HIV Structure And Genome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The

 The complete sequence of the HIV-1 genome, extracted from infectious virions, has been solved to single-
The complete sequence of the HIV-1 genome, extracted from infectious virions, has been solved to single-
 HIV has several major genes coding for structural proteins that are found in all retroviruses as well as several nonstructural ("accessory") genes unique to HIV. The HIV genome contains nine genes that encode fifteen viral proteins. These are synthesized as polyproteins which produce proteins for virion interior, called Gag, group specific antigen; the viral enzymes (Pol, polymerase) or the glycoproteins of the virion ''env'' (envelope). In addition to these, HIV encodes for proteins which have certain regulatory and auxiliary functions as well. HIV-1 has two important regulatory elements: Tat and Rev and few important accessory proteins such as Nef, Vpr, Vif and Vpu which are not essential for replication in certain tissues. The ''gag'' gene provides the basic physical infrastructure of the virus, and ''pol'' provides the basic mechanism by which retroviruses reproduce, while the others help HIV to enter the host cell and enhance its reproduction. Though they may be altered by mutation, all of these genes except ''tev'' exist in all known variants of HIV; see Genetic variability of HIV.
HIV employs a sophisticated system of differential
HIV has several major genes coding for structural proteins that are found in all retroviruses as well as several nonstructural ("accessory") genes unique to HIV. The HIV genome contains nine genes that encode fifteen viral proteins. These are synthesized as polyproteins which produce proteins for virion interior, called Gag, group specific antigen; the viral enzymes (Pol, polymerase) or the glycoproteins of the virion ''env'' (envelope). In addition to these, HIV encodes for proteins which have certain regulatory and auxiliary functions as well. HIV-1 has two important regulatory elements: Tat and Rev and few important accessory proteins such as Nef, Vpr, Vif and Vpu which are not essential for replication in certain tissues. The ''gag'' gene provides the basic physical infrastructure of the virus, and ''pol'' provides the basic mechanism by which retroviruses reproduce, while the others help HIV to enter the host cell and enhance its reproduction. Though they may be altered by mutation, all of these genes except ''tev'' exist in all known variants of HIV; see Genetic variability of HIV.
HIV employs a sophisticated system of differential
 * ''
* ''
Rfam entry for HIV pol-1 stem loop
3D model of the complete HIV1 virion
* {{Viral proteins HIV/AIDS
genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
and proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
of HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune ...
(human immunodeficiency virus) have been the subject of extensive research since the discovery of the virus in 1983. "In the search for the causative agent, it was initially believed that the virus was a form of the Human T-cell leukemia virus
The primate T-lymphotropic viruses (PTLVs) are a group of retroviruses that infects primates, using their lymphocytes to reproduce. The ones that infect humans are known as human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV), and the ones that infect Old World mo ...
(HTLV), which was known at the time to affect the human immune system and cause certain leukemias. However, researchers at the Pasteur Institute
The Pasteur Institute (french: Institut Pasteur) is a French non-profit private foundation dedicated to the study of biology, micro-organisms, diseases, and vaccines. It is named after Louis Pasteur, who invented pasteurization and vaccines f ...
in Paris isolated a previously unknown and genetically distinct retrovirus
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase ...
in patients with AIDS which was later named HIV." Each virion
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ...
comprises a viral envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes.
Numerous human pathogenic viruses in circulation are encase ...
and associated matrix enclosing a capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may ...
, which itself encloses two copies of the single-stranded RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
genome and several enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s. The discovery of the virus itself occurred two years following the report of the first major cases of AIDS-associated illnesses.
Structure

 The complete sequence of the HIV-1 genome, extracted from infectious virions, has been solved to single-
The complete sequence of the HIV-1 genome, extracted from infectious virions, has been solved to single-nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules wi ...
resolution.
The HIV genome encodes a small number of viral protein
A viral protein is both a component and a product of a virus. Viral proteins are grouped according to their functions, and groups of viral proteins include structural proteins, nonstructural proteins, regulatory proteins, and accessory proteins. Vi ...
s, invariably establishing cooperative associations among HIV proteins and between HIV and host proteins, to invade host cell
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include a ...
s and hijack their internal machineries. HIV is different in structure from other retrovirus
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase ...
es. The HIV virion is ~100 nm in diameter. Its innermost region consists of a cone-shaped core
Core or cores may refer to:
Science and technology
* Core (anatomy), everything except the appendages
* Core (manufacturing), used in casting and molding
* Core (optical fiber), the signal-carrying portion of an optical fiber
* Core, the central ...
that includes two copies of the (positive sense) ssRNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
genome, the enzymes reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, ...
, integrase
Retroviral integrase (IN) is an enzyme produced by a retrovirus (such as HIV) that integrates—forms covalent links between—its genetic information into that of the host cell it infects. Retroviral INs are not to be confused with phage int ...
and protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
, some minor proteins, and the major core protein. The genome of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) encodes 8 viral proteins playing essential roles during the HIV life cycle.
HIV-1 is composed of two copies of noncovalently linked, unspliced, positive-sense
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context, ...
single-stranded RNA enclosed by a conical capsid composed of the viral protein p24, typical of lentivirus
''Lentivirus'' is a genus of retroviruses that cause chronic and deadly diseases characterized by long incubation periods, in humans and other mammalian species. The genus includes the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which causes AIDS. Lent ...
es.
The two copies of RNA strands are vital in contributing to HIV-1 recombination, which occurs during reverse transcription of viral replication. The containment of two copies of single-stranded RNA within a virion but the production of only a single DNA provirus is called pseudodiploidy. The RNA component is 9749 nucleotides
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules w ...
long and bears a 5’ cap (Gppp), a 3’ poly(A) tail
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In euk ...
, and many open reading frame
In molecular biology, open reading frames (ORFs) are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible readin ...
s (ORFs). Viral structural proteins are encoded by long ORFs, whereas smaller ORFs encode regulators of the viral life cycle: attachment, membrane fusion, replication, and assembly.
The single-strand RNA is tightly bound to p7 nucleocapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may ...
proteins, late assembly protein p6, and enzymes
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
essential to the development of the virion, such as reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, ...
and integrase
Retroviral integrase (IN) is an enzyme produced by a retrovirus (such as HIV) that integrates—forms covalent links between—its genetic information into that of the host cell it infects. Retroviral INs are not to be confused with phage int ...
. Lysine tRNA is the primer of the magnesium-dependent reverse transcriptase. The nucleocapsid associates with the genomic RNA (one molecule per hexamer) and protects the RNA from digestion by nuclease
A nuclease (also archaically known as nucleodepolymerase or polynucleotidase) is an enzyme capable of cleaving the phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides of nucleic acids. Nucleases variously effect single and double stranded breaks in their ta ...
s. Also enclosed within the virion particle are Vif, Vpr
Vpr is a Human immunodeficiency virus gene and protein product.
Vpr stands for "Viral Protein R". Vpr, a 96 amino acid 14-kDa protein, plays an important role in regulating nuclear import of the HIV-1 pre-integration complex, and is required for ...
, Nef, and viral protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
. The envelope
An envelope is a common packaging item, usually made of thin, flat material. It is designed to contain a flat object, such as a letter or card.
Traditional envelopes are made from sheets of paper cut to one of three shapes: a rhombus, a shor ...
of the virion is formed by a plasma membrane of host cell origin, which is supported by a matrix composed of the viral p17 protein, ensuring the integrity of the virion particle. At the surface of the virion can be found a limited number of the envelope glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycos ...
(Env) of HIV, a trimer formed by heterodimers of gp120
Envelope glycoprotein GP120 (or gp120) is a glycoprotein exposed on the surface of the HIV envelope. It was discovered by Professors Tun-Hou Lee and Myron "Max" Essex of the Harvard School of Public Health in 1988. The 120 in its name comes from ...
and gp41
Gp41 also known as glycoprotein 41 is a subunit of the envelope protein complex of retroviruses, including human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Gp41 is a transmembrane protein that contains several sites within its ectodomain that are required fo ...
. Env is responsible for binding to its primary host receptor, CD4, and its co-receptor (mainly CCR5
C-C chemokine receptor type 5, also known as CCR5 or CD195, is a protein on the surface of white blood cells that is involved in the immune system as it acts as a receptor for chemokines.
In humans, the ''CCR5'' gene that encodes the CCR5 pro ...
or CXCR4
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR-4) also known as fusin or CD184 (cluster of differentiation 184) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CXCR4'' gene. The protein is a CXC chemokine receptor.
Function
CXCR-4 is an alpha-chemokin ...
), leading to viral entry into its target cell.
As the only proteins on the surface of the virus, the envelope glycoproteins (gp120 and gp41) are the major targets for HIV vaccine
An HIV vaccine is a potential vaccine that could be either a preventive vaccine or a therapeutic vaccine, which means it would either protect individuals from being infected with HIV or treat HIV-infected individuals.
It is thought that an HIV v ...
efforts. Over half of the mass of the trimeric envelope spike is N-linked glycans. The density is high as the glycan
The terms glycans and polysaccharides are defined by IUPAC as synonyms meaning "compounds consisting of a large number of monosaccharides linked glycosidically". However, in practice the term glycan may also be used to refer to the carbohydrate p ...
s shield underlying viral protein from neutralisation by antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
. This is one of the most densely glycosylated
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or 'glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not alw ...
molecules known and the density is sufficiently high to prevent the normal maturation process of glycans during biogenesis in the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ( ...
and Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles ins ...
. The majority of the glycans are therefore stalled as immature 'high-mannose
Mannose is a sugar monomer of the aldohexose series of carbohydrates. It is a C-2 epimer of glucose. Mannose is important in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylation of certain proteins. Several congenital disorders of glycosylation ...
' glycans not normally present on secreted or cell surface human glycoproteins. The unusual processing and high density means that almost all broadly neutralising antibodies that have so far been identified (from a subset of patients that have been infected for many months to years) bind to or, are adapted to cope with, these envelope glycans.
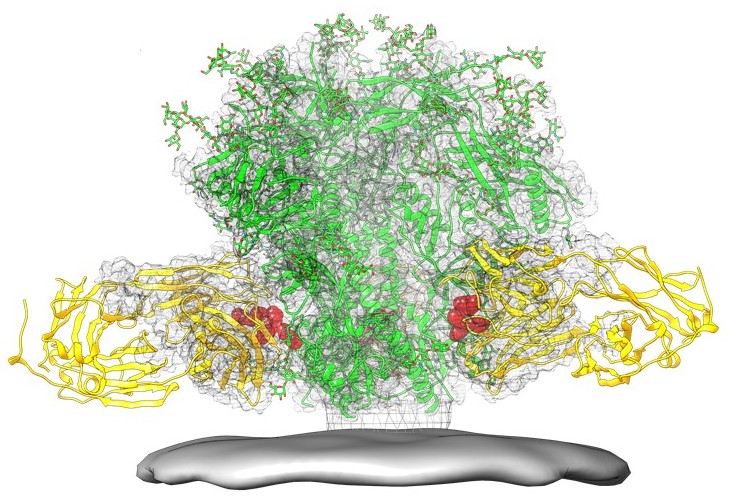
The molecular structure of the viral spike has now been determined by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
and cryo-electron microscopy
Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is a cryomicroscopy technique applied on samples cooled to cryogenic temperatures. For biological specimens, the structure is preserved by embedding in an environment of vitreous ice. An aqueous sample sol ...
. These advances in structural biology were made possible due to the development of stable recombinant forms of the viral spike by the introduction of an intersubunit disulphide bond
In biochemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) refers to a functional group with the structure . The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and is usually derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. In ...
and an isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprot ...
to proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the prot ...
mutation in gp41. The so-called SOSIP trimers not only reproduce the antigenic properties of the native viral spike but also display the same degree of immature glycans as presented on the native virus. Recombinant trimeric viral spikes are promising vaccine candidates as they display less non-neutralising epitope
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The epitope is the specific piece of the antigen to which an antibody binds. The p ...
s than recombinant monomeric gp120 which act to suppress the immune response to target epitopes.
Genome organization
 HIV has several major genes coding for structural proteins that are found in all retroviruses as well as several nonstructural ("accessory") genes unique to HIV. The HIV genome contains nine genes that encode fifteen viral proteins. These are synthesized as polyproteins which produce proteins for virion interior, called Gag, group specific antigen; the viral enzymes (Pol, polymerase) or the glycoproteins of the virion ''env'' (envelope). In addition to these, HIV encodes for proteins which have certain regulatory and auxiliary functions as well. HIV-1 has two important regulatory elements: Tat and Rev and few important accessory proteins such as Nef, Vpr, Vif and Vpu which are not essential for replication in certain tissues. The ''gag'' gene provides the basic physical infrastructure of the virus, and ''pol'' provides the basic mechanism by which retroviruses reproduce, while the others help HIV to enter the host cell and enhance its reproduction. Though they may be altered by mutation, all of these genes except ''tev'' exist in all known variants of HIV; see Genetic variability of HIV.
HIV employs a sophisticated system of differential
HIV has several major genes coding for structural proteins that are found in all retroviruses as well as several nonstructural ("accessory") genes unique to HIV. The HIV genome contains nine genes that encode fifteen viral proteins. These are synthesized as polyproteins which produce proteins for virion interior, called Gag, group specific antigen; the viral enzymes (Pol, polymerase) or the glycoproteins of the virion ''env'' (envelope). In addition to these, HIV encodes for proteins which have certain regulatory and auxiliary functions as well. HIV-1 has two important regulatory elements: Tat and Rev and few important accessory proteins such as Nef, Vpr, Vif and Vpu which are not essential for replication in certain tissues. The ''gag'' gene provides the basic physical infrastructure of the virus, and ''pol'' provides the basic mechanism by which retroviruses reproduce, while the others help HIV to enter the host cell and enhance its reproduction. Though they may be altered by mutation, all of these genes except ''tev'' exist in all known variants of HIV; see Genetic variability of HIV.
HIV employs a sophisticated system of differential RNA splicing
RNA splicing is a process in molecular biology where a newly-made precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) transcript is transformed into a mature messenger RNA (mRNA). It works by removing all the introns (non-coding regions of RNA) and ''splicing'' b ...
to obtain nine different gene products from a less than 10kb genome. HIV has a 9.2kb unspliced genomic transcript which encodes for gag and pol precursors; a singly spliced, 4.5 kb encoding for env, Vif, Vpr and Vpu and a multiply spliced, 2 kb mRNA encoding for Tat, Rev and Nef.
Viral structural proteins
 * ''
* ''gag
A gag is usually an item or device designed to prevent speech, often as a restraint device to stop the subject from calling for help and keep its wearer silent. This is usually done by blocking the mouth, partially or completely, or attempting ...
'' (group-specific antigen) codes for the precursor gag polyprotein
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called protease ...
which is processed by viral protease during maturation to MA (matrix protein
Viral matrix proteins are structural proteins linking the viral envelope with the virus core. They play a crucial role in virus assembly, and interact with the RNP complex as well as with the viral membrane. They are found in many enveloped viruses ...
, p17); CA (capsid protein, p24); SP1 (spacer peptide 1, p2); NC ( nucleocapsid protein, p7); SP2 (spacer peptide 2, p1) and P6 protein.
* '' pol'' codes for viral enzymes reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, ...
(RT) and RNase H
Ribonuclease H (abbreviated RNase H or RNH) is a family of non-sequence-specific endonuclease enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of RNA in an RNA/ DNA substrate via a hydrolytic mechanism. Members of the RNase H family can be found in nearly a ...
, integrase
Retroviral integrase (IN) is an enzyme produced by a retrovirus (such as HIV) that integrates—forms covalent links between—its genetic information into that of the host cell it infects. Retroviral INs are not to be confused with phage int ...
(IN), and HIV protease
HIV-1 protease (PR) is a retroviral aspartyl protease (retropepsin), an enzyme involved with peptide bond hydrolysis in retroviruses, that is essential for the life-cycle of HIV, the retrovirus that causes AIDS. HIV protease cleaves newly synthesi ...
(PR). HIV protease is required to cleave the precursor Gag polyprotein to produce structural proteins, RT is required to transcribe DNA from RNA template, and IN is necessary to integrate the double-stranded viral DNA into the host genome.
* ''env
env is a shell command for Unix and Unix-like operating systems. It is used to either print a list of environment variables or run another utility in an altered environment without having to modify the currently existing environment. Using env, ...
'' (for "envelope") codes for gp160
''Env'' is a viral gene that encodes the protein forming the viral envelope. The expression of the ''env'' gene enables retroviruses to target and attach to specific cell types, and to infiltrate the target cell membrane.
Analysis of the structure ...
, which is cleaved by a host protease, furin
Furin is a protease, a proteolytic enzyme that in humans and other animals is encoded by the ''FURIN'' gene. Some proteins are inactive when they are first synthesized, and must have sections removed in order to become active. Furin cleaves these s ...
, within the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ( ...
of the host cell. The post-translational processing produces a surface glycoprotein, gp120
Envelope glycoprotein GP120 (or gp120) is a glycoprotein exposed on the surface of the HIV envelope. It was discovered by Professors Tun-Hou Lee and Myron "Max" Essex of the Harvard School of Public Health in 1988. The 120 in its name comes from ...
or SU, which attaches to the CD4
In molecular biology, CD4 (cluster of differentiation 4) is a glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). CD4 is found on the surface of immune cells such as T helper cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic ...
receptors present on lymphocytes, and gp41
Gp41 also known as glycoprotein 41 is a subunit of the envelope protein complex of retroviruses, including human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Gp41 is a transmembrane protein that contains several sites within its ectodomain that are required fo ...
or TM, which embeds in the viral envelope to enable the virus to attach to and fuse with target cells.
Essential regulatory elements
* '' tat'' (HIV trans-activator) plays an important role in regulating the reverse transcription of viral genome RNA, ensuring efficient synthesis of viral mRNAs and regulating the release of virions from infected cells. Tat is expressed as 72-amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
one-exon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequen ...
Tat as well as the 86–101-amino-acid two-exon Tat, and plays an important role early in HIV infection. Tat (14–15kDa) binds to the bulged genomic RNA stem-loop
Stem-loop intramolecular base pairing is a pattern that can occur in single-stranded RNA. The structure is also known as a hairpin or hairpin loop. It occurs when two regions of the same strand, usually complementary in nucleotide sequence when ...
secondary structure near the 5' LTR region forming the trans-activation response element (TAR)
The HIV trans-activation response (TAR) element is an RNA element which is known to be required for the trans-activation of the viral promoter and for virus replication. The TAR hairpin is a dynamic structure that acts as a binding site for the ...
.
* ''rev
Rev or Rév may refer to:
Abbreviations Rev.
* Rev., an abbreviation for revolution, as in Revolutions per minute
* Rev., an abbreviation for the religious style The Reverend
* Rev., the abbreviation for Runtime Revolution, a development environ ...
'' (regulator of expression of virion proteins): The Rev protein binds to the viral genome via an arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the am ...
-rich RNA-binding motif that also acts as a NLS (nuclear localization signal A nuclear localization signal ''or'' sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines o ...
s), required for the transport of Rev to the nucleus from cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells (intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
during viral replication. Rev recognizes a complex stem-loop structure of the mRNA ''env'' located in the intron
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gene. ...
separating coding exon of Tat and Rev, known as the HIV Rev response element The HIV-1 Rev response element (RRE) is a highly structured, ~350 nucleotide RNA segment present in the Env coding region of unspliced and partially spliced viral mRNAs. In the presence of the HIV-1 accessory protein Rev, HIV-1 mRNAs that contain ...
(RRE). Rev is important for the synthesis of major viral proteins and is hence essential for viral replication
Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome an ...
.
Accessory regulatory proteins
* ''vpr
Vpr is a Human immunodeficiency virus gene and protein product.
Vpr stands for "Viral Protein R". Vpr, a 96 amino acid 14-kDa protein, plays an important role in regulating nuclear import of the HIV-1 pre-integration complex, and is required for ...
'' (lentivirus
''Lentivirus'' is a genus of retroviruses that cause chronic and deadly diseases characterized by long incubation periods, in humans and other mammalian species. The genus includes the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which causes AIDS. Lent ...
protein R): Vpr is a virion-associated, nucleocytoplasmic shuttling regulatory protein
Regulation of gene expression, or gene regulation, includes a wide range of mechanisms that are used by cells to increase or decrease the production of specific gene products (protein or RNA). Sophisticated programs of gene expression are wide ...
. It is believed to play an important role in replication of the virus, specifically, nuclear import A nuclear localization signal ''or'' sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines o ...
of the preintegration complex. Vpr also appears to cause its host cells to arrest their cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subs ...
in the G2 phase
G2 phase, Gap 2 phase, or Growth 2 phase, is the third subphase of interphase in the cell cycle directly preceding mitosis. It follows the successful completion of S phase, during which the cell’s DNA is replicated. G2 phase ends with the o ...
. This arrest activates the host DNA repair machinery which may enable integration of the viral DNA. HIV-2
The subtypes of HIV include two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to viruses found in chimpanzees and gorillas living in western Africa, while HIV-2 viruses are related to viruses found in the sooty mangabey, ...
and SIV encode an additional Vpr related protein called Vpx which functions in association with Vpr.
* '' vif'' - Vif is a highly conserved, 23 kDa phosphoprotein
A phosphoprotein is a protein that is posttranslationally modified by the attachment of either a single phosphate group, or a complex molecule such as 5'-phospho-DNA, through a phosphate group. The target amino acid is most often serine, threonin ...
important for the infectivity of HIV-1 virions depending on the cell type. HIV-1 has been found to require Vif to synthesize infectious viruses in lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adap ...
, macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
, and certain human cell line
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. The term "tissue culture" was coined by American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows. This te ...
s. It does not appear to require Vif for the same process in HeLa
HeLa (; also Hela or hela) is an immortalized cell line used in scientific research. It is the oldest and most commonly used human cell line. The line is derived from cervical cancer cells taken on February 8, 1951, named after Henrietta La ...
cells or COS cells
COS are fibroblast-like cell lines derived from monkey kidney tissue. COS cells are obtained by immortalizing CV-1 cells with a version of the SV40 virus that can produce large T antigen but has a defect in genomic replication. The CV-1 cell line ...
, among others.
* '' nef''- Nef, negative factor, is a N-terminal myristoylated
Myristoylation is a lipidation modification where a myristoyl group, derived from myristic acid, is covalently attached by an amide bond to the alpha-amino group of an N-terminal glycine residue. Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty ac ...
membrane-associated phosphoprotein. It is involved in multiple functions during the replication cycle of the virus. It is believed to play an important role in cell apoptosis and increase virus infectivity
In epidemiology, infectivity is the ability of a pathogen to establish an infection. More specifically, infectivity is a pathogen's capacity for horizontal transmission — that is, how frequently it spreads among hosts that are not in a parent� ...
.
* ''vpu
VPU may refer to:
Technology
* Video processing unit and visual processing unit, related to graphics processing units
* Vision processing unit, a class of processor intended for accelerating machine vision tasks
* Vector processing unit, a specia ...
'' (Virus protein U) - Vpu is specific to HIV-1. It is a class I oligomeric
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relativ ...
integral membrane phosphoprotein with numerous biological functions. Vpu is involved in CD4
In molecular biology, CD4 (cluster of differentiation 4) is a glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). CD4 is found on the surface of immune cells such as T helper cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic ...
degradation involving the ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Fo ...
proteasome
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases.
Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by w ...
pathway as well as in the successful release of virions from infected cells.
* ''tev'': This gene is only present in a few HIV-1 isolates. It is a fusion of parts of the ''tat'', ''env'', and ''rev'' genes, and codes for a protein with some of the properties of tat, but little or none of the properties of rev
Rev or Rév may refer to:
Abbreviations Rev.
* Rev., an abbreviation for revolution, as in Revolutions per minute
* Rev., an abbreviation for the religious style The Reverend
* Rev., the abbreviation for Runtime Revolution, a development environ ...
.
RNA secondary structure
Several conservedsecondary structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional conformational isomerism, form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta ...
elements have been identified within the HIV RNA genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
. The HIV viral RNA structures regulates the progression of reverse transcription. The 5'UTR structure consists of series of stem-loop structures connected by small linkers. These stem-loops (5' to 3') include the trans-activation region (TAR) element, the 5' polyadenylation signal oly(A) the PBS, the DIS, the major SD and the ψ hairpin structure located within the 5' end of the genome and the HIV Rev response element The HIV-1 Rev response element (RRE) is a highly structured, ~350 nucleotide RNA segment present in the Env coding region of unspliced and partially spliced viral mRNAs. In the presence of the HIV-1 accessory protein Rev, HIV-1 mRNAs that contain ...
(RRE) within the env gene. Another RNA structure that has been identified is gag stem loop 3 (GSL3), thought to be involved in viral packaging. RNA secondary structures have been proposed to affect the HIV life cycle by altering the function of HIV protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
and reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, ...
, although not all elements identified have been assigned a function.
An RNA secondary structure determined by SHAPE
A shape or figure is a graphics, graphical representation of an object or its external boundary, outline, or external Surface (mathematics), surface, as opposed to other properties such as color, Surface texture, texture, or material type.
A pl ...
analysis has shown to contain three stem loop
Stem-loop intramolecular base pairing is a pattern that can occur in single-stranded RNA. The structure is also known as a hairpin or hairpin loop. It occurs when two regions of the same strand, usually complementary in nucleotide sequence when ...
s and is located between the HIV protease and reverse transcriptase genes. This ''cis'' regulatory RNA has been shown to be conserved throughout the HIV family and is thought to influence the viral life cycle.
V3 loop
The third variable loop or V3 loop is a part or region of theHuman Immunodeficiency Virus
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the ...
. The V3 loop of the viron's envelope glycoprotein, gp120
Envelope glycoprotein GP120 (or gp120) is a glycoprotein exposed on the surface of the HIV envelope. It was discovered by Professors Tun-Hou Lee and Myron "Max" Essex of the Harvard School of Public Health in 1988. The 120 in its name comes from ...
, allows it to infect human immune cells by binding to a cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
receptor on the target human immune cell, such as a CCR5
C-C chemokine receptor type 5, also known as CCR5 or CD195, is a protein on the surface of white blood cells that is involved in the immune system as it acts as a receptor for chemokines.
In humans, the ''CCR5'' gene that encodes the CCR5 pro ...
cell or CXCR4
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR-4) also known as fusin or CD184 (cluster of differentiation 184) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CXCR4'' gene. The protein is a CXC chemokine receptor.
Function
CXCR-4 is an alpha-chemokin ...
cell, depending on the strain of HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune ...
.
The envelope glycoprotein (Env) gp 120/41 is essential for HIV-1 entry into cells. Env serves as a molecular target of a medicine treating individuals with HIV-1 infection, and a source of immunogen to develop AIDS vaccine. However, the structure of the functional Env trimer has remained elusive.
See also
*HIV/AIDS research
HIV/AIDS research includes all medical research that attempts to prevent, treat, or cure HIV/AIDS, as well as fundamental research about the nature of HIV as an infectious agent and AIDS as the disease caused by HIV.
Transmission
A body of sci ...
References
External links
Rfam entry for HIV pol-1 stem loop
3D model of the complete HIV1 virion
* {{Viral proteins HIV/AIDS