HIV Ribosomal Frameshift Signal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
HIV ribosomal frameshift signal is a ribosomal frameshift (PRF) that
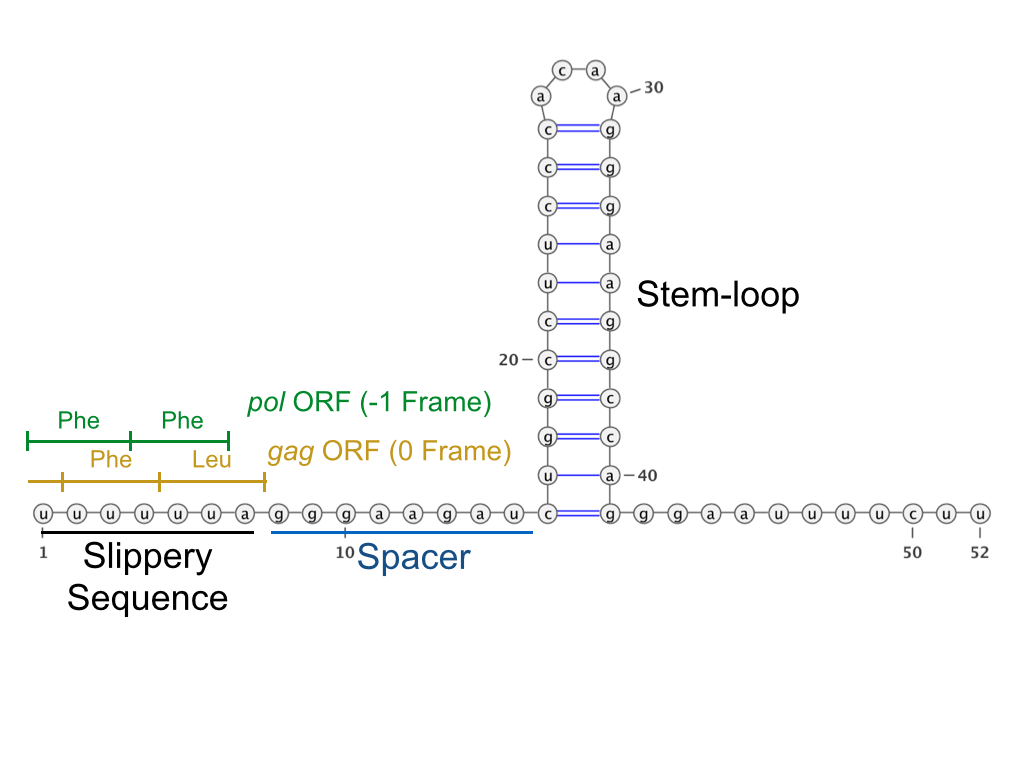 The HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal requires two cis-acting elements: a heptameric "slippery site" and a
The HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal requires two cis-acting elements: a heptameric "slippery site" and a
 The HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal has emerged as a potential therapeutic target for the HIV-1 virus due to the requirement of the programmed ribosomal frameshift for the regulation of the Gag/Gag-Pol protein ratio and the relatively conserved structure. Additionally, because the HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal relies on interactions between the viral mRNA and the host translational machinery, it is likely a more stable therapeutic target, because any
The HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal has emerged as a potential therapeutic target for the HIV-1 virus due to the requirement of the programmed ribosomal frameshift for the regulation of the Gag/Gag-Pol protein ratio and the relatively conserved structure. Additionally, because the HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal relies on interactions between the viral mRNA and the host translational machinery, it is likely a more stable therapeutic target, because any
human immunodeficiency virus
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immun ...
(HIV) uses to translate several different proteins from the same sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is calle ...
.
Intact and consistent protein biosynthesis relies on the ability of the ribosome to stay in the correct open reading frame
In molecular biology, open reading frames (ORFs) are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible readin ...
(ORF) during translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
. When the ribosome fails to maintain the proper ORF, translation usually results in either incorrect protein synthesis or early termination as a result of the introduction of a premature stop codon
In molecular biology (specifically protein biosynthesis), a stop codon (or termination codon) is a codon (nucleotide triplet within messenger RNA) that signals the termination of the translation process of the current protein. Most codons in mess ...
. However, a shift in the ORF is not universally deleterious, as many virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsk ...
es capitalize on this phenomenon by using a programmed ribosomal frameshift (PRF) to translate several proteins from the same sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is calle ...
, thereby maximizing the storage capacity of their genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
. Thus, many viruses (including HIV-1
The subtypes of HIV include two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to viruses found in chimpanzees and gorillas living in western Africa, while HIV-2 viruses are related to viruses found in the sooty mangabey ...
) are categorized as having a polycistronic
A cistron is an alternative term for "gene". The word cistron is used to emphasize that genes exhibit a specific behavior in a cis-trans test; distinct positions (or loci) within a genome are cistronic.
History
The words ''cistron'' and ''gene ...
genome, meaning they employ multiple active ORF's in a single gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
.
The HIV-1 virus requires a programmed -1 ribosomal frameshift signal (the HIV-1 Ribosomal Frameshift Signal) for the expression of the Pol gene, which is an example of a cis-acting element of gene regulation
Regulation of gene expression, or gene regulation, includes a wide range of mechanisms that are used by cells to increase or decrease the production of specific gene products (protein or RNA). Sophisticated programs of gene expression are wi ...
. In HIV-1, the ''gag'' ORF that encodes the 55 kDa
The dalton or unified atomic mass unit (symbols: Da or u) is a non-SI unit of mass widely used in physics and chemistry. It is defined as of the mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state and at re ...
Gag protein, the major viral structural protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
, is located at the 5' end of the full-length viral mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
. Translation of the 160 kDa Gag-Pol polyprotein is contingent on a -1 ribosomal frameshift event revealing the ''pol'' ORF. The ''pol'' ORF is located 3' to the gag ORF and encodes the Pol polyprotein, which is eventually cleaved into the viral enzymatic proteins (protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
, reverse transcriptase, and integrase).
As a result, the HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal is highly regulated, as it modulates the expression levels of the Gag protein relative to the Gag-Pol polyprotein. The efficiency of the HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal determines the ratio of the Gag to Gag-Pol proteins synthesized, with a frameshift event occurring in approximately 5% of the total translation events, resulting in a roughly 20:1 Gag/Gag-Pol ratio. Preservation of this ratio has been shown to be essential to HIV-1 infectivity and structure, as even small changes in the efficiency of the frameshift lead to inhibition of viral propagation. The dependence of the HIV-1 virus on this ribosomal frameshift signal has generated interest in the frameshift as a target for novel antiviral
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Unlike most antibiotics, antiviral drugs do no ...
therapeutics.
Structure and mechanism
 The HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal requires two cis-acting elements: a heptameric "slippery site" and a
The HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal requires two cis-acting elements: a heptameric "slippery site" and a downstream
Downstream may refer to:
* Downstream (bioprocess)
* Downstream (manufacturing)
* Downstream (networking)
* Downstream (software development)
* Downstream (petroleum industry)
* Upstream and downstream (DNA), determining relative positions on DNA ...
secondary RNA structure separated by an 8-nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecule ...
spacer. The "Slippery Site" in HIV-1 is the heptamer 5'-U UUU UUA-3' (gag ORF indicated by the spaces), where frameshifting occurs. This heptamer is inherently "slippery", as data has shown that even in the absence of the downstream secondary RNA structure, frameshifting still occurs at roughly 0.0001% to 0.1% per codon. It is generally accepted that the downstream secondary RNA structure exists as a stem-loop structure as shown below. However, there is also evidence that the frameshift signal may exist as a pseudoknot structure or as an intramolecular RNA triplex. Regardless of the exact conformation of the downstream secondary RNA structure, it is believed that the structure leads to the translocating ribosome stalling over the slippery site, increasing the probability of a -1 ribosomal frameshift to reveal the pol ORF (5'-UUU UUU A-3'), bypassing a downstream stop codon present in the gag ORF and allowing the Gag-Pol polyprotein to be translated. Data has shown that the 8-nucleotide spacer is essential to the programmed ribosomal frameshift as well, as deletions within the spacer region decrease the stability of the downstream secondary RNA structure, thereby affecting the ability of the HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal to induce a -1 frameshift.
Modulators
Endogenous cellular factors may also modulate the HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal, as it has been reported that the eukaryotic release factor eRF1 plays a role in programmed ribosomal frameshift in HIV-1, as decreased levels of eRF1 lead to an increase in programmed ribosomal frameshift in HIV-1. However, because eRF1 is known to complex with at least 32 cellular binding partners, it remains unclear if eRF1 acts independently to modulate PRF in HIV-1 or if it is part of a larger regulatory protein complex.As a potential therapeutic target
 The HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal has emerged as a potential therapeutic target for the HIV-1 virus due to the requirement of the programmed ribosomal frameshift for the regulation of the Gag/Gag-Pol protein ratio and the relatively conserved structure. Additionally, because the HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal relies on interactions between the viral mRNA and the host translational machinery, it is likely a more stable therapeutic target, because any
The HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal has emerged as a potential therapeutic target for the HIV-1 virus due to the requirement of the programmed ribosomal frameshift for the regulation of the Gag/Gag-Pol protein ratio and the relatively conserved structure. Additionally, because the HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal relies on interactions between the viral mRNA and the host translational machinery, it is likely a more stable therapeutic target, because any selective pressure
Any cause that reduces or increases reproductive success in a portion of a population potentially exerts evolutionary pressure, selective pressure or selection pressure, driving natural selection. It is a quantitative description of the amount of ...
caused by a therapeutic compound would have to occur on the evolutionary time scale of the host instead of the rapidly evolving HIV-1 virus. As a result, this may also reduce the risk of drug-resistant mutants experienced by other HIV-1 antiretroviral therapies.
Recently (January 2014), the first therapeutic compound targeted at the HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal was reported by Ofori et al. The lead compound was developed from a "hit" compound discovered through a resin-bound dynamic combinatorial library screen, and the structure is shown at right. The EC50
]
Half maximal effective concentration (EC50) is a measure of the concentration of a drug, antibody or toxicant which induces a Stimulus%E2%80%93response_model, response halfway between the baseline and maximum after a specified exposure time. Mo ...
values were reported to be 3.9uM for the Z conformation and 25.6uM for the E conformation. The lead compound is symmetrical whereas the target downstream secondary RNA structure is non-symmetrical, suggesting that both supposed Intercalation (biochemistry), intercalators are necessary for high-affinity binding. Using a dual- luciferase assay, they concluded that the compound functions by enhancing the frameshifting efficiency of the HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal, resulting in a decrease in the Gag/Gag-Pol protein ratio and thereby preventing the proper maturation of the viral particle and ultimately inhibiting infection. Moving forward, structural studies of the interactions between the lead compound and the downstream secondary RNA structure of the HIV-1 ribosomal frameshift signal will be vital to understanding the reason for high affinity and the method of action.
See also
*HIV Rev response element The HIV-1 Rev response element (RRE) is a highly structured, ~350 nucleotide RNA segment present in the Env coding region of unspliced and partially spliced viral mRNAs. In the presence of the HIV-1 accessory protein Rev, HIV-1 mRNAs that conta ...
* Retrovirus direct repeat 1 (dr1)
* Ribosomal pause
References
External links
* {{Rfam, id=RF00480, name=HIV Ribosomal frameshift signal Cis-regulatory RNA elements