Stonehouse
The Royal Naval Hospital, Stonehouse was a medical facility for naval officers and other ranks at Stonehouse, Plymouth.
History
The naval hospital was built between 1758 and 1765 to a design by the little-known Alexander Rovehead. The design was ...
(1760, closed 1995)
* Stonehouse Barracks (1779), headquarters of 3 Commando Brigade, Royal Marines
The Corps of Royal Marines (RM), also known as the Royal Marines Commandos, are the UK's special operations capable commando force, amphibious light infantry and also one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy. The Corps of Royal Marine ...
.
* Admiralty House, Mount Wise (1789), former headquarters of the Commander-in-Chief, Plymouth (together with the Second World War Combined Military Headquarters (later Plymouth Maritime Headquarters) it was decommissioned in 2004).
* Plymouth Breakwater (1812)
* Royal William Victualling Yard (1835) built by the Victualling Commissioners in nearby Stonehouse for supplying the Royal Navy (closed 1992 and converted into housing).
* HMS ''Raleigh'', RN basic training establishment, across the Hamoaze at Torpoint, Cornwall.
* RM Turnchapel
Royal Marines Turnchapel is a former Royal Marines military installation in South Devon located east of Plymouth, Devon, and north east of Torpoint, Cornwall, England.
History
The site was established as a shipyard in the 17th century and ...
, a former Royal Marines
The Corps of Royal Marines (RM), also known as the Royal Marines Commandos, are the UK's special operations capable commando force, amphibious light infantry and also one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy. The Corps of Royal Marine ...
military installation (decommissioned 2014).
References
Bibliography
*External links
*Devonport Naval Heritage Centre
{{DEFAULTSORT:Devonport Buildings and structures in Plymouth, Devon Royal Navy bases in England Royal Navy dockyards in England Tourist attractions in Plymouth, Devon Economy of Devon Trident (UK nuclear programme) Royal Navy submarine bases Industrial archaeological sites in Devon 1691 establishments in England